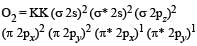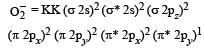All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure for NEET Exam
Bond order of 1.5 is shown by : [2012] - a)O2+
- b)O2-
- c)O22+
- d)O2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond order of 1.5 is shown by : [2012]
a)
O2+
b)
O2-
c)
O22+
d)
O2
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
N₂=N+N = 7e⁻+7e⁻ = 14e- which has bond order =3
O₂=8e⁻+8e⁻ = 16e⁻ which has bond order = 2
O₂⁺=8e⁻+8e⁻ - 1e⁻ = 15e⁻ which has bond order= 2.5
O₂⁻ = 8e⁻ +8e⁻ +1e⁻ =17 e⁻ which has bond order=1.5
So option B is correct .
Which of the following compounds has a 3-centre bond?[1996]- a)Diborane
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Boron trifluroide
- d)Ammonia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds has a 3-centre bond?[1996]
a)
Diborane
b)
Carbon dioxide
c)
Boron trifluroide
d)
Ammonia

|
Krish Saha answered |
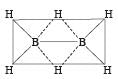
The bond represented by dots form the 3-centred electron pair bond. The idea of three centred electron pair bond B–H–B bridges is necessitated because diborane does not have sufficient electrons to form normal covalent bonds. It has only 12 electrons instead of 14 required to give simple ethane like structure for diborane.
N2 and O2 are converted into monocations, N2+ and O2+ respectively. Which of the following statements is wrong ? [1997]- a)In N2, the N—N bond weakens
- b)In O2, the O—O bond order increases
- c)In O2, paramagnetism decreases
- d)N2+ becomes diamagnetic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
N2 and O2 are converted into monocations, N2+ and O2+ respectively. Which of the following statements is wrong ? [1997]
a)
In N2, the N—N bond weakens
b)
In O2, the O—O bond order increases
c)
In O2, paramagnetism decreases
d)
N2+ becomes diamagnetic

|
Rohan Unni answered |
We know that in O2 bond, the order is 2 and in O2– bond, the order is 1.5. Therefore the wrong statements is (b)
Which of the following has pπ – dπ bonding?- a)NO3–
- b)SO32– [2002]
- c)BO33–
- d)CO32–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has pπ – dπ bonding?
a)
NO3–
b)
SO32– [2002]
c)
BO33–
d)
CO32–

|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
Answer is b bcoz Sulphur has d orbital...
In BrF3 molecule, the lone pairs occupy equatorial positions to minimize [2004]- a)lone pair - bond pair repulsion only
- b)bond pair - bond pair repulsion only
- c)lone pair - lone pair repulsion and lone pair -bond pair repulsion
- d)lone pair - lone pair repulsion only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In BrF3 molecule, the lone pairs occupy equatorial positions to minimize [2004]
a)
lone pair - bond pair repulsion only
b)
bond pair - bond pair repulsion only
c)
lone pair - lone pair repulsion and lone pair -bond pair repulsion
d)
lone pair - lone pair repulsion only

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
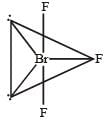
In BrF3, both bond pairs as well as lone pairs of electrons are present. Due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons (lp) in the valence shell, the bond angle is contracted and the molecule takes the T-shape. This is due to greater repulsion between two lone pairs or between a lone pair and a bond pair than between the two bond pairs.
Which one of the following arrangements represents the increasing bond orders of the given species? [1999]- a)NO+ < NO < NO– < O2–
- b)O2– < NO– < NO <NO+
- c)NO– < O2– < NO < NO+
- d)NO < NO+ < O2– < NO–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements represents the increasing bond orders of the given species? [1999]
a)
NO+ < NO < NO– < O2–
b)
O2– < NO– < NO <NO+
c)
NO– < O2– < NO < NO+
d)
NO < NO+ < O2– < NO–
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |

Bond order of NO+ =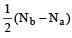
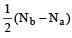
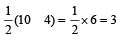
Similarly, Bond order of NO = 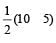
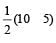
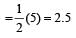
Bond order of NO– 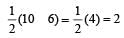
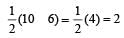
Bon d order of 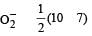
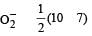
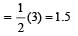
By above calculation, we get Decreasing bond order NO+ > NO > NO– > O-2
In a regular octahedral molecule, MX6 the number of X - M - X bonds at 180° is [2004]- a)three
- b)two
- c)six
- d)four
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a regular octahedral molecule, MX6 the number of X - M - X bonds at 180° is [2004]
a)
three
b)
two
c)
six
d)
four
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
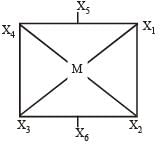
Thus here bond angles between X4 - M - X2 = 180°
X1 - M - X3 = 180°
X5 - M - X6 = 180°
X1 - M - X3 = 180°
X5 - M - X6 = 180°
The relationship between the dissociation energy of N2 and N2+ is : [2000]- a)Dissociation energy of N2+ > dissociation energy of N2
- b)Dissociation energy of N2 = dissociation energy of N2+
- c)Dissociation energy of N2 > dissociation energy of N2+
- d)Dissociation energy of N2 can either be lower or higher than the dissociation energy of N2+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The relationship between the dissociation energy of N2 and N2+ is : [2000]
a)
Dissociation energy of N2+ > dissociation energy of N2
b)
Dissociation energy of N2 = dissociation energy of N2+
c)
Dissociation energy of N2 > dissociation energy of N2+
d)
Dissociation energy of N2 can either be lower or higher than the dissociation energy of N2+

|
Mahi Shah answered |
Dissociation energy of any molecules depends upon bond order. Bond order in N2 molecule is 3 while bond order in N+2 is 2.5.
Further we know that more the Bond order, more is the stability and more is the BDE.
Further we know that more the Bond order, more is the stability and more is the BDE.
Which of the following bonds will be most polar?- a)N – Cl
- b)O – F [1992]
- c)N – F
- d)N – N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following bonds will be most polar?
a)
N – Cl
b)
O – F [1992]
c)
N – F
d)
N – N

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Polarity of the bond depends upon the electronegativity difference of the two atoms forming the bond. Greater the electronegativity difference, more is the polarity of the bond.

As the electronegativity difference between N and F is maximum hence this bond is most polar.
Which of the following would have a permanent dipolemoment? [2005]- a)SiF4
- b)SF4
- c)XeF4
- d)BF3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following would have a permanent dipolemoment? [2005]
a)
SiF4
b)
SF4
c)
XeF4
d)
BF3

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
SF4 has permanent dipole moment.
SF4 has sp3d hybridization and see saw shape (irregular geometry).
SF4 has sp3d hybridization and see saw shape (irregular geometry).
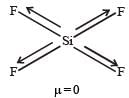
Whereas XeF4 shows squre planar geometry SiF4 has tetrahedral shape and BF3 has Trigonal planar shape. All these are symmetric molecules. Hence μ ≠ 0.
The BCl3 is a planar molecule whereas NCl3 is pyramidal because [1995]- a)B-Cl bond is more polar than N-Cl bond
- b)N-Cl bond is more covalent than B-Cl bond
- c)nitrogen atom is smaller than boron atom
- d)BCl3 has no lone pair but NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The BCl3 is a planar molecule whereas NCl3 is pyramidal because [1995]
a)
B-Cl bond is more polar than N-Cl bond
b)
N-Cl bond is more covalent than B-Cl bond
c)
nitrogen atom is smaller than boron atom
d)
BCl3 has no lone pair but NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
As there is no lone pair on boron in BCl3 therefore no repulsion takes place. But there is a lone pair on nitrogen in NCl3. Therefore repulsion takes place. Thus BCl3 is planar molecule but NCl3 is a pyramidal molecule.
The angle between the overlapping of one s-orbital and one p-orbital is [1988]- a)180°
- b)120°
- c)109°28'
- d)120°, 60°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle between the overlapping of one s-orbital and one p-orbital is [1988]
a)
180°
b)
120°
c)
109°28'
d)
120°, 60°
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
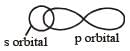
The overlap between s- and p-orbitals occurs along internuclear axis and hence the angle is 180°.
Which structure is linear ? [1992]- a)SO2
- b)CO2
- c)CO32-
- d)SO24-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure is linear ? [1992]
a)
SO2
b)
CO2
c)
CO32-
d)
SO24-

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
CO2 has sp-hybridization and is linear. SO2 and CO2-3 are planar (sp2) while SO2-4 is tetrahedral (sp3).
H2O is polar, whereas BeF2 is not. It is because [2004]- a)the electronegativity of F is greater than that of O
- b)H2O involves hydrogen bonding wher eas BeF2 is a discrete molecule
- c)H2O is linear and BeF2 is angular
- d)H2O is angular and BeF2 is linear
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
H2O is polar, whereas BeF2 is not. It is because [2004]
a)
the electronegativity of F is greater than that of O
b)
H2O involves hydrogen bonding wher eas BeF2 is a discrete molecule
c)
H2O is linear and BeF2 is angular
d)
H2O is angular and BeF2 is linear
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
In a linear symmetrical molecule like BeF2, the bond angle between three atoms is 180°, hence the polarity due to one bond is cancelled by the equal polarity due to other bond, while it is not so in angular molecules, like H2O
Four diatomic species are listed below in different sequences. Which of these presents the correct order of their increasing bond order ? [2008]- a)
- b)
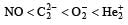
- c)
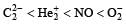
- d)
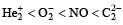
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Four diatomic species are listed below in different sequences. Which of these presents the correct order of their increasing bond order ? [2008]
a)
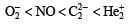
b)
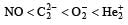
c)
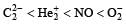
d)
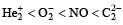
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Calculating the bond order of various species.
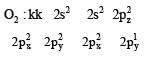

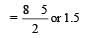
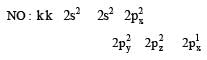
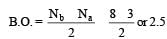
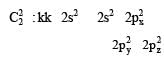
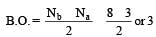
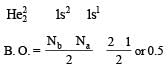
From these values we find the correct order of increasing bond order is
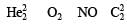
Which of the following species has a linear shape ?- a)SO2
- b)NO2+ [2006]
- c)O3
- d)NO2–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following species has a linear shape ?
a)
SO2
b)
NO2+ [2006]
c)
O3
d)
NO2–

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
NO2+ will have linear shape as it will have sp hybridisation.
Among the following orbital bonds, the angle is minimum between [1994]- a)sp3 bonds
- b)px and py orbitals
- c)H – O – H in water
- d)sp bonds.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following orbital bonds, the angle is minimum between [1994]
a)
sp3 bonds
b)
px and py orbitals
c)
H – O – H in water
d)
sp bonds.

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
The angle between the bonds formed by px and py orbitals is the minimum i.e. 90°
The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following triatomic species is : [2008] - a)NO2- <NO+2<NO2
- b)NO2- <NO2<NO2+
- c)NO2+ <NO-2<NO
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following triatomic species is : [2008]
a)
NO2- <NO+2<NO2
b)
NO2- <NO2<NO2+
c)
NO2+ <NO-2<NO
d)
none

|
Sneha Basak answered |
From the structure of three species we can determine the number of lone pair electrons on central atom (i.e. N atom) and thus the bond angle.
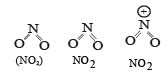
We know that higher the number of lone pair of electron on central atom, greater is the lp – lp repulsion between Nitrogen and oxygen atoms. Thus smaller is bond angle..
The correct order of bond angle is
The correct order of bond angle is
NO2 NO2 NO2 i .e. opti on (b) is correct.
In an octahedral structure, the pair of d orbitals involved in d2sp3 hybridization is [2004]- a)
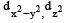
- b)
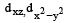
- c)dz2 , dxz
- d)dxy,dyz
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an octahedral structure, the pair of d orbitals involved in d2sp3 hybridization is [2004]
a)
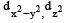
b)
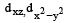
c)
dz2 , dxz
d)
dxy,dyz

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Only those d or bital s whose l obes are directed along X, Y and Z directions hybridise with s and p orbitals. In other three d or bitals n amely dxy, dyz and dxz, the lobes are at an angle of 45° from both axis, hence the extent of their overlap with s and p orbitals is much lesser than 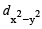 and
and 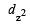 orbitals.
orbitals.
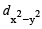 and
and 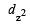 orbitals.
orbitals.Which of the following molecules has trigonal planar geometry? [2005]
- a)BF3
- b)NH3
- c)PCl3
- d)IF3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecules has trigonal planar geometry? [2005]
a)
BF3
b)
NH3
c)
PCl3
d)
IF3

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
3 is sp2 hybridised. So, it is trigon al planner. NH3, PCl3 has sp3 hybridisation hence has trigonal bipyramidal shape, IF3, has sp3d hydridization and has linear shape.
Strongest bond is in between [1993]- a)CsF
- b)NaCl
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Strongest bond is in between [1993]
a)
CsF
b)
NaCl
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None of above

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
According to Fajan rules, ionic character increases with increase in size of the cation and decrease in size of the anion. Thus, CsF has higher ionic character than NaCl and hence bond in CsF is stronger than in NaCl.
The correct order of C–O bond length among CO, CO32- , CO2 is [2007]- a)CO < CO32– < CO2
- b)CO32– < CO2 < CO
- c)CO < CO2 < CO32–
- d)CO2 < CO32– < CO
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of C–O bond length among CO, CO32- , CO2 is [2007]
a)
CO < CO32– < CO2
b)
CO32– < CO2 < CO
c)
CO < CO2 < CO32–
d)
CO2 < CO32– < CO
|
|
Anitha Bathula answered |
But bond order inversely proportional to bond length then option a is correct answer
In which of the following the bond angle is maximum? [2001]- a)NH3
- b)SCl2
- c)NH4+
- d)PCl3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following the bond angle is maximum? [2001]
a)
NH3
b)
SCl2
c)
NH4+
d)
PCl3

|
Gowri Nair answered |
We know that bond angles of NH3 = 107º, 4+ = 109.5º, PCl3 = 100º. Therefore bond angle of NH4+ is maximum.
Which one shows the strongest hydrogen bonding?- a)H2O
- b)CH3OH
- c) NH3
- d)HF.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one shows the strongest hydrogen bonding?
a)
H2O
b)
CH3OH
c)
NH3
d)
HF.
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Among the F, O, and N, Fluorine has a higher value of electronegativity, this is the reason that fluorine can form the strongest hydrogen bond with the H atom of another molecule.
Just take an idea from the value of the energy of hydrogen bond that is formed with HF, H2O, and NH3
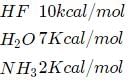
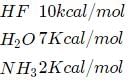
means to break the hydrogen of one mole HF molecules, 10Kcal energy is required.
The angular shape of ozone molecule (O3) consists of : [2008]- a)1 sigma and 2 pi bonds
- b)2 sigma and 2 pi bonds
- c)1 sigma and 1 pi bonds
- d)2 sigma and 1 pi bonds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The angular shape of ozone molecule (O3) consists of : [2008]
a)
1 sigma and 2 pi bonds
b)
2 sigma and 2 pi bonds
c)
1 sigma and 1 pi bonds
d)
2 sigma and 1 pi bonds

|
Arya Khanna answered |
The shape of ozone molecule is
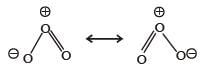
In it we find 2σ and 1π bond, i.e., option (d) is correct.
The boiling point of p-nitrophenol is higher than that of o-nitrophenol because [1994]- a)NO2 group at p-position behave in a different way from that at o-position.
- b)intramolecular hydrogen bonding exists in p-nitrophenol
- c)there is intermolecular hydrogen bonding in p-nitrophenol
- d)p-nitrophenol has a higher molecular weight than o-nitrophenol.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The boiling point of p-nitrophenol is higher than that of o-nitrophenol because [1994]
a)
NO2 group at p-position behave in a different way from that at o-position.
b)
intramolecular hydrogen bonding exists in p-nitrophenol
c)
there is intermolecular hydrogen bonding in p-nitrophenol
d)
p-nitrophenol has a higher molecular weight than o-nitrophenol.

|
Anand Jain answered |
The b.p. of p-nitrophenol is higher than that of o-nitrophenol because in p-nitrophenol there is intermolecular H-bonding but in onitrophenol it is intramolecular H-bonding.
Which one of the following is the correct order of interactions ? [1993]- a)Covalent < hydrogen bonding < vander Waals < dipole-dipole
- b)vander Waals < hydrogen bonding < dipole < covalent
- c)vander Waals < dipole-dipole < hydrogen bonding < covalent
- d)Dipole-dipole < vander Waals < hydrogen bonding < covalent.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the correct order of interactions ? [1993]
a)
Covalent < hydrogen bonding < vander Waals < dipole-dipole
b)
vander Waals < hydrogen bonding < dipole < covalent
c)
vander Waals < dipole-dipole < hydrogen bonding < covalent
d)
Dipole-dipole < vander Waals < hydrogen bonding < covalent.
|
|
Muskaan Kumar answered |
B)Ionic
c)Hydrogen bonding
d)Van der Waals interactions
The correct order of interactions is:
a) Covalent
b) Ionic
c) Hydrogen bonding
d) Van der Waals interactions
This order is based on the strength of the interactions, with covalent bonds being the strongest and van der Waals interactions being the weakest.
c)Hydrogen bonding
d)Van der Waals interactions
The correct order of interactions is:
a) Covalent
b) Ionic
c) Hydrogen bonding
d) Van der Waals interactions
This order is based on the strength of the interactions, with covalent bonds being the strongest and van der Waals interactions being the weakest.
In which of the following molecules / ions BF3, NO2-, NH2- and H2O , [2009] the central atom is sp2 hybridized ?- a)NH2- and H2O
- b)NO2- and H2O
- c)BF3 and NO2-
- d)NO2- and NH2-
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following molecules / ions BF3, NO2-, NH2- and H2O , [2009] the central atom is sp2 hybridized ?
a)
NH2- and H2O
b)
NO2- and H2O
c)
BF3 and NO2-
d)
NO2- and NH2-

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
For neutral molecules: No. of electron pairs = No. of atoms bonded
to it +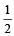 [Group number of central atom –Valency of the central atom].
[Group number of central atom –Valency of the central atom].
For ions : No. of electron pairs = No. of atoms bonded
to it +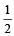 [Group no. of central atom – valency of the central atom ± no. of electrons] On calcuting no. of electron pairs in given molecules. We find that in the given molecules hybridisation is
[Group no. of central atom – valency of the central atom ± no. of electrons] On calcuting no. of electron pairs in given molecules. We find that in the given molecules hybridisation is
to it +
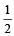 [Group number of central atom –Valency of the central atom].
[Group number of central atom –Valency of the central atom].For ions : No. of electron pairs = No. of atoms bonded
to it +
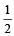 [Group no. of central atom – valency of the central atom ± no. of electrons] On calcuting no. of electron pairs in given molecules. We find that in the given molecules hybridisation is
[Group no. of central atom – valency of the central atom ± no. of electrons] On calcuting no. of electron pairs in given molecules. We find that in the given molecules hybridisation is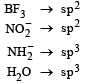
Which of the following molecules is planar?- a)SF4
- b)XeF4 [1998]
- c)NF3
- d)SiF4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecules is planar?
a)
SF4
b)
XeF4 [1998]
c)
NF3
d)
SiF4

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
XeF4 hybridisation is = 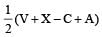
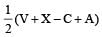
hence V = 8 (no. of valence e–) X = 4 (no of monovalent atom)
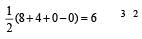
C = 0 charge on cation A = 0 (charge on anion). The shape is
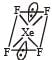 Square planar shape.
Square planar shape.Which of the following is the electron deficient molecule? [2005]- a)C2H6
- b)B2H6
- c)SiH4
- d)PH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the electron deficient molecule? [2005]
a)
C2H6
b)
B2H6
c)
SiH4
d)
PH3
|
|
Anand Kapoor answered |
**Answer:**
**B2H6** is the electron deficient molecule.
- In order to determine which molecule is electron deficient, we need to consider the number of valence electrons in each molecule and compare it to the number of electrons required for a stable octet or duet.
- Boron (B) has an atomic number of 5, which means it has 5 electrons in its neutral state. Hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1, so it has 1 electron in its neutral state.
- In B2H6, we have 2 boron atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms.
- The total number of valence electrons in B2H6 is calculated by adding the valence electrons of each atom:
- 2 boron atoms x 3 valence electrons = 6 valence electrons
- 6 hydrogen atoms x 1 valence electron = 6 valence electrons
- Total = 6 + 6 = 12 valence electrons
- In order to determine if B2H6 is electron deficient, we need to compare the number of valence electrons to the number of electrons required for a stable octet or duet.
- For boron, it requires 8 electrons for a stable octet, and for hydrogen, it requires 2 electrons for a stable duet.
- Therefore, the total number of electrons required for a stable octet or duet in B2H6 is:
- 2 boron atoms x 8 electrons = 16 electrons
- 6 hydrogen atoms x 2 electrons = 12 electrons
- Total = 16 + 12 = 28 electrons
- Since B2H6 has only 12 valence electrons, it is electron deficient because it does not have enough electrons to achieve a stable octet or duet.
- On the other hand, molecules such as C2H6, SiH4, and PH3 have enough valence electrons to achieve a stable octet or duet, so they are not electron deficient.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option **B) B2H6**.
**B2H6** is the electron deficient molecule.
- In order to determine which molecule is electron deficient, we need to consider the number of valence electrons in each molecule and compare it to the number of electrons required for a stable octet or duet.
- Boron (B) has an atomic number of 5, which means it has 5 electrons in its neutral state. Hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1, so it has 1 electron in its neutral state.
- In B2H6, we have 2 boron atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms.
- The total number of valence electrons in B2H6 is calculated by adding the valence electrons of each atom:
- 2 boron atoms x 3 valence electrons = 6 valence electrons
- 6 hydrogen atoms x 1 valence electron = 6 valence electrons
- Total = 6 + 6 = 12 valence electrons
- In order to determine if B2H6 is electron deficient, we need to compare the number of valence electrons to the number of electrons required for a stable octet or duet.
- For boron, it requires 8 electrons for a stable octet, and for hydrogen, it requires 2 electrons for a stable duet.
- Therefore, the total number of electrons required for a stable octet or duet in B2H6 is:
- 2 boron atoms x 8 electrons = 16 electrons
- 6 hydrogen atoms x 2 electrons = 12 electrons
- Total = 16 + 12 = 28 electrons
- Since B2H6 has only 12 valence electrons, it is electron deficient because it does not have enough electrons to achieve a stable octet or duet.
- On the other hand, molecules such as C2H6, SiH4, and PH3 have enough valence electrons to achieve a stable octet or duet, so they are not electron deficient.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option **B) B2H6**.
In PO43– ion, the formal charge on each oxygen atom and P—O bond order respectively are- a)–0.75, 0.6
- b)– 0.75, 1.0 [1998]
- c)– 0.75, 1.25
- d)–3, 1.25
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In PO43– ion, the formal charge on each oxygen atom and P—O bond order respectively are
a)
–0.75, 0.6
b)
– 0.75, 1.0 [1998]
c)
– 0.75, 1.25
d)
–3, 1.25

|
Mrprince answered |
C is correct
formal charge =3/4= -0.75
p_o bond order = 1.25
formal charge =3/4= -0.75
p_o bond order = 1.25
In which of the following molecules the central atom does not have sp3 hybridization? [2010]- a)NH+4
- b)CH4
- c)SF4
- d)BF4–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following molecules the central atom does not have sp3 hybridization? [2010]
a)
NH+4
b)
CH4
c)
SF4
d)
BF4–

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
(a) NH+4 : sp3 hybridisation
(b) CH4: sp3 hybridisation
(c) SF4: sp3 d hybridisation
(d) BF4– : sp3 hybridisation
∴ Correct choice : (c)
(b) CH4: sp3 hybridisation
(c) SF4: sp3 d hybridisation
(d) BF4– : sp3 hybridisation
∴ Correct choice : (c)
Which of the following is paramagnetic ? [NEET 2013]- a)O2-
- b)CN–
- c)NO+
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is paramagnetic ? [NEET 2013]
a)
O2-
b)
CN–
c)
NO+
d)
CO

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Molecular orbital configuration of O2- is
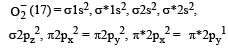
Which one of the following molecules will form a linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding? [2000]
- a)NH3
- b)H2O
- c)HCl
- d)HF
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following molecules will form a linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding? [2000]
a)
NH3
b)
H2O
c)
HCl
d)
HF

|
Arnav Chawla answered |
Explanation:
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F). This type of bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction where the hydrogen atom acts as a bridge between two electronegative atoms.
In the given options, only HF (hydrogen fluoride) contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (fluorine), making it capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonding in HF:
- In HF, the hydrogen atom is bonded to fluorine, which is highly electronegative.
- The fluorine atom attracts the electron pair in the H-F bond, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the fluorine atom.
- This partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom can then form a hydrogen bond with another electronegative atom, such as another HF molecule.
- The hydrogen bond is formed between the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom of one HF molecule and the partial negative charge on the fluorine atom of another HF molecule.
Linear polymeric structure:
- In the case of HF, the hydrogen bonds can form between multiple HF molecules, resulting in the formation of a linear polymeric structure.
- The hydrogen bonds act as bridges between the HF molecules, connecting them in a linear chain-like structure.
Other options:
- NH3 (ammonia), H2O (water), and HCl (hydrochloric acid) do not contain a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, so they cannot form hydrogen bonds.
- NH3 and HCl can form dipole-dipole interactions, but these interactions are not strong enough to result in the formation of a linear polymeric structure.
- H2O can form hydrogen bonds, but the arrangement of the hydrogen bonds in water molecules does not lead to the formation of a linear polymeric structure.
Therefore, the molecule that will form a linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding is HF.
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F). This type of bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction where the hydrogen atom acts as a bridge between two electronegative atoms.
In the given options, only HF (hydrogen fluoride) contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (fluorine), making it capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonding in HF:
- In HF, the hydrogen atom is bonded to fluorine, which is highly electronegative.
- The fluorine atom attracts the electron pair in the H-F bond, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the fluorine atom.
- This partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom can then form a hydrogen bond with another electronegative atom, such as another HF molecule.
- The hydrogen bond is formed between the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom of one HF molecule and the partial negative charge on the fluorine atom of another HF molecule.
Linear polymeric structure:
- In the case of HF, the hydrogen bonds can form between multiple HF molecules, resulting in the formation of a linear polymeric structure.
- The hydrogen bonds act as bridges between the HF molecules, connecting them in a linear chain-like structure.
Other options:
- NH3 (ammonia), H2O (water), and HCl (hydrochloric acid) do not contain a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, so they cannot form hydrogen bonds.
- NH3 and HCl can form dipole-dipole interactions, but these interactions are not strong enough to result in the formation of a linear polymeric structure.
- H2O can form hydrogen bonds, but the arrangement of the hydrogen bonds in water molecules does not lead to the formation of a linear polymeric structure.
Therefore, the molecule that will form a linear polymeric structure due to hydrogen bonding is HF.
Strongest hydrogen bond is shown by [1992]- a)Water
- b)Ammonia
- c)Hydrogen fluoride
- d)Hydrogen sulphide.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Strongest hydrogen bond is shown by [1992]
a)
Water
b)
Ammonia
c)
Hydrogen fluoride
d)
Hydrogen sulphide.
|
|
Stuti Joshi answered |
Strongest Hydrogen Bond: Hydrogen Fluoride (HF)
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom (such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine) and is attracted to another electronegative atom. Among the given options, hydrogen fluoride (HF) exhibits the strongest hydrogen bonding.
Properties of Hydrogen Fluoride (HF):
- Electronegativity: Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and hydrogen has a relatively low electronegativity. This large difference in electronegativity creates a highly polar bond between hydrogen and fluorine, resulting in a strong dipole moment in HF.
- Size of Atom: Fluorine is smaller in size compared to other elements like oxygen or nitrogen. The smaller size allows for closer proximity between the hydrogen and fluorine atoms, enhancing the strength of hydrogen bonding.
- Bond Length: The bond length between hydrogen and fluorine is shorter compared to other hydrogen bonds, such as in water or ammonia. The shorter bond length contributes to a stronger hydrogen bond.
- Bond Strength: The bond energy of HF is higher compared to other hydrogen compounds. This means that more energy is required to break the hydrogen bond in HF, indicating a stronger bond.
Comparison with Other Options:
a) Water (H2O): Water exhibits hydrogen bonding due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen. However, the electronegativity of oxygen is lower than that of fluorine, resulting in weaker hydrogen bonding in water compared to hydrogen fluoride.
b) Ammonia (NH3): Ammonia also exhibits hydrogen bonding due to the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen. However, nitrogen is less electronegative than fluorine, resulting in weaker hydrogen bonding in ammonia compared to hydrogen fluoride.
d) Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): Hydrogen sulfide exhibits weaker hydrogen bonding compared to hydrogen fluoride. Sulfur is less electronegative than fluorine, resulting in a smaller electronegativity difference and weaker hydrogen bonding in hydrogen sulfide.
In conclusion, hydrogen fluoride (HF) exhibits the strongest hydrogen bonding among the given options due to the combination of high electronegativity of fluorine, smaller size of the atom, shorter bond length, and higher bond energy.
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom (such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine) and is attracted to another electronegative atom. Among the given options, hydrogen fluoride (HF) exhibits the strongest hydrogen bonding.
Properties of Hydrogen Fluoride (HF):
- Electronegativity: Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and hydrogen has a relatively low electronegativity. This large difference in electronegativity creates a highly polar bond between hydrogen and fluorine, resulting in a strong dipole moment in HF.
- Size of Atom: Fluorine is smaller in size compared to other elements like oxygen or nitrogen. The smaller size allows for closer proximity between the hydrogen and fluorine atoms, enhancing the strength of hydrogen bonding.
- Bond Length: The bond length between hydrogen and fluorine is shorter compared to other hydrogen bonds, such as in water or ammonia. The shorter bond length contributes to a stronger hydrogen bond.
- Bond Strength: The bond energy of HF is higher compared to other hydrogen compounds. This means that more energy is required to break the hydrogen bond in HF, indicating a stronger bond.
Comparison with Other Options:
a) Water (H2O): Water exhibits hydrogen bonding due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen. However, the electronegativity of oxygen is lower than that of fluorine, resulting in weaker hydrogen bonding in water compared to hydrogen fluoride.
b) Ammonia (NH3): Ammonia also exhibits hydrogen bonding due to the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen. However, nitrogen is less electronegative than fluorine, resulting in weaker hydrogen bonding in ammonia compared to hydrogen fluoride.
d) Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): Hydrogen sulfide exhibits weaker hydrogen bonding compared to hydrogen fluoride. Sulfur is less electronegative than fluorine, resulting in a smaller electronegativity difference and weaker hydrogen bonding in hydrogen sulfide.
In conclusion, hydrogen fluoride (HF) exhibits the strongest hydrogen bonding among the given options due to the combination of high electronegativity of fluorine, smaller size of the atom, shorter bond length, and higher bond energy.
Among the following the electron deficient compound is : [2000]
- a)BCl3
- b)CCl4
- c)PCl5
- d)SiF4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following the electron deficient compound is : [2000]
a)
BCl3
b)
CCl4
c)
PCl5
d)
SiF4

|
Devika Banerjee answered |
Electron Deficient Compound:
An electron deficient compound is one that lacks sufficient electrons to complete its valence shell. These compounds typically have an incomplete octet or less than eight valence electrons around the central atom.
Analysis of Options:
a) BCl3: Boron (B) has three valence electrons, and each chlorine (Cl) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, BCl3 has a total of six valence electrons. It is an electron deficient compound as it lacks two electrons to complete its octet.
b) CCl4: Carbon (C) has four valence electrons, and each chlorine (Cl) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, CCl4 has a total of eight valence electrons, fulfilling the octet rule. It is not an electron deficient compound.
c) PCl5: Phosphorus (P) has five valence electrons, and each chlorine (Cl) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, PCl5 has a total of ten valence electrons, exceeding the octet rule. It is not an electron deficient compound.
d) SiF4: Silicon (Si) has four valence electrons, and each fluorine (F) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, SiF4 has a total of eight valence electrons, fulfilling the octet rule. It is not an electron deficient compound.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, BCl3 is the only compound that is electron deficient. It lacks two electrons to complete its valence shell and satisfy the octet rule. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - BCl3.
An electron deficient compound is one that lacks sufficient electrons to complete its valence shell. These compounds typically have an incomplete octet or less than eight valence electrons around the central atom.
Analysis of Options:
a) BCl3: Boron (B) has three valence electrons, and each chlorine (Cl) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, BCl3 has a total of six valence electrons. It is an electron deficient compound as it lacks two electrons to complete its octet.
b) CCl4: Carbon (C) has four valence electrons, and each chlorine (Cl) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, CCl4 has a total of eight valence electrons, fulfilling the octet rule. It is not an electron deficient compound.
c) PCl5: Phosphorus (P) has five valence electrons, and each chlorine (Cl) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, PCl5 has a total of ten valence electrons, exceeding the octet rule. It is not an electron deficient compound.
d) SiF4: Silicon (Si) has four valence electrons, and each fluorine (F) atom contributes one electron. Therefore, SiF4 has a total of eight valence electrons, fulfilling the octet rule. It is not an electron deficient compound.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, BCl3 is the only compound that is electron deficient. It lacks two electrons to complete its valence shell and satisfy the octet rule. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - BCl3.
Which of the following statements is not correct for sigma and pi-bonds formed between two carbon atoms? [2003]- a)Sigma-bond deter mines the directi on between carbon atoms but a pi-bond has no primary effect in this regard
- b)Sigma-bond is stronger than a pi-bond
- c)Bond energies of sigma- and pi-bonds are of the order of 264 kJ/mol and 347 kJ/mol, respectively
- d)Free rotation of atoms about a sigma-bond is allowed but not in case of a pi-bond
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct for sigma and pi-bonds formed between two carbon atoms? [2003]
a)
Sigma-bond deter mines the directi on between carbon atoms but a pi-bond has no primary effect in this regard
b)
Sigma-bond is stronger than a pi-bond
c)
Bond energies of sigma- and pi-bonds are of the order of 264 kJ/mol and 347 kJ/mol, respectively
d)
Free rotation of atoms about a sigma-bond is allowed but not in case of a pi-bond

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
As sigma bond is stronger than the π(pi) bond, so it must be having higher bond energy than π (pi) bond.
Which one of the following has the shortest carbon carbon bond length ? [1992]- a)Benzene
- b)Ethene
- c)Ethyne
- d)Ethane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has the shortest carbon carbon bond length ? [1992]
a)
Benzene
b)
Ethene
c)
Ethyne
d)
Ethane

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
The bond length decreases in the order sp3 > sp2 > sp.
Because of the triple bond, the carbon-carbon bond distance in ethyne is shortest.
Because of the triple bond, the carbon-carbon bond distance in ethyne is shortest.
Which of the following pairs will form the most stable ionic bond ? [1994]- a)Na and Cl
- b)Mg and F
- c)Li and F
- d)Na and F
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs will form the most stable ionic bond ? [1994]
a)
Na and Cl
b)
Mg and F
c)
Li and F
d)
Na and F

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
The stability of the ionic bond depends upon the lattice energy which is expected to be more between Mg and F due to +2 charge on Mg atom.
Which statement is NOT correct ? [1990]- a)A sigma bond is weaker than a π -bond.
- b)A sigma bond is stronger than a π -bond.
- c)A double bond is stronger than a single bond.
- d)A double bond is shorter than a single bond.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is NOT correct ? [1990]
a)
A sigma bond is weaker than a π -bond.
b)
A sigma bond is stronger than a π -bond.
c)
A double bond is stronger than a single bond.
d)
A double bond is shorter than a single bond.
|
|
Anirban Shah answered |
Understanding Sigma and Pi Bonds
A sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond are two types of covalent bonds that differ in their formation and strength.
Strength of Sigma vs. Pi Bonds
- Sigma bonds are formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals.
- Pi bonds are formed by the side-to-side overlap of atomic orbitals.
- Sigma bonds are generally stronger than pi bonds due to the direct overlap, which allows for a greater electron density between the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
Analysis of Statement A
- Statement A claims that a sigma bond is weaker than a pi bond.
- This statement is incorrect because, as discussed, sigma bonds are stronger due to the nature of their orbital overlap.
Comparison of Single and Double Bonds
- A double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond, making it stronger than a single bond (which consists only of a sigma bond).
- Consequently, a double bond is not only stronger but also shorter than a single bond, due to the additional attraction from the pi bond.
Summary of Correct Statements
- Statement B (Sigma bond is stronger than a pi bond) is correct.
- Statement C (A double bond is stronger than a single bond) is correct.
- Statement D (A double bond is shorter than a single bond) is also correct.
Conclusion
In summary, the incorrect statement is option A, as sigma bonds are indeed stronger than pi bonds, contradicting the claim made in that statement. Understanding these bond types is crucial in grasping the fundamentals of molecular structure and stability.
A sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond are two types of covalent bonds that differ in their formation and strength.
Strength of Sigma vs. Pi Bonds
- Sigma bonds are formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals.
- Pi bonds are formed by the side-to-side overlap of atomic orbitals.
- Sigma bonds are generally stronger than pi bonds due to the direct overlap, which allows for a greater electron density between the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
Analysis of Statement A
- Statement A claims that a sigma bond is weaker than a pi bond.
- This statement is incorrect because, as discussed, sigma bonds are stronger due to the nature of their orbital overlap.
Comparison of Single and Double Bonds
- A double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond, making it stronger than a single bond (which consists only of a sigma bond).
- Consequently, a double bond is not only stronger but also shorter than a single bond, due to the additional attraction from the pi bond.
Summary of Correct Statements
- Statement B (Sigma bond is stronger than a pi bond) is correct.
- Statement C (A double bond is stronger than a single bond) is correct.
- Statement D (A double bond is shorter than a single bond) is also correct.
Conclusion
In summary, the incorrect statement is option A, as sigma bonds are indeed stronger than pi bonds, contradicting the claim made in that statement. Understanding these bond types is crucial in grasping the fundamentals of molecular structure and stability.
The electronegativity difference between N and F is greater than that between N and H yet the dipole moment of NH3 (1.5 D) is larger than that of NF3 (0.2D). This is because [2006]- a)in NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction whereas in NF3 these are in opposite directions
- b)in NH3 as well as NF3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions
- c)in NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the opposite directions whereas in NF3 these are in the same direction
- d)in NH3 as well as in NF3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The electronegativity difference between N and F is greater than that between N and H yet the dipole moment of NH3 (1.5 D) is larger than that of NF3 (0.2D). This is because [2006]
a)
in NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction whereas in NF3 these are in opposite directions
b)
in NH3 as well as NF3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions
c)
in NH3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the opposite directions whereas in NF3 these are in the same direction
d)
in NH3 as well as in NF3 the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction

|
Aniket Basu answered |
Electronegativity Difference
- The electronegativity difference between two atoms in a molecule is a measure of the inequality of sharing of electrons between them.
- In the case of NH3 (ammonia), the electronegativity difference between nitrogen (N) and hydrogen (H) is relatively small, but still greater than that between nitrogen (N) and fluorine (F).
- This is because fluorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, resulting in a larger electronegativity difference between N and F compared to N and H.
Dipole Moment
- The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the overall polarity of the molecule.
- It is determined by the magnitude and direction of the individual bond moments within the molecule.
- In the case of NH3, the dipole moment is 1.5 D, which indicates that the molecule is polar.
- In the case of NF3, the dipole moment is 0.2 D, which also indicates that the molecule is polar but to a lesser extent.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option A)
- In NH3, the atomic dipole (due to the electronegativity difference between N and H) and the bond dipole (due to the geometry of the molecule) are in the same direction.
- This means that the individual bond moments reinforce each other, resulting in a larger overall dipole moment.
- In NF3, the atomic dipole (due to the electronegativity difference between N and F) and the bond dipole (due to the geometry of the molecule) are in opposite directions.
- This means that the individual bond moments partially cancel each other out, resulting in a smaller overall dipole moment.
Other Options Explanation
- Option B states that in both NH3 and NF3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions. This is incorrect because the atomic dipole and bond dipole in NH3 are in the same direction.
- Option C states that in NH3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions, whereas in NF3, they are in the same direction. This is incorrect because in NH3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction.
- Option D states that in both NH3 and NF3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction. This is incorrect because in NF3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, where the atomic dipole and bond dipole in NH3 are in the same direction, resulting in a larger dipole moment compared to NF3.
- The electronegativity difference between two atoms in a molecule is a measure of the inequality of sharing of electrons between them.
- In the case of NH3 (ammonia), the electronegativity difference between nitrogen (N) and hydrogen (H) is relatively small, but still greater than that between nitrogen (N) and fluorine (F).
- This is because fluorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, resulting in a larger electronegativity difference between N and F compared to N and H.
Dipole Moment
- The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of the overall polarity of the molecule.
- It is determined by the magnitude and direction of the individual bond moments within the molecule.
- In the case of NH3, the dipole moment is 1.5 D, which indicates that the molecule is polar.
- In the case of NF3, the dipole moment is 0.2 D, which also indicates that the molecule is polar but to a lesser extent.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option A)
- In NH3, the atomic dipole (due to the electronegativity difference between N and H) and the bond dipole (due to the geometry of the molecule) are in the same direction.
- This means that the individual bond moments reinforce each other, resulting in a larger overall dipole moment.
- In NF3, the atomic dipole (due to the electronegativity difference between N and F) and the bond dipole (due to the geometry of the molecule) are in opposite directions.
- This means that the individual bond moments partially cancel each other out, resulting in a smaller overall dipole moment.
Other Options Explanation
- Option B states that in both NH3 and NF3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions. This is incorrect because the atomic dipole and bond dipole in NH3 are in the same direction.
- Option C states that in NH3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions, whereas in NF3, they are in the same direction. This is incorrect because in NH3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction.
- Option D states that in both NH3 and NF3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in the same direction. This is incorrect because in NF3, the atomic dipole and bond dipole are in opposite directions.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, where the atomic dipole and bond dipole in NH3 are in the same direction, resulting in a larger dipole moment compared to NF3.
Some of the properties of the two species, NO3- and H3O+ are described below. Which one of them is correct? [2010]- a)Similar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures.
- b)Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures.
- c)isostructural with same hybridization for the central atom.
- d)Isostructural with different hybridization for the central atom.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Some of the properties of the two species, NO3- and H3O+ are described below. Which one of them is correct? [2010]
a)
Similar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures.
b)
Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures.
c)
isostructural with same hybridization for the central atom.
d)
Isostructural with different hybridization for the central atom.

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
In NO3-2 , nitrogen is in sp2 hybridisation, thus planar in shape. In H3O+ , oxygen is in sp3 hybridisation, thus tetrahedral in shape.
∴ Correct choice : (b)
∴ Correct choice : (b)
Among the following which one is not paramagnetic? [Atomic numbers : Be = 4, Ne = 10, As = 33, Cl = 17] [1998]- a)Cl–
- b)Be+
- c)Ne+2
- d)As+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following which one is not paramagnetic? [Atomic numbers : Be = 4, Ne = 10, As = 33, Cl = 17] [1998]
a)
Cl–
b)
Be+
c)
Ne+2
d)
As+

|
Gowri Nair answered |
Paramagnetic character is based upon presence of unpaired electron
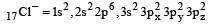

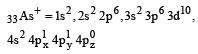
Hence only Cl– do not have unpaired electrons.
In which of the following pairs, the two species are iso-structure? [2007]- a)SO32– and NO3–
- b)BF3 an NF3
- c)BrO3– and XeO3
- d)SF4 and XeF4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following pairs, the two species are iso-structure? [2007]
a)
SO32– and NO3–
b)
BF3 an NF3
c)
BrO3– and XeO3
d)
SF4 and XeF4

|
Diya Datta answered |
Hybridization of Br is BrO3–
Total valence elctrons = 7 + 3 × 6 = 25
Charge = –1 hence
Total = 25 + 1 = 26
Total valence elctrons = 7 + 3 × 6 = 25
Charge = –1 hence
Total = 25 + 1 = 26
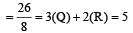
hybridization = dsp3 hybridization of Xe in XeO3 Total valence electrons
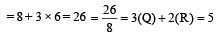
Hybridization = dsp3 In both cases, the structure is trigonal pyramidal.
Which of the following does not apply to metallic bond ?[1989]- a)Overlapping valence orbitals
- b)Mobile valency electrons
- c)Delocalized electrons
- d)Highly directed bonds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not apply to metallic bond ?[1989]
a)
Overlapping valence orbitals
b)
Mobile valency electrons
c)
Delocalized electrons
d)
Highly directed bonds

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
In metallic bonds each ion is surrounded by equal no. of oppositely charged ions hence have electrostatic attraction on all sides and hence do not have directional characteristics.
Among LiCl, BeCl2 BCl3 and CCl4, the covalent bond character follows the order [1990]- a)LiCl < BeCl2 > BCl3 > CCl4
- b)BeCl2 < BCl3 < CCl4 < LiCl
- c)LiCl < BeCl2 < BCl3 < CCl4
- d)LiCl > BeCl2 > BCl3 > CCl4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among LiCl, BeCl2 BCl3 and CCl4, the covalent bond character follows the order [1990]
a)
LiCl < BeCl2 > BCl3 > CCl4
b)
BeCl2 < BCl3 < CCl4 < LiCl
c)
LiCl < BeCl2 < BCl3 < CCl4
d)
LiCl > BeCl2 > BCl3 > CCl4

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
As we move in period from Li → Be → B → C, the electronegativity (EN) increases and hence the EN difference between the element and Cl decreases and accordingly the covalent character increases Thus option (c) i.e., LiCl < BeCl2 < BCl3< CCl4 is correct.
Which one of the following has the pyramidal shape?[1999]- a)CO32–
- b)SO3
- c)BF3
- d)PF3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has the pyramidal shape?[1999]
a)
CO32–
b)
SO3
c)
BF3
d)
PF3

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
PF3 has pyramidal shape
Phosphorus exist in sp3 hybridiation state hence it exist in tetrahedral shape. But due to presence of lone pair its shape is pyramidal.
F—H-----F—H-----F—H-----F
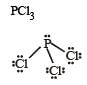
Phosphorus exist in sp3 hybridiation state hence it exist in tetrahedral shape. But due to presence of lone pair its shape is pyramidal.
F—H-----F—H-----F—H-----F
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup