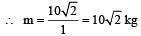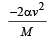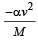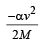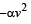All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Laws of Motion for NEET Exam
300 J of work is done in sliding a 2 kg block up an inclined plane of height 10 m. Taking g = 10 m/s2, work done against friction is [2006]- a)100 J
- b)zero
- c)1000 J
- d)200 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
300 J of work is done in sliding a 2 kg block up an inclined plane of height 10 m. Taking g = 10 m/s2, work done against friction is [2006]
a)
100 J
b)
zero
c)
1000 J
d)
200 J

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Work done against gravity = mg sinθ × d = 2 × 10 × 10 (dsinθ = 10) = 200J
Actual work done = 300J
Work done against friction = 300 – 200 = 100J
Actual work done = 300J
Work done against friction = 300 – 200 = 100J
The mass of a lift is 2000 kg. When the tension in the supporting cable is 28000 N, then its acceleration is: [2009]a)4 ms–2 upwardsb)4 ms–2 downwardsc)14 ms–2 upwardsd)30 ms–2 downwardsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The gravitational force in the downward direction is 20000 N and the tension force in the upward direction is 28000 N.
By newton's second law of motion, ΣF=ma
Net force, F = T – mg
ma = T – mg
2000 * a = 28000 – 20000 = 8000
ma = T – mg
2000 * a = 28000 – 20000 = 8000
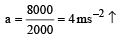
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block (g is acceleration due to gravity) will be[2004]- a)mg/cosθ
- b)mg cosθ
- c)mg sinθ
- d)mg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block (g is acceleration due to gravity) will be[2004]
a)
mg/cosθ
b)
mg cosθ
c)
mg sinθ
d)
mg
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
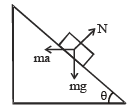
According to Newton's second Law:
N = masinθ + mgcosθ .....(1)
Also, mgsinθ = macosθ .....(2)
Also, mgsinθ = macosθ .....(2)
From (1) & (2) we get, a = gtanθ
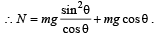
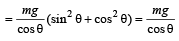
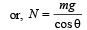
A stone is dropped from a height h. It hits the ground with a certain momentum P. If the same stone is dropped from a height 100% more than the previous height, the momentum when it hits the ground will change by : [2012M]- a)68%
- b)41%
- c)200%
- d)100%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone is dropped from a height h. It hits the ground with a certain momentum P. If the same stone is dropped from a height 100% more than the previous height, the momentum when it hits the ground will change by : [2012M]
a)
68%
b)
41%
c)
200%
d)
100%

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Momentum 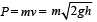
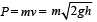
(v2 = u2 + 2gh; Here u = 0)
When stone hits the ground momentum
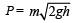
when same stone dropped from 2h (100% of initial) then momentum
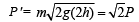
Which is changed by 41% of initial.
Three blocks with masses m, 2 m and 3 m are connected by strings as shown in the figure.After an upward force F is applied on block m, the masses move upward at constant speed v.What is the net force on the block of mass 2m? (g is the acceleration due to gravity) [NEET 2013]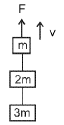
- a)2 mg
- b)3 mg
- c)6 mg
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Three blocks with masses m, 2 m and 3 m are connected by strings as shown in the figure.After an upward force F is applied on block m, the masses move upward at constant speed v.What is the net force on the block of mass 2m? (g is the acceleration due to gravity) [NEET 2013]

a)
2 mg
b)
3 mg
c)
6 mg
d)
zero

|
Diya Datta answered |
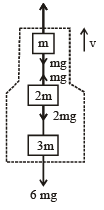
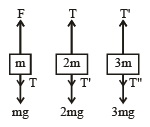
From figure F = 6 mg, As speed is constant, acceleration a = 0
∴ 6 mg = 6ma = 0, F = 6 mg
∴ T = 5 mg , T' = 3 mg T" = 0
Fnet on block of mass 2 m = T – T' – 2 mg = 0
ALTERNATE :
v = constantso, a = 0, Hence, Fnet = ma = 0
∴ 6 mg = 6ma = 0, F = 6 mg
∴ T = 5 mg , T' = 3 mg T" = 0
Fnet on block of mass 2 m = T – T' – 2 mg = 0
ALTERNATE :
v = constantso, a = 0, Hence, Fnet = ma = 0
A person of mass 60 kg is inside a lift of mass 940 kg and presses the button on control panel.The lift starts moving upwards with an acceleration 1.0 m/s2. If g = 10 ms–2, the tension in the supporting cable is [2011]- a)8600 N
- b)9680 N
- c)11000 N
- d)1200 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A person of mass 60 kg is inside a lift of mass 940 kg and presses the button on control panel.The lift starts moving upwards with an acceleration 1.0 m/s2. If g = 10 ms–2, the tension in the supporting cable is [2011]
a)
8600 N
b)
9680 N
c)
11000 N
d)
1200 N

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Total mass = (60 + 940) kg = 1000 kg
Let T be the tension in the supporting cable, then T – 1000g = 1000 × 1
⇒ T = 1000 × 11 = 11000 N
Let T be the tension in the supporting cable, then T – 1000g = 1000 × 1
⇒ T = 1000 × 11 = 11000 N
A person slides freely down a frictionless inclined plane while his bag falls down vertically from the same height. The final speeds of the man (VM) and the bag (VB) should be such that [2000]- a)VM < VB
- b)VM = VB
- c)they depend on the masses
- d)VM > VB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person slides freely down a frictionless inclined plane while his bag falls down vertically from the same height. The final speeds of the man (VM) and the bag (VB) should be such that [2000]
a)
VM < VB
b)
VM = VB
c)
they depend on the masses
d)
VM > VB

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
As there is only gravitational field which works.
We know it is conservative field and depends only on the end points. So, VM = VB
We know it is conservative field and depends only on the end points. So, VM = VB
A car is moving in a circular horizontal track of radius 10 m with a constant speed of 10 m/s. A bob is suspended from the roof of the car by a light wire of length 1.0 m. The angle made by the wire with the vertical is [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)0°
- b)
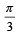
- c)
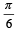
- d)
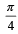
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A car is moving in a circular horizontal track of radius 10 m with a constant speed of 10 m/s. A bob is suspended from the roof of the car by a light wire of length 1.0 m. The angle made by the wire with the vertical is [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
0°
b)
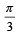
c)
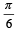
d)
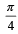

|
Kunal Rane answered |
Given; speed = 10 m/s; radius r = 10 m
Angle made by the wire with the vertical
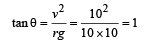
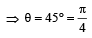
Starting from rest, a body slides down a 45° inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction.The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is [1988]- a)0.80
- b)0.75
- c)0.25
- d)0.33
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Starting from rest, a body slides down a 45° inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction.The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is [1988]
a)
0.80
b)
0.75
c)
0.25
d)
0.33

|
Anand Jain answered |
In presence of friction a = (g sinθ – μg cosθ)
∴ Time taken to slide down the plane
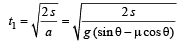
In absence of friction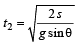
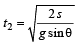
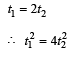
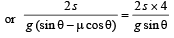
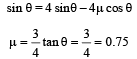
Sand is being dropped on a conveyor belt at the rate of M kg/s. The force necessary to keep the belt moving with a constant velocity of v m/s will be:[2008]- a)Mv newton
- b)2 Mv newton
- c)
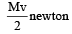
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sand is being dropped on a conveyor belt at the rate of M kg/s. The force necessary to keep the belt moving with a constant velocity of v m/s will be:[2008]
a)
Mv newton
b)
2 Mv newton
c)
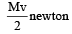
d)
zero

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
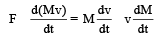
∴ v is constant,
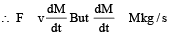
∴ F = vM newton.
A 600 kg rocket is set for a vertical firing. If the exhaust speed is 1000 ms–1 , the mass of the gas ejected per second to supply the thrust needed to overcome the weight of rocket is [1990]- a)117.6 kg s–1
- b)58.6 kg s–1
- c)6 kg s–1
- d)76.4 kg s–1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 600 kg rocket is set for a vertical firing. If the exhaust speed is 1000 ms–1 , the mass of the gas ejected per second to supply the thrust needed to overcome the weight of rocket is [1990]
a)
117.6 kg s–1
b)
58.6 kg s–1
c)
6 kg s–1
d)
76.4 kg s–1

|
Charvi Shah answered |
Thrust 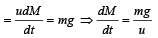
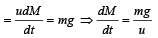
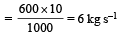
A mass of 1 kg is suspended by a thread. It is (i) lifted up with an acceleration 4.9 m/s2, (ii) lowered with an acceleration 4.9 m/s2.The ratio of the tensions is [1998]- a)3 : 1
- b)1 : 2
- c)1 : 3
- d)2 : 1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A mass of 1 kg is suspended by a thread. It is (i) lifted up with an acceleration 4.9 m/s2, (ii) lowered with an acceleration 4.9 m/s2.The ratio of the tensions is [1998]
a)
3 : 1
b)
1 : 2
c)
1 : 3
d)
2 : 1

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
In case (i) we have
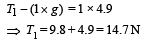
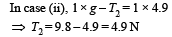
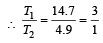
A block B is pushed momen tarily along a horizontal surface with an initial velocity V. If μ is the coefficient of sliding friction between B and the surface, block B will come to rest after a time[2007]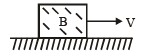
- a)gμ/V
- b)g/V
- c)V/g
- d)V/(gμ).
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A block B is pushed momen tarily along a horizontal surface with an initial velocity V. If μ is the coefficient of sliding friction between B and the surface, block B will come to rest after a time[2007]

a)
gμ/V
b)
g/V
c)
V/g
d)
V/(gμ).

|
Kunal Rane answered |
Friction is the retarding force for the block F = ma = μR = μmg
Therefore, from the first equation of motion v = u – at
Therefore, from the first equation of motion v = u – at
A block of mass 1 kg lies on a horizontal surface in a truck the coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is 0.6. If the acceleration of the truck is 5 m/s2, the frictional force acting on the block is
- a)5.88 N
- b)6 N
- c)5 N
- d)4.6 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass 1 kg lies on a horizontal surface in a truck the coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is 0.6. If the acceleration of the truck is 5 m/s2, the frictional force acting on the block is
a)
5.88 N
b)
6 N
c)
5 N
d)
4.6 N

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
a = 5m/s2, m = 1 kg, μ = 0.6
Frictional force = μmg = 0.6 × 1 × 9.8 = 5.88 N
Frictional force = μmg = 0.6 × 1 × 9.8 = 5.88 N
A monkey of mass 20 kg is holding a vertical rope. The rope will not break when a mass of 25 kg is suspended from it but will break if the mass exceeds 25 kg. What is the maximum acceleration with which the monkey can climb up along the rope ? (g = 10 m/s2) [2003]- a)2.5 m/s2
- b)5 m/s2
- c)10 m/s2
- d)25 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A monkey of mass 20 kg is holding a vertical rope. The rope will not break when a mass of 25 kg is suspended from it but will break if the mass exceeds 25 kg. What is the maximum acceleration with which the monkey can climb up along the rope ? (g = 10 m/s2) [2003]
a)
2.5 m/s2
b)
5 m/s2
c)
10 m/s2
d)
25 m/s2

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
T = Tension caused in string by monkey
= m (g + a)
= m (g + a)
Consider a car moving along a straight horizontal road with a speed of 72 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the tyres and the road is 0.5, the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is (taking g = 10 m/s2) [1992]- a)30 m
- b)40 m
- c)72 m
- d)20 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a car moving along a straight horizontal road with a speed of 72 km/h. If the coefficient of static friction between the tyres and the road is 0.5, the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is (taking g = 10 m/s2) [1992]
a)
30 m
b)
40 m
c)
72 m
d)
20 m

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
Here u = 72 km/h = 20 m/s; v = 0;
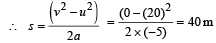
A conveyor belt is moving at a constant speed of 2m/s. A box is gently dropped on it. The coefficient of friction between them is µ = 0.5. The distance that the box will move relative to belt before coming to rest on it taking g = 10 ms–2, is [2011M]- a)1.2 m
- b)0.6 m
- c)zero
- d)0.4 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A conveyor belt is moving at a constant speed of 2m/s. A box is gently dropped on it. The coefficient of friction between them is µ = 0.5. The distance that the box will move relative to belt before coming to rest on it taking g = 10 ms–2, is [2011M]
a)
1.2 m
b)
0.6 m
c)
zero
d)
0.4 m

|
Kajal Bose answered |
Frictional force on the box f = μmg
∴ Acceleration in the box
∴ Acceleration in the box
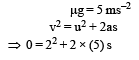
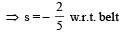
⇒ distance = 0.4 m
A shell is fired from a cannon, it explodes in mid air, its total [1994]- a)momentum increases
- b)momentum decreases
- c)K.E. increases
- d)K.E. decreases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A shell is fired from a cannon, it explodes in mid air, its total [1994]
a)
momentum increases
b)
momentum decreases
c)
K.E. increases
d)
K.E. decreases

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |
When shell explodes in mid air its chemical energy is partly converted into mechanical energy, hence K.E. increases.
Physical independence of force is a consequence of[1991]- a)third law of motion
- b)second law of motion
- c)first law of motion
- d)all of these laws
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Physical independence of force is a consequence of[1991]
a)
third law of motion
b)
second law of motion
c)
first law of motion
d)
all of these laws

|
Surbhi Das answered |
Newton’s first law of motion is related to physical independence of force.
A body of mass M hits normally a rigid wall with velocity V and bounces back with the same velocity. The impulse experienced by the body is[2011]- a)MV
- b)1.5 MV
- c)2 MV
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass M hits normally a rigid wall with velocity V and bounces back with the same velocity. The impulse experienced by the body is[2011]
a)
MV
b)
1.5 MV
c)
2 MV
d)
zero

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Impulse experienced by the body = change in momentum = MV – (–MV)
= 2MV.
= 2MV.
A ball of mass 0.15 kg is dropped from a height 10 m, strikes the ground and rebounds to the same height. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the ball is (g = 10 m/s2) nearly: [2021]- a)2.1 kg m/s
- b)1.4 kg m/s
- c)0 kg m/s
- d)4.2 kg m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball of mass 0.15 kg is dropped from a height 10 m, strikes the ground and rebounds to the same height. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the ball is (g = 10 m/s2) nearly: [2021]
a)
2.1 kg m/s
b)
1.4 kg m/s
c)
0 kg m/s
d)
4.2 kg m/s
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Velocity just before striking the ground
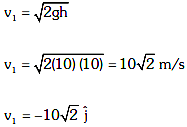
If it reaches the same height, speed remains same after collision only the direction changes.
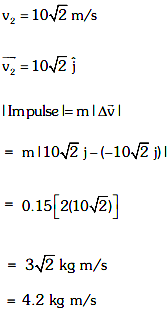
If it reaches the same height, speed remains same after collision only the direction changes.
A bullet is fired from a gun. The force on the bullet is given by F = 600 – 2 × 105 t where, F is in newton and t in second. The force on the bullet becomes zero as soon as it leaves the barrel.What is the average impulse imparted to the bullet?[1998]- a)1.8 N-s
- b)zero
- c)9 N-s
- d)0.9 N-s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A bullet is fired from a gun. The force on the bullet is given by F = 600 – 2 × 105 t where, F is in newton and t in second. The force on the bullet becomes zero as soon as it leaves the barrel.What is the average impulse imparted to the bullet?[1998]
a)
1.8 N-s
b)
zero
c)
9 N-s
d)
0.9 N-s

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Given F = 600 – (2 x 105t ) The force is zero at time t, given by
0 = 600 – 2 x 105t
0 = 600 – 2 x 105t
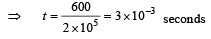
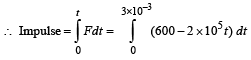
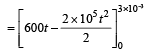
= 600 x 3 x 10 –3 – 105 (3 x10 –3)2
= 1.8 – 0.9 = 0.9Ns
= 1.8 – 0.9 = 0.9Ns
If the force on a rocket moving with a velocity of 300 m/sec is 345 N, then the rate of combustion of the fuel, is [1995]- a)0.55 kg/sec
- b)0.75 kg/sec
- c)1.15 kg/sec
- d)2.25 kg/sec
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the force on a rocket moving with a velocity of 300 m/sec is 345 N, then the rate of combustion of the fuel, is [1995]
a)
0.55 kg/sec
b)
0.75 kg/sec
c)
1.15 kg/sec
d)
2.25 kg/sec

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Velocity of the rocket (u) = 300 m/s and force (F) = 345N. Rate of combustion of fuel
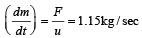
A particle of mass m is moving with a uniform velocity v1. It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes v2. The impulse is equal to [1990]- a)m[| v2 | – | v1|]
- b)
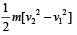
- c)m[v1 + v2]
- d)m [v2 – v1]
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass m is moving with a uniform velocity v1. It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes v2. The impulse is equal to [1990]
a)
m[| v2 | – | v1|]
b)
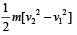
c)
m[v1 + v2]
d)
m [v2 – v1]

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
Impulse = final momentum – initial momentum = m (v2 – v1)
A particle of mass M is moving in a horizontal circle of radius R with uniform speed V. When it moves from one point to a diametrically opposite point, its [1992]- a)kinetic energy changes by MV2/4
- b)momentum does not change
- c)momentum changes by 2 MV
- d)kinetic energy changes by MV2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass M is moving in a horizontal circle of radius R with uniform speed V. When it moves from one point to a diametrically opposite point, its [1992]
a)
kinetic energy changes by MV2/4
b)
momentum does not change
c)
momentum changes by 2 MV
d)
kinetic energy changes by MV2

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
On the diametrically opposite points, the velocities have same magnitude but opposite directions. Therefore, change in momentum is MV – (– MV) = 2MV
A ball of mass 150 g, moving with an acceleration 20 m/s2, is hit by a force, which acts on it for 0.1 sec. The impulsive force is [1996]- a)0.5 N
- b)0.1 N
- c)0.3 N
- d)1.2 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball of mass 150 g, moving with an acceleration 20 m/s2, is hit by a force, which acts on it for 0.1 sec. The impulsive force is [1996]
a)
0.5 N
b)
0.1 N
c)
0.3 N
d)
1.2 N
|
|
Maya Gupta answered |
Given:
- Mass of the ball (m) = 150 g = 0.15 kg
- Acceleration (a) = 20 m/s^2
- Time (t) = 0.1 s
To find:
- Impulsive force (F)
Solution:
The impulsive force can be calculated using the formula:
F = ma
where:
- F is the force
- m is the mass of the ball
- a is the acceleration
Step 1: Convert the mass from grams to kilograms:
- Mass (m) = 150 g = 0.15 kg
Step 2: Substitute the values into the formula:
F = (0.15 kg) * (20 m/s^2)
Step 3: Calculate the force:
F = 3 N
Step 4: Round the answer to the nearest tenth:
F ≈ 0.3 N
Therefore, the impulsive force acting on the ball is approximately 0.3 N, which corresponds to option C.
- Mass of the ball (m) = 150 g = 0.15 kg
- Acceleration (a) = 20 m/s^2
- Time (t) = 0.1 s
To find:
- Impulsive force (F)
Solution:
The impulsive force can be calculated using the formula:
F = ma
where:
- F is the force
- m is the mass of the ball
- a is the acceleration
Step 1: Convert the mass from grams to kilograms:
- Mass (m) = 150 g = 0.15 kg
Step 2: Substitute the values into the formula:
F = (0.15 kg) * (20 m/s^2)
Step 3: Calculate the force:
F = 3 N
Step 4: Round the answer to the nearest tenth:
F ≈ 0.3 N
Therefore, the impulsive force acting on the ball is approximately 0.3 N, which corresponds to option C.
A 4 kg mass and 1 kg are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momenta is [1989]- a)1 : 2
- b)1 : 1
- c)2 : 1
- d)4 : 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 4 kg mass and 1 kg are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momenta is [1989]
a)
1 : 2
b)
1 : 1
c)
2 : 1
d)
4 : 1

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
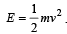 . Hence, mv = (2mE)1/2. For same
. Hence, mv = (2mE)1/2. For sameKE, momentum 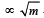 Hence, the ratio is 2 : 1.
Hence, the ratio is 2 : 1.
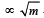 Hence, the ratio is 2 : 1.
Hence, the ratio is 2 : 1.What will be the maximum speed of a car on a road turn of radius 30 m if the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road is 0.4 (Take g = 9.8 m/s2) [1995]- a)10.84 m/s
- b)9.84 m/s
- c)8.84 m/s
- d)6.84 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the maximum speed of a car on a road turn of radius 30 m if the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road is 0.4 (Take g = 9.8 m/s2) [1995]
a)
10.84 m/s
b)
9.84 m/s
c)
8.84 m/s
d)
6.84 m/s

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
r = 30 m and μ = 0.4.
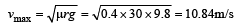
The coeffici ent of static friction , μs, between block A of mass 2 kg and the table as shown in the figure is 0.2. What would be the maximum mass value of block B so that the two blocks do not move? The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless. (g = 10 m/s2) [2004]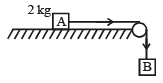
- a)0.4 kg
- b)2.0 kg
- c)4.0 kg
- d)0.2 kg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The coeffici ent of static friction , μs, between block A of mass 2 kg and the table as shown in the figure is 0.2. What would be the maximum mass value of block B so that the two blocks do not move? The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless. (g = 10 m/s2) [2004]

a)
0.4 kg
b)
2.0 kg
c)
4.0 kg
d)
0.2 kg

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
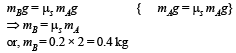
A 100 N force acts horizontally on a block of 10 kg placed on a horizontal rough surface of coefficient of friction μ = 0.5. If the acceleration due to gravity (g) is taken as 10 ms–2, the acceleration of the block (in ms–2) is [2002]
- a)2.5
- b)10
- c)5
- d)7.5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A 100 N force acts horizontally on a block of 10 kg placed on a horizontal rough surface of coefficient of friction μ = 0.5. If the acceleration due to gravity (g) is taken as 10 ms–2, the acceleration of the block (in ms–2) is [2002]
a)
2.5
b)
10
c)
5
d)
7.5

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |

A car of mass m is moving on a level circular track of radius R. If μs represents the static friction between the road and tyres of the car, the maximum speed of the car in circular motion is given by : [2012M]- a)
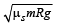
- b)
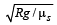
- c)
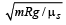
- d)
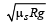
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A car of mass m is moving on a level circular track of radius R. If μs represents the static friction between the road and tyres of the car, the maximum speed of the car in circular motion is given by : [2012M]
a)
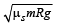
b)
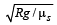
c)
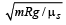
d)
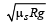

|
Rohan Unni answered |
For smooth driving maximum speed of car v then
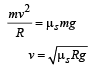
A man weighing 80 kg, stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5m/s2. What would be the reading on the scale ? (g = 10 m/s2) [2003]- a)1200 N
- b)zero
- c)400 N
- d)800 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A man weighing 80 kg, stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5m/s2. What would be the reading on the scale ? (g = 10 m/s2) [2003]
a)
1200 N
b)
zero
c)
400 N
d)
800 N

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Reading of the scale = Apparent wt. of the man = m(g + a) = 80 (10 + 5) = 1200 N
Two blocks m1 = 5 gm and m2 = 10 gm are hung vertically over a light frictionless pulley as shown here. What is the acceleration of the masses when they are left free? [2000] (where g is acceleration due to gravity)- a)g/3
- b)g/2
- c)g
- d)g/5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two blocks m1 = 5 gm and m2 = 10 gm are hung vertically over a light frictionless pulley as shown here. What is the acceleration of the masses when they are left free? [2000] (where g is acceleration due to gravity)
a)
g/3
b)
g/2
c)
g
d)
g/5

|
Surbhi Das answered |
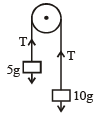
Let T be the tension in the string.
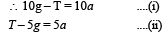
Adding (i) and (ii),
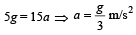
If a cricketer catches a ball of mass 150 gm moving with a velocity of 20 m/s, then he experiences a force of (Time taken to complete the catch is 0.1 sec.)[2001]- a)300 N
- b)30 N
- c)3 N
- d)0.3 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a cricketer catches a ball of mass 150 gm moving with a velocity of 20 m/s, then he experiences a force of (Time taken to complete the catch is 0.1 sec.)[2001]
a)
300 N
b)
30 N
c)
3 N
d)
0.3 N
|
|
Maya Gupta answered |
Given:
- Mass of the ball (m) = 150 gm = 0.15 kg
- Velocity of the ball (v) = 20 m/s
- Time taken to complete the catch (t) = 0.1 sec
To find:
The force experienced by the cricketer while catching the ball.
Solution:
The force experienced by an object can be calculated using Newton's second law of motion, which states that the force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of momentum.
Momentum (p) is defined as the product of mass and velocity of an object.
Momentum (p) = mass (m) × velocity (v)
Therefore, the momentum of the ball is given by:
Momentum (p) = 0.15 kg × 20 m/s
= 3 kg·m/s
The change in momentum (∆p) of the ball is equal to the momentum of the ball when caught, as the ball comes to rest in the cricketer's hand.
The time taken to complete the catch (t) is given as 0.1 sec.
The change in momentum (∆p) can be calculated using the formula:
∆p = Force (F) × time (t)
Rearranging the formula to find the force experienced by the cricketer:
Force (F) = ∆p / t
Substituting the given values:
Force (F) = 3 kg·m/s / 0.1 sec
= 30 kg·m/s²
The unit of force in the SI system is Newton (N). Therefore, the force experienced by the cricketer while catching the ball is 30 N.
Answer:
The cricketer experiences a force of 30 N. Therefore, the correct answer is option (b) 30 N.
- Mass of the ball (m) = 150 gm = 0.15 kg
- Velocity of the ball (v) = 20 m/s
- Time taken to complete the catch (t) = 0.1 sec
To find:
The force experienced by the cricketer while catching the ball.
Solution:
The force experienced by an object can be calculated using Newton's second law of motion, which states that the force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of momentum.
Momentum (p) is defined as the product of mass and velocity of an object.
Momentum (p) = mass (m) × velocity (v)
Therefore, the momentum of the ball is given by:
Momentum (p) = 0.15 kg × 20 m/s
= 3 kg·m/s
The change in momentum (∆p) of the ball is equal to the momentum of the ball when caught, as the ball comes to rest in the cricketer's hand.
The time taken to complete the catch (t) is given as 0.1 sec.
The change in momentum (∆p) can be calculated using the formula:
∆p = Force (F) × time (t)
Rearranging the formula to find the force experienced by the cricketer:
Force (F) = ∆p / t
Substituting the given values:
Force (F) = 3 kg·m/s / 0.1 sec
= 30 kg·m/s²
The unit of force in the SI system is Newton (N). Therefore, the force experienced by the cricketer while catching the ball is 30 N.
Answer:
The cricketer experiences a force of 30 N. Therefore, the correct answer is option (b) 30 N.
A 5000 kg rocket is set for vertical firing. The exhaust speed is 800 ms–1. To give an initial upward acceleration of 20 ms–2, the amount of gas ejected per second to supply the needed thrust will be (g = 10 ms–2) [1998]- a)127.5 kg s–1
- b)187.5 kg s–1
- c)185.5 kg s–1
- d)137.5 kg s–1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 5000 kg rocket is set for vertical firing. The exhaust speed is 800 ms–1. To give an initial upward acceleration of 20 ms–2, the amount of gas ejected per second to supply the needed thrust will be (g = 10 ms–2) [1998]
a)
127.5 kg s–1
b)
187.5 kg s–1
c)
185.5 kg s–1
d)
137.5 kg s–1

|
Anand Jain answered |
Given : Mass of rocket (m) = 5000 kg
Exhaust speed (v) = 800 m/s
Acceleration of rocket (a) = 20 m/s2
Gravitational acceleration (g) = 10 m/s2
We know that upward force F = m (g + a) = 5000 (10 +20)
= 5000 × 30 = 150000 N.
We also know that amount of gas ejected
Exhaust speed (v) = 800 m/s
Acceleration of rocket (a) = 20 m/s2
Gravitational acceleration (g) = 10 m/s2
We know that upward force F = m (g + a) = 5000 (10 +20)
= 5000 × 30 = 150000 N.
We also know that amount of gas ejected
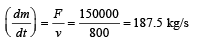
A body of mass 5 kg explodes at rest into three fragments with masses in the ratio 1 : 1 : 3. The fragments with equal masses fly in mutually perpendicular directions with speeds of 21 m/s.The velocity of heaviest fragment in m/s will be- a)
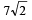
- b)
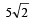 [1989]
[1989] - c)
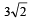
- d)
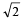
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass 5 kg explodes at rest into three fragments with masses in the ratio 1 : 1 : 3. The fragments with equal masses fly in mutually perpendicular directions with speeds of 21 m/s.The velocity of heaviest fragment in m/s will be
a)
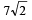
b)
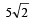 [1989]
[1989]c)
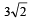
d)
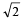

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Masses of the pieces are 1, 1, 3 kg. Hence
(1 x 21)2 + (1 x 21)2 = (3 x V)2
That is, 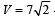
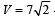
A monkey is decending from the branch of a tree with constant acceleration. If the breaking strength is 75% of the weight of the monkey, the minimum acceleration with which monkey can slide down without breaking the branch is [1993]- a)g
- b)
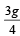
- c)
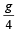
- d)
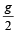
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A monkey is decending from the branch of a tree with constant acceleration. If the breaking strength is 75% of the weight of the monkey, the minimum acceleration with which monkey can slide down without breaking the branch is [1993]
a)
g
b)
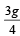
c)
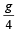
d)
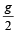

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Let T be the tension in the branch of a tree when monkey is descending with acceleration a. Then mg – T = ma; and T = 75% of weight of monkey
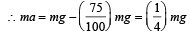
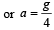
A heavy uniform chain lies on horizontal table top. If the coefficient of friction between the chain and the table surface is 0.25, then the maximum fraction of the length of the chain that can hang over one edge of the table is [1991]- a)20%
- b)25%
- c)35%
- d)15%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A heavy uniform chain lies on horizontal table top. If the coefficient of friction between the chain and the table surface is 0.25, then the maximum fraction of the length of the chain that can hang over one edge of the table is [1991]
a)
20%
b)
25%
c)
35%
d)
15%

|
Pooja Saha answered |
The force of friction on the chain lying on the table should be equal to the weight of the hanging chain.
Let ρ = mass per unit length of the chain
µ = coefficient of friction
l = length of the total chain
x = length of hanging chain
Let ρ = mass per unit length of the chain
µ = coefficient of friction
l = length of the total chain
x = length of hanging chain
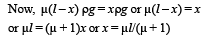
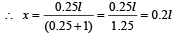
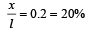
Chapter doubts & questions for Laws of Motion - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Laws of Motion - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

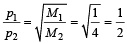

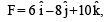 acquires an acceler ation of 1 m/s2. The mass of this body must be [2009]
acquires an acceler ation of 1 m/s2. The mass of this body must be [2009]