All Exams >
NEET >
NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Microbes in Human Welfare for NEET Exam
Organic farming does not include:- a)green manures
- b)chemical fertilisers
- c)farmyard manures
- d)compost
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic farming does not include:
a)
green manures
b)
chemical fertilisers
c)
farmyard manures
d)
compost

|
Shivkumar Tandale. answered |
Organic farming includes all fertilizers made by biotic components and which are not artificial synthesise it includes green manure,farmyard manure, compost , cattle dung etc. so the option is B)
Select the correct option to fill up the blanks.
(i) ___________are used in detergent formulations and are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry.
(ii) _____________are ripened by growing Penicillium roqueforti on them.
(iii) ___________are produced without distillation whereas,__________are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
(iv) ___________antibiotic was used to teat American soldiers wounded in world war II.
(v) _______is also called as Kusht rog.
- a)(i) Lipases (ii) Camebert Cheese (iii) Whisky and rum, wine and beer (iv) Penicillin (v) Leprosy
- b)(i) Lipases (ii) Roquefort cheese (iii) Whisky and rum, wine and beer (iv) Penicillin (v) Leprosy
- c)(i) Streptokinase (ii) Roquefort cheese (iii) Wine and beer, Whisky and rum (iv) Streptomycin (v) Whooping cough
- d)(i) Amylase (ii) Swiss cheese (iii) Whisky and rum, wine and beer (iv) Penicillin (v) Diphtheria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct option to fill up the blanks.
(i) ___________are used in detergent formulations and are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry.
(ii) _____________are ripened by growing Penicillium roqueforti on them.
(iii) ___________are produced without distillation whereas,__________are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
(iv) ___________antibiotic was used to teat American soldiers wounded in world war II.
(v) _______is also called as Kusht rog.
(i) ___________are used in detergent formulations and are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry.
(ii) _____________are ripened by growing Penicillium roqueforti on them.
(iii) ___________are produced without distillation whereas,__________are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
(iv) ___________antibiotic was used to teat American soldiers wounded in world war II.
(v) _______is also called as Kusht rog.
a)
(i) Lipases (ii) Camebert Cheese (iii) Whisky and rum, wine and beer (iv) Penicillin (v) Leprosy
b)
(i) Lipases (ii) Roquefort cheese (iii) Whisky and rum, wine and beer (iv) Penicillin (v) Leprosy
c)
(i) Streptokinase (ii) Roquefort cheese (iii) Wine and beer, Whisky and rum (iv) Streptomycin (v) Whooping cough
d)
(i) Amylase (ii) Swiss cheese (iii) Whisky and rum, wine and beer (iv) Penicillin (v) Diphtheria
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Lipases are used in detergent formulations and are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry.
Roquefort cheese are ripened by growing Penicillium roqueforti on them.
Wine and beer are produced without distillation whereas, whiskey, brandy and rum are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
Penicillin antibiotic was used to teat American soldiers wounded in World War II.
Leprosy is also called as Kusht rog.
Roquefort cheese are ripened by growing Penicillium roqueforti on them.
Wine and beer are produced without distillation whereas, whiskey, brandy and rum are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
Penicillin antibiotic was used to teat American soldiers wounded in World War II.
Leprosy is also called as Kusht rog.
A nitrogen fixing microbe associated with the fern Azolla in rice fields is:- a)Frankia
- b)Rhizobium
- c)Spirulina
- d)Anabaena
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A nitrogen fixing microbe associated with the fern Azolla in rice fields is:
a)
Frankia
b)
Rhizobium
c)
Spirulina
d)
Anabaena
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Anabaena azollae, a cyanobacterium that lives in symbiotic association with the free-floating water fern Azolla. Anabaena azollae can grow Photo-autotrophically and fixes atmospheric nitrogen. The inoculation of cyanobacteria in rice crops significantly influences the growth of rice crop by secretion of ammonia in flood water.
Which of the following options contains the end products formed during anaerobic respiration in Yeast?- a)H2O,CO2 and energy
- b)H2S,C6H12O6 and energy
- c)CO2,C2H5OH and energy
- d)H2O and CO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options contains the end products formed during anaerobic respiration in Yeast?
a)
H2O,CO2 and energy
b)
H2S,C6H12O6 and energy
c)
CO2,C2H5OH and energy
d)
H2O and CO2
|
|
Janani Singh answered |
Anaerobic respiration in yeast produces carbon dioxide (CO2) and ethanol (C2H5OH) as end products. This process is also known as fermentation.
1. Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast:
Yeast is a single-celled organism that can undergo both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells switch to anaerobic respiration to generate energy.
2. Glycolysis:
The first step in anaerobic respiration is glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm of yeast cells. During glycolysis, glucose (C6H12O6) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (C3H4O3). This process involves a series of enzymatic reactions and produces a small amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
3. Fermentation:
After glycolysis, yeast cells undergo fermentation to regenerate NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is required for glycolysis to continue. There are two types of fermentation that yeast can undergo:
a. Alcoholic Fermentation:
In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate is converted into ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide (CO2). This process occurs in the absence of oxygen and is carried out by enzymes called alcohol dehydrogenase and pyruvate decarboxylase. The release of carbon dioxide is responsible for the formation of bubbles in dough during bread-making or the fizz in carbonated beverages.
b. Lactic Acid Fermentation:
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. This process is not commonly observed in yeast, but it occurs in some bacteria and human muscle cells during intense exercise when oxygen is limited.
4. End Products:
The end products of anaerobic respiration in yeast are carbon dioxide (CO2) and ethanol (C2H5OH). These molecules are released into the surrounding environment. The release of carbon dioxide creates bubbles, and the accumulation of ethanol contributes to the characteristic flavor and alcohol content of fermented products, such as beer, wine, and bread.
Therefore, option C, which includes CO2, C2H5OH, and energy, is the correct answer.
1. Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast:
Yeast is a single-celled organism that can undergo both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells switch to anaerobic respiration to generate energy.
2. Glycolysis:
The first step in anaerobic respiration is glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm of yeast cells. During glycolysis, glucose (C6H12O6) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (C3H4O3). This process involves a series of enzymatic reactions and produces a small amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
3. Fermentation:
After glycolysis, yeast cells undergo fermentation to regenerate NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is required for glycolysis to continue. There are two types of fermentation that yeast can undergo:
a. Alcoholic Fermentation:
In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate is converted into ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide (CO2). This process occurs in the absence of oxygen and is carried out by enzymes called alcohol dehydrogenase and pyruvate decarboxylase. The release of carbon dioxide is responsible for the formation of bubbles in dough during bread-making or the fizz in carbonated beverages.
b. Lactic Acid Fermentation:
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. This process is not commonly observed in yeast, but it occurs in some bacteria and human muscle cells during intense exercise when oxygen is limited.
4. End Products:
The end products of anaerobic respiration in yeast are carbon dioxide (CO2) and ethanol (C2H5OH). These molecules are released into the surrounding environment. The release of carbon dioxide creates bubbles, and the accumulation of ethanol contributes to the characteristic flavor and alcohol content of fermented products, such as beer, wine, and bread.
Therefore, option C, which includes CO2, C2H5OH, and energy, is the correct answer.
Process of biogas production is:- a)Aerobic process
- b)Anaerobic process
- c)Active process
- d)Passive process
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Process of biogas production is:
a)
Aerobic process
b)
Anaerobic process
c)
Active process
d)
Passive process

|
Vedika Patel answered |
It's an anaerobic process because it does not require oxygen and after the process methane gas is produced . This is process is done by methanogens a type of archebacteria.
Microbes are present in- a)soil
- b)thermal vents
- c)polluted water
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Microbes are present in
a)
soil
b)
thermal vents
c)
polluted water
d)
all of the above
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Microbes are omnipresent, which means they are found everywhere. They can be found in soil, water, air, ice, inside bodies of human beings, animals, and plants, and even in thermal vents.
The reason that the chemical/synthetic fertilisers should be replaced by biofertilisers is that the former:- a)are source of environmental pollution
- b)are expensive
- c)exhaust the valuable energy resources for their manufacture
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reason that the chemical/synthetic fertilisers should be replaced by biofertilisers is that the former:
a)
are source of environmental pollution
b)
are expensive
c)
exhaust the valuable energy resources for their manufacture
d)
all of these
|
|
Nandita Dey answered |
Introduction:
Chemical/synthetic fertilizers have been widely used in agriculture to promote plant growth and increase crop yields. However, there is a growing realization that these fertilizers have negative impacts on the environment, human health, and the economy. Biofertilizers, on the other hand, offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers. In this response, we will discuss the reasons why chemical/synthetic fertilizers should be replaced by biofertilizers.
Environmental Pollution:
- Chemical/synthetic fertilizers contain high concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential nutrients for plant growth.
- When these fertilizers are applied to the soil, excess nutrients can leach into groundwater or runoff into nearby water bodies, causing water pollution.
- This nutrient pollution leads to the growth of harmful algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems.
- Moreover, chemical fertilizers contribute to air pollution through the release of greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide, which is a potent contributor to climate change.
- Biofertilizers, on the other hand, are made from natural sources such as plant residues, animal manure, and microbial cultures.
- They release nutrients slowly and in a form that is readily available to plants, minimizing the risk of nutrient runoff and pollution.
Expensive:
- Chemical/synthetic fertilizers are typically produced through energy-intensive processes that require fossil fuels.
- The manufacturing, transportation, and storage of these fertilizers contribute to their high cost.
- On the other hand, biofertilizers can be produced locally using organic waste materials, reducing the cost of production.
- Additionally, the use of biofertilizers can improve soil fertility and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers in the long run, leading to cost savings for farmers.
Exhaustion of Energy Resources:
- The production of chemical/synthetic fertilizers relies heavily on non-renewable energy sources such as natural gas and petroleum.
- These energy resources are limited and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- In contrast, biofertilizers utilize renewable energy resources such as solar energy through the process of photosynthesis in plants.
- By replacing chemical fertilizers with biofertilizers, we can reduce the demand for non-renewable energy resources and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Conclusion:
The replacement of chemical/synthetic fertilizers with biofertilizers is crucial for addressing environmental pollution, reducing costs, and conserving valuable energy resources. Biofertilizers offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative that promotes soil health, improves crop productivity, and minimizes the negative impacts on the environment. By adopting biofertilizers, we can move towards a more sustainable agricultural system that benefits both the present and future generations.
Chemical/synthetic fertilizers have been widely used in agriculture to promote plant growth and increase crop yields. However, there is a growing realization that these fertilizers have negative impacts on the environment, human health, and the economy. Biofertilizers, on the other hand, offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers. In this response, we will discuss the reasons why chemical/synthetic fertilizers should be replaced by biofertilizers.
Environmental Pollution:
- Chemical/synthetic fertilizers contain high concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential nutrients for plant growth.
- When these fertilizers are applied to the soil, excess nutrients can leach into groundwater or runoff into nearby water bodies, causing water pollution.
- This nutrient pollution leads to the growth of harmful algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems.
- Moreover, chemical fertilizers contribute to air pollution through the release of greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide, which is a potent contributor to climate change.
- Biofertilizers, on the other hand, are made from natural sources such as plant residues, animal manure, and microbial cultures.
- They release nutrients slowly and in a form that is readily available to plants, minimizing the risk of nutrient runoff and pollution.
Expensive:
- Chemical/synthetic fertilizers are typically produced through energy-intensive processes that require fossil fuels.
- The manufacturing, transportation, and storage of these fertilizers contribute to their high cost.
- On the other hand, biofertilizers can be produced locally using organic waste materials, reducing the cost of production.
- Additionally, the use of biofertilizers can improve soil fertility and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers in the long run, leading to cost savings for farmers.
Exhaustion of Energy Resources:
- The production of chemical/synthetic fertilizers relies heavily on non-renewable energy sources such as natural gas and petroleum.
- These energy resources are limited and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- In contrast, biofertilizers utilize renewable energy resources such as solar energy through the process of photosynthesis in plants.
- By replacing chemical fertilizers with biofertilizers, we can reduce the demand for non-renewable energy resources and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Conclusion:
The replacement of chemical/synthetic fertilizers with biofertilizers is crucial for addressing environmental pollution, reducing costs, and conserving valuable energy resources. Biofertilizers offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative that promotes soil health, improves crop productivity, and minimizes the negative impacts on the environment. By adopting biofertilizers, we can move towards a more sustainable agricultural system that benefits both the present and future generations.
Biopesticides are- a)The chemical, which are used to destroy the pests
- b)The living organism or their products which are used for the pest control
- c)The organisms, which destroy the crops
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Biopesticides are
a)
The chemical, which are used to destroy the pests
b)
The living organism or their products which are used for the pest control
c)
The organisms, which destroy the crops
d)
None of the above
|
|
Poulomi Basu answered |
Introduction:
Biopesticides are a type of pest control method that involves the use of living organisms or their natural products to control or eliminate pests. They are considered to be a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional chemical pesticides.
Explanation:
Definition:
Biopesticides are defined as substances derived from natural materials such as animals, plants, bacteria, and certain minerals. They can be either living organisms or their byproducts.
Types of Biopesticides:
There are three main categories of biopesticides:
1. Microbial pesticides: These are biopesticides that consist of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, or protozoa. They can control pests by infecting them with diseases, producing toxins, or competing for resources.
2. Plant-Incorporated Protectants (PIPs): PIPs are biopesticides that are produced by genetically modifying plants to express proteins that are toxic to pests. When the pests feed on these plants, they are exposed to the biopesticide and are controlled or killed.
3. Biochemical pesticides: These are naturally occurring substances that are extracted from plants, animals, or microorganisms. They can repel, disrupt, or kill pests by affecting their behavior, physiology, or development.
Advantages of Biopesticides:
- Environmental safety: Biopesticides are less toxic to non-target organisms and do not persist in the environment for long periods of time. They have minimal impact on ecosystems and reduce the risk of water and soil contamination.
- Target specificity: Biopesticides are usually designed to target specific pests, minimizing harm to beneficial organisms such as pollinators and natural enemies.
- Reduced resistance: Since biopesticides have multiple modes of action, pests are less likely to develop resistance compared to chemical pesticides.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Biopesticides can be integrated into IPM programs, which aim to manage pests using a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical control methods.
Limitations of Biopesticides:
- Variable efficacy: The effectiveness of biopesticides can vary depending on environmental conditions, target pests, and application methods.
- Shorter shelf life: Biopesticides generally have a shorter shelf life compared to chemical pesticides, which may require more frequent applications.
- Higher cost: Biopesticides can be more expensive to produce and formulate compared to chemical pesticides.
Conclusion:
In summary, biopesticides are living organisms or their products that are used for pest control. They provide a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, with advantages such as environmental safety, target specificity, and reduced resistance. However, they also have limitations such as variable efficacy and higher cost.
Biopesticides are a type of pest control method that involves the use of living organisms or their natural products to control or eliminate pests. They are considered to be a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional chemical pesticides.
Explanation:
Definition:
Biopesticides are defined as substances derived from natural materials such as animals, plants, bacteria, and certain minerals. They can be either living organisms or their byproducts.
Types of Biopesticides:
There are three main categories of biopesticides:
1. Microbial pesticides: These are biopesticides that consist of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, or protozoa. They can control pests by infecting them with diseases, producing toxins, or competing for resources.
2. Plant-Incorporated Protectants (PIPs): PIPs are biopesticides that are produced by genetically modifying plants to express proteins that are toxic to pests. When the pests feed on these plants, they are exposed to the biopesticide and are controlled or killed.
3. Biochemical pesticides: These are naturally occurring substances that are extracted from plants, animals, or microorganisms. They can repel, disrupt, or kill pests by affecting their behavior, physiology, or development.
Advantages of Biopesticides:
- Environmental safety: Biopesticides are less toxic to non-target organisms and do not persist in the environment for long periods of time. They have minimal impact on ecosystems and reduce the risk of water and soil contamination.
- Target specificity: Biopesticides are usually designed to target specific pests, minimizing harm to beneficial organisms such as pollinators and natural enemies.
- Reduced resistance: Since biopesticides have multiple modes of action, pests are less likely to develop resistance compared to chemical pesticides.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Biopesticides can be integrated into IPM programs, which aim to manage pests using a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical control methods.
Limitations of Biopesticides:
- Variable efficacy: The effectiveness of biopesticides can vary depending on environmental conditions, target pests, and application methods.
- Shorter shelf life: Biopesticides generally have a shorter shelf life compared to chemical pesticides, which may require more frequent applications.
- Higher cost: Biopesticides can be more expensive to produce and formulate compared to chemical pesticides.
Conclusion:
In summary, biopesticides are living organisms or their products that are used for pest control. They provide a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, with advantages such as environmental safety, target specificity, and reduced resistance. However, they also have limitations such as variable efficacy and higher cost.
Which of the following statements regarding baculoviruses as biocontrol agents is/are correct?- a)The majority of baculovirus used as biocontrol agents are included in the genus - Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
- b)Infection with baculoviruses occurs when susceptible hosts (e.g., some specific insects) eat virus particle present on foliage and dies.
- c)These are important in organic farming because of their specific action on harmful insects without causing any damage to beneficial insects as well as to the environment.
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding baculoviruses as biocontrol agents is/are correct?
a)
The majority of baculovirus used as biocontrol agents are included in the genus - Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
b)
Infection with baculoviruses occurs when susceptible hosts (e.g., some specific insects) eat virus particle present on foliage and dies.
c)
These are important in organic farming because of their specific action on harmful insects without causing any damage to beneficial insects as well as to the environment.
d)
All of these.
|
|
Mansi Gupta answered |
Statement a: The majority of baculoviruses used as biocontrol agents are included in the genus - Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baculoviruses are a family of viruses that infect insects. The majority of baculoviruses used as biocontrol agents belong to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus (NPV). NPVs are highly specific to certain insect species and are widely used in biocontrol programs to target specific pests.
Statement b: Infection with baculoviruses occurs when susceptible hosts (e.g., some specific insects) eat virus particles present on foliage and die.
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baculoviruses have a unique mode of transmission. Infection occurs when susceptible hosts, such as specific insects, consume virus particles that are present on foliage or other food sources. Once ingested, the virus particles replicate within the insect's body, leading to the death of the host.
Statement c: Baculoviruses are important in organic farming because of their specific action on harmful insects without causing any damage to beneficial insects as well as to the environment.
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baculoviruses are highly specific to certain insect species and do not have a broad spectrum of activity. This specificity makes them ideal for use in organic farming, where the goal is to control harmful insect pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects and the environment. Baculoviruses have been successfully used in organic agriculture to control pests like the corn earworm, cabbage looper, and gypsy moth.
Therefore, all of the given statements (a, b, and c) are correct. Baculoviruses, specifically those belonging to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus, are widely used as biocontrol agents. Infection occurs when susceptible hosts consume virus particles, and these viruses are important in organic farming due to their specific action on harmful insects without causing damage to beneficial insects or the environment.
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baculoviruses are a family of viruses that infect insects. The majority of baculoviruses used as biocontrol agents belong to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus (NPV). NPVs are highly specific to certain insect species and are widely used in biocontrol programs to target specific pests.
Statement b: Infection with baculoviruses occurs when susceptible hosts (e.g., some specific insects) eat virus particles present on foliage and die.
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baculoviruses have a unique mode of transmission. Infection occurs when susceptible hosts, such as specific insects, consume virus particles that are present on foliage or other food sources. Once ingested, the virus particles replicate within the insect's body, leading to the death of the host.
Statement c: Baculoviruses are important in organic farming because of their specific action on harmful insects without causing any damage to beneficial insects as well as to the environment.
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baculoviruses are highly specific to certain insect species and do not have a broad spectrum of activity. This specificity makes them ideal for use in organic farming, where the goal is to control harmful insect pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects and the environment. Baculoviruses have been successfully used in organic agriculture to control pests like the corn earworm, cabbage looper, and gypsy moth.
Therefore, all of the given statements (a, b, and c) are correct. Baculoviruses, specifically those belonging to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus, are widely used as biocontrol agents. Infection occurs when susceptible hosts consume virus particles, and these viruses are important in organic farming due to their specific action on harmful insects without causing damage to beneficial insects or the environment.
Which of the following statements is correct with regard to biocontrol agents?- a)Ladybird and dragonflies are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes respectively.
- b)Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria are used to control butterfly caterpillars.
- c)Trichoderma species are used to control several plant pathogen.
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct with regard to biocontrol agents?
a)
Ladybird and dragonflies are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes respectively.
b)
Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria are used to control butterfly caterpillars.
c)
Trichoderma species are used to control several plant pathogen.
d)
All of these.
|
|
Pranab Mehta answered |
Introduction:
Biocontrol agents are organisms that are used to control pests, diseases, and weeds in agriculture and other ecosystems. They are a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides. In this question, we are given four statements about biocontrol agents and asked to choose the correct one.
Explanation:
Statement a: Ladybird and dragonflies are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes respectively.
Explanation:
Ladybirds are commonly used as biocontrol agents to control aphids, which are pests that damage crops. Ladybirds feed on aphids and help in reducing their population. Dragonflies, on the other hand, are natural predators of mosquitoes. They feed on mosquito larvae, helping to control their population. Therefore, statement a is correct.
Statement b: Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria are used to control butterfly caterpillars.
Explanation:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a type of bacteria that produces toxins that are harmful to certain insect pests, including butterfly caterpillars. When these bacteria are ingested by the caterpillars, the toxins disrupt their digestive system, leading to their death. Bt is commonly used as a biocontrol agent to control butterfly caterpillars in agricultural settings. Therefore, statement b is correct.
Statement c: Trichoderma species are used to control several plant pathogens.
Explanation:
Trichoderma is a genus of fungus that is known for its biocontrol properties. It has the ability to suppress the growth of various plant pathogens, including fungi, bacteria, and nematodes. Trichoderma species produce enzymes and secondary metabolites that inhibit the growth of pathogens and promote plant growth. They are commonly used as biocontrol agents in agriculture to control diseases caused by plant pathogens. Therefore, statement c is correct.
Conclusion:
From the explanations provided above, it can be concluded that all of the given statements (a, b, and c) are correct. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - All of these.
Biocontrol agents are organisms that are used to control pests, diseases, and weeds in agriculture and other ecosystems. They are a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides. In this question, we are given four statements about biocontrol agents and asked to choose the correct one.
Explanation:
Statement a: Ladybird and dragonflies are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes respectively.
Explanation:
Ladybirds are commonly used as biocontrol agents to control aphids, which are pests that damage crops. Ladybirds feed on aphids and help in reducing their population. Dragonflies, on the other hand, are natural predators of mosquitoes. They feed on mosquito larvae, helping to control their population. Therefore, statement a is correct.
Statement b: Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria are used to control butterfly caterpillars.
Explanation:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a type of bacteria that produces toxins that are harmful to certain insect pests, including butterfly caterpillars. When these bacteria are ingested by the caterpillars, the toxins disrupt their digestive system, leading to their death. Bt is commonly used as a biocontrol agent to control butterfly caterpillars in agricultural settings. Therefore, statement b is correct.
Statement c: Trichoderma species are used to control several plant pathogens.
Explanation:
Trichoderma is a genus of fungus that is known for its biocontrol properties. It has the ability to suppress the growth of various plant pathogens, including fungi, bacteria, and nematodes. Trichoderma species produce enzymes and secondary metabolites that inhibit the growth of pathogens and promote plant growth. They are commonly used as biocontrol agents in agriculture to control diseases caused by plant pathogens. Therefore, statement c is correct.
Conclusion:
From the explanations provided above, it can be concluded that all of the given statements (a, b, and c) are correct. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - All of these.
Farmers have reported over 50% higher yields of rice by using which of the following biofertilisers?- a)Bacillus thuringiensis
- b)Lagume-Rhizobium symbiosis
- c)Mycorrhizae
- d)Azolla pinnata
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Farmers have reported over 50% higher yields of rice by using which of the following biofertilisers?
a)
Bacillus thuringiensis
b)
Lagume-Rhizobium symbiosis
c)
Mycorrhizae
d)
Azolla pinnata
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Azolla pinnata is a small free floating freshwater fern which multiplies rapidly, doubling every 5-7 days. The fern can live with Anabaena symbiotically in rice field to fix atmospheric nitrogen. It does not interfere with their growth. In some South-East Asian countries, especially China, the rice fields are regularly provided with Azolla.
Which of the following statements regarding antibiotics is not correct?
(i) Antibiotic is the attenuated microorganisms which in small concentrations, can kill or retard the growth of other harmful microorganisms.
(ii) Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered by Alexander Fleming (1928) while working on bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
(iii) The full potential of penicillin as an effective antibiotic was established by Ernest Chain and Howard Florey.
(iv) Fleming, Chain, and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1945.- a)(i) Only
- b)(ii) Only
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding antibiotics is not correct?
(i) Antibiotic is the attenuated microorganisms which in small concentrations, can kill or retard the growth of other harmful microorganisms.
(ii) Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered by Alexander Fleming (1928) while working on bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
(iii) The full potential of penicillin as an effective antibiotic was established by Ernest Chain and Howard Florey.
(iv) Fleming, Chain, and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1945.
(i) Antibiotic is the attenuated microorganisms which in small concentrations, can kill or retard the growth of other harmful microorganisms.
(ii) Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered by Alexander Fleming (1928) while working on bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
(iii) The full potential of penicillin as an effective antibiotic was established by Ernest Chain and Howard Florey.
(iv) Fleming, Chain, and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1945.
a)
(i) Only
b)
(ii) Only
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Antibiotics are chemical substances secreted by certain microbes which inhibit the growth and development of other microbes. Most of them produced by actinomycetes and filamentous fungi. Some inportant antibiotics are tetracycline, chloramphenicol, steptomycin etc.
Unicellular symbiotic organisms that improve the yield of legumes by- a)fixing atmospheric nitrogen without colonising roots of host plant
- b)fixing atmospheric nitrogen and colonising roots of host plant
- c)inducing the host plant to absorb more phosphours
- d)stimulating the host plant to become tolerant to drought
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Unicellular symbiotic organisms that improve the yield of legumes by
a)
fixing atmospheric nitrogen without colonising roots of host plant
b)
fixing atmospheric nitrogen and colonising roots of host plant
c)
inducing the host plant to absorb more phosphours
d)
stimulating the host plant to become tolerant to drought
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria form a mutually beneficial association with the plants. The bacteria obtain food and shelter from plants. In return, they give a part of their fixied nitrogen to the plants. The most important of the symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria is Rhizobium. it forms nodule on the roots of legume plants. They develop the ability to fix nitrogen only when they are present inside the root nodules. in the nodule cells, bacteria (bacteroids) lie in groups surrounded by membrane of the host which is lined by a pink-red pigment called leghaemoglobin.
These bacteria grow anaerobically on cellulosic material, produce large amount of methane along with CO2 and H2 and are collectively called as methanogens. Examples of such bacteria are:- a)Methanobacterium
- b)Mathanobrevibacter
- c)Methanococcus
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
These bacteria grow anaerobically on cellulosic material, produce large amount of methane along with CO2 and H2 and are collectively called as methanogens. Examples of such bacteria are:
a)
Methanobacterium
b)
Mathanobrevibacter
c)
Methanococcus
d)
All of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic by product in anoxic condition. They include Methanobacterium, Methanobrevibacter and Methanococcus.
Stains used for lowering blood cholesterol level are extracted from- a)algae
- b)bacteria
- c)viruses
- d)yeast
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stains used for lowering blood cholesterol level are extracted from
a)
algae
b)
bacteria
c)
viruses
d)
yeast
|
|
Nishtha Joshi answered |
Introduction:
The question asks about the source of stains used for lowering blood cholesterol levels. Cholesterol is a type of fat found in the bloodstream and is essential for various bodily functions. However, high levels of cholesterol can lead to health problems, particularly cardiovascular diseases. Thus, it is important to manage cholesterol levels. Stains are commonly prescribed medications that help in reducing cholesterol levels.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option 'D' - yeast. Stains used for lowering blood cholesterol levels are extracted from yeast. Here's an explanation of why yeast is used and how it helps in reducing cholesterol:
1. Yeast and Lovastatin:
- Yeast is a type of fungus that is commonly used in the production of various food and beverage products like bread, beer, and wine.
- Certain species of yeast, particularly Monascus purpureus, produce a compound called lovastatin.
- Lovastatin is a type of statin, which is a class of medications commonly prescribed as cholesterol-lowering drugs.
- Statins work by inhibiting an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the production of cholesterol in the body.
- Lovastatin specifically inhibits this enzyme, leading to a decrease in the production of cholesterol.
2. Production of Lovastatin:
- Lovastatin is produced by fermenting Monascus purpureus with a specific strain of yeast, Aspergillus terreus.
- During the fermentation process, Aspergillus terreus converts certain compounds present in Monascus purpureus into lovastatin.
- The resulting lovastatin is then extracted and purified to be used as a medication for lowering blood cholesterol levels.
3. Effectiveness and Safety:
- Lovastatin and other stains derived from yeast have been extensively studied and proven to be effective in reducing cholesterol levels.
- They are commonly prescribed by healthcare professionals for individuals with high cholesterol levels or those at risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- However, like any medication, stains may have potential side effects and should be used under medical supervision.
Conclusion:
Stains used for lowering blood cholesterol levels are extracted from yeast. Yeast, specifically Monascus purpureus, produces a compound called lovastatin, which is a type of statin medication. Lovastatin inhibits the enzyme involved in cholesterol production, thereby helping to reduce cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. It is important to note that stains should be used under medical supervision, as they may have potential side effects.
The question asks about the source of stains used for lowering blood cholesterol levels. Cholesterol is a type of fat found in the bloodstream and is essential for various bodily functions. However, high levels of cholesterol can lead to health problems, particularly cardiovascular diseases. Thus, it is important to manage cholesterol levels. Stains are commonly prescribed medications that help in reducing cholesterol levels.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option 'D' - yeast. Stains used for lowering blood cholesterol levels are extracted from yeast. Here's an explanation of why yeast is used and how it helps in reducing cholesterol:
1. Yeast and Lovastatin:
- Yeast is a type of fungus that is commonly used in the production of various food and beverage products like bread, beer, and wine.
- Certain species of yeast, particularly Monascus purpureus, produce a compound called lovastatin.
- Lovastatin is a type of statin, which is a class of medications commonly prescribed as cholesterol-lowering drugs.
- Statins work by inhibiting an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the production of cholesterol in the body.
- Lovastatin specifically inhibits this enzyme, leading to a decrease in the production of cholesterol.
2. Production of Lovastatin:
- Lovastatin is produced by fermenting Monascus purpureus with a specific strain of yeast, Aspergillus terreus.
- During the fermentation process, Aspergillus terreus converts certain compounds present in Monascus purpureus into lovastatin.
- The resulting lovastatin is then extracted and purified to be used as a medication for lowering blood cholesterol levels.
3. Effectiveness and Safety:
- Lovastatin and other stains derived from yeast have been extensively studied and proven to be effective in reducing cholesterol levels.
- They are commonly prescribed by healthcare professionals for individuals with high cholesterol levels or those at risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- However, like any medication, stains may have potential side effects and should be used under medical supervision.
Conclusion:
Stains used for lowering blood cholesterol levels are extracted from yeast. Yeast, specifically Monascus purpureus, produces a compound called lovastatin, which is a type of statin medication. Lovastatin inhibits the enzyme involved in cholesterol production, thereby helping to reduce cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. It is important to note that stains should be used under medical supervision, as they may have potential side effects.
A microbial biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars is:- a)Trichoderma polysporum
- b)Bacillus thuringiensis
- c)Streptococcus
- d)Mycorrhiza
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A microbial biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars is:
a)
Trichoderma polysporum
b)
Bacillus thuringiensis
c)
Streptococcus
d)
Mycorrhiza
|
|
Sinjini Patel answered |
Introduction:
Biocontrol agents are organisms that are used to control pests, diseases, or weeds. They are an effective and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides. One type of biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars is Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt):
- Bacillus thuringiensis is a naturally occurring soil bacterium that produces crystal toxins called delta-endotoxins. These toxins are toxic to a wide range of insect larvae, including butterfly caterpillars.
- Bt produces different types of delta-endotoxins, each specific to certain insect groups. The delta-endotoxins that are effective against butterfly caterpillars are called Cry toxins.
- When butterfly caterpillars ingest Bt spores or the toxins produced by the bacterium, the toxins bind to their gut lining and disrupt the normal functioning of their digestive system.
- This leads to paralysis and death of the caterpillars within a few days of ingestion.
Advantages of using Bacillus thuringiensis:
- Specificity: Bt toxins are highly specific to certain insect groups, such as butterfly caterpillars. They have minimal impact on non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, birds, and mammals.
- Environmentally friendly: Bt is a natural and safe alternative to chemical insecticides. It does not persist in the environment, as it degrades rapidly under sunlight and microbial action.
- Effective: Bt has been extensively studied and proven to be effective against a wide range of butterfly caterpillars. It is commonly used in organic farming and integrated pest management programs.
- Resistance management: Bt toxins act through a unique mode of action, making it unlikely for insects to develop resistance. However, it is important to use Bt in a responsible manner to prevent the emergence of resistant insect populations.
Conclusion:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is an effective microbial biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars. Its specificity, environmental safety, and effectiveness make it a valuable tool in sustainable pest management strategies. By using Bt, farmers and gardeners can reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides and promote a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
Biocontrol agents are organisms that are used to control pests, diseases, or weeds. They are an effective and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical pesticides. One type of biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars is Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt):
- Bacillus thuringiensis is a naturally occurring soil bacterium that produces crystal toxins called delta-endotoxins. These toxins are toxic to a wide range of insect larvae, including butterfly caterpillars.
- Bt produces different types of delta-endotoxins, each specific to certain insect groups. The delta-endotoxins that are effective against butterfly caterpillars are called Cry toxins.
- When butterfly caterpillars ingest Bt spores or the toxins produced by the bacterium, the toxins bind to their gut lining and disrupt the normal functioning of their digestive system.
- This leads to paralysis and death of the caterpillars within a few days of ingestion.
Advantages of using Bacillus thuringiensis:
- Specificity: Bt toxins are highly specific to certain insect groups, such as butterfly caterpillars. They have minimal impact on non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, birds, and mammals.
- Environmentally friendly: Bt is a natural and safe alternative to chemical insecticides. It does not persist in the environment, as it degrades rapidly under sunlight and microbial action.
- Effective: Bt has been extensively studied and proven to be effective against a wide range of butterfly caterpillars. It is commonly used in organic farming and integrated pest management programs.
- Resistance management: Bt toxins act through a unique mode of action, making it unlikely for insects to develop resistance. However, it is important to use Bt in a responsible manner to prevent the emergence of resistant insect populations.
Conclusion:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is an effective microbial biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars. Its specificity, environmental safety, and effectiveness make it a valuable tool in sustainable pest management strategies. By using Bt, farmers and gardeners can reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides and promote a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
Baculoviruses (Nucleopolyhedrovirus) do not show- a)host specificity
- b)narrow spectrum applications
- c)effects on non-target pathogens
- d)utility in IPM programme
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Baculoviruses (Nucleopolyhedrovirus) do not show
a)
host specificity
b)
narrow spectrum applications
c)
effects on non-target pathogens
d)
utility in IPM programme
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Nucleopolyhedrovirus are excellent candidates for species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications. They have been shown to have no negative impacts on plants, mammals, birds, fish or even on non-target insects. This is especially desirable when beneficial insects are being conserved to aid in an overall integrated pest management (IPM) programme, or when an ecologically sensitive area is being treated.
Identify the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the table given below and select the correct answer.
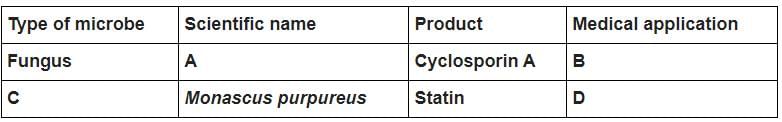
- a)A- Trichoderma polysporum, B- As an immunosuppressive agent, C- Yeast (Fungus), D- Lowering of blood cholesterol
- b)A- Trichoderma polysporum, B- Lowering of blood cholesterol, C- Yeast (Fungus), D- As an immunosuppressive agent
- c)B- Lowering of blood cholesterol, A- Trichoderma polysporum, C- Yeast (Fungus), D- As an immunosuppressive agent
- d)D- An immunosuppressive agent, A- Trichoderma polysporum, C- Yeast (Fungus), B- Lowering of blood cholesterol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the table given below and select the correct answer.


a)
A- Trichoderma polysporum, B- As an immunosuppressive agent, C- Yeast (Fungus), D- Lowering of blood cholesterol
b)
A- Trichoderma polysporum, B- Lowering of blood cholesterol, C- Yeast (Fungus), D- As an immunosuppressive agent
c)
B- Lowering of blood cholesterol, A- Trichoderma polysporum, C- Yeast (Fungus), D- As an immunosuppressive agent
d)
D- An immunosuppressive agent, A- Trichoderma polysporum, C- Yeast (Fungus), B- Lowering of blood cholesterol

|
Krish Kshatriya answered |
A
Which of the following food items is produced by the fermenting activity of microbes?
(A) Idli
(B) Dosa
(C) Toddy
(D) Cheese- a)A and C
- b)C and D
- c)A, B and C
- d)A, B, C and D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following food items is produced by the fermenting activity of microbes?
(A) Idli
(B) Dosa
(C) Toddy
(D) Cheese
(A) Idli
(B) Dosa
(C) Toddy
(D) Cheese
a)
A and C
b)
C and D
c)
A, B and C
d)
A, B, C and D
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Cheese is one of the oldest milk products prepared with the help of microbes.The curd is separated from liquid part or whey to form cheese. Dosa, Upma are fermented preparation of rice and black gram. The two are allowed to ferment for 3-12 hours with air borne Leuconostoc and Streptococcus species of bacteria. Toddy is a traditional drink of some parts of South India which is made by fermentation of sap of palms.
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding mycorrhiza?- a)It helps in absorption of phosphorus from the soil
- b)It is a symbiotic assocaition of fungi with the roots of higher plants
- c)It helps the plant in developing resistance to rootborne pathogens
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding mycorrhiza?
a)
It helps in absorption of phosphorus from the soil
b)
It is a symbiotic assocaition of fungi with the roots of higher plants
c)
It helps the plant in developing resistance to rootborne pathogens
d)
None of these
|
|
Jaya Chavan answered |
Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between fungi and the roots of higher plants. It is a mutually beneficial relationship where both the fungus and the plant derive certain advantages. Mycorrhiza plays a crucial role in the nutrient uptake and overall health of plants.
Statement a: Mycorrhiza helps in the absorption of phosphorus from the soil.
This statement is correct. Mycorrhizal fungi have the ability to extend their hyphae (filamentous structures) into the soil, increasing the surface area for nutrient absorption. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic forms of phosphorus into simpler, more readily available forms that can be absorbed by the plant.
Statement b: Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungi with the roots of higher plants.
This statement is correct. Mycorrhiza is indeed a symbiotic association between fungi and the roots of higher plants. The fungi colonize the root system of the plant, forming a network of mycelium that extends into the soil, while the plant provides the fungi with carbohydrates and other nutrients.
Statement c: Mycorrhiza helps the plant in developing resistance to rootborne pathogens.
This statement is also correct. Mycorrhizal fungi can enhance the plant's resistance to various rootborne pathogens. They can produce antimicrobial compounds or compete with pathogens for nutrients and space, thereby reducing pathogen colonization and disease development. Additionally, mycorrhizal symbiosis can stimulate the plant's immune responses, leading to an overall increase in plant defense mechanisms.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, "None of these." All of the given statements are correct regarding mycorrhiza.
Statement a: Mycorrhiza helps in the absorption of phosphorus from the soil.
This statement is correct. Mycorrhizal fungi have the ability to extend their hyphae (filamentous structures) into the soil, increasing the surface area for nutrient absorption. They secrete enzymes that break down complex organic forms of phosphorus into simpler, more readily available forms that can be absorbed by the plant.
Statement b: Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungi with the roots of higher plants.
This statement is correct. Mycorrhiza is indeed a symbiotic association between fungi and the roots of higher plants. The fungi colonize the root system of the plant, forming a network of mycelium that extends into the soil, while the plant provides the fungi with carbohydrates and other nutrients.
Statement c: Mycorrhiza helps the plant in developing resistance to rootborne pathogens.
This statement is also correct. Mycorrhizal fungi can enhance the plant's resistance to various rootborne pathogens. They can produce antimicrobial compounds or compete with pathogens for nutrients and space, thereby reducing pathogen colonization and disease development. Additionally, mycorrhizal symbiosis can stimulate the plant's immune responses, leading to an overall increase in plant defense mechanisms.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, "None of these." All of the given statements are correct regarding mycorrhiza.
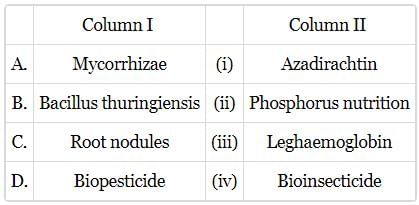
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
- a)A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv)
- b)A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(i)
- c)A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
- d)A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.


a)
A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv)
b)
A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(i)
c)
A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
d)
A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
- Mycorrhizae helps in phosphorus uptake from the soil.
- Bacillus thuringiensis is a bioinsecticide.
- Leghaemoglobin is present in the root nodules in leguminous plants.
- Azadiractin is a secondary metabolite present in the neem seeds and it acts as a biopesticide.
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?- a)Rhizobium – Parasite in the roots of leguminous plants
- b)Mycorrhizae – Mineral uptake from soil
- c)Yeast – Production of biogas
- d)Azospirillum - Symbiotic N2 - fixing bacterium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?
a)
Rhizobium – Parasite in the roots of leguminous plants
b)
Mycorrhizae – Mineral uptake from soil
c)
Yeast – Production of biogas
d)
Azospirillum - Symbiotic N2 - fixing bacterium
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of a fungus with the roots of a higher plant. Ectomycorrhiza, which lie on surface of the root, help in direct absorption of minerals from the soil over a large area. Rhizobium is a symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria and Azospirillum is a free living nitrogen fixing bacteria. Methanogenic bacteria help in production of biogas
When a natural predator (living organism) is applied on the other pathogen organisms to control them, this process is called as- a)biological control
- b)genetic engineering
- c)arifificial control
- d)confusion technique
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a natural predator (living organism) is applied on the other pathogen organisms to control them, this process is called as
a)
biological control
b)
genetic engineering
c)
arifificial control
d)
confusion technique
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Indiscriminate eradication of pests is undesirable because without them the beneficial predatory and parasitic organisms which depend upon them for food would also be eliminated. The biocontrol method of pest and pathogen control involves use of viruses, bacteria and other insects (with are their natural predators and pests).
____________ is the first step of sewage treatment.- a)Precipitation
- b)Chlorination
- c)Sedimentation
- d)Aeration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
____________ is the first step of sewage treatment.
a)
Precipitation
b)
Chlorination
c)
Sedimentation
d)
Aeration
|
|
Mahi Desai answered |
Sedimentation is the first step of sewage treatment. This process involves the separation of solid particles from the wastewater.
Explanation:
Sewage treatment is a process that aims to remove contaminants from wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. The primary goal of sewage treatment is to protect public health and the environment by treating the wastewater to remove harmful substances and reduce pollution.
The process of sewage treatment involves several steps, one of which is sedimentation. Let's understand this step in detail:
1. Sedimentation:
Sedimentation is the first step in the sewage treatment process. It involves the separation of solid particles from the wastewater. During this step, the wastewater is allowed to sit in a large tank called a sedimentation tank or clarifier. The wastewater enters the tank and is left undisturbed for a certain period.
During this time, the solid particles present in the wastewater, such as sand, grit, organic matter, and other suspended solids, settle down to the bottom of the tank due to gravity. These settling particles form a layer of sludge at the bottom of the tank.
The clarified liquid, also known as effluent, is then removed from the top of the tank and transferred to the next stage of the treatment process. This effluent contains fewer suspended solids and is relatively cleaner than the original wastewater.
The sedimentation process helps in the removal of large solid particles and heavy organic matter that can settle down. It also aids in the removal of floating debris, such as oil and grease, which can be skimmed off the surface of the tank.
Advantages of sedimentation:
- Removes large solid particles and heavy organic matter.
- Reduces the load of suspended solids in the wastewater.
- Improves the efficiency of subsequent treatment processes.
- Helps in the removal of floating debris.
Conclusion:
Sedimentation is the first step of sewage treatment, where solid particles are separated from the wastewater. This process plays a crucial role in reducing the contamination of the wastewater and preparing it for further treatment processes.
Explanation:
Sewage treatment is a process that aims to remove contaminants from wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. The primary goal of sewage treatment is to protect public health and the environment by treating the wastewater to remove harmful substances and reduce pollution.
The process of sewage treatment involves several steps, one of which is sedimentation. Let's understand this step in detail:
1. Sedimentation:
Sedimentation is the first step in the sewage treatment process. It involves the separation of solid particles from the wastewater. During this step, the wastewater is allowed to sit in a large tank called a sedimentation tank or clarifier. The wastewater enters the tank and is left undisturbed for a certain period.
During this time, the solid particles present in the wastewater, such as sand, grit, organic matter, and other suspended solids, settle down to the bottom of the tank due to gravity. These settling particles form a layer of sludge at the bottom of the tank.
The clarified liquid, also known as effluent, is then removed from the top of the tank and transferred to the next stage of the treatment process. This effluent contains fewer suspended solids and is relatively cleaner than the original wastewater.
The sedimentation process helps in the removal of large solid particles and heavy organic matter that can settle down. It also aids in the removal of floating debris, such as oil and grease, which can be skimmed off the surface of the tank.
Advantages of sedimentation:
- Removes large solid particles and heavy organic matter.
- Reduces the load of suspended solids in the wastewater.
- Improves the efficiency of subsequent treatment processes.
- Helps in the removal of floating debris.
Conclusion:
Sedimentation is the first step of sewage treatment, where solid particles are separated from the wastewater. This process plays a crucial role in reducing the contamination of the wastewater and preparing it for further treatment processes.
Which of the following bacteria is present in the rumen of cattle?- a)Azotobacter
- b)Rhizobium
- c)Methanobacterium
- d)Azospirillum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following bacteria is present in the rumen of cattle?
a)
Azotobacter
b)
Rhizobium
c)
Methanobacterium
d)
Azospirillum
|
|
Puja Chakraborty answered |
Bacteria Present in the Rumen of Cattle
The rumen of cattle is a specialized chamber of the stomach where microbial fermentation of ingested plant material takes place. This fermentation process is crucial for the digestion of cellulose and other complex carbohydrates found in plant cell walls. Several bacteria are present in the rumen of cattle, playing a vital role in breaking down plant material and providing nutrients to the host animal.
Methanobacterium in the Rumen
Among the bacteria present in the rumen, Methanobacterium is one of the significant groups. Methanobacterium is a type of methanogenic archaea that produces methane gas as a byproduct of their metabolism. These bacteria are anaerobic and use hydrogen and carbon dioxide produced by other rumen microbes as substrates to generate methane.
Importance of Methanobacterium in Rumen
1. Methane Production: Methanobacterium is responsible for the production of methane gas in the rumen. The methane produced is then eructated (burped) by the cattle and released into the atmosphere. Methane is considered a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming and climate change.
2. Energy Harvesting: The production of methane by Methanobacterium allows for the removal of hydrogen produced during fermentation. This removal of hydrogen helps to maintain the fermentation process by preventing its accumulation, which could inhibit the activity of other microorganisms involved in the digestion process.
3. Symbiotic Relationship: The presence of Methanobacterium in the rumen is part of a symbiotic relationship between the bacteria, protozoa, and the host animal. These microorganisms work together to break down complex carbohydrates into simpler compounds that can be absorbed by the cattle. Methanobacterium benefits from the hydrogen and carbon dioxide produced by other rumen microbes, while the host animal benefits from the breakdown of cellulose and the release of nutrients.
In conclusion, Methanobacterium is a bacteria present in the rumen of cattle. It plays a crucial role in methane production, energy harvesting, and the overall digestion process in the rumen. However, it is important to note that other bacteria, such as Fibrobacter, Ruminococcus, and Prevotella, are also present in the rumen and contribute to the fermentation and digestion of plant material.
The rumen of cattle is a specialized chamber of the stomach where microbial fermentation of ingested plant material takes place. This fermentation process is crucial for the digestion of cellulose and other complex carbohydrates found in plant cell walls. Several bacteria are present in the rumen of cattle, playing a vital role in breaking down plant material and providing nutrients to the host animal.
Methanobacterium in the Rumen
Among the bacteria present in the rumen, Methanobacterium is one of the significant groups. Methanobacterium is a type of methanogenic archaea that produces methane gas as a byproduct of their metabolism. These bacteria are anaerobic and use hydrogen and carbon dioxide produced by other rumen microbes as substrates to generate methane.
Importance of Methanobacterium in Rumen
1. Methane Production: Methanobacterium is responsible for the production of methane gas in the rumen. The methane produced is then eructated (burped) by the cattle and released into the atmosphere. Methane is considered a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming and climate change.
2. Energy Harvesting: The production of methane by Methanobacterium allows for the removal of hydrogen produced during fermentation. This removal of hydrogen helps to maintain the fermentation process by preventing its accumulation, which could inhibit the activity of other microorganisms involved in the digestion process.
3. Symbiotic Relationship: The presence of Methanobacterium in the rumen is part of a symbiotic relationship between the bacteria, protozoa, and the host animal. These microorganisms work together to break down complex carbohydrates into simpler compounds that can be absorbed by the cattle. Methanobacterium benefits from the hydrogen and carbon dioxide produced by other rumen microbes, while the host animal benefits from the breakdown of cellulose and the release of nutrients.
In conclusion, Methanobacterium is a bacteria present in the rumen of cattle. It plays a crucial role in methane production, energy harvesting, and the overall digestion process in the rumen. However, it is important to note that other bacteria, such as Fibrobacter, Ruminococcus, and Prevotella, are also present in the rumen and contribute to the fermentation and digestion of plant material.
Biogas is produced by:- a)Aerobic breakdown of biomass
- b)Anaerobic breakdown of biomass
- c)With the help of methanogenic bacteria
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biogas is produced by:
a)
Aerobic breakdown of biomass
b)
Anaerobic breakdown of biomass
c)
With the help of methanogenic bacteria
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
- Biogas is a methane rich fuel gas produced by anerobic breakdown or digestion of biomass with the help of methanogenic bacteria.
- Biogas is a mixture of gases, containing predominantly methane (50-70%), CO2 (30-40%) and traces of hydrogen, H2S and nitrogen.
Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of alnus is brought about by- a)Frankia
- b)Azorhizobium
- c)Bradyrhizobium
- d)Clostridium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of alnus is brought about by
a)
Frankia
b)
Azorhizobium
c)
Bradyrhizobium
d)
Clostridium
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Frankia, a nitrogen fixing mycelial bacterium(actinomycete), is associated symbiotically with roots nodules of several non - legume plants like Alnus(Alder), Myrica, rubus etc.
______ produced by bacterium Streptococcus and modified by genetic engineering is used as a clot buster for removing clots from the blood vessels of patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack. - a)Lipase
- b)Streptokinase
- c)Cyclosporin A
- d)Antibiotic streptomycin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
______ produced by bacterium Streptococcus and modified by genetic engineering is used as a clot buster for removing clots from the blood vessels of patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack.
a)
Lipase
b)
Streptokinase
c)
Cyclosporin A
d)
Antibiotic streptomycin
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Streptokinase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator or TPA) is an enzyme obtained from the cultures of some haemolytic bacterium Streptococcus and modified genetically to function as clot buster. It has fibrinolytic effect. Therefore, it helps in clearing blood clots inside the blood vessels in patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack, through dissolution of intravascular fibrin.
Which one of the following combinations of organisms are responsible for the formation and flavour of yoghurt?- a)Lactobacillus bulgaricus and streptococcus thermophilus
- b)Rhizobium melioti and Aztobactor
- c)Bacillus subtillis and Escherichia coli
- d)Bacillus megathermus and Xanthomonas species
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following combinations of organisms are responsible for the formation and flavour of yoghurt?
a)
Lactobacillus bulgaricus and streptococcus thermophilus
b)
Rhizobium melioti and Aztobactor
c)
Bacillus subtillis and Escherichia coli
d)
Bacillus megathermus and Xanthomonas species
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Yoghut (yogurt) is produced by curdling milk with the help of Streptococcus thermophillus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. The temperature is maintained at about 45∘C(40∘−60∘C) for four hours. It has a flavour of lactic acid and acetaldehyde.
Which of the following statements regarding biofertilizers and their symbiotic associations is incorrect?- a)Glomus is a genus of cyanobacteria that forms symbiotic associations with plants, aiding phosphorus absorption.
- b)Azospirillum and Azotobacter are bacteria that fix atmospheric nitrogen while living freely in the soil, enriching the nitrogen content.
- c)Rhizobium forms nodules on the roots of leguminous plants and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms.
- d)Cyanobacteria, such as Anabaena and Nostoc, are widely distributed in aquatic and terrestrial environments and can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding biofertilizers and their symbiotic associations is incorrect?
a)
Glomus is a genus of cyanobacteria that forms symbiotic associations with plants, aiding phosphorus absorption.
b)
Azospirillum and Azotobacter are bacteria that fix atmospheric nitrogen while living freely in the soil, enriching the nitrogen content.
c)
Rhizobium forms nodules on the roots of leguminous plants and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms.
d)
Cyanobacteria, such as Anabaena and Nostoc, are widely distributed in aquatic and terrestrial environments and can fix atmospheric nitrogen.

|
Top Rankers answered |
The incorrect statement is Glomus is not a genus of cyanobacteria but a type of fungus that forms symbiotic relationships (mycorrhiza) with plants, helping in the absorption of phosphorus. Cyanobacteria, on the other hand, like Anabaena and Nostoc, are known for nitrogen fixation, especially in environments like paddy fields.
Which of the following organisms is used in the production of beverages?- a)Penicillium notatum
- b)Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- c)Aspergillus niger
- d)Clostridium butyricum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organisms is used in the production of beverages?
a)
Penicillium notatum
b)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
c)
Aspergillus niger
d)
Clostridium butyricum
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The yeast Saccharmyces cerevisiae, also known as brewer's yeast, is used for fermenting malted cereals an fruit juices to produce ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Microbes (yeasts in particular) have been used for the production of beverages, such as wine, beer, whisky, brandy and rum.
Wine and beer are produced directly by fermentation. Brandy and whisky require both fermentation and distillation. This is because- a)Fermentation is inhibited at an alcohol level of 10-18%.
- b)Distillation prolongs storage.
- c)Distillation improves quality.
- d)Distillation purifies the beverage.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Wine and beer are produced directly by fermentation. Brandy and whisky require both fermentation and distillation. This is because
a)
Fermentation is inhibited at an alcohol level of 10-18%.
b)
Distillation prolongs storage.
c)
Distillation improves quality.
d)
Distillation purifies the beverage.
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Beverages of low alcoholic content (less than about 9% alcohol) are fermented from grains and are usually considered to be beers. Wines, on the other hand, are fermented to a higher percentage of alcohol (10 - 18% alcohol) and are usually fermented from fruit juice. Higher levels of alcohol kill or inhibit bacteria stopping spoilage as well as fermentation. Vodka, whiskey, and other alcoholic beverages with alcohol contents well above 20% are produced by distilling alcohol from a yeast-fermented beverage. Many liquors are produced by using distilled alcohol (as high as 95% alcohol) to extract various flavoring materials after which the resulting extract is diluted with water and often sugar to make a flavored alcoholic beverages. Unless the alcoholic content of the resulting beverage is well above 15%, the material will not be stable and may start to ferment or even decay in storage. Hence, most liquors are atleast 20% alcohol.
Which of the following microbes is a proteinacious infectious agent? - a)Fungi
- b)Prions
- c)Bacteria
- d)Protozoa
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following microbes is a proteinacious infectious agent?
a)
Fungi
b)
Prions
c)
Bacteria
d)
Protozoa
|
|
Lakshmi Bose answered |
Prions: Proteinaceous Infectious Agents
Prions are a type of infectious agent that are composed solely of protein, with no nucleic acid component. They are responsible for a variety of neurodegenerative diseases in humans and animals, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), mad cow disease (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), and chronic wasting disease in deer and elk.
Prion Structure and Replication
Prions are misfolded proteins that can induce normal proteins to adopt an abnormal conformation. The normal form of the protein, known as PrPc, is found on the surface of cells in the brain and other tissues. The abnormal form, known as PrPSc, has a different conformation and is resistant to degradation by proteases. It can accumulate in the brain, forming aggregates that damage neural tissue.
The mechanism by which prions replicate is still not fully understood. It is believed that PrPSc acts as a template, inducing the misfolding of normal PrPc molecules into the abnormal conformation. These newly formed PrPSc molecules can then go on to induce the misfolding of additional PrPc molecules, leading to the accumulation of PrPSc aggregates in the brain.
Transmission of Prions
Prions can be transmitted through a variety of routes, including ingestion, transplantation, and exposure to contaminated medical equipment. Ingestion of contaminated meat, particularly from infected cattle, is a common route of transmission for humans. Prions can survive cooking and other forms of food processing, making it difficult to eliminate them from the food supply.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of prion diseases is typically based on clinical symptoms, as there are no reliable laboratory tests for the presence of PrPSc. Treatment options for prion diseases are currently limited, as there are no effective drugs that can target the abnormal PrPSc protein. However, researchers are actively investigating new treatment options, including immunotherapy and gene therapy approaches.
Conclusion
In summary, prions are a unique type of infectious agent that are composed solely of protein. They are responsible for a variety of neurodegenerative diseases in humans and animals, and can be transmitted through ingestion, transplantation, and exposure to contaminated medical equipment. While there are currently no effective treatments for prion diseases, researchers are actively investigating new approaches to target these proteinaceous infectious agents.
Prions are a type of infectious agent that are composed solely of protein, with no nucleic acid component. They are responsible for a variety of neurodegenerative diseases in humans and animals, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), mad cow disease (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), and chronic wasting disease in deer and elk.
Prion Structure and Replication
Prions are misfolded proteins that can induce normal proteins to adopt an abnormal conformation. The normal form of the protein, known as PrPc, is found on the surface of cells in the brain and other tissues. The abnormal form, known as PrPSc, has a different conformation and is resistant to degradation by proteases. It can accumulate in the brain, forming aggregates that damage neural tissue.
The mechanism by which prions replicate is still not fully understood. It is believed that PrPSc acts as a template, inducing the misfolding of normal PrPc molecules into the abnormal conformation. These newly formed PrPSc molecules can then go on to induce the misfolding of additional PrPc molecules, leading to the accumulation of PrPSc aggregates in the brain.
Transmission of Prions
Prions can be transmitted through a variety of routes, including ingestion, transplantation, and exposure to contaminated medical equipment. Ingestion of contaminated meat, particularly from infected cattle, is a common route of transmission for humans. Prions can survive cooking and other forms of food processing, making it difficult to eliminate them from the food supply.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of prion diseases is typically based on clinical symptoms, as there are no reliable laboratory tests for the presence of PrPSc. Treatment options for prion diseases are currently limited, as there are no effective drugs that can target the abnormal PrPSc protein. However, researchers are actively investigating new treatment options, including immunotherapy and gene therapy approaches.
Conclusion
In summary, prions are a unique type of infectious agent that are composed solely of protein. They are responsible for a variety of neurodegenerative diseases in humans and animals, and can be transmitted through ingestion, transplantation, and exposure to contaminated medical equipment. While there are currently no effective treatments for prion diseases, researchers are actively investigating new approaches to target these proteinaceous infectious agents.
What is the primary purpose of passing effluent into a settling tank after reducing BOD?- a) To aerate the water
- b) To allow bacterial flocs to sediment
- c) To cool the water
- d) To add chemicals for disinfection
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary purpose of passing effluent into a settling tank after reducing BOD?
a)
To aerate the water
b)
To allow bacterial flocs to sediment
c)
To cool the water
d)
To add chemicals for disinfection
|
|
Pooja Mukherjee answered |
Understanding Settling Tanks and BOD Reduction
After reducing Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in effluent treatment, the primary purpose of using a settling tank is to facilitate the sedimentation of bacterial flocs. This process is essential for effective wastewater management.
Why Use a Settling Tank?
- Sedimentation Process:
- The settling tank allows for gravity-based separation of solid particles from the liquid effluent.
- The reduced BOD effluent contains bacterial flocs, which are aggregates of bacteria and organic material. These flocs are heavier and can settle when given enough time.
- Removal of Suspended Solids:
- By allowing the effluent to sit in the tank, suspended solids can settle at the bottom.
- This improves the clarity of the water, making subsequent treatment processes more effective.
Benefits of Sedimentation
- Enhanced Efficiency:
- Removing solid particles reduces the load on further treatment processes, such as filtration or disinfection.
- Improved Water Quality:
- Sedimentation leads to cleaner effluent, which is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems and complying with environmental regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary purpose of passing effluent into a settling tank after BOD reduction is to allow bacterial flocs to sediment. This process not only removes suspended solids but also enhances the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment, leading to improved water quality.
After reducing Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in effluent treatment, the primary purpose of using a settling tank is to facilitate the sedimentation of bacterial flocs. This process is essential for effective wastewater management.
Why Use a Settling Tank?
- Sedimentation Process:
- The settling tank allows for gravity-based separation of solid particles from the liquid effluent.
- The reduced BOD effluent contains bacterial flocs, which are aggregates of bacteria and organic material. These flocs are heavier and can settle when given enough time.
- Removal of Suspended Solids:
- By allowing the effluent to sit in the tank, suspended solids can settle at the bottom.
- This improves the clarity of the water, making subsequent treatment processes more effective.
Benefits of Sedimentation
- Enhanced Efficiency:
- Removing solid particles reduces the load on further treatment processes, such as filtration or disinfection.
- Improved Water Quality:
- Sedimentation leads to cleaner effluent, which is crucial for protecting aquatic ecosystems and complying with environmental regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary purpose of passing effluent into a settling tank after BOD reduction is to allow bacterial flocs to sediment. This process not only removes suspended solids but also enhances the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment, leading to improved water quality.
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
- a)A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(iv) D-(i)
- b)A-(ii) B-(iv) C-(i) D-(iii)
- c)A-(iii) B-(i) C-(ii) D-(iv)
- d)A-(iv) B-(ii) C-(i) D-(iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.


a)
A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(iv) D-(i)
b)
A-(ii) B-(iv) C-(i) D-(iii)
c)
A-(iii) B-(i) C-(ii) D-(iv)
d)
A-(iv) B-(ii) C-(i) D-(iii)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
- Tricoderma is a biocontrol agent.
- Streptomyces is the source of antibiotic streptomycin.
- Azospirillum is a free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria.
- Lactobacillus produces lactic acid.
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: BOD represents the amount of dissolved oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by microorganisms.
Statement 2: High value of BOD indicates that water is highly polluted by organic matter.
- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: BOD represents the amount of dissolved oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by microorganisms.
Statement 2: High value of BOD indicates that water is highly polluted by organic matter.
Statement 1: BOD represents the amount of dissolved oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by microorganisms.
Statement 2: High value of BOD indicates that water is highly polluted by organic matter.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) refers to the amount of the oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by bacteria. The BOD test measures the rate of update of oxygen by microorganisms in a sample of water and thus, indirectly BOD is the measure of the organic matter present in the water. The greater the BOD of wastewater, more is its polluting potential.
Yeast is used in the production of- a)citric acid and lactic acid
- b)lipase and pectinase
- c)bread and beer
- d)cheese and butter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Yeast is used in the production of
a)
citric acid and lactic acid
b)
lipase and pectinase
c)
bread and beer
d)
cheese and butter

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Microbes especially yeasts have been used from time immemorial for the production of beverages like wine, beer, whisky, brandy or rum.
- For this purpose the same yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae used for bread-making and commonly called brewer’s yeast, is used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices, to produce ethanol
In the sewage treatment, bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment in a setting tank. This sediment is called as- a)inactivated sludge
- b)activated sludge
- c)primary sludge
- d)secondary sluge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the sewage treatment, bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment in a setting tank. This sediment is called as
a)
inactivated sludge
b)
activated sludge
c)
primary sludge
d)
secondary sluge
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Activated sludge, is formed during secondary sewage treatment. It posses flocs of decomposer microbes. Formation of activated sludge requires aeration.
What role do cyanobacteria play in paddy fields?- a)They absorb phosphorus for plants.
- b)They fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching soil fertility.
- c)They form root nodules in rice plants.
- d)They prevent soil erosion.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
They absorb phosphorus for plants.
b)
They fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching soil fertility.
c)
They form root nodules in rice plants.
d)
They prevent soil erosion.
|
|
Rahul Das answered |
The Role of Cyanobacteria in Paddy Fields
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, play a crucial role in enhancing soil fertility in paddy fields, primarily through their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Nitrogen Fixation
- Cyanobacteria possess specialized cells called heterocysts that enable them to convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3).
- This process enriches the soil with nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth.
- Nitrogen is vital for synthesizing proteins, nucleic acids, and other cellular components in rice plants.
Benefits to Rice Cultivation
- By fixing nitrogen, cyanobacteria reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- The organic matter produced by cyanobacteria also enhances soil structure, water retention, and microbial diversity.
- Their presence can lead to improved yields in rice cultivation due to better nutrient availability.
Interactions with Rice Plants
- Cyanobacteria coexist with rice plants in flooded conditions typical of paddy fields, where they thrive and contribute to the ecosystem.
- The symbiotic relationships formed can lead to enhanced nutrient uptake by rice roots.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary role of cyanobacteria in paddy fields is their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, thereby enriching soil fertility. This process not only supports rice growth but also promotes environmentally sustainable farming practices, making cyanobacteria valuable allies in agricultural ecosystems.
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, play a crucial role in enhancing soil fertility in paddy fields, primarily through their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Nitrogen Fixation
- Cyanobacteria possess specialized cells called heterocysts that enable them to convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3).
- This process enriches the soil with nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth.
- Nitrogen is vital for synthesizing proteins, nucleic acids, and other cellular components in rice plants.
Benefits to Rice Cultivation
- By fixing nitrogen, cyanobacteria reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- The organic matter produced by cyanobacteria also enhances soil structure, water retention, and microbial diversity.
- Their presence can lead to improved yields in rice cultivation due to better nutrient availability.
Interactions with Rice Plants
- Cyanobacteria coexist with rice plants in flooded conditions typical of paddy fields, where they thrive and contribute to the ecosystem.
- The symbiotic relationships formed can lead to enhanced nutrient uptake by rice roots.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary role of cyanobacteria in paddy fields is their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, thereby enriching soil fertility. This process not only supports rice growth but also promotes environmentally sustainable farming practices, making cyanobacteria valuable allies in agricultural ecosystems.
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Physical removal of large and small particles through filtration and sedimentation is called primary sewage treatment.
(ii) Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
(iii) Activated sludge sediment in a sewage treatment plant is a rich source of aerobic bacteria.
(iv) Biogas, commonly called as gobar gas, is pure methane.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Physical removal of large and small particles through filtration and sedimentation is called primary sewage treatment.
(ii) Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
(iii) Activated sludge sediment in a sewage treatment plant is a rich source of aerobic bacteria.
(iv) Biogas, commonly called as gobar gas, is pure methane.
(i) Physical removal of large and small particles through filtration and sedimentation is called primary sewage treatment.
(ii) Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
(iii) Activated sludge sediment in a sewage treatment plant is a rich source of aerobic bacteria.
