All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper's Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Reproductive Health for NEET Exam
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is considered safe up to how many weeks of pregnancy?[2011]- a)Eight weeks
- b)Twelve weeks
- c)Eighteen weeks
- d)Six weeks
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is considered safe up to how many weeks of pregnancy?
[2011]
a)
Eight weeks
b)
Twelve weeks
c)
Eighteen weeks
d)
Six weeks

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Medical termination of pregnancy is considered safe up to twelve weeks of pregnancy.
Which of the following is a technique of direct introduction of gametes into the oviduct?- a)ET
- b)IVF
- c)POST
- d)MTS
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a technique of direct introduction of gametes into the oviduct?
a)
ET
b)
IVF
c)
POST
d)
MTS
|
|
Keerthana Iyer answered |
The technique of direct introduction of gametes into oviduct is called GIFT (gamete intrafallopian transfer).
Reproductive health includes:- a)Protection from STD’s, contraceptive and ARTs
- b)Financial independence
- c)Child education
- d)Child and mother care only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reproductive health includes:
a)
Protection from STD’s, contraceptive and ARTs
b)
Financial independence
c)
Child education
d)
Child and mother care only
|
|
Pankaj Singh answered |
Answer :
- a)Protection from STD’s, contraceptive and ARTs
Successful implementation of various action plans to attainreproductive health requires strong infrastructural facilities, professionalexpertise and material support. These are essential to provide medicalassistance and care to people in reproduction-related problems likepregnancy, delivery, STDs, abortions, contraception, menstrual problems,infertility, etc. Implementation of better techniques and new strategiesfrom time to time are also required to provide more efficient care andassistance to people. Statutory ban on amniocentesis (a foetal sexdetermination test based on the chromosomal pattern in the amnioticfluid surrounding the developing embryo) for sex-determination to legallycheck increasing female foeticides, massive child immunisation, etc., aresome programmes that merit mention in this connection.
Preventive birth control measure is__________.- a)Preventing sperms from entering uterus
- b)Preventing union of ovum and sperm
- c)Test-tube babies
- d)MTP
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Preventive birth control measure is__________.
a)
Preventing sperms from entering uterus
b)
Preventing union of ovum and sperm
c)
Test-tube babies
d)
MTP
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Preventive birth control measures is preventing sperms from entering the uterus.
► Barrier methods of contraception: Diaphragms, Sponges, and Cervical caps that prevent the sperm from entering the uterine cavity.
Which of the following birth control measures can be considered as the safest?- a)Termination of unwanted pregnancy
- b)The use of physical barriers
- c)Sterilisation techniques
- d)The rhythm method
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following birth control measures can be considered as the safest?
a)
Termination of unwanted pregnancy
b)
The use of physical barriers
c)
Sterilisation techniques
d)
The rhythm method

|
Sharvari Kuber answered |
In sterilisation method method, tubectomy or vasectomy is used in which the fallopian tube and vas deferens are cut respectively. This prevents the transfer of sperms in males and ova in females for fertilisation permanently. So this is the safest method.
Copper-T is a device that prevents: [2000]
- a)Implantation of blastocyst
- b)Ovulation
- c)Fertilization
- d)Both A and C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Copper-T is a device that prevents: [2000]
a)
Implantation of blastocyst
b)
Ovulation
c)
Fertilization
d)
Both A and C
|
|
Jeshika Maurya answered |
Option d is correct.. becoz.... Copper T when placed in uterus it realeses copper which make the uterus walls unfavorable for implantation it also hinders ovulation.. Hope It helps u...
Which one of the following groups includes sexually transmitted diseases?- a)Gonorrhoea, Hepatitis B, Chlamydiasis
- b)AIDS, Syphilis, Cholera
- c)HIV, Malaria, Trichomoniasis
- d)Hepatitis B, Haemophilia, AIDS
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following groups includes sexually transmitted diseases?
a)
Gonorrhoea, Hepatitis B, Chlamydiasis
b)
AIDS, Syphilis, Cholera
c)
HIV, Malaria, Trichomoniasis
d)
Hepatitis B, Haemophilia, AIDS

|
Chandan Kumar answered |
Option A is the correct answer ! you see option D is incorrect because heamophilia is a genetic disorder related to blood clot , whereas in option A all the diseases are sexually transmitted ! it contains all veneral diseases.
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India, as at present ?[2011]- a)Cervical caps
- b)Tubectomy
- c)Diaphragms
- d)IUDs. (Intra uterine devices)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India, as at present ?
[2011]
a)
Cervical caps
b)
Tubectomy
c)
Diaphragms
d)
IUDs. (Intra uterine devices)

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Intra uterine device (IUD) is a method of contraception in India. The IUD is inserted in the woman’s uterus through the cervix.
Which of the following is hormone-releasing IUD? [NEET 2021]- a)LNG-20
- b)Multiload-375
- c)Lippes loop
- d)Cu-7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is hormone-releasing IUD? [NEET 2021]
a)
LNG-20
b)
Multiload-375
c)
Lippes loop
d)
Cu-7
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
These Intra Uterine Devices are presently available as the non-medicated IUDs (e.g., Lippes loop), copper releasing IUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375) and the hormone releasing IUDs (Progestasert, LNG-20)
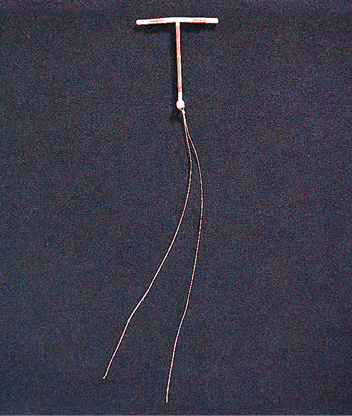

Saheli was developed by scientists at _______ in India.- a)Indian Institute of Science
- b)Indian Institute of Technology
- c)Central Drug Research Institute
- d)Acropolis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Saheli was developed by scientists at _______ in India.
a)
Indian Institute of Science
b)
Indian Institute of Technology
c)
Central Drug Research Institute
d)
Acropolis
|
|
Snehal Khanna answered |
Saheli is a contraceptive pill that was developed by scientists at the Central Drug Research Institute in India. It is a non-steroidal contraceptive pill that is effective in preventing pregnancy.
Details:
• Saheli was developed in the 1980s by a team of scientists at the Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow, India.
• The team was led by Dr. Pramila Srivastava.
• Saheli is a non-steroidal contraceptive pill that contains a compound called Centchroman.
• Centchroman is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that acts as an anti-estrogen.
• It is effective in preventing pregnancy and has fewer side effects compared to other contraceptive pills.
• Saheli is also known as the "weekend pill" as it is taken only once a week.
• It has been approved for use in India and several other countries.
• Saheli is considered to be a breakthrough in contraceptive research and has been hailed as a safe and effective method of birth control for women.
Details:
• Saheli was developed in the 1980s by a team of scientists at the Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow, India.
• The team was led by Dr. Pramila Srivastava.
• Saheli is a non-steroidal contraceptive pill that contains a compound called Centchroman.
• Centchroman is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that acts as an anti-estrogen.
• It is effective in preventing pregnancy and has fewer side effects compared to other contraceptive pills.
• Saheli is also known as the "weekend pill" as it is taken only once a week.
• It has been approved for use in India and several other countries.
• Saheli is considered to be a breakthrough in contraceptive research and has been hailed as a safe and effective method of birth control for women.
Which one is not a sexually transmitted disease?- a)Syphilis
- b)AIDS
- c)Encephalitis
- d)Genital herpes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a sexually transmitted disease?
a)
Syphilis
b)
AIDS
c)
Encephalitis
d)
Genital herpes
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) comprise a diverse group that includes blood-borne diseases, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and ulcerative lesions. Examples : Syphilis, Genital herpes, HIV /Aids
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. The majority of cases are caused by either a viral infection or the immune system mistakenly attacking brain tissue.
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. The majority of cases are caused by either a viral infection or the immune system mistakenly attacking brain tissue.
Which of the following contraceptive method is useful to control STD’s as well as unwanted pregnancy?- a)Tubectomy
- b)Condom
- c)Copper-T
- d)Oral pills
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following contraceptive method is useful to control STD’s as well as unwanted pregnancy?
a)
Tubectomy
b)
Condom
c)
Copper-T
d)
Oral pills
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Condoms are protective covering of penis that do not allow the passage of semen into vagina of female during sexual intercourse.
- This contracetive prevents the fusion of body fluid of male and female and protect from STDs.
Diaphragms are contraceptive devices used by females. Choose the correct option from the statements given below:
(i) They are introduced into the uterus.
(ii) They are placed to cover the cervical region.
(iii) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
(iv) They act as spermicidal agents.- a)(iii) and (iv)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Diaphragms are contraceptive devices used by females. Choose the correct option from the statements given below:
(i) They are introduced into the uterus.
(ii) They are placed to cover the cervical region.
(iii) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
(iv) They act as spermicidal agents.
(i) They are introduced into the uterus.
(ii) They are placed to cover the cervical region.
(iii) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
(iv) They act as spermicidal agents.
a)
(iii) and (iv)
b)
(i) and (ii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iii)

|
Vanshika Rastogi answered |
Answer is Option D. Diaphragms ain't spermicidal Because it doesn't kill the sperms..instead prevents sperm entry as they are to be placed in the cervical region as a barrier / cover .
In ET technique the embryo is transferred into _________.
- a)Always fallopian tube
- b)Always uterus
- c)Fallopian tube or uterus
- d)Ovary
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In ET technique the embryo is transferred into _________.
a)
Always fallopian tube
b)
Always uterus
c)
Fallopian tube or uterus
d)
Ovary
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
In ET (embryo transfer) technique, in vitro fertilized embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube or uterus for further development.
- In this type of technique, male and female gametes are fused outside the mother's body. It is used either when the male cannot produce enough sperms to fertilize the ovum or the females can not release ova for the purpose.
- After the embryo reaches 8 celled stages, known as the morula, it is transferred to the female fallopian tubule. If it is in the 16 celled stages, known as blastomere, it is transferred directly to the female uterus.
Embryo Transfer technique:
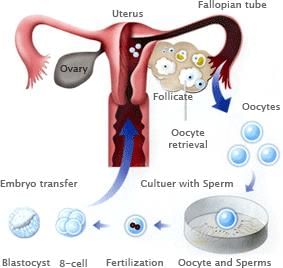

Hence, the correct option is C.
NCERT Reference: topic “INFERTILITY” of chapter: Reproductive Health of NCERT.
Now a day, there is less childless couple. This is due to_________.- a)Assisted reproductive technologies
- b)Awareness among the couples
- c)Educated population
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Now a day, there is less childless couple. This is due to_________.
a)
Assisted reproductive technologies
b)
Awareness among the couples
c)
Educated population
d)
None of these
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The couples can be assisted to have children through certain special techniques called the assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
The applications of reproductive technology are:
(i) Test tube baby
(ii) Artificial insemination technique (AIT)
(iii) Gamete intra Fallopian transfer (GIFT)
(iv) lntra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
(i) Test tube baby
(ii) Artificial insemination technique (AIT)
(iii) Gamete intra Fallopian transfer (GIFT)
(iv) lntra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called?- a)Venereal disease
- b)Fungal disease
- c)Bacterial disease
- d)Viral disease
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called?
a)
Venereal disease
b)
Fungal disease
c)
Bacterial disease
d)
Viral disease
|
|
Shubham Kulkarni answered |
Answer :
- a)Venereal disease
Diseases or infection which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called
sexually transmitted disease or venereal disease or reproductive tract infections.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Family planning programmes were initiated in 1951
(ii) According to WHO, reproductive health means total well being in the physical, social, behavioural and emotional aspects of reproduction
(iii) Saheli was developed at CDRI in Lucknow
(iv) Amniocentesis should not be banned as it is a foetal sex determination test- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (ii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Family planning programmes were initiated in 1951
(ii) According to WHO, reproductive health means total well being in the physical, social, behavioural and emotional aspects of reproduction
(iii) Saheli was developed at CDRI in Lucknow
(iv) Amniocentesis should not be banned as it is a foetal sex determination test
(i) Family planning programmes were initiated in 1951
(ii) According to WHO, reproductive health means total well being in the physical, social, behavioural and emotional aspects of reproduction
(iii) Saheli was developed at CDRI in Lucknow
(iv) Amniocentesis should not be banned as it is a foetal sex determination test
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (ii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
In India, family planning programmes were initiated in 1951 at a national level to attain total reproductive health as a social goal. According to World Health Organization (WHO), reproductive health means total well-being of an individual in the physical, social behavioural and emotional aspects of reproduction "Saheli', an oral contraceptive pill for the females was developed by scientists at Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow. Amniocentesis is being misused to determine the sex of the foetus and kill the normal female foetuses. Therefore, it should be legally banned to avoid female foeticide
The technique involving the transfer of ovum of a donor female into the fallopian tube of a recipient female is called- a)GIFT
- b)IVF-ET
- c)IUT
- d)ZIFT
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The technique involving the transfer of ovum of a donor female into the fallopian tube of a recipient female is called
a)
GIFT
b)
IVF-ET
c)
IUT
d)
ZIFT
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Gamete Intrafallopian transfer (GIFT):
It is a technique that involves the transfer of gamete (ovum) from a donor into the fallopian tube of the recipient female who is unable to produce eggs, but has the ability to conceive and can provide right conditions for the development of an embryo.
The technique called gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) is recommended for those females: [2011 M]
- a)Who cannot produce an ovum.
- b)Who cannot retain the foetus inside uterus.
- c)Whose cervical canal is too narrow to allow passage for the sperms.
- d)Who cannot provide a suitable environment for fertilization.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The technique called gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) is recommended for those females: [2011 M]
a)
Who cannot produce an ovum.
b)
Who cannot retain the foetus inside uterus.
c)
Whose cervical canal is too narrow to allow passage for the sperms.
d)
Who cannot provide a suitable environment for fertilization.

|
Arya Khanna answered |
GIFT- Gamete intra fallopian transfer method is used in females who cannot produce ova but can provide suitable envoirnment for fertilization and further development of embryo in the oviducts. In such cases, ovum from the donor female is surgically removed and is then introduced into the fallopian tube of such females. So, the correct answer is 'Who cannot produce an ovum'.
Correct answer is A.
Correct answer is A.
In which of the following techniques, the embryos are transferred to assist those females who cannot conceive? [NEET 2020]- a)ICSI and ZIFT
- b)GIFT and ICSI
- c)ZIFT and IUT
- d)GIFT and ZIFT
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following techniques, the embryos are transferred to assist those females who cannot conceive? [NEET 2020]
a)
ICSI and ZIFT
b)
GIFT and ICSI
c)
ZIFT and IUT
d)
GIFT and ZIFT
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
When females cannot conceive then embryo transfer is done by using ZIFT and IUT technique. In this method, ova from female & sperms from male is collected and are induced in the laboratory under simulated conditions to form a zygote. The zygote with up to 8 blastomeres is transferred into the fallopian tube through ZIFT or embryos with more than 8 blastomeres are transferred into the uterus through IUT.
1. Given below are four methods (A-D) and their modes of action (i) – (iv) in achieving contraception. Select their correct matching from the four options which follow.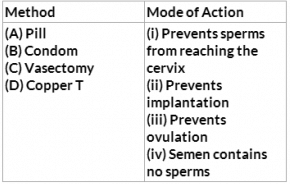
- a)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii)
- b)A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
- c)A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv)
- d)A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(ii)
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1. Given below are four methods (A-D) and their modes of action (i) – (iv) in achieving contraception. Select their correct matching from the four options which follow.
a)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii)
b)
A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iii)
c)
A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv)
d)
A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(ii)

|
Kishan Kumar answered |
Copper T decrease sperms motility and fertilisation capacity
Amniocentesis is a method to_________.- a)Detect genetic disorder
- b)Medical termination of pregnancy
- c)Fertilize the egg
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amniocentesis is a method to_________.
a)
Detect genetic disorder
b)
Medical termination of pregnancy
c)
Fertilize the egg
d)
None of these
|
|
Akash Menon answered |
Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic procedure that involves the removal of a small amount of amniotic fluid from the sac surrounding the fetus. This procedure is performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, typically between the 15th and 20th week.
Detection of Genetic Disorders:
The main purpose of amniocentesis is to detect genetic disorders in the developing fetus. The amniotic fluid contains cells shed by the fetus, which can be analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations. This information can help parents and healthcare providers prepare for the birth of a child with a genetic disorder.
Procedure:
During the procedure, a thin needle is inserted through the belly into the amniotic sac, where a small amount of amniotic fluid is collected. The procedure is guided by ultrasound imaging to ensure that the needle is safely inserted and to monitor the fetus during the procedure. The collected fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Risks:
Although amniocentesis is generally considered safe, there are some risks involved. These include a small risk of miscarriage or infection, as well as the possibility of injury to the fetus or mother during the procedure. However, the benefits of amniocentesis in detecting genetic disorders often outweigh these risks.
In conclusion, amniocentesis is a valuable tool for detecting genetic disorders during pregnancy, and it can help parents and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the care and treatment of the developing fetus.
Detection of Genetic Disorders:
The main purpose of amniocentesis is to detect genetic disorders in the developing fetus. The amniotic fluid contains cells shed by the fetus, which can be analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations. This information can help parents and healthcare providers prepare for the birth of a child with a genetic disorder.
Procedure:
During the procedure, a thin needle is inserted through the belly into the amniotic sac, where a small amount of amniotic fluid is collected. The procedure is guided by ultrasound imaging to ensure that the needle is safely inserted and to monitor the fetus during the procedure. The collected fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Risks:
Although amniocentesis is generally considered safe, there are some risks involved. These include a small risk of miscarriage or infection, as well as the possibility of injury to the fetus or mother during the procedure. However, the benefits of amniocentesis in detecting genetic disorders often outweigh these risks.
In conclusion, amniocentesis is a valuable tool for detecting genetic disorders during pregnancy, and it can help parents and healthcare providers make informed decisions about the care and treatment of the developing fetus.
Indian population is_________________.- a)Mature population
- b)Young population
- c)Ageing population
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Indian population is_________________.
a)
Mature population
b)
Young population
c)
Ageing population
d)
None of these
|
|
Maya Gupta answered |
Lactational amenorrhea is a natural form of birth control that occurs when a woman is breastfeeding. It is caused by the hormones that are released during breastfeeding, which suppress ovulation. This means that women who are breastfeeding may not ovulate and therefore may not have a menstrual period for a period of time after giving birth.
Maximum Period after Parturition:
The maximum period after parturition during which lactational amenorrhea can prevent chances of fertilization is six months. After this time, the hormones that suppress ovulation begin to decrease, and the chances of ovulation and subsequent fertilization increase. Therefore, women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should use another method of contraception after six months postpartum.
Effectiveness:
Lactational amenorrhea can be an effective form of birth control if certain conditions are met. These conditions include:
- The woman is exclusively breastfeeding, meaning that she is not giving the baby any other food or drink besides breast milk.
- The baby is less than six months old.
- The woman has not had a menstrual period since giving birth.
If these conditions are met, lactational amenorrhea can be up to 98% effective in preventing pregnancy. However, if any of these conditions change (for example, if the woman begins to supplement with formula or if the baby becomes older than six months), the effectiveness of lactational amenorrhea may decrease.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, lactational amenorrhea is a natural form of birth control that can be effective for up to six months postpartum. Women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should be aware of its limitations and should use another form of contraception after the six-month period has ended.
Maximum Period after Parturition:
The maximum period after parturition during which lactational amenorrhea can prevent chances of fertilization is six months. After this time, the hormones that suppress ovulation begin to decrease, and the chances of ovulation and subsequent fertilization increase. Therefore, women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should use another method of contraception after six months postpartum.
Effectiveness:
Lactational amenorrhea can be an effective form of birth control if certain conditions are met. These conditions include:
- The woman is exclusively breastfeeding, meaning that she is not giving the baby any other food or drink besides breast milk.
- The baby is less than six months old.
- The woman has not had a menstrual period since giving birth.
If these conditions are met, lactational amenorrhea can be up to 98% effective in preventing pregnancy. However, if any of these conditions change (for example, if the woman begins to supplement with formula or if the baby becomes older than six months), the effectiveness of lactational amenorrhea may decrease.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, lactational amenorrhea is a natural form of birth control that can be effective for up to six months postpartum. Women who rely on lactational amenorrhea as a form of birth control should be aware of its limitations and should use another form of contraception after the six-month period has ended.
Inability to conceive or produce children even after two years of unprotected sexual co-habitation is called?- a)Incapability
- b)Infertility
- c)Sterility
- d)Malfunction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inability to conceive or produce children even after two years of unprotected sexual co-habitation is called?
a)
Incapability
b)
Infertility
c)
Sterility
d)
Malfunction
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Inability to conceive or produce children even after 2 years of unprotected sexual cohabitation is called infertility
From the sexually transmitted diseases mentioned below, identify the one which does not specifically affect the sex organs:- a)AIDS
- b)Genital warts
- c)Syphilis
- d)Gonorrhoea
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
From the sexually transmitted diseases mentioned below, identify the one which does not specifically affect the sex organs:
a)
AIDS
b)
Genital warts
c)
Syphilis
d)
Gonorrhoea
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Syphilis, gonorrhoea and genital warts as STD caused by Treponemapallidum ,Neisseria gonorrhoeae and human papilloma virus. These pathogens directly infectand damage sex organs causing ichting fluid discharge, slight pain and swelling of genitalia. AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is a set of symptoms caused by HIVvirus in humans. It is transmitted through sexual contacts from infected to healthy person. The HIV virus does not directly affect sex organs as such but produce other set of symptoms in the body of infected person.
Identify the intra-uterine contraceptive device from the figure given below
- a)Copper-T
- b)Loop
- c)LNG-20
- d)Progestasert
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the intra-uterine contraceptive device from the figure given below
a)
Copper-T
b)
Loop
c)
LNG-20
d)
Progestasert
|
|
Anchal Maurya answered |
This intra uterine device is Cu- T .read ncert
One of the legal methods of birth control is :[NEET 2013]- a)abortion by taking an appropriate medicine
- b)by having coitus at the time of day break
- c)by a premature ejaculation during coitus
- d)by abstaining from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the legal methods of birth control is :
[NEET 2013]
a)
abortion by taking an appropriate medicine
b)
by having coitus at the time of day break
c)
by a premature ejaculation during coitus
d)
by abstaining from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle
|
|
Shounak Patel answered |
Method of Birth Control: Abstaining from Coitus from Day 10 to 17 of the Menstrual Cycle
Explanation:
Abstaining from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle is a legal method of birth control. This method is also known as the "rhythm method" or "calendar method." The menstrual cycle typically lasts for 28 days, and ovulation occurs around day 14. By abstaining from sexual intercourse during days 10-17, one can avoid the fertile period of the menstrual cycle and prevent pregnancy.
Advantages:
1. This method is free and does not require any special equipment or medication.
2. It is a natural method and does not involve any hormonal changes in the body.
3. It can be used by couples who have religious or moral objections to other forms of birth control.
Disadvantages:
1. This method requires a high degree of discipline and consistency to be effective.
2. It is not suitable for women with irregular menstrual cycles.
3. There is still a small risk of pregnancy, as ovulation can occur earlier or later than expected.
Conclusion:
Abstaining from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle is a legal and natural method of birth control. However, it requires careful planning and consistency to be effective. Couples should be aware of the advantages and disadvantages before choosing this method of birth control.
Explanation:
Abstaining from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle is a legal method of birth control. This method is also known as the "rhythm method" or "calendar method." The menstrual cycle typically lasts for 28 days, and ovulation occurs around day 14. By abstaining from sexual intercourse during days 10-17, one can avoid the fertile period of the menstrual cycle and prevent pregnancy.
Advantages:
1. This method is free and does not require any special equipment or medication.
2. It is a natural method and does not involve any hormonal changes in the body.
3. It can be used by couples who have religious or moral objections to other forms of birth control.
Disadvantages:
1. This method requires a high degree of discipline and consistency to be effective.
2. It is not suitable for women with irregular menstrual cycles.
3. There is still a small risk of pregnancy, as ovulation can occur earlier or later than expected.
Conclusion:
Abstaining from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle is a legal and natural method of birth control. However, it requires careful planning and consistency to be effective. Couples should be aware of the advantages and disadvantages before choosing this method of birth control.
_________involve the transfer of embryo at 8-celled stage in the fallopian tube of female.- a)POST
- b)ZIFT
- c)IVF
- d)GIFT
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_________involve the transfer of embryo at 8-celled stage in the fallopian tube of female.
a)
POST
b)
ZIFT
c)
IVF
d)
GIFT
|
|
Akanksha Das answered |
ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer) involves the transfer of an embryo at the 8-celled stage into the fallopian tube of a female. This is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to treat infertility.
Process of ZIFT:
The process of ZIFT involves the following steps:
1. Ovarian Stimulation: The female patient is given medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
2. Egg Retrieval: The eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a needle guided by ultrasound.
3. Fertilization: The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish to create embryos.
4. Embryo Transfer: The embryos are transferred into the fallopian tube through a laparoscopic procedure.
5. Pregnancy Test: The patient is monitored for pregnancy through a blood test or ultrasound.
Advantages of ZIFT:
1. Higher Success Rates: ZIFT has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods.
2. Natural Implantation: The embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube, which is a natural environment for implantation, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
3. Fewer Multiple Pregnancies: ZIFT reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies compared to other assisted reproductive technologies.
Disadvantages of ZIFT:
1. Invasive Procedure: ZIFT requires a laparoscopic procedure, which is an invasive procedure that carries risks.
2. Limited Availability: ZIFT is not widely available in all fertility clinics.
3. Higher Cost: ZIFT is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Conclusion:
ZIFT is a type of assisted reproductive technology that involves transferring an embryo at the 8-celled stage into the fallopian tube of a female. It has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods and reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies. However, it is an invasive procedure that is not widely available and is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Process of ZIFT:
The process of ZIFT involves the following steps:
1. Ovarian Stimulation: The female patient is given medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
2. Egg Retrieval: The eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a needle guided by ultrasound.
3. Fertilization: The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish to create embryos.
4. Embryo Transfer: The embryos are transferred into the fallopian tube through a laparoscopic procedure.
5. Pregnancy Test: The patient is monitored for pregnancy through a blood test or ultrasound.
Advantages of ZIFT:
1. Higher Success Rates: ZIFT has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods.
2. Natural Implantation: The embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube, which is a natural environment for implantation, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
3. Fewer Multiple Pregnancies: ZIFT reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies compared to other assisted reproductive technologies.
Disadvantages of ZIFT:
1. Invasive Procedure: ZIFT requires a laparoscopic procedure, which is an invasive procedure that carries risks.
2. Limited Availability: ZIFT is not widely available in all fertility clinics.
3. Higher Cost: ZIFT is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Conclusion:
ZIFT is a type of assisted reproductive technology that involves transferring an embryo at the 8-celled stage into the fallopian tube of a female. It has higher success rates compared to traditional IVF methods and reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies. However, it is an invasive procedure that is not widely available and is more expensive than traditional IVF methods.
Study of human population is called as?- a)Anthropology
- b)Sociology
- c)Ethnology
- d)Demography
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study of human population is called as?
a)
Anthropology
b)
Sociology
c)
Ethnology
d)
Demography
|
|
Shounak Chakraborty answered |
Preventing Transmission of STDs
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. The following measures can help in preventing the transmission of STDs:
Using Condoms during Intercourse
Using condoms is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of STDs during sexual activity. Condoms act as a barrier and reduce the risk of infection. They should be used consistently and correctly to maximize their effectiveness.
Avoiding Sex with Multiple Partners
Having sex with multiple partners increases the risk of contracting STDs. Limiting sexual partners or being in a mutually monogamous relationship can decrease the risk of transmission.
Visiting a Qualified Doctor if Symptoms are Observed
If an individual experiences symptoms such as genital sores, abnormal discharge, or pain during urination, they should visit a qualified doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of STDs.
Not Sharing Shaving Blades with Friends
Sharing personal items such as shaving blades, towels, or underwear can increase the risk of transmission of STDs. It is important to use personal items and avoid sharing them with others to prevent the spread of infection.
Conclusion
Preventing the transmission of STDs is crucial for maintaining sexual health. Using condoms, limiting sexual partners, seeking medical attention if symptoms are observed, and avoiding sharing personal items can all help decrease the risk of infection.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are spread through sexual contact. The following measures can help in preventing the transmission of STDs:
Using Condoms during Intercourse
Using condoms is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of STDs during sexual activity. Condoms act as a barrier and reduce the risk of infection. They should be used consistently and correctly to maximize their effectiveness.
Avoiding Sex with Multiple Partners
Having sex with multiple partners increases the risk of contracting STDs. Limiting sexual partners or being in a mutually monogamous relationship can decrease the risk of transmission.
Visiting a Qualified Doctor if Symptoms are Observed
If an individual experiences symptoms such as genital sores, abnormal discharge, or pain during urination, they should visit a qualified doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of STDs.
Not Sharing Shaving Blades with Friends
Sharing personal items such as shaving blades, towels, or underwear can increase the risk of transmission of STDs. It is important to use personal items and avoid sharing them with others to prevent the spread of infection.
Conclusion
Preventing the transmission of STDs is crucial for maintaining sexual health. Using condoms, limiting sexual partners, seeking medical attention if symptoms are observed, and avoiding sharing personal items can all help decrease the risk of infection.
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India at present?- a)Tubectomy
- b)Cervical caps
- c)Diaphragms
- d)IUDs (Intrauterine devices)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India at present?
a)
Tubectomy
b)
Cervical caps
c)
Diaphragms
d)
IUDs (Intrauterine devices)
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Intra uterine device (IUD) is a method of contraception in India. The IUD is inserted in the woman’s uterus through the cervix.
One of the following is NOT a method of contraception – which one?
[NEET Kar. 2013]
- a)Tubectomy
- b)Condoms
- c)Pills of a combination of oxytocin and vasopressin
- d)Lippes loop
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following is NOT a method of contraception – which one?
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Tubectomy
b)
Condoms
c)
Pills of a combination of oxytocin and vasopressin
d)
Lippes loop

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Oxytocin is birth hormone and acts on the smooth muscles of our body and stimulates their contraction. Vasopressin acts mainly at the kidney and stimulates resorption of water and electrolytes and reduces loss of water through urine. Hence, it is also called as anti-diuretic hormone (ADH).
Cu ions released from copper - releasing Intra Uterine Devices (IUDs): [2010]- a)make uterus unsuitable for implantation
- b)increase phagocytosis of sperms
- c)suppress sperm motility
- d)prevent ovulation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cu ions released from copper - releasing Intra Uterine Devices (IUDs): [2010]
a)
make uterus unsuitable for implantation
b)
increase phagocytosis of sperms
c)
suppress sperm motility
d)
prevent ovulation

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Cu ions released by copper releasing intra uterine devices suppresses sperm motility.
Intra-uterine devices are inserted by doctors in the uterus through vagina. They are available as the non-medicated IUDs, copper releasing IUDs and hormonereleasing IUDs.
Intra-uterine devices are inserted by doctors in the uterus through vagina. They are available as the non-medicated IUDs, copper releasing IUDs and hormonereleasing IUDs.
Which period of menstrual cycle is called risky period of conception?- a)7th to 13th day
- b)17th to 25th day
- c)3rd to 7th day
- d)10th to 17th day
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which period of menstrual cycle is called risky period of conception?
a)
7th to 13th day
b)
17th to 25th day
c)
3rd to 7th day
d)
10th to 17th day
|
|
Akshara Choudhary answered |
The risky period of conception in the menstrual cycle is the ovulation period, which occurs around the 14th day of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
Explanation:
- Menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible.
- The menstrual cycle is typically 28 days long, but can vary from 21 to 35 days.
- The cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase (days 1-14), ovulation (day 14), and the luteal phase (days 15-28).
- Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm.
- Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- The period around ovulation is considered the risky period of conception, as it is the time when the egg is available to be fertilized by sperm.
- Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so the fertile window for conception is actually the five days leading up to ovulation, as well as ovulation day itself.
- Therefore, the risky period of conception is considered to be from the 10th to the 17th day of the menstrual cycle (assuming a 28-day cycle).
Explanation:
- Menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible.
- The menstrual cycle is typically 28 days long, but can vary from 21 to 35 days.
- The cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase (days 1-14), ovulation (day 14), and the luteal phase (days 15-28).
- Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm.
- Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle.
- The period around ovulation is considered the risky period of conception, as it is the time when the egg is available to be fertilized by sperm.
- Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so the fertile window for conception is actually the five days leading up to ovulation, as well as ovulation day itself.
- Therefore, the risky period of conception is considered to be from the 10th to the 17th day of the menstrual cycle (assuming a 28-day cycle).
Induced abortion is also called- a)MTP
- b)PID
- c)SID
- d)IUD
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Induced abortion is also called
a)
MTP
b)
PID
c)
SID
d)
IUD
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
MTP is Medical Termination of Pregnancy. It also called induced abortion. It is the medical way of getting rid of unwanted pregnancy. Any qualified gynecologist (MD/DGO) can perform MTP. Any MBBS Doctor, who has obtained training in MTP, is allowed to perform this procedure. However, MTP should always be performed at a place recognized by government authorities.
The test-tube Baby Programme employs which one of the following techniques[2012]- a)Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
- b)Intra uterine insemination (IUI)
- c)Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT)
- d)Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The test-tube Baby Programme employs which one of the following techniques
[2012]
a)
Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
b)
Intra uterine insemination (IUI)
c)
Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT)
d)
Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
|
|
Lakshmi Deshpande answered |
Test-tube Baby Programme and Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
The Test-tube Baby Programme is a fertility treatment that involves combining sperm and eggs outside the body in a laboratory dish, and then transferring the resulting embryo into the woman's uterus. Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is one of the techniques used in the Test-tube Baby Programme.
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is a fertility treatment that involves the following steps:
1. Egg Retrieval: The woman undergoes ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved from the ovaries using a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle.
2. Fertilization: The retrieved eggs are combined with sperm in a laboratory dish.
3. Zygote Formation: The fertilized eggs develop into zygotes (fertilized eggs).
4. Zygote Transfer: The zygotes are transferred into the woman's fallopian tubes using a laparoscope.
5. Implantation: The zygotes implant in the woman's uterus and develop into embryos.
Comparison with other techniques
Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Intra uterine insemination (IUI), and Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT) are other techniques used in the Test-tube Baby Programme. However, Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is different from these techniques in the following ways:
- Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg. This technique is used when the man has a low sperm count or poor sperm motility. ZIFT, on the other hand, involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes.
- Intra uterine insemination (IUI) involves placing sperm inside the woman's uterus to increase the chances of fertilization. This technique is used when the man has a low sperm count or poor sperm motility. ZIFT, on the other hand, involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes.
- Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT) involves placing eggs and sperm into the woman's fallopian tubes to allow fertilization to occur naturally. This technique is used when the man's sperm count and motility are normal, and the woman's fallopian tubes are healthy. ZIFT, on the other hand, involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes.
Conclusion
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is a technique used in the Test-tube Baby Programme that involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the woman's fallopian tubes. ZIFT is different from other techniques like Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Intra uterine insemination (IUI), and Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT).
The Test-tube Baby Programme is a fertility treatment that involves combining sperm and eggs outside the body in a laboratory dish, and then transferring the resulting embryo into the woman's uterus. Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is one of the techniques used in the Test-tube Baby Programme.
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is a fertility treatment that involves the following steps:
1. Egg Retrieval: The woman undergoes ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are then retrieved from the ovaries using a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle.
2. Fertilization: The retrieved eggs are combined with sperm in a laboratory dish.
3. Zygote Formation: The fertilized eggs develop into zygotes (fertilized eggs).
4. Zygote Transfer: The zygotes are transferred into the woman's fallopian tubes using a laparoscope.
5. Implantation: The zygotes implant in the woman's uterus and develop into embryos.
Comparison with other techniques
Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Intra uterine insemination (IUI), and Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT) are other techniques used in the Test-tube Baby Programme. However, Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is different from these techniques in the following ways:
- Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg. This technique is used when the man has a low sperm count or poor sperm motility. ZIFT, on the other hand, involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes.
- Intra uterine insemination (IUI) involves placing sperm inside the woman's uterus to increase the chances of fertilization. This technique is used when the man has a low sperm count or poor sperm motility. ZIFT, on the other hand, involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes.
- Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT) involves placing eggs and sperm into the woman's fallopian tubes to allow fertilization to occur naturally. This technique is used when the man's sperm count and motility are normal, and the woman's fallopian tubes are healthy. ZIFT, on the other hand, involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tubes.
Conclusion
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is a technique used in the Test-tube Baby Programme that involves the transfer of fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the woman's fallopian tubes. ZIFT is different from other techniques like Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Intra uterine insemination (IUI), and Gamete intra fallopian transfer (GIFT).
A test-tube baby means a baby born when- a)It is developed by tissue culture method.
- b)The ovum is fertilised externally and thereafter implanted in the uterus.
- c)It is developed in a test tube
- d)It develops from a non-fertilised egg.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A test-tube baby means a baby born when
a)
It is developed by tissue culture method.
b)
The ovum is fertilised externally and thereafter implanted in the uterus.
c)
It is developed in a test tube
d)
It develops from a non-fertilised egg.
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Test tube bay production involves two main steps - in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer (ET). Historically the first attempt to produce the test tube baby was by an Italian scientise Petrucci (1959). In his experiment he removed an ovum from a patient and put it in the middle of spermatozoa in a glass dome. One of the sperms fertilized the egg and a small embryo formed, but this survived only for 29 days.
However Petrucci's experiment opened up a new horizon and a new hope for infertile parents. In recent years two British scientists Edwards and Steptoe have done pioneering work in the field of test tube babies. The first scientifically recorded test tube baby in the world was born on July 25 1978 and the baby girl was named Louise Joy Brown.
In our country the first recorded instane of a test tube baby was under the supervision of Dr. Indira Hinduja in KEM Hospital Bombay in 1986. Subsequently test tube babies have been reported by Dr. Baidyanath Chakravarthi of Calcutta.
What is the procedure for sterilization in males?- a)Vasectomy
- b)Tubectomy
- c)Decapitation
- d)Circumcision
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the procedure for sterilization in males?
a)
Vasectomy
b)
Tubectomy
c)
Decapitation
d)
Circumcision
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Vasectomy is the procedure used to sterilize males. It involves the removal of a part of vas deferens or it being tied up through an incision on the scrotum.
Which of the following contraceptive methods involve the role of hormone? [NEET 2019]- a)Pill, Emergency contraception, Barrier methods
- b)Lactational amenorrhea, Pills, Emergency contraceptives
- c)Barrier method, Lactational amenorrhea pills
- d)Cut, Pills, Emergency contraceptive
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following contraceptive methods involve the role of hormone? [NEET 2019]
a)
Pill, Emergency contraception, Barrier methods
b)
Lactational amenorrhea, Pills, Emergency contraceptives
c)
Barrier method, Lactational amenorrhea pills
d)
Cut, Pills, Emergency contraceptive
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
- Lactational amenorrhea method is based on the fact that ovulation and therefore the menstrual cycle does not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition. This is because breastfeeding disrupts the pulsatile release of GnRH from the hypothalamus and reduces gonadotropin-releasing hormones.

- Pills are hormonal preparations (either progesterone or progestogen- estrogen combinations) in the form of tablets which are administered orally by females. They inhibit ovulation, implantation as well as alter the quality of cervical mucus.
- Emergency contraceptives are pills that contain levonorgestrel, a type of progestin that helps to prevent pregnancy when taken in few days after sex.
Absence of menstruation during period of intense lactation following parturition is called as?- a)Coitus interruption
- b)Mellitus
- c)Lactational amenorrhea
- d)Lactationalgonorrhea
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Absence of menstruation during period of intense lactation following parturition is called as?
a)
Coitus interruption
b)
Mellitus
c)
Lactational amenorrhea
d)
Lactationalgonorrhea

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
During intense lactation just after the delivery the menstrual cycle get stopped and there is no chance of pregnancy. This absence of menstruation is called lactational amenorrhea.
Which of the following are the reasons for population explosion?
(i) Increased health facilities
(ii) Rapid increase in MMR
(iii) Rapid increase in IMR
(iv) Rapid decrease in MMR
(v) Decrease in number of people reaching reproductive age- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(iii) and (v)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (v)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the reasons for population explosion?
(i) Increased health facilities
(ii) Rapid increase in MMR
(iii) Rapid increase in IMR
(iv) Rapid decrease in MMR
(v) Decrease in number of people reaching reproductive age
(i) Increased health facilities
(ii) Rapid increase in MMR
(iii) Rapid increase in IMR
(iv) Rapid decrease in MMR
(v) Decrease in number of people reaching reproductive age
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(iii) and (v)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (v)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Rapid increase in population over a relatively short period of time is called population explosion. Reasons for population explosion are increased health facilities, decrease in MMR (maternal mortality rate), and IMR (infant mortality rate) and increase in number of people reaching reproductive age.
Which of the following is the correct reason for delivering sex education at schools?- a)Discouraging myths and misconceptions
- b)Encouraging rise in population
- c)Solve the issue of global warming
- d)Promote myths
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct reason for delivering sex education at schools?
a)
Discouraging myths and misconceptions
b)
Encouraging rise in population
c)
Solve the issue of global warming
d)
Promote myths
|
|
Manoj Majumdar answered |
Importance of Sex Education in Schools
Sex education is a critical aspect of education that should be delivered in schools to help students understand human sexuality and sexual behavior. The correct reason for delivering sex education in schools is to discourage myths and misconceptions. Here are some of the reasons why sex education is necessary in schools:
1. Preventing Unwanted Pregnancies: Sex education helps students understand how to protect themselves from unintended pregnancies. It provides information on different contraceptive methods, their effectiveness, and how to use them correctly.
2. Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Sex education helps students understand how to protect themselves from STIs. It provides information on how STIs are transmitted, their symptoms, and how to prevent them.
3. Encouraging Healthy Relationships: Sex education helps students understand the importance of healthy relationships. It provides information on how to build healthy relationships, how to communicate effectively, and how to recognize signs of an unhealthy relationship.
4. Reducing Sexual Violence: Sex education helps students understand the importance of consent and how to recognize sexual violence. It provides information on how to report sexual violence and where to seek help.
5. Overcoming Stigma: Sex education helps students overcome stigma and discrimination related to sexuality. It provides information on different sexual orientations and gender identities, and how to respect and accept diversity.
Conclusion
Sex education is an essential aspect of education that helps students make informed decisions about their sexual health and behavior. It provides information on how to protect themselves from unintended pregnancies, STIs, and sexual violence. It also encourages healthy relationships and respect for diversity. Therefore, it is necessary to deliver sex education in schools to discourage myths and misconceptions.
Sex education is a critical aspect of education that should be delivered in schools to help students understand human sexuality and sexual behavior. The correct reason for delivering sex education in schools is to discourage myths and misconceptions. Here are some of the reasons why sex education is necessary in schools:
1. Preventing Unwanted Pregnancies: Sex education helps students understand how to protect themselves from unintended pregnancies. It provides information on different contraceptive methods, their effectiveness, and how to use them correctly.
2. Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Sex education helps students understand how to protect themselves from STIs. It provides information on how STIs are transmitted, their symptoms, and how to prevent them.
3. Encouraging Healthy Relationships: Sex education helps students understand the importance of healthy relationships. It provides information on how to build healthy relationships, how to communicate effectively, and how to recognize signs of an unhealthy relationship.
4. Reducing Sexual Violence: Sex education helps students understand the importance of consent and how to recognize sexual violence. It provides information on how to report sexual violence and where to seek help.
5. Overcoming Stigma: Sex education helps students overcome stigma and discrimination related to sexuality. It provides information on different sexual orientations and gender identities, and how to respect and accept diversity.
Conclusion
Sex education is an essential aspect of education that helps students make informed decisions about their sexual health and behavior. It provides information on how to protect themselves from unintended pregnancies, STIs, and sexual violence. It also encourages healthy relationships and respect for diversity. Therefore, it is necessary to deliver sex education in schools to discourage myths and misconceptions.
Which of the following is wrongly matched?- a)IUI - semen collected crom husband or donor is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus
- b)GIFT - transfer of embroys with more than 8 blastomers intothe Fallopian tube
- c)ICSI- sperm directily injected into the ovum
- d)ZIFT- transfer of embrys with upto 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is wrongly matched?
a)
IUI - semen collected crom husband or donor is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus
b)
GIFT - transfer of embroys with more than 8 blastomers intothe Fallopian tube
c)
ICSI- sperm directily injected into the ovum
d)
ZIFT- transfer of embrys with upto 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
GIFT (Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer) is transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the Fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce ovum but can provide proper environment for fertilization and further development.
Contraceptive oral pills help in birth control by:- a)By preventing ovulation
- b)Killing the sperm
- c)Killing the ova
- d)Forming barrier between sperm and ova
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Contraceptive oral pills help in birth control by:
a)
By preventing ovulation
b)
Killing the sperm
c)
Killing the ova
d)
Forming barrier between sperm and ova
|
|
Ankit Patel answered |
Oral contraceptive pills are a type of hormonal birth control method that contain synthetic versions of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones work together to prevent pregnancy in several ways:
Preventing Ovulation
- The primary way that contraceptive pills prevent pregnancy is by preventing ovulation. Ovulation is the process in which an egg is released from the ovary and can be fertilized by sperm. By taking the pill regularly, the hormones in the pill signal to the body that ovulation has already occurred, which prevents the release of an egg. Without an egg, there is no chance of fertilization and pregnancy cannot occur.
Thickening Cervical Mucus
- In addition to preventing ovulation, contraceptive pills also thicken the cervical mucus. The cervix is the opening at the bottom of the uterus that leads to the vagina. Normally, the cervical mucus is thin and watery, which allows sperm to swim through it and reach the egg. However, when a woman is taking contraceptive pills, the hormones in the pill cause the cervical mucus to thicken and become more viscous, making it more difficult for sperm to penetrate and reach the egg.
Altering the Uterine Lining
- Lastly, contraceptive pills can also alter the lining of the uterus. The lining of the uterus is where a fertilized egg implants and grows into a fetus. The hormones in the pill can change the lining of the uterus to make it less hospitable to a fertilized egg, making it less likely that a pregnancy will occur even if an egg is released and fertilized.
By working together in these ways, contraceptive pills are highly effective at preventing pregnancy when taken correctly and consistently.
Preventing Ovulation
- The primary way that contraceptive pills prevent pregnancy is by preventing ovulation. Ovulation is the process in which an egg is released from the ovary and can be fertilized by sperm. By taking the pill regularly, the hormones in the pill signal to the body that ovulation has already occurred, which prevents the release of an egg. Without an egg, there is no chance of fertilization and pregnancy cannot occur.
Thickening Cervical Mucus
- In addition to preventing ovulation, contraceptive pills also thicken the cervical mucus. The cervix is the opening at the bottom of the uterus that leads to the vagina. Normally, the cervical mucus is thin and watery, which allows sperm to swim through it and reach the egg. However, when a woman is taking contraceptive pills, the hormones in the pill cause the cervical mucus to thicken and become more viscous, making it more difficult for sperm to penetrate and reach the egg.
Altering the Uterine Lining
- Lastly, contraceptive pills can also alter the lining of the uterus. The lining of the uterus is where a fertilized egg implants and grows into a fetus. The hormones in the pill can change the lining of the uterus to make it less hospitable to a fertilized egg, making it less likely that a pregnancy will occur even if an egg is released and fertilized.
By working together in these ways, contraceptive pills are highly effective at preventing pregnancy when taken correctly and consistently.
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is considered safe up to how many weeks of pregnancy?a)Six weeksb)Eight weeksc)Twelve weeksd)Eighteen weeksCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)Six weeks
b)Eight weeks
c)Twelve weeks
d)Eighteen weeks
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Twelve weeks
Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or induced abortion. MTPs are considered relatively safe during the first trimester, i.e., upto 12 weeks of pregnancy. Second trimseter abortions are much more risker.
Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or induced abortion. MTPs are considered relatively safe during the first trimester, i.e., upto 12 weeks of pregnancy. Second trimseter abortions are much more risker.
What test is used to determine the sex of the fetus?- a)Amniocentesis
- b)Amyliodogenesis
- c)Amnionic
- d)Fluidic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What test is used to determine the sex of the fetus?
a)
Amniocentesis
b)
Amyliodogenesis
c)
Amnionic
d)
Fluidic
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Fetal sex determination is based on the patterns of chromosomes in the amniotic fluid present around the embryo. Hence this test is called amniocentesis.
The world population is ________- a)rising
- b)declining
- c)stabilized
- d)unpredictable
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The world population is ________
a)
rising
b)
declining
c)
stabilized
d)
unpredictable
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The global population is rising exponentially. It increased from 2 billion in 1900 to 6 billion in 2000 and has currently crossed 10 billion.
Saheli is______.- a)A surgical sterilization
- b)An oral contraceptive for females
- c)A diaphragm for females
- d)A diaphragm for male
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Saheli is______.
a)
A surgical sterilization
b)
An oral contraceptive for females
c)
A diaphragm for females
d)
A diaphragm for male

|
Diya Datta answered |
Saheli is an oral contraceptive for females contain non-steroidal preparation. It is different from the other pills as it should be taken once in a week irrespective of daily in case of other pills.
The birth control device used by women is /are
- a)diaphragm
- b)condom
- c)copper T
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The birth control device used by women is /are
a)
diaphragm
b)
condom
c)
copper T
d)
all of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Diaphragm and Copper Tare used by women. Condon are oenerallv used by males although female condom are called femidoms are also available.
Which of the following is not the correct reason for the use of MTP?- a)Get rid of unwanted pregnancy
- b)Terminate pregnancies that are fatal to mother
- c)Terminate pregnancies that are fatal to foetus
- d)Female foeticide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not the correct reason for the use of MTP?
a)
Get rid of unwanted pregnancy
b)
Terminate pregnancies that are fatal to mother
c)
Terminate pregnancies that are fatal to foetus
d)
Female foeticide
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The purpose of MTP is to prevent an unwanted pregnancy that could have arisen due to casual unprotected coitus or incorrect use of contraceptive or due to rapes. They are also aimed at rescuing mothers from fatal pregnancies or from preventing parents from the shocks and expenses of a fatal fetus. They are not designed for female foeticide. Hence female foeticide has been illegalized by the Government of India.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproductive Health - 1 Year Dropper's Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproductive Health - 1 Year Dropper's Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









