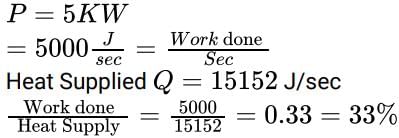All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Full Mock Tests Series for Mechanical Engineering Exam
Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions :A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a square table facing the centre in such a way that four of them sit at four corners of the square while four sit in the middle of each of the flour sides.(a) A sits second to right of F. F sits in the middle of one of the sides of the table(b) G who does not sit at any of the corners of the table sits second to the right of D(c) Only two people sit between D and B (taken from one side)(d) C is not an immediate neighbour of G(e) H is sits second to left of B(f) E is not an immediate neighbour of G or FWho sits exactly between F and A?- a)B
- b)C
- c)E
- d)H
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions :
A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a square table facing the centre in such a way that four of them sit at four corners of the square while four sit in the middle of each of the flour sides.
(a) A sits second to right of F. F sits in the middle of one of the sides of the table
(b) G who does not sit at any of the corners of the table sits second to the right of D
(c) Only two people sit between D and B (taken from one side)
(d) C is not an immediate neighbour of G
(e) H is sits second to left of B
(f) E is not an immediate neighbour of G or F
Who sits exactly between F and A?
a)
B
b)
C
c)
E
d)
H
|
|
Om Desai answered |

If a gas of volume 6000cm3 and at a pressure of 100kPa is compressed quasi-statically ac-cording to PV2 = constant until the volume becomes 2000cm3, determine the work transfer from the system- a)-1.2KJ
- b)-1.2MJ
- c)1.2KJ
- d)1.2MJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a gas of volume 6000cm3 and at a pressure of 100kPa is compressed quasi-statically ac-cording to PV2 = constant until the volume becomes 2000cm3, determine the work transfer from the system
a)
-1.2KJ
b)
-1.2MJ
c)
1.2KJ
d)
1.2MJ
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
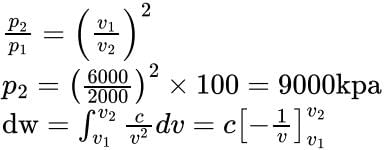
w = p1v1 − p2v2 = (100 × 6000 × 10
3 × 10−6 − 900 × 103 × 2000 × 10−6) = −1200j = −1.2kj
The steady flow energy equation:Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:- a)Nozzle
- b)Turbine
- c)Compressor
- d)Boiler
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The steady flow energy equation:
Q = m(h2 – h1) is applicable for:
a)
Nozzle
b)
Turbine
c)
Compressor
d)
Boiler

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
From Steady Flow Energy Equation (S.F.E.E.)
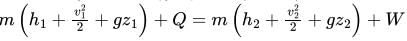
For Boiler: W=0, no work is done by the boiler,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected.
i.e. Q=m(h2−h1)
For Nozzle: Q=0, as the nozzle is perfectly insulated,
W=0, no work is done by nozzle, \(v_{1}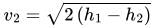
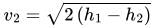
For Turbine: Q=0, for the adiabatic or perfectly insulated turbine,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected
i.e. W=m(h1−h2)
for Compressor: Q=0, for an adiabatic or perfectly insulated turbine,
Change in kinetic and potential energy is neglected
i.e. W = m (h2 − h1)
In a cam drive, it is essential to offset the axis of a follower to- a)Decrease the side thrust between the follower and guide
- b)Decrease the wear between follower and cam surface
- c)Take care of space limitation
- d)Reduce the cost
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a cam drive, it is essential to offset the axis of a follower to
a)
Decrease the side thrust between the follower and guide
b)
Decrease the wear between follower and cam surface
c)
Take care of space limitation
d)
Reduce the cost
|
|
Rajesh Khanna answered |
When the motion of the follower is along an axis away from the axis of the cam center, it is called an off-set follower.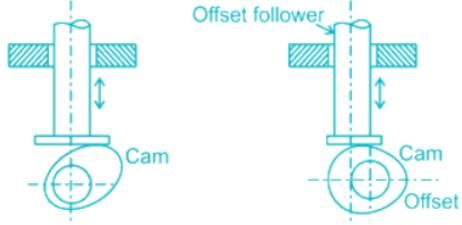

Follower with zero offsets and Follower with offset
If the follower movement is a displacement from the cam centre, then the follower is called an offset follower, offsetting results in reduced forces and stresses.
The offsetting eccentricity should be in the direction to improve force components tending to jam the translating follower in its bearing guide and decrease the wear between follower and cam surface.
Which one of the following is not a non-conventional source of energy?- a)Solar Energy
- b)Natural Gas
- c)Wind Energy
- d)Tidal Power
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a non-conventional source of energy?
a)
Solar Energy
b)
Natural Gas
c)
Wind Energy
d)
Tidal Power
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Natural Gas is a conventional source of energy and not a non-conventional source of energy
A cylinder of 0.12 m radius rotates concentrically inside a fixed hollow cylinder of 0.13 m radius. Both the cylinders are 0.3 m long. What will the viscosity of the liquid which fills the space between the cylinders if a torque of 0.88 Nm is required to maintain the angular velocity of 2π rad/s?- a)0.123
- b)0.216
- c)0.291
- d)0.397
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylinder of 0.12 m radius rotates concentrically inside a fixed hollow cylinder of 0.13 m radius. Both the cylinders are 0.3 m long. What will the viscosity of the liquid which fills the space between the cylinders if a torque of 0.88 Nm is required to maintain the angular velocity of 2π rad/s?
a)
0.123
b)
0.216
c)
0.291
d)
0.397

|
Naroj Boda answered |
Torque = Shear stress × Surface area × Torque arm

Transmission angle is the angle between- a)Output link and fixed link
- b)Input link and fixed link
- c)Input link and coupler
- d)Output link and coupler
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Transmission angle is the angle between
a)
Output link and fixed link
b)
Input link and fixed link
c)
Input link and coupler
d)
Output link and coupler

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
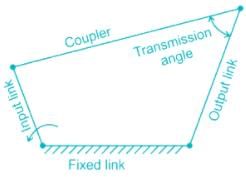
The transmission angle is the angle between the output link and the coupler. If the value of the transmission angle is zero, then the mechanism will lock or jam. If the transmission angle deviates from the 90O, then the torque on the output link decreases. So usually, the value of this angle is kept at more than 45O. The best mechanism is in which the transmission angle does not deviate much from the 90O.
During sensible heating of moist air, enthalpy- a)Increases
- b)Decreases
- c)Remains same
- d)Can increase or decrease
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During sensible heating of moist air, enthalpy
a)
Increases
b)
Decreases
c)
Remains same
d)
Can increase or decrease
|
|
Rajesh Khanna answered |
Sensible heating

During this process, the moisture content of air remains constant, and its temperature increases as it flows over a heating coil. The heat transfer rate during this process is given by:
Qh = ma(hB−ho) = macpm(TB−To)
where cpm is the humid specific heat (≈1.0216 kJ/kg dry air), tangent direction, and ma is the mass flow rate of dry air (kg/s).

Sensible heating process
on psychrometric chart
During sensible heating of moist air, enthalpy increases.
Sensible cooling:
During this process, the moisture content of air remains constant, but its temperature decreases as it flows over a cooling coil.
Sensible cooling process
on psychrometric chart
Figure out the odd point in the following- a)Proportional limit
- b)Elastic limit
- c)Yield point
- d)Fracture point
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure out the odd point in the following
a)
Proportional limit
b)
Elastic limit
c)
Yield point
d)
Fracture point
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
Proportional limit, Elastic limit, and yield point are points before metal failure, but fracture point is a point of failure where metal fractures.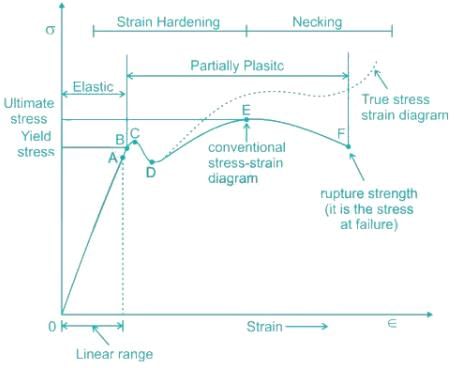

- So it is evident from the graph that the strain is proportional to stress or elongation is proportional to the load giving a straight-line relationship. This law of proportionality is valid up to a point A. Point A is known as the limit of proportionality or the proportionality limit.
- For a short period beyond point A, the material may still be elastic in the sense that the deformations are completely recovered when the load is removed. The limiting point B is termed as Elastic Limit.
- Beyond the elastic limit, plastic deformation occurs, and strains are not totally recoverable. There will be thus permanent deformation or permanent set when the load is removed. These two points are termed upper and lower yield points, respectively. The stress at the yield point is called the yield strength.
- A further increase in the load will cause marked deformation in the whole volume of the metal. The maximum load which the specimen can withstand without failure is called the load at the ultimate strength. The highest point ‘E' of the diagram corresponds to the ultimate strength of a material.
- Beyond point E, the bar begins to form the neck. The load falls from the maximum until a fracture occurs at F.
Separation of flow occurs when pressure gradient:- a)Tends to approach zero
- b)Becomes negative
- c)Changes abruptly
- d)Reduces to a value when vapour formation starts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Separation of flow occurs when pressure gradient:
a)
Tends to approach zero
b)
Becomes negative
c)
Changes abruptly
d)
Reduces to a value when vapour formation starts

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- Flow separation occurs when the boundary layer travels far enough against an adverse pressure gradient that the speed of the boundary layer relative to the object falls almost to zero.
- It has been observed that the flow is reversed in the vicinity of the wall under certain conditions.
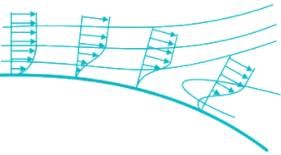
- A favourable pressure gradient is one in which the pressure decreases in the flow direction (i.e., dp/dx < 0)="" />
- It tends to overcome the slowing of fluid particles caused by friction in the boundary layer.
- This pressure gradient arises when the freestream velocity U increases with x, for example, in the converging flow field in a nozzle.
- On the other hand, an adverse pressure gradient is one in which pressure increases in the flow direction (i.e., dp/dx > 0)
- It will cause fluid particles in the boundary layer to slow down faster than that due to boundary-layer friction alone.
- If the adverse pressure gradient is severe enough, the fluid particles in the boundary layer will actually be brought to rest.
- When this occurs, the particles will be forced away from the body surface (a phenomenon called flow separation) as they make room for following particles, ultimately leading to a wake in which flow is turbulent.
Which of the following statements does NOT apply to the volumetric efficiency of a reciprocating air compressor?- a)It decreases with an increase in inlet temperature
- b)It increases with a decrease in pressure ratio
- c)It increases with a decrease in clearance ratio
- d)It decreases with an increase in clearance to stroke ratio
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements does NOT apply to the volumetric efficiency of a reciprocating air compressor?
a)
It decreases with an increase in inlet temperature
b)
It increases with a decrease in pressure ratio
c)
It increases with a decrease in clearance ratio
d)
It decreases with an increase in clearance to stroke ratio

|
Bank Exams India answered |
In actual compressors, a small clearance is left between the cylinder head and piston to accommodate the valves and to take care of thermal expansion and machining tolerances.
A large clearance volume results in low volumetric efficiency and hence large cylinder dimensions increase the contact area between the piston and cylinder and so, increases friction and work.
Volumetric efficiency is given by:
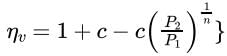
Where c = Clearance ratio.
P2/P1=Pressure;ratio
As the clearance ratio increases, the volumetric efficiency of the reciprocating compressor decreases as the pressure ratio increases.
A self-service store employs one cashier at its counter. Nine customers arrive on an average every 5 minutes, while the cashier can serve 10 customers in 5 minutes. Assuming poison distribution for arrival rate and exponential distribution for service rate, find the average number of customers in the queue.- a)6.7
- b)7.8
- c)9.6
- d)8.1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A self-service store employs one cashier at its counter. Nine customers arrive on an average every 5 minutes, while the cashier can serve 10 customers in 5 minutes. Assuming poison distribution for arrival rate and exponential distribution for service rate, find the average number of customers in the queue.
a)
6.7
b)
7.8
c)
9.6
d)
8.1
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
A thin cylindrical shell under internal pressure can fail along the- a)Longitudinal joint
- b)Circumferential joint
- c)Longitudinal as well as circumferential joint
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A thin cylindrical shell under internal pressure can fail along the
a)
Longitudinal joint
b)
Circumferential joint
c)
Longitudinal as well as circumferential joint
d)
None
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Type of failure: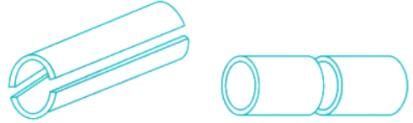
Such a component fails when subjected to an excessively high internal pressure. While it might fail by bursting along a path following the circumference of the cylinder. Under normal circumstances, it fails by bursting along a path parallel to the axis. This suggests that the hoop stress is significantly higher than the axial stress.
When a thin cylindrical shell is subjected to internal pressure, it is likely to fail in the following two ways:
1. It may fail along the longitudinal section (i.e., circumferentially), splitting the cylinder into two troughs
2. It may fail across the transverse section (i.e., longitudinally), splitting the cylinder into two cylindrical shells

Failure of a cylindrical shell along the longitudinal section and Failure of a cylindrical shell along the transverse section
The temperature strain in a bar is ________ to the change in temperature.- a)Indirectly proportional
- b)Directly proportional
- c)Independent
- d)Equal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The temperature strain in a bar is ________ to the change in temperature.
a)
Indirectly proportional
b)
Directly proportional
c)
Independent
d)
Equal
|
|
Rajesh Khanna answered |
When the temperature of the material changes, there will be a corresponding change in dimension.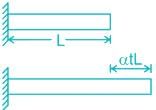
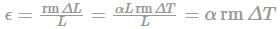
When a member is free to expand or contract due to the rise or fall of the temperature, no stress will be induced in the member.
But, if the material is constrained (i.e., the body is not allowed to expand or contract freely), change in length due to rise or fall of temperature is prevented, stresses are developed in the body, known as thermal stress.

The change in length (ΔL) due to change in temperature is found to be directly proportional to the total length of the specimen. Stresslength of the member (L) and to the change in temperature (ΔT).
ΔL ∝ L ΔT
ΔL = αLΔT
Where α is known as the coefficient of thermal expansion and is defined as the change in a unit length of the material due to a unit change in temperature.
Temperature strain: ϵ = change in length/original length
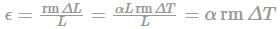
So thermal strain is directly proportional to the change in temperature.
Thermal Stress = Strain × E = αΔTE
The air standard Otto cycle consists of- a)Two constant volume and two isentropic processes
- b)Two constant pressure and two isentropic processes
- c)Two constant pressure and two constant volume processes
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The air standard Otto cycle consists of
a)
Two constant volume and two isentropic processes
b)
Two constant pressure and two isentropic processes
c)
Two constant pressure and two constant volume processes
d)
None of the above

|
Learners World answered |
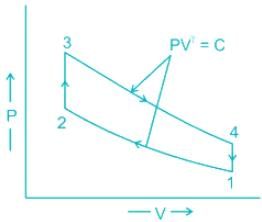
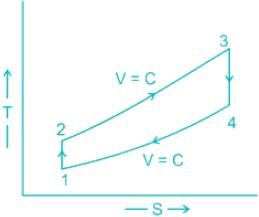
Air standard Otto cycle consists of two constant volume and two isentropic processes.
Process 1–2: An adiabatic (isentropic) compression
Process 2–3: A constant-volume heat addition
Process 3–4: An Adiabatic (isentropic) expansion
Process 4–1: A constant-volume heat rejection
For laminar flow in a pipe, average velocity is equal to:- a)2 Umax
- b)Umax
- c)0.5 Umax
- d)0.25 Umax
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For laminar flow in a pipe, average velocity is equal to:
a)
2 Umax
b)
Umax
c)
0.5 Umax
d)
0.25 Umax
|
|
Om Desai answered |
For a fully developed laminar viscous flow through a circular pipe, the maximum velocity is equal to twice the average velocity.
i.e. Vmax=2×Vavg
Vavg=0.5×Vmax
Point to be remembered:
For the fully developed laminar flow through the parallel plates, the maximum velocity is equal to the (3/2) times of the average velocity.
i.e. 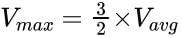
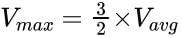
Select the option that is related to the third term in the same way as the second term is related to the first term.SECOND: CDENOS:: FIRST:?- a)FIRST
- b)FIRTS
- c)RFITS
- d)IRFTS
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the option that is related to the third term in the same way as the second term is related to the first term.
SECOND: CDENOS:: FIRST:?
a)
FIRST
b)
FIRTS
c)
RFITS
d)
IRFTS
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Given the first term SECOND and the second term is CDENOS.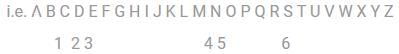

Here, the alphabets of the given second term are arranged in alphabetical order.
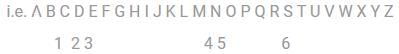
SECOND → CDENOS
Similarly, the third term FIRST will be written as

FIRST → FIRST (since all the alphabets are already in alphabetical order)
Hence, “FIRST” is the correct answer.
Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of:- a)Absolute viscosity to density of liquid
- b)Density of liquid to absolute viscosity
- c)Mass of liquid to absolute viscosity
- d)Absolute viscosity of the mass of the liquid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of:
a)
Absolute viscosity to density of liquid
b)
Density of liquid to absolute viscosity
c)
Mass of liquid to absolute viscosity
d)
Absolute viscosity of the mass of the liquid
|
|
Prem Prakash answered |
Kinematic viscosity is defined as
v=u/p
v=u/p
The design of thin cylindrical shells is based on- a)Radial stress
- b)Hoop stress
- c)Longitudinal stress
- d)Arithmetic mean of the hoop and the longitudinal stress
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The design of thin cylindrical shells is based on
a)
Radial stress
b)
Hoop stress
c)
Longitudinal stress
d)
Arithmetic mean of the hoop and the longitudinal stress

|
Learners World answered |
The wall of a cylindrical shell subjected to internal pressure has to withstand tensile stresses of the following two types:
Circumferential or hoop stress, and (b) Longitudinal stress
Longitudinal stress: 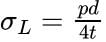
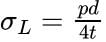
Hoop stress: 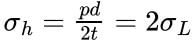
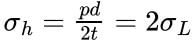
We see that the longitudinal stress is half of the circumferential or hoop stress. Therefore, the design of a pressure vessel must be based on the maximum stress i.e., hoop stress.
A circular bar 20 mm in diameter and 200 mm long is subjected to a force of 20 kN. Find the strain in the bar if the value of E = 80 GPa.- a)7.9 × 10-2
- b)7.9 × 10-4
- c)3.2 × 10-2
- d)3.2 × 10-3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A circular bar 20 mm in diameter and 200 mm long is subjected to a force of 20 kN. Find the strain in the bar if the value of E = 80 GPa.
a)
7.9 × 10-2
b)
7.9 × 10-4
c)
3.2 × 10-2
d)
3.2 × 10-3
|
|
Om Desai answered |
E = 80 GPa = 80 × 103 MPa = 80 × 103 N/mm2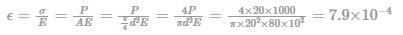
Stress = Load/Area
Strain = Stress/E
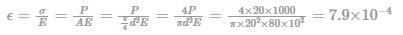
Lathe bed is usually made of_______.- a)Structural steel
- b)Stainless steel
- c)Cast iron
- d)Mild steel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lathe bed is usually made of_______.
a)
Structural steel
b)
Stainless steel
c)
Cast iron
d)
Mild steel

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Lathe is a machine tool that holds the job in between the centre and base and rotates the job, and rotates the job on its own axis.
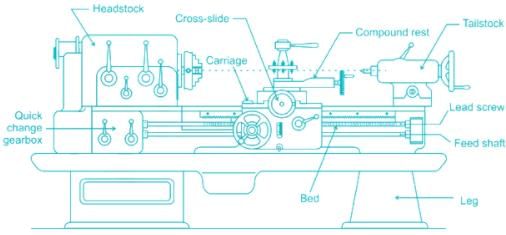
Main parts of Lathe:


Direction: In the following question, select the related words from the given alternatives.B4: D16:: F36:?- a)H49
- b)G49
- c)H64
- d)H68
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following question, select the related words from the given alternatives.
B4: D16:: F36:?
a)
H49
b)
G49
c)
H64
d)
H68
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Relationship between B4 and D16:
To understand the relationship between B4 and D16, we need to look at the pattern or rule that governs the transformation between the two.
First, let's break down the given values:
- B4 can be written as B * 4 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 = 16
- D16 can be written as D * 16 = 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 = 256
Pattern or Rule:
Based on the given values, it appears that the pattern or rule involves squaring the letter value and multiplying it by the number following the letter.
Applying the pattern to F36:
To find the related word for F36, we need to apply the same pattern or rule that we observed from the given values.
- F36 can be written as F * 36 = 6 * 6 * 6 * 6 = 1296
Matching with the given options:
Now let's check which of the given options matches the calculated value of 1296.
a) H49: H * 49 = 8 * 8 * 8 * 8 = 4096
b) G49: G * 49 = 7 * 7 * 7 * 7 = 2401
c) H64: H * 64 = 8 * 8 * 8 * 8 = 4096
d) H68: H * 68 = 8 * 8 * 8 * 8 = 4096
Out of the given options, only option C (H64) matches the calculated value of 1296. Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Conclusion:
The relationship between B4 and D16 is determined by squaring the letter value and multiplying it by the number following the letter. Applying the same pattern to F36, we find that the related word is H64.
To understand the relationship between B4 and D16, we need to look at the pattern or rule that governs the transformation between the two.
First, let's break down the given values:
- B4 can be written as B * 4 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 = 16
- D16 can be written as D * 16 = 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 = 256
Pattern or Rule:
Based on the given values, it appears that the pattern or rule involves squaring the letter value and multiplying it by the number following the letter.
Applying the pattern to F36:
To find the related word for F36, we need to apply the same pattern or rule that we observed from the given values.
- F36 can be written as F * 36 = 6 * 6 * 6 * 6 = 1296
Matching with the given options:
Now let's check which of the given options matches the calculated value of 1296.
a) H49: H * 49 = 8 * 8 * 8 * 8 = 4096
b) G49: G * 49 = 7 * 7 * 7 * 7 = 2401
c) H64: H * 64 = 8 * 8 * 8 * 8 = 4096
d) H68: H * 68 = 8 * 8 * 8 * 8 = 4096
Out of the given options, only option C (H64) matches the calculated value of 1296. Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Conclusion:
The relationship between B4 and D16 is determined by squaring the letter value and multiplying it by the number following the letter. Applying the same pattern to F36, we find that the related word is H64.
According to the linear law of machine, when P is the effort and w is the load, then.- a)P = mw + c
- b)P = pmc
- c)P = mw - c
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the linear law of machine, when P is the effort and w is the load, then.
a)
P = mw + c
b)
P = pmc
c)
P = mw - c
d)
None of these
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The law of the machine is (where P = Effort applied to lift the load, m = A constant which is equal to the slope of the line, W = Load lifted, and C = Another constant which represents the mechanical friction.)
A simply supported beam of span (l) carries a point load (W) at the centre of the beam. The bending moment diagram will be- a)parabola with maximum ordinate at the centre of the beam
- b)parabola with maximum ordinate at one end of the beam
- c)triangle with maximum ordinate at the centre of the beam
- d)triangle with maximum ordinate at one end of the beam
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A simply supported beam of span (l) carries a point load (W) at the centre of the beam. The bending moment diagram will be
a)
parabola with maximum ordinate at the centre of the beam
b)
parabola with maximum ordinate at one end of the beam
c)
triangle with maximum ordinate at the centre of the beam
d)
triangle with maximum ordinate at one end of the beam

|
Bank Exams India answered |
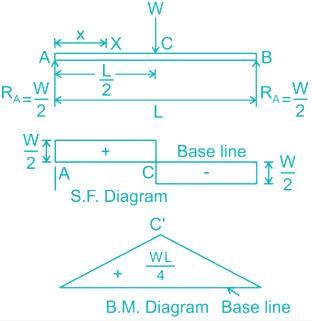
It may be observed that at the point of application of load, there is an abrupt change in the shear force; at this point, the B.M is maximum.
The bending moment diagram will be a triangle with maximum ordinate at the centre of the beam.
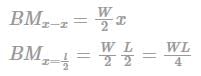
In an engine, the fluctuation of speed is ± 2% of mean speed. Then coefficient of fluctuation of speed is- a)0.01
- b)0.03
- c)0.05
- d)0.04
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an engine, the fluctuation of speed is ± 2% of mean speed. Then coefficient of fluctuation of speed is
a)
0.01
b)
0.03
c)
0.05
d)
0.04
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Concept:
The difference between the maximum and minimum speeds during a cycle is called the maximum fluctuation of speed. The ratio of the maximum fluctuation of speed to the mean speed is called the coefficient of fluctuation of speed (Cs).
Calculation:
ωmax – ωmin = ± 2% of ωmean
⇒ ωmax – ωmin = 4% of ωmean⇒ ωmax – ωmin = 0.04 ωmean
⇒ 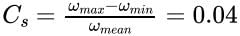
During the colonial period, British capital was mainly invested in:- a)Infrastructure
- b)Industry
- c)Agriculture
- d)Services
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During the colonial period, British capital was mainly invested in:
a)
Infrastructure
b)
Industry
c)
Agriculture
d)
Services
|
|
Om Desai answered |
During the British Raj(from 1858 to 1947), the Indian economy essentially remained stagnant, growing at the same rate (1.2%) as the population. India experienced deindustrialization during this period. After 1857, the inflow of British capital and enterprise into India rose to an appreciable extent. The bulk of the imperialist capital was mainly invested in the externally oriented sectors like plantations, jute, and coal, and the trading and banking infrastructure established to service this sector. This ultimately led to the perpetuation of the subordination of Indian capital to the British capital with the ulterior motive of feeding Britain and other countries with cheap raw materials and food.
An orifice meter, having an orifice of diameter ‘d’ is fitted in a pipe of diameter D. For this orifice meter, what is the coefficient of discharge Cd?- a)A function of Reynolds number only
- b)A function of d/D only
- c)A function of d/D and Reynolds number
- d)Independent of d/D and Reynolds number
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An orifice meter, having an orifice of diameter ‘d’ is fitted in a pipe of diameter D. For this orifice meter, what is the coefficient of discharge Cd?
a)
A function of Reynolds number only
b)
A function of d/D only
c)
A function of d/D and Reynolds number
d)
Independent of d/D and Reynolds number
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |
An orifice meter provides a simpler and cheaper arrangement for the measurement of flow through a pipe. An orifice meter is essentially a thin circular plate with a sharp-edged concentric circular hole in it.
Cd is defined as the ratio of the actual flow and the ideal flow and is always less than one.
For the orifice meter, the coefficient of discharge Cd depends on the shape of the nozzle, the ratio of pipe to nozzle diameter, and the Reynolds number of the flow.
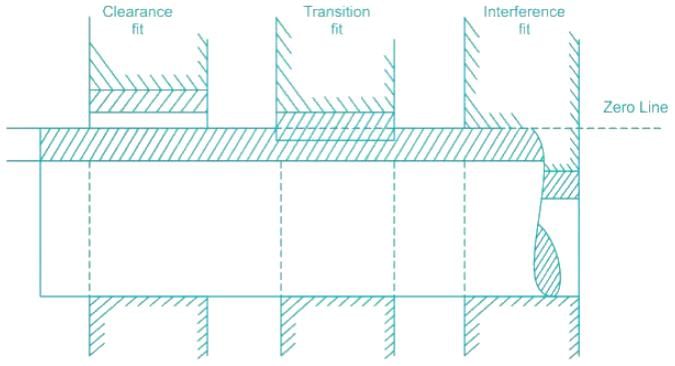
In limits and fits system, basic shaft system is one whose- a)Lower deviation is zero
- b)Upper deviation is zero
- c)Minimum clearance is zero
- d)Maximum clearance is zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In limits and fits system, basic shaft system is one whose
a)
Lower deviation is zero
b)
Upper deviation is zero
c)
Minimum clearance is zero
d)
Maximum clearance is zero
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Hole basis system: The hole is kept as a constant member (i.e. when the lower deviation of the hole is zero).
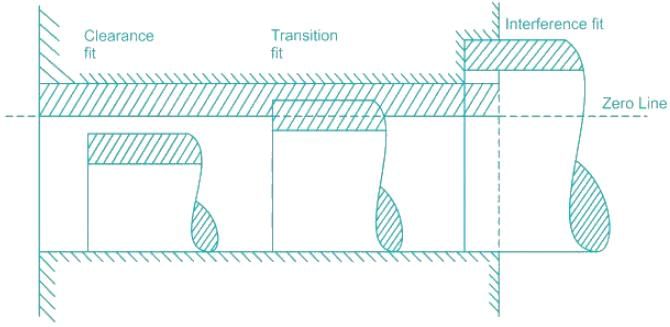
Shaft basis system: When the shaft is kept as a constant member (i.e. when the upper deviation of the shaft is zero).
The deflection of a simply supported rectangular beam is:- a)directly proportional to the cube of its length
- b)inversely proportional to the cube of its depth
- c)inversely proportional to its width
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The deflection of a simply supported rectangular beam is:
a)
directly proportional to the cube of its length
b)
inversely proportional to the cube of its depth
c)
inversely proportional to its width
d)
all of the above
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Deflection of simply supported beam
Concentrated load P at the center, 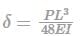
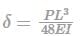
Uniformly distributed load w (N/m), 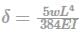
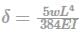
I = bd3/12
In a thermocouple, the potential between the two functions is due to the temperature gradient along the conductors in the circuit. This effect is named as- a)Peltiers effect
- b)Thomson's effect
- c)Seebak effect
- d)Maxwell's effect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a thermocouple, the potential between the two functions is due to the temperature gradient along the conductors in the circuit. This effect is named as
a)
Peltiers effect
b)
Thomson's effect
c)
Seebak effect
d)
Maxwell's effect
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Thomson effect, the evolution or absorption of heat when an electric current passes through a circuit composed of a single material that has a temperature difference along its length. This heat transfer is superimposed on the common production of heat associated with the electrical resistance to currents in conductors.
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given by- a)dp/dz = g
- b)dp/dz = 0
- c)dp/dz = ρg
- d)dp/dz = −ρg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given by
a)
dp/dz = g
b)
dp/dz = 0
c)
dp/dz = ρg
d)
dp/dz = −ρg

|
Bank Exams India answered |
The pressure at any point in a fluid at rest is obtained by the Hydrostatic Law, which states that the rate of increase of pressure in a vertically downward direction must be equal to the specific weight of the fluid at that point.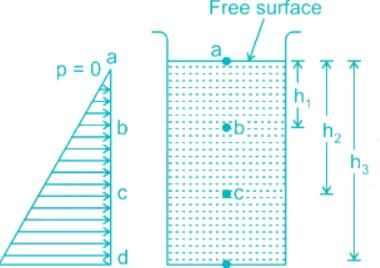

p = ρgh
Pressure distribution profile
dp/dz = -ω = -pg
dp = -ω.dz
It indicates that a negative pressure gradient exists upward along any vertical.
Thus, the pressure decreases in the upward direction and increases in the downward direction with a magnitude equal to a specific weight.
Find out the wrong term: 3, 2, 8, 9, 13, 22, 18, 32, 23, 42- a)8
- b)9
- c)13
- d)22
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the wrong term: 3, 2, 8, 9, 13, 22, 18, 32, 23, 42
a)
8
b)
9
c)
13
d)
22
|
|
Rajesh Khanna answered |
The given sequence is a combination of two series
I: 3, 8, 13, 18, 23 and
II: 2, 9, 22, 32, 42
The pattern in I: is + 5, and the pattern in II: is + 10
So, in II, 9 is wrong and must be replaced by (2 + 10), i.e., 12.
A submerged body will be in stable equilibrium if the- a)Centre of buoyancy B is below the centre of gravity G
- b)Centre of buoyancy B coincides with G
- c)Centre of buoyancy B is above the metacentre M
- d)Centre of buoyancy B is above G
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A submerged body will be in stable equilibrium if the
a)
Centre of buoyancy B is below the centre of gravity G
b)
Centre of buoyancy B coincides with G
c)
Centre of buoyancy B is above the metacentre M
d)
Centre of buoyancy B is above G
|
|
Om Desai answered |
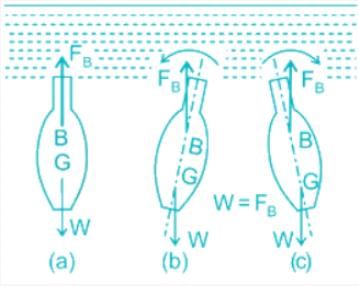
Stability of unconstrained Submerged Bodies in Fluid:
The equilibrium of a body submerged in a liquid requires that the weight of the body acting through its centre of gravity should be colinear with an equal hydrostatic lift acting through the centre of buoyancy.
- Stable Equilibrium: If the body returns to its original position by retaining the originally vertical axis as vertical
- Unstable Equilibrium: If the body does not return to its original position but moves further from it
- Neutral Equilibrium: If the body neither returns to its original position nor increases its displacement further, it will simply adopt its new position.
The relative position of the centre of gravity (G) and centre of buoyancy (B) of a body determines the stability of a submerged body.
Stable Equilibrium: B is above G
Free surface
A Submerged body in Stable Equilibrium
- Unstable Equilibrium: B is below G
The positions of first and the fourth letters of the word POUNDS are interchanged, similarly, the positions of second and fifth letters and third and sixth letters are interchanged. In the new arrangement thus formed, how many letters are there between the alphabet which is third from the right and the alphabet which is third from the left, in the English alphabetical order?- a)None
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The positions of first and the fourth letters of the word POUNDS are interchanged, similarly, the positions of second and fifth letters and third and sixth letters are interchanged. In the new arrangement thus formed, how many letters are there between the alphabet which is third from the right and the alphabet which is third from the left, in the English alphabetical order?
a)
None
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Given word = POUNDS
After interchanged, new word =NDSPOU
Hence, two letters (Q, R) are between the alphabet, third from the right (P) and third from the left (S).
An annealed copper strip of 228mm wide and 25mm thick is rolled to a thickness of 20mm in one pass. The roll radius is 300mm, and the rolls rotate at l00rpm. Then the power required in this operation is (assume two rolls system)- a)1340kW
- b)1220kW
- c)1760kW
- d)1010W
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An annealed copper strip of 228mm wide and 25mm thick is rolled to a thickness of 20mm in one pass. The roll radius is 300mm, and the rolls rotate at l00rpm. Then the power required in this operation is (assume two rolls system)
a)
1340kW
b)
1220kW
c)
1760kW
d)
1010W
|
|
Aisha Gupta answered |

A concentrated load P acts on a simply supported beam of span L at a distance L/4 from the left end. The bending moment at the point of application of load is given by:- a)PL/4
- b)3PL/9
- c)3PL/16
- d)PL/16
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A concentrated load P acts on a simply supported beam of span L at a distance L/4 from the left end. The bending moment at the point of application of load is given by:
a)
PL/4
b)
3PL/9
c)
3PL/16
d)
PL/16
|
|
Om Desai answered |
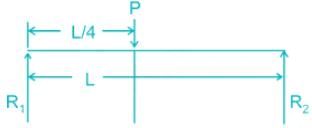
R1 + R2 = P
R2 × L = P × L/4
R2 = P/4
R1 = 3P/4
Bending moment at the point of applied load:
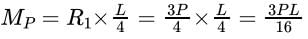
A for cylinder engine running at 1200rpm delivers 20kW. The average torque when one cylinder was cut is 110Nm. If the calorific value of the fuel is 43MJ/kg and the engine uses 360gms of gasoline per kWh. Then the mass of fuel consumption in kg/sec is- a)1×10−3kg/s
- b)2×10−3kg/s
- c)3×10−3kg/s
- d)4×10−3kg/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A for cylinder engine running at 1200rpm delivers 20kW. The average torque when one cylinder was cut is 110Nm. If the calorific value of the fuel is 43MJ/kg and the engine uses 360gms of gasoline per kWh. Then the mass of fuel consumption in kg/sec is
a)
1×10−3kg/s
b)
2×10−3kg/s
c)
3×10−3kg/s
d)
4×10−3kg/s

|
Bank Exams India answered |
Average BP for 3 cylinder
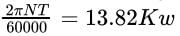
Average IP with one cylinder 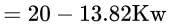
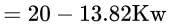
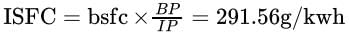
Fuel consumption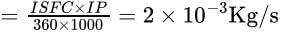
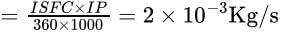
The curl of a given velocity field (∇ x -V) indicates the rate of- a)Increase or decrease of flow at a point
- b)Twisting of the lines of flow
- c)Deformation
- d)Translation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The curl of a given velocity field (∇ x -V) indicates the rate of
a)
Increase or decrease of flow at a point
b)
Twisting of the lines of flow
c)
Deformation
d)
Translation
|
|
Rajesh Khanna answered |
The curl indicates the rate of deformation.
The angular velocity vector is defined as:
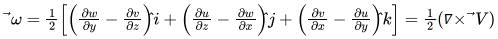
The vorticity of a flow field is defined as:
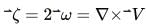
Rate of rotation of fluid element ABCD about the ?-axis is defined as the average of the angular speeds of two mutually perpendicular lines AB (dx element) and AD (dy element):
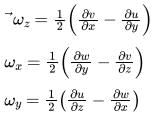
When inspection doors on the walls of boilers are opened, the flame does not leap out because- a)These holes are small
- b)Pressure inside is negative
- c)Flame always travels in the direction of flow
- d)These holes are located beyond the furnace
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When inspection doors on the walls of boilers are opened, the flame does not leap out because
a)
These holes are small
b)
Pressure inside is negative
c)
Flame always travels in the direction of flow
d)
These holes are located beyond the furnace
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The flame does not leap out during the opening of the inspection door because there is negative pressure in the combustion area. Negative pressure is achieved in balanced draft boilers by using forced draft fans to force air into the boiler (pressuring it) and Induced draft fans to remove air from the boilers to create negative pressure.
Which of the following a boiler accessory- a)ejector
- b)Superheater
- c)Pressure gauge
- d)Air preheater
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following a boiler accessory
a)
ejector
b)
Superheater
c)
Pressure gauge
d)
Air preheater
|
|
Tanvi Shah answered |
The important boiler accessories are economiser, air preheater and superheater, feed pump, ejector, steam strap, etc.
Which material has the highest value of poisson's ratio?- a)Elastic Rubber
- b)Wood
- c)Copper
- d)Steel
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which material has the highest value of poisson's ratio?
a)
Elastic Rubber
b)
Wood
c)
Copper
d)
Steel
|
|
Rajesh Khanna answered |
Elastic Rubber: 0.5
Wood: Because wood is orthotropic, 12 constants are required to describe elastic behaviour: 3 moduli of elasticity, 3 moduli of rigidity, and 6 Poisson’s ratios (vary from 0.02 to 0.47). These elastic constants vary within and among species and with moisture content and specific gravity.
Copper: 0.33
Steel: 0.27 - 0.30
The maximum shear stress in a shaft, of diameter ‘d’ subjected to torsion ‘T,’ is given by:- a)16T/πd3
- b)up>(B) 64T/πd3
- c)up>(C) 8T/πd3
- d)up>(D) 32T/πd3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum shear stress in a shaft, of diameter ‘d’ subjected to torsion ‘T,’ is given by:
a)
16T/πd3
b)
up>(B) 64T/πd3
c)
up>(C) 8T/πd3
d)
up>(D) 32T/πd3
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Torsion Equation:
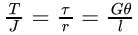
Where T is torque applied on the shaft in N−m
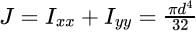 is the polar moment of inertia m4
is the polar moment of inertia m4T is shear stress in MPa, r is the radius of the shaft in m, G shear modulus or modulus of rigidity in MPa
θ is the angle of twist in radian, and 1 is the length of the shaft in m.Tmaxoccurs at rmax
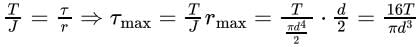
Find the odd number/letters / word from the given alternative:- a)27
- b)35
- c)18
- d)9
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the odd number/letters / word from the given alternative:
a)
27
b)
35
c)
18
d)
9
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
Explanation:
To determine the odd number/letters/word from the given alternatives, we need to identify the pattern or rule that is being followed by the options. Let's analyze each option:
a) 27: This is an odd number. It can be expressed as 3 * 3 * 3, which is the cube of 3.
b) 35: This is an odd number. There doesn't appear to be any specific pattern or rule.
c) 18: This is an even number. It can be expressed as 2 * 3 * 3, which is the product of 2 and the square of 3.
d) 9: This is an odd number. It can be expressed as 3 * 3, which is the square of 3.
From the given options, the only odd number is 35. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Summary:
- Option 'A' (27) is an odd number.
- Option 'B' (35) is an odd number.
- Option 'C' (18) is an even number.
- Option 'D' (9) is an odd number.
- The odd number/letters/word among the given alternatives is option 'B' (35).
To determine the odd number/letters/word from the given alternatives, we need to identify the pattern or rule that is being followed by the options. Let's analyze each option:
a) 27: This is an odd number. It can be expressed as 3 * 3 * 3, which is the cube of 3.
b) 35: This is an odd number. There doesn't appear to be any specific pattern or rule.
c) 18: This is an even number. It can be expressed as 2 * 3 * 3, which is the product of 2 and the square of 3.
d) 9: This is an odd number. It can be expressed as 3 * 3, which is the square of 3.
From the given options, the only odd number is 35. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Summary:
- Option 'A' (27) is an odd number.
- Option 'B' (35) is an odd number.
- Option 'C' (18) is an even number.
- Option 'D' (9) is an odd number.
- The odd number/letters/word among the given alternatives is option 'B' (35).
A long fin extends from the external surface of a cylinder through which hot fluid flows; the excess temperature at the tip of the fin would be- a)Zero
- b)Ambient temperature
- c)higher than ambient temperature
- d)Lower than ambient temperature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A long fin extends from the external surface of a cylinder through which hot fluid flows; the excess temperature at the tip of the fin would be
a)
Zero
b)
Ambient temperature
c)
higher than ambient temperature
d)
Lower than ambient temperature
|
|
Rahul Mandal answered |
Answer should be ambient temperature ...
there should no heat drop at temperature which is less than ambient temperature .
there should no heat drop at temperature which is less than ambient temperature .
Identify the correct arrangement (in ascending order) of the hardness of structures of steel while undergoing a heat treatment process.- a)Martensite < fine="" pearlite="" />< coarse="" pearlite="" />< />
- b)Fine Pearlite < martensite="" />< spherodite="" />< coarse="" />
- c)Martensite < coarse="" pearlite="" />< fine="" pearlite="" />< />
- d)Spherodite < coarse="" pearlite="" />< fine="" pearlite="" />< />
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct arrangement (in ascending order) of the hardness of structures of steel while undergoing a heat treatment process.
a)
Martensite < fine="" pearlite="" />< coarse="" pearlite="" />< />
b)
Fine Pearlite < martensite="" />< spherodite="" />< coarse="" />
c)
Martensite < coarse="" pearlite="" />< fine="" pearlite="" />< />
d)
Spherodite < coarse="" pearlite="" />< fine="" pearlite="" />< />

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Different phases of steel:
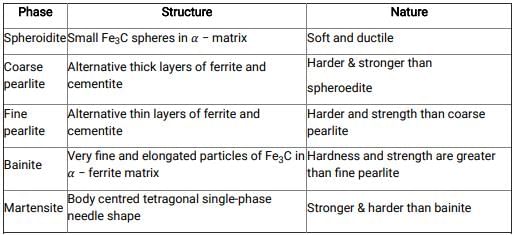
Ascending order of hardness:
Spheroidite < coarse="" pearlite="" />< fine="" pearlite="" />< />
To replace a pipe of diameter D by n parallel pipes of diameter d, the formula used is- a)d = D/n
- b)d = D/n1/2
- c)d = D/n3/2
- d)d = D/n2/5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To replace a pipe of diameter D by n parallel pipes of diameter d, the formula used is
a)
d = D/n
b)
d = D/n1/2
c)
d = D/n3/2
d)
d = D/n2/5
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The main pipeline divides into two or more parallel pipes, which again join together downstream.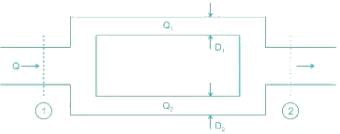
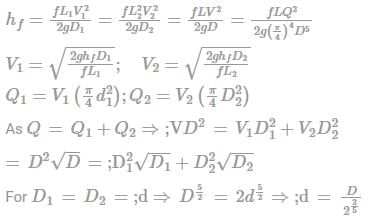

Q = Q1 + Q2
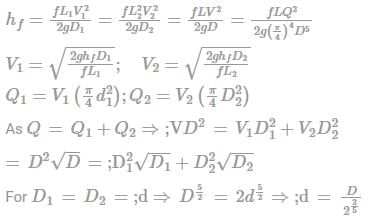
For n parallel pipes of diameter d, d = D/n2/5
Chapter doubts & questions for Full Mock Tests Series - SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Full Mock Tests Series - SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2026
3 videos|1 docs|55 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup