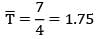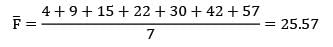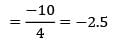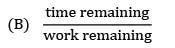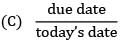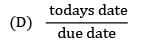All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical >
All Questions
All questions of Line Balancing, Loading & Scheduling for Mechanical Engineering Exam
The routing function in a production system design is concerned with
- a)man power utilization
- b)optimizing material flow through the plan
- c)quality assurance of the product
- d)machine utilization
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The routing function in a production system design is concerned with
a)
man power utilization
b)
optimizing material flow through the plan
c)
quality assurance of the product
d)
machine utilization
|
|
Avinash Sharma answered |
Routing: It is the path followed by products for being processed at various machine tools and departments. The sequence of operations required for least back-tracking is maintained. So, routing is determination of most economical path to be followed by raw-materials.
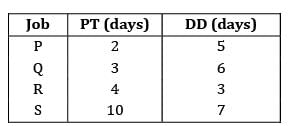
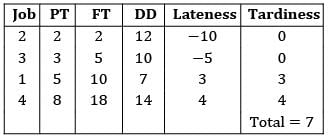
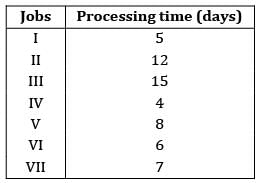
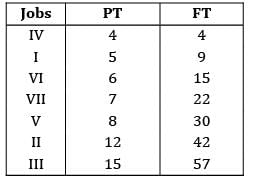
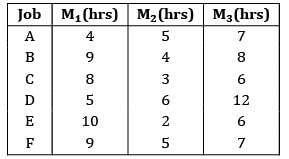
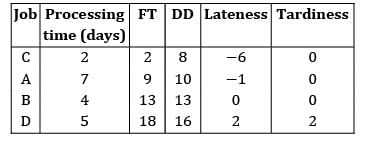
Four jobs has to be processed on a single machine. The details are given in the following data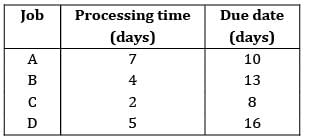 The minimum average tardiness is.
The minimum average tardiness is.- a) 2
- b) 0.5
- c) 1
- d) − 5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Four jobs has to be processed on a single machine. The details are given in the following data

The minimum average tardiness is.
a)
2
b)
0.5
c)
1
d)
− 5

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
The average tardiness is minimized when EDD rule is used sequence using EDD rule C −A − B − D
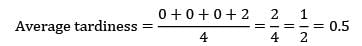
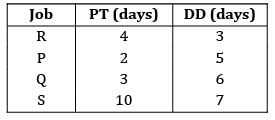
There are six cars waiting to be repaired at a car repair shop. Each car has first to be dented and then painted. The estimated times for each car are given below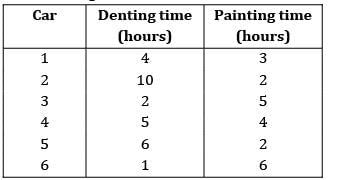 Find the total idle time for machine.
Find the total idle time for machine.- a) 8
- b) 8
Correct answer is option ''. Can you explain this answer?
There are six cars waiting to be repaired at a car repair shop. Each car has first to be dented and then painted. The estimated times for each car are given below

Find the total idle time for machine.
a)
8
b)
8

|
Pathways Academy answered |
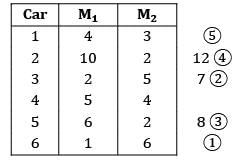
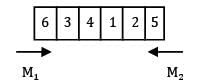
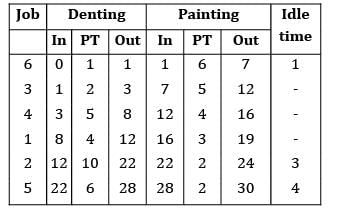
Idle time = 8 hours
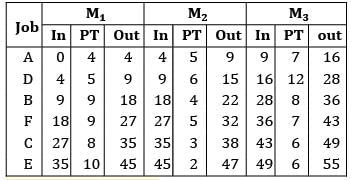
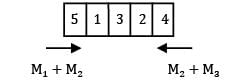
Consider the following data for a job-shop problem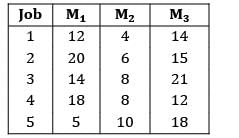 The optimal sequence for the above problem is
The optimal sequence for the above problem is- a) 4 − 2 − 3 − 1 − 5
- b) 5 − 3 − 1 − 2 − 4
- c) 5 − 1 − 3 − 2 − 4
- d) 4 − 5 − 1 − 3 − 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data for a job-shop problem

The optimal sequence for the above problem is
a)
4 − 2 − 3 − 1 − 5
b)
5 − 3 − 1 − 2 − 4
c)
5 − 1 − 3 − 2 − 4
d)
4 − 5 − 1 − 3 − 2

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
Convert the given problem into a two machine problem and apply Johnson’s algorithm
Max {M2} ≤ min{M1} or min{M3}
10 ≤ 5 ✘
10 ≤ 12✓
The problem can be converted
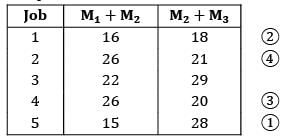
Applying Johnson’s algorithm
Using graphical method, determine the minimum time needed to process the two jobs on four machines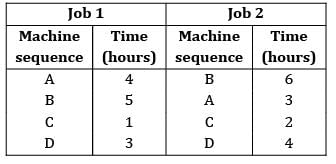
- a) 15
- b) 15
Correct answer is between ' 15, 15'. Can you explain this answer?
Using graphical method, determine the minimum time needed to process the two jobs on four machines

a)
15
b)
15

|
Pathways Academy answered |
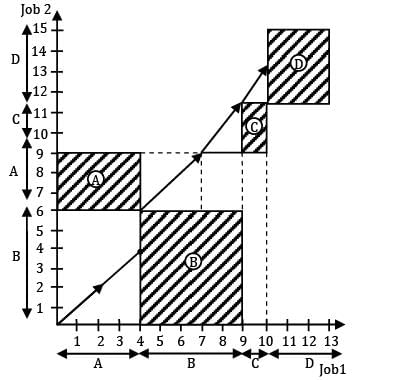
Total completion time = 4+2+5+7+3 = 15
= 15 hours
Which one of the following is not a function of production control?- a)Forecasting
- b)Routing
- c)Scheduling
- d)Dispatching
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a function of production control?
a)
Forecasting
b)
Routing
c)
Scheduling
d)
Dispatching

|
Athira Pillai answered |
Introduction:
Production control is an essential function in manufacturing operations that involves planning, coordinating, and controlling various activities to ensure efficient and effective production. It encompasses several key activities such as forecasting, routing, scheduling, and dispatching. However, forecasting is not considered a direct function of production control.
Explanation:
1. Forecasting:
Forecasting is the process of estimating future demand for a product or service based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It helps organizations in determining the production levels, resource requirements, and inventory management. While forecasting plays a crucial role in production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Instead, it is typically performed by specialized forecasting teams or departments within an organization.
2. Routing:
Routing involves determining the most appropriate sequence of operations and the path that a product or service should follow during the production process. It includes identifying the specific machines, workstations, or departments that will be involved in each operation. Routing helps in optimizing the flow of materials, minimizing transportation costs, and ensuring smooth production operations.
3. Scheduling:
Scheduling is the process of determining the start and end times for each operation in the production process. It involves allocating resources such as machines, equipment, and labor to specific tasks and activities. Scheduling helps in balancing workloads, meeting delivery deadlines, and maximizing production efficiency.
4. Dispatching:
Dispatching involves releasing work orders to the shop floor or specific workstations, assigning tasks to workers, and providing necessary instructions for carrying out the operations. It ensures that the production activities are executed as per the planned schedule and that the required resources are available.
Conclusion:
While forecasting is a crucial aspect of production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Production control primarily focuses on activities such as routing, scheduling, and dispatching, which involve the coordination and control of production operations to ensure efficient and effective production.
Production control is an essential function in manufacturing operations that involves planning, coordinating, and controlling various activities to ensure efficient and effective production. It encompasses several key activities such as forecasting, routing, scheduling, and dispatching. However, forecasting is not considered a direct function of production control.
Explanation:
1. Forecasting:
Forecasting is the process of estimating future demand for a product or service based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It helps organizations in determining the production levels, resource requirements, and inventory management. While forecasting plays a crucial role in production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Instead, it is typically performed by specialized forecasting teams or departments within an organization.
2. Routing:
Routing involves determining the most appropriate sequence of operations and the path that a product or service should follow during the production process. It includes identifying the specific machines, workstations, or departments that will be involved in each operation. Routing helps in optimizing the flow of materials, minimizing transportation costs, and ensuring smooth production operations.
3. Scheduling:
Scheduling is the process of determining the start and end times for each operation in the production process. It involves allocating resources such as machines, equipment, and labor to specific tasks and activities. Scheduling helps in balancing workloads, meeting delivery deadlines, and maximizing production efficiency.
4. Dispatching:
Dispatching involves releasing work orders to the shop floor or specific workstations, assigning tasks to workers, and providing necessary instructions for carrying out the operations. It ensures that the production activities are executed as per the planned schedule and that the required resources are available.
Conclusion:
While forecasting is a crucial aspect of production planning and decision-making, it is not considered a direct function of production control. Production control primarily focuses on activities such as routing, scheduling, and dispatching, which involve the coordination and control of production operations to ensure efficient and effective production.
Routing in production planning and controls refers to the
- a)balancing of load on machines
- b)authorization of work to be performed
- c)progress of operations to be performed
- d)sequence of operations to be performed
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Routing in production planning and controls refers to the
a)
balancing of load on machines
b)
authorization of work to be performed
c)
progress of operations to be performed
d)
sequence of operations to be performed

|
Sahana Dey answered |
Routing in production planning and controls refers to the sequence of operations to be performed in the manufacturing process. It involves determining the most efficient path for a product to follow as it moves through various workstations and processes.
Routing plays a crucial role in optimizing production and ensuring smooth operations. It involves the following key aspects:
1. Determining the sequence of operations: Routing involves deciding the order in which different operations are to be performed on a product. This includes identifying the specific tasks, such as cutting, drilling, assembly, and finishing, that need to be completed and arranging them in the most logical and efficient sequence.
2. Identifying the work centers or machines: Routing also involves determining the specific work centers or machines where each operation will be performed. This includes considering the capabilities and capacities of different machines and ensuring that the workload is balanced across them.
3. Allocating resources: Routing helps in allocating the necessary resources, such as manpower, materials, and tools, to each operation. It ensures that all the required resources are available at the right time and in the right quantity to avoid any delays or bottlenecks in the production process.
4. Estimating time and cost: Routing helps in estimating the time required to complete each operation and the overall cost of the production process. This information is crucial for production planning, scheduling, and cost estimation, allowing organizations to optimize their resources and make informed decisions.
5. Minimizing distance and movement: Routing aims to minimize the distance and movement of products within the production facility. By carefully planning the sequence of operations, unnecessary movements and transportation can be reduced, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced lead times.
6. Ensuring quality and consistency: Routing also considers the quality requirements of the product. It ensures that the required quality checks and inspections are performed at appropriate stages to maintain consistent product quality throughout the manufacturing process.
In summary, routing in production planning and controls involves determining the most efficient sequence of operations, allocating resources, optimizing production flow, and ensuring quality and consistency. It plays a critical role in optimizing production processes, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency in manufacturing operations.
Routing plays a crucial role in optimizing production and ensuring smooth operations. It involves the following key aspects:
1. Determining the sequence of operations: Routing involves deciding the order in which different operations are to be performed on a product. This includes identifying the specific tasks, such as cutting, drilling, assembly, and finishing, that need to be completed and arranging them in the most logical and efficient sequence.
2. Identifying the work centers or machines: Routing also involves determining the specific work centers or machines where each operation will be performed. This includes considering the capabilities and capacities of different machines and ensuring that the workload is balanced across them.
3. Allocating resources: Routing helps in allocating the necessary resources, such as manpower, materials, and tools, to each operation. It ensures that all the required resources are available at the right time and in the right quantity to avoid any delays or bottlenecks in the production process.
4. Estimating time and cost: Routing helps in estimating the time required to complete each operation and the overall cost of the production process. This information is crucial for production planning, scheduling, and cost estimation, allowing organizations to optimize their resources and make informed decisions.
5. Minimizing distance and movement: Routing aims to minimize the distance and movement of products within the production facility. By carefully planning the sequence of operations, unnecessary movements and transportation can be reduced, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced lead times.
6. Ensuring quality and consistency: Routing also considers the quality requirements of the product. It ensures that the required quality checks and inspections are performed at appropriate stages to maintain consistent product quality throughout the manufacturing process.
In summary, routing in production planning and controls involves determining the most efficient sequence of operations, allocating resources, optimizing production flow, and ensuring quality and consistency. It plays a critical role in optimizing production processes, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency in manufacturing operations.
Four jobs need to be processed sequentially on two machines, first on Machine X and then on Machine Y. Each machine can process only one job at a time. The processing times in(hours) are given below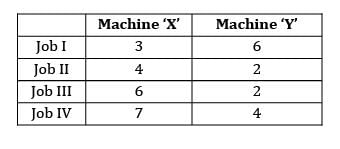 The make span of the jobs is ____________
The make span of the jobs is ____________- a) 20
- b) 22
- c) 24
- d) 26
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Four jobs need to be processed sequentially on two machines, first on Machine X and then on Machine Y. Each machine can process only one job at a time. The processing times in(hours) are given below

The make span of the jobs is ____________
a)
20
b)
22
c)
24
d)
26

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Apply Johnson’s algorithm to find the make span
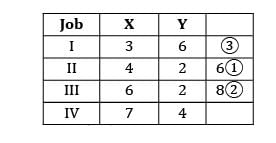
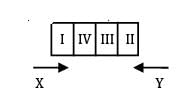
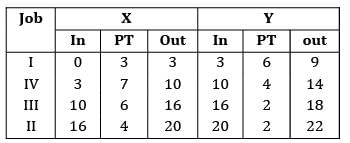
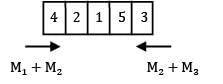
Using Johnson’s rule find the optimal sequence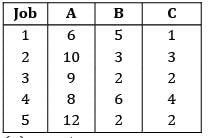
- a) 3 − 5 − 1 − 2 − 4
- b) 5 − 1 − 2 − 4 − 3
- c) 4 − 2 − 1 − 5 − 3
- d) Not applicable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Using Johnson’s rule find the optimal sequence

a)
3 − 5 − 1 − 2 − 4
b)
5 − 1 − 2 − 4 − 3
c)
4 − 2 − 1 − 5 − 3
d)
Not applicable
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Convert 3 machine problem into a two machine problem and apply Johnson’s rule
Max {M2} ≤ min{M1} or min{M3}
6 ≤ 6✓
6 ≤ 1✘

In manufacturing management, the term dispatching is used to describe- a)dispatch of sales order
- b)dispatch of faculty mail
- c)dispatch of finished product to the user
- d)dispatch of work orders through shop floor
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In manufacturing management, the term dispatching is used to describe
a)
dispatch of sales order
b)
dispatch of faculty mail
c)
dispatch of finished product to the user
d)
dispatch of work orders through shop floor

|
Samarth Ghoshal answered |
Dispatching: It is execution of planning. It is concerned with starting the work (or process), it therefore ensure that the plans are properly implemented. It is the physical handling over of a manufacturing order to the operating faciiity. it can be defined as release of orders and instructions for the starting of production for any item in accordance with the route sheet and schedule charts.
Consider the following data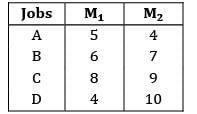 What will be the earliest time that B can be delivered to the customer?
What will be the earliest time that B can be delivered to the customer?- a) 21
- b) 21
Correct answer is between ' 21, 21'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data

What will be the earliest time that B can be delivered to the customer?
a)
21
b)
21

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
According to Johnson’s rule, the optimal sequence is
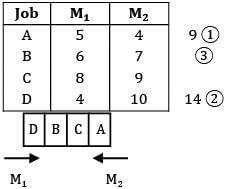
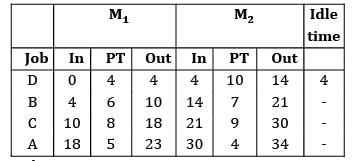
Make span = 34
Job B can be delivered at the end of 21 hours
Consider the following 2 job and M-Machine problemJob1 Lathe (2 hours) → Milling (1 hour)→→Drilling (4hours)Job 2 Milling (1 hour)→ Lathe (3 hours) → Drilling (3 hours)Find the make span.- a) 10
- b) 10
Correct answer is between ' 10, 10'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following 2 job and M-Machine problem
Job1 Lathe (2 hours) → Milling (1 hour)→→Drilling (4hours)
Job 2 Milling (1 hour)→ Lathe (3 hours) → Drilling (3 hours)
Find the make span.
a)
10
b)
10

|
Anirudh Kulkarni answered |
Make span refers to the total time required to complete all the jobs in a given scheduling problem. In this case, we have two jobs and three machines. Let's analyze the given problem to find the make span.
Job 1:
The first job starts with the lathe machine, which takes 2 hours to complete. After that, it moves to the milling machine, which takes 1 hour. Finally, it goes to the drilling machine, which requires 4 hours to finish.
Job 2:
The second job begins with the milling machine, which takes 1 hour. Then it moves to the lathe machine, which requires 3 hours. Lastly, it goes to the drilling machine, which takes 3 hours to complete.
To find the make span, we need to consider the longest path or the maximum time required to complete all the jobs.
Lathe Machine:
Both jobs require the lathe machine, but the lathe machine in job 2 takes 3 hours, which is longer than the 2 hours required in job 1. So, we consider the 3 hours.
Milling Machine:
Job 1 requires 1 hour on the milling machine, while job 2 also requires 1 hour. Hence, we consider the maximum time, which is 1 hour.
Drilling Machine:
Job 1 requires 4 hours on the drilling machine, while job 2 requires 3 hours. Here, we consider the maximum time, which is 4 hours.
Now, we add up the maximum times for each machine to find the make span:
Make span = Lathe + Milling + Drilling
= 3 hours + 1 hour + 4 hours
= 8 hours
Therefore, the make span for the given problem is 8 hours.
The correct answer is not between 10 and 10 (as mentioned in the question), but rather the make span is 8 hours.
Job 1:
The first job starts with the lathe machine, which takes 2 hours to complete. After that, it moves to the milling machine, which takes 1 hour. Finally, it goes to the drilling machine, which requires 4 hours to finish.
Job 2:
The second job begins with the milling machine, which takes 1 hour. Then it moves to the lathe machine, which requires 3 hours. Lastly, it goes to the drilling machine, which takes 3 hours to complete.
To find the make span, we need to consider the longest path or the maximum time required to complete all the jobs.
Lathe Machine:
Both jobs require the lathe machine, but the lathe machine in job 2 takes 3 hours, which is longer than the 2 hours required in job 1. So, we consider the 3 hours.
Milling Machine:
Job 1 requires 1 hour on the milling machine, while job 2 also requires 1 hour. Hence, we consider the maximum time, which is 1 hour.
Drilling Machine:
Job 1 requires 4 hours on the drilling machine, while job 2 requires 3 hours. Here, we consider the maximum time, which is 4 hours.
Now, we add up the maximum times for each machine to find the make span:
Make span = Lathe + Milling + Drilling
= 3 hours + 1 hour + 4 hours
= 8 hours
Therefore, the make span for the given problem is 8 hours.
The correct answer is not between 10 and 10 (as mentioned in the question), but rather the make span is 8 hours.
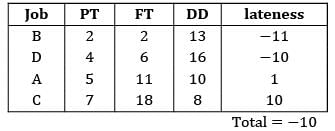
Consider the following data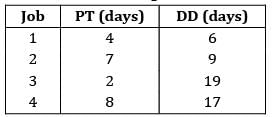 The no. of tardy jobs using SPT rule
The no. of tardy jobs using SPT rule- a) 3
- b) 2
- c) 1
- d) 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data

The no. of tardy jobs using SPT rule
a)
3
b)
2
c)
1
d)
4
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Sequence using SPT: 3 − 1 − 2 − 4
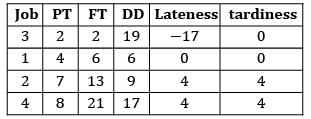
No. of tardy jobs = 2
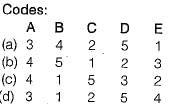
A defense contractor has six different jobs in process with the delivery requirements shown. Today is day (60) and if the contractor uses a critical ratio method for sequencing, find the sequence.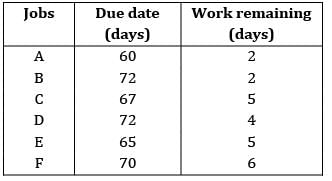 Ans. C
Ans. C- a) B − C − A − D − F − E
- b) C − B − E − F − A − D
- c) A − E − C − F − D − B
- d) E − C − B − D − A − F
Correct answer is option ''. Can you explain this answer?
A defense contractor has six different jobs in process with the delivery requirements shown. Today is day (60) and if the contractor uses a critical ratio method for sequencing, find the sequence.

Ans. C
a)
B − C − A − D − F − E
b)
C − B − E − F − A − D
c)
A − E − C − F − D − B
d)
E − C − B − D − A − F
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |

Job sequence = A − E − C − F − D − B
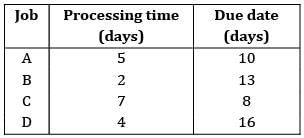
The todays date in a production calendar of an industry is 175. Sequence the jobs listed below by critical ratio rule and also find the number of jobs that are behind the schedule.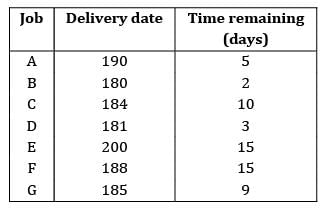
- a) F − C − G − E − D − B − A, 2
- b) A − B − D − E − G − C − F, 2
- c) F − C − G − E − A − B − D, 3
- d) A − B − D − F − C − G − E, 4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The todays date in a production calendar of an industry is 175. Sequence the jobs listed below by critical ratio rule and also find the number of jobs that are behind the schedule.

a)
F − C − G − E − D − B − A, 2
b)
A − B − D − E − G − C − F, 2
c)
F − C − G − E − A − B − D, 3
d)
A − B − D − F − C − G − E, 4
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
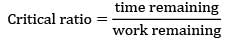
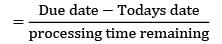
Jobs should be arranged in the increasing order of critical ratio.
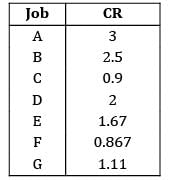
Sequence: F − C − G − E − D − B − A
Number of jobs behind schedule = no. of jobs whose critical ratio is less than 1
i.e., C & F in this case
∴ Number of jobs = 2
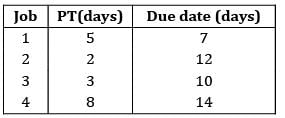
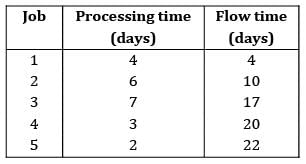
Apply FCFS rule and find the mean flow time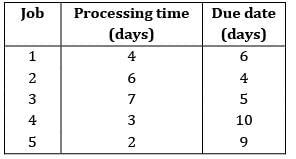
- a) 12
- b) 14.6
- c) 16
- d) 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Apply FCFS rule and find the mean flow time

a)
12
b)
14.6
c)
16
d)
20

|
Naroj Boda answered |
Sequence for FCFS will be 1 − 2 − 3 − 4 − 5
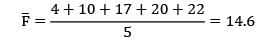
The sequence that would minimize the make span
- a) F − E − D − C − B − A
- b) C − F − A − B − D − E
- c) E − D − B − A − F − C
- d) C − A − F − B − D − E
- e) SPT Rule – minimizes inventory cost
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sequence that would minimize the make span

a)
F − E − D − C − B − A
b)
C − F − A − B − D − E
c)
E − D − B − A − F − C
d)
C − A − F − B − D − E
e)
SPT Rule – minimizes inventory cost
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Flow time will be minimum with SPT sequence = D − B − A − C
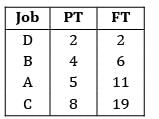
Total FT = 38
Minimum cost = 38 × 50 = Rs. 1900
Which of the following minimizes the idle time of an n-jobs and 2 machine problem?- a) SPT rule
- b) Johnson’s algorithm
- c) EDD rule
- d) Critical ratio rule
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following minimizes the idle time of an n-jobs and 2 machine problem?
a)
SPT rule
b)
Johnson’s algorithm
c)
EDD rule
d)
Critical ratio rule
|
|
Stuti Bajaj answered |
Johnson's Algorithm Minimizes Idle Time in 2-Machine Problem
Johnson's algorithm is an efficient way to minimize the idle time of an n-jobs and 2 machine problem. The algorithm is used to schedule jobs on two machines, such that the idle time on both machines is minimized. It is a greedy algorithm that works by selecting the job with the smallest processing time on either machine.
Steps of Johnson's Algorithm:
1. Transform the n-jobs and 2 machine problem into a modified 3-machine problem by adding a dummy machine with processing time 0 for each job.
2. Determine the processing time of each job on machine 1 and machine 2.
3. List the jobs in order of increasing processing time on machine 1.
4. List the jobs in order of decreasing processing time on machine 2.
5. Merge the two lists by selecting the job with the smallest processing time on either machine.
6. Assign the jobs to the machines based on the order of the merged list.
7. Compute the idle time on both machines.
8. Repeat steps 5-7 until all jobs have been assigned.
Why Johnson's Algorithm Minimizes Idle Time:
Johnson's algorithm minimizes idle time because it prioritizes jobs that have the shortest processing time on either machine. By selecting jobs in this way, the algorithm minimizes the time that either machine is idle, which in turn reduces the overall idle time for the system. This approach is more effective than other scheduling rules such as SPT, EDD, or critical ratio rule, which do not take into account the processing time on both machines.
Johnson's algorithm is an efficient way to minimize the idle time of an n-jobs and 2 machine problem. The algorithm is used to schedule jobs on two machines, such that the idle time on both machines is minimized. It is a greedy algorithm that works by selecting the job with the smallest processing time on either machine.
Steps of Johnson's Algorithm:
1. Transform the n-jobs and 2 machine problem into a modified 3-machine problem by adding a dummy machine with processing time 0 for each job.
2. Determine the processing time of each job on machine 1 and machine 2.
3. List the jobs in order of increasing processing time on machine 1.
4. List the jobs in order of decreasing processing time on machine 2.
5. Merge the two lists by selecting the job with the smallest processing time on either machine.
6. Assign the jobs to the machines based on the order of the merged list.
7. Compute the idle time on both machines.
8. Repeat steps 5-7 until all jobs have been assigned.
Why Johnson's Algorithm Minimizes Idle Time:
Johnson's algorithm minimizes idle time because it prioritizes jobs that have the shortest processing time on either machine. By selecting jobs in this way, the algorithm minimizes the time that either machine is idle, which in turn reduces the overall idle time for the system. This approach is more effective than other scheduling rules such as SPT, EDD, or critical ratio rule, which do not take into account the processing time on both machines.
Which of the following is not an assumption of scheduling and sequencing?- a) Set-up time is neglected
- b) Jobs are ready for processing
- c) Breakdowns are neglected
- d) Waiting time for jobs is neglected
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an assumption of scheduling and sequencing?
a)
Set-up time is neglected
b)
Jobs are ready for processing
c)
Breakdowns are neglected
d)
Waiting time for jobs is neglected
|
|
Stuti Bajaj answered |
Assumptions of Scheduling and Sequencing
Scheduling and sequencing refer to the processes of determining the order in which jobs or tasks will be processed in a manufacturing or production environment. Several assumptions are made when scheduling and sequencing, including:
1. Set-up time is neglected: This assumption means that the time required to set up a machine or production line for a new job is not taken into account when scheduling and sequencing.
2. Jobs are ready for processing: This assumption means that all the necessary materials, tools, and resources required to process a job are available and ready before scheduling and sequencing.
3. Breakdowns are neglected: This assumption means that the possibility of equipment breakdown or failure during production is not taken into account when scheduling and sequencing.
4. Waiting time for jobs is neglected: This assumption means that the time a job spends waiting to be processed or waiting for resources is not taken into account when scheduling and sequencing.
Not an Assumption of Scheduling and Sequencing
D. Waiting time for jobs is neglected: This is not an assumption of scheduling and sequencing. Waiting time is an important consideration when scheduling and sequencing as it affects the overall efficiency and productivity of the production process. Scheduling and sequencing should aim to minimize waiting time as much as possible to ensure timely delivery of products and optimal use of resources.
In conclusion, waiting time for jobs is not an assumption of scheduling and sequencing, and it is important to consider it when determining the order in which jobs are processed.
Scheduling and sequencing refer to the processes of determining the order in which jobs or tasks will be processed in a manufacturing or production environment. Several assumptions are made when scheduling and sequencing, including:
1. Set-up time is neglected: This assumption means that the time required to set up a machine or production line for a new job is not taken into account when scheduling and sequencing.
2. Jobs are ready for processing: This assumption means that all the necessary materials, tools, and resources required to process a job are available and ready before scheduling and sequencing.
3. Breakdowns are neglected: This assumption means that the possibility of equipment breakdown or failure during production is not taken into account when scheduling and sequencing.
4. Waiting time for jobs is neglected: This assumption means that the time a job spends waiting to be processed or waiting for resources is not taken into account when scheduling and sequencing.
Not an Assumption of Scheduling and Sequencing
D. Waiting time for jobs is neglected: This is not an assumption of scheduling and sequencing. Waiting time is an important consideration when scheduling and sequencing as it affects the overall efficiency and productivity of the production process. Scheduling and sequencing should aim to minimize waiting time as much as possible to ensure timely delivery of products and optimal use of resources.
In conclusion, waiting time for jobs is not an assumption of scheduling and sequencing, and it is important to consider it when determining the order in which jobs are processed.
If critical ratio is < 1="" />- a) the job is behind schedule
- b) the job is on schedule
- c) the job is ahead of schedule
- d) None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If critical ratio is < 1="" />
a)
the job is behind schedule
b)
the job is on schedule
c)
the job is ahead of schedule
d)
None
|
|
Anjali Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Critical ratio is a measure of the urgency of a job that needs to be completed. It is defined as the ratio of time remaining until the deadline to the time required to complete the job.
If the critical ratio is less than 1, it means that the time remaining until the deadline is less than the time required to complete the job. In this case, the job is behind schedule and needs to be expedited.
If the critical ratio is equal to 1, it means that the time remaining until the deadline is exactly equal to the time required to complete the job. In this case, the job is on schedule.
If the critical ratio is greater than 1, it means that the time remaining until the deadline is more than the time required to complete the job. In this case, the job is ahead of schedule and can be delayed if necessary.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', which states that if the critical ratio is less than 1, the job is behind schedule.
Critical ratio is a measure of the urgency of a job that needs to be completed. It is defined as the ratio of time remaining until the deadline to the time required to complete the job.
If the critical ratio is less than 1, it means that the time remaining until the deadline is less than the time required to complete the job. In this case, the job is behind schedule and needs to be expedited.
If the critical ratio is equal to 1, it means that the time remaining until the deadline is exactly equal to the time required to complete the job. In this case, the job is on schedule.
If the critical ratio is greater than 1, it means that the time remaining until the deadline is more than the time required to complete the job. In this case, the job is ahead of schedule and can be delayed if necessary.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', which states that if the critical ratio is less than 1, the job is behind schedule.
In sequencing for minimizing mean tardiness and average in process inventory, the rules to be used respectively are- a) SPT, EDD
- b) EDD, SPT
- c) EDD, LPT
- d) SPT, FCFS
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In sequencing for minimizing mean tardiness and average in process inventory, the rules to be used respectively are
a)
SPT, EDD
b)
EDD, SPT
c)
EDD, LPT
d)
SPT, FCFS
|
|
Ayush Chawla answered |
**Explanation:**
The sequencing rules used in minimizing mean tardiness and average in-process inventory are **EDD** (Earliest Due Date) and **SPT** (Shortest Processing Time).
**1. EDD (Earliest Due Date):**
- EDD is a scheduling rule that prioritizes jobs based on their due dates.
- Jobs with earlier due dates are given higher priority and are scheduled first.
- This rule aims to minimize the mean tardiness, which is the difference between the job completion time and its due date.
- By scheduling jobs with earlier due dates first, the overall tardiness is reduced, leading to a lower mean tardiness.
**2. SPT (Shortest Processing Time):**
- SPT is a scheduling rule that prioritizes jobs based on their processing times.
- Jobs with shorter processing times are given higher priority and are scheduled first.
- This rule aims to minimize the average in-process inventory, which is the average amount of work in progress at any given time.
- By scheduling jobs with shorter processing times first, the overall processing time is reduced, leading to a lower average in-process inventory.
**Why EDD and SPT are the correct choices:**
- Minimizing mean tardiness and average in-process inventory are two different objectives in sequencing.
- EDD is effective in minimizing mean tardiness because it prioritizes jobs based on their due dates, ensuring that jobs with earlier due dates are completed first.
- SPT is effective in minimizing average in-process inventory because it prioritizes jobs based on their processing times, ensuring that shorter jobs are completed first and the overall processing time is reduced.
- Combining EDD and SPT as sequencing rules allows for a balanced approach, addressing both objectives simultaneously.
- EDD ensures that jobs are completed on time, reducing tardiness, while SPT ensures that jobs are processed quickly, reducing in-process inventory.
Hence, the correct sequencing rules for minimizing mean tardiness and average in-process inventory are **EDD** (Earliest Due Date) and **SPT** (Shortest Processing Time), which corresponds to option **B**.
The sequencing rules used in minimizing mean tardiness and average in-process inventory are **EDD** (Earliest Due Date) and **SPT** (Shortest Processing Time).
**1. EDD (Earliest Due Date):**
- EDD is a scheduling rule that prioritizes jobs based on their due dates.
- Jobs with earlier due dates are given higher priority and are scheduled first.
- This rule aims to minimize the mean tardiness, which is the difference between the job completion time and its due date.
- By scheduling jobs with earlier due dates first, the overall tardiness is reduced, leading to a lower mean tardiness.
**2. SPT (Shortest Processing Time):**
- SPT is a scheduling rule that prioritizes jobs based on their processing times.
- Jobs with shorter processing times are given higher priority and are scheduled first.
- This rule aims to minimize the average in-process inventory, which is the average amount of work in progress at any given time.
- By scheduling jobs with shorter processing times first, the overall processing time is reduced, leading to a lower average in-process inventory.
**Why EDD and SPT are the correct choices:**
- Minimizing mean tardiness and average in-process inventory are two different objectives in sequencing.
- EDD is effective in minimizing mean tardiness because it prioritizes jobs based on their due dates, ensuring that jobs with earlier due dates are completed first.
- SPT is effective in minimizing average in-process inventory because it prioritizes jobs based on their processing times, ensuring that shorter jobs are completed first and the overall processing time is reduced.
- Combining EDD and SPT as sequencing rules allows for a balanced approach, addressing both objectives simultaneously.
- EDD ensures that jobs are completed on time, reducing tardiness, while SPT ensures that jobs are processed quickly, reducing in-process inventory.
Hence, the correct sequencing rules for minimizing mean tardiness and average in-process inventory are **EDD** (Earliest Due Date) and **SPT** (Shortest Processing Time), which corresponds to option **B**.
Consider the following statements:
Dispatching
1. is the action of operations, planning and control
2. release work to operation divisions
3. conveys instructions to the shop floorOf these statements:- a)1, 2 and 3 are correct
- b)1 and 2 are correct
- c)2 and 3 are correct
- d)1 and 3 are correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Dispatching
1. is the action of operations, planning and control
2. release work to operation divisions
3. conveys instructions to the shop floor
Dispatching
1. is the action of operations, planning and control
2. release work to operation divisions
3. conveys instructions to the shop floor
Of these statements:
a)
1, 2 and 3 are correct
b)
1 and 2 are correct
c)
2 and 3 are correct
d)
1 and 3 are correct

|
Navya Kaur answered |
Dispatching in Operations Management
Dispatching is a crucial function in operations management that involves the release of work orders to different departments for execution. Let's break down the statements provided:
Statement 1: Dispatching is the action of operations, planning, and control
- This statement is correct as dispatching plays a key role in coordinating and controlling the flow of work within an organization. It involves planning the sequence of operations and ensuring timely execution.
Statement 2: Dispatching releases work to operation divisions
- This statement is also accurate. Dispatching is responsible for assigning tasks to various departments or operation divisions based on their capabilities and capacity. It ensures that work is allocated efficiently.
Statement 3: Dispatching conveys instructions to the shop floor
- This statement is true as well. Dispatching involves communicating detailed instructions, including job priorities, deadlines, and specifications, to the shop floor workers. It helps in ensuring that the work is carried out as per the requirements.
Therefore, all three statements are correct, making option 'A' the correct choice. Dispatching is a critical function that helps in streamlining operations, reducing lead times, and improving overall productivity in an organization.
Dispatching is a crucial function in operations management that involves the release of work orders to different departments for execution. Let's break down the statements provided:
Statement 1: Dispatching is the action of operations, planning, and control
- This statement is correct as dispatching plays a key role in coordinating and controlling the flow of work within an organization. It involves planning the sequence of operations and ensuring timely execution.
Statement 2: Dispatching releases work to operation divisions
- This statement is also accurate. Dispatching is responsible for assigning tasks to various departments or operation divisions based on their capabilities and capacity. It ensures that work is allocated efficiently.
Statement 3: Dispatching conveys instructions to the shop floor
- This statement is true as well. Dispatching involves communicating detailed instructions, including job priorities, deadlines, and specifications, to the shop floor workers. It helps in ensuring that the work is carried out as per the requirements.
Therefore, all three statements are correct, making option 'A' the correct choice. Dispatching is a critical function that helps in streamlining operations, reducing lead times, and improving overall productivity in an organization.
The information about when should start and how much work should be completed during a certain period .is provided by the act referred to as- a)loading
- b)routing
- c)dispatching
- d)scheduling
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The information about when should start and how much work should be completed during a certain period .is provided by the act referred to as
a)
loading
b)
routing
c)
dispatching
d)
scheduling

|
Nidhi Tiwari answered |
Importance of Scheduling in Production Planning
Scheduling plays a crucial role in production planning as it provides a roadmap for when tasks should start and how much work should be completed during a certain period. It helps in optimizing resources, minimizing lead times, and meeting customer demands efficiently.
Definition of Scheduling
Scheduling is the process of determining when production activities should take place based on factors such as resource availability, task dependencies, and deadlines. It involves creating a timetable that outlines the sequence of tasks to be completed within a specific timeframe.
Key Functions of Scheduling
1. Time Management: Scheduling helps in managing time effectively by allocating resources and assigning tasks to ensure timely completion of production activities.
2. Resource Optimization: By scheduling tasks based on resource availability, it helps in optimizing the use of equipment, manpower, and materials.
3. Priority Setting: Scheduling helps in setting priorities for production tasks, ensuring that critical activities are given precedence.
4. Coordination: It facilitates coordination between different departments and teams involved in the production process by aligning their activities according to the schedule.
Role of Scheduling in Production Planning
Scheduling is a critical component of production planning as it provides a detailed plan for executing production activities in a systematic and organized manner. It ensures that resources are utilized efficiently, production targets are met, and customer orders are fulfilled on time.
In conclusion, scheduling is an essential act in production planning as it determines the timeline for completing tasks, allocates resources effectively, and helps in achieving production goals efficiently. It plays a vital role in optimizing production processes and ensuring smooth operations in manufacturing units.
Scheduling plays a crucial role in production planning as it provides a roadmap for when tasks should start and how much work should be completed during a certain period. It helps in optimizing resources, minimizing lead times, and meeting customer demands efficiently.
Definition of Scheduling
Scheduling is the process of determining when production activities should take place based on factors such as resource availability, task dependencies, and deadlines. It involves creating a timetable that outlines the sequence of tasks to be completed within a specific timeframe.
Key Functions of Scheduling
1. Time Management: Scheduling helps in managing time effectively by allocating resources and assigning tasks to ensure timely completion of production activities.
2. Resource Optimization: By scheduling tasks based on resource availability, it helps in optimizing the use of equipment, manpower, and materials.
3. Priority Setting: Scheduling helps in setting priorities for production tasks, ensuring that critical activities are given precedence.
4. Coordination: It facilitates coordination between different departments and teams involved in the production process by aligning their activities according to the schedule.
Role of Scheduling in Production Planning
Scheduling is a critical component of production planning as it provides a detailed plan for executing production activities in a systematic and organized manner. It ensures that resources are utilized efficiently, production targets are met, and customer orders are fulfilled on time.
In conclusion, scheduling is an essential act in production planning as it determines the timeline for completing tasks, allocates resources effectively, and helps in achieving production goals efficiently. It plays a vital role in optimizing production processes and ensuring smooth operations in manufacturing units.
The number of possible ways for ‘n’ jobs to sequence- a) n
- b) n!
- c) n2
- d) 2n
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of possible ways for ‘n’ jobs to sequence
a)
n
b)
n!
c)
n2
d)
2n
|
|
Ruchi Ahuja answered |
Answer:
Possible ways for sequencing ‘n’ jobs is n!.
Explanation:
n! (n factorial) is the product of all positive integers up to n. It is calculated by multiplying all the numbers from 1 to n. For example, 5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120.
Let's consider a scenario where we have three jobs: A, B, and C. The possible ways to sequence them are:
ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, CBA
This is equivalent to the number of possible permutations of three objects taken three at a time, which is 3! = 6.
Similarly, for ‘n’ jobs, the number of possible ways to sequence them is n!.
Therefore, the correct answer is option ‘B’.
Possible ways for sequencing ‘n’ jobs is n!.
Explanation:
n! (n factorial) is the product of all positive integers up to n. It is calculated by multiplying all the numbers from 1 to n. For example, 5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120.
Let's consider a scenario where we have three jobs: A, B, and C. The possible ways to sequence them are:
ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, CBA
This is equivalent to the number of possible permutations of three objects taken three at a time, which is 3! = 6.
Similarly, for ‘n’ jobs, the number of possible ways to sequence them is n!.
Therefore, the correct answer is option ‘B’.
Least slack is given by- a) processing time - due date
- b) due date - processing time
- c) flow time - due date
- d) due date - flow time
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Least slack is given by
a)
processing time - due date
b)
due date - processing time
c)
flow time - due date
d)
due date - flow time
|
|
Stuti Bajaj answered |
Explanation:
Slack is the amount of time available to start and complete a task or job after the due date. The least slack is given by subtracting the processing time from the due date.
Here is a detailed explanation of each option and why option B is the correct answer:
a) Processing time - due date:
- This calculation would result in a negative value, indicating that the task is already overdue before it even starts. This would not be useful in determining slack time.
b) Due date - processing time:
- This calculation determines the amount of time available to complete the task after it starts, taking into account the processing time. It gives the amount of slack time available for the task.
c) Flow time - due date:
- Flow time is the total time it takes for a task to complete, including processing time and any waiting times in between. Subtracting flow time from the due date would not give a useful measure of slack time.
d) Due date - flow time:
- This calculation determines the latest possible start time for the task, but does not take into account the processing time. Therefore, it does not give an accurate measure of slack time.
In summary, option B is the correct answer because it gives the most accurate measure of slack time by taking into account the processing time and the due date.
Slack is the amount of time available to start and complete a task or job after the due date. The least slack is given by subtracting the processing time from the due date.
Here is a detailed explanation of each option and why option B is the correct answer:
a) Processing time - due date:
- This calculation would result in a negative value, indicating that the task is already overdue before it even starts. This would not be useful in determining slack time.
b) Due date - processing time:
- This calculation determines the amount of time available to complete the task after it starts, taking into account the processing time. It gives the amount of slack time available for the task.
c) Flow time - due date:
- Flow time is the total time it takes for a task to complete, including processing time and any waiting times in between. Subtracting flow time from the due date would not give a useful measure of slack time.
d) Due date - flow time:
- This calculation determines the latest possible start time for the task, but does not take into account the processing time. Therefore, it does not give an accurate measure of slack time.
In summary, option B is the correct answer because it gives the most accurate measure of slack time by taking into account the processing time and the due date.
Dispatching is concerned with- a)better utilization of man power
- b)material handling layout
- c)getting the work started and ensuring that the plans are properly implemented
- d)sequence of operations to be performed from one machines to other
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dispatching is concerned with
a)
better utilization of man power
b)
material handling layout
c)
getting the work started and ensuring that the plans are properly implemented
d)
sequence of operations to be performed from one machines to other

|
Arjun Menon answered |
Dispatching in Manufacturing:
Dispatching in manufacturing is concerned with getting the work started and ensuring that the plans are properly implemented. It involves coordinating and directing the flow of work in a production facility to ensure efficient operation.
Key Aspects of Dispatching:
- Work Initiation: Dispatching ensures that work orders are issued to the appropriate departments or workstations to kickstart the production process.
- Monitoring Progress: Dispatching involves tracking the progress of work orders, ensuring that they are completed on time and according to the plan.
- Resource Allocation: Dispatching allocates resources such as manpower, materials, and equipment to different tasks based on priority and availability.
- Communication: Dispatching involves communicating instructions, schedules, and updates to various departments and workers to keep everyone informed and coordinated.
- Problem Solving: In case of any issues or delays, dispatching plays a key role in problem-solving and making necessary adjustments to ensure smooth operations.
Importance of Dispatching:
- Efficiency: By ensuring that work is started promptly and progresses as planned, dispatching helps in improving overall efficiency in manufacturing operations.
- Productivity: Proper dispatching leads to optimized resource utilization and minimizes idle time, thereby increasing productivity.
- Quality: Dispatching helps in maintaining quality standards by ensuring that work is carried out in a systematic and controlled manner.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Effective dispatching can lead to cost savings by reducing wastage, minimizing delays, and improving overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, dispatching plays a crucial role in the manufacturing process by facilitating the smooth execution of production plans, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring that work is completed efficiently and on time.
Dispatching in manufacturing is concerned with getting the work started and ensuring that the plans are properly implemented. It involves coordinating and directing the flow of work in a production facility to ensure efficient operation.
Key Aspects of Dispatching:
- Work Initiation: Dispatching ensures that work orders are issued to the appropriate departments or workstations to kickstart the production process.
- Monitoring Progress: Dispatching involves tracking the progress of work orders, ensuring that they are completed on time and according to the plan.
- Resource Allocation: Dispatching allocates resources such as manpower, materials, and equipment to different tasks based on priority and availability.
- Communication: Dispatching involves communicating instructions, schedules, and updates to various departments and workers to keep everyone informed and coordinated.
- Problem Solving: In case of any issues or delays, dispatching plays a key role in problem-solving and making necessary adjustments to ensure smooth operations.
Importance of Dispatching:
- Efficiency: By ensuring that work is started promptly and progresses as planned, dispatching helps in improving overall efficiency in manufacturing operations.
- Productivity: Proper dispatching leads to optimized resource utilization and minimizes idle time, thereby increasing productivity.
- Quality: Dispatching helps in maintaining quality standards by ensuring that work is carried out in a systematic and controlled manner.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Effective dispatching can lead to cost savings by reducing wastage, minimizing delays, and improving overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, dispatching plays a crucial role in the manufacturing process by facilitating the smooth execution of production plans, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring that work is completed efficiently and on time.
The function which authorizes production as well as control is
- a)Routing
- b)Dispatching
- c)Scheduling
- d)Expediting
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The function which authorizes production as well as control is
a)
Routing
b)
Dispatching
c)
Scheduling
d)
Expediting

|
Bijoy Mehra answered |
Dispatching as the Function which Authorizes Production and Control
Dispatching is a crucial function in production and control that authorizes the start of production activities and controls them to ensure their success. It involves the release of orders to the shop floor and the allocation of resources required to execute them. The primary objective of dispatching is to ensure that production activities are initiated and maintained according to the production schedule and that the products are produced in the required quantity, quality, and time.
The Role of Dispatching in Production and Control
Dispatching plays a critical role in production and control in the following ways:
1. Authorizing Production: Dispatching authorizes the start of production activities by releasing orders to the shop floor. It ensures that all the necessary resources, such as materials, machines, tools, and labor, are allocated to the production process.
2. Allocating Resources: Dispatching allocates the resources required to execute the production orders. It ensures that the resources are available at the right time and place and in the required quantity and quality.
3. Monitoring Progress: Dispatching monitors the progress of production activities to ensure that they are executed according to the production schedule. It tracks the status of the orders and takes corrective actions if there are any deviations from the plan.
4. Controlling Quality: Dispatching ensures that the products are produced in the required quality by setting quality standards and monitoring the production process. It takes corrective actions if there are any quality issues to prevent defective products from reaching the customer.
The Benefits of Dispatching in Production and Control
Dispatching provides the following benefits in production and control:
1. Improved Efficiency: Dispatching ensures that the production activities are executed efficiently by allocating the necessary resources and monitoring their use. It minimizes idle time, reduces waiting time, and optimizes resource utilization.
2. Improved Quality: Dispatching ensures that the products are produced in the required quality by setting quality standards and monitoring the production process. It prevents defective products from reaching the customer, which improves customer satisfaction and reduces rework costs.
3. Improved Delivery Performance: Dispatching ensures that the products are produced and delivered to the customer on time. It minimizes delays and improves delivery performance, which enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Improved Cost Control: Dispatching optimizes the use of resources, which reduces production costs. It also minimizes rework costs by preventing defective products from reaching the customer.
In conclusion, dispatching is a critical function in production and control that authorizes the start of production activities and controls them to ensure their success. It plays a crucial role in allocating resources, monitoring progress, controlling quality, and improving efficiency, quality, delivery performance, and cost control.
Dispatching is a crucial function in production and control that authorizes the start of production activities and controls them to ensure their success. It involves the release of orders to the shop floor and the allocation of resources required to execute them. The primary objective of dispatching is to ensure that production activities are initiated and maintained according to the production schedule and that the products are produced in the required quantity, quality, and time.
The Role of Dispatching in Production and Control
Dispatching plays a critical role in production and control in the following ways:
1. Authorizing Production: Dispatching authorizes the start of production activities by releasing orders to the shop floor. It ensures that all the necessary resources, such as materials, machines, tools, and labor, are allocated to the production process.
2. Allocating Resources: Dispatching allocates the resources required to execute the production orders. It ensures that the resources are available at the right time and place and in the required quantity and quality.
3. Monitoring Progress: Dispatching monitors the progress of production activities to ensure that they are executed according to the production schedule. It tracks the status of the orders and takes corrective actions if there are any deviations from the plan.
4. Controlling Quality: Dispatching ensures that the products are produced in the required quality by setting quality standards and monitoring the production process. It takes corrective actions if there are any quality issues to prevent defective products from reaching the customer.
The Benefits of Dispatching in Production and Control
Dispatching provides the following benefits in production and control:
1. Improved Efficiency: Dispatching ensures that the production activities are executed efficiently by allocating the necessary resources and monitoring their use. It minimizes idle time, reduces waiting time, and optimizes resource utilization.
2. Improved Quality: Dispatching ensures that the products are produced in the required quality by setting quality standards and monitoring the production process. It prevents defective products from reaching the customer, which improves customer satisfaction and reduces rework costs.
3. Improved Delivery Performance: Dispatching ensures that the products are produced and delivered to the customer on time. It minimizes delays and improves delivery performance, which enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Improved Cost Control: Dispatching optimizes the use of resources, which reduces production costs. It also minimizes rework costs by preventing defective products from reaching the customer.
In conclusion, dispatching is a critical function in production and control that authorizes the start of production activities and controls them to ensure their success. It plays a crucial role in allocating resources, monitoring progress, controlling quality, and improving efficiency, quality, delivery performance, and cost control.
A master production schedule specifies- a)the financial resources required for production
- b)what component is to be made, and when
- c)what product is to be made, and when
- d)the labor hours required for production
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A master production schedule specifies
a)
the financial resources required for production
b)
what component is to be made, and when
c)
what product is to be made, and when
d)
the labor hours required for production
|
|
Rajat Basu answered |
C) What product is to be made, and when
The master production schedule (MPS) is an important tool used in production planning and control. It is a detailed plan that specifies the quantity and timing of the products to be manufactured, based on the demand forecast and available resources. The correct answer to this question is option C, which states that the master production schedule specifies what product is to be made, and when.
1. Purpose of the Master Production Schedule:
The primary purpose of the master production schedule is to ensure that the production process is aligned with the demand for the final product. It helps in maintaining a balance between customer demand and production capacity.
2. Product Identification:
The MPS identifies the specific products that are to be manufactured. It includes information such as the product code, description, and other relevant details.
3. Timeframe:
The master production schedule also specifies the time period during which the production is planned. It provides a detailed timeline for each product, indicating when it should be started and completed.
4. Production Quantities:
Another crucial aspect of the MPS is the determination of production quantities. It specifies the number of units to be manufactured for each product during a specific time period. This information is based on the demand forecast, taking into consideration factors such as customer orders, inventory levels, and market trends.
5. Resource Planning:
While the MPS primarily focuses on the product and timing aspects, it indirectly influences resource planning. By providing information on the products to be manufactured and their quantities, it helps in estimating the required resources such as raw materials, labor, and equipment. However, the MPS does not directly specify financial resources or labor hours required for production, as mentioned in options A and D.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option C. The master production schedule specifies what product is to be made, and when, ensuring that production is aligned with customer demand and available resources.
The master production schedule (MPS) is an important tool used in production planning and control. It is a detailed plan that specifies the quantity and timing of the products to be manufactured, based on the demand forecast and available resources. The correct answer to this question is option C, which states that the master production schedule specifies what product is to be made, and when.
1. Purpose of the Master Production Schedule:
The primary purpose of the master production schedule is to ensure that the production process is aligned with the demand for the final product. It helps in maintaining a balance between customer demand and production capacity.
2. Product Identification:
The MPS identifies the specific products that are to be manufactured. It includes information such as the product code, description, and other relevant details.
3. Timeframe:
The master production schedule also specifies the time period during which the production is planned. It provides a detailed timeline for each product, indicating when it should be started and completed.
4. Production Quantities:
Another crucial aspect of the MPS is the determination of production quantities. It specifies the number of units to be manufactured for each product during a specific time period. This information is based on the demand forecast, taking into consideration factors such as customer orders, inventory levels, and market trends.
5. Resource Planning:
While the MPS primarily focuses on the product and timing aspects, it indirectly influences resource planning. By providing information on the products to be manufactured and their quantities, it helps in estimating the required resources such as raw materials, labor, and equipment. However, the MPS does not directly specify financial resources or labor hours required for production, as mentioned in options A and D.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option C. The master production schedule specifies what product is to be made, and when, ensuring that production is aligned with customer demand and available resources.
Which of the following is TRUE regarding services scheduling?- a)The critical ratio sequencing rule is widely used for fairness to customers.
- b)The emphasis is on staffing levels, not materials.
- c)Reservation systems are often used a means- of manipulating the supply of services.
- d)Labour use can be intensive, and labour demand is usually stable.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding services scheduling?
a)
The critical ratio sequencing rule is widely used for fairness to customers.
b)
The emphasis is on staffing levels, not materials.
c)
Reservation systems are often used a means- of manipulating the supply of services.
d)
Labour use can be intensive, and labour demand is usually stable.

|
Anand Mehta answered |
Staffing Levels Over Materials in Services Scheduling
Services scheduling typically places a greater emphasis on staffing levels rather than materials. This is due to the nature of services being more labor-intensive and reliant on human resources to deliver the service to customers.
Labour Intensive Nature
Services often require a high level of labor input, as they involve direct interaction between service providers and customers. This makes labor management a critical aspect of services scheduling, as the availability and productivity of staff directly impact the quality and efficiency of service delivery.
Stable Labour Demand
Labour demand in services scheduling is usually more stable compared to manufacturing processes, where demand can fluctuate based on production levels. Since services are often provided on a consistent basis, staffing levels can be more predictably planned and managed.
Importance of Staffing Levels
Having the right number of staff members with the appropriate skills and expertise is crucial for meeting customer demand and maintaining service quality. Understaffing can lead to long wait times and poor customer service, while overstaffing can result in unnecessary costs for the service provider.
In conclusion, services scheduling places a strong emphasis on staffing levels due to the labor-intensive nature of services and the need to ensure optimal resource allocation for efficient and effective service delivery.
Services scheduling typically places a greater emphasis on staffing levels rather than materials. This is due to the nature of services being more labor-intensive and reliant on human resources to deliver the service to customers.
Labour Intensive Nature
Services often require a high level of labor input, as they involve direct interaction between service providers and customers. This makes labor management a critical aspect of services scheduling, as the availability and productivity of staff directly impact the quality and efficiency of service delivery.
Stable Labour Demand
Labour demand in services scheduling is usually more stable compared to manufacturing processes, where demand can fluctuate based on production levels. Since services are often provided on a consistent basis, staffing levels can be more predictably planned and managed.
Importance of Staffing Levels
Having the right number of staff members with the appropriate skills and expertise is crucial for meeting customer demand and maintaining service quality. Understaffing can lead to long wait times and poor customer service, while overstaffing can result in unnecessary costs for the service provider.
In conclusion, services scheduling places a strong emphasis on staffing levels due to the labor-intensive nature of services and the need to ensure optimal resource allocation for efficient and effective service delivery.
Which of these is not part of the planning files of a production planning and control system?- a)a progress file
- b)a work center master file
- c)an item master life
- d)a routing file
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is not part of the planning files of a production planning and control system?
a)
a progress file
b)
a work center master file
c)
an item master life
d)
a routing file

|
Shreya Choudhary answered |
The correct answer is option 'A' - a progress file.
Explanation:
A production planning and control system is a set of tools and processes used by manufacturing companies to plan, schedule, and control their production operations. It involves various files and documents that are used to store and manage information related to production planning and execution.
Let's examine each of the given options to understand their roles in a production planning and control system:
a) Progress File:
A progress file is not typically part of the planning files in a production planning and control system. It refers to the documentation of the progress made during the production process, such as the completion status of work orders, production schedules, and reports on the actual production achieved. While monitoring progress is an essential aspect of production planning and control, it is not considered a planning file itself.
b) Work Center Master File:
A work center master file is a key planning file in a production planning and control system. It contains information about each work center or machine in the manufacturing facility, including its capacity, capabilities, availability, and assigned personnel. This file helps in scheduling and allocating work orders to the appropriate work centers based on their capacity and capabilities.
c) Item Master File:
An item master file is another crucial planning file in a production planning and control system. It contains information about the various items or products manufactured by the company, including their specifications, bill of materials (BOM), and inventory levels. This file helps in determining the material requirements, planning production quantities, and managing inventory.
d) Routing File:
A routing file is an essential planning file in a production planning and control system. It contains the sequence of operations or steps required to manufacture a product, along with the corresponding work centers or machines involved at each step. This file helps in defining the production process, estimating the production time, and scheduling the operations.
In summary, while a progress file is important for monitoring the progress of production, it is not considered a planning file in a production planning and control system. The other options, including the work center master file, item master file, and routing file, are all significant planning files that play crucial roles in managing and controlling production operations.
Explanation:
A production planning and control system is a set of tools and processes used by manufacturing companies to plan, schedule, and control their production operations. It involves various files and documents that are used to store and manage information related to production planning and execution.
Let's examine each of the given options to understand their roles in a production planning and control system:
a) Progress File:
A progress file is not typically part of the planning files in a production planning and control system. It refers to the documentation of the progress made during the production process, such as the completion status of work orders, production schedules, and reports on the actual production achieved. While monitoring progress is an essential aspect of production planning and control, it is not considered a planning file itself.
b) Work Center Master File:
A work center master file is a key planning file in a production planning and control system. It contains information about each work center or machine in the manufacturing facility, including its capacity, capabilities, availability, and assigned personnel. This file helps in scheduling and allocating work orders to the appropriate work centers based on their capacity and capabilities.
c) Item Master File:
An item master file is another crucial planning file in a production planning and control system. It contains information about the various items or products manufactured by the company, including their specifications, bill of materials (BOM), and inventory levels. This file helps in determining the material requirements, planning production quantities, and managing inventory.
d) Routing File:
A routing file is an essential planning file in a production planning and control system. It contains the sequence of operations or steps required to manufacture a product, along with the corresponding work centers or machines involved at each step. This file helps in defining the production process, estimating the production time, and scheduling the operations.
In summary, while a progress file is important for monitoring the progress of production, it is not considered a planning file in a production planning and control system. The other options, including the work center master file, item master file, and routing file, are all significant planning files that play crucial roles in managing and controlling production operations.
Which of the following are tools of shop floor control?- a)Daily dispatch lists
- b)Scrap reports
- c)Rework reports
- d)Ali of the abov
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are tools of shop floor control?
a)
Daily dispatch lists
b)
Scrap reports
c)
Rework reports
d)
Ali of the abov

|
Megha Choudhury answered |
Shop Floor Control Tools
Daily Dispatch Lists
Daily dispatch lists are a crucial tool for shop floor control as they provide a schedule of orders that need to be completed and shipped out each day. This helps in planning and managing the production process efficiently to meet delivery deadlines.
Scrap Reports
Scrap reports are used to track and analyze the amount of material wasted during the production process. By identifying the root causes of scrap, shop floor managers can implement corrective actions to reduce waste and improve overall efficiency.
Rework Reports
Rework reports are essential for identifying products that do not meet quality standards and need to be reworked. By tracking rework activities, shop floor control can ensure that defective products are corrected before they are shipped out to customers.
All of the Above
All the tools mentioned above - daily dispatch lists, scrap reports, and rework reports - are important for effective shop floor control. Together, they help in monitoring production activities, maintaining quality standards, and optimizing processes to ensure smooth operations and timely delivery of products. Using these tools in combination can lead to improved productivity, reduced waste, and increased customer satisfaction.
Daily Dispatch Lists
Daily dispatch lists are a crucial tool for shop floor control as they provide a schedule of orders that need to be completed and shipped out each day. This helps in planning and managing the production process efficiently to meet delivery deadlines.
Scrap Reports
Scrap reports are used to track and analyze the amount of material wasted during the production process. By identifying the root causes of scrap, shop floor managers can implement corrective actions to reduce waste and improve overall efficiency.
Rework Reports
Rework reports are essential for identifying products that do not meet quality standards and need to be reworked. By tracking rework activities, shop floor control can ensure that defective products are corrected before they are shipped out to customers.
All of the Above
All the tools mentioned above - daily dispatch lists, scrap reports, and rework reports - are important for effective shop floor control. Together, they help in monitoring production activities, maintaining quality standards, and optimizing processes to ensure smooth operations and timely delivery of products. Using these tools in combination can lead to improved productivity, reduced waste, and increased customer satisfaction.
Chart which is useful for scheduling and control is- a)Kanban
- b)Gantt Chart
- c)X and R chart
- d)Flow process char
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Chart which is useful for scheduling and control is
a)
Kanban
b)
Gantt Chart
c)
X and R chart
d)
Flow process char

|
Sandeep Sen answered |
Gantt Chart: Useful for Scheduling and Control
A Gantt chart is a useful tool for scheduling and control in various industries, including project management, manufacturing, and construction. It provides a visual representation of a project's timeline, tasks, and dependencies. With its ability to track progress and manage resources, a Gantt chart helps in effectively scheduling and controlling project activities.
Benefits of Gantt Chart for Scheduling
1. Visual Representation: The Gantt chart presents project tasks and their durations in a visually appealing format. It allows project managers and team members to easily understand the project schedule and its various components.
2. Task Dependencies: By using arrows or lines between tasks, a Gantt chart demonstrates the dependencies between different activities. This helps in identifying critical paths and understanding how delays in one task can impact the overall project timeline.
3. Resource Allocation: A Gantt chart can display the availability and allocation of resources, such as manpower, equipment, and materials, for each task. This allows project managers to assign resources effectively and avoid overloading or underutilizing them.
4. Milestone Tracking: Gantt charts often include milestones, which are significant events or achievements within a project. These milestones act as checkpoints for monitoring progress and ensuring that the project is on track.
Benefits of Gantt Chart for Control
1. Progress Monitoring: With a Gantt chart, project managers can track the progress of each task and compare it against the planned schedule. This helps in identifying any delays or deviations from the original plan and taking corrective actions.
2. Resource Management: By visualizing resource allocation, a Gantt chart enables project managers to monitor resource utilization and reallocate them if necessary. This ensures that resources are efficiently utilized throughout the project duration.
3. Schedule Adjustments: As projects progress, circumstances may change, and adjustments to the schedule may be required. A Gantt chart allows project managers to easily make modifications, such as adding or removing tasks, adjusting durations, or reassigning resources, while considering the impact on the overall project timeline.
4. Communication and Collaboration: Gantt charts facilitate communication and collaboration among project stakeholders by providing a clear and concise overview of the project's status and progress. It allows all team members to stay informed and aligned with the project objectives.
In conclusion, a Gantt chart is a valuable tool for scheduling and control in various industries. Its visual representation, task dependencies, resource allocation, milestone tracking, progress monitoring, resource management, schedule adjustments, and communication benefits make it an effective tool for project management.
A Gantt chart is a useful tool for scheduling and control in various industries, including project management, manufacturing, and construction. It provides a visual representation of a project's timeline, tasks, and dependencies. With its ability to track progress and manage resources, a Gantt chart helps in effectively scheduling and controlling project activities.
Benefits of Gantt Chart for Scheduling
1. Visual Representation: The Gantt chart presents project tasks and their durations in a visually appealing format. It allows project managers and team members to easily understand the project schedule and its various components.
2. Task Dependencies: By using arrows or lines between tasks, a Gantt chart demonstrates the dependencies between different activities. This helps in identifying critical paths and understanding how delays in one task can impact the overall project timeline.
3. Resource Allocation: A Gantt chart can display the availability and allocation of resources, such as manpower, equipment, and materials, for each task. This allows project managers to assign resources effectively and avoid overloading or underutilizing them.
4. Milestone Tracking: Gantt charts often include milestones, which are significant events or achievements within a project. These milestones act as checkpoints for monitoring progress and ensuring that the project is on track.
Benefits of Gantt Chart for Control
1. Progress Monitoring: With a Gantt chart, project managers can track the progress of each task and compare it against the planned schedule. This helps in identifying any delays or deviations from the original plan and taking corrective actions.
2. Resource Management: By visualizing resource allocation, a Gantt chart enables project managers to monitor resource utilization and reallocate them if necessary. This ensures that resources are efficiently utilized throughout the project duration.
3. Schedule Adjustments: As projects progress, circumstances may change, and adjustments to the schedule may be required. A Gantt chart allows project managers to easily make modifications, such as adding or removing tasks, adjusting durations, or reassigning resources, while considering the impact on the overall project timeline.
4. Communication and Collaboration: Gantt charts facilitate communication and collaboration among project stakeholders by providing a clear and concise overview of the project's status and progress. It allows all team members to stay informed and aligned with the project objectives.
In conclusion, a Gantt chart is a valuable tool for scheduling and control in various industries. Its visual representation, task dependencies, resource allocation, milestone tracking, progress monitoring, resource management, schedule adjustments, and communication benefits make it an effective tool for project management.
If the demand for product A is 50 units, what will be the gross requirement for component E?
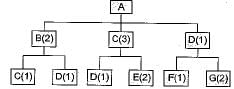
- a)300
- b)100
- c)200
- d)250
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the demand for product A is 50 units, what will be the gross requirement for component E?


a)
300
b)
100
c)
200
d)
250
|
|
Hrishikesh Chakraborty answered |
As per given dependent demand figure, Requirement of B = 50 x 2 = 100 Requirement of C = 50 x 3 = 150 Requirement of D = 150 x 1 = 150 Requirement of E= 150 x 2 = 300
In production, planning and control, the document which authorizes the start of an operation on the shop floor is the:- a)Dispatch order
- b)Route plan
- c)Loading chart
- d)Schedule
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In production, planning and control, the document which authorizes the start of an operation on the shop floor is the:
a)
Dispatch order
b)
Route plan
c)
Loading chart
d)
Schedule

|
Yash Joshi answered |
Dispatch Order
The dispatch order is a document that authorizes the start of an operation on the shop floor in production planning and control. It serves as a directive to the shop floor personnel to begin a specific task or operation. Here's why the dispatch order is crucial in production planning and control:
Authorization
- The dispatch order provides formal authorization to begin a particular operation. It ensures that the shop floor personnel are clear about what task needs to be carried out next.
Communication
- The dispatch order acts as a communication tool between the planning department and the shop floor. It conveys important information such as job specifications, quantity to be produced, deadlines, and any special instructions.
Coordination
- By issuing dispatch orders, the production planning and control team can ensure that all operations are executed in a coordinated manner. This helps in maintaining a smooth flow of work on the shop floor.
Tracking Progress
- Dispatch orders also aid in tracking the progress of operations. By monitoring the completion of tasks as per the dispatch orders, the production team can assess whether the production schedule is being adhered to or if there are any delays.
In conclusion, the dispatch order plays a vital role in production planning and control by providing authorization, facilitating communication, ensuring coordination, and tracking progress on the shop floor. It is a key document that helps in the efficient execution of operations in a manufacturing environment.
The dispatch order is a document that authorizes the start of an operation on the shop floor in production planning and control. It serves as a directive to the shop floor personnel to begin a specific task or operation. Here's why the dispatch order is crucial in production planning and control:
Authorization
- The dispatch order provides formal authorization to begin a particular operation. It ensures that the shop floor personnel are clear about what task needs to be carried out next.
Communication
- The dispatch order acts as a communication tool between the planning department and the shop floor. It conveys important information such as job specifications, quantity to be produced, deadlines, and any special instructions.
Coordination
- By issuing dispatch orders, the production planning and control team can ensure that all operations are executed in a coordinated manner. This helps in maintaining a smooth flow of work on the shop floor.
Tracking Progress
- Dispatch orders also aid in tracking the progress of operations. By monitoring the completion of tasks as per the dispatch orders, the production team can assess whether the production schedule is being adhered to or if there are any delays.
In conclusion, the dispatch order plays a vital role in production planning and control by providing authorization, facilitating communication, ensuring coordination, and tracking progress on the shop floor. It is a key document that helps in the efficient execution of operations in a manufacturing environment.
Routing and scheduling are integral part of- a)product planning
- b)work study
- c)job analysis
- d)quality control
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Routing and scheduling are integral part of
a)
product planning
b)
work study
c)
job analysis
d)
quality control

|
Rutuja Pillai answered |
Routing and Scheduling in Product Planning
In product planning, routing and scheduling are integral parts of the process. They involve determining the most efficient way to produce a product, considering various factors such as resources, time, and cost.
Routing
Routing is the process of determining the most optimal sequence of operations required to manufacture a product. It involves identifying the specific tasks, machines, and work centers involved in the production process. The goal of routing is to minimize the time and cost required to produce the product while maximizing efficiency.
Routing considers various factors such as the availability of machines and equipment, the skills and capabilities of the workforce, and the sequence of operations needed to complete the product. By carefully planning the routing, manufacturers can minimize bottlenecks, reduce production time, and optimize resource allocation.
Scheduling
Scheduling is the process of determining when each operation or task will be performed within the production process. It involves assigning start and end times to each operation, considering the availability of resources and the dependencies between tasks.
The scheduling process takes into account various factors such as the availability of machines, the skill level of workers, and the desired production rate. It aims to create a feasible and efficient production schedule that meets the production requirements while minimizing idle time and maximizing productivity.
Integration with Product Planning
Routing and scheduling are crucial components of product planning as they directly impact the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the manufacturing process. By carefully planning the routing and scheduling, manufacturers can achieve the following benefits:
- Improved productivity: Optimal routing and scheduling help minimize idle time and maximize resource utilization, leading to increased productivity.
- Reduced costs: Efficient routing and scheduling can help reduce production costs by minimizing wastage of resources and optimizing the use of machines and equipment.
- Shorter lead times: By streamlining the production process through effective routing and scheduling, manufacturers can reduce lead times and respond quickly to customer demands.
- Improved quality: Proper routing and scheduling ensure that each operation is performed in the correct sequence, reducing the chances of errors or defects.
In conclusion, routing and scheduling play a vital role in product planning. They help manufacturers optimize the production process, minimize costs, improve productivity, and enhance overall product quality.
Which of the following card is not used in dispatching?- a)Work order
- b)Timecard
- c)Inspection tickets
- d)Order scheduling
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following card is not used in dispatching?
a)
Work order
b)
Timecard
c)
Inspection tickets
d)
Order scheduling

|
Lekshmi Das answered |
Order Scheduling
Order scheduling card is not used in dispatching. Here is why:
Work Order
- Work orders are used to assign tasks to employees or departments. They specify the work that needs to be done, materials required, and deadlines.
Timecard
- Timecards are used to track the time employees spend on various tasks or projects. They help in monitoring productivity and managing payroll.
Inspection Tickets
- Inspection tickets are used to document inspections conducted on products or equipment. They help in ensuring quality control and compliance with regulations.
Order Scheduling
- Order scheduling typically involves setting timelines for tasks or projects, coordinating resources, and planning the sequence of operations. While important for overall project management, it is not a card used in dispatching specific tasks or work orders.
Order scheduling card is not used in dispatching. Here is why:
Work Order
- Work orders are used to assign tasks to employees or departments. They specify the work that needs to be done, materials required, and deadlines.
Timecard
- Timecards are used to track the time employees spend on various tasks or projects. They help in monitoring productivity and managing payroll.
Inspection Tickets
- Inspection tickets are used to document inspections conducted on products or equipment. They help in ensuring quality control and compliance with regulations.
Order Scheduling
- Order scheduling typically involves setting timelines for tasks or projects, coordinating resources, and planning the sequence of operations. While important for overall project management, it is not a card used in dispatching specific tasks or work orders.
Determination of the sequence of operations to be performed and the allocation of facilities where these operations are to be performed is- a)master scheduling
- b)aggregate planning
- c)routing
- d)forecasting
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Determination of the sequence of operations to be performed and the allocation of facilities where these operations are to be performed is
a)
master scheduling
b)
aggregate planning
c)
routing
d)
forecasting

|
Varun Banerjee answered |
Routing
Routing is the determination of the sequence of operations to be performed and the allocation of facilities where these operations are to be carried out. It involves creating a detailed plan that outlines the specific steps needed to complete a particular task or project.
Importance of Routing
- Efficient utilization of resources: By determining the most efficient sequence of operations and allocating resources accordingly, routing helps in maximizing the utilization of facilities and equipment.
- Minimization of delays: Proper routing ensures that work flows smoothly from one operation to the next, minimizing delays and bottlenecks in the production process.
- Improved productivity: By streamlining the workflow and eliminating unnecessary steps, routing helps in improving overall productivity and reducing lead times.
- Cost reduction: Effective routing can help in reducing costs by optimizing the use of resources and minimizing idle time.
Steps involved in Routing
1. Analysis of the product: The first step in routing is to analyze the product or service to determine the sequence of operations required for its production.
2. Determination of operations: Once the sequence of operations is identified, the next step is to determine the specific operations that need to be performed at each stage.
3. Allocation of resources: After determining the operations, resources such as equipment, machinery, and personnel need to be allocated for each operation.
4. Creation of a routing plan: Finally, a detailed routing plan is created that outlines the sequence of operations, the facilities where each operation will be performed, and the resources required for each operation.
In conclusion, routing plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of operations and maximizing the utilization of resources in a production process. It is essential for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing overall productivity.
Routing is the determination of the sequence of operations to be performed and the allocation of facilities where these operations are to be carried out. It involves creating a detailed plan that outlines the specific steps needed to complete a particular task or project.
Importance of Routing
- Efficient utilization of resources: By determining the most efficient sequence of operations and allocating resources accordingly, routing helps in maximizing the utilization of facilities and equipment.
- Minimization of delays: Proper routing ensures that work flows smoothly from one operation to the next, minimizing delays and bottlenecks in the production process.
- Improved productivity: By streamlining the workflow and eliminating unnecessary steps, routing helps in improving overall productivity and reducing lead times.
- Cost reduction: Effective routing can help in reducing costs by optimizing the use of resources and minimizing idle time.
Steps involved in Routing
1. Analysis of the product: The first step in routing is to analyze the product or service to determine the sequence of operations required for its production.
2. Determination of operations: Once the sequence of operations is identified, the next step is to determine the specific operations that need to be performed at each stage.
3. Allocation of resources: After determining the operations, resources such as equipment, machinery, and personnel need to be allocated for each operation.
4. Creation of a routing plan: Finally, a detailed routing plan is created that outlines the sequence of operations, the facilities where each operation will be performed, and the resources required for each operation.
In conclusion, routing plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of operations and maximizing the utilization of resources in a production process. It is essential for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing overall productivity.
Which of the following rules minimizes maximum lateness?- a) SPT
- b) EDD
- c) FCFS
- d) LS
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following rules minimizes maximum lateness?
a)
SPT
b)
EDD
c)
FCFS
d)
LS
|
|
Atharva Majumdar answered |
Explanation:
EDD (Earliest Due Date) Rule:
- EDD is a scheduling rule that minimizes the maximum lateness of jobs.
- In EDD rule, jobs are scheduled according to their due dates, with the job that has the earliest due date being scheduled first.
- By following the EDD rule, the job with the earliest due date is completed first, reducing the likelihood of lateness for that particular job.
- This rule helps to prioritize jobs based on their due dates, ensuring that jobs with earlier due dates are completed first to minimize lateness.
SPT (Shortest Processing Time) Rule:
- SPT is a scheduling rule that minimizes the total completion time of jobs.
- In SPT rule, jobs are scheduled based on their processing times, with the shortest processing time job being scheduled first.
- While SPT minimizes the total completion time, it may not necessarily minimize the maximum lateness of jobs.
- SPT focuses on completing jobs quickly, without considering their due dates, which can lead to some jobs being completed late if they have earlier due dates.
FCFS (First-Come, First-Served) Rule:
- FCFS is a scheduling rule that schedules jobs in the order they arrive.
- While FCFS is a simple and easy-to-implement rule, it does not prioritize jobs based on their due dates or processing times, which can result in increased lateness for jobs with earlier due dates.
LS (Largest Slack) Rule:
- LS is a scheduling rule that prioritizes jobs based on their slack time, which is the difference between the due date and the current time.
- While LS takes into account the due dates of jobs, it may not always minimize the maximum lateness as it focuses on jobs with the largest slack time rather than the earliest due date.
Therefore, the EDD rule is the most effective in minimizing the maximum lateness of jobs as it prioritizes jobs based on their due dates, ensuring that jobs with earlier due dates are completed first to reduce lateness.
Which of the following input data are needed for MRP?
1. Master production schedule
2. Inventory status
3. Bill of materials
4. Machine capacitySelect the correct answer from above:- a)1,2 and 4
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1,2 and 3
- d)1, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following input data are needed for MRP?
1. Master production schedule
2. Inventory status
3. Bill of materials
4. Machine capacity
1. Master production schedule
2. Inventory status
3. Bill of materials
4. Machine capacity
Select the correct answer from above:
a)
1,2 and 4
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1,2 and 3
d)
1, 3 and 4
|
|
Ishaan Malik answered |
Input Data for MRP
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is a computer-based inventory management system that helps organizations to manage their production process efficiently by ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time. The following input data are needed for MRP:
1. Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The MPS is a plan that outlines the quantity and timing of the finished products that an organization plans to produce. It is an essential input for MRP as it serves as a basis for determining the materials needed to produce the finished products.
2. Inventory Status
The inventory status provides information about the current inventory levels of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. It is needed for MRP to ensure that the required materials are available in the inventory when needed.
3. Bill of Materials (BOM)
The BOM is a list of all the materials that are required to manufacture a finished product. It includes information about the quantity, type, and location of the materials. It is an essential input for MRP as it helps in determining the materials needed to produce the finished products.
4. Machine Capacity
Machine capacity is the maximum amount of work that a machine can handle in a given period. It is needed for MRP to ensure that the production plan does not exceed the capacity of the machines.
Answer
Based on the above information, the correct answer is option 'C' - 1, 2 and 3. Machine capacity is not an essential input for MRP, although it can be considered in production planning. However, the other three inputs are necessary for the MRP system to function effectively.
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is a computer-based inventory management system that helps organizations to manage their production process efficiently by ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time. The following input data are needed for MRP:
1. Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The MPS is a plan that outlines the quantity and timing of the finished products that an organization plans to produce. It is an essential input for MRP as it serves as a basis for determining the materials needed to produce the finished products.
2. Inventory Status
The inventory status provides information about the current inventory levels of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. It is needed for MRP to ensure that the required materials are available in the inventory when needed.
3. Bill of Materials (BOM)
The BOM is a list of all the materials that are required to manufacture a finished product. It includes information about the quantity, type, and location of the materials. It is an essential input for MRP as it helps in determining the materials needed to produce the finished products.
4. Machine Capacity
Machine capacity is the maximum amount of work that a machine can handle in a given period. It is needed for MRP to ensure that the production plan does not exceed the capacity of the machines.
Answer
Based on the above information, the correct answer is option 'C' - 1, 2 and 3. Machine capacity is not an essential input for MRP, although it can be considered in production planning. However, the other three inputs are necessary for the MRP system to function effectively.
The process which determines the programme for the operations is called- a)loading
- b)dispatching
- c)scheduling
- d)routing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The process which determines the programme for the operations is called
a)
loading
b)
dispatching
c)
scheduling
d)
routing

|
Saikat Gupta answered |
Overview:
The process which determines the program for the operations is called scheduling. Scheduling involves allocating resources, such as people, machines, and materials, to specific tasks or jobs in a planned manner. This ensures that the operations are executed efficiently and effectively to meet the desired objectives.
Explanation:
Scheduling is a crucial process in operations management that involves determining the order and timing of activities or tasks to be performed. It is an essential part of production planning and control, as it helps in optimizing resources and minimizing idle time, thereby increasing productivity and reducing costs.
Key Points:
1. Loading: Loading is the process of assigning work to machines or work centers. It involves determining which tasks or jobs should be processed on each machine or work center.
2. Dispatching: Dispatching is the process of initiating the execution of tasks or jobs. It involves releasing the work orders to the appropriate work centers or machines for processing.
3. Routing: Routing is the process of determining the path or sequence through which the materials or products should flow. It involves defining the specific steps or operations that need to be performed and the order in which they should be executed.
4. Scheduling: Scheduling is the process of determining the start and end times of activities or tasks. It involves allocating resources, such as people, machines, and materials, to specific tasks or jobs in a planned manner.
5. The correct answer is option 'C' - scheduling. Scheduling ensures that the operations are executed in a timely and efficient manner, considering various factors such as resource availability, task dependencies, and priorities.
6. Scheduling helps in optimizing the use of resources, reducing idle time, improving throughput, and meeting production targets.
7. Various scheduling techniques and methods are used, such as Gantt charts, critical path method (CPM), program evaluation and review technique (PERT), and heuristic algorithms.
8. Scheduling can be done at different levels, such as long-term scheduling, medium-term scheduling, and short-term scheduling, depending on the time horizon and the level of detail required.
9. The scheduling process involves analyzing and prioritizing tasks, estimating task durations, considering resource constraints, and creating a schedule that meets the desired objectives and constraints.
10. Scheduling is a dynamic process that may need to be adjusted and updated in response to changes in demand, resource availability, or other factors.
Conclusion:
Scheduling is the process that determines the program for the operations by allocating resources to specific tasks or jobs in a planned manner. It is an essential part of production planning and control, helping to optimize resources, minimize idle time, and improve productivity.
The process which determines the program for the operations is called scheduling. Scheduling involves allocating resources, such as people, machines, and materials, to specific tasks or jobs in a planned manner. This ensures that the operations are executed efficiently and effectively to meet the desired objectives.
Explanation:
Scheduling is a crucial process in operations management that involves determining the order and timing of activities or tasks to be performed. It is an essential part of production planning and control, as it helps in optimizing resources and minimizing idle time, thereby increasing productivity and reducing costs.
Key Points:
1. Loading: Loading is the process of assigning work to machines or work centers. It involves determining which tasks or jobs should be processed on each machine or work center.
2. Dispatching: Dispatching is the process of initiating the execution of tasks or jobs. It involves releasing the work orders to the appropriate work centers or machines for processing.
3. Routing: Routing is the process of determining the path or sequence through which the materials or products should flow. It involves defining the specific steps or operations that need to be performed and the order in which they should be executed.
4. Scheduling: Scheduling is the process of determining the start and end times of activities or tasks. It involves allocating resources, such as people, machines, and materials, to specific tasks or jobs in a planned manner.
5. The correct answer is option 'C' - scheduling. Scheduling ensures that the operations are executed in a timely and efficient manner, considering various factors such as resource availability, task dependencies, and priorities.
6. Scheduling helps in optimizing the use of resources, reducing idle time, improving throughput, and meeting production targets.
7. Various scheduling techniques and methods are used, such as Gantt charts, critical path method (CPM), program evaluation and review technique (PERT), and heuristic algorithms.
8. Scheduling can be done at different levels, such as long-term scheduling, medium-term scheduling, and short-term scheduling, depending on the time horizon and the level of detail required.
9. The scheduling process involves analyzing and prioritizing tasks, estimating task durations, considering resource constraints, and creating a schedule that meets the desired objectives and constraints.
10. Scheduling is a dynamic process that may need to be adjusted and updated in response to changes in demand, resource availability, or other factors.
Conclusion:
Scheduling is the process that determines the program for the operations by allocating resources to specific tasks or jobs in a planned manner. It is an essential part of production planning and control, helping to optimize resources, minimize idle time, and improve productivity.
Routing decides- a)sequence in which order/work will be taken up
- b)sequence of operations to be followed
- c)how the machines can be properly loaded
- d)the stock control syste
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Routing decides
a)
sequence in which order/work will be taken up
b)
sequence of operations to be followed
c)
how the machines can be properly loaded
d)
the stock control syste
|
|
Shreya Choudhury answered |
Routing in Mechanical Engineering
Routing plays a crucial role in various aspects of mechanical engineering, including manufacturing processes, production planning, and scheduling. It involves determining the sequence of operations and the path to be followed for the production of a particular product. Routing decisions help in optimizing the overall production process and ensuring efficient utilization of resources.
Importance of Routing
Routing decisions have a significant impact on the overall efficiency and productivity of a manufacturing system. By determining the sequence of operations, routing helps in achieving the following objectives:
1. Optimal Order of Work: Routing decisions determine the sequence in which different tasks or operations are to be performed. This ensures that the work is completed in the most efficient and logical order, minimizing unnecessary movement and reducing the overall time required for production.
2. Optimal Sequence of Operations: Routing also determines the sequence of operations to be followed for the production of a particular product. This ensures that the operations are performed in the correct order, considering the dependencies and requirements of each operation. By following the optimal sequence, the production process can be streamlined, eliminating bottlenecks and reducing idle time.
3. Proper Machine Loading: Routing decisions also consider the capabilities and capacities of the machines involved in the production process. By assigning the appropriate operations to the respective machines, routing ensures that the machines are properly loaded and utilized. This helps in maximizing the throughput of the machines and avoiding overloading or underutilization.
4. Stock Control System: While routing primarily focuses on the production process, it also has implications for the stock control system. By determining the sequence and timing of operations, routing decisions impact the inventory levels and stock availability at different stages of production. This enables effective inventory management and control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, routing decisions in mechanical engineering play a vital role in determining the sequence of operations, the order of work, machine loading, and the stock control system. By optimizing these aspects, routing helps in improving the overall efficiency, productivity, and resource utilization in manufacturing processes.
Routing plays a crucial role in various aspects of mechanical engineering, including manufacturing processes, production planning, and scheduling. It involves determining the sequence of operations and the path to be followed for the production of a particular product. Routing decisions help in optimizing the overall production process and ensuring efficient utilization of resources.
Importance of Routing
Routing decisions have a significant impact on the overall efficiency and productivity of a manufacturing system. By determining the sequence of operations, routing helps in achieving the following objectives:
1. Optimal Order of Work: Routing decisions determine the sequence in which different tasks or operations are to be performed. This ensures that the work is completed in the most efficient and logical order, minimizing unnecessary movement and reducing the overall time required for production.
2. Optimal Sequence of Operations: Routing also determines the sequence of operations to be followed for the production of a particular product. This ensures that the operations are performed in the correct order, considering the dependencies and requirements of each operation. By following the optimal sequence, the production process can be streamlined, eliminating bottlenecks and reducing idle time.
3. Proper Machine Loading: Routing decisions also consider the capabilities and capacities of the machines involved in the production process. By assigning the appropriate operations to the respective machines, routing ensures that the machines are properly loaded and utilized. This helps in maximizing the throughput of the machines and avoiding overloading or underutilization.
4. Stock Control System: While routing primarily focuses on the production process, it also has implications for the stock control system. By determining the sequence and timing of operations, routing decisions impact the inventory levels and stock availability at different stages of production. This enables effective inventory management and control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, routing decisions in mechanical engineering play a vital role in determining the sequence of operations, the order of work, machine loading, and the stock control system. By optimizing these aspects, routing helps in improving the overall efficiency, productivity, and resource utilization in manufacturing processes.
Tardiness is the measure of- a) maximum lateness
- b) lateness
- c) positive lateness
- d) None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Tardiness is the measure of
a)
maximum lateness
b)
lateness
c)
positive lateness
d)
None
|
|
Gopal Choudhury answered |
Definition of Tardiness
Tardiness is a term used to describe the amount of time by which a task, project, or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time. In other words, it is the amount of time that a task exceeds its due date or deadline.
Types of Tardiness
There are different types of tardiness, depending on the context in which it is used. Some of the common types of tardiness include:
1. Lateness: This refers to the duration by which a task or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time. It is the most commonly used type of tardiness.
2. Positive Lateness: This refers to the amount of time by which a task or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time, but is still within the acceptable limit. For instance, if a task is scheduled to be completed by 5 pm, but it is completed at 5:30 pm, the positive lateness is 30 minutes.
3. Maximum Lateness: This refers to the maximum amount of time by which a task or job can be late beyond its scheduled completion time. It is often used in critical projects where any delay beyond the maximum lateness can result in serious consequences.
Conclusion
In summary, tardiness is a measure of lateness, which refers to the amount of time by which a task or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time. Positive lateness and maximum lateness are the other types of tardiness used in different contexts.
Tardiness is a term used to describe the amount of time by which a task, project, or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time. In other words, it is the amount of time that a task exceeds its due date or deadline.
Types of Tardiness
There are different types of tardiness, depending on the context in which it is used. Some of the common types of tardiness include:
1. Lateness: This refers to the duration by which a task or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time. It is the most commonly used type of tardiness.
2. Positive Lateness: This refers to the amount of time by which a task or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time, but is still within the acceptable limit. For instance, if a task is scheduled to be completed by 5 pm, but it is completed at 5:30 pm, the positive lateness is 30 minutes.
3. Maximum Lateness: This refers to the maximum amount of time by which a task or job can be late beyond its scheduled completion time. It is often used in critical projects where any delay beyond the maximum lateness can result in serious consequences.
Conclusion
In summary, tardiness is a measure of lateness, which refers to the amount of time by which a task or job is late beyond its scheduled completion time. Positive lateness and maximum lateness are the other types of tardiness used in different contexts.
Chapter doubts & questions for Line Balancing, Loading & Scheduling - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Line Balancing, Loading & Scheduling - 6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
6 Months Preparation for GATE Mechanical
499 videos|1037 docs|710 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup