NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Select the correct sequence about the life cy...
Start Learning for Free
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:
- a)Sporozoites (human) → RRCs → liver cells → gametocytes in blood → blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→ fertilisation (mosquito) → sporozoites (mosquito)
- b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)
- c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)
- d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporo...
The correct sequence of the Plasmodium life cycle involves the following steps:
Sporozoites are injected into humans by the female mosquito. The sporozoites travel to the liver where they mature. After the liver stage, the parasite enters the RBCs where it multiplies.Some of the parasites develop into gametocytes, which are released into the blood.These gametocytes are taken up by a female mosquito during a blood meal. Inside the mosquito, the gametocytes undergo sexual reproduction to form sporozoites.Finally, sporozoites are transmitted back to humans when the mosquito bites again.
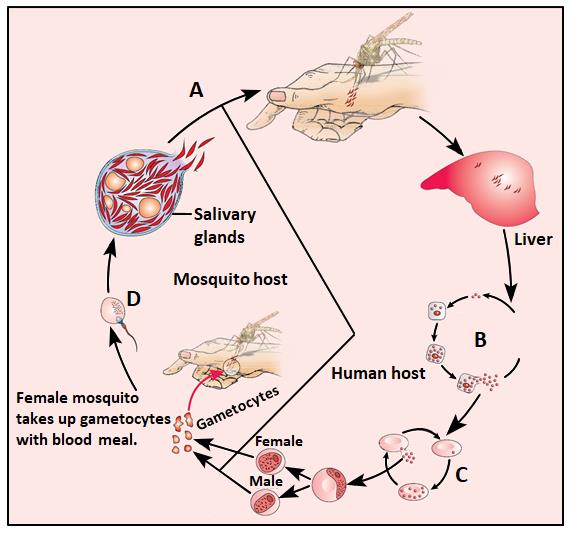
Sporozoites are injected into humans by the female mosquito. The sporozoites travel to the liver where they mature. After the liver stage, the parasite enters the RBCs where it multiplies.Some of the parasites develop into gametocytes, which are released into the blood.These gametocytes are taken up by a female mosquito during a blood meal. Inside the mosquito, the gametocytes undergo sexual reproduction to form sporozoites.Finally, sporozoites are transmitted back to humans when the mosquito bites again.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporo...
Life Cycle of Plasmodium
The life cycle of Plasmodium, the parasite responsible for malaria, involves two hosts: humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes. The correct sequence of the life cycle is crucial for understanding malaria transmission.
Sporozoites in Humans
- Plasmodium enters the human body through the bite of an infected female mosquito, introducing sporozoites into the bloodstream.
Liver Cells
- The sporozoites travel to the liver, where they invade liver cells (hepatocytes) and undergo asexual reproduction, developing into merozoites.
RBCs (Red Blood Cells)
- Merozoites are released into the bloodstream and invade red blood cells, where they multiply further, leading to the clinical symptoms of malaria.
Gametocytes in Blood
- Some of these merozoites differentiate into gametocytes, which are the sexual forms of the parasite found in the blood.
Blood Meal by Female Mosquito
- When a female mosquito takes a blood meal from an infected human, she ingests these gametocytes.
Fertilization in Mosquito
- In the mosquito’s gut, gametocytes undergo fertilization, forming zygotes, which develop into ookinetes and then oocysts.
Sporozoites in Mosquito
- These oocysts multiply and eventually release sporozoites, which migrate to the mosquito's salivary glands, ready to infect another human when the mosquito bites again.
Conclusion
Option B accurately describes this life cycle by outlining the critical stages: sporozoites infect liver cells, move to RBCs, form gametocytes, are taken up by a mosquito, and finally develop back into sporozoites, completing the cycle.
The life cycle of Plasmodium, the parasite responsible for malaria, involves two hosts: humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes. The correct sequence of the life cycle is crucial for understanding malaria transmission.
Sporozoites in Humans
- Plasmodium enters the human body through the bite of an infected female mosquito, introducing sporozoites into the bloodstream.
Liver Cells
- The sporozoites travel to the liver, where they invade liver cells (hepatocytes) and undergo asexual reproduction, developing into merozoites.
RBCs (Red Blood Cells)
- Merozoites are released into the bloodstream and invade red blood cells, where they multiply further, leading to the clinical symptoms of malaria.
Gametocytes in Blood
- Some of these merozoites differentiate into gametocytes, which are the sexual forms of the parasite found in the blood.
Blood Meal by Female Mosquito
- When a female mosquito takes a blood meal from an infected human, she ingests these gametocytes.
Fertilization in Mosquito
- In the mosquito’s gut, gametocytes undergo fertilization, forming zygotes, which develop into ookinetes and then oocysts.
Sporozoites in Mosquito
- These oocysts multiply and eventually release sporozoites, which migrate to the mosquito's salivary glands, ready to infect another human when the mosquito bites again.
Conclusion
Option B accurately describes this life cycle by outlining the critical stages: sporozoites infect liver cells, move to RBCs, form gametocytes, are taken up by a mosquito, and finally develop back into sporozoites, completing the cycle.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Select the correct sequence about the life cycle of Plasmodium:a)Sporozoites (human)→RRCs→liver cells→gametocytes in blood→blood meal, bite (female mosquito )→fertilisation (mosquito)→sporozoites (mosquito)b)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → RBCs → Gametocytes in blood → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)c)Gametocytes (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (human) → RBCs → Multiply → Sporozoites → Blood meal (human) → Sporozoites (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Gametocytes (female mosquito)d)Sporozoites (human) → Liver cells → Gametocytes in blood → RBCs → Blood meal (female mosquito) → Multiply (female mosquito) → Sporozoites (female mosquito)Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















