All Exams >
JEE >
Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of Solutions for JEE Exam
When the solvent is in solid state, solution is- a)Solid solution
- b)Gaseous solution
- c)Solution
- d)Liquid solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the solvent is in solid state, solution is
a)
Solid solution
b)
Gaseous solution
c)
Solution
d)
Liquid solution

|
Aditi answered |
When both the solute and solvent are in solid state ,then the solution is called as solid solution or solid sol .
Molality is expressed in- a)mol/kg
- b)mol/L
- c)L/mol
- d)g/L
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Molality is expressed in
a)
mol/kg
b)
mol/L
c)
L/mol
d)
g/L

|
Siddharth Abimanyu answered |
Molality=moles of solute/kg of solvent... so option A
The number of moles of KCl in 3 L of 3 M solution is- a)27 moles
- b)1 moles
- c)9 moles
- d)3 moles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of moles of KCl in 3 L of 3 M solution is
a)
27 moles
b)
1 moles
c)
9 moles
d)
3 moles
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In 3M there will be 3 moles per litre therefore in 3 litres there will be 9 moles.
the molarity ofa solution obtained by mixing 750 ml of 0.5(M) hcl with 250ml of 2(M) hcl will be?- a)1.25 M
- b)2.5 M
- c)1.00 M
- d)0.875 M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
the molarity ofa solution obtained by mixing 750 ml of 0.5(M) hcl with 250ml of 2(M) hcl will be?
a)
1.25 M
b)
2.5 M
c)
1.00 M
d)
0.875 M
|
|
Vilas Kumar answered |
M = M1V1+ M2V2 / V1+V2. M = 750*0.5+250*2 / 750+250. M = 875 / 1000. M = 0.875
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature and pressure is called a saturated solution. At saturated solution stage equilibrium gets established among which two processes?- a)Dissolution and crystallisation
- b)Dissolution and condensation
- c)Sublimation and crystallisation
- d)Evaporation and condensation
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature and pressure is called a saturated solution. At saturated solution stage equilibrium gets established among which two processes?
a)
Dissolution and crystallisation
b)
Dissolution and condensation
c)
Sublimation and crystallisation
d)
Evaporation and condensation
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
At saturated solution stage equilibrium gets established among dissolution and crystallisation.
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.
- A:
0.03, Ethyl chloride
- B:
0.08, cannot be determined
- C:
0.03, Methanol
- D:
0.08, Ethyl chloride
The answer is d.
Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.
0.03, Ethyl chloride
0.08, cannot be determined
0.03, Methanol
0.08, Ethyl chloride

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Mole fraction of third component is 1 - (0.6 + 0.32) = 0.08.
Since ethyl chloride has highest mole fraction so it is the solvent.
Since ethyl chloride has highest mole fraction so it is the solvent.
Which of the following components form an ideal solution?- a)Ethyl alcohol and benzene
- b)Acetone and aniline
- c)Water and nitric acid
- d)Benzene and toluene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following components form an ideal solution?
a)
Ethyl alcohol and benzene
b)
Acetone and aniline
c)
Water and nitric acid
d)
Benzene and toluene
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The correct answer is option D
The solutions which obey Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
For ideal solution, the enthalpy of mixing of the pure components to form the solution is zero and the volume of mixing is also zero, i.e.,
△mixH=0 and △mixV=0
Thus, this type of solution is a solution of benzene and toluene.
The solutions which obey Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
For ideal solution, the enthalpy of mixing of the pure components to form the solution is zero and the volume of mixing is also zero, i.e.,
△mixH=0 and △mixV=0
Thus, this type of solution is a solution of benzene and toluene.
Which of the following gases will be least soluble in water?- a)Hydrogen chloride
- b)Sulphur dioxide
- c)Ammonia
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gases will be least soluble in water?
a)
Hydrogen chloride
b)
Sulphur dioxide
c)
Ammonia
d)
Nitrogen
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
The reason for poor solubility of N2 in water is that they just occupy the intermolecular spaces and stay there by interaction with its surrounding molecules by weak van der Waals forces.So it is least soluble while other gases form hydrogen bonds with water.
The reason for poor solubility of N2 in water is that they just occupy the intermolecular spaces and stay there by interaction with its surrounding molecules by weak van der Waals forces.So it is least soluble while other gases form hydrogen bonds with water.
The level of contamination of chloroform was found to be 15 ppm. It means 15 g of chloroform is present in how many grams of solution?- a)1000 g
- b)106 g
- c)100 g
- d)1.0 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The level of contamination of chloroform was found to be 15 ppm. It means 15 g of chloroform is present in how many grams of solution?
a)
1000 g
b)
106 g
c)
100 g
d)
1.0 g
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
1 ppm is equivalent to 1 part out of 1 million (106) parts.
∴ Mass percent of 15 ppm chloroform in water
∴ Mass percent of 15 ppm chloroform in water

⇒ 1.5 x 10-3 g chloroform present in 100 g water
Thus, 15g chloroform will be present in water
Thus, 15g chloroform will be present in water

Mole fraction of glycerine, C3H5(OH)3 in a solution containing 36 gm of water and 46 gm of glycerine is:- a)0.40
- b)0.20
- c)0.46
- d)0.36
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mole fraction of glycerine, C3H5(OH)3 in a solution containing 36 gm of water and 46 gm of glycerine is:
a)
0.40
b)
0.20
c)
0.46
d)
0.36
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
No. of moles of glycerine= 46/92 (where 92 is M.M. of glycerine)
= 0.5moles
no. of moles of water= 36/18(where 18 is M.M. of water)
= 2moles
so mole fraction oh glycerine = No. of moles of glycerine/No. of moles of glycerine + No. of moles of water
= 0.5/2 + 0.5
= 0.20
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The value for Henry’s constant for helium, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen at 293 K are 144.97 kbar, 69.16 kbar, 76.48 kbar and 34.86 kbar respectively. Which of the gas will be having maximum solubility?
- A:
Hydrogen
- B:
Oxygen
- C:
Helium
- D:
Nitrogen
The answer is b.
The value for Henry’s constant for helium, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen at 293 K are 144.97 kbar, 69.16 kbar, 76.48 kbar and 34.86 kbar respectively. Which of the gas will be having maximum solubility?
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Helium
Nitrogen
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Higher the value of Henry’s constant lower is the solubility of gas.
Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.- a)0.03, Ethyl chloride
- b)0.08, cannot be determined
- c)0.03, Methanol
- d)0.08, Ethyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.
a)
0.03, Ethyl chloride
b)
0.08, cannot be determined
c)
0.03, Methanol
d)
0.08, Ethyl chloride

|
Anu answered |
•sum of mole fractions are always 1.so mole fraction of 3rd component =1-(0.6+0.32)=0.8 • solvent is the component of a solution that is present in the greatest amount. so ethyl chloride is solvent
According to Henry’s Law at a constant temperature the solubility of gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the- a)Mass of gas
- b)Density of gas
- c)Volume of gas
- d)Pressure of gas
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Henry’s Law at a constant temperature the solubility of gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the
a)
Mass of gas
b)
Density of gas
c)
Volume of gas
d)
Pressure of gas
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
According to Henry’s law the solubility of gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas
Mathematically mass of the dissolved gas α pressure of the gas
let mass of dissolved gas in unit volume = m
pressure of gas = p
to remove sign of proportional we us a constant here KH is Henry’s law constant
so we get
m = KH*p
we can measure mass of solute in term of molar fraction also
Hence our formula will
X = KH*p
Application:
1. In Packing of soda cans :- To increase the solubility of CO2 gas in soda water , bottles of soda water is always packed under higher pressure.
2. In Deep see diving: - As nitrogen is a more soluble gas in our blood and at deep see pressure increase so its solubility also increases, when scuba diver tries to come rapidly toward the surface of water, pressure decreased and Dissolved N2 gas comes back from the blood and make bubbles in his veins. It because bends .To avoid bends diver use oxygen diluted with helium because helium is less soluble in blood.
Henry's Law states that: The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of that gas above the surface of the solution.
The value for Henry’s constant for argon, carbon dioxide, methane and vinyl chloride at 298 K are 40.3 kbar, 1.67 kbar, 0.413 kbar and 0.611 kbar respectively. Which of the gas will be having least solubility?- a)Argon
- b)Vinyl chloride
- c)Methane
- d)Carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The value for Henry’s constant for argon, carbon dioxide, methane and vinyl chloride at 298 K are 40.3 kbar, 1.67 kbar, 0.413 kbar and 0.611 kbar respectively. Which of the gas will be having least solubility?
a)
Argon
b)
Vinyl chloride
c)
Methane
d)
Carbon dioxide
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Higher the value of Henry’s constant lower is the solubility of gas.
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Which of the following would be the correct unit of expressing Henry’s law constant?- A:K
- B:atm
- C:kg
- D:mol/L
The answer is b.
Which of the following would be the correct unit of expressing Henry’s law constant?
A:
K
B:
atm
C:
kg
D:
mol/L

|
Rutuja Pawar answered |
According to Henry's law, P=K × x Where...P=pressure, k=Henry's law constant, x=mole fraction .•.k=P/x x is unitless .•.unit of Henry's law constant is atm...Hope u get it...😄😄😄
Some solute particles in solution collide with other solid solute particles present and get separated out of solution. This process is known as- a)Condensation
- b)Dissolution
- c)Sublimation
- d)Crystalisation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Some solute particles in solution collide with other solid solute particles present and get separated out of solution. This process is known as
a)
Condensation
b)
Dissolution
c)
Sublimation
d)
Crystalisation
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is option D
Some solute particles in solution collide with the solid solute particles and get separated out of solution. This process is called crystallization. A stage is reached when the two processes take place at the same rate. Under such conditions, the number of solute particles going into solution will be equal to the solute particles separating out and a state of dynamic equilibrium is achieved.
Some solute particles in solution collide with the solid solute particles and get separated out of solution. This process is called crystallization. A stage is reached when the two processes take place at the same rate. Under such conditions, the number of solute particles going into solution will be equal to the solute particles separating out and a state of dynamic equilibrium is achieved.
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is- a)

- b)
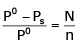
- c)

- d)
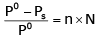
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
EduRev Support answered |
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is 
Here, Po represents the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, P represents the vapour pressure of the solution, n represents the number of moles of solute and N represents the number of moles of the solvent.
Here, Po represents the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, P represents the vapour pressure of the solution, n represents the number of moles of solute and N represents the number of moles of the solvent.
In which unit, the concentration of solution remains independent of temperature- a)molarity
- b)normaility
- c)molality
- d)formality
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which unit, the concentration of solution remains independent of temperature
a)
molarity
b)
normaility
c)
molality
d)
formality

|
Ritika Kulkarni answered |
It is independent of volume hence independent of Temperature.
The mass of sodium chloride in 2.5 M solution is- a)37.80 g
- b)146.25 g
- c)117 .00g
- d)58.50 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of sodium chloride in 2.5 M solution is
a)
37.80 g
b)
146.25 g
c)
117 .00g
d)
58.50 g
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
For preparing one molar solution we are required to dissolve one mole of the NaCl ( 58.5g) , for 2.5 mol we require 2.5 * 58.5= 146.25 g
Which expression correctly represents Henry’s Law?- a)
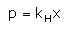
- b)
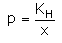
- c)
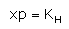
- d)
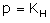
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which expression correctly represents Henry’s Law?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
The Henry's law constant (KH) (also called the air–water partition coefficient) is the ratio of a compound's partial pressure in air to the concentration of the compound in water at a given temperature. Values for Henry's law constants are expressed in units of atmospheres for air to moles per cubic meter for water (atm-m3/mol) or in a dimensionless unit described as KH′ = KH/(RT) where KH′ is the dimensionless Henry's law constant, KH is the Henry's law constant (atm-m3/mol), R is the ideal gas constant (8.20575 x 10−5 atm-m3/mol-K) and T is the water temperature (K). As a rule of thumb, compounds with a Henry's law constant greater than 10−3 atm-m3/mol and a molecular weight less than 200 grams per mole are considered volatile.
In a solution if the solute is non- volatile, pA0 is the vapour pressure of pure solvent A and the mole fraction of A is xA , the vapour pressure of the solvent (pA) will be :- a)
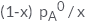
- b)
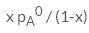
- c)
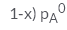
- d)
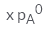
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a solution if the solute is non- volatile, pA0 is the vapour pressure of pure solvent A and the mole fraction of A is xA , the vapour pressure of the solvent (pA) will be :
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
The correct answer is option D
When a non - volatile solute is added into a volatile solvent to form an ideal solution. there will be a decrease in vapour pressure to that of solvent. According to roult's law the decrease in vapour is directly proportional to the mole fraction of solute in an ideal solution.
When a non - volatile solute is added into a volatile solvent to form an ideal solution. there will be a decrease in vapour pressure to that of solvent. According to roult's law the decrease in vapour is directly proportional to the mole fraction of solute in an ideal solution.
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?
- A:
2.85m
- B:
3.15m
- C:
1.45m
- D:
2.50m
The answer is c.
Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?
2.85m
3.15m
1.45m
2.50m
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
12.5% w/w means 12.5 g in 100 g of solution.
Weight of solvent = 100 g – 12.5 g= 87.5 g. Number of moles of sulphuric acid = 12.5/ 98 =0.127 mol
So molality = 0.127 X 1000/87.5 = 1.45 m
A sample of 300.0 g of drinking water is found to contain 38 mg Pb. What this concentration in parts per million?- a)3 x 102 ppm
- b)6.5 m
- c)130 ppm Pb
- d)21 ppm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sample of 300.0 g of drinking water is found to contain 38 mg Pb. What this concentration in parts per million?
a)
3 x 102 ppm
b)
6.5 m
c)
130 ppm Pb
d)
21 ppm
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
We use parts per million to express the concentrations of solutions that contain very, very small amounts, often called trace amounts, of a given solute.
More specifically, a solution's concentration in parts per millions tells you the number of parts of solute present for every
10^6=1,000,000
parts of solution. You can thus say that a 1 ppm
solution will contain exactly 1 g of solute for every 10^6g of solution.
In this case, you know that you have
38 mg Pb x (1 g/10^3 mg) = 3.8 x 10^-2 g Pb
in exactly
300.0 g = 3.000 x 10^2 g solution
This means that you can use this known composition as a conversion factor to scale up the mass of the solution to
10^6 g solution x (3.8 x 10^-2 g Pb/3.000 x 10^2 g solution)
= 130 g solution
Since this represents the mass of lead present in exactly 10^6 g of solution, you can say that the solution has a concentration of:
concentration (ppm) = 130 ppm Pb
Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?- a)2.85m
- b)3.15m
- c)1.45m
- d)2.50m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?
a)
2.85m
b)
3.15m
c)
1.45m
d)
2.50m
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
12.5% w/w means 12.5 g in 100 g of solution.
Weight of solvent = 100 g – 12.5 g= 87.5 g. Number of moles of sulphuric acid = 12.5/ 98 =0.127 mol
So molality = 0.127x1000/87.5 = 1.45 m
Solubility of which gas is maximum in water?- a)Carbon dioxide
- b)Oxygen
- c)Ammonia
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solubility of which gas is maximum in water?
a)
Carbon dioxide
b)
Oxygen
c)
Ammonia
d)
Nitrogen

|
Yash Kumar answered |
NH3 forms hydrogen Bonding with water.
Solutions which show positive or negative deviation from the Raoult’s law are called- a)Ideal solutions
- b)True solutions
- c)Non Ideal solutions
- d)Homogeneous solutions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solutions which show positive or negative deviation from the Raoult’s law are called
a)
Ideal solutions
b)
True solutions
c)
Non Ideal solutions
d)
Homogeneous solutions
|
|
Nabanita Pillai answered |
's law are:
Positive deviation: When the vapour pressure of the solution is higher than predicted by Raoult's law, it is known as positive deviation. This occurs when the interactions between the solvent and solute molecules are weaker than those between the solvent molecules. As a result, the solute molecules tend to escape into the vapour phase more readily, leading to higher vapour pressure. Examples of positive deviation include acetone-chloroform and ethanol-water mixtures.
Negative deviation: When the vapour pressure of the solution is lower than predicted by Raoult's law, it is known as negative deviation. This occurs when the interactions between the solvent and solute molecules are stronger than those between the solvent molecules. As a result, the solute molecules tend to remain in the liquid phase more readily, leading to lower vapour pressure. Examples of negative deviation include benzene-toluene and ethanol-ethyl acetate mixtures.
Positive deviation: When the vapour pressure of the solution is higher than predicted by Raoult's law, it is known as positive deviation. This occurs when the interactions between the solvent and solute molecules are weaker than those between the solvent molecules. As a result, the solute molecules tend to escape into the vapour phase more readily, leading to higher vapour pressure. Examples of positive deviation include acetone-chloroform and ethanol-water mixtures.
Negative deviation: When the vapour pressure of the solution is lower than predicted by Raoult's law, it is known as negative deviation. This occurs when the interactions between the solvent and solute molecules are stronger than those between the solvent molecules. As a result, the solute molecules tend to remain in the liquid phase more readily, leading to lower vapour pressure. Examples of negative deviation include benzene-toluene and ethanol-ethyl acetate mixtures.
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at the given temperature and pressure is called a- a)Unsaturated solution
- b)Dilute solution
- c)Solid solution
- d)Saturated solution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at the given temperature and pressure is called a
a)
Unsaturated solution
b)
Dilute solution
c)
Solid solution
d)
Saturated solution
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
In a saturated solution, more solute cannot be dissolved at a given temperature.
This is because, the solute dissolves in a solvent because of space between particles of solvent but on continuous addition of solute, the space between the solvent particles gets fulfilled. Thus no more solute particle can dissolve in a solvent.
In a saturated solution, more solute cannot be dissolved at a given temperature.
This is because, the solute dissolves in a solvent because of space between particles of solvent but on continuous addition of solute, the space between the solvent particles gets fulfilled. Thus no more solute particle can dissolve in a solvent.
Amalgam of mercury with sodium is an example of- a)Gas in solid
- b)Liquid in solid
- c)Solid in liquid
- d)Liquid in gas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Amalgam of mercury with sodium is an example of
a)
Gas in solid
b)
Liquid in solid
c)
Solid in liquid
d)
Liquid in gas
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted Na(Hg), is an alloy of mercury and sodium. The term amalgam is used for alloys, intermetallic compounds, and solutions (both solid solutions and liquid solutions) involving mercury as a major component.
Ethylene glycol is added to water as antifreeze. It will- a)Only increase the boiling point
- b)Only decrease the freezing point
- c)It is used to clean the radiator in car
- d)Increase the freezing point of water in winter and increase the boiling point of water in summer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethylene glycol is added to water as antifreeze. It will
a)
Only increase the boiling point
b)
Only decrease the freezing point
c)
It is used to clean the radiator in car
d)
Increase the freezing point of water in winter and increase the boiling point of water in summer
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Adding ethylene glycol to water reduces the freezing point of water. Water freezes at temperatures much less than 0 degree Celsius when ethylene glycol is added to it. It is used as an anti-freeze
The molal depression constant depends upon- a)Nature of the solute
- b)Vapour pressure of the solution
- c)Nature of the solvent
- d)Heat of solution of the solute in the solvent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The molal depression constant depends upon
a)
Nature of the solute
b)
Vapour pressure of the solution
c)
Nature of the solvent
d)
Heat of solution of the solute in the solvent
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Molal depression constant : It is defined as the depression in freezing point when the molality of the solution is unity, i.e., one mole of the solute is dissolved in 1000 gram or 1 kilogram of the solvent. Molality : It is defined as the number of moles of solute present in 1 kilogram of solvent.
Solution is defined as- a)Heterogeneous mixture
- b)Compound of two elements
- c)Homogeneous mixture
- d)Compound of more than two elements
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solution is defined as
a)
Heterogeneous mixture
b)
Compound of two elements
c)
Homogeneous mixture
d)
Compound of more than two elements
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
A homogeneous mixture is a solid, liquid, or gaseous mixture that has the same proportions of its components throughout any given sample. Conversely, a heterogeneous mixture has components whose proportions vary throughout the sample.
Which of the following solutions shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law?- a)Acetone and chloroform
- b)Acetone and carbon disulphide
- c)Ethyl alcohol and cyclohexane
- d)Benzene and toluene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solutions shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law?
a)
Acetone and chloroform
b)
Acetone and carbon disulphide
c)
Ethyl alcohol and cyclohexane
d)
Benzene and toluene
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
On mixing acetone and chloroform, hydrogen bond is formed between them. Due to this vapour pressure of the solution formed by them decreases. Hence solution shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Which of the following solutions of H2SO4 is more concentrated?- a)1 Molar solution
- b)1 molal solution
- c)1 normal solution
- d)NONE
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solutions of H2SO4 is more concentrated?
a)
1 Molar solution
b)
1 molal solution
c)
1 normal solution
d)
NONE
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
1M solution of H2SO4 means that 1 gram-molecular weight of H2SO4 is dissolved in 1 litre of water Molecular weight of H2SO4 is 2+32+64=98 which means that in 1M solution of H2SO4, 98 g of H2SO4 are dissolved in 1 litre of water whereas 1N solution of H2SO4, has 1gram equivalent weight of H2SO4 dissolved in 1 litre of water Now, the Equivalent wt of H2SO4 is 98/2=49 Therefore in 1N solution of H2SO4, 49 gram of H2SO4 are dissolved in 1 litre of water Comparing both the above solutions we can say that 1M solution of H2SO4 is more concentrated than 1N solution of H2SO4
Value of Henry’s constant KH is _ _ _ _.- a)Increases with increase in temperature
- b)Decreases with increase in temperature
- c)Remains constant
- d)First increases, then decreases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Value of Henry’s constant KH is _ _ _ _.
a)
Increases with increase in temperature
b)
Decreases with increase in temperature
c)
Remains constant
d)
First increases, then decreases
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Value of henry's constant KH is Increases with increase in temperature
Which has highest freezing point at 1 atm? - a)0.1 molal NaCl solution
- b)0.1 molal BaCl2 solution
- c)0.1 molal sugar solution
- d)0.1 molalFeCl3 solution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has highest freezing point at 1 atm?
a)
0.1 molal NaCl solution
b)
0.1 molal BaCl2 solution
c)
0.1 molal sugar solution
d)
0.1 molalFeCl3 solution
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Sugar solution has i=1 so ΔTf minimum so Tf will be maximum.
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure in Torr of a mixture of volatile components A and B is given by
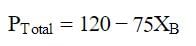
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
- a)120, 75
- b)120, 195
- c)120, 45
- d)75, 45
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure in Torr of a mixture of volatile components A and B is given by
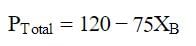
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
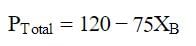
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
a)
120, 75
b)
120, 195
c)
120, 45
d)
75, 45
|
|
Om Desai answered |

Molality is preferred over molarity in handling solutions in chemistry laboratory because- a)Molality changes with pressure
- b)Molarity changes with temperature
- c)Molality changes with temperature
- d)Molarity changes with pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Molality is preferred over molarity in handling solutions in chemistry laboratory because
a)
Molality changes with pressure
b)
Molarity changes with temperature
c)
Molality changes with temperature
d)
Molarity changes with pressure
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Molarity is inversely proportional to volume . and
we know that from charles law i.e. volume is directly proportional to temperature.This implies that molarity is inversely proportional to temperature. Whereas molality is independent of temperature. Hence;option B is true.
we know that from charles law i.e. volume is directly proportional to temperature.This implies that molarity is inversely proportional to temperature. Whereas molality is independent of temperature. Hence;option B is true.
A complex containing K+, Pt (IV) and Cl- is 100% ionised giving i = 3. Thus, complex is- a)K2 [PtCl4]
- b)K2[PtCl6]
- c)K3[PtCl5]
- d)K[PtCl3]
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A complex containing K+, Pt (IV) and Cl- is 100% ionised giving i = 3. Thus, complex is
a)
K2 [PtCl4]
b)
K2[PtCl6]
c)
K3[PtCl5]
d)
K[PtCl3]
|
|
Dipika Rane answered |
In option (B) oxidaton state of platinum is (iv)
x – 6 = –2
x = + 4
x – 6 = –2
x = + 4
Aquatic animals are more comfortable in cold water rather that warm water because- a)Concentration increases with increase in temperature
- b)Solubility of gas in liquid increases with decrease in temperature
- c)Solubility of gas in liquid changes with pressure
- d)They are cold blooded animals
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Aquatic animals are more comfortable in cold water rather that warm water because
a)
Concentration increases with increase in temperature
b)
Solubility of gas in liquid increases with decrease in temperature
c)
Solubility of gas in liquid changes with pressure
d)
They are cold blooded animals

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
Because of increase in kinetic energy of gas molecules with temperature there tendency to escape from the liquid will increase.
Which of the following statements is correct, if the intermolecular force of attraction between the particles in liquid A, B, C is in the order A < B < C?- a)All the three evaporate at the same rate.
- b)B evaporates faster than A
- c)B evaporates more readily than C
- d)A evaporates more readily than C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct, if the intermolecular force of attraction between the particles in liquid A, B, C is in the order A < B < C?
a)
All the three evaporate at the same rate.
b)
B evaporates faster than A
c)
B evaporates more readily than C
d)
A evaporates more readily than C
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Inter molecular interaction cause to evaporation. When inter molecular interaction high, their evaporation power decrease.
In order to prepare 100 cm3 of 0.250 M barium chloride solution the amount of BaCl2.2H2O required will be-- a)0.250 moles
- b)0.0025 moles
- c)2.5 moles
- d)6.1 gram of BaCl2.2H2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In order to prepare 100 cm3 of 0.250 M barium chloride solution the amount of BaCl2.2H2O required will be-
a)
0.250 moles
b)
0.0025 moles
c)
2.5 moles
d)
6.1 gram of BaCl2.2H2O
|
|
Soumya Nair answered |
Molality of BaCl2 = 0.1 × 0.25 = 0.025
by calculation we get the values of (D)
by calculation we get the values of (D)
If 18 gram of glucose (C6H12O6) is present in 1000 gram of an aqueous solution of glucose it is said to be-- a)39.2 gram
- b)1.1 molal
- c)0.5 molal
- d)0.1 molal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 18 gram of glucose (C6H12O6) is present in 1000 gram of an aqueous solution of glucose it is said to be-
a)
39.2 gram
b)
1.1 molal
c)
0.5 molal
d)
0.1 molal
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
18 gm of glucose means 0.1mole of glucose as it present in 1000 gm of solvent so it is 0.1 mole
Which among the following is miscible in each other?- a)Benzene and water
- b)Methanol and water
- c)Methanol and benzene
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is miscible in each other?
a)
Benzene and water
b)
Methanol and water
c)
Methanol and benzene
d)
All of these
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Methanol and Water both are Polar. There is intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding interaction.
For a binary ideal solution, the total pressure of the solution is given as- a)
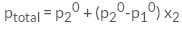
- b)
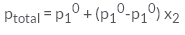
- c)
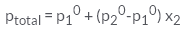
- d)
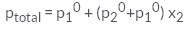
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a binary ideal solution, the total pressure of the solution is given as
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct option C
The partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in isolation.
Thus, for component 1
p1 ∝ x1
And p1 = pо1 x1
Where pо1 is the vapour pressure of pure component 1 at the same temperature.
Similarly, for component 2
p2 = pо2 x2
Where pо2 represents the vapour pressure of the pure component 2.
According to Dalton’s law of partial pressure, the total pressure ptotal over the solution phase in the container will be the sum of the partial pressures of the components of the solution and is given as:
ptotal =p1 + p2
Substituting the values of p1 and p2, we get.
ptotal = x1p10 + x2p20
=(1-x2)p10 + x2p20
=p10 +(p20 - p10) x2
The partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in isolation.
Thus, for component 1
p1 ∝ x1
And p1 = pо1 x1
Where pо1 is the vapour pressure of pure component 1 at the same temperature.
Similarly, for component 2
p2 = pо2 x2
Where pо2 represents the vapour pressure of the pure component 2.
According to Dalton’s law of partial pressure, the total pressure ptotal over the solution phase in the container will be the sum of the partial pressures of the components of the solution and is given as:
ptotal =p1 + p2
Substituting the values of p1 and p2, we get.
ptotal = x1p10 + x2p20
=(1-x2)p10 + x2p20
=p10 +(p20 - p10) x2
When a non-volatile solute is dissolved in a solvent, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to:- a)Mole fraction of solute
- b)Molality of solution
- c)Mole fraction of solvent
- d)Molarity of solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a non-volatile solute is dissolved in a solvent, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to:
a)
Mole fraction of solute
b)
Molality of solution
c)
Mole fraction of solvent
d)
Molarity of solution
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The vapor pressure of a solvent is lowered when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it to form a solution. The vapor pressure lowering relative to pure solvent is , which is proportional to the mole fraction of solute.
The tanks used by divers are filled with air diluted with- a)Helium
- b)Argon
- c)Nitrogen
- d)Hydrogen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The tanks used by divers are filled with air diluted with
a)
Helium
b)
Argon
c)
Nitrogen
d)
Hydrogen

|
Parth Iyer answered |
Size of Helium is small so does not causes “Bents” to divers when the dive back to surface.
Chapter doubts & questions for Solutions - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Solutions - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
353 videos|587 docs|309 tests
|
Related JEE Content
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily