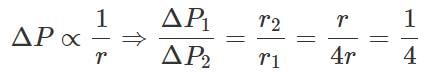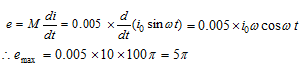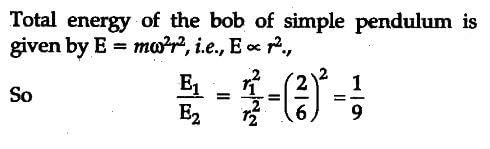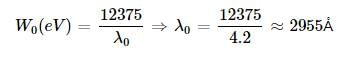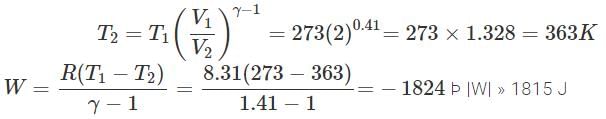All Exams >
NEET >
JIPMER: Subject wise Tests & Practice Mock Tests 2025 >
All Questions
All questions of Physics for NEET Exam
A body of mass m is taken to the bottom of a deep mine. Then- a)Its mass increases
- b)Its mass decreases
- c)Its weight increases
- d)Its weight decreases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Its mass increases
b)
Its mass decreases
c)
Its weight increases
d)
Its weight decreases

|
Ashish Bhoumick answered |
Because the body taken up against gravitation accelaration.
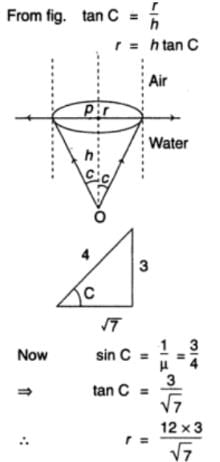
Two electric charge 12 μ C and − 6 μ C are places 20 cm apart in air. There will be a point P at which electric potential is zero on the line joining these two charges and outside, excluding the region between them. The distance of P from − 6 μ C charge is- a)0.10 m
- b)0.15 m
- c)0.20 m
- d)0.25 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two electric charge 12 μ C and − 6 μ C are places 20 cm apart in air. There will be a point P at which electric potential is zero on the line joining these two charges and outside, excluding the region between them. The distance of P from − 6 μ C charge is
a)
0.10 m
b)
0.15 m
c)
0.20 m
d)
0.25 m
|
|
Nirvikar Shakya answered |

The threshold frequency for photo electric effect for a metal surface is found to be 4.8 x 1016 Hz . The stopping potential required when the metal is irradiated by radiation of frequency 5.6 x 1016 Hz is (taking h = 6.6 x 10-34 J sec and e = 1.6 x 10-19 C)- a)22.4 V
- b)33 V
- c)66 V
- d)198 V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The threshold frequency for photo electric effect for a metal surface is found to be 4.8 x 1016 Hz . The stopping potential required when the metal is irradiated by radiation of frequency 5.6 x 1016 Hz is (taking h = 6.6 x 10-34 J sec and e = 1.6 x 10-19 C)
a)
22.4 V
b)
33 V
c)
66 V
d)
198 V
|
|
Sneha Goran answered |
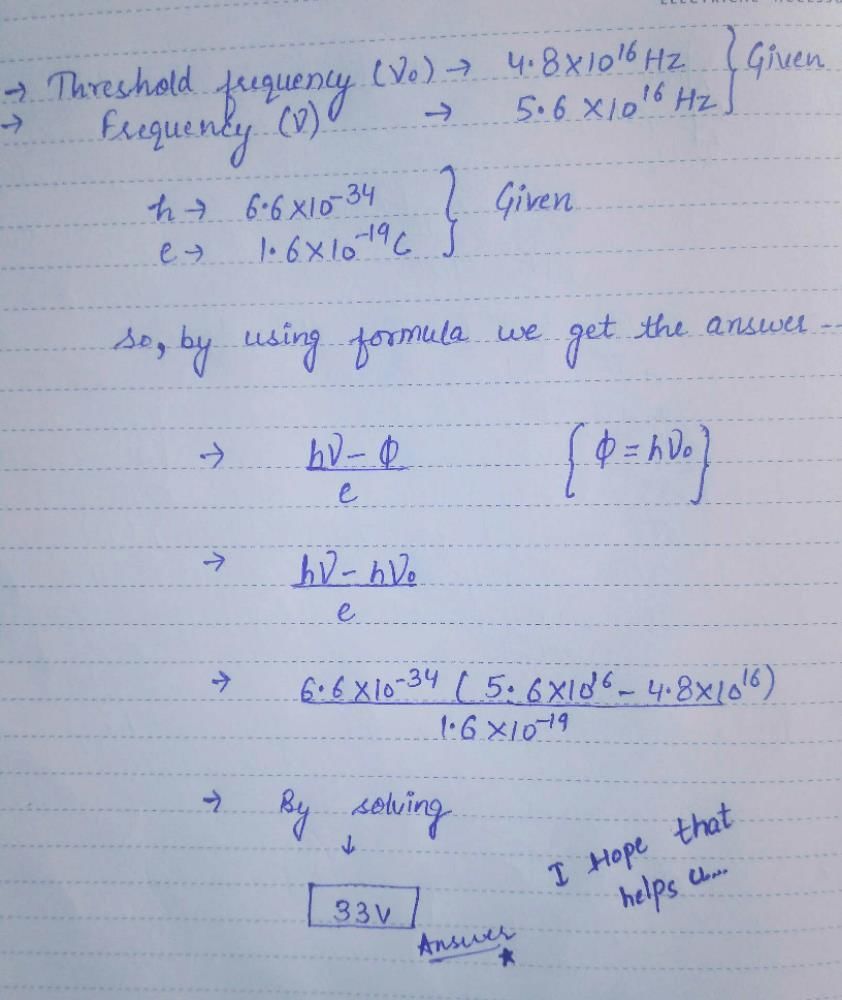
Can you explain the answer of this question below:An alternating e.m.f. of angular frequency ω is applied across an inductance. The instantaneous power developed in the circuit has an angular frequency- A: ω/4
- B: ω/2
- C: ω
- D: 2ω
The answer is d.

|
Divya Sara answered |
The instantaneous values of emf and current in inductive circuit are given by E=E0sinωt and i=i0sin(ωt−π2)respectively. So, Pinst=Ei=E0sinωt*i0sin(ωt−π2) =E0i0sinωt(sinωtcosπ2−cosωtsinπ2) =E0i0sinωt cosωt =12E0i0sin2ωt (sin2ωt=2sinωt cosωt) Hence, angular frequency of instantaneous power is 2ω.
The power of a pump, which can pump 200 kg of water to a height of 200 m in 10s is (Take g=10 ms-2)
a)40 kWb)80 kWc)400 kWd)960 kWCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
Power(p)= work /time.power=mgh/t.p=200×10×200/10.p=40,000.i.e.1K=1000....p=40k....
If a bullet of mass 5 gm moving with velocity 100 m/sec, penetrates the wooden block upto 6 cm. Then the average force imposed by the bullet on the block is- a)8300 N
- b)417 N
- c)830 N
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
8300 N
b)
417 N
c)
830 N
d)
Zero
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Here too we use equation of motion
v^2 = u^2 + 2as
2as = v^2 - u^2
2 x a x (6/100) = 0 - (100)^2
12a / 100 = - 10000
a = -1000000 / 12 m/s^2
This is the average retardation of the bullet
Avg force F = m a
= (5/1000) x 1000000 / 12 = 416.66 N
approx 417 newton
An air capacitor of capacity C = 10 μF is connected to a constant voltage battery of 12 volt. Now the space between the plates is filled with a liquid of dielectric constant 5. The charge that flows now from battery to the capacitor is- a)120 μC
- b)600 μC
- c)480 μC
- d)24 μC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An air capacitor of capacity C = 10 μF is connected to a constant voltage battery of 12 volt. Now the space between the plates is filled with a liquid of dielectric constant 5. The charge that flows now from battery to the capacitor is
a)
120 μC
b)
600 μC
c)
480 μC
d)
24 μC
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
C = 10 μF
Charge in capacitor q = CV
= 10 x 12
= 120 μC
On keeping liquid of dielectric constant5, capacity will becomes of 5 time.
∴ Charge q = 5 x 120
= 600 μC
Charge in capacitor q = CV
= 10 x 12
= 120 μC
On keeping liquid of dielectric constant5, capacity will becomes of 5 time.
∴ Charge q = 5 x 120
= 600 μC
Two wire with resistances R and 2R are connected in parallel, the ratio of heat generated in 2R and R is- a)1:2
- b)2:1
- c)1:4
- d)4:1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
1:2
b)
2:1
c)
1:4
d)
4:1
|
|
User2408930 answered |
=>P₁ = I²R₁ => P₂ = I²r₂ => P₁/P₂ = R₁/R₂ = R/2R = 1:2
Which of the following have minimum wavelength?- a)γ-rays
- b)X-rays
- c)cosmic rays
- d)ultra-violet rays
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
γ-rays
b)
X-rays
c)
cosmic rays
d)
ultra-violet rays

|
Msb Srinivas answered |
Cosmic rays have high frequency. So minimum wavelength.
Infrared radiation is detected by- a)spectrometer
- b)pyrometer
- c)nanometer
- d)photometer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Infrared radiation is detected by
a)
spectrometer
b)
pyrometer
c)
nanometer
d)
photometer
|
|
Kaneez Fatima answered |
A photometer is an instrument that measures light intensity or optical properties. ... A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of a surface. Infrared radiation can be detected by pyrometer.
Photons of energy of 6 eV are incident on a metal surface whose work function is 4 eV. The minimum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be- a) 0 eV
- b) 1 eV
- c) 2 eV
- d) 10 eV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
0 eV
b)
1 eV
c)
2 eV
d)
10 eV
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Minimum kinetic energy is always zero.
Maximum kinetic energy = E−W0=6eV−4eV=2eV
Radius of the earth is 6400 km. The radius of the orbit of a stationary satellite is about- a)36000 km
- b)29600 km
- c)42400 km
- d)infinity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
36000 km
b)
29600 km
c)
42400 km
d)
infinity
|
|
Mumtaj Ali answered |
For geostationary satellite,
Time period = 24 hrs, Height=35800km, Escape velocity= 3.1 km/s.These are called stationary satellite because such satellites appear stationary due to zero relative velocity w. r. t. earth.
Time period = 24 hrs, Height=35800km, Escape velocity= 3.1 km/s.These are called stationary satellite because such satellites appear stationary due to zero relative velocity w. r. t. earth.
A 2m long Aluminium pipe at 27 oC is heated until it is 2.0024m at 77 oC. The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminium is- a)24 x 10-6 oC-1
- b)24 x 10-4 oC-1
- c)25 x 10-6 oC-1
- d)25 x 10-4 oC-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 2m long Aluminium pipe at 27 oC is heated until it is 2.0024m at 77 oC. The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminium is
a)
24 x 10-6 oC-1
b)
24 x 10-4 oC-1
c)
25 x 10-6 oC-1
d)
25 x 10-4 oC-1
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
∆l= L c ∆T (here c is coefficient of linear expansion, ∆l is change in length, L is previous length and ∆T is change in temperature ) 0.0024 = 2 × c × 50c = 24× 10–6 °C
So (a) should be answer.
An ideal gas has a volume of V at 2 atm pressure. Keeping the temprature of gas constant, its pressure is doubled. The volume of gas will become- a)0.5 V
- b)V
- c)2 V
- d)4 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas has a volume of V at 2 atm pressure. Keeping the temprature of gas constant, its pressure is doubled. The volume of gas will become
a)
0.5 V
b)
V
c)
2 V
d)
4 V
|
|
Suyash Jain answered |
Explanation:
To solve this problem, we can use the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) of an ideal gas are related by the equation PV = nRT, where n is the number of moles of gas and R is the ideal gas constant.
Given that the temperature of the gas is constant, we can rewrite the ideal gas law as P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 are the final pressure and volume.
In this case, the initial pressure (P1) is 2 atm, and the final pressure (P2) is 4 atm (double the initial pressure). We want to find the final volume (V2).
Step 1:
Using the ideal gas law equation, we can write:
P1V1 = P2V2
Step 2:
Plugging in the given values, we have:
2 atm * V1 = 4 atm * V2
Step 3:
Simplifying the equation, we can cancel out the atm units:
2V1 = 4V2
Step 4:
Dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we get:
V1 = 2V2
Step 5:
Finally, rearranging the equation, we find:
V2 = 0.5V1
Therefore, the volume of the gas will become 0.5 times the initial volume. This means that the correct answer is option 'A' - 0.5V.
To solve this problem, we can use the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) of an ideal gas are related by the equation PV = nRT, where n is the number of moles of gas and R is the ideal gas constant.
Given that the temperature of the gas is constant, we can rewrite the ideal gas law as P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 are the final pressure and volume.
In this case, the initial pressure (P1) is 2 atm, and the final pressure (P2) is 4 atm (double the initial pressure). We want to find the final volume (V2).
Step 1:
Using the ideal gas law equation, we can write:
P1V1 = P2V2
Step 2:
Plugging in the given values, we have:
2 atm * V1 = 4 atm * V2
Step 3:
Simplifying the equation, we can cancel out the atm units:
2V1 = 4V2
Step 4:
Dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we get:
V1 = 2V2
Step 5:
Finally, rearranging the equation, we find:
V2 = 0.5V1
Therefore, the volume of the gas will become 0.5 times the initial volume. This means that the correct answer is option 'A' - 0.5V.
The average e.m.f. induced in a coil in which a current changes from 0 to 2 A in 0.05 s is 8 V. The self inductance of the coil is- a)0.1 H
- b)0.2 H
- c)0.4 H
- d)0.8 H
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The average e.m.f. induced in a coil in which a current changes from 0 to 2 A in 0.05 s is 8 V. The self inductance of the coil is
a)
0.1 H
b)
0.2 H
c)
0.4 H
d)
0.8 H
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
E= -L (di/dt)..given e=8 V .and di/dt will be 2÷0.05 ..therefore L (self inductance) will become 0.2 H..option B
A cyclotron can not accelerate- a)protons
- b)deuterons
- c)α-particles
- d)electrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cyclotron can not accelerate
a)
protons
b)
deuterons
c)
α-particles
d)
electrons

|
Jeeshan Ahmed answered |
Cyclotron cannot be used to accelerate electrons because electrons are of very small mass. Thus, the velocity will be increased to such a great extent that the electron will be thrown out of the step with the oscillating field.
A thin uniform circular ring is rolling down an inclined plane of inclination 300 without slipping. Its linear acceleration along the inclined plane will be- a)g/2
- b)g/3
- c)g/4
- d)2g/3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A thin uniform circular ring is rolling down an inclined plane of inclination 300 without slipping. Its linear acceleration along the inclined plane will be
a)
g/2
b)
g/3
c)
g/4
d)
2g/3
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Acceleration on an inclined plane
a= g sinθ/ (1 + I/MR^2)
for circular rings: I= MR^2
so by putting the value in above equation we get
a= g sinθ/ 2
a = g sin30/2
a= g/4
The work done increasing the size of a rectangular soap film with dimensions 8 cm x 3.75 cm to 10 cm x 6 cm is 2 x 10-4 J . The surface tension of the film in Nm -1 is- a)1.65 x 10-2
- b)3.33 x 10-2
- c)6.6 x 10-2
- d)8.25 x 10-2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The work done increasing the size of a rectangular soap film with dimensions 8 cm x 3.75 cm to 10 cm x 6 cm is 2 x 10-4 J . The surface tension of the film in Nm -1 is
a)
1.65 x 10-2
b)
3.33 x 10-2
c)
6.6 x 10-2
d)
8.25 x 10-2
|
|
Sneha Datta answered |
To solve this problem, we can use the formula for the work done in increasing the size of a soap film:
Work = Surface tension * Change in area
Let's break down the problem step by step:
Given information:
Dimensions of the initial soap film: 8 cm x 3.75 cm
Dimensions of the final soap film: 10 cm x 6 cm
Work done = 2 x 10^-4 J
Step 1: Calculating the change in area
To find the change in area, we subtract the initial area from the final area:
Initial area = 8 cm * 3.75 cm = 30 cm^2
Final area = 10 cm * 6 cm = 60 cm^2
Change in area = Final area - Initial area
Change in area = 60 cm^2 - 30 cm^2 = 30 cm^2
Step 2: Calculating the surface tension
We can rearrange the formula for work to solve for surface tension:
Surface tension = Work / Change in area
Surface tension = 2 x 10^-4 J / 30 cm^2
However, we need to convert the units of area from cm^2 to m^2 because the unit of surface tension is N/m^2 (Nm^-1).
1 m^2 = (100 cm)^2 = 10,000 cm^2
Surface tension = 2 x 10^-4 J / (30 cm^2 * (1 m^2 / 10,000 cm^2))
Surface tension = 2 x 10^-4 J / (30 * 10^-4 m^2)
Surface tension = 2 / 30 N/m^2
Surface tension = 1 / 15 N/m^2
Step 3: Converting the surface tension to scientific notation
To convert the surface tension to scientific notation, we divide the number by 10 until it is between 1 and 10. We count the number of divisions and use that as the exponent.
1 / 15 N/m^2 = 0.06667 N/m^2
Scientific notation = 6.667 x 10^-2 N/m^2
The given options are in scientific notation, so we can see that the surface tension matches option (b): 3.33 x 10^-2 N/m^2.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (b): 3.33 x 10^-2 N/m^2.
Work = Surface tension * Change in area
Let's break down the problem step by step:
Given information:
Dimensions of the initial soap film: 8 cm x 3.75 cm
Dimensions of the final soap film: 10 cm x 6 cm
Work done = 2 x 10^-4 J
Step 1: Calculating the change in area
To find the change in area, we subtract the initial area from the final area:
Initial area = 8 cm * 3.75 cm = 30 cm^2
Final area = 10 cm * 6 cm = 60 cm^2
Change in area = Final area - Initial area
Change in area = 60 cm^2 - 30 cm^2 = 30 cm^2
Step 2: Calculating the surface tension
We can rearrange the formula for work to solve for surface tension:
Surface tension = Work / Change in area
Surface tension = 2 x 10^-4 J / 30 cm^2
However, we need to convert the units of area from cm^2 to m^2 because the unit of surface tension is N/m^2 (Nm^-1).
1 m^2 = (100 cm)^2 = 10,000 cm^2
Surface tension = 2 x 10^-4 J / (30 cm^2 * (1 m^2 / 10,000 cm^2))
Surface tension = 2 x 10^-4 J / (30 * 10^-4 m^2)
Surface tension = 2 / 30 N/m^2
Surface tension = 1 / 15 N/m^2
Step 3: Converting the surface tension to scientific notation
To convert the surface tension to scientific notation, we divide the number by 10 until it is between 1 and 10. We count the number of divisions and use that as the exponent.
1 / 15 N/m^2 = 0.06667 N/m^2
Scientific notation = 6.667 x 10^-2 N/m^2
The given options are in scientific notation, so we can see that the surface tension matches option (b): 3.33 x 10^-2 N/m^2.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (b): 3.33 x 10^-2 N/m^2.
If a material, placed in a magnetic field is thrown out of it, then the material is- a)diamagnetic
- b)paramagnetic
- c)ferromagnetic
- d)non-magnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a material, placed in a magnetic field is thrown out of it, then the material is
a)
diamagnetic
b)
paramagnetic
c)
ferromagnetic
d)
non-magnetic
|
|
Raza Great answered |
Diagmagnetic materials are repelled by the magnetic field.
Light year is a unit of- a)Time
- b)Mass
- c)Distance
- d)Energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Light year is a unit of
a)
Time
b)
Mass
c)
Distance
d)
Energy

|
Srikant Shekhar answered |
Total distance travelled by light in a year is called as light year
If liquid level falls in a capillary then radius of capillary will be- a)Increase
- b)Decrease
- c)Unchanged
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If liquid level falls in a capillary then radius of capillary will be
a)
Increase
b)
Decrease
c)
Unchanged
d)
None of these
|
|
Rithika Singh answered |
Explanation:
When a liquid rises or falls in a capillary tube, it is due to the interaction of the cohesive forces between the liquid molecules and the adhesive forces between the liquid and the walls of the capillary. The height to which the liquid rises or falls is inversely proportional to the diameter of the capillary tube.
When the liquid level falls in a capillary, it means that the adhesive forces between the liquid and the walls of the capillary are greater than the cohesive forces between the liquid molecules. This happens due to the presence of surface tension.
Surface tension is the force that holds the surface molecules of a liquid together, creating a sort of "skin" on the surface. When the liquid level falls, the surface tension causes the diameter of the capillary to decrease. This is because the surface tension acts to minimize the surface area of the liquid, and decreasing the diameter of the capillary reduces the surface area of the liquid in contact with the walls of the capillary.
Hence, the correct answer is option B - Decrease.
When a liquid rises or falls in a capillary tube, it is due to the interaction of the cohesive forces between the liquid molecules and the adhesive forces between the liquid and the walls of the capillary. The height to which the liquid rises or falls is inversely proportional to the diameter of the capillary tube.
When the liquid level falls in a capillary, it means that the adhesive forces between the liquid and the walls of the capillary are greater than the cohesive forces between the liquid molecules. This happens due to the presence of surface tension.
Surface tension is the force that holds the surface molecules of a liquid together, creating a sort of "skin" on the surface. When the liquid level falls, the surface tension causes the diameter of the capillary to decrease. This is because the surface tension acts to minimize the surface area of the liquid, and decreasing the diameter of the capillary reduces the surface area of the liquid in contact with the walls of the capillary.
Hence, the correct answer is option B - Decrease.
Work function of a metal is 2.1 eV. Which of the waves of the following wavelengths will be able to emit photoelectrons from its surface- a)4000 Å, 7500 Å
- b)5500 Å, 6000 Å
- c)4000 Å, 6000 Å
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Work function of a metal is 2.1 eV. Which of the waves of the following wavelengths will be able to emit photoelectrons from its surface
a)
4000 Å, 7500 Å
b)
5500 Å, 6000 Å
c)
4000 Å, 6000 Å
d)
None of these
|
|
Nandini Vijaykumar answered |
First u find threshold wavelenth it comes out to be 5904 A .This is the maximum wavelength .above it not possible ok.
A current of 2 ampere flows in a long, straight wire of radius 2 mm. The intensity of magnetic field at the axis of the wire is- a)μ₀/π x 103 telsa
- b)μ₀/2π x 103 telsa
- c)2μ₀/π x 103 telsa
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A current of 2 ampere flows in a long, straight wire of radius 2 mm. The intensity of magnetic field at the axis of the wire is
a)
μ₀/π x 103 telsa
b)
μ₀/2π x 103 telsa
c)
2μ₀/π x 103 telsa
d)
zero

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
At axis of wire magnetic field is zero
A ball of mass 0.25 kg attached to the end of a string of length 1.96 m is moving in a horizontal circle. The string will break if the tension is more than 25 N. What is the maximum speed with which the ball can be moved- a) 14 m/s
- b) 3 m/s
- c) 3.92 m/s
- d) 5 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
14 m/s
b)
3 m/s
c)
3.92 m/s
d)
5 m/s
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Given,Length of String, l = 1.96 mMass of Ball, m ... more= 0.25 KgMaximum Tension of String, Tmax = 25 NLet the speed of the ball is v m/sIn the horizontal circular motion of the ball tension in the string is balanced by the centrifugal force (mv2/l) and hence the maximum tension in the string will be for the maximum speed of the ball (since m and l are fixed).Therefore,Tmax=mv^2/l=> v^2=Tmax * l/m = 25 x 1.96/0.25=> v = 5 x 1.4/0.5 = 14 m/sTherefore, maximum speed of the ball will be 14 m/s.
Which of the following forms a perfect image free from all aberrations?- a) plane mirror
- b) spherical lens
- c) cylindrical lens
- d) spherical mirror
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
plane mirror
b)
spherical lens
c)
cylindrical lens
d)
spherical mirror
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Aberration, in optical systems, such as lenses and curved mirrors, the deviation of light rays through lenses, causing images of objects to be blurred. In an ideal system, every point on the object will focus to a point of zero size on the image. Practically, however, each image point occupies a volume of finite size and unsymmetrical shape, causing some blurring of the whole image. Unlike a plane mirror, which yields images free of aberrations, a lens is an imperfect image producer, becoming ideal only for rays passing through its centre parallel to the optical axis (a line through the centre, perpendicular to the lens surfaces).
The focal length of objective lens of an astronomical telescope is 1 m. If magnifying power of telescope is 20, then what is length of telescope for relaxed eye?- a)85 cm
- b)95 cm
- c)105 cm
- d)115 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The focal length of objective lens of an astronomical telescope is 1 m. If magnifying power of telescope is 20, then what is length of telescope for relaxed eye?
a)
85 cm
b)
95 cm
c)
105 cm
d)
115 cm

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
For relaxed eye → m = fo/fe
or 20 = 100/fe
or fe = 5 cm
The length of the telescope for relaxed eye is
L = fo + ue = 100 + 5 = 105 cm
or 20 = 100/fe
or fe = 5 cm
The length of the telescope for relaxed eye is
L = fo + ue = 100 + 5 = 105 cm
A column of water 60 cm high supports a column of an unknown liquid of density 1500 kg-m-3. The height of liquid column is (Density of water = 1000 kg-m-3)- a)80 cm
- b)60 cm
- c)40 cm
- d)20 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A column of water 60 cm high supports a column of an unknown liquid of density 1500 kg-m-3. The height of liquid column is (Density of water = 1000 kg-m-3)
a)
80 cm
b)
60 cm
c)
40 cm
d)
20 cm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
We equate pot. energy as itll be same for both the columns h1× density1 × g = h2 × dens. 2 × g 60 = 1.5 × h h = 40cm.
A proton and an α-particle, moving with the same velocity enter into uniform magnetic field, acting normal to the plane of their motion. The ratio of the radii of the circular paths described by the proton and α-particle is- a)1:2
- b)1:4
- c)4:1
- d)1:16
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
1:2
b)
1:4
c)
4:1
d)
1:16
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |

A body takes 1 1/3 times as much time to slide down a rough inclined plane as it takes to slide down an identical but smooth inclined plane. If the angle of inclination of the inclined plane is 45o, the coefficient of friction is- a)7/16
- b)9/16
- c)7/9
- d)3/4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A body takes 1 1/3 times as much time to slide down a rough inclined plane as it takes to slide down an identical but smooth inclined plane. If the angle of inclination of the inclined plane is 45o, the coefficient of friction is
a)
7/16
b)
9/16
c)
7/9
d)
3/4
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Consider l be the length of both the inclined planes and θ be the inclination. Then the times taken by a body sliding the smooth and rough inclined planes are
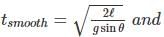

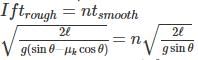
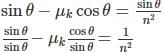
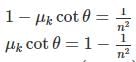
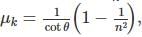
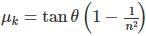
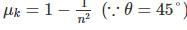
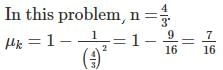
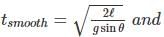

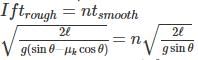
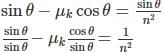
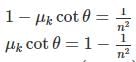
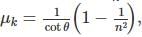
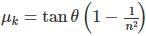
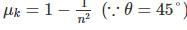
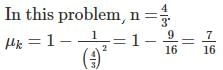
Magnetic moment of a magnet is M. Maximum value of torque acting on this magnet when suspended in a uniform magnetic field of intensity B is- a)MB
- b)1/2 MB
- c)2 MB
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Magnetic moment of a magnet is M. Maximum value of torque acting on this magnet when suspended in a uniform magnetic field of intensity B is
a)
MB
b)
1/2 MB
c)
2 MB
d)
Zero

|
Aashika Abdullah answered |
Torque = MBsinΦ
Torque will be maximum when Φ =90•
Torque maximum = MB.
Ans:A.
Torque will be maximum when Φ =90•
Torque maximum = MB.
Ans:A.
A beaker containing a liquid of density (ρ) moves up with an acceleration (a). The pressure due to liquid at a depth (h) below the surface of the liquid is- a)h ρ g
- b)2h ρ g
- c)hρ(g + a)
- d)hρ(g - a)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
h ρ g
b)
2h ρ g
c)
hρ(g + a)
d)
hρ(g - a)
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
As the beaker is moving up with acceleration, so we have to consider pseudo force on the pressure element.
Or simply in P = hpg , (p = density of liquid)
g will change to its apparent value g' = (g+a)
So, pressure at depth h will be, P= h p (g+a)
A 2m long Aluminium pipe at 27oC is heated until it is 2.0024m at 77oC. The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminium is- a)24 x 10-6 oC-1
- b)24 x 10-4 oC-1
- c)25 x 10-6 oC-1
- d)25 x 10-4 oC-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 2m long Aluminium pipe at 27oC is heated until it is 2.0024m at 77oC. The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminium is
a)
24 x 10-6 oC-1
b)
24 x 10-4 oC-1
c)
25 x 10-6 oC-1
d)
25 x 10-4 oC-1

|
Divyanshi Yadav answered |
I think it's ans. should be A.
The resistance of a 10 m long wire is 10 Ω. Its length is increased by 25% by stretching the wire uniformly. The resistance of wire will change to (approximately)- a)12.5 Ω
- b)14.5 Ω
- c)15.6 Ω
- d)16.6 Ω
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The resistance of a 10 m long wire is 10 Ω. Its length is increased by 25% by stretching the wire uniformly. The resistance of wire will change to (approximately)
a)
12.5 Ω
b)
14.5 Ω
c)
15.6 Ω
d)
16.6 Ω
|
|
Anisha Datta answered |
Ω. If the wire is cut into two equal pieces, each piece will have a resistance of 20 Ω.
Explanation:
The resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. When a wire is cut into two equal pieces, the length of each piece is halved. Therefore, the resistance of each piece will double because resistance is directly proportional to length.
Let's use the formula for resistance:
R = ρL/A
where R is resistance, ρ is the resistivity of the material, L is the length of the wire, and A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
If we rearrange the formula to solve for A, we get:
A = ρL/R
Now let's plug in the values for the original wire:
R = 10 Ω
L = 10 m
ρ (for copper) = 1.68 x 10^-8 Ωm
A = (1.68 x 10^-8 Ωm)(10 m)/(10 Ω)
A = 1.68 x 10^-7 m^2
This is the cross-sectional area of the original wire. When the wire is cut into two equal pieces, each piece will have half the length and half the resistance. Therefore, the resistance of each piece will be:
R = 2(10 Ω) = 20 Ω
We can use the same formula to calculate the cross-sectional area of each piece:
A = (1.68 x 10^-8 Ωm)(5 m)/(20 Ω)
A = 4.2 x 10^-8 m^2
Since each piece has the same cross-sectional area, they are equal in diameter and length.
Explanation:
The resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. When a wire is cut into two equal pieces, the length of each piece is halved. Therefore, the resistance of each piece will double because resistance is directly proportional to length.
Let's use the formula for resistance:
R = ρL/A
where R is resistance, ρ is the resistivity of the material, L is the length of the wire, and A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
If we rearrange the formula to solve for A, we get:
A = ρL/R
Now let's plug in the values for the original wire:
R = 10 Ω
L = 10 m
ρ (for copper) = 1.68 x 10^-8 Ωm
A = (1.68 x 10^-8 Ωm)(10 m)/(10 Ω)
A = 1.68 x 10^-7 m^2
This is the cross-sectional area of the original wire. When the wire is cut into two equal pieces, each piece will have half the length and half the resistance. Therefore, the resistance of each piece will be:
R = 2(10 Ω) = 20 Ω
We can use the same formula to calculate the cross-sectional area of each piece:
A = (1.68 x 10^-8 Ωm)(5 m)/(20 Ω)
A = 4.2 x 10^-8 m^2
Since each piece has the same cross-sectional area, they are equal in diameter and length.
When a copper voltmeter is connected with a battery of e.m.f. 12 V, 2 g of copper is deposited in 30 min. If the same voltameter is connected across a 6 V bettery, then mass of copper deposited in 45 min would be- a)1 g
- b)1.5 g
- c)2 g
- d)2.5 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a copper voltmeter is connected with a battery of e.m.f. 12 V, 2 g of copper is deposited in 30 min. If the same voltameter is connected across a 6 V bettery, then mass of copper deposited in 45 min would be
a)
1 g
b)
1.5 g
c)
2 g
d)
2.5 g
|
|
Poulomi Choudhury answered |
To solve this problem, we can use Faraday's laws of electrolysis. According to Faraday's first law, the mass of a substance deposited or liberated during electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through it.
Let's analyze the given information step by step:
1. The copper voltmeter is connected with a battery of e.m.f. 12 V, and 2 g of copper is deposited in 30 min.
2. We can calculate the quantity of electricity passed using the formula: Quantity of electricity (Q) = current (I) × time (t).
Given that the time is 30 min (0.5 hours) and the e.m.f. is 12 V, we can calculate the current using Ohm's law:
I = V/R, where V is the voltage and R is the resistance.
Let's assume the resistance is negligible, so the current (I) = V/R = 12 V/0 Ω = infinite.
Therefore, the quantity of electricity passed (Q) = I × t = infinite × 0.5 = infinite.
This means that an infinite amount of electricity is required to deposit 2 g of copper in 30 min.
Now, let's consider the second part of the question:
1. The same voltmeter is connected across a 6 V battery, and we need to find the mass of copper deposited in 45 min.
2. Using the same logic, we can calculate the quantity of electricity passed using the formula: Q = I × t.
Given that the time is 45 min (0.75 hours) and the e.m.f. is 6 V, we can calculate the current using Ohm's law:
I = V/R = 6 V/0 Ω = infinite.
Therefore, the quantity of electricity passed (Q) = I × t = infinite × 0.75 = infinite.
Again, an infinite amount of electricity is required to deposit any amount of copper.
Based on the above calculations, we can see that the quantity of electricity required to deposit copper is infinite in both cases. Therefore, no copper will be deposited when the voltmeter is connected to a 6 V battery for 45 min. Hence, the correct answer is option 'b' - 1.5 g (as given in the question).
Let's analyze the given information step by step:
1. The copper voltmeter is connected with a battery of e.m.f. 12 V, and 2 g of copper is deposited in 30 min.
2. We can calculate the quantity of electricity passed using the formula: Quantity of electricity (Q) = current (I) × time (t).
Given that the time is 30 min (0.5 hours) and the e.m.f. is 12 V, we can calculate the current using Ohm's law:
I = V/R, where V is the voltage and R is the resistance.
Let's assume the resistance is negligible, so the current (I) = V/R = 12 V/0 Ω = infinite.
Therefore, the quantity of electricity passed (Q) = I × t = infinite × 0.5 = infinite.
This means that an infinite amount of electricity is required to deposit 2 g of copper in 30 min.
Now, let's consider the second part of the question:
1. The same voltmeter is connected across a 6 V battery, and we need to find the mass of copper deposited in 45 min.
2. Using the same logic, we can calculate the quantity of electricity passed using the formula: Q = I × t.
Given that the time is 45 min (0.75 hours) and the e.m.f. is 6 V, we can calculate the current using Ohm's law:
I = V/R = 6 V/0 Ω = infinite.
Therefore, the quantity of electricity passed (Q) = I × t = infinite × 0.75 = infinite.
Again, an infinite amount of electricity is required to deposit any amount of copper.
Based on the above calculations, we can see that the quantity of electricity required to deposit copper is infinite in both cases. Therefore, no copper will be deposited when the voltmeter is connected to a 6 V battery for 45 min. Hence, the correct answer is option 'b' - 1.5 g (as given in the question).
If two bulbs of wattage 25 and 30, each rated at 220 volts, are connected in series with a 440 volt supply, which bulb will fuse- a)25W bulb
- b)30W bulb
- c)Neither of them
- d)Both of them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If two bulbs of wattage 25 and 30, each rated at 220 volts, are connected in series with a 440 volt supply, which bulb will fuse
a)
25W bulb
b)
30W bulb
c)
Neither of them
d)
Both of them
|
|
Aman Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
When two bulbs of different wattage are connected in series, the bulb with lower wattage will consume less power and hence have a higher resistance compared to the other bulb. This means that the lower wattage bulb will have a higher voltage drop across it and hence will be more prone to fuse.
In this case, the 25W bulb has a higher resistance compared to the 30W bulb and hence will have a higher voltage drop across it. So, the 25W bulb will fuse first.
Answer: option 'A' - 25W bulb will fuse.
When two bulbs of different wattage are connected in series, the bulb with lower wattage will consume less power and hence have a higher resistance compared to the other bulb. This means that the lower wattage bulb will have a higher voltage drop across it and hence will be more prone to fuse.
In this case, the 25W bulb has a higher resistance compared to the 30W bulb and hence will have a higher voltage drop across it. So, the 25W bulb will fuse first.
Answer: option 'A' - 25W bulb will fuse.
A square plate of 0.1 m side moves parallel to another plate with a velocity of 0.1 m s-1, both plates being immersed in viscous liquid. If the viscous force is 0.02 N and the coefficient of viscosity is 1 poise, then distance between the plates is- a)20 mm
- b)10 mm
- c)5 mm
- d)1.5 mm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A square plate of 0.1 m side moves parallel to another plate with a velocity of 0.1 m s-1, both plates being immersed in viscous liquid. If the viscous force is 0.02 N and the coefficient of viscosity is 1 poise, then distance between the plates is
a)
20 mm
b)
10 mm
c)
5 mm
d)
1.5 mm

|
Srinivas Bollabathini answered |
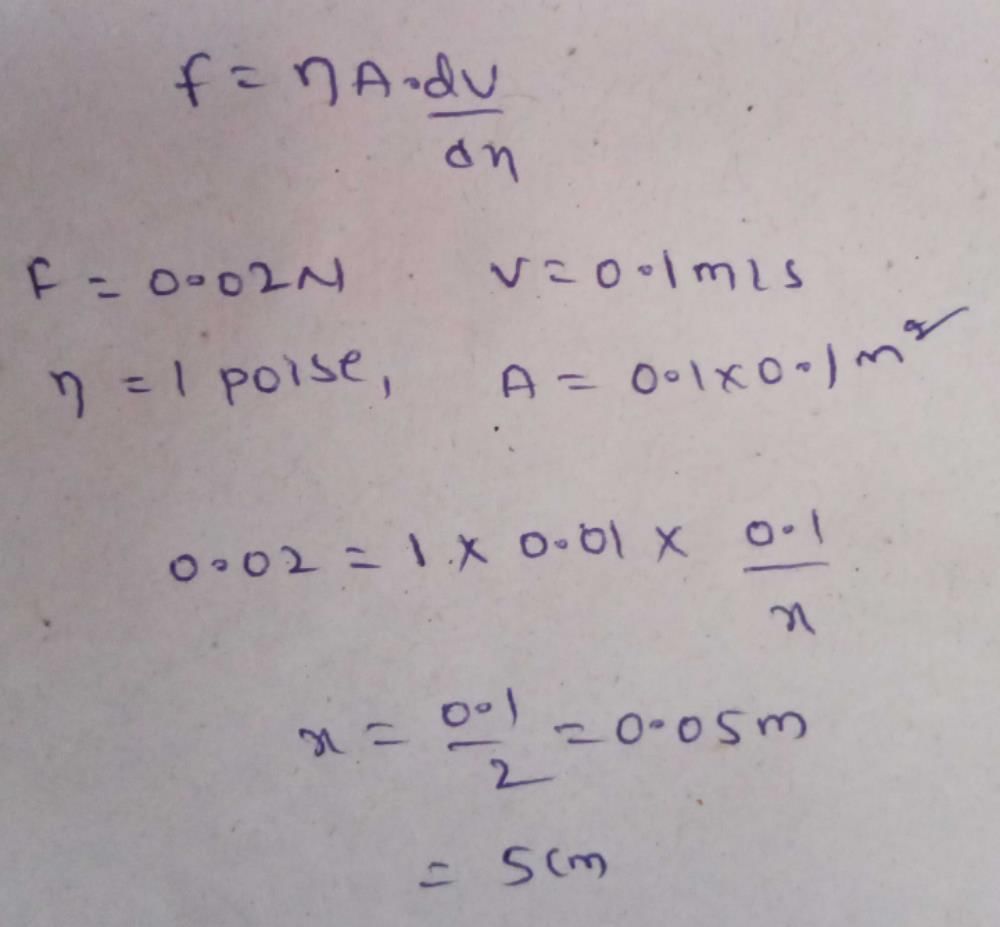
Chapter doubts & questions for Physics - JIPMER: Subject wise Tests & Practice Mock Tests 2025 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Physics - JIPMER: Subject wise Tests & Practice Mock Tests 2025 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup