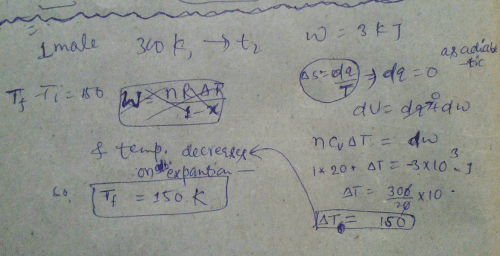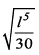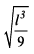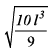All Exams >
Chemistry >
Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry >
All Questions
All questions of Practice MCQ Tests for Chemistry Exam
The most stable canonical structure among all of above is: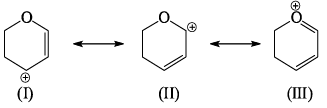
- a)Only I
- b)Only II
- c)Only III
- d)All are equally stable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most stable canonical structure among all of above is:

a)
Only I
b)
Only II
c)
Only III
d)
All are equally stable
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
The structure which has a maximum double bond is more stable.
Strength of following bases decrease in the order?
(I) Br- (II) F- (III) NH2 (IV) CH3-
- a)IV > III > I>II
- b)III > IV > I > II
- c)II > I > III > IV
- d)IV > I > II > III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Strength of following bases decrease in the order?
(I) Br- (II) F- (III) NH2 (IV) CH3-
a)
IV > III > I>II
b)
III > IV > I > II
c)
II > I > III > IV
d)
IV > I > II > III
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
-
Br⁻ (bromide ion): This is a halide ion. Halide ions become stronger bases as the size of the ion increases (i.e., as we move down the periodic table). Bromide is quite large, but it is not as large as iodide, making it a relatively weaker base compared to other larger halides.
-
F⁻ (fluoride ion): Fluoride is a small ion with high electronegativity, which means it holds onto its electron pair tightly and is less inclined to share it to form a bond with a proton. Thus, in an aqueous solution, fluoride is a weaker base than larger halide ions.
-
NH₂⁻ (amide ion): This ion has a nitrogen atom, which is less electronegative than fluorine, holding the negative charge. Nitrogen can share its electron pair more easily than fluorine. Also, the negative charge on the amide ion is not as effectively stabilized because nitrogen is less electronegative than fluorine.
-
CH₃⁻ (methide ion): This ion has a carbon atom bearing the negative charge. Carbon is less electronegative than nitrogen and fluorine, so it is more ready to share its electron pair compared to NH₂⁻ and F⁻. However, the negative charge is not delocalized and is concentrated on a single carbon atom, making it a strong base.
Considering these factors, the order of increasing base strength from weakest to strongest should be:
F⁻ < Br⁻ < NH₂⁻ < CH₃⁻
This order takes into account that fluoride is very electronegative and holds onto its electron pair tightly, bromide is a larger halogen and can distribute its negative charge over a larger volume, the amide ion is less stable due to the higher energy of nitrogen-based anions, and the methide ion is a strong base due to carbon's low electronegativity and the localized negative charge.
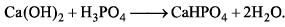 Equivalent weight of H3PO4 in the above reaction is:
Equivalent weight of H3PO4 in the above reaction is:
Correct answer is '49'. Can you explain this answer?
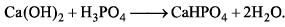 Equivalent weight of H3PO4 in the above reaction is:
Equivalent weight of H3PO4 in the above reaction is:

|
Bhavana Pillai answered |
H3PO4 is an acid and the equivalent mass of an acid is calculated by using the formula:
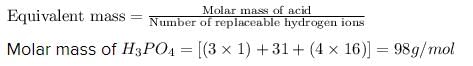
From the given reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + H3PO4 → CaHPO4 + 2H2O
As, the replaceable hydrogen ions in acid is 2, by putting the values in above equation, we get:
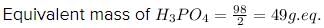
Hence, The equivalent mass of H3PO4 for the given reaction is 49 g eq.
Which of the following is the most stable conformer of the following molecule:
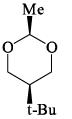
- a)
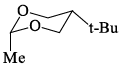
- b)

- c)

- d)
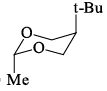
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the most stable conformer of the following molecule:

a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Asf Institute answered |
Correct Answer :- B
Explanation : When the methyl group in the structure above occupies an axial position it suffers steric crowding by the two axial hydrogens located on the same side of the ring. The conformation in which the methyl group is equatorial is more stable, and thus the equilibrium lies in this direction.
Therefore,the equatorial bonds are the most stable in chair form.
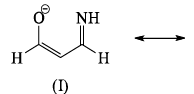
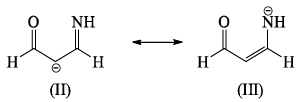 The correct order of stability among the following canonical structure is:
The correct order of stability among the following canonical structure is: - a)I > II > III
- b)II > I > III
- c)III > I > II
- d)I > III > II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?


The correct order of stability among the following canonical structure is:
a)
I > II > III
b)
II > I > III
c)
III > I > II
d)
I > III > II

|
Sinjini Nair answered |
Negative charge are stable at more Electronegative atom so the order of Electronegative is
O>N>C
stability order
1>3>2
O>N>C
stability order
1>3>2
How many of the following inter halogen species have 2 lone pairs of electrons on the central atom? ClF3, ClF2-, CIF5 ICl2- and XeF2
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
How many of the following inter halogen species have 2 lone pairs of electrons on the central atom? ClF3, ClF2-, CIF5 ICl2- and XeF2
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
Chlorine trifluoride has 5 regions of electron density around the central chlorine atom (3 bonds and 2 lone pairs). These are arranged in a trigonal bipyramidal shape with a 175° F(axial)-Cl-F(axial) bond angle.
In a ClF5 molecule, chlorine is the central atom featuring five single bonds with fluorine atoms. Since chlorine has 7 electrons in the valence shell, the remaining two electrons form a lone pair.
In a ClF5 molecule, chlorine is the central atom featuring five single bonds with fluorine atoms. Since chlorine has 7 electrons in the valence shell, the remaining two electrons form a lone pair.
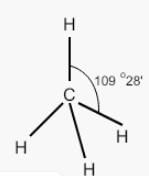
Consider two molecules A & B.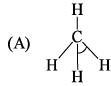
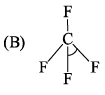 ∠α = ∠HCH; ∠β = ∠FCFWhich of following is true?
∠α = ∠HCH; ∠β = ∠FCFWhich of following is true?- a)α = β
- b)α > β
- c)β > α
- d)Insufficient information
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider two molecules A & B.
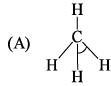

∠α = ∠HCH; ∠β = ∠FCF
Which of following is true?
a)
α = β
b)
α > β
c)
β > α
d)
Insufficient information
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Though the substituting atoms are different in both cases but the hybridization of carbon is the same that is sp3, having the bond angle of 109′28″.
If a particle has linear momentum 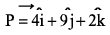 at position
at position 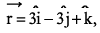 , then its angular momentum is:
, then its angular momentum is:
- a)
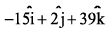
- b)
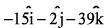
- c)-15i -2j +39k
- d)
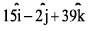
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a particle has linear momentum 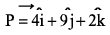 at position
at position 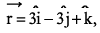 , then its angular momentum is:
, then its angular momentum is:
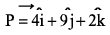 at position
at position 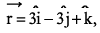 , then its angular momentum is:
, then its angular momentum is:a)
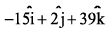
b)
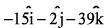
c)
-15i -2j +39k
d)
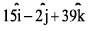

|
Veda Institute answered |
Angular momentum is equal to the cross product of the position vector and the linear mamentum.
J=r×p
(4i + 9j + 2k) × (3i - 3j + k)
= -15i-2j+39k
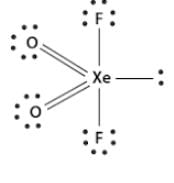
XeO2F2 has shape: a) See-Sawb)TBPc)Octahedrald) Square pyramidalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sinjini Nair answered |
XeO2F2 molecular geometry is originally said to be trigonal bipyramidal but due to the presence of lone pair on equatorial position, the actual shape will be see-saw. The repulsion between bond pair and lone pair of electrons will be more.
Lattice energy (numerical value) of chloride of alkali metals is in order:- a)LiCl > NaCl > KCl > RbCl > CsCl
- b)LiCl < NaCl < KCl < RbCl < CsCl
- c)NaCl < KCl < LiCl < RbCl < CsCl
- d)NaCl < KCl < RbCl < CsCl < LiCl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lattice energy (numerical value) of chloride of alkali metals is in order:
a)
LiCl > NaCl > KCl > RbCl > CsCl
b)
LiCl < NaCl < KCl < RbCl < CsCl
c)
NaCl < KCl < LiCl < RbCl < CsCl
d)
NaCl < KCl < RbCl < CsCl < LiCl

|
Milan Majumdar answered |
Lattice energy is the attraction force acting between the cation and anion.
Greater the size of cation, lower is the attractive force.
On moving down the group, size of cation increases then,
- Attractive force decreases.
- Lattice energy decreases.
Select incorrect statement(s):- a)At very low pressure, real gases show minimum deviation from ideal behaviour.
- b)The compressibility factor for an ideal gas is zero.
- c)At Boyle temperature, real gas behave as ideal gas in high pressure region
- d)Real gas show minimum deviation at high pressure and low temperature
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select incorrect statement(s):
a)
At very low pressure, real gases show minimum deviation from ideal behaviour.
b)
The compressibility factor for an ideal gas is zero.
c)
At Boyle temperature, real gas behave as ideal gas in high pressure region
d)
Real gas show minimum deviation at high pressure and low temperature

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
(b) Compressibility factor of an ideal gas is 1.
(c) Real gas behaves like ideal gas at high temperature and low pressure.
(c) Real gas behaves like ideal gas at high temperature and low pressure.
Examine the following resonating structures of formic acid for their individual stability and then answer the question given below: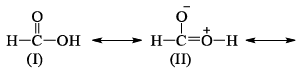
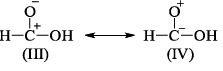 Which of the following arrangements gives the correct order of decreasing stability of the above- mentioned resonance contributors?
Which of the following arrangements gives the correct order of decreasing stability of the above- mentioned resonance contributors?- a)II > I > III > IV
- b)I > II > III > IV
- c)IV > III > I > II
- d)IV > III > II > I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Examine the following resonating structures of formic acid for their individual stability and then answer the question given below:
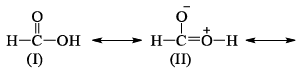
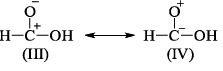
Which of the following arrangements gives the correct order of decreasing stability of the above- mentioned resonance contributors?
a)
II > I > III > IV
b)
I > II > III > IV
c)
IV > III > I > II
d)
IV > III > II > I
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
There are certain sets of rules that must be followed in order to check the stability of resonating structures.
These rules have a preference so we have to follow the order:
These rules have a preference so we have to follow the order:
- Uncharged species are more stable than charged species.
- Charged species having more number of covalent bond are more stable.
- The species in which octet rule is followed by every atom is more stable than the species in which octet rule is violated.
- Species in which opposite charges are closer are more stable than species having same charges closer.
- Species with negative charge on more electronegative atoms while positive charge on more electropositive atoms are more stable.
According to the above discussion, B is the correct answer.
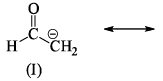
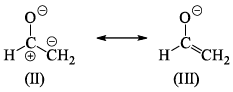 The correct order of stability for the given canonical structures is:
The correct order of stability for the given canonical structures is:- a)I > III > II
- b)III > I > II
- c)II > III > I
- d)II > I > III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
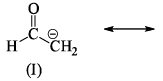
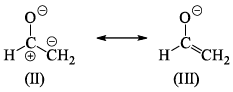
The correct order of stability for the given canonical structures is:
a)
I > III > II
b)
III > I > II
c)
II > III > I
d)
II > I > III

|
Veda Institute answered |
There are a certain set of rules that must be followed in order to check the stability of resonating structures.
These rules have a preference so we have to follow the order:
These rules have a preference so we have to follow the order:
- Uncharged species is more stable than charged species.
- Charged species having more number of covalent bond are more stable.
- The species in which the octet rule is followed by every atom is more stable than the species in which the octet rule is violated.
- Species in which opposite charges are closer are more stable than species having same charges closer.
- Species with negative charge on more electronegative atom while positive charge on more electropositive atom is more stable.
According to above discussion, B is the correct answer.
Find the corresponding subshell utilizing the information from graph. 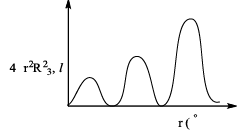
- a)3s
- b)3p
- c)3d
- d)2p
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the corresponding subshell utilizing the information from graph.

a)
3s
b)
3p
c)
3d
d)
2p
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
According to radial nodes formula:
Radial Nodes = n - l – 1
= 3 – 0 – 1
=2 nodes.
Therefore 3s.
Hence, A is the correct answer.
Therefore 3s.
Hence, A is the correct answer.
Total number of delocalized lone pairs (combined) in [Adenine & Guanine]: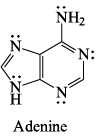
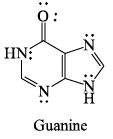
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of delocalized lone pairs (combined) in [Adenine & Guanine]:



|
Pawan Kajal answered |
The line pair of an atom will undergo conjugation if it is attached by single bond to that atom which has further multiple bond in conjugation.
 The table indicates the value of van-der Waal’s constant ‘a’. The gas which can be liquefied most easily is:
The table indicates the value of van-der Waal’s constant ‘a’. The gas which can be liquefied most easily is:- a)02
- b)N2
- c)NH3
- d)CH4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

The table indicates the value of van-der Waal’s constant ‘a’. The gas which can be liquefied most easily is:
a)
02
b)
N2
c)
NH3
d)
CH4

|
Aryan Gupta answered |
The ease of liquification of a gas depends on their intermolecular force of attraction which in turn is measured in terms of van der Waals’ constant ‘a’. Hence, higher the value of ‘a’, greater the intermolecular force of attraction, easier the liquification. In the present case, NH3 has highest ‘a’, can most easily be liquefied.
What is the value of PV/nRT for ideal gas?
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the value of PV/nRT for ideal gas?
|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
In SI units, P is measured in pascals, V is measured in cubic metres, n is measured in moles, and T in kelvins (the Kelvin scale is a shifted Celsius scale, where 0.00 K = −273.15 degree C, the lowest possible temperature). R has the value 8.314 J/(K. mol) ≈ 2 cal/(K. mol), or 0.08206 L.
Of the following acids, the one that is strongest is:- a)HBrO4
- b)HOC1
- c)HNO2
- d)H3PO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the following acids, the one that is strongest is:
a)
HBrO4
b)
HOC1
c)
HNO2
d)
H3PO3

|
Swara Dasgupta answered |
So HCl is strongest of all. There are some super acids, like fluroantimonic acid, that are 100 times more stronger than sulfuric acid.
Some or more species give belowhave pH less than 7.- a)10-8 M HCl
- b)10-8 M NaOH
- c)10 mL of 10-6 M HCl diluted to 100 mL
- d)10 mL of 0.01 M CH3COOH at the end point after addition of 10 mL 0.01 M NaOH
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Some or more species give belowhave pH less than 7.
a)
10-8 M HCl
b)
10-8 M NaOH
c)
10 mL of 10-6 M HCl diluted to 100 mL
d)
10 mL of 0.01 M CH3COOH at the end point after addition of 10 mL 0.01 M NaOH

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
The pH of 10-8M HCl solution is 6.98
The pH of NaoH solution will be 8
The pH of 10 mL of 10-6 M HCl diluted to 100 mL is 6.99
The pH of NaoH solution will be 8
The pH of 10 mL of 10-6 M HCl diluted to 100 mL is 6.99
Consider AB2 molecule 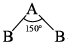 Calculate % s-character in A—B bond:
Calculate % s-character in A—B bond:
Correct answer is '46-47'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider AB2 molecule  Calculate % s-character in A—B bond:
Calculate % s-character in A—B bond:
 Calculate % s-character in A—B bond:
Calculate % s-character in A—B bond:

|
Saikat Ghoshal answered |
From Bent’s Rule equation, cosx = s/s-1
where x is an bond angle and s is the % s character in the bond, it is clear that if we increase bond angle, the %s Character will be maximum.
Here angle is 150,
⇒ Cosx = s/(s-1)
⇒ Cos 150° = s/(s-1)
⇒ -0.86 = s/(s-1)
⇒ -0.86s +0.86 = s
⇒ 0.86 = 1.86s
⇒ s = 0.86/1.86
⇒ s = 0.462
⇒ %s = 0.462 X 10
⇒ %s = 46.2%
Total number of nucleophiles among following molecules is/are___________.
CH3O-, carbene, Nitrene, H2O , ROH, ZnCl2, NHR2, SnCl4, -NH2 , Cl-.
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Total number of nucleophiles among following molecules is/are___________.
CH3O-, carbene, Nitrene, H2O , ROH, ZnCl2, NHR2, SnCl4, -NH2 , Cl-.
CH3O-, carbene, Nitrene, H2O , ROH, ZnCl2, NHR2, SnCl4, -NH2 , Cl-.

|
Bijoy Patel answered |
-
Nucleophiles are molecules or ions that are attracted to electron-deficient sites and have a tendency to donate electrons. Let's identify the nucleophiles among the given molecules:
- CH3O- (methoxide ion) - Nucleophile
- Carbene - Nucleophile
- Nitrene - Nucleophile
- H2O - Nucleophile
- ROH (alcohol) - Nucleophile
- ZnCl2 - Not a nucleophile (does not have lone pairs to donate)
- NHR2 - Nucleophile
- SnCl4 - Not a nucleophile (does not have lone pairs to donate)
- -NH2 (amide ion) - Nucleophile
- Cl- - Nucleophile
-
So, the total number of nucleophiles among the given molecules is 8.
Select the correct statement:- a)
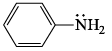 is more basic than
is more basic than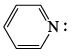
- b)
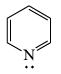 is more basic than
is more basic than 
- c)
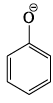 is more basic than
is more basic than 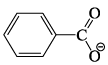
- d) All of them
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement:
a)
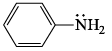 is more basic than
is more basic than
b)
 is more basic than
is more basic than 
c)
 is more basic than
is more basic than 
d)
All of them

|
Bhavana Dasgupta answered |
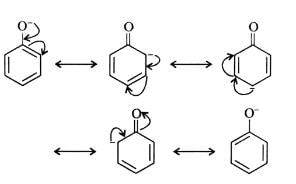
Benzoic acid is a stronger acid than phenol because the benzoate ion is stabilised by two equivalent resonance structures in which the negative charge is present at the more electronegative oxygen atom.
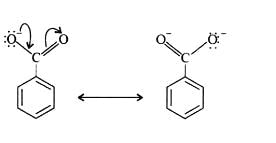
The conjugate base of phenol, a phenoxide ion, has non-equivalent resonance structures in which the negative charge is at the less electronegative carbon atom. Thus, the benzoate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion. Hence, benzoic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
Which of the following is an electrophile?- a) PCl5
- b)ZnCl2
- c)
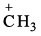
- d)Carbene
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an electrophile?
a)
PCl5
b)
ZnCl2
c)
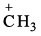
d)
Carbene

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
Electrophile is an electron pair acceptor. Electrophiles are positively charged or neutral species having vacant orbitals that are attracted to an electron rich centre. It participates in a chemical reaction by accepting an electron pair in order to bond to a nucleophile.
Which of the following is most basic?- a)
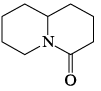
- b)
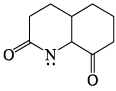
- c)
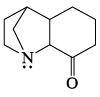
- d)
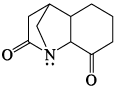
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is most basic?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Tejas Goyal answered |
Basicity is the tendency of an atom to donate their lone pair.
In case of (a), (b),(d), lone pair of Nitrogen atom is in conjugation which is not available to be donated.
Hence (c) is more basic.
Correct order of stability of the following carbocation is: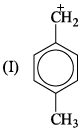
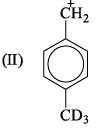

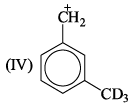
- a)I > II > III > IV
- b)II > I > IV > III
- c)I > II > IV > III
- d)I > IV > II > III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct order of stability of the following carbocation is:




a)
I > II > III > IV
b)
II > I > IV > III
c)
I > II > IV > III
d)
I > IV > II > III
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
At metaposition, hyperconjugation do not take place.
Inductive effect order −H<−D i.e R−CH3<R−CD3 (Stability)
Hyperconjugation order −H<−D i.e R−CH3>R−CD3 (Stability)
and Hyperconjugated compound is always more stable than inductive effect.
Therefore, Order is I>II>IV>III
What is the strength (in g/litre) of a solution of H2SO4, 12 mL of which neutralized 15 mL of N/10 NaOH solution:
Correct answer is between '6.12,6.13'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the strength (in g/litre) of a solution of H2SO4, 12 mL of which neutralized 15 mL of N/10 NaOH solution:
|
|
Kiran Punj answered |
N1 V1 = N2 V2
(H2SO4) (NAOH)
N1*12 = 1/10*15
N2 = 0.125
WE KNOW THAT
N = XM WHERE X FOR H2SO4 IS 2
0.125 = 2*W/MW*V
0.125*98/2 = W/V
W/V= 6.125 g/litre
Which of the following drawings is not a resonance structure of 1 -nitrocyclohexane: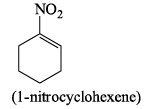
- a)
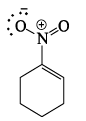
- b)
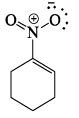
- c)
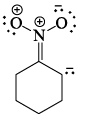
- d)
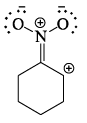
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following drawings is not a resonance structure of 1 -nitrocyclohexane:

a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Study Sesh answered |
In structure C, oxygen - the atom more electronegative than carbon - has a positive charge. This would be a highly unstable form and hence does not contribute to the resonating structure.
Another way to look at it would be that -NO2, a -I and -R group appears to show +R effect in structure C, which is incorrect.
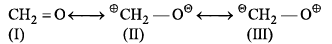 Which of these structures is practically not a valid resonance structure for formaldehyde?
Which of these structures is practically not a valid resonance structure for formaldehyde?- a)I
- b)II
- c)III
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
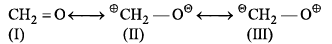
Which of these structures is practically not a valid resonance structure for formaldehyde?
a)
I
b)
II
c)
III
d)
None of these

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
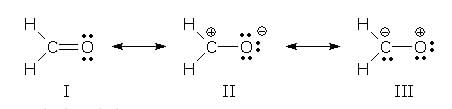
The lowest energy form is I, because every atom has a complete octet. It is the major contributor.
II is lower in energy than III, because the negative charge is in the more electronegative O atom.
The set representing the correct order of ionic radius is:- a)Na+ > Mg2+ > Al3+ > Li+ > Be2+
- b)Na+ > Li+ > Mg2+ > Al3+ > Be2+
- c)Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ > Al3+ > Be2+
- d)Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ > Be2+ > Al3+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The set representing the correct order of ionic radius is:
a)
Na+ > Mg2+ > Al3+ > Li+ > Be2+
b)
Na+ > Li+ > Mg2+ > Al3+ > Be2+
c)
Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ > Al3+ > Be2+
d)
Na+ > Mg2+ > Li+ > Be2+ > Al3+

|
Rising Star answered |
When positive ion increase,radious is decreases due to effective nuclear charge.
Strongest base among the following species is:- a)
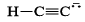
- b)
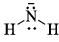
- c)
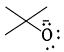
- d)
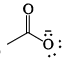
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Strongest base among the following species is:
a)
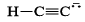
b)
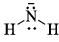
c)
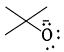
d)


|
Anshul Mehra answered |
Nitrogen atom is more basic than other two oxygen and carbon . Also it has an available lone pair.
Which of the following is not resonating structure of each other?- a)
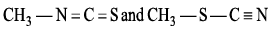
- b)
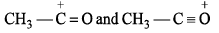
- c)
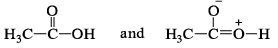
- d)
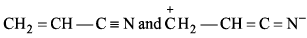
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not resonating structure of each other?
a)
b)
c)
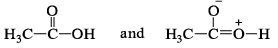
d)
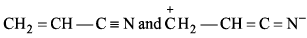

|
Rishabh Mehta answered |
Molecules in option (a) are linkage isomers of each other.
According to rules of Resonance, no change in position of atom should take place.
Solubility of BaSO4 in aqueous solution is 1 × 10–5 M. Hence, solubility in 0.1 M BaCl2 is: - a)1 × 10–10 M
- b)1 × 10–9 M
- c)1 × 10–4 M
- d)1 × 10–5 M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solubility of BaSO4 in aqueous solution is 1 × 10–5 M. Hence, solubility in 0.1 M BaCl2 is:
a)
1 × 10–10 M
b)
1 × 10–9 M
c)
1 × 10–4 M
d)
1 × 10–5 M
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
BaSO₄ ---------> Ba²⁺ + SO₄²⁻
According to ICE table
BaSO₄ -----------------> Ba²⁺ + SO₄²⁻
I 0.1 M 0
C +s +s
E s + 0.1 s
therefore we can write
ksp = ( s + 0.01) . s
as the value of ksp is very small as compared to silver ions initial concentration
we can use approximation
s + 0.1 ≈ 0.1
Ksp = 0.01 . s
s = 1 X 10⁻⁵ / 0.1
s = 0.0001 mol/ L
s = 1 X 10⁻4 mol/ L
According to ICE table
BaSO₄ -----------------> Ba²⁺ + SO₄²⁻
I 0.1 M 0
C +s +s
E s + 0.1 s
therefore we can write
ksp = ( s + 0.01) . s
as the value of ksp is very small as compared to silver ions initial concentration
we can use approximation
s + 0.1 ≈ 0.1
Ksp = 0.01 . s
s = 1 X 10⁻⁵ / 0.1
s = 0.0001 mol/ L
s = 1 X 10⁻4 mol/ L
Predict the shape of 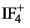 molecule using VSEPR theory:
molecule using VSEPR theory:- a)TBP
- b)See-Saw
- c)Octahedral
- d)Sq. Planar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Predict the shape of 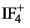 molecule using VSEPR theory:
molecule using VSEPR theory:
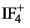 molecule using VSEPR theory:
molecule using VSEPR theory:a)
TBP
b)
See-Saw
c)
Octahedral
d)
Sq. Planar

|
Mihir Singh answered |
The electron geometry of IF4+ is trigonal bipyramidal. This is because it has five total electron groups. The central atom is bonded to four other atoms and has one lone pair of electrons. The lone pair of electrons will affect the molecular geometry of the compound as well as the bond angles.
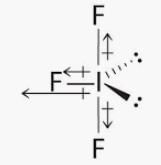
The ground state electronic configuration of valence shell electrons in a molecule A2 is written as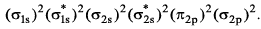 • Hence bond order is_____________________.
• Hence bond order is_____________________.- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ground state electronic configuration of valence shell electrons in a molecule A2 is written as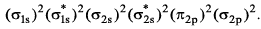 • Hence bond order is_____________________.
• Hence bond order is_____________________.
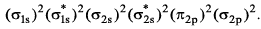 • Hence bond order is_____________________.
• Hence bond order is_____________________.a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3

|
Nilotpal Basu answered |
Bond Order = 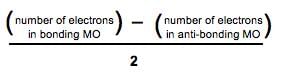
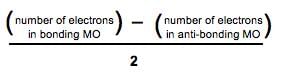
Number of electrons in bonding MO = 8
Number of electrons in anti-bonding MO = 4
Bond order = (8 - 4)/2
Bond order = 4/2
Bond order = 2
Find ΔE for states n = 3,4 in Bohr’s model of hydrogenic atoms (in eV):
Correct answer is '0.64-0.66'. Can you explain this answer?
Find ΔE for states n = 3,4 in Bohr’s model of hydrogenic atoms (in eV):

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
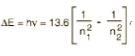
ΔE = 13.6 [ 1/9 - 1/16]
ΔE = 13.6 [7/144]
ΔE = 13.6 x 0.048
ΔE = 0.66
The ratio of van der Waal’s constant a and b, 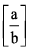 has the dimensions of:
has the dimensions of:- a)Atm b-1
- b)L atm mol-1
- c)L mol-1
- d)atm L mol-2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of van der Waal’s constant a and b, 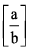 has the dimensions of:
has the dimensions of:
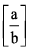 has the dimensions of:
has the dimensions of:a)
Atm b-1
b)
L atm mol-1
c)
L mol-1
d)
atm L mol-2

|
Partho Gupta answered |
The ratio of van der Waals’ constants a and b has the dimensions of atm L mole-1
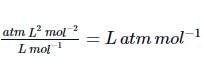
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomena:- a)Ice floats in water
- b)Higher Lewis basicity of primary amines than tertiary amines in aqueous solutions
- c)Formic acid is more acidic than acetic acid
- d)Dimerisation of acetic acid in benzene
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomena:
a)
Ice floats in water
b)
Higher Lewis basicity of primary amines than tertiary amines in aqueous solutions
c)
Formic acid is more acidic than acetic acid
d)
Dimerisation of acetic acid in benzene
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |

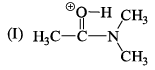
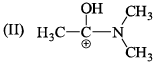
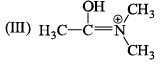 The correct stability order of the given resonating structures is:
The correct stability order of the given resonating structures is:- a)I > II > III
- b)III > I > II
- c)I > III > II
- d)II > III > I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?



The correct stability order of the given resonating structures is:
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > I > II
c)
I > III > II
d)
II > III > I

|
Shivani Mehta answered |
Here 2 rule of resonance stabilising rule works
1 More the number of bond more stable in resonance
2. + ve charge in electronegative decreasing resonance stability .Now for 1 2 3 , 1 and 3 has greater number of bond so 1 and 3 is greater stable than 2 . Compare 1 and 3 for 1 positive charge on oxygen which is more electronegative than N so 1 has less stable than 3 . So order is 3 > 1 >2
Distribution of molecules with velocity is represented by curve as shown: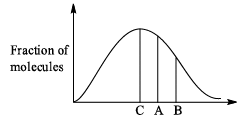 Velocity at point A is:
Velocity at point A is:- a)
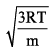
- b)
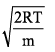
- c)
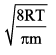
- d)
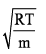
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Distribution of molecules with velocity is represented by curve as shown:

Velocity at point A is:
a)
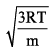
b)
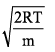
c)
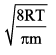
d)
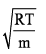

|
Dharshini Raghavan answered |
We know that RMS>Average speed>Most probable. Point B has highest velocity and has to be RMS. Next,
the lowest speed is also the one possessed by the highest fraction of molecules and this is the Most probable speed, which is point C.
Now average speed has values in between RMS and MPS. So, point A has got to be average speed.
In trigonal bipyramidal geometry, which of the following holds true?- a)Equatorial bonds are longer and weaker
- b)Arial bonds are shorter and stronger
- c)Both have same strength & length
- d)All are wrong statements.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In trigonal bipyramidal geometry, which of the following holds true?
a)
Equatorial bonds are longer and weaker
b)
Arial bonds are shorter and stronger
c)
Both have same strength & length
d)
All are wrong statements.

|
Shruti Datta answered |
The axial bonds are longer than equatorial bonds because of greater repulsion from equatorial bonds. The 2-axial bonds are at 90º degree angle to 3-equatorial bonds while all equatorial bonds are at 120º angle to each other. So, none of the statements is correct hence option(d)
The atomicity and the total number of bonds in the elemental white phosphorous molecule are:
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomicity and the total number of bonds in the elemental white phosphorous molecule are:

|
Srishti Khanna answered |
Atomicity and Total Number of Bonds in White Phosphorus Molecule
Atomicity
- Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule of an element.
- White phosphorus is a non-metallic element with the chemical symbol P and atomic number 15.
- It exists as a molecule with four atoms of phosphorus, hence the atomicity of white phosphorus is 4.
Total Number of Bonds
- White phosphorus molecule is made up of four atoms of phosphorus, each with five valence electrons.
- In order to achieve stability, each phosphorus atom shares its valence electrons with the other three atoms, forming a covalent bond.
- Therefore, the total number of bonds in the white phosphorus molecule is 4, as each phosphorus atom forms a bond with the other three atoms.
Conclusion
- White phosphorus molecule has an atomicity of 4, which means it is made up of four atoms of phosphorus.
- The total number of bonds in the white phosphorus molecule is 4, as each phosphorus atom forms a bond with the other three atoms.
Atomicity
- Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule of an element.
- White phosphorus is a non-metallic element with the chemical symbol P and atomic number 15.
- It exists as a molecule with four atoms of phosphorus, hence the atomicity of white phosphorus is 4.
Total Number of Bonds
- White phosphorus molecule is made up of four atoms of phosphorus, each with five valence electrons.
- In order to achieve stability, each phosphorus atom shares its valence electrons with the other three atoms, forming a covalent bond.
- Therefore, the total number of bonds in the white phosphorus molecule is 4, as each phosphorus atom forms a bond with the other three atoms.
Conclusion
- White phosphorus molecule has an atomicity of 4, which means it is made up of four atoms of phosphorus.
- The total number of bonds in the white phosphorus molecule is 4, as each phosphorus atom forms a bond with the other three atoms.
Which of the following is/are true about zero point energy?- a)It is the energy in lowest energy state.
- b)It applies to only quantum mechanics
- c)It is non-zero for 1-D box and S.H.O
- d)It is non-zero for Rigid Rotors, H-atom models as well.
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are true about zero point energy?
a)
It is the energy in lowest energy state.
b)
It applies to only quantum mechanics
c)
It is non-zero for 1-D box and S.H.O
d)
It is non-zero for Rigid Rotors, H-atom models as well.

|
Anushka Chavan answered |
Zero-point energy (ZPE) is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical system may have. Unlike in classical mechanics, quantum systems constantly fluctuate in their lowest energy state as described by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Chapter doubts & questions for Practice MCQ Tests - Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Practice MCQ Tests - Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry in English & Hindi are available as part of Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry
2 docs|25 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup