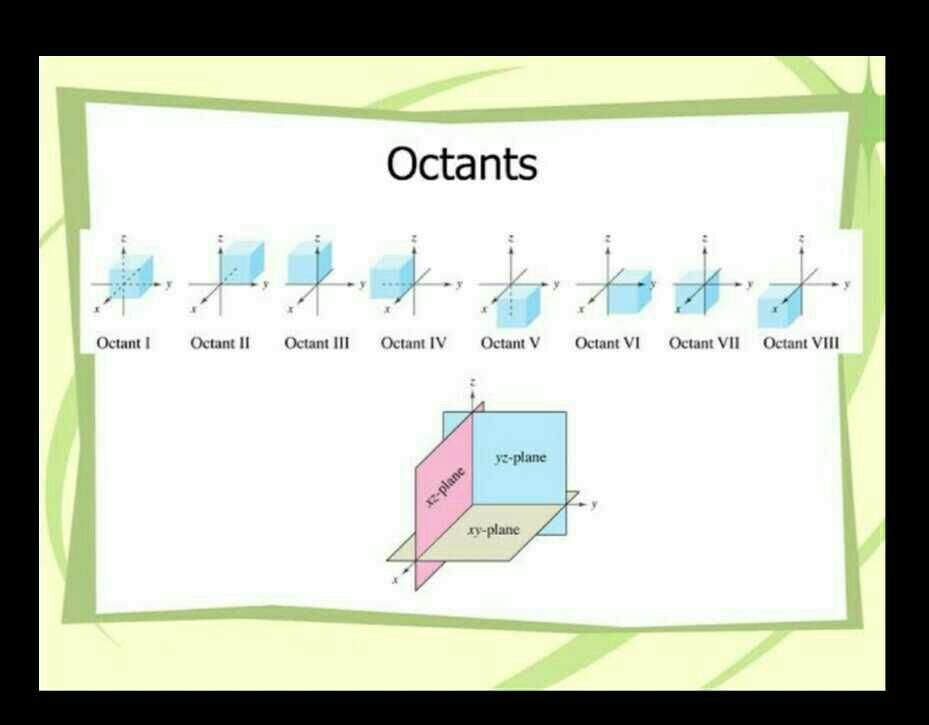
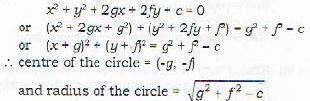All Exams >
Mathematics >
Topic-wise Tests & Solved Examples for Mathematics >
All Questions
All questions of Dimensional Geometry for Mathematics Exam
xx1 + yy1 = a2 is the equation of the- a)Tangent to the circle x2+ y2=a2 at point (x1,y1)
- b)chord of contact of tangents drawn from the external point (x1, y1) to the circle x2+ y2 = a2
- c)polar of the point (x1, y1) w.r.t the circle x2 + y2 = a2
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
xx1 + yy1 = a2 is the equation of the
a)
Tangent to the circle x2+ y2=a2 at point (x1,y1)
b)
chord of contact of tangents drawn from the external point (x1, y1) to the circle x2+ y2 = a2
c)
polar of the point (x1, y1) w.r.t the circle x2 + y2 = a2
d)
all of the above

|
Vivek Kumar answered |
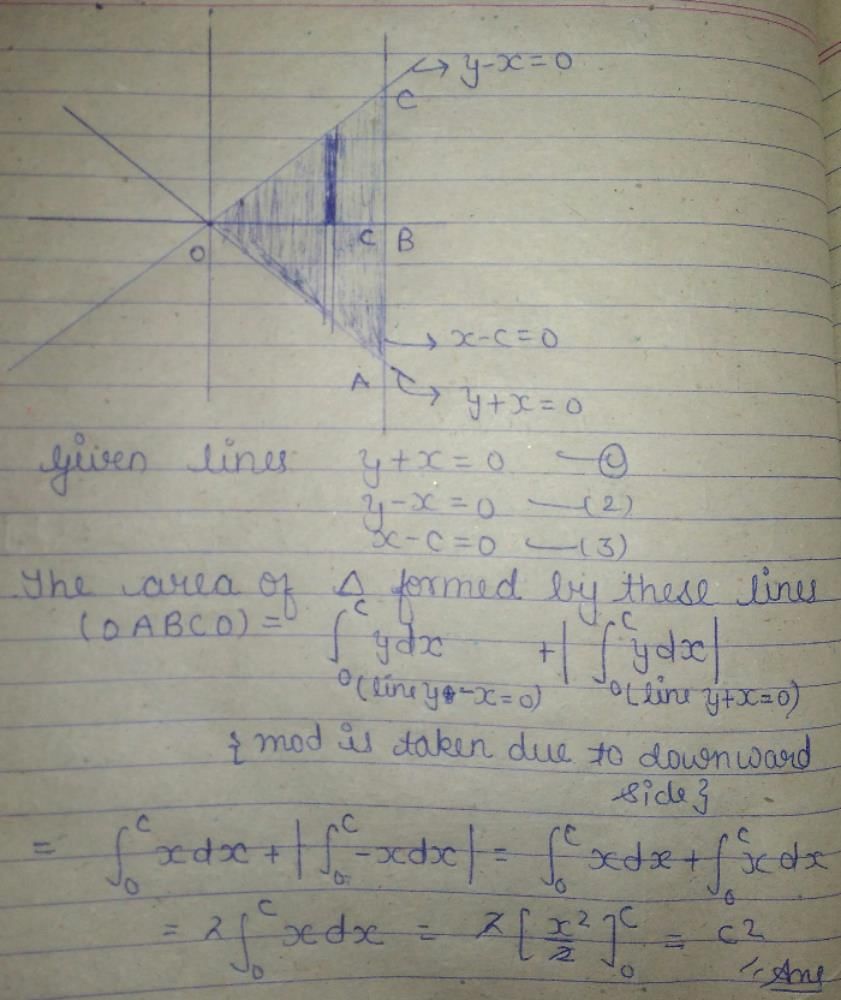
Remark : 1. The following three equations coincide:
(i) Equation of the tangent to a circle at a point P(x1, y1)
(ii) Equation of the chord of contact of the tangents to the circle from an outside point (x1, y1)
(iii) Equation of the polar of a point (x, y) inside or outside the circle (but not on the circle), with repsect to the circle.
Remark: 2. If the point P(x1, y1) is on the circle, then its polar coincides with the tangent at that point.
Remark: 3. If the polar of a point P passes through a point Q, then the polar of Q passes through P.
(i) Equation of the tangent to a circle at a point P(x1, y1)
(ii) Equation of the chord of contact of the tangents to the circle from an outside point (x1, y1)
(iii) Equation of the polar of a point (x, y) inside or outside the circle (but not on the circle), with repsect to the circle.
Remark: 2. If the point P(x1, y1) is on the circle, then its polar coincides with the tangent at that point.
Remark: 3. If the polar of a point P passes through a point Q, then the polar of Q passes through P.
If two pairs of opposite edges of a tetrahedron art; at right angles, then the third pair- a)is also at right angles always
- b)can never be at right angle
- c)is inclined at. some acute angle
- d)is inclined at some obtuse an
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If two pairs of opposite edges of a tetrahedron art; at right angles, then the third pair
a)
is also at right angles always
b)
can never be at right angle
c)
is inclined at. some acute angle
d)
is inclined at some obtuse an
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let the coordinates of the vertices O, A, B, C o f tetrahedron be (α, β, γ), (a, 0, 0), (0, b, 0) and (0. 0, c) respectively. Then it is given that
OA is perpendicular to BC
and OB is perpendicular to CA
To prove that
OC is perpendicular to AB
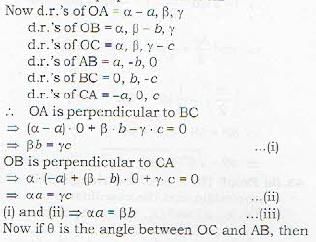
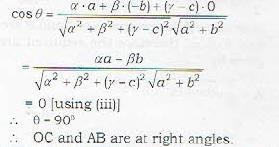
OA is perpendicular to BC
and OB is perpendicular to CA
To prove that
OC is perpendicular to AB
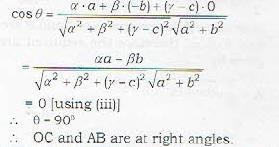
What is the locus of a point for which x = a and y= b?- a)a line parallel to XY plane
- b)a plane parallel to XY plane
- c)a line parallel to z-axis
- d)a plane perpendicular tpo XY plane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the locus of a point for which x = a and y= b?
a)
a line parallel to XY plane
b)
a plane parallel to XY plane
c)
a line parallel to z-axis
d)
a plane perpendicular tpo XY plane
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
x = a is a plane | | to YZ plane
y = b is a plane | | to ZX plane
Therefore x = a and y = b is a line parallel to z-axis
Note : Remember that two planes intersect in a line
y = b is a plane | | to ZX plane
Therefore x = a and y = b is a line parallel to z-axis
Note : Remember that two planes intersect in a line
The angle between the lines in which the planes 3x - 7y - 5z = 1 and 5x - 13y + 3x + 2 = 0 cut the plane 8x - 11y + 3z = 0, is equal to- a)0
- b)π/3
- c)π/2
- d)π/6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle between the lines in which the planes 3x - 7y - 5z = 1 and 5x - 13y + 3x + 2 = 0 cut the plane 8x - 11y + 3z = 0, is equal to
a)
0
b)
π/3
c)
π/2
d)
π/6
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let (l1, m1, n1) be the d.c.’s of the line of intersection of the planes
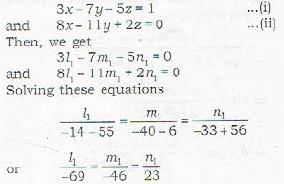
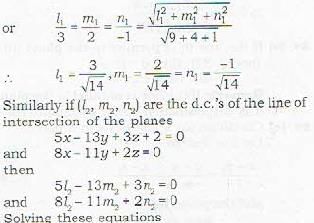
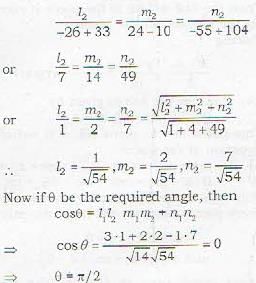
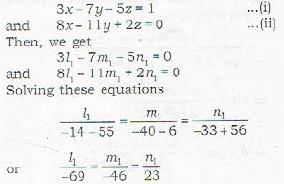
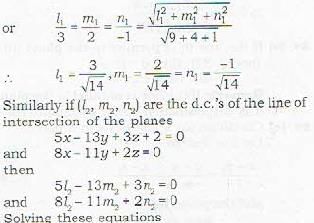
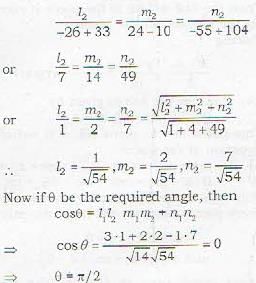
The distance between the parallel planes 2x -2y + z + 3 = 0 and 4x -4y + 2z + 5 = 0 is- a)1/2
- b)1/3
- c)1/6
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance between the parallel planes 2x -2y + z + 3 = 0 and 4x -4y + 2z + 5 = 0 is
a)
1/2
b)
1/3
c)
1/6
d)
none of the above

|
Veda Institute answered |
To find the distance between two parallel planes, we follow the method given below. Method:Find the perpendicular distance of each plane from the origin with proper sign (i.e. do not. lake the mod). Ther. their differeee is the required distance between two parallel planes. Let d. and d, be the distances of the planes
2x -2y + z + 3 =0 ...(i)
and 4x - 4y + 2z + 5 = 0 ...(ii)
from the origin. Then
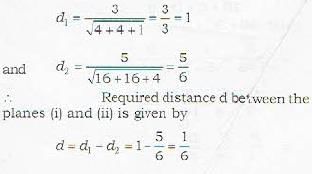
2x -2y + z + 3 =0 ...(i)
and 4x - 4y + 2z + 5 = 0 ...(ii)
from the origin. Then
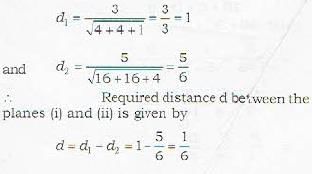
The distance of the point (2, 3, 4) from the plane 3x - 6y + 2z + 11 =0 is- a)1
- b)43/√7
- c)1/49
- d)-1/49
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance of the point (2, 3, 4) from the plane 3x - 6y + 2z + 11 =0 is
a)
1
b)
43/√7
c)
1/49
d)
-1/49
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Proof: If d is the required distance of the point (2, 3, 4) from the plane
3x -6y + 2z + 11 = 0
Then
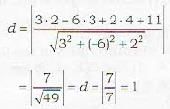
3x -6y + 2z + 11 = 0
Then
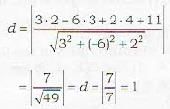
The equation
ax2 + ay2 + az2 + 2ux - 2vy - 2wz + d - 0 (a ≠ 0)
represents a sphere if- a)u2+v2+w2-d≥0
- b)u2+v2+w2-ad≥0
- c)u2+v2+w2-d≤0
- d)u2+v2+w2-ad≤0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation
ax2 + ay2 + az2 + 2ux - 2vy - 2wz + d - 0 (a ≠ 0)
represents a sphere if
ax2 + ay2 + az2 + 2ux - 2vy - 2wz + d - 0 (a ≠ 0)
represents a sphere if
a)
u2+v2+w2-d≥0
b)
u2+v2+w2-ad≥0
c)
u2+v2+w2-d≤0
d)
u2+v2+w2-ad≤0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The given equation is
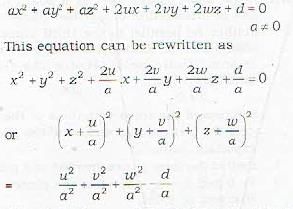
Note that the equation of a sphere has three characteristics :
1. it is of second degree in x, y, y
2. the coefficients of x2, y2 and z2 and equal
3. the product icrins xy, yzand zx are absent.
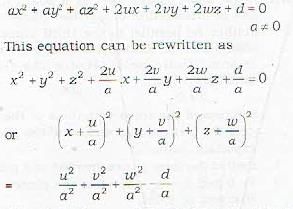
Note that the equation of a sphere has three characteristics :
1. it is of second degree in x, y, y
2. the coefficients of x2, y2 and z2 and equal
3. the product icrins xy, yzand zx are absent.
The line joining the origin to the point of intersection of 2x + 5y- 4 = 0 and 3x-2y+ 2 = 0 is given by- a)5x+3y=0
- b)8x+y=0
- c)x-7y=0
- d)8x+9y=0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The line joining the origin to the point of intersection of 2x + 5y- 4 = 0 and 3x-2y+ 2 = 0 is given by
a)
5x+3y=0
b)
8x+y=0
c)
x-7y=0
d)
8x+9y=0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The given straight lines are

Their point of intersection is obtained on solving equations (i) and (ii) and is
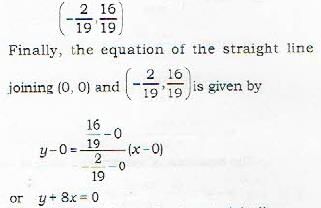

Their point of intersection is obtained on solving equations (i) and (ii) and is
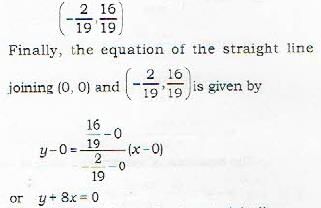
The equation of the plane passing through the point (x1, y1, z1) and through the line 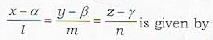
- a)
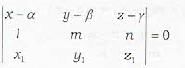
- b)
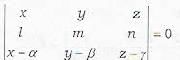
- c)
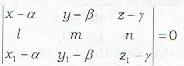
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the plane passing through the point (x1, y1, z1) and through the line 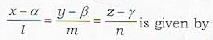
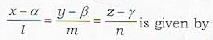
a)
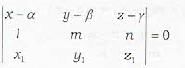
b)
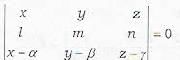
c)
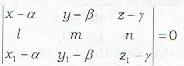
d)
none of the above
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
To find the equation of a plane passing through a given point (x1, y1, z1) and a given line 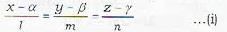
The equation of the plane through the line (i) is
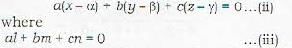
Since the plane (ii) passes through the point (x1, y1, z1), therefore
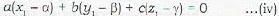
Eliminating a, b, c from equations (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get the required equation of the plane as
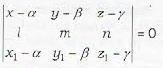
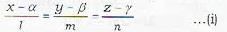
The equation of the plane through the line (i) is
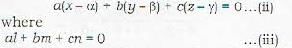
Since the plane (ii) passes through the point (x1, y1, z1), therefore
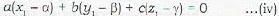
Eliminating a, b, c from equations (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get the required equation of the plane as
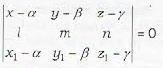
What is the magnitude of the line of shortest distance between the lines 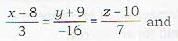
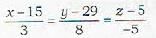
- a)√14
- b)14
- c)7
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the magnitude of the line of shortest distance between the lines 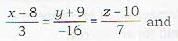
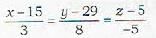
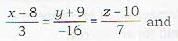
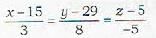
a)
√14
b)
14
c)
7
d)
2
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Magnitude and equations of Shortest Distance (S.D)
Here we have to find the magnitude and the equation of shorttest distance between two given lines.
* It
By definition, the line of shortest distance between (i) and (ii) is perpendicular to both (i) and (ii). Therefore, if [λ,μ,ν] an; the d.c.’s of the line of shortest distance we have
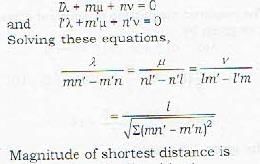
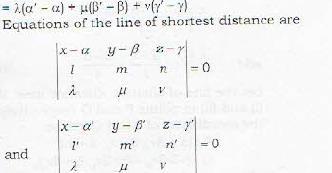
Remark: Two lines given by (i) and (ii) will intersect, i.e. these lines will be coplanar if shortest distance between them is zero. Thus the condition for two lines to be coplanar is
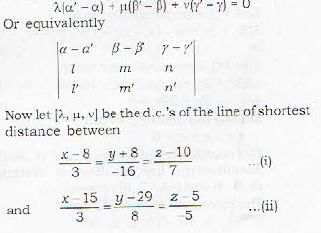
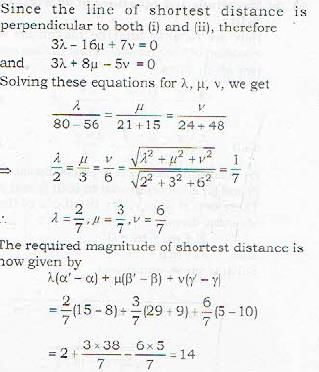
Here we have to find the magnitude and the equation of shorttest distance between two given lines.
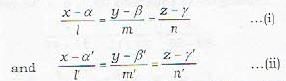
* It
By definition, the line of shortest distance between (i) and (ii) is perpendicular to both (i) and (ii). Therefore, if [λ,μ,ν] an; the d.c.’s of the line of shortest distance we have
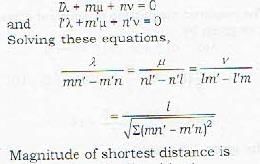
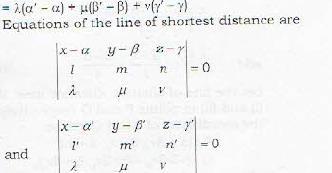
Remark: Two lines given by (i) and (ii) will intersect, i.e. these lines will be coplanar if shortest distance between them is zero. Thus the condition for two lines to be coplanar is
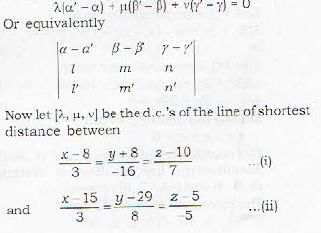
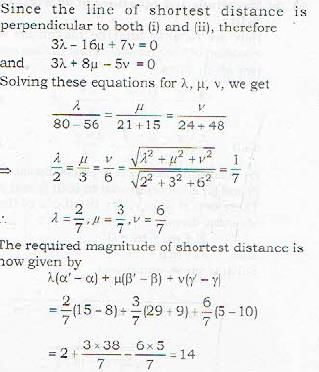
To transform the equations of a line from unsymmeirieal form to the symmetrical form, it is necessary to know about- a)The direction ratio of the line
- b)The coordinates of any one point on it
- c)The coordinates of any two points on it and its direction ratio
- d)Its direction ratios and the coordinates of any one point on it only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To transform the equations of a line from unsymmeirieal form to the symmetrical form, it is necessary to know about
a)
The direction ratio of the line
b)
The coordinates of any one point on it
c)
The coordinates of any two points on it and its direction ratio
d)
Its direction ratios and the coordinates of any one point on it only
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The equations of the line in the symmetrical form are
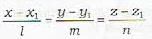
where (x1, y1 ,z1) is a given point on the line and (l, m, n) are the direction ratios of the line. Therefore the equations of a straight line can be written in symmetrical form if we know.
(i) the direction ratios of the line and
(ii) a point on it.
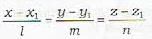
where (x1, y1 ,z1) is a given point on the line and (l, m, n) are the direction ratios of the line. Therefore the equations of a straight line can be written in symmetrical form if we know.
(i) the direction ratios of the line and
(ii) a point on it.
The area of the quadrilateral ABCD with coordinates of A, B, C and D as (-4, 2), (3, -5), (1, 7) and (6, -2) respectively is- a)14
- b)56
- c)28
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of the quadrilateral ABCD with coordinates of A, B, C and D as (-4, 2), (3, -5), (1, 7) and (6, -2) respectively is
a)
14
b)
56
c)
28
d)
none of the above
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Proof: Let the given points be
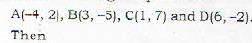
= Area of triangle ABC + Area of triangle BCD
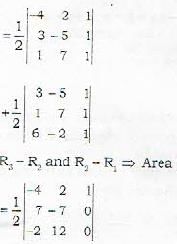
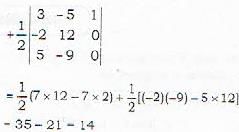
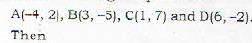
= Area of triangle ABC + Area of triangle BCD
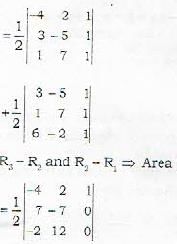
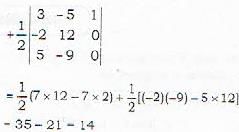
The angle between the line 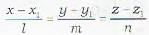 and the plane ax+by+cz+d=0, is given by
and the plane ax+by+cz+d=0, is given by- a)
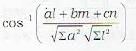
- b)
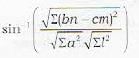
- c)
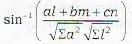
- d)
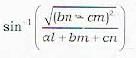
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle between the line 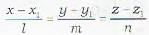 and the plane ax+by+cz+d=0, is given by
and the plane ax+by+cz+d=0, is given by
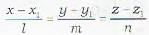 and the plane ax+by+cz+d=0, is given by
and the plane ax+by+cz+d=0, is given bya)
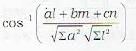
b)
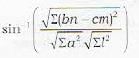
c)
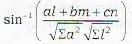
d)
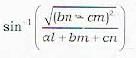
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
To find the angle between the line
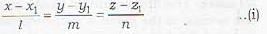

Let θ be 1 he angle between the line (i) and the plane (ii). Then 90 - θ is the angle between the line and the normal to the plane.
Now th2 d.r.’s of the line (i) are l, m, n and the d.r/s of the line perpendicular lo (ii) are a, b, c
∴ cos (90 - θ)
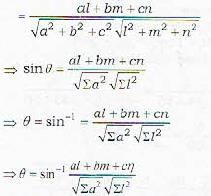
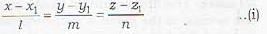

Let θ be 1 he angle between the line (i) and the plane (ii). Then 90 - θ is the angle between the line and the normal to the plane.
Now th2 d.r.’s of the line (i) are l, m, n and the d.r/s of the line perpendicular lo (ii) are a, b, c
∴ cos (90 - θ)
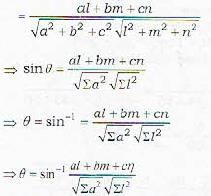
Which is a wrong statement? The three planes
a1x + b1y + c1z + d1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2z + d2 = 0
a3x + b3y + c3z + d3 = 0
have a common line of intersection, if- a)
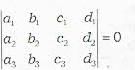
- b)
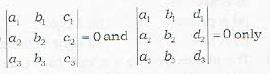
- c)
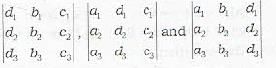 all vanish
all vanish - d)
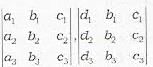
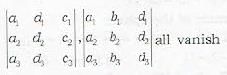
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is a wrong statement? The three planes
a1x + b1y + c1z + d1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2z + d2 = 0
a3x + b3y + c3z + d3 = 0
have a common line of intersection, if
a1x + b1y + c1z + d1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2z + d2 = 0
a3x + b3y + c3z + d3 = 0
have a common line of intersection, if
a)
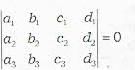
b)
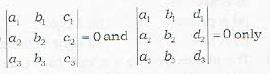
c)
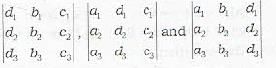 all vanish
all vanishd)
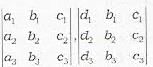
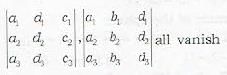
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The three planes are
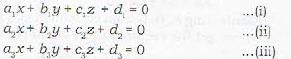
Denote the determinants as follows:
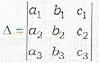
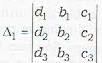
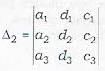
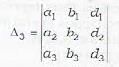
Note that Δ is th e coefficients of x, y and z . Δ1, Δ2 and Δ3, are obtained from Δ by replacing its first column, 2nd column and 3rd column by d1, d2 and d3, respectively.
Also note that if the three planes are to intersect in a line, then no two of them are parallel. Under this case, the line of intersection of any two planes will lie on the third plane. Now the line of intersection of (i) and (ii) is given by
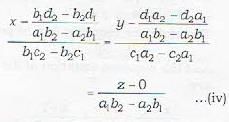
Since line (iv) lies on plane (iii), therefore is perpendicuar to the normal to the plane (iii)
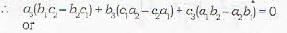
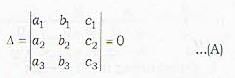
Also since line (iv) lies on plane (iii), therefore the coordinates of any point on the line will satisfy the equation of plane (iii), since
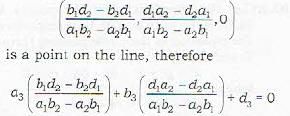
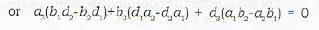
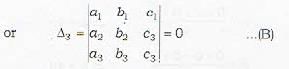
Thus (A) and (R) are the required conditions for the three planes to have a common line of intersection.
In a similar way, it can he shown that Δ = 0 and Δ1 = 0 or Δ = 0 and Δ2 = 0 are also the required conditions.
∴ (b), (c), (d) are correct.
Remark: To prove that three planes intersect in a line, verify that Δ = 0 and any one: of Δ1,Δ2 and Δ
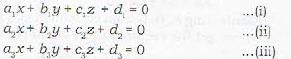
Denote the determinants as follows:
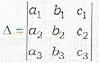
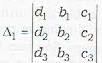
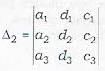
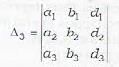
Note that Δ is th e coefficients of x, y and z . Δ1, Δ2 and Δ3, are obtained from Δ by replacing its first column, 2nd column and 3rd column by d1, d2 and d3, respectively.
Also note that if the three planes are to intersect in a line, then no two of them are parallel. Under this case, the line of intersection of any two planes will lie on the third plane. Now the line of intersection of (i) and (ii) is given by
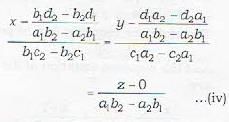
Since line (iv) lies on plane (iii), therefore is perpendicuar to the normal to the plane (iii)
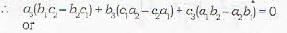
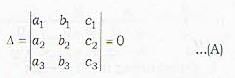
Also since line (iv) lies on plane (iii), therefore the coordinates of any point on the line will satisfy the equation of plane (iii), since
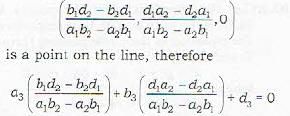
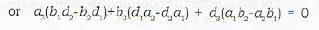
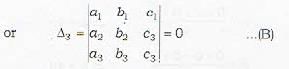
Thus (A) and (R) are the required conditions for the three planes to have a common line of intersection.
In a similar way, it can he shown that Δ = 0 and Δ1 = 0 or Δ = 0 and Δ2 = 0 are also the required conditions.
∴ (b), (c), (d) are correct.
Remark: To prove that three planes intersect in a line, verify that Δ = 0 and any one: of Δ1,Δ2 and Δ
3
becomes zero.The rectangular coordinates of the point (-4, -π/4) are- a)(2√2,2√2)
- b)(-2√2,2√2)
- c)(√2,-2)
- d)(-√2,2√2)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The rectangular coordinates of the point (-4, -π/4) are
a)
(2√2,2√2)
b)
(-2√2,2√2)
c)
(√2,-2)
d)
(-√2,2√2)
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The point (-4, -π/4) will lie in the 3rd quadrant and its coordinates in rectangular (cartesian) coordinates shall be
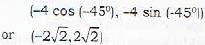
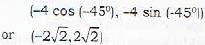
The lines represented by the equation Ax2 + 2Bxy + Cy2 = 0 are real, coincident or imaginary according as B2 - AC is- a)Negative, zero or positive
- b)zero, positive or negative
- c)positive, negative or zero
- d)Positive, zero or negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The lines represented by the equation Ax2 + 2Bxy + Cy2 = 0 are real, coincident or imaginary according as B2 - AC is
a)
Negative, zero or positive
b)
zero, positive or negative
c)
positive, negative or zero
d)
Positive, zero or negative
|
|
Arghya answered |
The lines are represented by
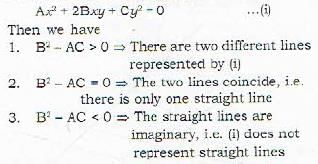
The circles x2 + y2 + 2px + 2fy + c = 0 and x2 y2 + 2g' + 2f'y - c = 0 cut each other orthogonally if- a)2(gg' + f f') = c + c'
- b)gg' + f f' = 2(c + c')
- c)2(gg' - f f') = c - c'
- d)(gg' - f f') = 2(c - c')
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The circles x2 + y2 + 2px + 2fy + c = 0 and x2 y2 + 2g' + 2f'y - c = 0 cut each other orthogonally if
a)
2(gg' + f f') = c + c'
b)
gg' + f f' = 2(c + c')
c)
2(gg' - f f') = c - c'
d)
(gg' - f f') = 2(c - c')

|
Veda Institute answered |
Proof: let the two circles
Let C1, and C2 be the center of S1 and S2 resoectivelv. Then
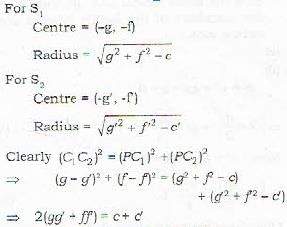
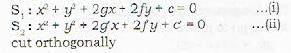
Let C1, and C2 be the center of S1 and S2 resoectivelv. Then
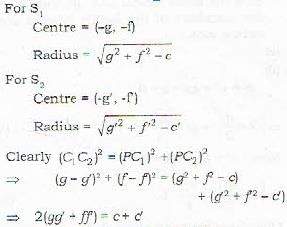
The equation of a straight line which makes an angle of 60° with x-axis and passes through the point (√3, 2) is given by- a)y = √3x + 1
- b)√3x- y = 1
- c)x - √y = √3
- d)x-√2y=√2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of a straight line which makes an angle of 60° with x-axis and passes through the point (√3, 2) is given by
a)
y = √3x + 1
b)
√3x- y = 1
c)
x - √y = √3
d)
x-√2y=√2
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The required equation
(i) makes an angle of 60° with x-axis
(ii) passes through the point (√3 , 2)
Now
(i) ⇒ equation of the straight line will be
y = tan 60° x + c
or y = √3 x + c ...(i)
(ii) ⇒ the coordinates of the point will satisfy equation (i)
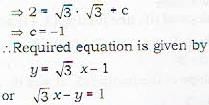
(i) makes an angle of 60° with x-axis
(ii) passes through the point (√3 , 2)
Now
(i) ⇒ equation of the straight line will be
y = tan 60° x + c
or y = √3 x + c ...(i)
(ii) ⇒ the coordinates of the point will satisfy equation (i)
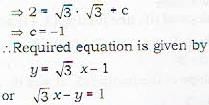
Let A(-1,2, -3), B(5, 0, -6), C(0, 4, -1) be the three points. Then the direction cosines of the internal bisector of the angle BAC are proportional to- a)(25,8,5)
- b)(-11,20,23)
- c)(7,-6,-9)
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Let A(-1,2, -3), B(5, 0, -6), C(0, 4, -1) be the three points. Then the direction cosines of the internal bisector of the angle BAC are proportional to
a)
(25,8,5)
b)
(-11,20,23)
c)
(7,-6,-9)
d)
none of the above
|
|
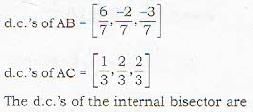
Chirag Verma answered |
Proof in short : verify that
AB = 7 and AC = 3
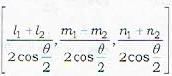
where θ is the angle between AB (with d.c.'s [l1, m1, n1]) and AC (with d.c.’s [l2, m2, n2)
∴ the d.c.’s of the internal bisector are proprotional to l1+l2, m1+m2, n1+n2
or proportional to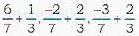
or proportional to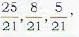
or proportional to 25, 8, 5
AB = 7 and AC = 3

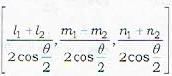
where θ is the angle between AB (with d.c.'s [l1, m1, n1]) and AC (with d.c.’s [l2, m2, n2)
∴ the d.c.’s of the internal bisector are proprotional to l1+l2, m1+m2, n1+n2
or proportional to
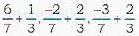
or proportional to
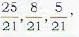
or proportional to 25, 8, 5
Which one of following statements is incorrect?- a)the radical axes of the three circles, taken in pairs, meet in a point
- b)the radical axis of two circles is the locus of a poinl which moves so thal the lengths of the tangents drawn from it to the two circles arc equal
- c)The radical centre is the point of intersection of the three radical axes, taken in pairs
- d)one of the above statements is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of following statements is incorrect?
a)
the radical axes of the three circles, taken in pairs, meet in a point
b)
the radical axis of two circles is the locus of a poinl which moves so thal the lengths of the tangents drawn from it to the two circles arc equal
c)
The radical centre is the point of intersection of the three radical axes, taken in pairs
d)
one of the above statements is incorrect
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
All the three statements (a), (b) and (c) arc correct.
Remark: Remember these properties about radical axis.
Remark: Remember these properties about radical axis.
The two planes represented by ax2 - by2 + cz2 + 2fyz + 2gzx + 2 hxy = 0 are perpendicular if- a)abc + 2fgh + af2 + bg- + ch2 = 0
- b)af + bg + ch - 0
- c)a + b + c = 0
- d)f2 + g2 + h2 - bc - ca - ab = 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The two planes represented by ax2 - by2 + cz2 + 2fyz + 2gzx + 2 hxy = 0 are perpendicular if
a)
abc + 2fgh + af2 + bg- + ch2 = 0
b)
af + bg + ch - 0
c)
a + b + c = 0
d)
f2 + g2 + h2 - bc - ca - ab = 0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let the two planes r epresented by
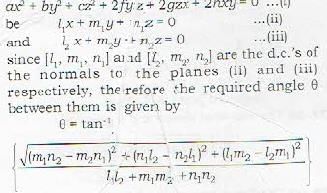
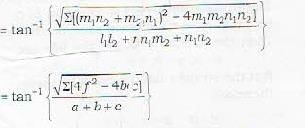
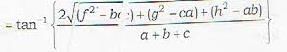
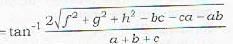
Condition of perpendicularity.
The two planes are perpendicular if
θ = 90° or tan θ = ∞
or a + b + c = 0
Remark: since the two planes pass through the origin, therefore the two planes are never parallel. The two planes can however coincide.
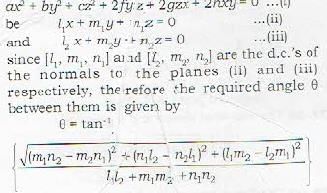
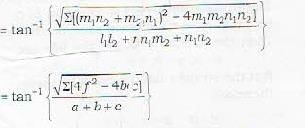
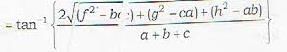
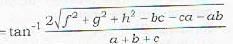
Condition of perpendicularity.
The two planes are perpendicular if
θ = 90° or tan θ = ∞
or a + b + c = 0
Remark: since the two planes pass through the origin, therefore the two planes are never parallel. The two planes can however coincide.
The condition that one of the straight lines given by the equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 may coincide with one of those given by the equation a'x2 + 2h'xy - b'y2 = 0 is given b- a)(ab'- a’b)2 = 4(ha'- h'a) (bh' - b'h)
- b)(ab'- a’b)2 = 4(ha'- h'a) (hb' - h'b)
- c)(ab'- a’b)2 = (ha'- h'a) (bh' - b'h)
- d)(ab'- a'b)2 = 2(ha'- h'a) (hb' - h'b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The condition that one of the straight lines given by the equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 may coincide with one of those given by the equation a'x2 + 2h'xy - b'y2 = 0 is given b
a)
(ab'- a’b)2 = 4(ha'- h'a) (bh' - b'h)
b)
(ab'- a’b)2 = 4(ha'- h'a) (hb' - h'b)
c)
(ab'- a’b)2 = (ha'- h'a) (bh' - b'h)
d)
(ab'- a'b)2 = 2(ha'- h'a) (hb' - h'b)

|
Veda Institute answered |
Proof: Let y = mx be die straight line common to ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = 0 ...(i)
and a'x2 + 2h'xy + b'y2 = 0 ...(ii)
So diat let the straight lines represented by (i) be
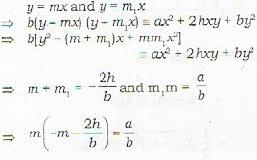
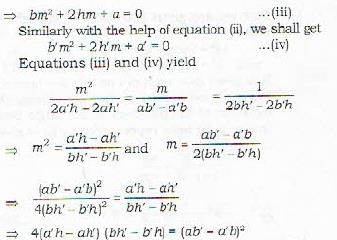
and a'x2 + 2h'xy + b'y2 = 0 ...(ii)
So diat let the straight lines represented by (i) be
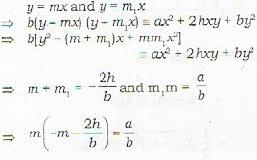
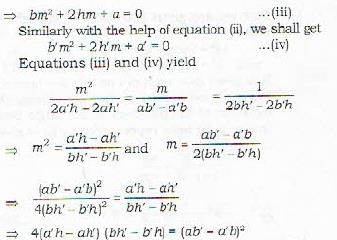
The distance of the plane 6x -3y + 2z - 14 = 0 from the origin is- a)2
- b)14
- c)-14
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance of the plane 6x -3y + 2z - 14 = 0 from the origin is
a)
2
b)
14
c)
-14
d)
7
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The length of the perpendicular from (x1, y1 ,z1) to the plane Ax+ By - Cz + D = 0
is given by
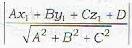
∴ perpendicular distance d of the plane
6x-3y-2z -14=0
from the origin is given by
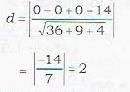
is given by
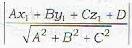
∴ perpendicular distance d of the plane
6x-3y-2z -14=0
from the origin is given by
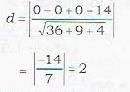
The three planes
2x + 3y - z - 2 = 0
3x + 3y + z - 4 - 0
x - y + 2z - 5 = 0
intersect in- a)A prism
- b)A point
- c)A line
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The three planes
2x + 3y - z - 2 = 0
3x + 3y + z - 4 - 0
x - y + 2z - 5 = 0
intersect in
2x + 3y - z - 2 = 0
3x + 3y + z - 4 - 0
x - y + 2z - 5 = 0
intersect in
a)
A prism
b)
A point
c)
A line
d)
none of the above
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The equations of the planes are
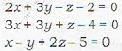
Let us calculate the determinant A of coefficients.
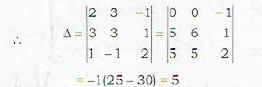
Since A ≠ 0, therefore the planes will intersect at a point.
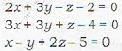
Let us calculate the determinant A of coefficients.
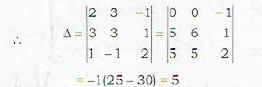
Since A ≠ 0, therefore the planes will intersect at a point.
In the equation of the plane given by ax + by + cz + d = 0: a. b, c denote the- a)Direction cosines of the normal to the plane
- b)Direction ratios of the normal to the plane
- c)Direction cosines of any line on the plane
- d)Direction cosines of a line parallel to the plane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the equation of the plane given by ax + by + cz + d = 0: a. b, c denote the
a)
Direction cosines of the normal to the plane
b)
Direction ratios of the normal to the plane
c)
Direction cosines of any line on the plane
d)
Direction cosines of a line parallel to the plane
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Note that an equation of first degree in x, y, z of the form
Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 ...(i)
represents a plane
d.r.’s of the normal to (i) are A,B,C.
∴ d.e.'s of the normal to (i) are
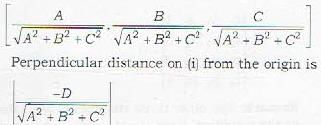
Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 ...(i)
represents a plane
d.r.’s of the normal to (i) are A,B,C.
∴ d.e.'s of the normal to (i) are
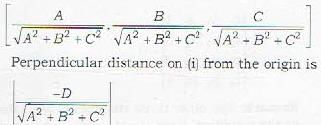
The equation of the bisector of the angle between the lines 3x - 4y + 7 = 0 and 12x - 3y -8 =0 , in w hich the origin lines, is given by- a)21x+27y-131=0
- b)99x-77y+51=0
- c)21x+27y+131=0
- d)99x-77y-51=0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the bisector of the angle between the lines 3x - 4y + 7 = 0 and 12x - 3y -8 =0 , in w hich the origin lines, is given by
a)
21x+27y-131=0
b)
99x-77y+51=0
c)
21x+27y+131=0
d)
99x-77y-51=0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Equations of Bisectors of the Angles between two non-parallel lines.
Let the straight lines
Ax+ By + C = 0 and
A'x + B'y + C = 0
be non-parallel. Then the bisectors are
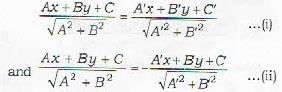
Rules:
1. if C > 0, C' > 0 and AA' + BB' > 0, then (i) is the equation of obtuse - angle bisector (so the equation (ii) gives the acute - angle bisector).
2. If C > 0, C' > 0 and AA' * BB' < 0, then (i) is the equation of acute - angle bisector (so (ii) gives the obtuse - angle bisector)
3. If C and C' are of the same sign (cither both positive or both negative), then (i) is the bisector of that angle (acute or obtuse) in which the origin lies.
In Problem 42, the given equations are
3x-4y + 7= 0 and
12x - 5y = 8 = 0
Since C and C' are of opposite sign, therefore the bisector of the angle between (iii) and (iv), in which the origin lies in given by
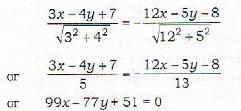
Let the straight lines
Ax+ By + C = 0 and
A'x + B'y + C = 0
be non-parallel. Then the bisectors are
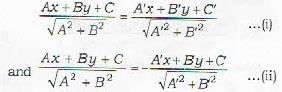
Rules:
1. if C > 0, C' > 0 and AA' + BB' > 0, then (i) is the equation of obtuse - angle bisector (so the equation (ii) gives the acute - angle bisector).
2. If C > 0, C' > 0 and AA' * BB' < 0, then (i) is the equation of acute - angle bisector (so (ii) gives the obtuse - angle bisector)
3. If C and C' are of the same sign (cither both positive or both negative), then (i) is the bisector of that angle (acute or obtuse) in which the origin lies.
In Problem 42, the given equations are
3x-4y + 7= 0 and
12x - 5y = 8 = 0
Since C and C' are of opposite sign, therefore the bisector of the angle between (iii) and (iv), in which the origin lies in given by
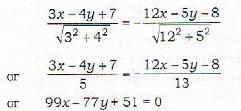
Which of the following equation represent pair of perpendicular planes?- a)2x2 - 2y2 + 4z2 - 2yz+ 6xz - 3xy = 0
- b)6x2+4y2-10z2+3yz+4zx-11xy=0
- c)12x2-y2+6z2+7yz+6zx+2xy=0
- d)12x2-y2+2z2-yz+5zx+xy=0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following equation represent pair of perpendicular planes?
a)
2x2 - 2y2 + 4z2 - 2yz+ 6xz - 3xy = 0
b)
6x2+4y2-10z2+3yz+4zx-11xy=0
c)
12x2-y2+6z2+7yz+6zx+2xy=0
d)
12x2-y2+2z2-yz+5zx+xy=0

|
Veda Institute answered |
Planes represented by (b) are perpendicular planes.
Proof: The planes are given by
6x2+4y2-10z2+3yz+4zx-11xy=0
∴ a=6, b=4, c=-10
∴ a+b+c=6-4-10=0
Remark. Two planes arc perpendicular if the sum of the coefficients of x2, y2 and z2 is zero.
Proof: The planes are given by
6x2+4y2-10z2+3yz+4zx-11xy=0
∴ a=6, b=4, c=-10
∴ a+b+c=6-4-10=0
Remark. Two planes arc perpendicular if the sum of the coefficients of x2, y2 and z2 is zero.
The radical axis of the two circles
x2 + y2 +2gx + 2fy + c = 0 and
x2 + y2 + 2g1x + 2f1y + c1 =0 is given by- a)x(g-g1) + y(f-f1) +( c-c1) =0
- b)x(g-g1) + y(f-f1) +2( c-c1) =0
- c)x(g-g1) + y(f+f1) +( c-c1) =0
- d)2x(g-g1) + 2y(f-f1) +( c-c1) =0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The radical axis of the two circles
x2 + y2 +2gx + 2fy + c = 0 and
x2 + y2 + 2g1x + 2f1y + c1 =0 is given by
x2 + y2 +2gx + 2fy + c = 0 and
x2 + y2 + 2g1x + 2f1y + c1 =0 is given by
a)
x(g-g1) + y(f-f1) +( c-c1) =0
b)
x(g-g1) + y(f-f1) +2( c-c1) =0
c)
x(g-g1) + y(f+f1) +( c-c1) =0
d)
2x(g-g1) + 2y(f-f1) +( c-c1) =0

|
Veda Institute answered |
Comments about Radical Axis
1. Definition : The radical axis of two circles is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that the lengths of the tangents drawn from it to the two circles are equal.
2. The radical axis of two circles is perpendicular !<> the line joining their centres.
3. Equation of the Radical Axis
Let [h, k) be the point on the radical axis. Then the lengths of the tangents from (h, k) to the two circles are equal.
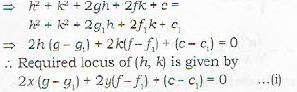
1. Definition : The radical axis of two circles is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that the lengths of the tangents drawn from it to the two circles are equal.
2. The radical axis of two circles is perpendicular !<> the line joining their centres.
3. Equation of the Radical Axis
Let [h, k) be the point on the radical axis. Then the lengths of the tangents from (h, k) to the two circles are equal.
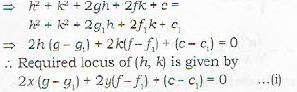
If the projection of a line segment on the X- axis , Y-axis and Z axis be 12, 4 and 3 respectiveIv, then it’s length will be- a)19
- b)13
- c)17
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the projection of a line segment on the X- axis , Y-axis and Z axis be 12, 4 and 3 respectiveIv, then it’s length will be
a)
19
b)
13
c)
17
d)
none
|
|
Pranav Sharma answered |
Is not possible to determine the length of the line segment solely based on the information given. The projection lengths on the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis only provide information about the components of the line segment along each axis, but they do not give the actual length of the line segment.
The length of ihe. perpendicular from the origin on the straight line 5x+12y=0 is given by- a)676/169
- b)26/169
- c)-2
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of ihe. perpendicular from the origin on the straight line 5x+12y=0 is given by
a)
676/169
b)
26/169
c)
-2
d)
2

|
Vivek Kumar answered |
If p is the length of the perpendicular from the origin on the line
5x + 12y - 26 = 0
then

5x + 12y - 26 = 0
then

The equation of the plane through the points (2, 3, 1) and (-4. 5. 3) and parallel to X - axis is given by- a)x - z - 1 = 0
- b)4x - y - 11 = 0
- c)y + 4z - 7 = 0
- d)6x - 2y - 2x + 4 = 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the plane through the points (2, 3, 1) and (-4. 5. 3) and parallel to X - axis is given by
a)
x - z - 1 = 0
b)
4x - y - 11 = 0
c)
y + 4z - 7 = 0
d)
6x - 2y - 2x + 4 = 0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The plane is parallel' to x-axis. Therefore, it is perpendicular to yzplane.
Hence its equation should be of the form
By Cz + D = 0
Since, the plane passes through (2, 3, 1) and (4, -5, 3), therefore.
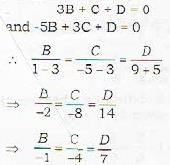

Hence its equation should be of the form
By Cz + D = 0
Since, the plane passes through (2, 3, 1) and (4, -5, 3), therefore.
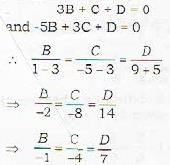

The two planes ax + by +by + cz + d = 0 and a'x + b'y + c'z + d = 0 are perpendicular if- a)aa' + bb' + cc' +dd' =0
- b)a/a' = b/b' + c/c' + d/d' =0
- c)a/a'=b/b' =c/c'
- d)aa' +bb' + cc' =0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The two planes ax + by +by + cz + d = 0 and a'x + b'y + c'z + d = 0 are perpendicular if
a)
aa' + bb' + cc' +dd' =0
b)
a/a' = b/b' + c/c' + d/d' =0
c)
a/a'=b/b' =c/c'
d)
aa' +bb' + cc' =0
|
|
Rajat Agrawal answered |
Explanation:
To determine if two planes are perpendicular, we need to check the dot product of their normal vectors. Let's consider the two planes:
Plane 1: ax + by + cz + d = 0
Plane 2: ax + by + cz + d = 0
Step 1: Finding the normal vectors:
The coefficients of x, y, and z in the equations of the planes give us the normal vectors. In this case, the normal vectors for both planes are given by:
Normal vector 1: (a, b, c)
Normal vector 2: (a, b, c)
Step 2: Calculating the dot product:
The dot product of two vectors is given by the sum of the products of their corresponding components. In this case, the dot product of the normal vectors is:
(a, b, c) • (a, b, c) = a*a + b*b + c*c
Step 3: Checking for perpendicularity:
For two vectors to be perpendicular, their dot product must be zero. Therefore, we need to check if:
a*a + b*b + c*c = 0
Step 4: Simplifying the equation:
To simplify the equation further, we can divide both sides by a*a, b*b, and c*c (assuming they are not zero):
(a*a + b*b + c*c)/(a*a) = 0/(a*a)
1 + (b*b)/(a*a) + (c*c)/(a*a) = 0
Step 5: Simplifying further:
We can rewrite (b*b)/(a*a) as (b/a)^2 and (c*c)/(a*a) as (c/a)^2:
1 + (b/a)^2 + (c/a)^2 = 0
Step 6: Final conclusion:
For the equation to hold true, each of the terms on the left side must be zero. Therefore, we have:
a = 0
b/a = 0
c/a = 0
This implies that a, b, and c are all zero. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D': aa + bb + cc = 0.
To determine if two planes are perpendicular, we need to check the dot product of their normal vectors. Let's consider the two planes:
Plane 1: ax + by + cz + d = 0
Plane 2: ax + by + cz + d = 0
Step 1: Finding the normal vectors:
The coefficients of x, y, and z in the equations of the planes give us the normal vectors. In this case, the normal vectors for both planes are given by:
Normal vector 1: (a, b, c)
Normal vector 2: (a, b, c)
Step 2: Calculating the dot product:
The dot product of two vectors is given by the sum of the products of their corresponding components. In this case, the dot product of the normal vectors is:
(a, b, c) • (a, b, c) = a*a + b*b + c*c
Step 3: Checking for perpendicularity:
For two vectors to be perpendicular, their dot product must be zero. Therefore, we need to check if:
a*a + b*b + c*c = 0
Step 4: Simplifying the equation:
To simplify the equation further, we can divide both sides by a*a, b*b, and c*c (assuming they are not zero):
(a*a + b*b + c*c)/(a*a) = 0/(a*a)
1 + (b*b)/(a*a) + (c*c)/(a*a) = 0
Step 5: Simplifying further:
We can rewrite (b*b)/(a*a) as (b/a)^2 and (c*c)/(a*a) as (c/a)^2:
1 + (b/a)^2 + (c/a)^2 = 0
Step 6: Final conclusion:
For the equation to hold true, each of the terms on the left side must be zero. Therefore, we have:
a = 0
b/a = 0
c/a = 0
This implies that a, b, and c are all zero. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D': aa + bb + cc = 0.
If each of the pairs of straight lines x2 - 2pxy - y2 = 0 and x2 - 2qxy- y2 = 0 bisects the angles between the other pair, then- a)pq=1
- b)pq=-1
- c)p2=-q2
- d)p2q2 = -1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If each of the pairs of straight lines x2 - 2pxy - y2 = 0 and x2 - 2qxy- y2 = 0 bisects the angles between the other pair, then
a)
pq=1
b)
pq=-1
c)
p2=-q2
d)
p2q2 = -1
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The equation of the bisectors of the angles between the two straight lines given by ax2+2hxy+by2=0 is given by

Now we are given two pairs of straight lines, namely,
x2- 2 pxy - y2 = 0 ...(I)
and x2- 2qxy-y2 = 0 ...(II)
It is given that each of I or II is the bisectors of the angle between the other pair. Using (A) the equation of the bisectors of the angle between the straight lines represented by (I) is given by
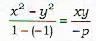
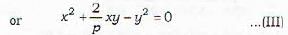


Now we are given two pairs of straight lines, namely,
x2- 2 pxy - y2 = 0 ...(I)
and x2- 2qxy-y2 = 0 ...(II)
It is given that each of I or II is the bisectors of the angle between the other pair. Using (A) the equation of the bisectors of the angle between the straight lines represented by (I) is given by
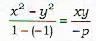
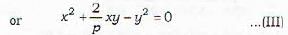

The straight line passing through (a, b, c) and perpendicular to x-axis is given by- a)
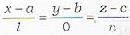
- b)
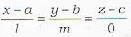
- c)
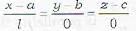
- d)
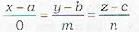
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The straight line passing through (a, b, c) and perpendicular to x-axis is given by
a)
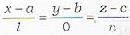
b)
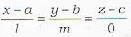
c)
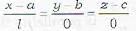
d)
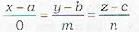
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The d.c.’s of the line perpendicular to x-axis are (0, m, n)
∴ Required equation will be
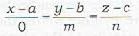
∴ Required equation will be
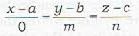
The equation of the plane containing the lines 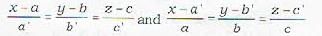 is not given by
is not given by- a)
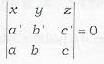
- b)
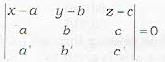
- c)
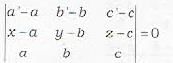
- d)
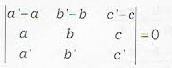
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the plane containing the lines 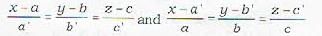 is not given by
is not given by
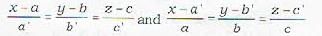 is not given by
is not given bya)
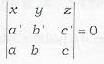
b)
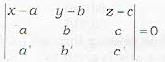
c)
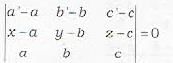
d)
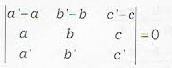
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
To find the equation of the plane containing the lines
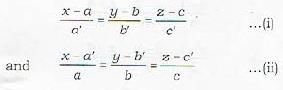
The plant: containing (i) is
A ( x - a) + B ( y - b) + C ( z - c) = 0 ...(iii)
where Aa' + Bb‘ + Cc' 3 =0 ...(iv)
Further, since the plane (iii) also contains line (ii), therefore , the normal to plane (iii) is perpendicular to line (ii).
∴ Aa + Bb + Cc = 0 ...(v)
Eliminating A, B, C from equations (iii), (iv) and (v), we get the required equation of plane
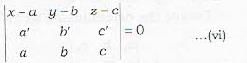
This is statement (b). The statements (a) and (c) can be deduced from this by simple propert ies of determinants. Thus (a), (b|, (c) are correct.
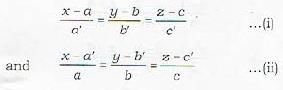
The plant: containing (i) is
A ( x - a) + B ( y - b) + C ( z - c) = 0 ...(iii)
where Aa' + Bb‘ + Cc' 3 =0 ...(iv)
Further, since the plane (iii) also contains line (ii), therefore , the normal to plane (iii) is perpendicular to line (ii).
∴ Aa + Bb + Cc = 0 ...(v)
Eliminating A, B, C from equations (iii), (iv) and (v), we get the required equation of plane
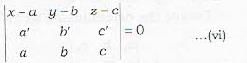
This is statement (b). The statements (a) and (c) can be deduced from this by simple propert ies of determinants. Thus (a), (b|, (c) are correct.
The point of intersection of the lines drawn from the vertices of any tetrahedron to the centroids of the opposite faces divides the distance from each vertex to the opposite face in which of the following ratios?- a)3:1
- b)3:4
- c)2:1
- d)2:3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The point of intersection of the lines drawn from the vertices of any tetrahedron to the centroids of the opposite faces divides the distance from each vertex to the opposite face in which of the following ratios?
a)
3:1
b)
3:4
c)
2:1
d)
2:3
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
About Direction Cosines and Direction Ratios.
1. If a given line makes angles α, β, γ with positive directions of the axes of x, y and x respectively, then cosα, cosβ, cosγ are called the direction cosines (in short d.c.’s) of the given line.
Direction cosines of a line are generally denoted by l, m, n and are written as [l, m, n]
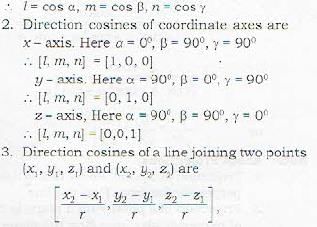
where r is the distance between the given points.
In particular, the d.c.'s of a line joining a point (a1, y1, z1) to the origin are
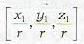
4. Direction Cosines satisfy
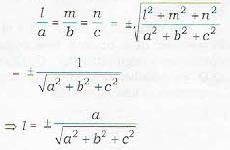
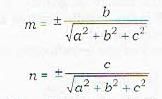
Thus if the d.r.’s of a line are a,b, c, then the direction cosines of the line are
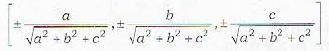
1. If a given line makes angles α, β, γ with positive directions of the axes of x, y and x respectively, then cosα, cosβ, cosγ are called the direction cosines (in short d.c.’s) of the given line.
Direction cosines of a line are generally denoted by l, m, n and are written as [l, m, n]
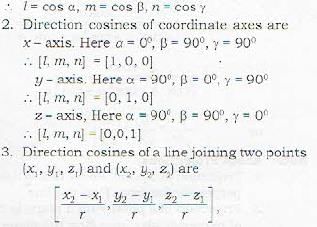
where r is the distance between the given points.
In particular, the d.c.'s of a line joining a point (a1, y1, z1) to the origin are
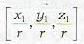
4. Direction Cosines satisfy
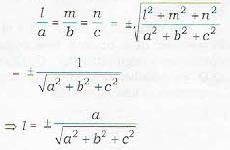
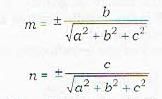
Thus if the d.r.’s of a line are a,b, c, then the direction cosines of the line are
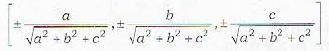
The direction ratios of the line, which is equally inclined to the three mutually perpendicular lines with direction cosines l1, m1, n1: l2, m2, n2 : l3, m3, n3; are given by- a)l1+ m1+ n1: l2+ m2+ n2 : l3+ m3+ n3
- b)l1+l2+l3 ; m1+m2+m3; n1+n2+n3
- c)m1n2-m2n1; n1l2-n2l1; m2-l2m1
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The direction ratios of the line, which is equally inclined to the three mutually perpendicular lines with direction cosines l1, m1, n1: l2, m2, n2 : l3, m3, n3; are given by
a)
l1+ m1+ n1: l2+ m2+ n2 : l3+ m3+ n3
b)
l1+l2+l3 ; m1+m2+m3; n1+n2+n3
c)
m1n2-m2n1; n1l2-n2l1; m2-l2m1
d)
none of the above
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Proof: Let the three mutually perpendicular lines be
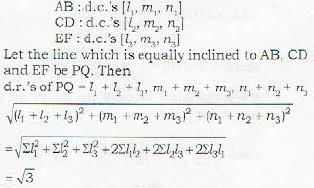
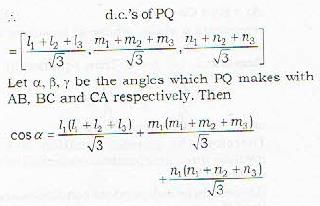
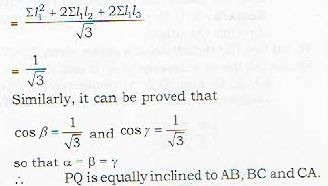
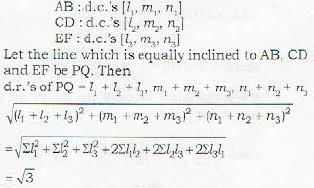
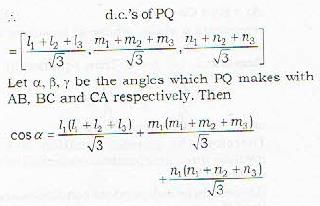
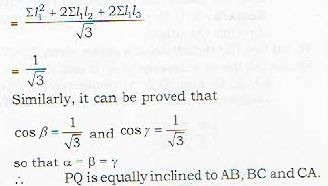
The equation of the circle, passing through the origin such that the x-axis is its diameter, is given by- a)x2 + y2 - 2ky = 0
- b)x2 + y2 - 2hx = 0
- c)x2 + y2 - 2hx + h2 = 0
- d)x2 + y2 - 2ky + k2 = 0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the circle, passing through the origin such that the x-axis is its diameter, is given by
a)
x2 + y2 - 2ky = 0
b)
x2 + y2 - 2hx = 0
c)
x2 + y2 - 2hx + h2 = 0
d)
x2 + y2 - 2ky + k2 = 0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Since the circle passes through the origin and has x-axis as its diameter, therefore its centre is [h, 0) and radius = h
∴ Required equation of the circle is
(x-h)2 + (y-0)2 = h2
or x2 + y2 -2hx = 0
∴ Required equation of the circle is
(x-h)2 + (y-0)2 = h2
or x2 + y2 -2hx = 0
The equation of the straight line passing through (4, 5) and parallel to the line 2x - 3y = 5 is given by- a)2 x - 3 y = 7
- b)2 x - 3 y = -7
- c)3 x - 2 y = 7
- d)3 x - 2 y = -7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the straight line passing through (4, 5) and parallel to the line 2x - 3y = 5 is given by
a)
2 x - 3 y = 7
b)
2 x - 3 y = -7
c)
3 x - 2 y = 7
d)
3 x - 2 y = -7
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
The given straight line is

The equation of a straight line parallel to (i) will be

Since (ii) passes through P(4, 5), therefore the coordinates of P A\*ill satisfy equation (ii)
∴ Required equation of the straight line is
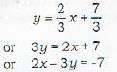

The equation of a straight line parallel to (i) will be

Since (ii) passes through P(4, 5), therefore the coordinates of P A\*ill satisfy equation (ii)
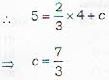
∴ Required equation of the straight line is
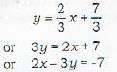
What is the locus of a point for which y=b?- a)A plane parallel to ZX plane at a distance b from it
- b)A plane parallel to YX plane at a distance b from it
- c)A plane parallel to YZ plane at a distance b from it
- d)A line parallel to X axis at a distance b from it
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the locus of a point for which y=b?
a)
A plane parallel to ZX plane at a distance b from it
b)
A plane parallel to YX plane at a distance b from it
c)
A plane parallel to YZ plane at a distance b from it
d)
A line parallel to X axis at a distance b from it

|
Veda Institute answered |
Note: We have
- Plane | | to xy piane at a distance c, z = c
- Plane; | | to t/x plane ai a distance a, x = a
- Plane | to xx plane at a distance b ,y = b
Remark:- In particular, the equations of YZ, ZX and XY planes are x = 0, y = 0 and z = 0 respectively.
The polar equation of a line through two given points (r1, θ1) and (r2, θ2) is given by- a)r1r2[sin(θ2-θ1] + sin(θ-θ2) + sin(θ1-θ)] =0
- b)r1r2[cos(θ2-θ1] + cos(θ-θ2) + cos(θ1-θ)] =0
- c)r1r2[sin(θ1-θ2] +r2 rsin(θ2-θ) + rr1sin(θ-θ1)] =0
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The polar equation of a line through two given points (r1, θ1) and (r2, θ2) is given by
a)
r1r2[sin(θ2-θ1] + sin(θ-θ2) + sin(θ1-θ)] =0
b)
r1r2[cos(θ2-θ1] + cos(θ-θ2) + cos(θ1-θ)] =0
c)
r1r2[sin(θ1-θ2] +r2 rsin(θ2-θ) + rr1sin(θ-θ1)] =0
d)
none of the above
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
A (r1, θ) and B(r2, θ2) arc two given points through them passes the straight line L. Let P(r, θ) be an arbitrary point on L.
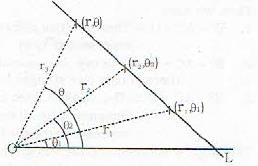
Then the points P, A and B are collinear.
=>the area of the triangle formed by these three points is zero
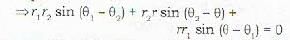

Then the points P, A and B are collinear.
=>the area of the triangle formed by these three points is zero
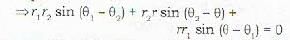
The equation of the plane passing through (2, -3, 1) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (3, 4. -1) and (2, -1, 5) is given by- a)5x+ 3y + 4z -5 = 0
- b)x + 5y - 6z + 19 = 0
- c)5x + 3y + 4z + 5 = 0
- d)x + 5y +6z - 19 = 0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The equation of the plane passing through (2, -3, 1) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (3, 4. -1) and (2, -1, 5) is given by
a)
5x+ 3y + 4z -5 = 0
b)
x + 5y - 6z + 19 = 0
c)
5x + 3y + 4z + 5 = 0
d)
x + 5y +6z - 19 = 0
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Let P(x, y, z) be an arbitrary point on the plane. Then the line PA joining the points P(x, y, z) and A(2, -3, 1) lies on the plane and the d.r.’s of PA are
x - 2, y + 3, z- 1
Further, the direction ratios of the line joining points B(3, 4. - 1 ) and C(2, 1,5) are
3 - 2 , 4 - ( - 1 ),- 1 -5
i.e. 1, 5, -6
Since BC is perpendicular to the plane and hence is perpendicular to line PA, therefore
( x - 2) 1 + (y + 3) 5 + ( z - 1) (- 6 ) = 0
or x + 5y - 6z + 19 = 0
x - 2, y + 3, z- 1
Further, the direction ratios of the line joining points B(3, 4. - 1 ) and C(2, 1,5) are
3 - 2 , 4 - ( - 1 ),- 1 -5
i.e. 1, 5, -6
Since BC is perpendicular to the plane and hence is perpendicular to line PA, therefore
( x - 2) 1 + (y + 3) 5 + ( z - 1) (- 6 ) = 0
or x + 5y - 6z + 19 = 0
The area of the triangle ABC formed by the intercepts OA a, OB = h, OC = con the coordinate axes respectively by a plane is given by- a)
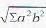
- b)
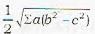
- c)
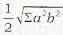
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of the triangle ABC formed by the intercepts OA a, OB = h, OC = con the coordinate axes respectively by a plane is given by
a)
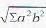
b)
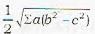
c)
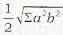
d)
none of the above

|
Veda Institute answered |
If Ax, Ay, Az be the areas of projection of an area A on the three coordinate planes then A2=Ax2 + Ay2 + Az2
we have to find the area A of triangle ABC Ax = the projection of A on yz plane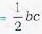
Ay = the projection of A on zx plane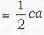
Az = the projection of A on xy plane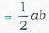
∴ A2=Ax2 + Ay2 + Az2
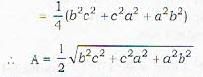
we have to find the area A of triangle ABC Ax = the projection of A on yz plane
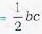
Ay = the projection of A on zx plane
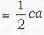
Az = the projection of A on xy plane
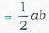
∴ A2=Ax2 + Ay2 + Az2
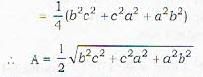
Projection on line segment joining P(6, 3, 2) and Q(5, 1, 4) on the line AB, where A and B are (3, -4, 7) and (0, 2, 5) respectively is- a)13
- b)-13/7
- c)7
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Projection on line segment joining P(6, 3, 2) and Q(5, 1, 4) on the line AB, where A and B are (3, -4, 7) and (0, 2, 5) respectively is
a)
13
b)
-13/7
c)
7
d)
none
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Direction cosines of the line joining A{3, -4, 7) and B(0, 2, 5) are given by


Now the required projection of line joining P(6, 3, 2) and Q(5, 1. 4) on the line AB is given by



Now the required projection of line joining P(6, 3, 2) and Q(5, 1. 4) on the line AB is given by

Chapter doubts & questions for Dimensional Geometry - Topic-wise Tests & Solved Examples for Mathematics 2025 is part of Mathematics exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mathematics exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mathematics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Dimensional Geometry - Topic-wise Tests & Solved Examples for Mathematics in English & Hindi are available as part of Mathematics exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mathematics Exam by signing up for free.
Topic-wise Tests & Solved Examples for Mathematics
27 docs|150 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup