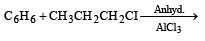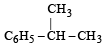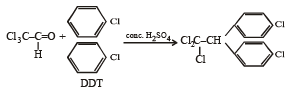All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes for NEET Exam
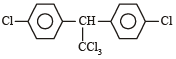
C5H11Br is least soluble in:- a)Ether
- b)Alcohol
- c)Water
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
C5H11Br is least soluble in:
a)
Ether
b)
Alcohol
c)
Water
d)
None of these
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
C5H11Br is only very slightly soluble in water. It is more soluble in organic solvents.
Which of the following is not true about optical isomers?- a)They rotate the plane polarized light.
- b)They are superimposable on their mirror image.
- c)They posses at least one chiral carbon atom.
- d)They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true about optical isomers?
a)
They rotate the plane polarized light.
b)
They are superimposable on their mirror image.
c)
They posses at least one chiral carbon atom.
d)
They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image.
|
|
Nisha Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Optical isomers are stereoisomers that exist in two mirror-image forms that are non-superimposable on each other. They are also known as enantiomers.
a) They rotate the plane polarized light: Optical isomers have the property of rotating the plane of polarized light in opposite directions. One isomer rotates the plane of polarized light in the clockwise direction and the other in the counterclockwise direction.
b) They are superimposable on their mirror image: This statement is false. Optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. If we try to superimpose them, they will not match perfectly.
c) They possess at least one chiral carbon atom: Optical isomers possess chiral carbon atoms. Chiral carbon atoms are those carbon atoms that are attached to four different groups or atoms.
d) They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image: As mentioned earlier, optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have the same physical and chemical properties but differ in their biological activity, as they interact differently with other chiral molecules in living organisms.
Conclusion: Optical isomers are important in fields like medicinal chemistry, where knowing the activity of each isomer can help in designing drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the properties of optical isomers.
Optical isomers are stereoisomers that exist in two mirror-image forms that are non-superimposable on each other. They are also known as enantiomers.
a) They rotate the plane polarized light: Optical isomers have the property of rotating the plane of polarized light in opposite directions. One isomer rotates the plane of polarized light in the clockwise direction and the other in the counterclockwise direction.
b) They are superimposable on their mirror image: This statement is false. Optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. If we try to superimpose them, they will not match perfectly.
c) They possess at least one chiral carbon atom: Optical isomers possess chiral carbon atoms. Chiral carbon atoms are those carbon atoms that are attached to four different groups or atoms.
d) They are nonsuperimposable on their mirror image: As mentioned earlier, optical isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have the same physical and chemical properties but differ in their biological activity, as they interact differently with other chiral molecules in living organisms.
Conclusion: Optical isomers are important in fields like medicinal chemistry, where knowing the activity of each isomer can help in designing drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the properties of optical isomers.
Which of the following is a tertiary halogenoalkanes?- a)2-Bromopentane
- b)2-Bromo 3-methylpentane
- c)Bromopentane
- d)2-Bromo 2-methylpentane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a tertiary halogenoalkanes?
a)
2-Bromopentane
b)
2-Bromo 3-methylpentane
c)
Bromopentane
d)
2-Bromo 2-methylpentane
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
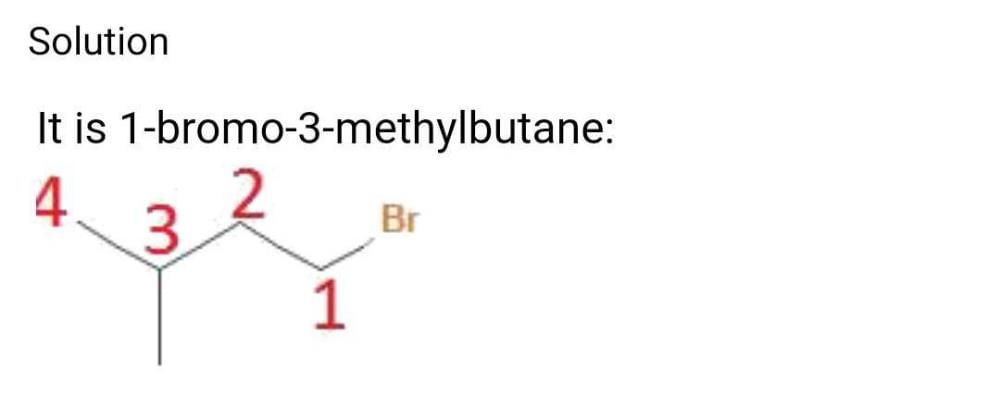
√Br CH3 -( CH )- CH2 - CH2 - CH3 √CH3 The carbon with which the Br is bonded is bonded with another 3 carbon atoms. So haloalkane is 3.
The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with one mole HI gives- a)CH3OH
- b)C2H5OH
- c)CH3I + C2H5OH
- d)C2H5I + CH3OH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with one mole HI gives
a)
CH3OH
b)
C2H5OH
c)
CH3I + C2H5OH
d)
C2H5I + CH3OH
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option C
When ethers are treated with a strong acid in the presence of a nucleophile, they can be cleaved to give alcohols and alkyl halides. If the ether is on a primary carbon this may occur through an SN2 pathway. The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with HI gives CH3I+C2H5OH.
When ethers are treated with a strong acid in the presence of a nucleophile, they can be cleaved to give alcohols and alkyl halides. If the ether is on a primary carbon this may occur through an SN2 pathway. The reaction of CH3OC2H5 with HI gives CH3I+C2H5OH.
Which of the following compound does have chiral carbon atom?- a)(CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br
- b)CH3CH2CH2CH (Br)CH3
- c)CH3CH2CH(Br) CH2CH3
- d)CH3CH2CH2 CH2Br
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compound does have chiral carbon atom?
a)
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br
b)
CH3CH2CH2CH (Br)CH3
c)
CH3CH2CH(Br) CH2CH3
d)
CH3CH2CH2 CH2Br
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
The chiral carbon atom is one in which there are an unequal number of carbon atoms, this happens only in option (B) as it forms a non superimposable mirror image.
Which of the following is intermediate in Sandmeyer’s reaction?- a)Diazonium salt
- b)Hydronium ion
- c)Ammonium salt
- d)Nitronium ion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is intermediate in Sandmeyer’s reaction?
a)
Diazonium salt
b)
Hydronium ion
c)
Ammonium salt
d)
Nitronium ion
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Diazonium salt is intermediate in Sandmeyer’s reaction.
Reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN1 nucleophilic substitution reaction is:- a)3° > 2° > 1°
- b)3° < 2° < 1°
- c)2° < 1° < 3°
- d)3° < 1° < 2°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN1 nucleophilic substitution reaction is:
a)
3° > 2° > 1°
b)
3° < 2° < 1°
c)
2° < 1° < 3°
d)
3° < 1° < 2°
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The correct answer is option A
Reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN1 nucleophilic substitution reaction is 3o > 2o > 1o because in SN1 nucleophilic reaction, the first and the slow step is the formation of a carbocation. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than a secondary carbocation which is more stable than a primary carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, greater will be the ease of formation of carbocation, and hence faster will be the rate of the reaction.
Reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN1 nucleophilic substitution reaction is 3o > 2o > 1o because in SN1 nucleophilic reaction, the first and the slow step is the formation of a carbocation. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than a secondary carbocation which is more stable than a primary carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, greater will be the ease of formation of carbocation, and hence faster will be the rate of the reaction.
Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution?- a)CHCl3
- b)(CH3)3CCl
- c)CH2=CH-Cl
- d)CCl4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution?
a)
CHCl3
b)
(CH3)3CCl
c)
CH2=CH-Cl
d)
CCl4
|
|
Gargi Ahuja answered |
Precipitation Reaction
A precipitation reaction is a chemical reaction that produces a precipitate, which is an insoluble solid that forms from the reaction of two soluble compounds.
AgNO3 Solution
AgNO3 is a soluble salt that dissociates to give Ag+ and NO3- ions in an aqueous solution.
Likely Precipitate
A compound is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution if it contains Cl- ions, as AgCl is insoluble in water and will form a white precipitate.
Analysis of Options
a) CHCl3
CHCl3 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
b) (CH3)3CCl
(CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
c) CH2=CH-Cl
CH2=CH-Cl does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
d) CCl4
CCl4 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
Conclusion
Out of the given options, only (CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution, making option 'B' the correct answer.
A precipitation reaction is a chemical reaction that produces a precipitate, which is an insoluble solid that forms from the reaction of two soluble compounds.
AgNO3 Solution
AgNO3 is a soluble salt that dissociates to give Ag+ and NO3- ions in an aqueous solution.
Likely Precipitate
A compound is likely to give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution if it contains Cl- ions, as AgCl is insoluble in water and will form a white precipitate.
Analysis of Options
a) CHCl3
CHCl3 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
b) (CH3)3CCl
(CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
c) CH2=CH-Cl
CH2=CH-Cl does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
d) CCl4
CCl4 does not contain Cl- ions and will not give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution.
Conclusion
Out of the given options, only (CH3)3CCl contains Cl- ions and will give a precipitate with AgNO3 solution, making option 'B' the correct answer.
Decreasing order of reactivity of alkyl halide is:- a)RI > RCl > RBr
- b)RI > RBr > RCl
- c)RBr > RCl > RI
- d)RCl > RBr > RI
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Decreasing order of reactivity of alkyl halide is:
a)
RI > RCl > RBr
b)
RI > RBr > RCl
c)
RBr > RCl > RI
d)
RCl > RBr > RI
|
|
Anu Sharma answered |
The decreasing order of reactivity of alkyl halides is based on the ease with which they undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Order of Reactivity:
The alkyl halides can be arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity as follows:
R-I > R-Br > R-Cl
Explanation:
The reactivity of alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions is influenced by the following factors:
1. The nature of the halogen:
The reactivity of alkyl halides decreases in the order: iodide > bromide > chloride. This is because the size of the halogen increases down the group, leading to a decrease in the bond strength and an increase in the polarizability of the C-X bond. As a result, the carbon-halogen bond becomes more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
2. The nature of the alkyl group:
The reactivity of alkyl halides increases with increasing branching of the alkyl group. This is because the steric hindrance caused by the bulky alkyl groups makes it difficult for the nucleophile to approach the carbon atom, leading to a decrease in the reaction rate.
3. The nature of the nucleophile:
The reactivity of alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions is also influenced by the nature of the nucleophile. Generally, stronger nucleophiles are more reactive towards alkyl halides.
Based on the above factors, the decreasing order of reactivity of alkyl halides is:
R-I > R-Br > R-Cl
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Order of Reactivity:
The alkyl halides can be arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity as follows:
R-I > R-Br > R-Cl
Explanation:
The reactivity of alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions is influenced by the following factors:
1. The nature of the halogen:
The reactivity of alkyl halides decreases in the order: iodide > bromide > chloride. This is because the size of the halogen increases down the group, leading to a decrease in the bond strength and an increase in the polarizability of the C-X bond. As a result, the carbon-halogen bond becomes more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
2. The nature of the alkyl group:
The reactivity of alkyl halides increases with increasing branching of the alkyl group. This is because the steric hindrance caused by the bulky alkyl groups makes it difficult for the nucleophile to approach the carbon atom, leading to a decrease in the reaction rate.
3. The nature of the nucleophile:
The reactivity of alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions is also influenced by the nature of the nucleophile. Generally, stronger nucleophiles are more reactive towards alkyl halides.
Based on the above factors, the decreasing order of reactivity of alkyl halides is:
R-I > R-Br > R-Cl
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Which of the following is major product of following reaction?
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr 
- a)2-Bromo propene
- b)1-Bromo propane
- c)1-Bromo propene
- d)2-Bromo propane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is major product of following reaction?
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr

a)
2-Bromo propene
b)
1-Bromo propane
c)
1-Bromo propene
d)
2-Bromo propane

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
As HBr in the presence of a peroxide follows antimarkonikoff rule where the negative group should attach to the carbon having less no of hydrogen atoms.

As HBr in the presence of a peroxide follows antimarkonikoff rule where the negative group should attach to the carbon having less no of hydrogen atoms.
Which of the following alcohols will yield the corresponding alkyl chloride on reaction with concentrated HCl at room temperature?- a)
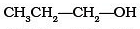
- b)
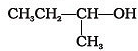
- c)
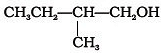
- d)
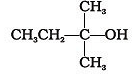
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following alcohols will yield the corresponding alkyl chloride on reaction with concentrated HCl at room temperature?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Option D is correct.
At room temperature more stable carbocation is formed by any alkyl halide then that will give a stable and more efficient product.
Formation of 3o carbocation as intermediate during reaction which is highly stable,this reaction does not require any heating to occur at only room temperature.
At room temperature more stable carbocation is formed by any alkyl halide then that will give a stable and more efficient product.
Formation of 3o carbocation as intermediate during reaction which is highly stable,this reaction does not require any heating to occur at only room temperature.
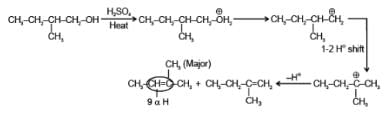
Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing rate of hydrolysis for SN1 reaction(I) 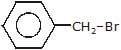
(II) 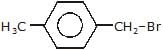
(III) 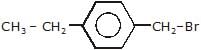
(IV) 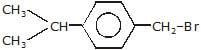
- a)II > III > IV > I
- b)IV > III > II > I
- c)III > IV > II > I
- d)I > II > III > IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing rate of hydrolysis for SN1 reaction
(I) 
(II)
(III)
(IV)
(II)
(III)
(IV)
a)
II > III > IV > I
b)
IV > III > II > I
c)
III > IV > II > I
d)
I > II > III > IV

|
EduRev Support answered |
Order of decreasing rate of hydrolysis for SN1 reaction in SN1 reaction intermediate corbocation is formed.
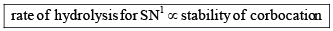

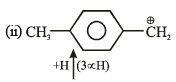
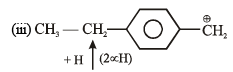
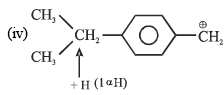
decreasing stability order of following corbocation.

decreasing stability order of following corbocation.
Racemic mixture is obtained due to the halogenation of- a)n-pentane
- b)isopentane
- c)neopentane
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Racemic mixture is obtained due to the halogenation of
a)
n-pentane
b)
isopentane
c)
neopentane
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Sreemoyee Choudhury answered |
If free radical halogenation generate a chiral carbon, racemic mixture of halides are always formed due to equal probability of halogenation from both sides of planar free radical.
Which one of the following compounds has zero dipole moment?- a)CCl4
- b)CH3Cl
- c)CHI3
- d)CHCl3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following compounds has zero dipole moment?
a)
CCl4
b)
CH3Cl
c)
CHI3
d)
CHCl3
|
|
Abhijeet Sharma answered |
Explanation:
A dipole moment is the measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is a vector quantity and has both magnitude and direction. When the molecule has a polar covalent bond, it has a dipole moment. If the bond dipoles cancel out each other, then the molecule is nonpolar, and its dipole moment is zero.
The given compounds are:
a) CCl4
b) CH3Cl
c) CHI3
d) CHCl3
Now, let's analyze each compound based on its molecular geometry and bond polarity to determine its dipole moment.
a) CCl4:
CCl4 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry with four C-Cl bonds arranged symmetrically around the central carbon atom. The C-Cl bond is polar covalent, with chlorine being more electronegative than carbon. However, due to the symmetry of the molecule, the bond dipoles cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. Therefore, CCl4 has zero dipole moment.
b) CH3Cl:
CH3Cl has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry with three C-H bonds and one C-Cl bond. The C-Cl bond is polar covalent, with chlorine being more electronegative than carbon. The three C-H bonds are also polar covalent, with carbon being more electronegative than hydrogen. However, due to the asymmetrical arrangement of the bonds, the bond dipoles do not cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment. Therefore, CH3Cl has a dipole moment.
c) CHI3:
CHI3 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry with three I-H bonds and one I-C bond. The I-C bond is polar covalent, with iodine being more electronegative than carbon. The three I-H bonds are also polar covalent, with iodine being more electronegative than hydrogen. However, due to the symmetry of the molecule, the bond dipoles cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. Therefore, CHI3 has zero dipole moment.
d) CHCl3:
CHCl3 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry with three C-H bonds and one C-Cl bond. The C-Cl bond is polar covalent, with chlorine being more electronegative than carbon. The three C-H bonds are also polar covalent, with carbon being more electronegative than hydrogen. However, due to the asymmetrical arrangement of the bonds, the bond dipoles do not cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment. Therefore, CHCl3 has a dipole moment.
Conclusion:
Among the given compounds, CCl4 has zero dipole moment because the bond dipoles cancel out each other due to the symmetrical arrangement of the bonds around the central atom.
A dipole moment is the measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is a vector quantity and has both magnitude and direction. When the molecule has a polar covalent bond, it has a dipole moment. If the bond dipoles cancel out each other, then the molecule is nonpolar, and its dipole moment is zero.
The given compounds are:
a) CCl4
b) CH3Cl
c) CHI3
d) CHCl3
Now, let's analyze each compound based on its molecular geometry and bond polarity to determine its dipole moment.
a) CCl4:
CCl4 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry with four C-Cl bonds arranged symmetrically around the central carbon atom. The C-Cl bond is polar covalent, with chlorine being more electronegative than carbon. However, due to the symmetry of the molecule, the bond dipoles cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. Therefore, CCl4 has zero dipole moment.
b) CH3Cl:
CH3Cl has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry with three C-H bonds and one C-Cl bond. The C-Cl bond is polar covalent, with chlorine being more electronegative than carbon. The three C-H bonds are also polar covalent, with carbon being more electronegative than hydrogen. However, due to the asymmetrical arrangement of the bonds, the bond dipoles do not cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment. Therefore, CH3Cl has a dipole moment.
c) CHI3:
CHI3 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry with three I-H bonds and one I-C bond. The I-C bond is polar covalent, with iodine being more electronegative than carbon. The three I-H bonds are also polar covalent, with iodine being more electronegative than hydrogen. However, due to the symmetry of the molecule, the bond dipoles cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. Therefore, CHI3 has zero dipole moment.
d) CHCl3:
CHCl3 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry with three C-H bonds and one C-Cl bond. The C-Cl bond is polar covalent, with chlorine being more electronegative than carbon. The three C-H bonds are also polar covalent, with carbon being more electronegative than hydrogen. However, due to the asymmetrical arrangement of the bonds, the bond dipoles do not cancel out each other, resulting in a net dipole moment. Therefore, CHCl3 has a dipole moment.
Conclusion:
Among the given compounds, CCl4 has zero dipole moment because the bond dipoles cancel out each other due to the symmetrical arrangement of the bonds around the central atom.
Which of the following compound will not give addition reaction with bromine?- a)Propene
- b)1-Butene
- c)Iso butane
- d)Iso butene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compound will not give addition reaction with bromine?
a)
Propene
b)
1-Butene
c)
Iso butane
d)
Iso butene
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
For Addition reaction π bond is required .Iso butane has no pi Bond .
Which of the following is formed in reaction mechanism of halogenation of alkanes in presence of UV light?- a)Carbocation
- b)Carbanion
- c)Diazonium ion
- d)Free radical
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is formed in reaction mechanism of halogenation of alkanes in presence of UV light?
a)
Carbocation
b)
Carbanion
c)
Diazonium ion
d)
Free radical

|
Niloni Soni answered |
In presence of uv light free radical mechanism takes place that is homolytic cleavage of covalent bond takes place. Carbocation and carbanion and diazonium ion forms when heterolytic cleavage of bond takes place.
The inversion of configuration of optically active alkyl halides occurs in- a)SN1 nucleophilic substitution reaction
- b)SN2 electrophilic substitution reaction
- c)SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)SN1 electrophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The inversion of configuration of optically active alkyl halides occurs in
a)
SN1 nucleophilic substitution reaction
b)
SN2 electrophilic substitution reaction
c)
SN2 nucleophilic substitution reaction
d)
SN1 electrophilic substitution reaction
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option C
Nucleophilic substitution reaction on an optically active alkyl halide gives a mixture of enantiomers.
Because the reaction occurs by SN1 mechanism.
SN1 mechanism involves racemisation as the nucleophile can attack from either side. In SN2 reaction, inversion of configuration is involved as the nucleophile can attack from the opposite side.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction on an optically active alkyl halide gives a mixture of enantiomers.
Because the reaction occurs by SN1 mechanism.
SN1 mechanism involves racemisation as the nucleophile can attack from either side. In SN2 reaction, inversion of configuration is involved as the nucleophile can attack from the opposite side.
. 
This reaction is known as:- a)Wurtz reaction
- b)Frankland reaction
- c)Fittig reaction
- d)Finkelstein reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
. 
This reaction is known as:
This reaction is known as:
a)
Wurtz reaction
b)
Frankland reaction
c)
Fittig reaction
d)
Finkelstein reaction
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option D
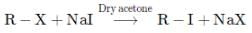
where, X=Cl or Br.
This reaction is known as the Finkelstein reaction. Finkelstein's reaction is used to prepare alkyl iodides starting from alkyl chlorides and alkyl bromides.
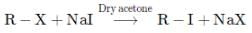
where, X=Cl or Br.
This reaction is known as the Finkelstein reaction. Finkelstein's reaction is used to prepare alkyl iodides starting from alkyl chlorides and alkyl bromides.
Which of the following is the major product of following reaction?
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr in the presence of peroxide gives:- a)2 – bromopropane
- b)1 – bromopropene
- c)1 – bromopropane
- d)2 – bromopropene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the major product of following reaction?
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr in the presence of peroxide gives:
CH3CH = CH2 + HBr in the presence of peroxide gives:
a)
2 – bromopropane
b)
1 – bromopropene
c)
1 – bromopropane
d)
2 – bromopropene
|
|
Garima Kunwar answered |
In presence of HBr and peroxide anti markonikov's addition in supported. Hence 1-bromopropane will we major product
Which of the following is not an aryl halide?- a)m-ClCH2C6H4CH2C(CH3)3
- b)(CH3)3CCH2CH3
- c)o-Br-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3
- d)p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an aryl halide?
a)
m-ClCH2C6H4CH2C(CH3)3
b)
(CH3)3CCH2CH3
c)
o-Br-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3
d)
p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2
|
|
Ankita Datta answered |
Because it is Open chain compound /Aliphatic Compound and not aryl halide as does not contain halogen atom. it's alkane simply.
The yield of alkyl bromide obtained as a result of heating the dry silver salt of carboxylic acid with bromine in CCI4 is
a) 1°> 3°> 2° bromides
b) 3 ° > 2° > 1°bromides
c) 1°> 2° > 3° bromides
d) 3 ° > 1°> 2 ° bromidesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shraddha Chavan answered |
The reaction follows free radical mechanism and alkyl free radical is formed in the propagation step as
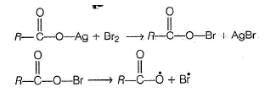
Hence, stability of alkyl free radical (3° > 2° > 1°) determine the reactivity.
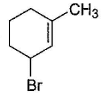
Consider the following reaction,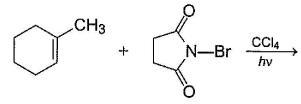 Q. The expected product(s) is/are
Q. The expected product(s) is/are- a)
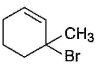
- b)
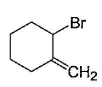
- c)
- d)
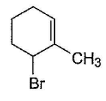
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
The expected product(s) is/are
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
NBS in CCI4 brings about allylic brom ination by free radical mechanism:
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 13-15) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
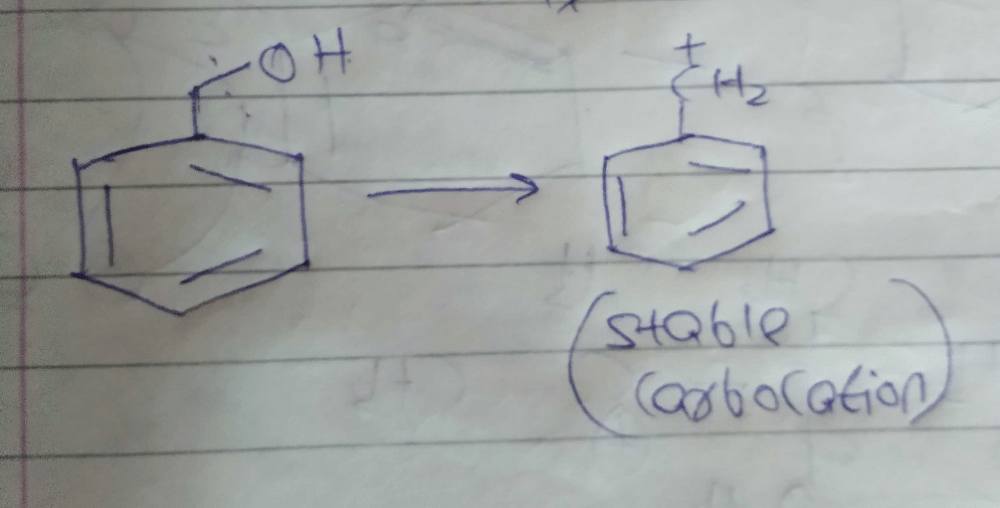
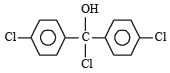
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageAn alcohol (R — OH) can be converted into alkyl chloride by the treatm ent with HCI. Reaction involves protonation of alcohol followed by the formation of carbocation intermediate. Carbocation intermediate in the final step undergo nucleophilic attack by Cl- ion as :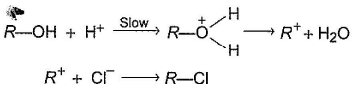 Q. Which of the following alcohol reacts most easily?
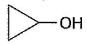
Q. Which of the following alcohol reacts most easily?- a)
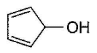
- b)
- c)
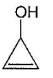
- d)
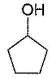
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-15) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc.
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Three questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
An alcohol (R — OH) can be converted into alkyl chloride by the treatm ent with HCI. Reaction involves protonation of alcohol followed by the formation of carbocation intermediate. Carbocation intermediate in the final step undergo nucleophilic attack by Cl- ion as :
Q.
Which of the following alcohol reacts most easily?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Om Desai answered |
As mentioned in mechanism, reaction proceed via carbocation intermediate. Hence, alcohol forming most stable carbocation reacts most easily. Alcohol (c) forms aromatic (highly stable) carbocation, hence most reactive.
On reacting ethene with HCl we get:- a)Chloroethane
- b)Chloropropane
- c)Chloromethane
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
On reacting ethene with HCl we get:
a)
Chloroethane
b)
Chloropropane
c)
Chloromethane
d)
None of these

|
Divey Sethi answered |
hydrogen chloride adds to ethene to make chloroethane:
CH2=CH2 + HCl → CH3CH2Cl
What is the order of reactivity of following halogen acids on alcohols?
HI, HBr, HCl- a)HI < HBr < HCl
- b)HI > HBr > HCl
- c)HI > HCl > HBr
- d)HBr > HCl> HI
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the order of reactivity of following halogen acids on alcohols?
HI, HBr, HCl
HI, HBr, HCl
a)
HI < HBr < HCl
b)
HI > HBr > HCl
c)
HI > HCl > HBr
d)
HBr > HCl> HI
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
That atomic size increases from F to I, so bond length of H-X bond also gets increased and so bond dissociation energy decreases. Hence, ionisation of H-X increases, therefore acidic strength increases in the order
HF < HCl < HBr < HI
So, the reactivity of alcohols towards haloacids is in the order - HI>HBr>HCl
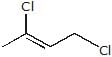
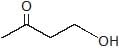
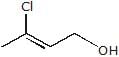
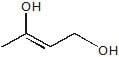
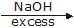 A. A is :
A. A is :- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
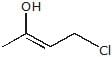
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
(T.S will be stable due to electron cloud of p orbital)
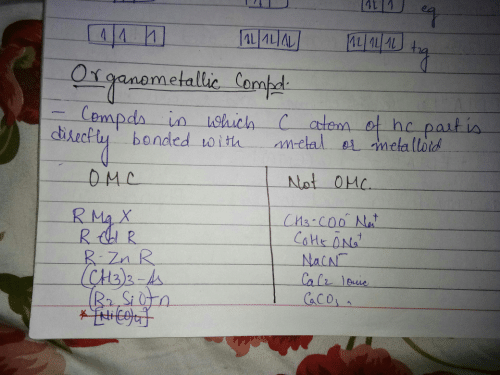
Which of the following is formed by Swarts Reaction?- a)Alkyl iodide
- b)Alkyl fluoride
- c)Alkyl bromide
- d)Alkyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is formed by Swarts Reaction?
a)
Alkyl iodide
b)
Alkyl fluoride
c)
Alkyl bromide
d)
Alkyl chloride
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
In Swarts’ reaction, heavy metal fluorides are used as reagents. It is a reaction in which alkyl fluorides are formed when alkyl bromide or chloride reacts with metal fluorides. In the reaction, higher alkyl halide(R-Cl) react with lower metal halide (AgF) to form lower alkyl halide(R-F). If we don’t use heavy metal fluoride F ion cannot displace Cl/Br. The reaction will not occur or it may form some other compound.
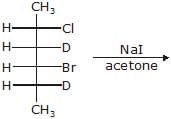 (A),Major-product (A) is
(A),Major-product (A) is- a)
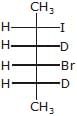
- b)
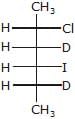
- c)
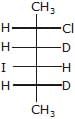
- d)
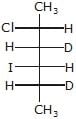
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Major-product (A) is
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
This is SN2 reaction (Halide exchange method)
(i) CH3 – CH2 – Br + NaOH 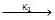 CH3 – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (i)(ii)
CH3 – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (i)(ii) 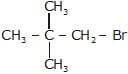 + NaOH
+ NaOH 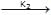 (CH3)3 C – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (ii)K1 & K2 are rate constant for above reaction correct relation is
(CH3)3 C – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (ii)K1 & K2 are rate constant for above reaction correct relation is- a)K1 = K2
- b)K1 > K2
- c)K1 < K2
- d)K1 << K2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
(i) CH3 – CH2 – Br + NaOH 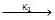 CH3 – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (i)
CH3 – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (i)
(ii)  + NaOH
+ NaOH 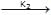 (CH3)3 C – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (ii)
(CH3)3 C – CH2 – OH + NaBr → reaction ... (ii)
K1 & K2 are rate constant for above reaction correct relation is
a)
K1 = K2
b)
K1 > K2
c)
K1 < K2
d)
K1 << K2

|
Utsav Srivastava answered |
Option B is correct because in first reaction there is less steric hindrance as compared to second reaction so there is fast attack of reagent on the reactant in first reaction as compared to the second reaction
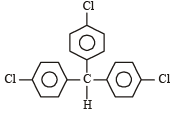
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?- a)C6 H5CH(C6 H5 )Br [2010]
- b)C6 H5CH(CH3)Br
- c)C6 H5C(CH3)(C6 H5)Br
- d)C6 H5CH2Br
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?
a)
C6 H5CH(C6 H5 )Br [2010]
b)
C6 H5CH(CH3)Br
c)
C6 H5C(CH3)(C6 H5)Br
d)
C6 H5CH2Br

|
Rajat Roy answered |
SN1 reactions involve the formation of carbocations, hence higher the stability of carbocation, more will be reactivity of the parent alkyl halide. Thus tertiary carbocation formed from (c) is stabilized by two phenyl groups and one methyl group, hence most stable.
Which is incorrect about Hunsdiecker's reaction ?- a)Only Cl2 can give alkyl halide
- b)I2 will give ester when treated with RCOOAg
- c)The reaction proceeds through free radical
- d)F2 cannot give alkyl halide
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is incorrect about Hunsdiecker's reaction ?
a)
Only Cl2 can give alkyl halide
b)
I2 will give ester when treated with RCOOAg
c)
The reaction proceeds through free radical
d)
F2 cannot give alkyl halide
|
|
Priya Chavan answered |
Except F2, almost all halogens react with RCOOAg giving alkyl halide via Hunsdiecker reaction. With l2 if RCOOAg is in excess, R— I formed in first step reacts further with unreacted salt to give ester as
R — COOAg+ R — I → R — COOR + AgI
R — COOAg+ R — I → R — COOR + AgI
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the SN2 reaction is fastest?- a)
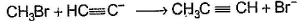
- b)
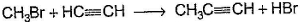
- c)
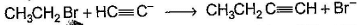
- d)
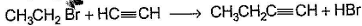
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the SN2 reaction is fastest?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Monika Devi answered |
SN2 reaction means this will be applicable for primary or 1 degree carbon atom and attack by the reagent is forwarded so on doing mechanism we getted that CH3 carry + charge & Br get - charge so acetyl group that have negative charge goes on methyl group & Br react with electronic species
Addition of bromine on propene in the presence of brine yields a mixture of- a)CH3CHCICH2Br and CH3CHBrCH2CI
- b)CH3CHCICH2Br and CH3CHBrCH2Br
- c)CH3CHCICH2CI and CH3CHBrCH2Br
- d)CH3CHCICH2Cl and CH3CHBrCH2Cl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Addition of bromine on propene in the presence of brine yields a mixture of
a)
CH3CHCICH2Br and CH3CHBrCH2CI
b)
CH3CHCICH2Br and CH3CHBrCH2Br
c)
CH3CHCICH2CI and CH3CHBrCH2Br
d)
CH3CHCICH2Cl and CH3CHBrCH2Cl
|
|
Snehal Iyer answered |
Nucleophilic attack in step-ll occur at the carbon atom which can better accommodate the positive charge. Hence, attack of Br- or Cl- in second step occur at 2° carbon rather that at 1° carbon.
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ' X' and reaction in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are : [2010]- a)X = Benzal chloride, Y = o – Chlorotoluene
- b)X = m – Chlorotoluene , Y = p – Chlorotoluene
- c)X = o –and p – Chlorotoluene, Y = Trichloromethyl – benzene
- d)X = Benzyl chloride, Y = m – Chlorotoluene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ' X' and reaction in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are : [2010]
a)
X = Benzal chloride, Y = o – Chlorotoluene
b)
X = m – Chlorotoluene , Y = p – Chlorotoluene
c)
X = o –and p – Chlorotoluene, Y = Trichloromethyl – benzene
d)
X = Benzyl chloride, Y = m – Chlorotoluene
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
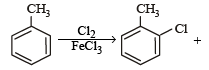
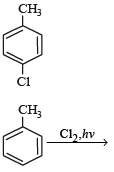
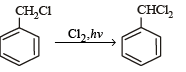
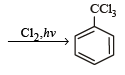
The reaction of SOCl2 on alkanols to form alkyl chlorides gives good yields because- a)Alkyl chlorides are immiscible with SOCl2
- b)The other products of the reaction are gaseous and escape out
- c)Alcohol and SOCl2 are soluble in water
- d)The reaction does not occur via intermediate formation of an alkyl chloro sulphite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of SOCl2 on alkanols to form alkyl chlorides gives good yields because
a)
Alkyl chlorides are immiscible with SOCl2
b)
The other products of the reaction are gaseous and escape out
c)
Alcohol and SOCl2 are soluble in water
d)
The reaction does not occur via intermediate formation of an alkyl chloro sulphite
|
|
Deepak Kapoor answered |
side product
Chapter doubts & questions for Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Chemistry Class 12 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Chemistry Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup