All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Amino Acids and Protein Structure (BIO, BC, OC) for MCAT Exam
Electrophoretic separation at pH 6 of a sample of polypeptide 1 (mw 100) polypeptide 2 (mw 200) and polypeptide 3 (mw 400) would result in which of the following?
(Note: the isoelectric point of each polypeptide occurs at pH 6)- a)Polypeptide 1 would move the farthest
- b)Polypeptide 2 would move the farthest
- c)Polypeptide 3 would move the farthest
- d)None of the polypeptides would move
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrophoretic separation at pH 6 of a sample of polypeptide 1 (mw 100) polypeptide 2 (mw 200) and polypeptide 3 (mw 400) would result in which of the following?
(Note: the isoelectric point of each polypeptide occurs at pH 6)
(Note: the isoelectric point of each polypeptide occurs at pH 6)
a)
Polypeptide 1 would move the farthest
b)
Polypeptide 2 would move the farthest
c)
Polypeptide 3 would move the farthest
d)
None of the polypeptides would move
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- The isoelectric point for a polypeptide is the pH at which the molecule does not have a net charge.
- Electrophoretic separation depends on the existence of a negative net charge.
- None of the polypeptides would move at pH 6.
The amino acids in hemoglobin (or any protein) uniformly have which of the following configurations?- a)L
- b)R
- c)S
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amino acids in hemoglobin (or any protein) uniformly have which of the following configurations?
a)
L
b)
R
c)
S
d)
D
|
|
Hannah Jenkins answered |
Amino Acid Configurations in Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. It is composed of four subunits, each containing a heme group that binds to oxygen. The amino acids in hemoglobin, like in any protein, have a specific configuration that determines the protein's structure and function.
Primary Structure
The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. In hemoglobin, the primary structure consists of a specific sequence of about 574 amino acids. These amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain.
Chirality of Amino Acids
Amino acids are chiral molecules, meaning they have a central carbon atom (the α-carbon) bonded to four different groups: a hydrogen atom, an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and an R group (side chain) that varies between different amino acids. The chirality of amino acids arises from the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom, and they exist in two stereoisomeric forms called L-amino acids and D-amino acids.
L-Amino Acid Configuration
In proteins, only L-amino acids are found. L-amino acids have the amino group (NH2) located on the left side of the α-carbon when the molecule is drawn in the Fischer projection. This configuration is determined by the way the amino acid is synthesized within cells. The synthesis of amino acids occurs through enzymes that specifically produce L-amino acids, resulting in the predominance of L-amino acids in proteins.
Uniform L-Amino Acid Configuration
Every amino acid in hemoglobin, as well as in any other protein, has an L-configuration. This uniformity in the configuration of amino acids is essential for the proper folding and function of the protein. The specific sequence and arrangement of amino acids determine the protein's three-dimensional structure, which directly influences its function. Any deviation from the L-configuration could disrupt the protein's folding and lead to a loss of function.
Conclusion
In summary, the amino acids in hemoglobin, and in proteins in general, have a uniform configuration of L-amino acids. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining the protein's structure and function. The L-configuration is determined by the enzymatic synthesis of amino acids and ensures the proper folding and activity of the protein.
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. It is composed of four subunits, each containing a heme group that binds to oxygen. The amino acids in hemoglobin, like in any protein, have a specific configuration that determines the protein's structure and function.
Primary Structure
The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. In hemoglobin, the primary structure consists of a specific sequence of about 574 amino acids. These amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain.
Chirality of Amino Acids
Amino acids are chiral molecules, meaning they have a central carbon atom (the α-carbon) bonded to four different groups: a hydrogen atom, an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and an R group (side chain) that varies between different amino acids. The chirality of amino acids arises from the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom, and they exist in two stereoisomeric forms called L-amino acids and D-amino acids.
L-Amino Acid Configuration
In proteins, only L-amino acids are found. L-amino acids have the amino group (NH2) located on the left side of the α-carbon when the molecule is drawn in the Fischer projection. This configuration is determined by the way the amino acid is synthesized within cells. The synthesis of amino acids occurs through enzymes that specifically produce L-amino acids, resulting in the predominance of L-amino acids in proteins.
Uniform L-Amino Acid Configuration
Every amino acid in hemoglobin, as well as in any other protein, has an L-configuration. This uniformity in the configuration of amino acids is essential for the proper folding and function of the protein. The specific sequence and arrangement of amino acids determine the protein's three-dimensional structure, which directly influences its function. Any deviation from the L-configuration could disrupt the protein's folding and lead to a loss of function.
Conclusion
In summary, the amino acids in hemoglobin, and in proteins in general, have a uniform configuration of L-amino acids. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining the protein's structure and function. The L-configuration is determined by the enzymatic synthesis of amino acids and ensures the proper folding and activity of the protein.
Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at which of the following pH values?- a)7.4
- b)2.4
- c)1.4
- d)0.4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at which of the following pH values?
a)
7.4
b)
2.4
c)
1.4
d)
0.4
|
|
Julian Gray answered |
Explanation:
Electrophoretic separation of leucine
- Leucine is a neutral, nonpolar amino acid.
- In electrophoretic separation, the movement of molecules is influenced by their charge.
Effectiveness at different pH values:
pH 7.4
- At pH 7.4, leucine will be in its neutral form.
- Since it is not charged, it will not migrate significantly in an electric field.
- Therefore, electrophoretic separation of leucine would be least effective at pH 7.4.
pH 2.4, 1.4, and 0.4
- At lower pH values (2.4, 1.4, 0.4), leucine will become positively charged.
- Positively charged molecules migrate towards the negative electrode in electrophoresis.
- Therefore, at lower pH values, leucine would exhibit more movement and better separation in an electric field compared to pH 7.4.
Conclusion:
- Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at pH 7.4 due to its neutral charge, which results in minimal migration in an electric field.
Electrophoretic separation of leucine
- Leucine is a neutral, nonpolar amino acid.
- In electrophoretic separation, the movement of molecules is influenced by their charge.
Effectiveness at different pH values:
pH 7.4
- At pH 7.4, leucine will be in its neutral form.
- Since it is not charged, it will not migrate significantly in an electric field.
- Therefore, electrophoretic separation of leucine would be least effective at pH 7.4.
pH 2.4, 1.4, and 0.4
- At lower pH values (2.4, 1.4, 0.4), leucine will become positively charged.
- Positively charged molecules migrate towards the negative electrode in electrophoresis.
- Therefore, at lower pH values, leucine would exhibit more movement and better separation in an electric field compared to pH 7.4.
Conclusion:
- Electrophoretic separation of leucine from a protein sample would be least effective at pH 7.4 due to its neutral charge, which results in minimal migration in an electric field.
The pI for a polyelectrolyte that contains three carboxyl groups and three amino groups whose pKa values are 4.0, 4.6, 6.3, 7.7, 8.9, and 10.2 is _______________
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
The pI for a polyelectrolyte that contains three carboxyl groups and three amino groups whose pKa values are 4.0, 4.6, 6.3, 7.7, 8.9, and 10.2 is _______________

|
Jay Nambiar answered |
Example the pI is a pH midway between the 3rd and 4th pKa values: pI = (6.3 + 7.7)/2 = 7.0. To confirm this conclusion, imagine how the net charge on the molecule will change as the solution is adjusted from strongly acidic to strongly basic pH. As the carboxylate groups and subsequently the ammonium groups begin to ionize, the net charge will change successively as follows: +3, +2, +1, 0, “1, “2, “3.
The net charge on the following peptide at pH 1 is _________________.
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
The net charge on the following peptide at pH 1 is _________________.

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
At pH 1 the charge distribution on the peptide will be as follows:
NH3+-Ala-Asp-Asn-Ile-Pro-Gln-Thr-Agr-COOH
Note that every peptide is written from amino to carboxy terminal, and at a very low pH such as 1 every side chain and main chain ionizable groups will be protonated. Hence net change will be decided by amino groups, as the sequence contain one basic amino acid (arginine) and only alanine contain free amino group, so the charge is due to positively charged amino group.
NH3+-Ala-Asp-Asn-Ile-Pro-Gln-Thr-Agr-COOH
Note that every peptide is written from amino to carboxy terminal, and at a very low pH such as 1 every side chain and main chain ionizable groups will be protonated. Hence net change will be decided by amino groups, as the sequence contain one basic amino acid (arginine) and only alanine contain free amino group, so the charge is due to positively charged amino group.
Which of the following amino acids will have Diastereomers.- a)Isoleucine
- b)Threonine
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acids will have Diastereomers.
a)
Isoleucine
b)
Threonine
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
None

|
Aashna Shah answered |
Stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other are called diastereomers.
Diastereomers are present only in those molecules which have more than one chiral carbon atoms, and isoleucine as well as threonine both have two chiral centers. Since both threonine and isoleucine have two chiral centres each, maximum number of stereoisomers in each case will be 2n = 22 = 4 (n is the number of chiral centres).
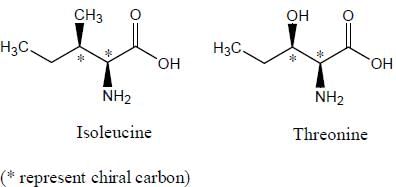
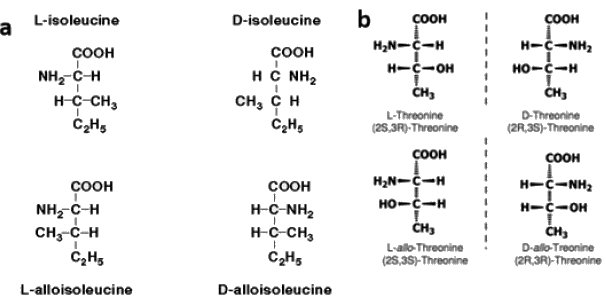
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other are called diastereomers.
Diastereomers are present only in those molecules which have more than one chiral carbon atoms, and isoleucine as well as threonine both have two chiral centers. Since both threonine and isoleucine have two chiral centres each, maximum number of stereoisomers in each case will be 2n = 22 = 4 (n is the number of chiral centres).


Which of the following type of secondary conformation is in the same quadrant of the ramachandran plot- a)Right handed Alpha helix
- b)310 helix
- c)Beta sheets
- d)Left handed alpha helix
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following type of secondary conformation is in the same quadrant of the ramachandran plot
a)
Right handed Alpha helix
b)
310 helix
c)
Beta sheets
d)
Left handed alpha helix

|
Anushka Basak answered |
Only right handed alpha helix and 310 helix lie in the same quadrant

Ramachandran Plot

Ramachandran Plot
The isoelectric point of lysine which has pKb 9.06, pKa 2.16 and pKR as 10.54 is ____________[Answer upto two decimal places]
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
- e)
Correct answer is '9.8'. Can you explain this answer?
The isoelectric point of lysine which has pKb 9.06, pKa 2.16 and pKR as 10.54 is ____________[Answer upto two decimal places]
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
Isoelectric point: In proteins the isoelectric point (pI) is defined as the pH at which a protein has no net charge.
In case of a basic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKR and is equal to the average of pKb and pKR(10.54+9.06)/2 = 9.77 = ~ 9.8.
In case of an acidic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKa and pKR and is equal to the average of pKa and pKR.
In case of a neutral amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKa and is equal to the average of pKa and pKb.
In case of a basic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKR and is equal to the average of pKb and pKR(10.54+9.06)/2 = 9.77 = ~ 9.8.
In case of an acidic amino acid, pI lies in between the pKa and pKR and is equal to the average of pKa and pKR.
In case of a neutral amino acid, pI lies in between the pKb and pKa and is equal to the average of pKa and pKb.
An amino acid that yields acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism of its carbon skeleton will be considered as ________.- a)Glycogenic
- b)Ketogenic
- c)Both glycogenic and ketogenic
- d)Essential
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An amino acid that yields acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism of its carbon skeleton will be considered as ________.
a)
Glycogenic
b)
Ketogenic
c)
Both glycogenic and ketogenic
d)
Essential

|
Orion Classes answered |
In case of Glycogenic amino acids pyruvate metabolites are formed and in case of ketogenic amino acids acetoacyl CoA is formed during the catabolism.
If pK1 = 2.34 and pK2 = 9.60, then the isoelectric point pI is?- a)5.87
- b)5.97
- c)3.67
- d)11.94
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If pK1 = 2.34 and pK2 = 9.60, then the isoelectric point pI is?
a)
5.87
b)
5.97
c)
3.67
d)
11.94

|
Orion Classes answered |
pI = 1⁄2 (pK1 + pK2) = 1⁄2 (2.34 + 9.60) = 5.97.
Which of the following represents the two-dimensional structure of proteins?- a)Quaternary
- b)Tertiary
- c)Secondary
- d)Primary
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the two-dimensional structure of proteins?
a)
Quaternary
b)
Tertiary
c)
Secondary
d)
Primary

|
Orion Classes answered |
The primary structure of Protein represents the two-dimensional structure of proteins. The primary structure of proteins just contains amino acids linked together to form a long chain of a polypeptide. Quaternary, tertiary, and secondary structure refers to the three-dimensional structure of proteins.
Total number of known amino acids in biological systems is- a)20
- b)21
- c)22
- d)More than 900
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of known amino acids in biological systems is
a)
20
b)
21
c)
22
d)
More than 900

|
Juhi Sen answered |
There are various groups of amino acids:
• 20 standard amino acids
• 22 proteinogenic amino acids
• Over 80 amino acids created abiotically in high concentrations
• About 900 are produced by natural pathways
• Over 118 engineered amino acids have been placed into protein
• 20 standard amino acids
• 22 proteinogenic amino acids
• Over 80 amino acids created abiotically in high concentrations
• About 900 are produced by natural pathways
• Over 118 engineered amino acids have been placed into protein
A new amino acid was found on the surface of moon with no ionizable side chain and pKa value 1.8 and pKb value 9.5. The isoelectric point of this new amino acid is _____________ [Answer upto two decimal places]
Correct answer is between '5.64,5.66'. Can you explain this answer?
A new amino acid was found on the surface of moon with no ionizable side chain and pKa value 1.8 and pKb value 9.5. The isoelectric point of this new amino acid is _____________ [Answer upto two decimal places]

|
Niti Mukherjee answered |
Isoelectric point in case of no ionizable side chain is the average of pKa and pKb, (1.8+9.5)/2 = 5.65
If an amino acid with neutral side chain has pKa value of 3.4 and pKb value of 9.6 at which of the following pH the amino acid will migrate towards anode- a)6
- b)7.4
- c)2.3
- d)3.4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an amino acid with neutral side chain has pKa value of 3.4 and pKb value of 9.6 at which of the following pH the amino acid will migrate towards anode
a)
6
b)
7.4
c)
2.3
d)
3.4

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
The isoelectric point here is the average of pKa and pKb which is (3.4+9.6)/2 = 6.5.
Every amino acid is negatively charged at pH above its pI and move towards Anode (+). So at pH 7.4 the overall charge on amino acid will be negative and it will move towards Anode. Only pH 7.4 is above the isoelectric part of amino acid (isoelectric point = 6.5)
Every amino acid is negatively charged at pH above its pI and move towards Anode (+). So at pH 7.4 the overall charge on amino acid will be negative and it will move towards Anode. Only pH 7.4 is above the isoelectric part of amino acid (isoelectric point = 6.5)
Amino acids that are most likely to be phosphorylated in a protein during a signalling event are- a)Serine and threonine
- b)Leucine and Isoleucine
- c)Tryptophan and Tyrosine
- d)Threonine and Arginine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amino acids that are most likely to be phosphorylated in a protein during a signalling event are
a)
Serine and threonine
b)
Leucine and Isoleucine
c)
Tryptophan and Tyrosine
d)
Threonine and Arginine

|
Anisha Banerjee answered |
Phosphorylation is most likely to occur at hydroxyl group of side chain of amino acids i.e. serine and threonine. Hydroxyl group is not present in leucine, isoleucine, arginine and tryptophan.
Which of the following names do not represent the name of a peptide- a)WATSON
- b)EINSTEIN
- c)KENDREW
- d)LIPMAN
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following names do not represent the name of a peptide
a)
WATSON
b)
EINSTEIN
c)
KENDREW
d)
LIPMAN

|
Maitri Sen answered |
There are 20 amino acids and 26 letters in English alphabet, hence 6 letters viz B, J, O, U, X , Z do not represent any amino acids, which means the name containing these amino acids will not be representing a peptide O is present in option (a), hence option (a), does not represent a peptide.
All hydrophobic amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine, etc.) share which of the following properties?- a)Nonpolar uncharged R groups
- b)Polar uncharged R groups
- c)Basic R groups
- d)Acidic R groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
All hydrophobic amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine, etc.) share which of the following properties?
a)
Nonpolar uncharged R groups
b)
Polar uncharged R groups
c)
Basic R groups
d)
Acidic R groups
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Hydrophobic amino acids prefer to minimize their interactions with water molecules.
- Polar, acidic, and basic R groups all share partial or full charges, which interact favorably with polar water molecules.
- All hydrophobic amino acids share nonpolar uncharged R groups.
Which of the following amino acids has a net negative charge at physiologic pH (~7.4)?- a)Glutamic Acid
- b)Histidine
- c)Lysine
- d)Asparagine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acids has a net negative charge at physiologic pH (~7.4)?
a)
Glutamic Acid
b)
Histidine
c)
Lysine
d)
Asparagine
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Amino acids with acidic side groups carry a net negative charge at physiologic pH.
- Glutamate (glutamic acid) has a side group containing a carboxylic acid.
- Glutamate has a net negative charge at physiologic pH.
Which of the following amino acid shows highest absorbance at 280 nm- a)Phenylalanine
- b)Tyrosine
- c)Alanine
- d)Tryptophan
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acid shows highest absorbance at 280 nm
a)
Phenylalanine
b)
Tyrosine
c)
Alanine
d)
Tryptophan

|
Shivam Khanna answered |
Three aromatic amino acids (Tyr, Trp, and Phe) absorb most of the UV light in a protein. Tyrosine and tryptophan both absorb more than phenylalanine. Tryptophan shows four times more absorbance than tyrosine.

A person having a syndrome, where he has excessive flexibility in his body and can fold his arms and legs like a rubber, which is clinically known as Ehler Danlos Syndrome. Which of the following is true about this disease- a)It is due to malformation of cross links in collagen
- b)People with this syndrome were also called as Indian Rubber Man
- c)It is not found in world now
- d)It is lethal disease
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person having a syndrome, where he has excessive flexibility in his body and can fold his arms and legs like a rubber, which is clinically known as Ehler Danlos Syndrome. Which of the following is true about this disease
a)
It is due to malformation of cross links in collagen
b)
People with this syndrome were also called as Indian Rubber Man
c)
It is not found in world now
d)
It is lethal disease

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of related disorders caused by different genetic defects in collagen.Patients also have excessively flexible, loose joints. Ehler danlos syndrome is not lethal and individuals are still present so it is not eradicated from the world.
Identify the amino acids containing nonpolar, aliphatic R groups.- a)Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
- b)Glycine, alanine, leucine
- c)Lysine, arginine, histidine
- d)Serine, threonine, cysteine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the amino acids containing nonpolar, aliphatic R groups.
a)
Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
b)
Glycine, alanine, leucine
c)
Lysine, arginine, histidine
d)
Serine, threonine, cysteine

|
Orion Classes answered |
Glycine: H3 N+ – CH2 – COO–
Alanine: H3 N+ – CH(CH3) – COO–
Leucine: H3 N+ – CH(C4 H9) – COO–.
Alanine: H3 N+ – CH(CH3) – COO–
Leucine: H3 N+ – CH(C4 H9) – COO–.
Which among the following is both glucogenic and ketogenic?- a)Isoleucine
- b)Leucine
- c)Lysine
- d)Histidine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is both glucogenic and ketogenic?
a)
Isoleucine
b)
Leucine
c)
Lysine
d)
Histidine
|
|
Ava Brown answered |
Understanding Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids
Amino acids can be classified based on their metabolic fate into glucogenic and ketogenic categories.
Glucogenic Amino Acids
- Glucogenic amino acids can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis.
- They provide a carbon skeleton that can enter the citric acid cycle, ultimately leading to glucose production.
Ketogenic Amino Acids
- Ketogenic amino acids are converted into ketone bodies or fatty acids instead of glucose.
- They can be utilized during periods of prolonged fasting or carbohydrate restriction.
Isoleucine as a Dual-Function Amino Acid
- Isoleucine is unique because it can be both glucogenic and ketogenic.
- When metabolized, isoleucine can yield substrates that enter pathways for both glucose and ketone body synthesis.
Comparison with Other Options
- Leucine: Exclusively ketogenic; it cannot be converted to glucose.
- Lysine: Also exclusively ketogenic; it does not contribute to glucose production.
- Histidine: Primarily glucogenic; it does not yield significant ketone bodies.
Conclusion
Isoleucine stands out as the only amino acid among the options that can be converted into both glucose and ketone bodies, making it both glucogenic and ketogenic. Understanding this classification is essential for grasping metabolic pathways and their implications in nutrition and health.
Amino acids can be classified based on their metabolic fate into glucogenic and ketogenic categories.
Glucogenic Amino Acids
- Glucogenic amino acids can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis.
- They provide a carbon skeleton that can enter the citric acid cycle, ultimately leading to glucose production.
Ketogenic Amino Acids
- Ketogenic amino acids are converted into ketone bodies or fatty acids instead of glucose.
- They can be utilized during periods of prolonged fasting or carbohydrate restriction.
Isoleucine as a Dual-Function Amino Acid
- Isoleucine is unique because it can be both glucogenic and ketogenic.
- When metabolized, isoleucine can yield substrates that enter pathways for both glucose and ketone body synthesis.
Comparison with Other Options
- Leucine: Exclusively ketogenic; it cannot be converted to glucose.
- Lysine: Also exclusively ketogenic; it does not contribute to glucose production.
- Histidine: Primarily glucogenic; it does not yield significant ketone bodies.
Conclusion
Isoleucine stands out as the only amino acid among the options that can be converted into both glucose and ketone bodies, making it both glucogenic and ketogenic. Understanding this classification is essential for grasping metabolic pathways and their implications in nutrition and health.
A polypeptide chain contains two terminals – one carboxyl-terminal (C terminal) and the other amino-terminal (N terminal). Which of the following is true?- a)N terminal is synthesized last during translation
- b)C terminal is synthesized first during translation
- c)N terminal is represented on the right side and C terminal on the left side
- d)N terminal is represented on the left side and C terminal on the right side
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A polypeptide chain contains two terminals – one carboxyl-terminal (C terminal) and the other amino-terminal (N terminal). Which of the following is true?
a)
N terminal is synthesized last during translation
b)
C terminal is synthesized first during translation
c)
N terminal is represented on the right side and C terminal on the left side
d)
N terminal is represented on the left side and C terminal on the right side
|
|
Wyatt Gonzales answered |
Understanding Polypeptide Chains
A polypeptide chain is a sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, and it has distinct ends: the amino-terminal (N terminal) and carboxyl-terminal (C terminal).
Translation Process
- During protein synthesis (translation), the ribosome assembles amino acids in a specific order.
- The synthesis begins at the N terminal and proceeds toward the C terminal.
Synthesis Directionality
- The N terminal is synthesized first, and thus it is represented on the left side of the polypeptide chain.
- The C terminal, being the last part synthesized, is found on the right side.
Visual Representation
- In a linear representation of a polypeptide:
- N terminal is on the left side (amino group, -NH2).
- C terminal is on the right side (carboxyl group, -COOH).
Correct Answer Explanation
- Therefore, the statement "N terminal is represented on the left side and C terminal on the right side" is correct.
- This understanding is crucial for interpreting protein structure and function, as the orientation plays a significant role in biochemical interactions.
In summary, the N terminal is always on the left, while the C terminal is on the right, which aligns with the synthesis direction in translation.
A polypeptide chain is a sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, and it has distinct ends: the amino-terminal (N terminal) and carboxyl-terminal (C terminal).
Translation Process
- During protein synthesis (translation), the ribosome assembles amino acids in a specific order.
- The synthesis begins at the N terminal and proceeds toward the C terminal.
Synthesis Directionality
- The N terminal is synthesized first, and thus it is represented on the left side of the polypeptide chain.
- The C terminal, being the last part synthesized, is found on the right side.
Visual Representation
- In a linear representation of a polypeptide:
- N terminal is on the left side (amino group, -NH2).
- C terminal is on the right side (carboxyl group, -COOH).
Correct Answer Explanation
- Therefore, the statement "N terminal is represented on the left side and C terminal on the right side" is correct.
- This understanding is crucial for interpreting protein structure and function, as the orientation plays a significant role in biochemical interactions.
In summary, the N terminal is always on the left, while the C terminal is on the right, which aligns with the synthesis direction in translation.
The unique cyclic structure of which of the following amino acids plays a central role in the formation of alpha helices and beta sheets?- a)Proline
- b)Arginine
- c)Valine
- d)Lysine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The unique cyclic structure of which of the following amino acids plays a central role in the formation of alpha helices and beta sheets?
a)
Proline
b)
Arginine
c)
Valine
d)
Lysine
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Alpha helices and beta sheets are two three dimensional motifs that regularly appear in local segments of amino acids.
- Proline has a unique cyclic structure which differentiates it from the other common amino acids.
- Proline plays a central role in the FORMATION of alpha helices and beta sheets. While proline's unique structure may also disrupt both alpha helixes and beta sheets, it's ability to make sharp turns facilitates the FORMATION of both structures, with proline commonly being found at the beginning of alpha helices or at the turns in beta sheets.
The two amino acids having R groups with a negative net charge at pH 7.0 are __________.- a)Aspartate and glutamate
- b)Arginine and histidine
- c)Cysteine and methionine
- d)Proline and valine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The two amino acids having R groups with a negative net charge at pH 7.0 are __________.
a)
Aspartate and glutamate
b)
Arginine and histidine
c)
Cysteine and methionine
d)
Proline and valine

|
Orion Classes answered |
H3 N+ – CH( CH2 COO–) – COO–
Glutamate: H3 N+ – CH( C2 H4 COO–) – COO–.
Glutamate: H3 N+ – CH( C2 H4 COO–) – COO–.
Which of the following is a true statement?- a)Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine
- b)Leucine is commonly used as an ingredient in the buffers of SDS page
- c)Aspartate is an essential amino acid
- d)Lysine is a non-essential amino acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a true statement?
a)
Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine
b)
Leucine is commonly used as an ingredient in the buffers of SDS page
c)
Aspartate is an essential amino acid
d)
Lysine is a non-essential amino acid
|
|
Elizabeth Lee answered |
Explanation:
Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine:
- Tryptophan and tyrosine contain polar functional groups such as hydroxyl and amino groups, making them more polar compared to phenylalanine which lacks such groups.
- The presence of polar groups in tryptophan and tyrosine allows for interactions with water molecules, leading to their higher polarity.
This statement is true because tryptophan and tyrosine have more polar side chains compared to phenylalanine, which is a nonpolar amino acid. The polarity of an amino acid side chain is determined by the presence of polar functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH) and amino (-NH2) groups. Tryptophan and tyrosine both contain these polar functional groups in their side chains, making them significantly more polar than phenylalanine, which lacks such groups. This increased polarity allows tryptophan and tyrosine to interact more readily with water molecules and other polar substances, influencing their behavior in biological systems.
Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more polar than phenylalanine:
- Tryptophan and tyrosine contain polar functional groups such as hydroxyl and amino groups, making them more polar compared to phenylalanine which lacks such groups.
- The presence of polar groups in tryptophan and tyrosine allows for interactions with water molecules, leading to their higher polarity.
This statement is true because tryptophan and tyrosine have more polar side chains compared to phenylalanine, which is a nonpolar amino acid. The polarity of an amino acid side chain is determined by the presence of polar functional groups such as hydroxyl (-OH) and amino (-NH2) groups. Tryptophan and tyrosine both contain these polar functional groups in their side chains, making them significantly more polar than phenylalanine, which lacks such groups. This increased polarity allows tryptophan and tyrosine to interact more readily with water molecules and other polar substances, influencing their behavior in biological systems.
Hydrogen bonding between separate subunits of DNA polymerase is an example of which of the following?- a)1 degree structure
- b)2 degree structure
- c)3 degree structure
- d)4 degree structure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding between separate subunits of DNA polymerase is an example of which of the following?
a)
1 degree structure
b)
2 degree structure
c)
3 degree structure
d)
4 degree structure

|
Orion Classes answered |
- 1 degree structure through 3 degree structure have to do with individual polypeptides.
- 4 degree structure refers to the global three dimensional arrangements found in multi-subunit proteins.
- Hydrogen bonding between separate subunits of DNA polymerase is an example of 4 degree structure.
A polypeptide with a net positive charge at physiologic pH (~7.4) most likely contains amino acids with R groups of what type?- a)Acidic R groups
- b)Aromatic R groups
- c)Aliphatic R groups
- d)Basic R groups
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A polypeptide with a net positive charge at physiologic pH (~7.4) most likely contains amino acids with R groups of what type?
a)
Acidic R groups
b)
Aromatic R groups
c)
Aliphatic R groups
d)
Basic R groups
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- At physiologic pH, basic functional groups will be protonated, attaining a positive charge.
- Aliphatic R groups are saturated hydrocarbons.
- A polypeptide with a net positive charge at physiologic pH most likely has a basic R group.
The naturally occurring proteins consist of- a)D-amino acids
- b)L-amino acids
- c)Both a and b
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The naturally occurring proteins consist of
a)
D-amino acids
b)
L-amino acids
c)
Both a and b
d)
None of these

|
Anshika Chavan answered |
All naturally occurring proteins from all living organisms consist of L amino acids.
Which of the following properties of a protein is least likely to be affected by changes in pH?- a)Tertiary structure
- b)Primary structure
- c)Secondary structure
- d)Net charge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following properties of a protein is least likely to be affected by changes in pH?
a)
Tertiary structure
b)
Primary structure
c)
Secondary structure
d)
Net charge
|
|
Ella Baker answered |
Tertiary structure
Changes in pH can disrupt the ionic interactions and hydrogen bonds that contribute to the stability of a protein's tertiary structure. This can lead to denaturation of the protein and loss of its functional properties.
Primary structure
The primary structure of a protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids. Changes in pH do not directly affect the sequence of amino acids, so the primary structure is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
Secondary structure
Changes in pH can disrupt the hydrogen bonds that stabilize secondary structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets. This can lead to unfolding or distortion of the secondary structure.
Net charge
The net charge of a protein is determined by the presence of charged amino acids and the pH of the environment. As the pH changes, the ionization state of the charged amino acids can change, leading to changes in the net charge of the protein. However, this does not directly affect the structure of the protein, but it can influence its interactions with other molecules.
Explanation
The primary structure of a protein is the linear sequence of amino acids. Changes in pH do not directly affect the sequence of amino acids. The stability of the primary structure is primarily determined by covalent peptide bonds, which are not influenced by changes in pH. Therefore, the primary structure is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
On the other hand, changes in pH can significantly affect the tertiary structure of a protein. Tertiary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the protein, which is mainly stabilized by non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions. Changes in pH can disrupt these interactions, leading to denaturation of the protein.
Similarly, changes in pH can also disrupt the hydrogen bonds that stabilize secondary structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets. This can lead to unfolding or distortion of the secondary structure.
The net charge of a protein is determined by the presence of charged amino acids and the pH of the environment. As the pH changes, the ionization state of the charged amino acids can change, leading to changes in the net charge of the protein. However, this does not directly affect the structure of the protein, but it can influence its interactions with other molecules.
In summary, while changes in pH can affect the tertiary and secondary structure as well as the net charge of a protein, the primary structure is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
Changes in pH can disrupt the ionic interactions and hydrogen bonds that contribute to the stability of a protein's tertiary structure. This can lead to denaturation of the protein and loss of its functional properties.
Primary structure
The primary structure of a protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids. Changes in pH do not directly affect the sequence of amino acids, so the primary structure is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
Secondary structure
Changes in pH can disrupt the hydrogen bonds that stabilize secondary structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets. This can lead to unfolding or distortion of the secondary structure.
Net charge
The net charge of a protein is determined by the presence of charged amino acids and the pH of the environment. As the pH changes, the ionization state of the charged amino acids can change, leading to changes in the net charge of the protein. However, this does not directly affect the structure of the protein, but it can influence its interactions with other molecules.
Explanation
The primary structure of a protein is the linear sequence of amino acids. Changes in pH do not directly affect the sequence of amino acids. The stability of the primary structure is primarily determined by covalent peptide bonds, which are not influenced by changes in pH. Therefore, the primary structure is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
On the other hand, changes in pH can significantly affect the tertiary structure of a protein. Tertiary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the protein, which is mainly stabilized by non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions. Changes in pH can disrupt these interactions, leading to denaturation of the protein.
Similarly, changes in pH can also disrupt the hydrogen bonds that stabilize secondary structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets. This can lead to unfolding or distortion of the secondary structure.
The net charge of a protein is determined by the presence of charged amino acids and the pH of the environment. As the pH changes, the ionization state of the charged amino acids can change, leading to changes in the net charge of the protein. However, this does not directly affect the structure of the protein, but it can influence its interactions with other molecules.
In summary, while changes in pH can affect the tertiary and secondary structure as well as the net charge of a protein, the primary structure is least likely to be affected by changes in pH.
Which of the following amino acid is/are not encoded by standard codons- a)Serine
- b)Selenocysteine
- c)Pyrolysine
- d)both b and c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amino acid is/are not encoded by standard codons
a)
Serine
b)
Selenocysteine
c)
Pyrolysine
d)
both b and c

|
Akshat Saini answered |
Amino acids Selenocysteine and Pyrolysine are not encoded by standard codons but by stop codons.Selenocysteine is coded by UGA and Pyrolysine is coded by UAG.
UAG and UGA both are stop codon. Serine is encoded by 6 different codons.
UAG and UGA both are stop codon. Serine is encoded by 6 different codons.
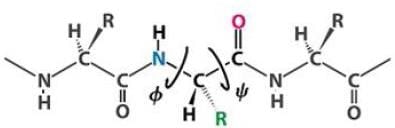
On the Ramachandran plot two kind of angles are presented on the x and y axis named phi and psi respectively. These angles represent the:-- a)Torsion between Calpha – C and N – C respectively
- b)Torsion between N – C and Calpha – C respectively
- c)Torsion between N – Calpha and Calpha – C respectively
- d)Torsion between C – C and N – C respectively
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On the Ramachandran plot two kind of angles are presented on the x and y axis named phi and psi respectively. These angles represent the:-
a)
Torsion between Calpha – C and N – C respectively
b)
Torsion between N – C and Calpha – C respectively
c)
Torsion between N – Calpha and Calpha – C respectively
d)
Torsion between C – C and N – C respectively

|
Aditi Basak answered |
Following figure represent the location of psi and phi angle:

Which of the following proteins primarily have alpha helix in their structure- a)Myoglobin
- b)Silk fibroin
- c)Ribonuclease
- d)Porin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following proteins primarily have alpha helix in their structure
a)
Myoglobin
b)
Silk fibroin
c)
Ribonuclease
d)
Porin

|
Shreya Chauhan answered |
Myoglobin contains only α helix. Around 75% of Myoglobin is α helix. Myoglobin consists of eight alpha helixes connected through turns. Silk fibroin and Porin contain only β sheets. Ribonuclease contains a combination of alpha helix and beta sheets.
The correct statement about the biosynthesis of amino acids are- a)Amino acids are synthesised from glycolytic and citric acid cycle intermediates
- b)Glutamate can be formed by amination of alpha ketogluterate
- c)Pyruvate on amination can form alanine
- d)There are 9 families of amino acids based on the metabolic precursors.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement about the biosynthesis of amino acids are
a)
Amino acids are synthesised from glycolytic and citric acid cycle intermediates
b)
Glutamate can be formed by amination of alpha ketogluterate
c)
Pyruvate on amination can form alanine
d)
There are 9 families of amino acids based on the metabolic precursors.

|
Saranya Mehta answered |
Only statement d is incorrect, there are 6 families of amino acids in which they can be grouped on the basis of their metabolic precursors.
1. α -Ketoglutarate
Glutamate → Glutamine/Proline (also form Ornithine)/Arginine
2. 3-Phosphoglycerate
Serine → Glycine/Cysteine (also form Methionine SAM-sulfur donar in mammals)
3. Oxaloacetate
Aspaitate/Asparagine/Methionine/Threonine/Lysine
4. Pyruvate
Alanine/Valine/Leucine/Isoleucine
5. Phosphoenolypyruvate and erythrose 4-phosphate Tryptophan/Phenylalanine Tyrosine (from Phenylalanine by hydroxylation)
6. Ribose 5-phosphate
Histidine
1. α -Ketoglutarate
Glutamate → Glutamine/Proline (also form Ornithine)/Arginine
2. 3-Phosphoglycerate
Serine → Glycine/Cysteine (also form Methionine SAM-sulfur donar in mammals)
3. Oxaloacetate
Aspaitate/Asparagine/Methionine/Threonine/Lysine
4. Pyruvate
Alanine/Valine/Leucine/Isoleucine
5. Phosphoenolypyruvate and erythrose 4-phosphate Tryptophan/Phenylalanine Tyrosine (from Phenylalanine by hydroxylation)
6. Ribose 5-phosphate
Histidine
Which of the following is not true about the secondary conformation of proteins- a)Secondary conformations arise from folding of backbone
- b)Random coils are most abundant secondary conformations
- c)Pi helix and 2.27 are alternate names of alpha helix
- d)Ramachandran plot explains the formation of peptide bond.
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true about the secondary conformation of proteins
a)
Secondary conformations arise from folding of backbone
b)
Random coils are most abundant secondary conformations
c)
Pi helix and 2.27 are alternate names of alpha helix
d)
Ramachandran plot explains the formation of peptide bond.

|
Sahana Sharma answered |
(a) is coll ect as formation of a secondary structure is the first step in the folding process that a protein takes to assume its native structure, (b) is incorrect as the most common secondary structures are alpha helices and beta sheets, (c) is incorrect as pi helix (or π -helix) is believed to be an evolutionary adaptation derived by the insertion of a single amino acid into a α -helix and 2.27 and d is incorrect as a Ramachandran plot is a way to visualize backbone dihedral angles ψ against φ of amino acid residues in protein structure. A Ramachandran plot can be used in two somewhat different ways. One is to show in theory which values, or conformations, of the ψ and φ angles are possible for an amino-acid residue in a protein.
For a protein with 100 amino acids, how many possible sequences are there?- a)(100)20
- b)(2)100
- c)(100)2
- d)(20)100
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For a protein with 100 amino acids, how many possible sequences are there?
a)
(100)20
b)
(2)100
c)
(100)2
d)
(20)100

|
Orion Classes answered |
The general rule is, for a protein having ‘n’ residues, there are (20)n possible combinations. There are 20 different types of amino acids occurring naturally in proteins. Therefore, (20)100 is the correct answer.
The peptide C=O bond of the nth residue of the backbone of alpha-helix points along and forms a hydrogen bond with the peptide N—H group of which among the following residue?- a)(n+1)th
- b)(n+2)th
- c)(n+3)th
- d)(n+4)th
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The peptide C=O bond of the nth residue of the backbone of alpha-helix points along and forms a hydrogen bond with the peptide N—H group of which among the following residue?
a)
(n+1)th
b)
(n+2)th
c)
(n+3)th
d)
(n+4)th
|
|
Aiden Davis answered |
Explanation:
Hydrogen bonding in alpha-helix structure:
- In an alpha-helix structure, the peptide C=O bond of the nth residue forms a hydrogen bond with the peptide N-H group of the (n+4)th residue.
- This hydrogen bonding pattern helps stabilize the alpha-helix structure.
Specific interaction:
- In this case, the peptide C=O bond of the nth residue points along and forms a hydrogen bond with the peptide N-H group of the (n+4)th residue.
- This specific interaction is a characteristic feature of the alpha-helix structure.
Correct answer:
- The correct option is (n+4)th residue, as the hydrogen bonding occurs between the C=O bond of the nth residue and the N-H group of the (n+4)th residue.
Who discovered the alpha-helix structure in a protein molecule?- a)Lynn Margulis
- b)Francis Collins
- c)Louis Pasteur
- d)Linus Pauling
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who discovered the alpha-helix structure in a protein molecule?
a)
Lynn Margulis
b)
Francis Collins
c)
Louis Pasteur
d)
Linus Pauling

|
Orion Classes answered |
Linus Pauling discovered the alpha-helix structure in a protein molecule. Lynn Margulis gave the theory of endosymbiosis. Francis Collins discovered the gene for Cystic Fibrosis. Louis Pasteur is also known as the father of immunology.
Which disease results from the dietary deficiency of vitamin C?- a)Jaundice
- b)Malaria
- c)Cancer
- d)Scurvy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which disease results from the dietary deficiency of vitamin C?
a)
Jaundice
b)
Malaria
c)
Cancer
d)
Scurvy

|
Orion Classes answered |
The deficiency of vitamin C in diet results in Scurvy. Collagen is a triple helix and contains some hydroxylated residues. The enzyme (prolyl hydroxylase) that catalyzes this reaction requires vitamin C to maintain its activity.
Which of the following is an essential amino acid?- a)Cysteine
- b)Asparagine
- c)Glutamine
- d)Phenylalanine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
a)
Cysteine
b)
Asparagine
c)
Glutamine
d)
Phenylalanine

|
Orion Classes answered |
Phenylalanine is one of the 9 essential amino acids.
Which type of interactions are involved in the quaternary structure?- a)Only hydrogen bonds
- b)Hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions
- c)Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds
- d)Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bonds, and ionic interactions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of interactions are involved in the quaternary structure?
a)
Only hydrogen bonds
b)
Hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions
c)
Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds
d)
Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bonds, and ionic interactions

|
Orion Classes answered |
Quaternary structure of a protein is made of a combination of any of the following interactions: i) Hydrogen bonds, ii) hydrophobic interactions, iii) disulfide bonds, iv) ionic interactions. Thus, the option containing all of the above options is correct.
In metal chelate affinity chromatography, divalent cations such as Zn+2 or Ni+2 is attached on the electrophoretic matrix and it binds to ___________- a)Trp tag
- b)Ala tag
- c)Gly tag
- d)His tag
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In metal chelate affinity chromatography, divalent cations such as Zn+2 or Ni+2 is attached on the electrophoretic matrix and it binds to ___________
a)
Trp tag
b)
Ala tag
c)
Gly tag
d)
His tag

|
Orion Classes answered |
When 6 histidine residues are inserted consecutively through recombinant DNA technology, it is called as His tag. It has a high affinity for nickel. This strategy is used for the purification of recombinant proteins.
Which of the following interactions is shown in the figure below?
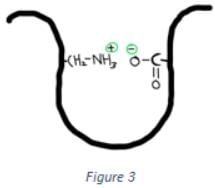
- a)Disulfide bond
- b)Hydrophobic interactions
- c)Hydrogen bonds
- d)Ionic interactions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following interactions is shown in the figure below?


a)
Disulfide bond
b)
Hydrophobic interactions
c)
Hydrogen bonds
d)
Ionic interactions

|
Orion Classes answered |
The interaction shown in the above figure is ionic interactions. Ionic interaction is the interaction between two charged groups. If the two charged groups are oppositely charged then they will attract, while two similar charges repel each other.
Which of the following interactions is crucial for the primary structure of proteins?- a)Hydrogen bond
- b)Di-sulfide bond
- c)Vander Waals interactions
- d)Peptide bond
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following interactions is crucial for the primary structure of proteins?
a)
Hydrogen bond
b)
Di-sulfide bond
c)
Vander Waals interactions
d)
Peptide bond

|
Orion Classes answered |
Protein’s primary structure is made of amino acids linked together by a peptide bond. Thus, the peptide bond is crucial for the primary structure of proteins. Hydrogen bond, disulfide bond, Vander Waals interactions are all required in a higher level of organization.
______ is used as a reducing agent in SDS PAGE.- a)Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
- b)Ammonium persulphate (APS)
- c)Bisacrylamide
- d)2-mercaptoethanol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
______ is used as a reducing agent in SDS PAGE.
a)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
b)
Ammonium persulphate (APS)
c)
Bisacrylamide
d)
2-mercaptoethanol

|
Orion Classes answered |
2-mercaptoethanol (beta-mercaptoethanol) is used as a reducing agent in SDS PAGE. It breaks the disulfide bonds and denatures the protein molecule. SDS is not a reducing agent, it disrupts non-covalent interactions between peptides. Ammonium persulphate (APS) and Bisacrylamide do not show any reducing properties.
Which structure of a protein is the arrangement of protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex?- a)Primary
- b)Secondary
- c)Tertiary
- d)Quaternary
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure of a protein is the arrangement of protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex?
a)
Primary
b)
Secondary
c)
Tertiary
d)
Quaternary

|
Orion Classes answered |
Quaternary structure of a protein is the arrangement of protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. Many proteins are composed of more than one polypeptide chain. These polypeptide chains fold to form a subunit of a complex protein. All subunits combine to form a complete functional protein.
The term “electron density maps” is related to which of the following technique?- a)Optical microscopy
- b)NMR spectroscopy
- c)cryo-electron microscopy
- d)X-ray crystallography
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The term “electron density maps” is related to which of the following technique?
a)
Optical microscopy
b)
NMR spectroscopy
c)
cryo-electron microscopy
d)
X-ray crystallography

|
Orion Classes answered |
X-ray crystallography is a technique where in electron density maps are obtained. Thus, the term “electron density maps” is related to X-ray crystallography. Other techniques mentioned do not involve electron density maps.
Which of the following elements is not visible in the maps of X-ray crystallography?- a)Nitrogen
- b)Carbon
- c)Oxygen
- d)Hydrogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following elements is not visible in the maps of X-ray crystallography?
a)
Nitrogen
b)
Carbon
c)
Oxygen
d)
Hydrogen

|
Orion Classes answered |
Hydrogen atom is not visible in the electron density maps of X-ray crystallography. The reason behind this is the low electron density of the hydrogen atom. Hydrogen contains a minimum of one electron.
Which among the following residues is most likely to be present on the surface of a protein?- a)Val
- b)Leu
- c)Ile
- d)Arg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following residues is most likely to be present on the surface of a protein?
a)
Val
b)
Leu
c)
Ile
d)
Arg

|
Orion Classes answered |
Arg is most likely to be present on the surface of a protein because it is a polar residue. Generally, polar residues reside on the surface of a protein. Val, leu, and Ile are non-polar residues, hence, they are not likely to be present on the surface of a protein.
What are multi-subunit proteins called when some or all of its subunits are identical?- a)Monomers
- b)Polymers
- c)Protomers
- d)Oligomers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are multi-subunit proteins called when some or all of its subunits are identical?
a)
Monomers
b)
Polymers
c)
Protomers
d)
Oligomers

|
Orion Classes answered |
Many proteins have a complex structure i.e. they have a multi-subunit structure. When some or all the sub-units of a complex protein are identical it is called oligomers.
Chapter doubts & questions for Amino Acids and Protein Structure (BIO, BC, OC) - MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Amino Acids and Protein Structure (BIO, BC, OC) - MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations
367 videos|157 docs|88 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









