All Exams >
MCAT >
MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations >
All Questions
All questions of Immune System (BIO) for MCAT Exam
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:- a)ESR-Test
- b)PCR-Test
- c)Widal-Test
- d)ELISA-Test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
a)
ESR-Test
b)
PCR-Test
c)
Widal-Test
d)
ELISA-Test

|
Jeeshan Ahmed answered |
The Widal test is one method that may be used to help make a presumptive diagnosis of enteric fever, also known as typhoid fever.The test was based on demonstrating the presence of agglutinin (antibody) in the serum of an infected patient, against the H (flagellar) and O (somatic) antigens ofSalmonella typhi.
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:- a)ESR-Test
- b)PCR-Test
- c)Widal-Test
- d)ELISA-Test
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
a)
ESR-Test
b)
PCR-Test
c)
Widal-Test
d)
ELISA-Test

|
Dilip answered |
Its given in 12th NCERT.... widal test for typhoid
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by- A:Cockroach
- B:Aedes mosquitoes
- C:House flies
- D:Female Anopheles
The answer is b.
The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by
A:
Cockroach
B:
Aedes mosquitoes
C:
House flies
D:
Female Anopheles
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
When a mosquito feeds on an infected person, the mosquito can become infected and can bite and infect others. The Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes transmit chikungunya. They also transmit dengue fever, another disease caused by a virus.
Antibodies are produced by:- a)T-cells
- b)B-cells
- c)Monocytes
- d)Phagocytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Antibodies are produced by:
a)
T-cells
b)
B-cells
c)
Monocytes
d)
Phagocytes
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells). When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone.
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:- a)Innate immunity
- b)Acquired immunity
- c)Passive immunity
- d)Active immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:
a)
Innate immunity
b)
Acquired immunity
c)
Passive immunity
d)
Active immunity
|
|
Shalini Basu answered |
The combination of antibodies and complement promotes rapid clearing of pathogens. The production of antibodies by plasma cells in response to an antigen is called active immunity and describes the host's active response of theimmune system to an infection or to a vaccination.
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in
- a)Liver of person
- b)RBCs of mosquito
- c)Salivary glands of mosquito
- d)Intestine of person
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in
a)
Liver of person
b)
RBCs of mosquito
c)
Salivary glands of mosquito
d)
Intestine of person
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Sporozoites enter the female Anopheles mosquito when they bite an infected person where these sporozoite fertilise and multiply in the stomach wall of the female Anopheles and stored in the salivary gland of mosquito till it is again transferred to the human body by a mosquito bite.
- After entering the human body the sporozoites reach the liver cells, where they multiply. This is followed by their attack on red blood cells resulting in their rupture. The ruptured RBCs release a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for high recurring fever, chills and shivering.
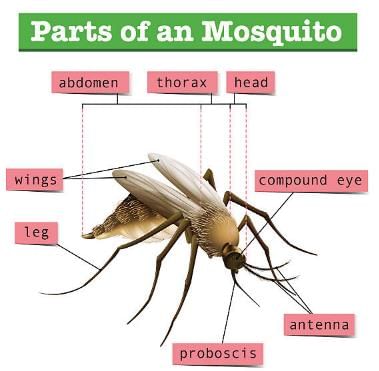
- Mosquito Anatomy:
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to- a)Defective liver
- b)AIDS virus
- c)Defective thymus
- d)Weak immune system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to
a)
Defective liver
b)
AIDS virus
c)
Defective thymus
d)
Weak immune system
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).Following initial infection, a person may not notice any symptoms or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged period with no symptoms. As the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors that rarely affect people who have working immune systems.[5] These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss.
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?- a)Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
- b)Spleen of infected humans
- c)Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
- d)Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from malaria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?
a)
Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
b)
Spleen of infected humans
c)
Salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito
d)
Red blood corpuscles of human suffering from malaria
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Sporozoite is the infective stage of the malarial parasite. They are present in the saliva of infected female anopheles mosquito.
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?- a)Chondrocyte
- b)Erythrocyte
- c)Lymphocyte
- d)Parasite
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?
a)
Chondrocyte
b)
Erythrocyte
c)
Lymphocyte
d)
Parasite

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
Lymphocytes are one of several different types of white blood cells. Lymphocytes are of two types B cells and T cells. When a macrophage engulfs organisms, B cells (humoral immunity) release antibodies which cause the destruction of bacteria. The T cells (cell-mediated immunity) destroy the infectious organisms by killing the body cells that are affected. Hence lymphocytes is a unit of the immune system.
So, the correct answer is 'Lymphocytes'.
Anti venom against snake poison contains:- a)Antigens
- b)Enzymes
- c)Antigen-antibody complexes
- d)Antibodies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Anti venom against snake poison contains:
a)
Antigens
b)
Enzymes
c)
Antigen-antibody complexes
d)
Antibodies
|
|
Madhavan Ghosh answered |
Anti venom against snake poison contains antibodies.
Explanation:
Anti venom is a serum that is used to treat snake bites. It contains antibodies that are specifically produced to neutralize the venom of a particular snake species. The antibodies are produced by injecting a small amount of the snake venom into an animal, usually a horse, and then collecting the blood serum from the animal after a certain period of time. This serum contains the antibodies that have been produced in response to the venom.
The antibodies in the anti venom work by binding to the venom molecules and neutralizing their toxic effects. This prevents the venom from causing damage to the body and allows the body's own immune system to clear the venom from the bloodstream.
It is important to note that anti venom is specific to the species of snake that produced the venom. This means that anti venom for one species of snake will not be effective against the venom of another species. It is also important to administer anti venom as soon as possible after a snake bite, as the venom can rapidly spread through the body and cause severe damage if left untreated.
Explanation:
Anti venom is a serum that is used to treat snake bites. It contains antibodies that are specifically produced to neutralize the venom of a particular snake species. The antibodies are produced by injecting a small amount of the snake venom into an animal, usually a horse, and then collecting the blood serum from the animal after a certain period of time. This serum contains the antibodies that have been produced in response to the venom.
The antibodies in the anti venom work by binding to the venom molecules and neutralizing their toxic effects. This prevents the venom from causing damage to the body and allows the body's own immune system to clear the venom from the bloodstream.
It is important to note that anti venom is specific to the species of snake that produced the venom. This means that anti venom for one species of snake will not be effective against the venom of another species. It is also important to administer anti venom as soon as possible after a snake bite, as the venom can rapidly spread through the body and cause severe damage if left untreated.
The function of IgE is- a)Protection from inhaled/ingested pathogens
- b)Mediate in allergic response
- c)Activation of B-cells
- d)Stimulation of complement system, passive immunity to foetus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of IgE is
a)
Protection from inhaled/ingested pathogens
b)
Mediate in allergic response
c)
Activation of B-cells
d)
Stimulation of complement system, passive immunity to foetus
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The function of IgE antibody as mediators in allergic reactions of Type I is explained by their ability to interact both with antigen and with receptor molecules on the membrane of blood basophils and tissue mast cells. However, it is not understood how the interaction of an allergen with cell-bound IgE antibody will induce basophil (mast) cells to release a great number of biologically active substances of which some will be further discussed at this meeting, nor is it known what role the IgE-mast cell system plays in the development and control of a normal immune response.
Japanese encephalitis is transmitted by- a)Tse tse fly
- b)Sand fly
- c)Housefly
- d)Mosquito
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Japanese encephalitis is transmitted by
a)
Tse tse fly
b)
Sand fly
c)
Housefly
d)
Mosquito
|
|
Uday Jain answered |
Transmission of Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese Encephalitis is a viral disease that is transmitted by mosquitoes. The Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a flavivirus that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. The virus is primarily found in rural and agricultural areas of Asia, but cases have been reported in other parts of the world as well.
Mosquitoes that transmit Japanese encephalitis
The Culex mosquitoes are the primary vector for the transmission of Japanese encephalitis. These mosquitoes are common in rural areas and are most active during the evening and early morning hours. The mosquito becomes infected with the virus when it feeds on an infected animal, usually a pig or a bird. The virus then multiplies in the mosquito's salivary glands and can be transmitted to humans when the mosquito bites a person.
Risk factors for Japanese encephalitis
People who live or travel to areas where Japanese encephalitis is endemic are at risk of contracting the disease. The risk is greatest during the monsoon season when mosquitoes are most active. Children and older adults are at greater risk of developing severe disease if they become infected with the virus.
Prevention of Japanese encephalitis
The best way to prevent Japanese encephalitis is to get vaccinated before traveling to areas where the disease is endemic. Other preventive measures include:
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when outdoors
- Use insect repellent containing DEET on exposed skin
- Use mosquito nets or screens in sleeping areas
- Eliminate standing water around homes where mosquitoes breed
Conclusion
Japanese encephalitis is a serious disease that is transmitted by mosquitoes. The primary vector for the transmission of the virus is the Culex mosquito. People who live or travel to areas where Japanese encephalitis is endemic should take preventive measures to reduce their risk of contracting the disease. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent Japanese encephalitis.
Japanese Encephalitis is a viral disease that is transmitted by mosquitoes. The Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a flavivirus that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes. The virus is primarily found in rural and agricultural areas of Asia, but cases have been reported in other parts of the world as well.
Mosquitoes that transmit Japanese encephalitis
The Culex mosquitoes are the primary vector for the transmission of Japanese encephalitis. These mosquitoes are common in rural areas and are most active during the evening and early morning hours. The mosquito becomes infected with the virus when it feeds on an infected animal, usually a pig or a bird. The virus then multiplies in the mosquito's salivary glands and can be transmitted to humans when the mosquito bites a person.
Risk factors for Japanese encephalitis
People who live or travel to areas where Japanese encephalitis is endemic are at risk of contracting the disease. The risk is greatest during the monsoon season when mosquitoes are most active. Children and older adults are at greater risk of developing severe disease if they become infected with the virus.
Prevention of Japanese encephalitis
The best way to prevent Japanese encephalitis is to get vaccinated before traveling to areas where the disease is endemic. Other preventive measures include:
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when outdoors
- Use insect repellent containing DEET on exposed skin
- Use mosquito nets or screens in sleeping areas
- Eliminate standing water around homes where mosquitoes breed
Conclusion
Japanese encephalitis is a serious disease that is transmitted by mosquitoes. The primary vector for the transmission of the virus is the Culex mosquito. People who live or travel to areas where Japanese encephalitis is endemic should take preventive measures to reduce their risk of contracting the disease. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent Japanese encephalitis.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus causes aids by attacking a type of white blood cell called- a)CD4
- b)CD3
- c)CD8
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus causes aids by attacking a type of white blood cell called
a)
CD4
b)
CD3
c)
CD8
d)
None of these
|
|
Bhaskar Ala answered |
"HIV " Attacks CD4 cells (T- helper, T- cells) .. this cells plays important role in immune system..
The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by- a)Cockroach
- b)Aedes mosquitoes
- c)House flies
- d)Female Anopheles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The disease chikunguniya is transmitted by
a)
Cockroach
b)
Aedes mosquitoes
c)
House flies
d)
Female Anopheles
|
|
Abhay Iyer answered |
Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on a person already infected with the virus. Infectedmosquitoes can then spread the virus to other people through bites. Chikungunya virus is most often spread to people by Aedes aegypti andAedes albopictus mosquitoes. These are the samemosquitoes that transmit dengue virus.
Assertion (A): Malaria is caused by a virus.Reason (R): Malaria is transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Malaria is caused by a virus.
Reason (R): Malaria is transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Answer: Option D.
Solution: Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, not a virus. The statement in R is true as the disease is indeed transmitted by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes, making A false and R true.
Recognition of self vs. non-self by the adaptive immune system in humans is accomplished in which of the following ways?- a)Exposure of B cells to the body’s own antigens in the thymus
- b)Exposure of B cells to the body’s own antigens in the bursa of Fabricius
- c)Exposure of T cells to the body’s own antigens in the bursa of Fabricius
- d)Exposure of T cells to the body’s own antigens in the thymus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Recognition of self vs. non-self by the adaptive immune system in humans is accomplished in which of the following ways?
a)
Exposure of B cells to the body’s own antigens in the thymus
b)
Exposure of B cells to the body’s own antigens in the bursa of Fabricius
c)
Exposure of T cells to the body’s own antigens in the bursa of Fabricius
d)
Exposure of T cells to the body’s own antigens in the thymus
|
|
Oliver Williams answered |
's own antigens during development
b)Detection of foreign antigens by T cells
c)Recognition of self antigens by natural killer cells
d)Binding of antibodies to self antigens
b)Detection of foreign antigens by T cells
c)Recognition of self antigens by natural killer cells
d)Binding of antibodies to self antigens
Monocytes move from the systemic circulatory system into general connective tissues, where they differentiate into what phagocytic cell type?- a)Macrophage
- b)T cell
- c)B cell
- d)Neutrophil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Monocytes move from the systemic circulatory system into general connective tissues, where they differentiate into what phagocytic cell type?
a)
Macrophage
b)
T cell
c)
B cell
d)
Neutrophil

|
Orion Classes answered |
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell that circulate in the bloodstream. When they migrate from the systemic circulatory system into the general connective tissues, they differentiate into macrophages. Macrophages are highly phagocytic cells that play a key role in the immune response by engulfing and digesting pathogens, cellular debris, and other foreign substances. They are important components of the innate immune system.
Myelogenous leukemias are caused by the cancerous production of innate (non-specific) immune system cells: in which tissue is such production most likely to occur?- a)Bone marrow
- b)Thymus
- c)Spleen
- d)Lymph nodes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Myelogenous leukemias are caused by the cancerous production of innate (non-specific) immune system cells: in which tissue is such production most likely to occur?
a)
Bone marrow
b)
Thymus
c)
Spleen
d)
Lymph nodes
|
|
Matthew Turner answered |
Understanding Myelogenous Leukemias
Myelogenous leukemias are a type of cancer that arises from the uncontrolled proliferation of myeloid cells, which are part of the innate immune system. To understand why the bone marrow is the most likely site for this production, let’s delve into the roles of different tissues involved in hematopoiesis.
Bone Marrow: The Primary Site of Hematopoiesis
- The bone marrow is the primary site where all blood cells, including myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are produced.
- Myelogenous leukemias specifically involve myeloid cells, which include granulocytes, monocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets, all generated from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
- In cases of myelogenous leukemia, mutations occur in the DNA of these progenitor cells, leading to the uncontrolled growth of myeloid lineage cells.
Other Tissues: Thymus, Spleen, and Lymph Nodes
- The thymus primarily functions in the maturation of T lymphocytes, not myeloid cells, making it irrelevant for myelogenous leukemias.
- The spleen and lymph nodes are involved in filtering blood and lymph, respectively, and play roles in the adaptive immune response, but they are not the sites of initial blood cell production.
- While these organs can be affected by leukemic cells as the disease progresses, they do not produce myelogenous leukemias.
Conclusion
In summary, the bone marrow is indeed the correct answer as it is the primary site where myeloid cells are produced and where the malignant transformation leading to myelogenous leukemias occurs.
Myelogenous leukemias are a type of cancer that arises from the uncontrolled proliferation of myeloid cells, which are part of the innate immune system. To understand why the bone marrow is the most likely site for this production, let’s delve into the roles of different tissues involved in hematopoiesis.
Bone Marrow: The Primary Site of Hematopoiesis
- The bone marrow is the primary site where all blood cells, including myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are produced.
- Myelogenous leukemias specifically involve myeloid cells, which include granulocytes, monocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets, all generated from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
- In cases of myelogenous leukemia, mutations occur in the DNA of these progenitor cells, leading to the uncontrolled growth of myeloid lineage cells.
Other Tissues: Thymus, Spleen, and Lymph Nodes
- The thymus primarily functions in the maturation of T lymphocytes, not myeloid cells, making it irrelevant for myelogenous leukemias.
- The spleen and lymph nodes are involved in filtering blood and lymph, respectively, and play roles in the adaptive immune response, but they are not the sites of initial blood cell production.
- While these organs can be affected by leukemic cells as the disease progresses, they do not produce myelogenous leukemias.
Conclusion
In summary, the bone marrow is indeed the correct answer as it is the primary site where myeloid cells are produced and where the malignant transformation leading to myelogenous leukemias occurs.
Which of the following cell types of the innate immune system does not perform phagocytosis?- a)Neutrophils
- b)Basophils
- c)Macrophages
- d)Eosinophils
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cell types of the innate immune system does not perform phagocytosis?
a)
Neutrophils
b)
Basophils
c)
Macrophages
d)
Eosinophils
|
|
Zoe Brooks answered |
Overview of Innate Immune Cell Types
The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense against pathogens. It includes various cell types that perform different functions, notably phagocytosis, which is the process of engulfing and digesting harmful entities like bacteria and dead cells.
Cell Types Discussed
- Neutrophils:
- These are the most abundant white blood cells in the immune system.
- They are highly effective at phagocytosing bacteria and fungi, serving as the first responders to sites of infection.
- Macrophages:
- Derived from monocytes, macrophages are large phagocytic cells.
- They play a crucial role in engulfing pathogens, dead cells, and debris, and also help activate other immune cells.
- Eosinophils:
- These cells are primarily involved in combating multicellular parasites and certain infections.
- They can also perform phagocytosis, although it's not their primary function.
- Basophils:
- Basophils are the least common type of granulocytes and do not perform phagocytosis.
- They primarily release histamines and other mediators during allergic reactions and inflammatory responses, aiding in vasodilation and increasing blood flow to affected tissues.
Conclusion
In summary, basophils (option B) are the correct answer as they do not engage in phagocytosis. Instead, they release substances that play a role in allergic reactions and inflammation, differentiating them from neutrophils, macrophages, and eosinophils, which are all capable of phagocytosis.
The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense against pathogens. It includes various cell types that perform different functions, notably phagocytosis, which is the process of engulfing and digesting harmful entities like bacteria and dead cells.
Cell Types Discussed
- Neutrophils:
- These are the most abundant white blood cells in the immune system.
- They are highly effective at phagocytosing bacteria and fungi, serving as the first responders to sites of infection.
- Macrophages:
- Derived from monocytes, macrophages are large phagocytic cells.
- They play a crucial role in engulfing pathogens, dead cells, and debris, and also help activate other immune cells.
- Eosinophils:
- These cells are primarily involved in combating multicellular parasites and certain infections.
- They can also perform phagocytosis, although it's not their primary function.
- Basophils:
- Basophils are the least common type of granulocytes and do not perform phagocytosis.
- They primarily release histamines and other mediators during allergic reactions and inflammatory responses, aiding in vasodilation and increasing blood flow to affected tissues.
Conclusion
In summary, basophils (option B) are the correct answer as they do not engage in phagocytosis. Instead, they release substances that play a role in allergic reactions and inflammation, differentiating them from neutrophils, macrophages, and eosinophils, which are all capable of phagocytosis.
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:- a)Sporozoites (human) → RRCs → liver cells → gametocytes in blood → blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→ fertilisation (mosquito) → sporozoites (mosquito)
- b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)
- c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)
- d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:
a)
Sporozoites (human) → RRCs → liver cells → gametocytes in blood → blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→ fertilisation (mosquito) → sporozoites (mosquito)
b)
Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)
c)
Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)
d)
Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The correct sequence of the Plasmodium life cycle involves the following steps:
Sporozoites are injected into humans by the female mosquito. The sporozoites travel to the liver where they mature. After the liver stage, the parasite enters the RBCs where it multiplies.Some of the parasites develop into gametocytes, which are released into the blood.These gametocytes are taken up by a female mosquito during a blood meal. Inside the mosquito, the gametocytes undergo sexual reproduction to form sporozoites.Finally, sporozoites are transmitted back to humans when the mosquito bites again.
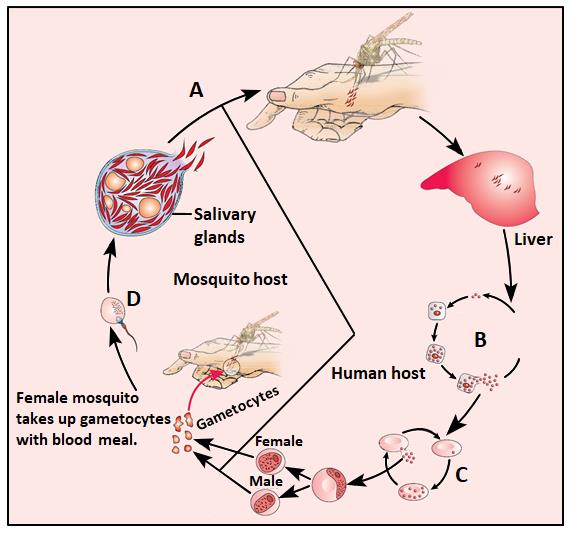
Sporozoites are injected into humans by the female mosquito. The sporozoites travel to the liver where they mature. After the liver stage, the parasite enters the RBCs where it multiplies.Some of the parasites develop into gametocytes, which are released into the blood.These gametocytes are taken up by a female mosquito during a blood meal. Inside the mosquito, the gametocytes undergo sexual reproduction to form sporozoites.Finally, sporozoites are transmitted back to humans when the mosquito bites again.
Which type of immune response is the first line of defense against pathogens and does not require prior exposure to the pathogen?- a)Innate immunity
- b)Adaptive immunity
- c)Active immunity
- d)Passive immunity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of immune response is the first line of defense against pathogens and does not require prior exposure to the pathogen?
a)
Innate immunity
b)
Adaptive immunity
c)
Active immunity
d)
Passive immunity

|
Orion Classes answered |
Innate immunity is the nonspecific defense mechanism that is present at birth. It provides immediate protection against a wide range of pathogens and does not require prior exposure to the pathogen.
Fill in the blanks in the different columns of the table given below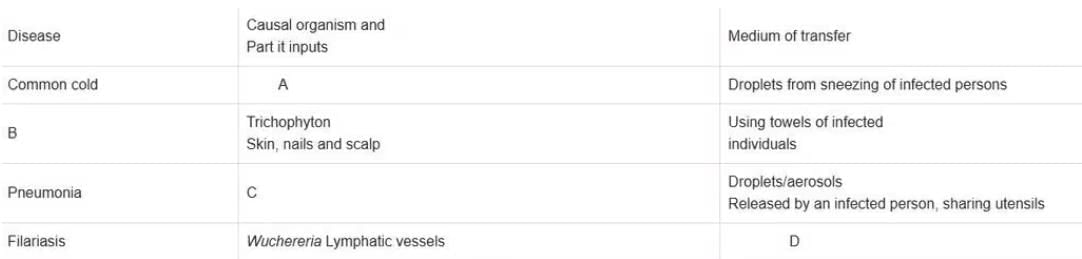
- a)A- Rhinovirus. Nose and respiratory passage not lungs
B - Ringworm
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Alveoli of lungs
D - Contaminated food and water - b) A- Coryza virus. Alveoli of lungs
B - Ringworm
C - Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nose and respiratory passage
D - Culex mosquito - c) A- Rhinovirus. Nose and respiratory passage not lungs
B - Ascariasis
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Lungs
D - Culex mosquito - d)A- Rhinovirus. Nose and respiratory passage not lungs
B - Ringworm
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Alveoli of lungs
D - Culex mosquito
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Fill in the blanks in the different columns of the table given below

a)
A- Rhinovirus. Nose and respiratory passage not lungs
B - Ringworm
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Alveoli of lungs
D - Contaminated food and water
B - Ringworm
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Alveoli of lungs
D - Contaminated food and water
b)
A- Coryza virus. Alveoli of lungs
B - Ringworm
C - Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nose and respiratory passage
D - Culex mosquito
B - Ringworm
C - Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nose and respiratory passage
D - Culex mosquito
c)
A- Rhinovirus. Nose and respiratory passage not lungs
B - Ascariasis
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Lungs
D - Culex mosquito
B - Ascariasis
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Lungs
D - Culex mosquito
d)
A- Rhinovirus. Nose and respiratory passage not lungs
B - Ringworm
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Alveoli of lungs
D - Culex mosquito
B - Ringworm
C - Haemophilus influenzae. Alveoli of lungs
D - Culex mosquito

|
Ambition Institute answered |
-Rhino viruses represent one such group of viruses which cause one of the most infectious human ailments – the common cold. They infect the nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs. The common cold is characterised by nasal congestion and discharge, sore throat, hoarseness, cough, headache, tiredness, etc., which usually last for 3-7 days. Droplets resulting from cough or sneezes of an infected person.
-Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are responsible for the disease pneumonia in humans which infects the alveoli (air filled sacs) of the lungs. As a result of the infection, the alveoli get filled with fluid leading to severe problems in respiration. The symptoms of pneumonia include fever, chills, cough and headache.
- Wuchereria (W. bancrofti and W. malayi), the filarial worms cause a slowly developing chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live for many years, usually the lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs and the disease is called elephantiasis or filariasis . The genital organs are also often affected, resulting in gross deformities. The pathogens are transmitted to a healthy person through the bite by the female mosquito vectors - culex mosquito
- Many fungi belonging to the genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton are responsible for ringworms which is one of the most common infectious diseases in man. Appearance of dry, scaly lesions on various parts of the body such as skin, nails and scalp (Figure 7.3) are the main symptoms of the disease
-Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are responsible for the disease pneumonia in humans which infects the alveoli (air filled sacs) of the lungs. As a result of the infection, the alveoli get filled with fluid leading to severe problems in respiration. The symptoms of pneumonia include fever, chills, cough and headache.
- Wuchereria (W. bancrofti and W. malayi), the filarial worms cause a slowly developing chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live for many years, usually the lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs and the disease is called elephantiasis or filariasis . The genital organs are also often affected, resulting in gross deformities. The pathogens are transmitted to a healthy person through the bite by the female mosquito vectors - culex mosquito
- Many fungi belonging to the genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton are responsible for ringworms which is one of the most common infectious diseases in man. Appearance of dry, scaly lesions on various parts of the body such as skin, nails and scalp (Figure 7.3) are the main symptoms of the disease
Which type of immunity is temporary and acquired through the transfer of antibodies from another individual?- a)Innate immunity
- b)Adaptive immunity
- c)Active immunity
- d)Passive immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of immunity is temporary and acquired through the transfer of antibodies from another individual?
a)
Innate immunity
b)
Adaptive immunity
c)
Active immunity
d)
Passive immunity

|
Orion Classes answered |
Passive immunity is temporary and acquired through the transfer of pre-formed antibodies from another individual or through maternal transfer to a fetus or newborn. It provides immediate protection but does not result in long-term immunity.
Which cells are responsible for phagocytosis and engulfing pathogens or cellular debris?- a)B cells
- b)T cells
- c)Macrophages
- d)Natural killer cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which cells are responsible for phagocytosis and engulfing pathogens or cellular debris?
a)
B cells
b)
T cells
c)
Macrophages
d)
Natural killer cells

|
Orion Classes answered |
Macrophages are specialized immune cells that engulf and digest pathogens, cellular debris, and other foreign substances through a process called phagocytosis. They are important components of the innate immune response.
Which portion of an antibody provides antigen-binding sites?- a)Light chain
- b)Constant portion
- c)Heavy chain
- d)Variable portion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which portion of an antibody provides antigen-binding sites?
a)
Light chain
b)
Constant portion
c)
Heavy chain
d)
Variable portion

|
Orion Classes answered |
The variable portion of an antibody, which is part of the heavy chain and the light chain, is responsible for providing antigen-binding sites. The variable regions contain hypervariable regions, also known as complementarity-determining regions (CDRs), which directly interact with antigens. The CDRs exhibit high variability in their amino acid sequences, allowing antibodies to recognize and bind to a wide range of antigens. The constant portion of the antibody, on the other hand, is responsible for other functions such as effector mechanisms and determining the antibody's class or isotype.
Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that results in the circulation of which of the following throughout the blood?- a)Antigens
- b)Macrophages
- c)Natural killer cells
- d)Antibodies
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Humoral immunity is a type of adaptive immunity that results in the circulation of which of the following throughout the blood?
a)
Antigens
b)
Macrophages
c)
Natural killer cells
d)
Antibodies

|
Orion Classes answered |
Humoral immunity refers to the component of adaptive immunity that involves the production and circulation of antibodies in the blood. Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are proteins produced by B cells (a type of lymphocyte) in response to the presence of specific antigens. Once produced, antibodies are released into the bloodstream and other body fluids, where they can recognize and bind to specific antigens. This binding triggers various immune responses, including neutralization of pathogens, activation of complement system, and recruitment of other immune cells to eliminate the antigen. The circulation of antibodies in the blood allows them to reach various tissues and organs, providing a systemic defense against pathogens and foreign substances.
Which type of immune cells are responsible for producing antibodies?- a)B cells
- b)T cells
- c)Macrophages
- d)Natural killer cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of immune cells are responsible for producing antibodies?
a)
B cells
b)
T cells
c)
Macrophages
d)
Natural killer cells

|
Orion Classes answered |
B cells are immune cells that produce antibodies. When activated by antigens, B cells differentiate into plasma cells, which secrete large amounts of antibodies specific to the encountered antigen.
Chapter doubts & questions for Immune System (BIO) - MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Immune System (BIO) - MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations
367 videos|157 docs|88 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









