All Exams >
CLAT >
Weekly Test for CLAT UG >
All Questions
All questions of Week 13 for CLAT Exam
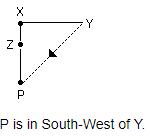
Salim started walking from point 'P' towards South. After walking 40 metres, he took a left turn and walked 30 metres and reached point Q. What is the straight line distance between P and Q, and Q is towards which direction of P?
- a)35 meters South-East
- b)50 meters South-West
- c)35 meters South-West
- d)50 meters South-East
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Salim started walking from point 'P' towards South. After walking 40 metres, he took a left turn and walked 30 metres and reached point Q. What is the straight line distance between P and Q, and Q is towards which direction of P?
a)
35 meters South-East
b)
50 meters South-West
c)
35 meters South-West
d)
50 meters South-East

|
Arya Roy answered |
As per the given information;

Point Q is in South East of Point P.
Distance between P and Q (PQ) = √(PO2 + OQ2)
PQ = √(402 + 302)
PQ = √(1600 + 900)
PQ = √2500
PQ = 50 m
Hence, "50 metres, Southeast" is the correct answer.
Sonu started from his house and walked 3 km Eastward, then he turned right and walked 2 km, then again he turned left and walked 1 km. Again he turned left and walked 3 km, then turned right and walked 2 km. He turned right again and walked 1 km and reached his school. What is the shortest distance between Sonu's house and his school?
- a)12 km
- b)9km
- c)5 km
- d)6 km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sonu started from his house and walked 3 km Eastward, then he turned right and walked 2 km, then again he turned left and walked 1 km. Again he turned left and walked 3 km, then turned right and walked 2 km. He turned right again and walked 1 km and reached his school. What is the shortest distance between Sonu's house and his school?
a)
12 km
b)
9km
c)
5 km
d)
6 km

|
Vertex Academy answered |
To solve this, let's break down Hemant's movements step by step and visualize his path:
- Hemant starts from his house and walks 3 km eastward.
- He turns right and walks 2 km south.
- He turns left and walks 1 km east.
- He turns right and walks 2 km south.
- He turns right and walks 1 km west and reaches his school.
Now, let's consider the overall east-west and north-south movement:
- East-West: Hemant initially walked 3 km east, then 1 km east, and finally 1 km west. So, the net eastward distance is 3 + 1 − 1 = 3 km.
- North-South: Hemant walked 2 km south, then another 2 km south, so he walked a total of 2 + 2 = 4 km south.
The minimum distance from Hemant’s house to the school can be found using the Pythagorean theorem (since he moved in perpendicular directions):
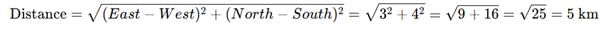
Thus, the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school is: D: 5 km
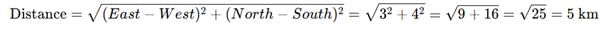
Thus, the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school is: D: 5 km
A starts from his house and moves towards B’s house which is 4km North. After walking for three-fourth of the distance he finds B coming towards him along with C, who is A’s enemy. Wanting to avoid him, A takes a left turn and runs for a distance of 2kms.Now, if from this point (say ‘P’) he decides to go to B’s house
How far is A, from his own house?
A. √5km
B. √3km
C. √7km
D. √13km
Correct answer is option is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Vertex Academy answered |
1. A walks three-fourths of the distance towards B's house, which is:
(3/4) × 4 km = 3 km (north).
After walking 3 km north, A takes a left turn and runs 2 km west.
(3/4) × 4 km = 3 km (north).
After walking 3 km north, A takes a left turn and runs 2 km west.
2. Now, we have a right-angled triangle, where:
- One leg (north) = 3 km,
- Another leg (west) = 2 km.
- One leg (north) = 3 km,
- Another leg (west) = 2 km.
3. The distance from A’s current position (P) to his house is the hypotenuse of this right-angled triangle:
Distance = √(3² + 2²) = √(9 + 4) = √13 km.
Distance = √(3² + 2²) = √(9 + 4) = √13 km.
Thus, the distance from A’s current position to his own house is √13 km.
The ore of Aluminium is - a) Bauxite
- b) Chromium
- c) Mica
- d) Manganese
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ore of Aluminium is
a)
Bauxite
b)
Chromium
c)
Mica
d)
Manganese
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Bauxite, an aluminium ore, is the world’s main source of aluminium. It consists mostly of the minerals gibbsite.
If a man on the moped starts from a point and rides 4km south, then turns left and rides 2km, then turn again to the right to ride 4km more, towards which direction is he moving?- a)North
- b)West
- c)East
- d)South
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a man on the moped starts from a point and rides 4km south, then turns left and rides 2km, then turn again to the right to ride 4km more, towards which direction is he moving?
a)
North
b)
West
c)
East
d)
South

|
Raghavendra Sharma answered |
Man's walking directions are as follows:
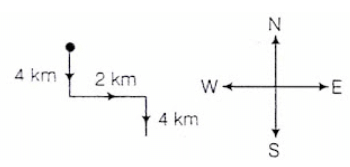

If A is to the south of B, and C is to the east of B, in what direction is A with respect to C?- a)North-East
- b)North-West
- c)South-East
- d)South-West
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is to the south of B, and C is to the east of B, in what direction is A with respect to C?
a)
North-East
b)
North-West
c)
South-East
d)
South-West

|
Sameer Rane answered |
Clearly comparing the direction of A w.r.t C in the second diagram with that in the first diagram, A will be south-west of C
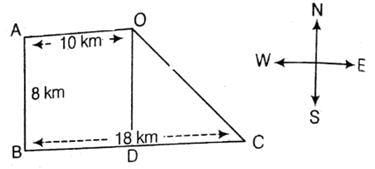
Lakshay starting walking towards west and goes 10km. Then he turns left and goes 8km. He again turns left and goes 18km. In which direction is he now from his starting point? - a)South-West
- b)North-East
- c)South-East
- d)North-West
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lakshay starting walking towards west and goes 10km. Then he turns left and goes 8km. He again turns left and goes 18km. In which direction is he now from his starting point?
a)
South-West
b)
North-East
c)
South-East
d)
North-West

|
Vertex Academy answered |
From the figure given, clearly the direction is OC which is South-East.

Little care on your part (A) / would have made you (B) / more successful than your friend. (C) / no error (D)- a)Little care on your part
- b)would have made you
- c)more successful than your friend
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Little care on your part (A) / would have made you (B) / more successful than your friend. (C) / no error (D)
a)
Little care on your part
b)
would have made you
c)
more successful than your friend
d)
no error

|
Ayush Roy answered |
Add ‘a’ before ‘little’.
Sushant started from his house and walked 5km north of his house. Then he turned left and walked 3km, then he turned right and walked 5km. Again he turned right and walked 3km. Where is his final destination from his house?- a)Back to his house
- b)7.5 km North-West
- c)7.5 km North-East
- d)10 km North
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sushant started from his house and walked 5km north of his house. Then he turned left and walked 3km, then he turned right and walked 5km. Again he turned right and walked 3km. Where is his final destination from his house?
a)
Back to his house
b)
7.5 km North-West
c)
7.5 km North-East
d)
10 km North

|
Vertex Academy answered |
To solve this question, let's analyze Sushant's path step-by-step based on the directions provided:
- Sushant starts at his house and walks 5 km north.
- He then turns left and walks 3 km west.
- Next, he turns right and walks 5 km north again.
- Finally, he turns right and walks 3 km east.
Now let’s assess Sushant's final position relative to his starting point:
- North-South movement: He walked 5 km north, then another 5 km north, totaling 10 km north.
- East-West movement: He walked 3 km west and then 3 km back east, which brings him back to the original east-west position he started from.
Given this analysis, Sushant's final destination is directly north of his house without any deviation east or west. Therefore, the correct answer is:
D: 10 km North
Neither she is intelligent (A) / nor hard working (B) / and still she expects to secure first class.(C) / no error (D)- a)Neither she is intelligent
- b)nor hard working
- c)and still she expects to secure first class
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Neither she is intelligent (A) / nor hard working (B) / and still she expects to secure first class.(C) / no error (D)
a)
Neither she is intelligent
b)
nor hard working
c)
and still she expects to secure first class
d)
no error

|
Jhanvi Nambiar answered |
Replace ‘Neither she is intelligent’ by ‘She is neither intelligent’
If South East becomes North, North East becomes West and this trend is continued, what will be the original West become?- a)North-East
- b)South-East
- c)South
- d)South-West
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If South East becomes North, North East becomes West and this trend is continued, what will be the original West become?
a)
North-East
b)
South-East
c)
South
d)
South-West

|
Manoj Ghosh answered |
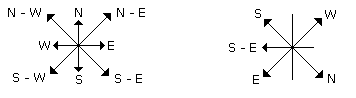
It is clear from the diagrams that new name of West will become South-East.
Rohan starts for morning walk towards west. He walks 1 km, then turns left and walks 600m, then turns left and walks 1.3km, again he turns right and walks 600m further. In which direction is he moving now?- a)North
- b)East
- c)West
- d)South
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Rohan starts for morning walk towards west. He walks 1 km, then turns left and walks 600m, then turns left and walks 1.3km, again he turns right and walks 600m further. In which direction is he moving now?
a)
North
b)
East
c)
West
d)
South
|
|
Kiran Reddy answered |
Rohan is walking in south now
Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow.Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions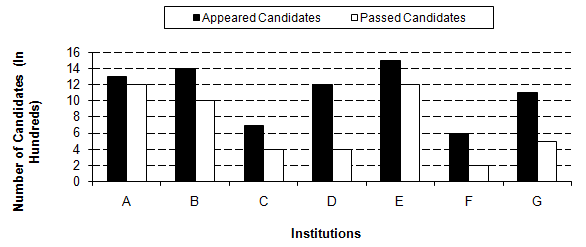 Q. What is the difference between the number of candidates appeared from institutions B, C, D and F together and candidates passed from institutions A, E and G together?
Q. What is the difference between the number of candidates appeared from institutions B, C, D and F together and candidates passed from institutions A, E and G together?- a)100
- b)900
- c)1000
- d)540
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow.
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions
Q. What is the difference between the number of candidates appeared from institutions B, C, D and F together and candidates passed from institutions A, E and G together?
a)
100
b)
900
c)
1000
d)
540
e)
None of these
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Required difference:-
=> ( 14+7+12+6) -(12+12+5)
=> 39 - 29 = 10 hundred
=> 1000
Gaurav walks 20 metres towards North. He then turns left and walks 40 metres. He again turns left and walks 20 metres. Further, he moves 20 metres after turning to the right. How far is he from his original position ?- a)40 metres
- b)50 metres
- c)60 metres
- d)70 metres
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gaurav walks 20 metres towards North. He then turns left and walks 40 metres. He again turns left and walks 20 metres. Further, he moves 20 metres after turning to the right. How far is he from his original position ?
a)
40 metres
b)
50 metres
c)
60 metres
d)
70 metres
|
|
Kiran Reddy answered |
Final distance from original position = AE = AD + DE = 60 metres
Of all the students (A) / Rita was less worried (B) / when the date for the annual examination was announced. (C) / no error (D)- a)Of all the students
- b)Rita was less worried
- c)when the date for the annual examination was announced
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Of all the students (A) / Rita was less worried (B) / when the date for the annual examination was announced. (C) / no error (D)
a)
Of all the students
b)
Rita was less worried
c)
when the date for the annual examination was announced
d)
no error
|
|
Gita choudhary answered |
Explanation:
The sentence is grammatically correct, and the error lies in the word choice.
- Of all the students: This phrase is correct as it sets up the comparison between Rita and the other students.
- Rita was less worried: This phrase is incorrect as it should be "Rita was the least worried," as it is clear that Rita is worried but less so than the other students. Using "less worried" implies that there is someone else who is even less worried than Rita, which is not stated in the sentence.
- When the date for the annual examination was announced: This phrase is correct as it gives the reason for Rita's level of worry.
- No error: This option is incorrect as there is an error in the sentence.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer as it correctly identifies the error in the sentence.
The sentence is grammatically correct, and the error lies in the word choice.
- Of all the students: This phrase is correct as it sets up the comparison between Rita and the other students.
- Rita was less worried: This phrase is incorrect as it should be "Rita was the least worried," as it is clear that Rita is worried but less so than the other students. Using "less worried" implies that there is someone else who is even less worried than Rita, which is not stated in the sentence.
- When the date for the annual examination was announced: This phrase is correct as it gives the reason for Rita's level of worry.
- No error: This option is incorrect as there is an error in the sentence.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer as it correctly identifies the error in the sentence.
Which type of rocks in India produces manganese? - a) Gondwana
- b) Dharwar
- c) Vindhya
- d) Tertiary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of rocks in India produces manganese?
a)
Gondwana
b)
Dharwar
c)
Vindhya
d)
Tertiary
|
|
Deepa Iyer answered |
The rocks of the Dharwar system are mainly sedimentary in origin and occur in narrow elongated synclines resting on the gneisses found in Bellary district, Mysore and the Aravallis of Rajputana. These rocks are enriched in manganese and iron ore which represents a significant resource of these metals.
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow.
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years
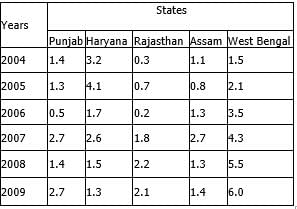 Q. What is the difference between the number of flights cancelled in Assam in the year 2007 and the total number of flights cancelled in Rajasthan in the year 2005, 2007 and 2008 together?
Q. What is the difference between the number of flights cancelled in Assam in the year 2007 and the total number of flights cancelled in Rajasthan in the year 2005, 2007 and 2008 together?
- a)200
- b)230
- c)210
- d)240
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow.
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years

Q. What is the difference between the number of flights cancelled in Assam in the year 2007 and the total number of flights cancelled in Rajasthan in the year 2005, 2007 and 2008 together?
a)
200
b)
230
c)
210
d)
240
e)
None of these

|
Knowledge Center answered |
In Assam = 2.7
Rajasthan in the year 2005, 2007 and 2008 together = 0.7 + 1.8 + 2.2 = 4.7
so difference = 4.7 - 2.7 = 2
as in hundreds so 200
Rajasthan in the year 2005, 2007 and 2008 together = 0.7 + 1.8 + 2.2 = 4.7
so difference = 4.7 - 2.7 = 2
as in hundreds so 200
Of the three ministers (A) / who do you think (B) / is going to prove more successful. (C) / no error (D)- a)Of the three ministers
- b)who do you think
- c)is going to prove more successful
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the three ministers (A) / who do you think (B) / is going to prove more successful. (C) / no error (D)
a)
Of the three ministers
b)
who do you think
c)
is going to prove more successful
d)
no error

|
Aashna Roy answered |
Replace ‘more’ by ‘the most’.
Bishrampur is famous for the mining of - a) Copper ore
- b) Iron ore
- c) Coal
- d) Manganese
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bishrampur is famous for the mining of
a)
Copper ore
b)
Iron ore
c)
Coal
d)
Manganese
|
|
Vijay Kumar answered |
Chhattisgarh is the second most coal-producing state. It has 15% coal quantity of the country while it produces 16% coal in the country. The main coalfield of North Chhattisgarh includes Chirmiri, Kursia Bishrampur, Ghilmili, Sonhat, Lakhanpur Sendouorgarh and Ramkola.
 I cooked this meal ---- for you, so I hope you like it.Correct answer is 'specially'. Can you explain this answer?
I cooked this meal ---- for you, so I hope you like it.Correct answer is 'specially'. Can you explain this answer?
I cooked this meal ---- for you, so I hope you like it.
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
"I cooked this meal specially for you", so I hope you like it.
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023, replaced the Indian Penal Code, 1860, to modernize India’s criminal justice framework. It defines a criminal offence as an act or omission that causes harm to society or individuals and is punishable by law. The BNS requires both mens rea (guilty mind) and actus reus (guilty act) for most offences, except in strict liability cases, where only the act suffices for conviction.
Section 103 of the BNS defines murder as intentionally causing a person’s death or performing an act knowing it is likely to cause death, punishable by life imprisonment or death. However, Section 105 provides for culpable homicide not amounting to murder if the act occurs under grave and sudden provocation, reducing the punishment to imprisonment up to seven years. Section 69 defines criminal conspiracy as an agreement between two or more persons to commit an illegal act, accompanied by an overt act in furtherance of the agreement, punishable by imprisonment up to seven years for serious offences. Under Section 303, theft is the dishonest taking of movable property from another’s possession without consent, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, a fine, or both. For minor thefts (e.g., property worth less than ₹5,000), courts may impose community service instead (Section 303(2)).
The BNS also recognizes the right of private defence under Section 96, allowing reasonable force to protect oneself or others, provided the force is proportionate to the threat. Additionally, the BNS emphasizes restorative justice, encouraging courts to consider victim compensation in sentencing.
Consider the following scenarios: Rhea, in a heated argument, slaps Mohan, who falls, hits his head, and dies. Rhea claims she was provoked by Mohan’s abusive language. In another case, Karan and Simran plan to steal a bicycle worth ₹3,000 from a shop, with Simran distracting the shopkeeper while Karan takes the bicycle.For stealing a bicycle worth ₹3,000, what punishment could the court impose on Karan and Simran under the BNS?- a)Imprisonment up to seven years only
- b)Imprisonment up to three years and a fine
- c)Community service or a fine
- d)Mandatory imprisonment for seven years
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023, replaced the Indian Penal Code, 1860, to modernize India’s criminal justice framework. It defines a criminal offence as an act or omission that causes harm to society or individuals and is punishable by law. The BNS requires both mens rea (guilty mind) and actus reus (guilty act) for most offences, except in strict liability cases, where only the act suffices for conviction.
Section 103 of the BNS defines murder as intentionally causing a person’s death or performing an act knowing it is likely to cause death, punishable by life imprisonment or death. However, Section 105 provides for culpable homicide not amounting to murder if the act occurs under grave and sudden provocation, reducing the punishment to imprisonment up to seven years. Section 69 defines criminal conspiracy as an agreement between two or more persons to commit an illegal act, accompanied by an overt act in furtherance of the agreement, punishable by imprisonment up to seven years for serious offences. Under Section 303, theft is the dishonest taking of movable property from another’s possession without consent, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, a fine, or both. For minor thefts (e.g., property worth less than ₹5,000), courts may impose community service instead (Section 303(2)).
The BNS also recognizes the right of private defence under Section 96, allowing reasonable force to protect oneself or others, provided the force is proportionate to the threat. Additionally, the BNS emphasizes restorative justice, encouraging courts to consider victim compensation in sentencing.
Consider the following scenarios: Rhea, in a heated argument, slaps Mohan, who falls, hits his head, and dies. Rhea claims she was provoked by Mohan’s abusive language. In another case, Karan and Simran plan to steal a bicycle worth ₹3,000 from a shop, with Simran distracting the shopkeeper while Karan takes the bicycle.
Section 103 of the BNS defines murder as intentionally causing a person’s death or performing an act knowing it is likely to cause death, punishable by life imprisonment or death. However, Section 105 provides for culpable homicide not amounting to murder if the act occurs under grave and sudden provocation, reducing the punishment to imprisonment up to seven years. Section 69 defines criminal conspiracy as an agreement between two or more persons to commit an illegal act, accompanied by an overt act in furtherance of the agreement, punishable by imprisonment up to seven years for serious offences. Under Section 303, theft is the dishonest taking of movable property from another’s possession without consent, punishable by up to seven years’ imprisonment, a fine, or both. For minor thefts (e.g., property worth less than ₹5,000), courts may impose community service instead (Section 303(2)).
The BNS also recognizes the right of private defence under Section 96, allowing reasonable force to protect oneself or others, provided the force is proportionate to the threat. Additionally, the BNS emphasizes restorative justice, encouraging courts to consider victim compensation in sentencing.
Consider the following scenarios: Rhea, in a heated argument, slaps Mohan, who falls, hits his head, and dies. Rhea claims she was provoked by Mohan’s abusive language. In another case, Karan and Simran plan to steal a bicycle worth ₹3,000 from a shop, with Simran distracting the shopkeeper while Karan takes the bicycle.
For stealing a bicycle worth ₹3,000, what punishment could the court impose on Karan and Simran under the BNS?
a)
Imprisonment up to seven years only
b)
Imprisonment up to three years and a fine
c)
Community service or a fine
d)
Mandatory imprisonment for seven years

|
Crafty Classes answered |
Section 303(2) allows community service for theft of property worth less than ₹5,000, applicable to the ₹3,000 bicycle.
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow:
Number of Students Appeared (A) and Failed (F) in Five
Classes of a school over the years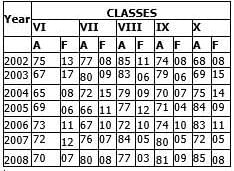 Q. What is the average number of failed students from Class VIII for the given years?
Q. What is the average number of failed students from Class VIII for the given years? - a)9
- b)7
- c)6
- d)8
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow:
Number of Students Appeared (A) and Failed (F) in Five
Classes of a school over the years
Number of Students Appeared (A) and Failed (F) in Five
Classes of a school over the years

Q. What is the average number of failed students from Class VIII for the given years?
a)
9
b)
7
c)
6
d)
8
e)
None of these

|
Knowledge Center answered |
To find the average number of failed students of Class 8th , we need to first add up the number of failed students
= 11+6+9+12+10+5+3= 56
Now total number of years = 7
Average = 56/7= 8
= 11+6+9+12+10+5+3= 56
Now total number of years = 7
Average = 56/7= 8
Jenny walked 2.5 km towards North and turned towards West. After covering 2 km’s he turned to South and walked 1.5 km’s. He then turned to East and covered 2 km’s. How far is Jenny from original point?- a)5 km
- b)2.5 km
- c)1.5 km
- d)1 km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Jenny walked 2.5 km towards North and turned towards West. After covering 2 km’s he turned to South and walked 1.5 km’s. He then turned to East and covered 2 km’s. How far is Jenny from original point?
a)
5 km
b)
2.5 km
c)
1.5 km
d)
1 km
|
|
Dibyajyoti answered |
Exactly
He had to cut a sorry figure (A) / when he realised that he had (B) / no any money in his purse.(C) / no error (D)
- a)He had to cut a sorry figure
- b)when he realised that he had
- c)no any money in his purse
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
He had to cut a sorry figure (A) / when he realised that he had (B) / no any money in his purse.(C) / no error (D)
a)
He had to cut a sorry figure
b)
when he realised that he had
c)
no any money in his purse
d)
no error
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The error in the sentence is in part (C). The phrase "no any money" is incorrect. It should be either "no money" or "any money" depending on the context, but in this case, "no money" is the correct form.
The corrected sentence is:
He had to cut a sorry figure when he realized that he had no money in his purse.
So, the correct answer is:
3. no any money in his purse
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow.
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years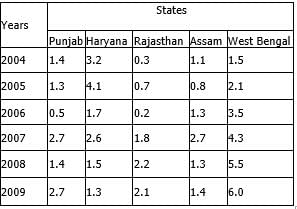 Q. What was the average number of flights cancelled in all the state together in the year 2008?
Q. What was the average number of flights cancelled in all the state together in the year 2008?- a)278
- b)232
- c)238
- d)272
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow.
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years

Q. What was the average number of flights cancelled in all the state together in the year 2008?
a)
278
b)
232
c)
238
d)
272
e)
None of these
|
|
Kunal Vats answered |
Average = 2008 total sum/5.
so, 1.4+1.5+2.2+1.3+5.5 = 11.9×100/5=238
so, 1.4+1.5+2.2+1.3+5.5 = 11.9×100/5=238
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow:
Number of Students Appeared (A) and Failed (F) in Five
Classes of a school over the years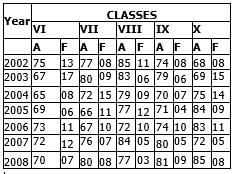 Q. What is the number of passed students for all the classes together in the year 2007?
Q. What is the number of passed students for all the classes together in the year 2007? - a)358
- b)317
- c)350
- d)327
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow:
Number of Students Appeared (A) and Failed (F) in Five
Classes of a school over the years
Number of Students Appeared (A) and Failed (F) in Five
Classes of a school over the years

Q. What is the number of passed students for all the classes together in the year 2007?
a)
358
b)
317
c)
350
d)
327
e)
None of these
|
|
Prity Biswas answered |
VI=72-12=60
VII=76-7=69
VIII=84-5=79
IX=80-5=75
X=72-5=67
TOTAL = 60+69+79+75+67=350(C)
VII=76-7=69
VIII=84-5=79
IX=80-5=75
X=72-5=67
TOTAL = 60+69+79+75+67=350(C)
Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow.
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions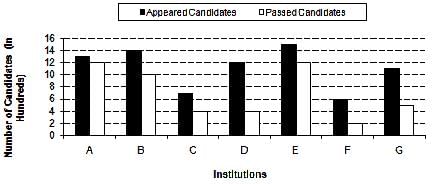
Q. What is the ratio of the number of candidates who have failed Institution B to the number of candidates who have appeared from institution F?- a)2: 5
- b)2: 3
- c)4: 3
- d)1: 3
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow.
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions

Q. What is the ratio of the number of candidates who have failed Institution B to the number of candidates who have appeared from institution F?
a)
2: 5
b)
2: 3
c)
4: 3
d)
1: 3
e)
None of these

|
Tusharvyas Tusharvyas answered |
From B 1400 appeared and 1000 passed it means 400 failed and from F 600 appeared so
400:600 makes 2:3
400:600 makes 2:3
Study the following graph carefully and answer the question.
Water level of four major Rivers (in metres) in four different Months
Water level of four Rivers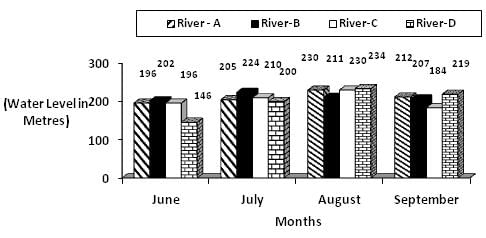 Q. What is the average water level of River –A in all the four months together?
Q. What is the average water level of River –A in all the four months together? - a)224.50 m
- b)212.25 m
- c)210.75 m
- d)222.25 m
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following graph carefully and answer the question.
Water level of four major Rivers (in metres) in four different Months
Water level of four Rivers
Water level of four major Rivers (in metres) in four different Months
Water level of four Rivers

Q. What is the average water level of River –A in all the four months together?
a)
224.50 m
b)
212.25 m
c)
210.75 m
d)
222.25 m
e)
None of these

|
Shanaya Sharma answered |
Average water level of river A = (196+205+230+212)/4 = 210.75 m
A man walks 1 km to East and then he turns to South and walks 5 km. Again he turns to East and walks 2 km. After this he turns to North and walks 9 km. Now, how far is he from his starting point?- a)3 km
- b)4 km
- c)5 km
- d)7 km
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A man walks 1 km to East and then he turns to South and walks 5 km. Again he turns to East and walks 2 km. After this he turns to North and walks 9 km. Now, how far is he from his starting point?
a)
3 km
b)
4 km
c)
5 km
d)
7 km

|
Akanksha Dey answered |
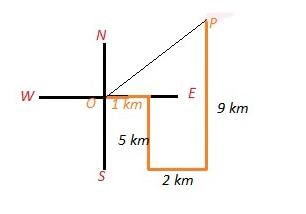
The last position of the man is P and OEP is a Right angled triangle in which
EP = 3 km and OE = 4 km
Thus,
OP = √(32 +42)
OP = √25
OP = 5 km.
EP = 3 km and OE = 4 km
Thus,
OP = √(32 +42)
OP = √25
OP = 5 km.
Even the most perfect person (A) / in the world is said to have erred (B) / when there was time to perform. (C) / no error (D)- a)Even the most perfect person
- b)in the world is said to have erred
- c)when there was time to perform
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Even the most perfect person (A) / in the world is said to have erred (B) / when there was time to perform. (C) / no error (D)
a)
Even the most perfect person
b)
in the world is said to have erred
c)
when there was time to perform
d)
no error

|
Sanaya Das answered |
Delete ‘most’ and replace ‘the’ by ‘a’
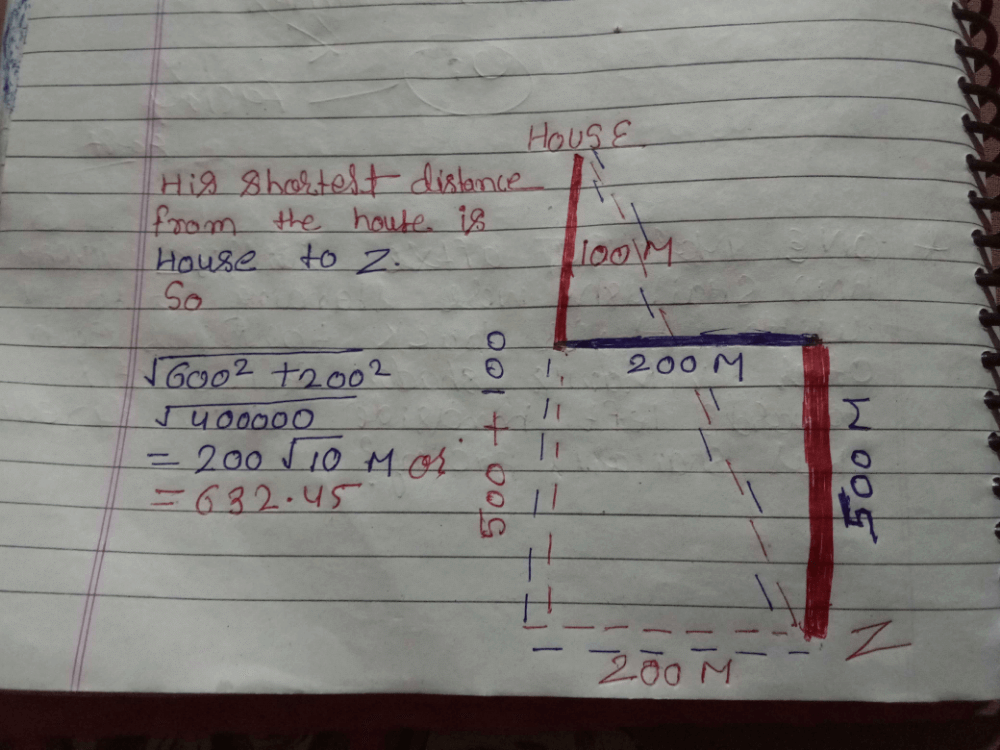
Hemant started from his house and walked 3km eastward, then he turned right and walked 2km, then again he turned left and walked 1 km, then turned right and walked 2 km. He turned right again and walked 1 km and reached his school. What is the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school?- a)12 km
- b)9km
- c)6 km
- d)5 km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hemant started from his house and walked 3km eastward, then he turned right and walked 2km, then again he turned left and walked 1 km, then turned right and walked 2 km. He turned right again and walked 1 km and reached his school. What is the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school?
a)
12 km
b)
9km
c)
6 km
d)
5 km

|
Vertex Academy answered |
To solve this, let's break down Hemant's movements step by step and visualize his path:
- Hemant starts from his house and walks 3 km eastward.
- He turns right and walks 2 km south.
- He turns left and walks 1 km east.
- He turns right and walks 2 km south.
- He turns right and walks 1 km west and reaches his school.
Now, let's consider the overall east-west and north-south movement:
- East-West: Hemant initially walked 3 km east, then 1 km east, and finally 1 km west. So, the net eastward distance is 3 + 1 − 1 = 3 km.
- North-South: Hemant walked 2 km south, then another 2 km south, so he walked a total of 2 + 2 = 4 km south.
The minimum distance from Hemant’s house to the school can be found using the Pythagorean theorem (since he moved in perpendicular directions):
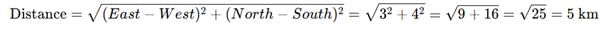
Thus, the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school is: D: 5 km
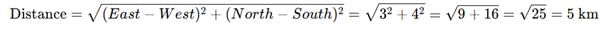
Thus, the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school is: D: 5 km
Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow.
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions
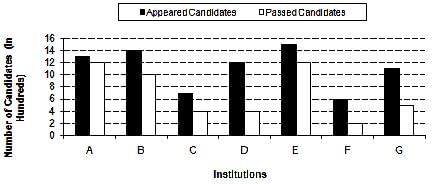 Q. What is the average number of candidates passed from all the institutions together?
Q. What is the average number of candidates passed from all the institutions together?
- a)700
- b)490
- c)350
- d)675
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following graph and answer the questions that follow.
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions
Number of Appeared Candidates and Passed Candidates (in hundreds) in a test from seven different Institutions

Q. What is the average number of candidates passed from all the institutions together?
a)
700
b)
490
c)
350
d)
675
e)
None of these
|
|
Gopu Gajpal answered |
(1200+1000+400+400+1200+200+500)/7=700
He is as intelligent if not more intelligent (A) / than his brother who has qualified (B) / for this post.(C) / no error (D)- a)He is as intelligent if not more intelligent
- b)than his brother who has qualified
- c)for this post.
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
He is as intelligent if not more intelligent (A) / than his brother who has qualified (B) / for this post.(C) / no error (D)
a)
He is as intelligent if not more intelligent
b)
than his brother who has qualified
c)
for this post.
d)
no error

|
Devanshi Datta answered |
Add ‘as’ after ‘as intelligent’.
Starting from a point X Jayant walked 15 metres towards West, he turned to his left and walked 20 metres. He then turned to his left and walked 15 metres. He then further turned to his right and walked 12 metres. How far is Jayant from the point X and in which direction?- a)32 metres South
- b)47 metres East
- c)42 metres North
- d)27 metres South
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Starting from a point X Jayant walked 15 metres towards West, he turned to his left and walked 20 metres. He then turned to his left and walked 15 metres. He then further turned to his right and walked 12 metres. How far is Jayant from the point X and in which direction?
a)
32 metres South
b)
47 metres East
c)
42 metres North
d)
27 metres South
|
|
Kiran Reddy answered |
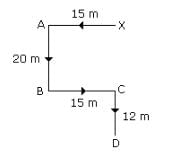
Required distance= 20 +12
= 32 m in south direction
= 32 m in south direction
Which mineral is mined in Turamdih?- a) Kyanite
- b) Asbestos
- c) Mica
- d) Uranium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which mineral is mined in Turamdih?
a)
Kyanite
b)
Asbestos
c)
Mica
d)
Uranium
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
- Turamdih Uranium deposit is located about 24 km west of Jaduguda.
Hemant started from his house and walked 3km eastward, then he turned right and walked 2km, then again he turned left and walked 1 km, then turned right and walked 2 km. He turned right again and walked 1 km and reached his school. What is the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school?- a)12 km
- b)9km
- c)6 km
- d)5 km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hemant started from his house and walked 3km eastward, then he turned right and walked 2km, then again he turned left and walked 1 km, then turned right and walked 2 km. He turned right again and walked 1 km and reached his school. What is the minimum distance between Hemant’s house and his school?
a)
12 km
b)
9km
c)
6 km
d)
5 km
|
|
Faizan Khan answered |
Yes, the correct one is 5 Km
using pythagoras theoram.
using pythagoras theoram.
√3 ^2 + 4^ 2 = √9+16= √25
= 5 km is required answer
A starts from his house and moves towards B’s house which is 4km North. After walking for three-fourth of the distance he finds B coming towards him along with C, who is A’s enemy. Wanting to avoid him, A takes a left turn and runs for a distance of 2kms.Now, if from this point (say ‘P’) he decides to go to B’s house, how much distance would he need to cover?- a)3km
- b)Ö5km
- c)1km
- d)Ö3km
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A starts from his house and moves towards B’s house which is 4km North. After walking for three-fourth of the distance he finds B coming towards him along with C, who is A’s enemy. Wanting to avoid him, A takes a left turn and runs for a distance of 2kms.Now, if from this point (say ‘P’) he decides to go to B’s house, how much distance would he need to cover?
a)
3km
b)
Ö5km
c)
1km
d)
Ö3km

|
Vertex Academy answered |
Let's analyze the path taken by A and the distances involved:
- A moves towards B's house: A starts moving north towards B's house which is 4 km away.
- A covers three-fourth of the distance: He covers 4 × 3/4 = 3 km towards the north.
- A takes a left turn: At this point, A is 1 km away from B's house (since he has covered 3 km out of 4 km). He then takes a left turn, which would be towards the west and runs 2 km.
Now, A is 1 km south of B's house and 2 km west of a direct line north from B’s house. To find the distance from point P (A's new location) to B's house, we use the Pythagorean theorem:
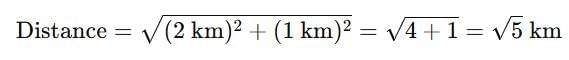
Thus, A would need to cover a distance of: B: √5km
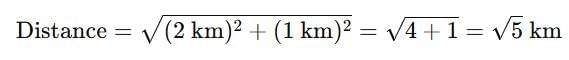
Thus, A would need to cover a distance of: B: √5km
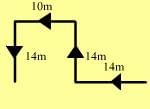
Namratha walks 14 metres towards west, then turns to her right and walks 14 meters and then turns to her left and walks 10 metres. Again turning to her left she walks 14 metres. What is the shortest distance (in metres) between her starting point and her present position?
- a)38m
- b)28m
- c)24m
- d)10m
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Namratha walks 14 metres towards west, then turns to her right and walks 14 meters and then turns to her left and walks 10 metres. Again turning to her left she walks 14 metres. What is the shortest distance (in metres) between her starting point and her present position?
a)
38m
b)
28m
c)
24m
d)
10m
e)
None of these

|
Hridoy Das answered |
Let's break down Namratha's movements step by step:
- First Movement: She walks 14 meters west.
- Second Movement: She turns right and walks 14 meters north.
- Third Movement: She turns left and walks 10 meters west.
- Fourth Movement: She turns left again and walks 14 meters south.
Now, let's analyze her position.
- After the first movement, she's 14 meters west of the starting point.
- After the second movement, she's 14 meters west and 14 meters north of the starting point.
- After the third movement, she's 24 meters west and 14 meters north of the starting point.
- After the fourth movement, she moves 14 meters south, so she's now 24 meters west and at the same latitude as her starting point (because the south movement cancels out the north movement).
To find the shortest distance between her starting point and her present position, we just need to calculate the straight-line distance (which is the horizontal distance since her vertical displacement is zero).
Since she is 24 meters west of her starting point, the shortest distance is:
Distance=24 meters\text{Distance} = 24 \text{ meters}Distance=24 meters
So the correct answer is 24 meters (Option 3).
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow.Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years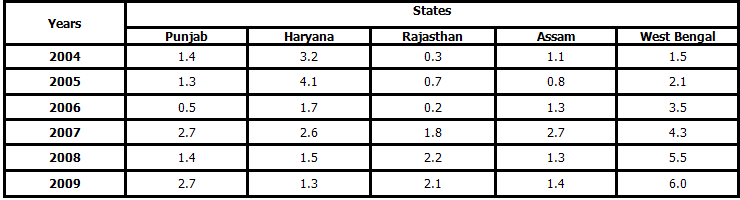 Q. Number of flights cancelled in Haryana in the year 2004 was what percent of the total number of flights cancelled in Punjab over all the years together?
Q. Number of flights cancelled in Haryana in the year 2004 was what percent of the total number of flights cancelled in Punjab over all the years together? - a)12
- b)32
- c)36
- d)24
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following table carefully to answer the questions that follow.
Number of flights (in hundreds) cancelled in five different sates during six different years
Q. Number of flights cancelled in Haryana in the year 2004 was what percent of the total number of flights cancelled in Punjab over all the years together?
a)
12
b)
32
c)
36
d)
24
e)
None of these

|
Richa Shukla answered |
Flights cancelled in haryana in 2004 are 320 and that in punjab over all the years together are 1000.
so 320÷1000×100=32%
so 320÷1000×100=32%
Privatization offers the most ideal situation (A) / for consumers because private sector (B) / is very conscious of quality. (C) / no error (D)- a)Privatization offers the most ideal situation
- b)for consumers because private sector
- c)is very conscious of quality
- d)no error
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Privatization offers the most ideal situation (A) / for consumers because private sector (B) / is very conscious of quality. (C) / no error (D)
a)
Privatization offers the most ideal situation
b)
for consumers because private sector
c)
is very conscious of quality
d)
no error

|
Megha Patel answered |
Delete ‘most’.
 Alice and Stan are very ---- married.Correct answer is 'happily'. Can you explain this answer?
Alice and Stan are very ---- married.Correct answer is 'happily'. Can you explain this answer?
Alice and Stan are very ---- married.

|
Talent Skill Learning answered |
The correct sentence is: "Alice and Stan are very happily married."
"Happily" is the adverb that modifies the adjective "married." It describes how Alice and Stan are married.
In which one of the following is a higher percentage of carbon found? - a) Lignite coal
- b) Peat coal
- c) Bituminous coal
- d) Anthracite coal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following is a higher percentage of carbon found?
a)
Lignite coal
b)
Peat coal
c)
Bituminous coal
d)
Anthracite coal
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Anthracite has a higher percentage of Carbon. It has a carbon content of over 87% on a dry ash-free basis.
Chapter doubts & questions for Week 13 - Weekly Test for CLAT UG 2025 is part of CLAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CLAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CLAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Week 13 - Weekly Test for CLAT UG in English & Hindi are available as part of CLAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CLAT Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily