All Exams >
NEET >
Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Cell: The Unit of Life for NEET Exam
Which one of the following cell organelles is enclosed by a single membrane ? [2016]- a)Mitochondria
- b)Chloroplasts
- c)Lysosomes
- d)Nuclei
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following cell organelles is enclosed by a single membrane ? [2016]
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Chloroplasts
c)
Lysosomes
d)
Nuclei

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
(c) Double Membrane bound Organelles: Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Body, and Nucleus. Single Membrane bound Organelles: Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, and Vacuoles. Organelles lacking any membrane: Ribosomes, Centrioles, Nucleolus.
Which structures perform the function of mitochondria in bacteria? [2014]- a)Nucleoid
- b)Ribosomes
- c)Cell wall
- d)Mesosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structures perform the function of mitochondria in bacteria? [2014]
a)
Nucleoid
b)
Ribosomes
c)
Cell wall
d)
Mesosomes

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
(d) In some bacteria (e.g., Bacillus subtilis) the plasma membrane form certain invaginations or in foldings called mesosomes in the cytoplasm. The mesosomes have various functions, viz., respiratory, secretory etc.
Which of the following are not membranebound? [2015 RS]- a)Ribosomes
- b)Lysosomes
- c)Mesosomes
- d)Vacuoles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are not membranebound? [2015 RS]
a)
Ribosomes
b)
Lysosomes
c)
Mesosomes
d)
Vacuoles

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
(a) Ribosomes are not membrance-bound cell organelle.
The Golgi complex plays a major role[NEET 2013]- a)in digesting proteins and carbohydrates
- b)as energy transferring organelles
- c)in post translational modification of proteins and glycosidation of lipids
- d)in trapping the light and transforming it into chemical energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Golgi complex plays a major role
[NEET 2013]
a)
in digesting proteins and carbohydrates
b)
as energy transferring organelles
c)
in post translational modification of proteins and glycosidation of lipids
d)
in trapping the light and transforming it into chemical energy

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Golgi apparatus plays a major role in post translational modification of proteins forming glycoprotein and glycosidation of lipid forming glycolipids. A number of proteins and lipids synthesised on endoplasmic reticulum (rough and smooth respectively) are modified in the cisternae of the Golgi apparatus before they are released from it trans face.
Select the correct matching in the following pairs: [2015 RS]- a)Smooth ER – Synthesis of lipids
- b)Rough ER – Synthesis of glycogen
- c)Rough ER – Oxidation of fatty acids
- d)Smooth ER – Oxidation of phospholipids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct matching in the following pairs: [2015 RS]
a)
Smooth ER – Synthesis of lipids
b)
Rough ER – Synthesis of glycogen
c)
Rough ER – Oxidation of fatty acids
d)
Smooth ER – Oxidation of phospholipids

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
(a) Lipid synthesis takes place in smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Cellular organelles with membranes are : [2015 RS]- a)chormosomes, ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum
- b)endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and nuclei
- c)lysosomes, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria
- d)nuclei, ribosomes and mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellular organelles with membranes are : [2015 RS]
a)
chormosomes, ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum
b)
endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and nuclei
c)
lysosomes, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria
d)
nuclei, ribosomes and mitochondria

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
(c) Lysosomes, golgi apparatus and mitochondria are the cell organelles which have membranes.
Peptide synthesis inside a cell takes place in:[2011]- a)chloroplast
- b)mitochondria
- c)chromoplast
- d)ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Peptide synthesis inside a cell takes place in:
[2011]
a)
chloroplast
b)
mitochondria
c)
chromoplast
d)
ribosomes

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
Peptide synthesis takes place in ribosome inside a cell.
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred as: (2021)- a)Sub-metacentric
- b)Acrocentric
- c)Metacentric
- d)Telocentric
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred as: (2021)
a)
Sub-metacentric
b)
Acrocentric
c)
Metacentric
d)
Telocentric
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The metacentric chromosome has middle centromere forming two equal arms of the chromosome.
Which one of the following is not a constituent of cell membrane?[2007]- a)glycolipids
- b)proline
- c)phospholipids
- d)cholesterol.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a constituent of cell membrane?
[2007]
a)
glycolipids
b)
proline
c)
phospholipids
d)
cholesterol.
|
|
Bhavya Pillai answered |
Cell Membrane Constituents
Cell membrane is a thin, delicate and selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell. It is composed of a complex mixture of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. The major constituents of the cell membrane are:
1. Phospholipids: They are the most abundant lipids in the cell membrane. They consist of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail. They form a bilayer with the hydrophobic tails facing each other and the hydrophilic heads pointing outwards.
2. Proteins: They are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer and are responsible for various functions like transport, communication, and enzymatic activities. They can be peripheral or integral proteins.
3. Cholesterol: It is a type of lipid that is found in the cell membrane. It helps to maintain the fluidity and stability of the membrane.
4. Glycolipids: They are lipids with attached carbohydrate groups. They are found on the outer surface of the cell membrane and help in cell recognition and communication.
5. Carbohydrates: They are present on the outer surface of the cell membrane and are attached to proteins or lipids. They play a role in cell recognition and communication.
Answer
Out of the given options, proline is not a constituent of the cell membrane. Proline is an amino acid and is not a lipid, protein or carbohydrate. It is a non-polar amino acid that is found in the interior of proteins.
Cell membrane is a thin, delicate and selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell. It is composed of a complex mixture of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. The major constituents of the cell membrane are:
1. Phospholipids: They are the most abundant lipids in the cell membrane. They consist of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail. They form a bilayer with the hydrophobic tails facing each other and the hydrophilic heads pointing outwards.
2. Proteins: They are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer and are responsible for various functions like transport, communication, and enzymatic activities. They can be peripheral or integral proteins.
3. Cholesterol: It is a type of lipid that is found in the cell membrane. It helps to maintain the fluidity and stability of the membrane.
4. Glycolipids: They are lipids with attached carbohydrate groups. They are found on the outer surface of the cell membrane and help in cell recognition and communication.
5. Carbohydrates: They are present on the outer surface of the cell membrane and are attached to proteins or lipids. They play a role in cell recognition and communication.
Answer
Out of the given options, proline is not a constituent of the cell membrane. Proline is an amino acid and is not a lipid, protein or carbohydrate. It is a non-polar amino acid that is found in the interior of proteins.
The term ‘glycocalyx’ is used for
[NEET Kar. 2013]
- a)A layer surrounding the cell wall of bacteria
- b)A layer present between cell wall and membrane of bacteria
- c)Cell wall of bacteria
- d)Bacterial cell glyco-engineered to possess N-glycosylated proteins
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The term ‘glycocalyx’ is used for
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
A layer surrounding the cell wall of bacteria
b)
A layer present between cell wall and membrane of bacteria
c)
Cell wall of bacteria
d)
Bacterial cell glyco-engineered to possess N-glycosylated proteins

|
Kajal Bose answered |
The correct answer is (A) A layer surrounding the cell wall of bacteria.
A carbohydrate-protein layer that is covered on many of the eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells is called the glycocalyx. In prokaryotes particularly it is covered on the cell wall of bacteria. Many of the eukaryotic cells use glycocalyx to recognize the cell. To protect from the host factors bacterial cells are covered with glycocalyx. The glycocalyx in bacterial cells has the ability to establish an infection.
A carbohydrate-protein layer that is covered on many of the eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells is called the glycocalyx. In prokaryotes particularly it is covered on the cell wall of bacteria. Many of the eukaryotic cells use glycocalyx to recognize the cell. To protect from the host factors bacterial cells are covered with glycocalyx. The glycocalyx in bacterial cells has the ability to establish an infection.
Ribosomes are produced in[2002]- a)nucleolus
- b)cytoplasm
- c)mitochondria
- d)golgi body
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ribosomes are produced in
[2002]
a)
nucleolus
b)
cytoplasm
c)
mitochondria
d)
golgi body
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Eukaryote ribosomes are produced and assembled in the nucleolus. Ribosomal proteins enter the nucleolus and combine with the four rRNA strands to create the two ribosomal subunits (one small and one large) that will make up the completed ribosome
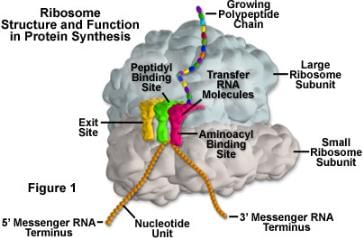

Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs[2005]- a)only on the ribosomes present in cytosol
- b)only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum
- c)on-ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in cytoplasm
- d)on ribosomes present in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs
[2005]
a)
only on the ribosomes present in cytosol
b)
only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum
c)
on-ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in cytoplasm
d)
on ribosomes present in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
|
|
Sadiya Siddique answered |
Protein synthesis occurs in ribosomes regardless of whether their in cytoplasm or in mitochondria. thus,op D.
Select the wrong statement from the following[2007]- a)Both chloroplasts and mitochondria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by the thylakoid membrane
- b)Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain DNA
- c)The chloroplasts are generally much large than mitochondria
- d)Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain an inner and an outer membrane.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the wrong statement from the following
[2007]
a)
Both chloroplasts and mitochondria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by the thylakoid membrane
b)
Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain DNA
c)
The chloroplasts are generally much large than mitochondria
d)
Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain an inner and an outer membrane.

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Both chloroplasts and mitochoridria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by double membrane
The solid linear cytoskeletal elements having a diameter of 6 nm and made up of a single type of monomer are known as: [2014]- a)Microtubules
- b)Microfilaments
- c)Intermediate filaments
- d)Lamins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The solid linear cytoskeletal elements having a diameter of 6 nm and made up of a single type of monomer are known as: [2014]
a)
Microtubules
b)
Microfilaments
c)
Intermediate filaments
d)
Lamins

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
(b) Microtubule, microfilament and intermediate filaments along with ER form cytoskeleton. Microfilaments are nonliving, solid and consist of actin protein. They are 4-6 nm in diameter.
According to widely accepted “fluid mosaic model” cell membranes are semi-fluid, where lipids and integral proteins can diffuse randomly. In recent years, this model has been modified in several respects. In this regard, which of the following statements is incorrect?[2005]- a)Proteins in cell membranes can travel within the lipid bilayer.
- b)Proteins can also undergo flip-flop movements in the lipid bilayer.
- c)Proteins can remain confined within certain domains of the membrane.
- d)Many proteins remain completely embedded within the lipid bilayer.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to widely accepted “fluid mosaic model” cell membranes are semi-fluid, where lipids and integral proteins can diffuse randomly. In recent years, this model has been modified in several respects. In this regard, which of the following statements is incorrect?
[2005]
a)
Proteins in cell membranes can travel within the lipid bilayer.
b)
Proteins can also undergo flip-flop movements in the lipid bilayer.
c)
Proteins can remain confined within certain domains of the membrane.
d)
Many proteins remain completely embedded within the lipid bilayer.

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Flip-Flop movement is due to migration of lipid molecules from one lipid monolayer to other monolayer of lipid bilayer.
Which is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells? (2020)- a)Golgi bodies
- b)Polysomes
- c)Endoplasmic reticulum
- d)Peroxisomes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells? (2020)
a)
Golgi bodies
b)
Polysomes
c)
Endoplasmic reticulum
d)
Peroxisomes
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Proteins and lipids are formed in the endoplasmic reticulum and some of them are modified to form glycoproteins and glycolipids in the Golgi apparatus.

The two sub-units of ribosome remain united a critical ion level of[2008]- a)copper
- b)manganese
- c)magnesium
- d)calcium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The two sub-units of ribosome remain united a critical ion level of
[2008]
a)
copper
b)
manganese
c)
magnesium
d)
calcium

|
Gowri Nair answered |
The two subunits of ribosome remain united at a critical ion level of magnesium. The presence of magnesium and its amount plays an important role in the appearance and structure of the ribosomes. If magnesium is absent in medium, the large particles fall apart to present a group of smaller particles.
Polysome is formed by- a)several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
- b)many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum
- c)a ribosome with several subunits
- d)ribosomes attached to each other in a linear arrangement
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Polysome is formed by
a)
several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
b)
many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum
c)
a ribosome with several subunits
d)
ribosomes attached to each other in a linear arrangement

|
Mahi Shah answered |
Polysome (Polyribosome) is a complex formed by several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA molecule in the process of translation.
In fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane[2002] - a)upper layer is non-polar and hydrophilic
- b)upper layer is polar and hydrophobic
- c)phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in middle part
- d)proteins form a middle layer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane
[2002]
a)
upper layer is non-polar and hydrophilic
b)
upper layer is polar and hydrophobic
c)
phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in middle part
d)
proteins form a middle layer
|
|
Rajeev Banerjee answered |
Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma Membrane
The fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid and dynamic layer composed of different molecules. This model was proposed by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson in 1972. The model explains that the cell membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipids, in which proteins are embedded.
Phospholipid Bilayer
The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer, which consists of two layers of phospholipid molecules. The phospholipids are composed of a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. The hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tail is repelled by water. The phospholipids arrange themselves in such a way that the hydrophilic heads face the outside of the membrane, while the hydrophobic tails face inward.
Bimolecular Layer
The phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in the middle part of the membrane. This layer acts as a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment. The barrier is selectively permeable, which means that it allows only certain molecules to pass through it.
Proteins
Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. They are either partially or fully embedded in the membrane. The proteins perform a variety of functions, including transport of molecules across the membrane, signal transduction, and cell recognition.
Fluidity
The fluidity of the plasma membrane allows it to change shape and move. The fluidity is due to the presence of unsaturated fatty acids in the phospholipid bilayer, which prevent the phospholipids from packing tightly together.
Conclusion
In summary, the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid and dynamic layer composed of different molecules. The phospholipid bilayer forms a bimolecular layer in the middle of the membrane, which is selectively permeable. Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer and perform various functions. The fluidity of the membrane allows it to change shape and move.
The fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid and dynamic layer composed of different molecules. This model was proposed by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson in 1972. The model explains that the cell membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipids, in which proteins are embedded.
Phospholipid Bilayer
The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer, which consists of two layers of phospholipid molecules. The phospholipids are composed of a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. The hydrophilic head is attracted to water, while the hydrophobic tail is repelled by water. The phospholipids arrange themselves in such a way that the hydrophilic heads face the outside of the membrane, while the hydrophobic tails face inward.
Bimolecular Layer
The phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in the middle part of the membrane. This layer acts as a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment. The barrier is selectively permeable, which means that it allows only certain molecules to pass through it.
Proteins
Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. They are either partially or fully embedded in the membrane. The proteins perform a variety of functions, including transport of molecules across the membrane, signal transduction, and cell recognition.
Fluidity
The fluidity of the plasma membrane allows it to change shape and move. The fluidity is due to the presence of unsaturated fatty acids in the phospholipid bilayer, which prevent the phospholipids from packing tightly together.
Conclusion
In summary, the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid and dynamic layer composed of different molecules. The phospholipid bilayer forms a bimolecular layer in the middle of the membrane, which is selectively permeable. Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer and perform various functions. The fluidity of the membrane allows it to change shape and move.
Which one of the following is not considered as a part of the endomembrane system ?[2011M]- a)Golgi complex
- b)Peroxisome
- c)Vacuole
- d)Lysosome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not considered as a part of the endomembrane system ?
[2011M]
a)
Golgi complex
b)
Peroxisome
c)
Vacuole
d)
Lysosome

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Cell organelles, whose functions are coordinated, are considered together as an endomembrane system. The endomembrane system includes endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi complex, lysosomes and vacuoles. Since the functions of the mitochondria, chloroplast and peroxisomes are not coordinated with the above components, these are not considered as part of the endomembrane system.
Which of the following statement regarding mitochondrial membrane is not correct ?[2006]- a)The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane
- b)The inner membrane is highly convoluted forming a series of infoldings
- c)The outer membrane resembles a sieve
- d)The outer membrane is permeable to all kinds of molecules
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement regarding mitochondrial membrane is not correct ?
[2006]
a)
The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane
b)
The inner membrane is highly convoluted forming a series of infoldings
c)
The outer membrane resembles a sieve
d)
The outer membrane is permeable to all kinds of molecules

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
The enzymes of electron transport system are present in inner mitochondrial membrane.
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by: [2014]- a)Mitochondria
- b)Vacuoles
- c)Plastids
- d)Ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by: [2014]
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Vacuoles
c)
Plastids
d)
Ribosomes

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
(b) The vacuole is bound by a single membrane called tonoplast. It also functions as semipermeable membrane. It segregates vacuolar contents from cytoplasm, allows osmotic entry or exit of water, concentration and storage of nutrients as well as wastes.
Which of the following type of plastids does not contain stored food material?[NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Amyloplasts
- b)Chromoplasts
- c)Elaioplasts
- d)Aleuroplasts
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following type of plastids does not contain stored food material?
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Amyloplasts
b)
Chromoplasts
c)
Elaioplasts
d)
Aleuroplasts

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Chromoplasts are non-photosynthetic coloured plastides which synthesise and stored carotenoid pigmentes. They, therefore, appear orange red and yellow where as amyloplast (store starch), aleuroplast (store proteins) and elaioplast (store oil droplets and fats) are leucoplasts, colourless plastids.
Which one of the following structures is an organelle within an organelle?[2012M]- a)Ribosome
- b)Peroxisome
- c)ER
- d)Mesosome
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following structures is an organelle within an organelle?
[2012M]
a)
Ribosome
b)
Peroxisome
c)
ER
d)
Mesosome

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Ribosome are small naked (non membrane bound) particles made of r-RNA and proteins. Ribosomes are also seen in the organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. They are the cell’s protein factories and are found on RER and scattered in the cytoplasm as polyribosomes. Ribosomes are the sites at which information carried in the genetic code is converted into protein molecules.
Why is a capsule advantageous to abacterium?
[NEET Kar. 2013]
- a)It allows the bacterium to attach to the surface
- b)It protects the bacterium from desiccation
- c)It provides means of locomotion
- d)It allows bacterium to “hide” from host’s immune system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is a capsule advantageous to abacterium?
[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
It allows the bacterium to attach to the surface
b)
It protects the bacterium from desiccation
c)
It provides means of locomotion
d)
It allows bacterium to “hide” from host’s immune system

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Correct option is D.
The capsule is the protective covering of the bacterial cell made up of polymers of simple sugars (polysaccharides). Most capsules are hydrophilic and may help the bacterium avoid desiccation. It protects a bacterial cell from ingestion and destruction by white blood cells (phagocytosis) and helps it to hide from host immune system.
The capsule is the protective covering of the bacterial cell made up of polymers of simple sugars (polysaccharides). Most capsules are hydrophilic and may help the bacterium avoid desiccation. It protects a bacterial cell from ingestion and destruction by white blood cells (phagocytosis) and helps it to hide from host immune system.
Given below is a sample of a portion of DNA strand. What is so special shown in it?5’ —— GAATTC —— 3’
3’ —— CTTAAG —— 5’[2011]- a)Replication completed
- b)Deletion mutation
- c)Start codon at the 5’ end
- d)Palindromic sequence of base pairs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given below is a sample of a portion of DNA strand. What is so special shown in it?
5’ —— GAATTC —— 3’
3’ —— CTTAAG —— 5’
3’ —— CTTAAG —— 5’
[2011]
a)
Replication completed
b)
Deletion mutation
c)
Start codon at the 5’ end
d)
Palindromic sequence of base pairs

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
The sample of a portion of DNA strand shown in the figure is palindromic sequence of base pairs.
Which of the following statements is true for a secretory cell?- a)Golgi apparatus is absent
- b)Only Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is present
- c)Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) is easily observed in the cell
- d)Secretory granules are formed in nucleus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true for a secretory cell?
a)
Golgi apparatus is absent
b)
Only Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is present
c)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) is easily observed in the cell
d)
Secretory granules are formed in nucleus
|
|
Shatabdi Malik answered |
The RER often occurs deep in the cytoplasm. It is particularly highly developed in the cells that synthesise and secrete proteins. These include liver cells, pancreatic cells, goblet cells, plasma cells, fibroblasts, etc.So, the correct answer is 'RER is easily observed in the cell'.
Cell wall is absent in : [2015 RS]- a)Funaria
- b)Mycoplasma
- c)Nostoc
- d)Aspergillus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall is absent in : [2015 RS]
a)
Funaria
b)
Mycoplasma
c)
Nostoc
d)
Aspergillus

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
(b) Mycoplasma lacks cell wall.
What is true about ribosomes[2012]- a)The prokaryotic ribosomes are 80S, where “S” stands for sedimentation coefficient
- b)These are composed of ribonucleic acid and proteins
- c)These are found only in eukaryotic cells
- d)These are self-splicing introns of some RNAs.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about ribosomes
[2012]
a)
The prokaryotic ribosomes are 80S, where “S” stands for sedimentation coefficient
b)
These are composed of ribonucleic acid and proteins
c)
These are found only in eukaryotic cells
d)
These are self-splicing introns of some RNAs.

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Ribosomes are amembraneous (ie. without membrane) cell organelle composed of rRNA and protein. These are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In prokaryotes, ribosomes are 70S type while in eukaryotes, it is 80S type.
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesized in[2012]- a)Lysosomes
- b)Nucleolus
- c)Nucleoplasm
- d)Ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesized in
[2012]
a)
Lysosomes
b)
Nucleolus
c)
Nucleoplasm
d)
Ribosomes

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesized in nucleolus. Nucleolus is also known as ribosomal factory.
The main organelle involved in modification and routing of newly synthesized proteins to their destinations is[2005]- a)chloroplast
- b)mitochondria
- c)lysosome
- d)endoplasmic Reticulum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main organelle involved in modification and routing of newly synthesized proteins to their destinations is
[2005]
a)
chloroplast
b)
mitochondria
c)
lysosome
d)
endoplasmic Reticulum

|
Mahi Shah answered |
Endoplasmic reticulum transport proteins and enzymes to their destinations i.e. within the cell and outside the cell.
The plasma membrane consists mainly of:[2010]- a)phospholipids embedded in a protein bilayer
- b)proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer
- c)proteins embedded in a polymer of glucose molecules
- d)proteins embedded in a carbohydrate bilayer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The plasma membrane consists mainly of:
[2010]
a)
phospholipids embedded in a protein bilayer
b)
proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer
c)
proteins embedded in a polymer of glucose molecules
d)
proteins embedded in a carbohydrate bilayer

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Plasma membrane comprises mainly proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer. Protein molecules occur at places both inside and outer side of the lipid bilayer.
A major break through in the studies of cells came with the development of electron microscope. This is because[2006]- a)the resolving power of the electron microscope is 200 – 350 nm as compared to 0.1 – 0.2 for the light microscope
- b)electron beam can pass through thick materials, whereas light microscopy requires thin sections
- c)the electron microscope is more powerful than the light microscope as it uses a beam of electrons which has wavelength much longer than that of photons
- d)the resolution power of the electron microscope in much higher than that of the light microscope
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A major break through in the studies of cells came with the development of electron microscope. This is because
[2006]
a)
the resolving power of the electron microscope is 200 – 350 nm as compared to 0.1 – 0.2 for the light microscope
b)
electron beam can pass through thick materials, whereas light microscopy requires thin sections
c)
the electron microscope is more powerful than the light microscope as it uses a beam of electrons which has wavelength much longer than that of photons
d)
the resolution power of the electron microscope in much higher than that of the light microscope

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
A major break through in cell studies came with the development of EM having great resolution power due to which we can see the ultrastructures of cell organelles.
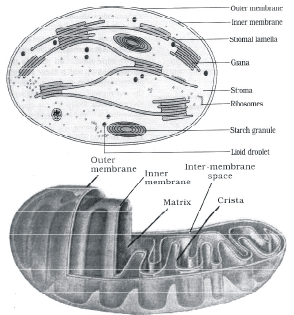
The figure below shows the structure of a mitochondrion with its four parts labelled (A), (B), (C) and (D).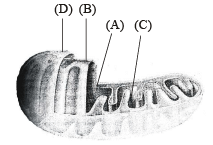 Select the part correctly matched with its function.[2011M]
Select the part correctly matched with its function.[2011M]- a)Part (D): Outer membrane – gives rise to inner membrane by splitting
- b)Part (B): Inner membrane – forms infoldings called cristae
- c)Part (C): Cristae – possess single circular DNA molecule and ribosomes
- d)Part (A): Matrix – major site for respiratory chain enzymes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure below shows the structure of a mitochondrion with its four parts labelled (A), (B), (C) and (D).

Select the part correctly matched with its function.
[2011M]
a)
Part (D): Outer membrane – gives rise to inner membrane by splitting
b)
Part (B): Inner membrane – forms infoldings called cristae
c)
Part (C): Cristae – possess single circular DNA molecule and ribosomes
d)
Part (A): Matrix – major site for respiratory chain enzymes

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
The mitochondrial inner membrane forms infoldings known as cristae, which allow greater surface area for protein such as cytochrome to function properly and efficiently.
Vacuole in a plant cell[2008]- a)is membrane-bound and contains storage proteins and lipids
- b)is membrane-bound and contains water and excretory substances
- c)lacks membrane and contains air
- d)lacks membrane and contains water and excretory substances
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vacuole in a plant cell
[2008]
a)
is membrane-bound and contains storage proteins and lipids
b)
is membrane-bound and contains water and excretory substances
c)
lacks membrane and contains air
d)
lacks membrane and contains water and excretory substances

|
Snehal Shah answered |
Vacuole in a plant cell is membrane bound and contains water and excretory substance. Vacuole is a space within the cytoplasm of living cell that is filled with air, water or other liquid, cell sap or food particles. In plant cells, there is usually one large vacuole bounded by a single layered membrane (tonoplast or vacuole membrane); animal cells usually have several small vacuoles.
Which of the following occurs more than one and less than five in a chromosome?[2002] - a)Telomere
- b)Chromosome
- c)Centromere
- d)Chromatid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following occurs more than one and less than five in a chromosome?
[2002]
a)
Telomere
b)
Chromosome
c)
Centromere
d)
Chromatid
|
|
Raza Great answered |
A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a chromosome. Sister chromatids are 2 identical halves which are joined by the centromere in a chromosome. A chromomere is serially arranged beads of a chromosome which have resulted from super coiling of a continuous DNA thread. It is more distinct during prophase. Telomere is a cap like structure present at the end of each strand of DNA. It protects the chromosome from sticking to another chromosome. It also protects the genetic material during cell division. It occurs 4 times in a chromosome.
Which of the following statements is not correct? (2019)- a)Lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- b)Lysosomes have numerous hydrolytic enzymes.
- c)The hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes are active under acidic pH.
- d)Lysosomes are membrane-bound structures.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
a)
Lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum.
b)
Lysosomes have numerous hydrolytic enzymes.
c)
The hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes are active under acidic pH.
d)
Lysosomes are membrane-bound structures.
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
- Lysosomes bud off from trans face to Golgi bodies.Precursor of lysosomal enzymes are synthesized by RER and then send to Golgi bodies for further processing.
So, the correct answer is 'Lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum'
A major site for synthesis of lipids is :[NEET 2013]- a)SER
- b)Symplast
- c)Nucleoplasm
- d)RER
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A major site for synthesis of lipids is :
[NEET 2013]
a)
SER
b)
Symplast
c)
Nucleoplasm
d)
RER

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the major site for synthesis of lipid. In animal cells lipid like steroidal hormones are synthesised in SER.
Middle lamella is composed mainly of:[2009]- a)muramic acid
- b)calcium pectate
- c)phosphoglycerides
- d)hemicellulose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Middle lamella is composed mainly of:
[2009]
a)
muramic acid
b)
calcium pectate
c)
phosphoglycerides
d)
hemicellulose

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Middle lamella is mainly composed of calcium pectate. Calcium is deposited in plants cell walls during their formation - it is required for the stability and function of cell membranes and acts as a type of ‘cementing agent’ in the cell walls in the form of calcium pectate’. Calcium pectate is like a glue binding adjacent cells together so if inadequate calcium is not transported during cell formation, tissues become less stable and prone to disintegration.
Identify the correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest : [2015 RS]- a)Genome, chromosome, nucleotide, gene
- b)Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
- c)Chromosome, genome, nucleotide, gene
- d)Chromosome, gene, genome, nucleotide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest : [2015 RS]
a)
Genome, chromosome, nucleotide, gene
b)
Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
c)
Chromosome, genome, nucleotide, gene
d)
Chromosome, gene, genome, nucleotide

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
(b) Genome > chromosomes > gene > nucleotide.
Which one of the following structures between two adjacent cells is an effective transport pathway?[2010]- a)Plasmodesmata
- b)Plastoquinones
- c)Endoplasmic reticulum
- d)Plasmalemma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following structures between two adjacent cells is an effective transport pathway?
[2010]
a)
Plasmodesmata
b)
Plastoquinones
c)
Endoplasmic reticulum
d)
Plasmalemma

|
Maheshwar Saini answered |
Plasmodesmata are the structure between two adjacent cells that permits the transport and communication between them. They are the fine cytoplasmic strands that connect the protoplasts of adjacent plant cells by passing through the cell walls.
What are those structures that appear as beads - on- string in the chromosomes when viewed under electron microscope ?[2011]- a)Genes
- b)Nucleotides
- c)Nucleosomes
- d)Base pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What are those structures that appear as beads - on- string in the chromosomes when viewed under electron microscope ?
[2011]
a)
Genes
b)
Nucleotides
c)
Nucleosomes
d)
Base pairs

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Under electron microscope the nucleosomes appear as beads on string in chromosome, due to a short length of DNA wrapped around a core of histone proteins.
Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in[2004]- a)type of movement and placement in cell
- b)location in cell and mode of functioning
- c)microtubular organization and type of movement
- d)microtubular organization and function
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in
[2004]
a)
type of movement and placement in cell
b)
location in cell and mode of functioning
c)
microtubular organization and type of movement
d)
microtubular organization and function

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
Prokaryotes have simple flagella without microtubules whereas eukaryotes have complex cilia and flagella which consists of microtubules arranged in 9+2 fashion (an outer ring of nine pairs surrounding 1 center pair). Further in prokaryotes the arrangement is 9+0.
Which one of the following does not differ in E.coli and Chlamydomonas[2012]- a)Ribosomes
- b)Chromosomal Organization
- c)Cell wall
- d)Cellmembrane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following does not differ in E.coli and Chlamydomonas
[2012]
a)
Ribosomes
b)
Chromosomal Organization
c)
Cell wall
d)
Cellmembrane

|
Swara Desai answered |
Cell membrane of E.coli, a bacteria and Chlamydomonas a unicellular green alga does not differ. As in both cell membrane is composed of lipids and proteins.
In which one of the following is nitrogen not a constituent ?[2003]- a)Pepsin
- b)Idioblast
- c)Bacteriochlorophyll
- d)Invertase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following is nitrogen not a constituent ?
[2003]
a)
Pepsin
b)
Idioblast
c)
Bacteriochlorophyll
d)
Invertase

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Raphides are needle-shaped crystals of calcium carbonate or calcium oxalate found in specialized plant cells called idioblasts. It is believed that the raphides are a defense mechanism against plant predators, as they are likely to tear the soft tissues of the throat or esophagus of a plant predator chewing on the plant’s leaves. They are non-nitrogenous substances.
In mitochondria, proteins accumulate in the[2011M]- a)outer membrane
- b)inner membrane
- c)intermembrane space
- d)matrix
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In mitochondria, proteins accumulate in the
[2011M]
a)
outer membrane
b)
inner membrane
c)
intermembrane space
d)
matrix

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
The inner membrane of mitochondria contains more than 151 different polypeptides, and has a very high protein-to- phospholipid ration.
The main arena of various types of activities of a cell is:[2010]- a)plasma membrane
- b)mitochondrian
- c)cytoplasm
- d)nucleus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The main arena of various types of activities of a cell is:
[2010]
a)
plasma membrane
b)
mitochondrian
c)
cytoplasm
d)
nucleus

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
The main arena of various types of activities of a cell is cytoplasm. It forms the living protoplasm of a cell excluding the nucleus. It consists of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, vitamins, waste metabolites and all organelles.
Which one of the following has its own DNA?[2010]- a)Mitochondria
- b)Dictyosome
- c)Lysosome
- d)Peroxisome
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has its own DNA?
[2010]
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Dictyosome
c)
Lysosome
d)
Peroxisome

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
Mitochondria has its own DNA. It is as structure within cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that carries out aerobic respiration. It is the site of Kreb’s cycle and ETS.
Therefore, it is also called as cell’s energy production site.
Therefore, it is also called as cell’s energy production site.
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell: The Unit of Life - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell: The Unit of Life - Biology 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily