All questions of Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance for Grade 9 Exam
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called?
- a)Lagging strand
- b)Coding strand
- c)Antisense strand
- d)Template strand
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called?
a)
Lagging strand
b)
Coding strand
c)
Antisense strand
d)
Template strand
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called the template strand or the antisense strand. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds, and one of the strands (the template strand) is used as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule, which is called messenger RNA (mRNA). The other strand of DNA, which is not used as a template during transcription, is called the coding strand or the sense strand because it has the same sequence as the mRNA molecule (except for the presence of thymine instead of uracil).
Protein synthesis occurs over- a)Cytoplasm
- b)Ribosomes
- c)Amino acids
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Protein synthesis occurs over
a)
Cytoplasm
b)
Ribosomes
c)
Amino acids
d)
Mitochondria
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Ribosomes are site of protein synthesis and are known as protein factory
Repressor proteins are coded for by ______ genes.- a)Promoter
- b)Structural
- c)Regulator
- d)Operator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Repressor proteins are coded for by ______ genes.
a)
Promoter
b)
Structural
c)
Regulator
d)
Operator
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Regulator genes codes for repressor proteins during translation of DNA into protein via mRNA.
Why are UGA, UAG and UAA called termination codons?- a)They terminate anticodons
- b)They are presenting at the beginning of mRNA
- c)They indicate initiation of translation
- d)They do not specify any amino acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are UGA, UAG and UAA called termination codons?
a)
They terminate anticodons
b)
They are presenting at the beginning of mRNA
c)
They indicate initiation of translation
d)
They do not specify any amino acid
|
|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Since The stop codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA. They encode no amino acid. The ribosome pauses and falls off the mRNA.
Which chromosome of human genome contains least number of genes?- a)Chromosome 12
- b)Chromosome X
- c)Chromosome Y
- d)Chromosome 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which chromosome of human genome contains least number of genes?
a)
Chromosome 12
b)
Chromosome X
c)
Chromosome Y
d)
Chromosome 1
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
Chromosomes are thread like structures of DNA and proteins that carry genetic information of organisms in the form of genes. The human chromosomes with least number of genes is Your chromosome.
Option " C " is correct answer.
Option " C " is correct answer.
DNA is made of two chains that twist about one another in the shape of a _______.- a)Broken ladder
- b)Straight ladder
- c)Straight spiral
- d)Double helix
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA is made of two chains that twist about one another in the shape of a _______.
a)
Broken ladder
b)
Straight ladder
c)
Straight spiral
d)
Double helix
|
|
Ananya Duney answered |
They are twist in a right handed double helical way therefore it's called double helix DNA which was given by Watson and crick
"hope it'll help"
"hope it'll help"
The code AUG stands for- a)Aniline
- b)Methionine
- c)Glycine
- d)N-formyl methionine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The code AUG stands for
a)
Aniline
b)
Methionine
c)
Glycine
d)
N-formyl methionine
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The genetic code consists of 64 triplets of nucleotides. These triplets are called codons.With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in the code: most of the amino acids being encoded by more than one codon.
One codon, AUG serves two related functions:
1. it signals the start of translation
2. it codes for the incorporation of the amino acid methionine (Met) into the growing polypeptide chain
What is called Griffith effect?- a)DNA transcription
- b)RNA translation
- c)Bacterial transduction
- d)Bacterial transformation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is called Griffith effect?
a)
DNA transcription
b)
RNA translation
c)
Bacterial transduction
d)
Bacterial transformation
|
|
Mathi Mathi answered |
Bacteria can take up forigen DNA in a process called transformation. It occurs after restriction digest and ligation and transfers newly made plasmid to bacteria.
Bacteria with a plasmid are antibiotic resistant, and each will form a colony.
Bacteria with a plasmid are antibiotic resistant, and each will form a colony.
By which bonds the purine & pyrimidine pairs of Complementary Strands of DNA held together?- a)N – bonds
- b)H – bonds
- c)O - bonds
- d)C - bonds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
By which bonds the purine & pyrimidine pairs of Complementary Strands of DNA held together?
a)
N – bonds
b)
H – bonds
c)
O - bonds
d)
C - bonds
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
In complementary strands of DNA, purines and pyrimidine are held together by Hydrogen bond (H-bond). Adenine and Thymine have double hydrogen bond and cytosine and guanine are held by triple hydrogen bond.
RNA polymerase is only capable of catalyzing the process of- a)Elongation
- b)Initiation
- c)Termination
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
RNA polymerase is only capable of catalyzing the process of
a)
Elongation
b)
Initiation
c)
Termination
d)
All of the above

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
During protein synthesis, elongation of peptide chain is catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase. Elongation continuous until a non-sense or stop codon is reached.
Genetic information is carried out by long chain molecule made up of- a)Nucleotides
- b)Enzymes
- c)Histone proteins
- d)Amino acids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic information is carried out by long chain molecule made up of
a)
Nucleotides
b)
Enzymes
c)
Histone proteins
d)
Amino acids
|
|
Aarya Khanna answered |
Genetic information is carried out by DNA and RNA. Both DNA and RNA are called genetic material, made up of long chain of nucleotide having-nitrogenous base, sugar and phosphate ions.
The hybridization of probes having radioactive isotopes with various sequence of nitrogen bases with ssVNTR is called?- a)Eastern blotting
- b)Southern blotting
- c)Western blotting
- d)Northern blotting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The hybridization of probes having radioactive isotopes with various sequence of nitrogen bases with ssVNTR is called?
a)
Eastern blotting
b)
Southern blotting
c)
Western blotting
d)
Northern blotting
|
|
Ankita Raj answered |
The hybridization of probes having radioactive isotopes with various sequence of nitrogen bases with ssVNTR is called southern blotting. Southern blotting is a laboratory technique used to detect a specific DNA sequence in a blood or tissue sample. A restriction enzyme is used to cut a sample of DNA into fragments that are separated using gel electrophoresis. The DNA fragments are transferred out of the gel to the surface of a membrane. The membrane is exposed to a DNA probe labeled with a radioactive or chemical tag. If the probe binds to the membrane, then the probe sequence is present in the sample. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Assertion: UAA codon is a termination codon.Reason: If in a mRNA, a termination codon is present, the protein synthesis stops abruptly whether the protein synthesis is complete or not.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- c)Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: UAA codon is a termination codon.
Reason: If in a mRNA, a termination codon is present, the protein synthesis stops abruptly whether the protein synthesis is complete or not.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
c)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
d)
None of these
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
UAA of mRNA do not code for any amino acids so it is a termination codon. If termination codon is present on mRNA, the protein synthesis stops abruptly at that point.
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched with regard to the codon and the amino acid coded by it?- a)AAA-Lysine
- b)AUG-Cysteine
- c)UUA-Valine
- d)CCC-Alanine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched with regard to the codon and the amino acid coded by it?
a)
AAA-Lysine
b)
AUG-Cysteine
c)
UUA-Valine
d)
CCC-Alanine
|
|
Raza Great answered |
A set of three nucleotide bases specify particular amino acid; the set is called as triplet codon. The triplet "UUA" codes for leucine while valine is encoded by GUA, GUG, GUC, GUU; option A is wrong. The triplet "AAA" codes for lysine; option B is right. The triplet "AUG" codes for methionine while cysteine is encoded by UGU and UGC; option C is wrong. The triplet "CCC" codes for proline while alanine is encoded by GCA, GCC, GCG, GCU;
Removal of introns and joining of exons in a defined order during transcription is called?- a)Slicing
- b)Splicing
- c)Inducing
- d)Looping
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Removal of introns and joining of exons in a defined order during transcription is called?
a)
Slicing
b)
Splicing
c)
Inducing
d)
Looping
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The mRNA produced by transcription of DNA consists of exons and introns. The removal of introns and joining of exons to obtain mature mRNA is called splicing. It is followed by capping and tailing.
Genetic and physical map of genome was generated using information on
a. Polymorphism of restriction endonuclease recognition sites.
b. Repetitive DNA sequence called microsatellites.- a)Only ‘a’ is correct
- b)Only ‘b’ is correct
- c)Both ‘a’ and ‘b’ is correct
- d)Both ‘a’ and ‘b’ are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Genetic and physical map of genome was generated using information on
a. Polymorphism of restriction endonuclease recognition sites.
b. Repetitive DNA sequence called microsatellites.
a. Polymorphism of restriction endonuclease recognition sites.
b. Repetitive DNA sequence called microsatellites.
a)
Only ‘a’ is correct
b)
Only ‘b’ is correct
c)
Both ‘a’ and ‘b’ is correct
d)
Both ‘a’ and ‘b’ are incorrect

|
Charvi Shah answered |
Genetic and physical map of genome was generated using information on polymorphism of restriction endonuclease recognition sites and repetitive DNA sequence called microsatellites.
The sensitivity of fingerprinting technique has been increased by use of- a)Repetitive DNA
- b)ELISA
- c)Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- d)VNTR
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sensitivity of fingerprinting technique has been increased by use of
a)
Repetitive DNA
b)
ELISA
c)
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
d)
VNTR
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The sensitivity of fingerprinting technique has been increased by use of Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). After that single cell obtained from organism in enough for this technique.
A DNA segment which serves as a kind of “ON-OFF switch” for transcription is a/an- a)Operator
- b)Structural gene
- c)Regulator gene
- d)Promoter
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A DNA segment which serves as a kind of “ON-OFF switch” for transcription is a/an
a)
Operator
b)
Structural gene
c)
Regulator gene
d)
Promoter
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The DNA segment which serves as ON-OFF switch for transcription is called an operator. Operator attach with template strand to initiate transcription process.
Satellite DNA is useful tool in
- a)Organ transplantation
- b)Sex determination
- c)Genetic engineering
- d)Forensic science
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Satellite DNA is useful tool in
a)
Organ transplantation
b)
Sex determination
c)
Genetic engineering
d)
Forensic science
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
About 3% or so of the human genome has highly repetitive sequences or simple-sequence DNA or simple sequence repeats or satellite DNA. It does not encode proteins or RNAs but have identifiable functional importance owing to their presence in centromeres and telomeres; which makes option B wrong as genetic engineering mainly aims at transfer of genes producing desired products. Satellite DNA show relative uniformity within species and great variability between closely related species. This DNA polymorphism is revealed during DNA finger printing in identification of suspect. For the purpose, restriction enzyme digested DNA samples are sorted by gel electrophoresis followed by southern blotting. Finally, radioactive probes are washed over the nylon surface to allow their joining to any DNA fragments of same composition. Correct option is A. Sex determination in human is governed by presence or absence of Y-chromosome, not by satellite DNA which makes option D wrong. Organ transplantation mainly aims at immune system; option C is wrong.
So, the correct answer is 'Forensic science'
For DNA finger printing, the DNA is obtained from- a)White blood corpuscles only
- b)Hair root cells only
- c)WBCs, hair root cells and body secretion
- d)Body secretion only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For DNA finger printing, the DNA is obtained from
a)
White blood corpuscles only
b)
Hair root cells only
c)
WBCs, hair root cells and body secretion
d)
Body secretion only
|
|
Awantika Gupta answered |
It is possible to extract DNA from WBC, a root hair cell but not from body secretion ex sweat.
Human genome project was closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called as- a)Genomics
- b)Genetic engineering
- c)Bioinformatics
- d)Biotechnology
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Human genome project was closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called as
a)
Genomics
b)
Genetic engineering
c)
Bioinformatics
d)
Biotechnology
|
|
Amar Choudhary answered |
Human genome project was associated with the rapid development of new area of biology called as bioinformatics. This branch of biological science is used to known the sequence of gene on Chromosome of living organisms.
Autoradiogram of VNTR probe gives many band of different size. It differ from individual to individual except- a)Real sisters
- b)Monozygotic twins or identical twins
- c)Heterozygotic twins
- d)Real brothers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Autoradiogram of VNTR probe gives many band of different size. It differ from individual to individual except
a)
Real sisters
b)
Monozygotic twins or identical twins
c)
Heterozygotic twins
d)
Real brothers
|
|
Partho Chawla answered |
Autoradiogram of VNTR probe gives many band of different size. It differs from individual to individual except monozygotic twins or identical twins.
Assertion: Genetic map up of an organism or individual lies in the DNA sequence.Reason: If two individual differs, then their DNA sequence should also be different.- a)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
- b)Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
- c)Both assertion and reason are incorrect
- d)Both assertion and reason are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: Genetic map up of an organism or individual lies in the DNA sequence.
Reason: If two individual differs, then their DNA sequence should also be different.
a)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
b)
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
c)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect
d)
Both assertion and reason are correct
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Genetic map up of an organism or individual lies in the DNA sequence. If two individual differs, then their DNA sequence should also be different.
What does A & B represent?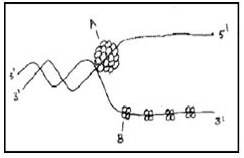
- a)Grycase, Helicase
- b)Topoisomerase Helicase
- c)Helicase, Single strand binding protein
- d)Double Stranded Protein, Helicase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does A & B represent?
a)
Grycase, Helicase
b)
Topoisomerase Helicase
c)
Helicase, Single strand binding protein
d)
Double Stranded Protein, Helicase
|
|
Kushagra Budhgaya answered |
A is helicase, it unwind the DNA and B is SSB protien or single strand bonding protien it prevent the strands of DNA from sticking together again so that the replication can be made forward
Assertion: VNTR of two persons may be similar at certain sites but could be different at other sites.Reason: A child inherits 50% of chromosomes from mother and remaining 50% from father.- a)Reason does not explain the assertion correctly
- b)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
- c)Assertion and reason both are correct
- d)Both assertion and reason are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: VNTR of two persons may be similar at certain sites but could be different at other sites.
Reason: A child inherits 50% of chromosomes from mother and remaining 50% from father.
a)
Reason does not explain the assertion correctly
b)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
c)
Assertion and reason both are correct
d)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
VNTR of two persons may be similar at certain sites but could be different at other sites because a child inherits 50% of chromosomes from mother and remaining 50% from father. VNTR genes also undergoes different kinds of mutations.
Gel electrophoresis is used for- a)Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
- b)Cutting of DNA into fragments
- c)Isolation of DNA molecule
- d)Construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gel electrophoresis is used for
a)
Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
b)
Cutting of DNA into fragments
c)
Isolation of DNA molecule
d)
Construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
|
|
Sapna Patel answered |
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. DNA fragments are loaded into well at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel. DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode. Small fragments move farther while large fragments comes closer
In human genome project, commonly used host were bacteria and yeast and their vectors are called as- a)BAC and YBC
- b)BAC and YCB
- c)BBC and YBC
- d)BAC and YAC
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In human genome project, commonly used host were bacteria and yeast and their vectors are called as
a)
BAC and YBC
b)
BAC and YCB
c)
BBC and YBC
d)
BAC and YAC
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
BAC = bacterial artificial chromosome
YAC= yeast artificial chromosome... refer ncert class 12 bio..
YAC= yeast artificial chromosome... refer ncert class 12 bio..
Which of the following important biochemical reactions in living systems is catalyzed by a ribozyme?- a)Repair of DNA
- b)Electron transport chain
- c)Formation of peptide bond
- d)Organization of MTOC during cell division
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following important biochemical reactions in living systems is catalyzed by a ribozyme?
a)
Repair of DNA
b)
Electron transport chain
c)
Formation of peptide bond
d)
Organization of MTOC during cell division
|
|
Pragati Pillai answered |
Ribozymes: Catalysts of Life
Ribozymes are unique RNA molecules capable of catalyzing biochemical reactions, a role traditionally associated with proteins. The formation of peptide bonds is one of the key reactions facilitated by ribozymes.
Understanding Peptide Bond Formation
- Translation Process: During protein synthesis, ribosomes play a crucial role in linking amino acids together to form proteins.
- Role of rRNA: Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a component of ribosomes, acts as a ribozyme. It catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids in the growing polypeptide chain.
Mechanism of Action
- Amino Acid Activation: Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome, where the ribozyme catalyzes the reaction.
- Peptide Bond Formation: The ribozyme facilitates the nucleophilic attack of the amino group of one amino acid on the carbonyl carbon of another, resulting in the formation of a covalent peptide bond.
Significance in Biology
- Evolutionary Perspective: The presence of ribozymes supports the RNA world hypothesis, suggesting that early life forms relied on RNA for both genetic information and catalysis.
- Diversity of Functions: Beyond peptide bond formation, ribozymes are involved in various biological processes, including self-splicing introns and RNA processing.
Conclusion
In summary, the formation of peptide bonds is a crucial biochemical reaction catalyzed by ribozymes, particularly the rRNA in ribosomes. This highlights the versatility of RNA in essential biological functions, underscoring its importance in the molecular machinery of life.
Ribozymes are unique RNA molecules capable of catalyzing biochemical reactions, a role traditionally associated with proteins. The formation of peptide bonds is one of the key reactions facilitated by ribozymes.
Understanding Peptide Bond Formation
- Translation Process: During protein synthesis, ribosomes play a crucial role in linking amino acids together to form proteins.
- Role of rRNA: Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a component of ribosomes, acts as a ribozyme. It catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids in the growing polypeptide chain.
Mechanism of Action
- Amino Acid Activation: Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome, where the ribozyme catalyzes the reaction.
- Peptide Bond Formation: The ribozyme facilitates the nucleophilic attack of the amino group of one amino acid on the carbonyl carbon of another, resulting in the formation of a covalent peptide bond.
Significance in Biology
- Evolutionary Perspective: The presence of ribozymes supports the RNA world hypothesis, suggesting that early life forms relied on RNA for both genetic information and catalysis.
- Diversity of Functions: Beyond peptide bond formation, ribozymes are involved in various biological processes, including self-splicing introns and RNA processing.
Conclusion
In summary, the formation of peptide bonds is a crucial biochemical reaction catalyzed by ribozymes, particularly the rRNA in ribosomes. This highlights the versatility of RNA in essential biological functions, underscoring its importance in the molecular machinery of life.
Which of the following is not a feature of the double helix model of DNA ?- a)The two chains have anti-parallel polarity
- b)A purine always comes opposite to a pyrimidine
- c)The pitch of the DNA is 3.4 nm
- d)The two chains are coiled in a left-handed fashion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a feature of the double helix model of DNA ?
a)
The two chains have anti-parallel polarity
b)
A purine always comes opposite to a pyrimidine
c)
The pitch of the DNA is 3.4 nm
d)
The two chains are coiled in a left-handed fashion

|
EduRev NEET answered |
The two chains are coiled in a right handed fashion.
What does "lac" refer to in what we call the lac operon?- a)Lactose
- b)Lactase
- c)Lac insect
- d)The number 1,00,000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does "lac" refer to in what we call the lac operon?
a)
Lactose
b)
Lactase
c)
Lac insect
d)
The number 1,00,000
|
|
Awantika Gupta answered |
The operating system of lactose is done by lac operan.
Enzymes called ______ add complementary nucleotides, floating inside the nucleus.- a)DNA polymerase
- b)Lipoprotein lipase
- c)DNA synthetase
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes called ______ add complementary nucleotides, floating inside the nucleus.
a)
DNA polymerase
b)
Lipoprotein lipase
c)
DNA synthetase
d)
None of these
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
DNA polymerases are enzymes that synthesize DNA molecules from deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.
Okazaki is known for his contribution to the understanding of- a)DNA replication
- b)Translation
- c)Mutation
- d)Transcription
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Okazaki is known for his contribution to the understanding of
a)
DNA replication
b)
Translation
c)
Mutation
d)
Transcription

|
Aaksc Chemistry answered |
Okazaki discovered the way in which the lagging strand of DNA is replicated via fragments by conducting an experiment using E. coli named the strand Okazaki fragment. Okazaki fragments are the fragmented piece of newly synthesized DNA strand called as lagging strand during DNA replication. They are complementary to the lagging template strand, together forming short double-stranded DNA sections.
Statement I: DNA finger printing is highly reliable method of identification of individual involved in crimes.
Statement II: DNA a fingerprinting is a sure method in solving paternity and maternity disputes.
Statement III: DNA fingerprinting can be used to cure HIV infection.- a)Statement I and II is correct
- b)All statements are correct
- c)Statement I and III is correct
- d)Statement II and III is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I: DNA finger printing is highly reliable method of identification of individual involved in crimes.
Statement II: DNA a fingerprinting is a sure method in solving paternity and maternity disputes.
Statement III: DNA fingerprinting can be used to cure HIV infection.
Statement II: DNA a fingerprinting is a sure method in solving paternity and maternity disputes.
Statement III: DNA fingerprinting can be used to cure HIV infection.
a)
Statement I and II is correct
b)
All statements are correct
c)
Statement I and III is correct
d)
Statement II and III is correct
|
|
Swara Dey answered |
DNA finger printing is highly reliable method of identification of individual involved in crimes. DNA a fingerprinting is a sure method in solving paternity and maternity disputes.DNA fingerprinting cannot be used to cure HIV infection.
Which of the following statements is true about DNA replication?- a)One DNA molecule becomes two identical ones as a result of this process.
- b)It occurs during meiosis but not mitosis.
- c)It is part of the protein synthesis process.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true about DNA replication?
a)
One DNA molecule becomes two identical ones as a result of this process.
b)
It occurs during meiosis but not mitosis.
c)
It is part of the protein synthesis process.
d)
None of the above
|
|
Prerna Chauhan answered |
DNA molecules are replicated in both meiosis and mitosis. DNA unwinds and unzips along its base pair chemical bonds. Free nucleotides then connect to the exposed base pairs on both strands resulting in the formation of the missing side of each new DNA.
What does the structural gene (y) of a lac operon code for?- a) β-galactosidase
- b)Transacetylase
- c)Glucagon
- d)Permease
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the structural gene (y) of a lac operon code for?
a)
β-galactosidase
b)
Transacetylase
c)
Glucagon
d)
Permease

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The structural gene (z) of the lac operon codes for β-galactosidase. It is responsible for the hydrolysis of polysaccharides. The ‘y’ genes code for permease. It increases the permeability of a cell to β-galactosidase. The ‘a’ genes code for transacetylase.
What is the length of the DNA double helix, if the total number of bp (base pair) is 6.6 x 109?- a)2.2 m
- b)2.5 m/bp
- c)2.2 m/bp
- d)2.5 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the length of the DNA double helix, if the total number of bp (base pair) is 6.6 x 109?
a)
2.2 m
b)
2.5 m/bp
c)
2.2 m/bp
d)
2.5 m

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- The distance between 2 consecutive bp is 0.34 nm. The formula to calculate the length of the DNA double helix:
- The length of the DNA double helix = The total number of bp x distance between two consecutive bp.
- As a result, we get 2.2 m as the length of the DNA double helix.
What are the set of positively charged basic proteins called as?- a)Histidine
- b)DNA
- c)RNA
- d)Histones
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the set of positively charged basic proteins called as?
a)
Histidine
b)
DNA
c)
RNA
d)
Histones

|
Top Rankers answered |
- Histones are rich in basic amino acid (AA) residues such as lysine and arginine.
- These two amino acids carry a positive charge at their side chains.
- Due to this reason, histones are called as the set of positively charged basic proteins.
How many bp are present in a typical nucleosome?- a)100 bp
- b)200 bp
- c)300 bp
- d)90 bp
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many bp are present in a typical nucleosome?
a)
100 bp
b)
200 bp
c)
300 bp
d)
90 bp

|
Top Rankers answered |
- Nucleosomes are the bead-like structures which are present on a chromatin.
- These nucleosomes contain the DNA, which is the genetic material.
- Such a typical nucleosome contains nearly 200 bp.
What does X replesent in the followwing diagram: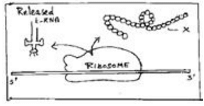
- a)Released tertiary protein
- b)Released secondary protein
- c)Released 3D protein molecule
- d)Released polypeptide chain
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does X replesent in the followwing diagram:
a)
Released tertiary protein
b)
Released secondary protein
c)
Released 3D protein molecule
d)
Released polypeptide chain
|
|
Kushagra Budhgaya answered |
D option is correct bcz protein is a polypeptide and it's a primary structure of protein
How many structural genes are present in a lac operon?- a)One
- b)Five
- c)Three
- d)Seven
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many structural genes are present in a lac operon?
a)
One
b)
Five
c)
Three
d)
Seven

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- A lac operon consists of one regulatory gene (i) and three structural genes (z, y and a).
- The “i” in regulatory gene is derived from the word “inhibitor”.
In prokaryotes, the predominant site for control of gene expression is the :- a)transcription initiation
- b)processing level
- c)transport of mRNA
- d)translation level
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In prokaryotes, the predominant site for control of gene expression is the :
a)
transcription initiation
b)
processing level
c)
transport of mRNA
d)
translation level

|
Top Rankers answered |
In prokaryotes, control of the rate of transcriptional initiation is the predominant site for control of gene expression.
What is the regulation of a lac operon by a repressor known as?- a)Neutral regulation
- b)Positive regulation
- c)Mixed regulation
- d)Negative regulation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the regulation of a lac operon by a repressor known as?
a)
Neutral regulation
b)
Positive regulation
c)
Mixed regulation
d)
Negative regulation

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- The regulation of a lac operon by the repressor is known as negative regulation.
- At rare occasions, lac operons are also observed to be under the control of positive regulation.
- In negative regulation, the operon cannot transcribe the RNA polymerase enzyme.
Chapter doubts & questions for Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance - Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance - Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology
153 videos|283 docs|127 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