(iv) Biogas, commonly called as gobar gas, is pure methane.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Stuti Sen answered |
Incorrect Statements:
Statement (ii): Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
- Secondary sewage treatment involves biological processes such as activated sludge, trickling filters, or rotating biological contactors. These processes use microorganisms to break down organic matter in the sewage.
- Mechanical processes are more common in primary sewage treatment, which involves physical processes like screening, grit removal, and sedimentation.
Statement (iv): Biogas, commonly called as gobar gas, is pure methane.
- Biogas, also known as gobar gas in some regions, is a mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. It typically consists of methane (50-70%), carbon dioxide (30-40%), and small amounts of other gases like hydrogen sulfide.
- Pure methane is not commonly found in biogas as it is usually mixed with other gases during the fermentation process.
Therefore, the incorrect statements are (ii) and (iv), making option (b) the correct choice.
Statement (ii): Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
- Secondary sewage treatment involves biological processes such as activated sludge, trickling filters, or rotating biological contactors. These processes use microorganisms to break down organic matter in the sewage.
- Mechanical processes are more common in primary sewage treatment, which involves physical processes like screening, grit removal, and sedimentation.
Statement (iv): Biogas, commonly called as gobar gas, is pure methane.
- Biogas, also known as gobar gas in some regions, is a mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. It typically consists of methane (50-70%), carbon dioxide (30-40%), and small amounts of other gases like hydrogen sulfide.
- Pure methane is not commonly found in biogas as it is usually mixed with other gases during the fermentation process.
Therefore, the incorrect statements are (ii) and (iv), making option (b) the correct choice.
Study the following statements regarding lactic acid bacteria (LAB) which are used to convert milk into curd.
(i) They produce adds that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins.
(ii) A small amount of curd added to the fresh milk as an inoculum contains millions of LAB, which at suitable temperature, multiply and convert milk into curd.
(iii) Conversion of milk into curd improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12.
(iv) LAB may result in acidity in the stomach of human beings.
Which of the given statements are correct?
- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements regarding lactic acid bacteria (LAB) which are used to convert milk into curd.
(i) They produce adds that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins.
(ii) A small amount of curd added to the fresh milk as an inoculum contains millions of LAB, which at suitable temperature, multiply and convert milk into curd.
(iii) Conversion of milk into curd improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12.
(iv) LAB may result in acidity in the stomach of human beings.
Which of the given statements are correct?
(i) They produce adds that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins.
(ii) A small amount of curd added to the fresh milk as an inoculum contains millions of LAB, which at suitable temperature, multiply and convert milk into curd.
(iii) Conversion of milk into curd improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12.
(iv) LAB may result in acidity in the stomach of human beings.
Which of the given statements are correct?
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Microbes such as. Lactobacillus and others commonly called lactic acid bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it into curd. During growth, such bacteria produce adds (mainly lactic add) that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins. A small amount of curd, known as starter, is added to the milk and kept at a suitable temperature, where lactic acid bacteria multiply in millions and converts milk into curd that also improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12. It also checks the growth of disease-causing microbes in the stomach.
The purpose of biological treatment of waste water is to- a)reduce BOD
- b)increase BOD
- c)reduce sedimentation
- d)increase sedimentation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The purpose of biological treatment of waste water is to
a)
reduce BOD
b)
increase BOD
c)
reduce sedimentation
d)
increase sedimentation
|
|
Ayush Saini answered |
Introduction:
The biological treatment of wastewater is a process that utilizes microorganisms to break down organic matter and remove pollutants from the water. This process plays a crucial role in wastewater treatment plants as it helps in reducing the biological oxygen demand (BOD) of the water.
Explanation:
The purpose of biological treatment of wastewater is to reduce BOD. Here's why:
1. Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD):
BOD is a measure of the amount of oxygen required by microorganisms to decompose the organic matter present in wastewater. The higher the BOD, the greater the organic pollution in the water. Reducing BOD is important as high levels of organic pollutants can deplete oxygen levels in water bodies, leading to the death of aquatic organisms.
2. Role of Microorganisms:
During biological treatment, microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi are introduced to the wastewater. These microorganisms utilize the organic matter present in the water as a food source. As they metabolize the organic compounds, they consume oxygen from the water, thereby reducing the BOD.
3. Aerobic and Anaerobic Processes:
Biological treatment can occur through aerobic or anaerobic processes, depending on the availability of oxygen. In aerobic treatment, oxygen is supplied to support the growth of aerobic bacteria that require oxygen for their metabolic activity. These bacteria break down organic matter and reduce the BOD. In anaerobic treatment, microorganisms function in the absence of oxygen and convert organic matter into biogas (methane and carbon dioxide).
4. Treatment Methods:
There are various biological treatment methods used to reduce BOD in wastewater:
- Activated Sludge Process: In this process, wastewater is mixed with a culture of microorganisms called activated sludge. The sludge contains a diverse population of bacteria that consume organic matter and reduce BOD.
- Trickling Filters: Wastewater is passed over a bed of rocks or plastic media where a biofilm of microorganisms develops. These microorganisms degrade the organic pollutants and reduce BOD.
- Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR): This process involves filling a reactor tank with wastewater, allowing microorganisms to degrade the organic matter, and then settling the solids. The treated water is then discharged, reducing the BOD.
Conclusion:
The biological treatment of wastewater is aimed at reducing the biological oxygen demand (BOD) by utilizing microorganisms to break down organic matter. This process is crucial in wastewater treatment plants to ensure the removal of organic pollutants and protect water bodies from oxygen depletion. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - to reduce BOD.
The biological treatment of wastewater is a process that utilizes microorganisms to break down organic matter and remove pollutants from the water. This process plays a crucial role in wastewater treatment plants as it helps in reducing the biological oxygen demand (BOD) of the water.
Explanation:
The purpose of biological treatment of wastewater is to reduce BOD. Here's why:
1. Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD):
BOD is a measure of the amount of oxygen required by microorganisms to decompose the organic matter present in wastewater. The higher the BOD, the greater the organic pollution in the water. Reducing BOD is important as high levels of organic pollutants can deplete oxygen levels in water bodies, leading to the death of aquatic organisms.
2. Role of Microorganisms:
During biological treatment, microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi are introduced to the wastewater. These microorganisms utilize the organic matter present in the water as a food source. As they metabolize the organic compounds, they consume oxygen from the water, thereby reducing the BOD.
3. Aerobic and Anaerobic Processes:
Biological treatment can occur through aerobic or anaerobic processes, depending on the availability of oxygen. In aerobic treatment, oxygen is supplied to support the growth of aerobic bacteria that require oxygen for their metabolic activity. These bacteria break down organic matter and reduce the BOD. In anaerobic treatment, microorganisms function in the absence of oxygen and convert organic matter into biogas (methane and carbon dioxide).
4. Treatment Methods:
There are various biological treatment methods used to reduce BOD in wastewater:
- Activated Sludge Process: In this process, wastewater is mixed with a culture of microorganisms called activated sludge. The sludge contains a diverse population of bacteria that consume organic matter and reduce BOD.
- Trickling Filters: Wastewater is passed over a bed of rocks or plastic media where a biofilm of microorganisms develops. These microorganisms degrade the organic pollutants and reduce BOD.
- Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR): This process involves filling a reactor tank with wastewater, allowing microorganisms to degrade the organic matter, and then settling the solids. The treated water is then discharged, reducing the BOD.
Conclusion:
The biological treatment of wastewater is aimed at reducing the biological oxygen demand (BOD) by utilizing microorganisms to break down organic matter. This process is crucial in wastewater treatment plants to ensure the removal of organic pollutants and protect water bodies from oxygen depletion. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - to reduce BOD.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Word antibiotic is a misnomer. Anti Is a Greek word that means 'against', and bios means 'life', together they mean 'against life' (in the context of disease-causing organisms); whereas with reference to human beings, they are 'pro life' and not against
- b)Flocs are masses of bacteria with interwoven fungal filaments which form mesh-like structures
- c)Components of biogas are methane (50 70%); carbon dioxide (30-40%) and traces of hydrogen, nitrogen and H2S
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Word antibiotic is a misnomer. Anti Is a Greek word that means 'against', and bios means 'life', together they mean 'against life' (in the context of disease-causing organisms); whereas with reference to human beings, they are 'pro life' and not against
b)
Flocs are masses of bacteria with interwoven fungal filaments which form mesh-like structures
c)
Components of biogas are methane (50 70%); carbon dioxide (30-40%) and traces of hydrogen, nitrogen and H2S
d)
None of these
|
|
Rajeev Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option D: None of these.
Let's analyze each statement to understand why options A, B, and C are correct:
a) Word antibiotic is a misnomer. Anti Is a Greek word that means against, and bios means life, together they mean against life (in the context of disease-causing organisms); whereas with reference to human beings, they are pro life and not against
This statement is correct. The term "antibiotic" is derived from the Greek words "anti" meaning against and "bios" meaning life. Antibiotics are substances that are used to treat infections caused by bacteria or other microorganisms. They work by inhibiting the growth or killing the microorganisms. However, when it comes to human beings, antibiotics are actually pro-life as they help in fighting against harmful bacteria and improving health.
b) Flocs are masses of bacteria with interwoven fungal filaments which form mesh-like structures
This statement is also correct. Flocs are clusters or aggregates of microorganisms, typically bacteria, that are held together by a matrix of extracellular substances. Flocs can form in various environments such as wastewater treatment plants, natural water bodies, and soil. In some cases, these flocs can also contain fungal filaments, which contribute to the structure of the flocs.
c) Components of biogas are methane (50-70%); carbon dioxide (30-40%) and traces of hydrogen, nitrogen, and H2S
This statement is correct as well. Biogas is a mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. The main component of biogas is methane, which typically makes up around 50-70% of the gas composition. Carbon dioxide is another major component, accounting for 30-40% of the gas. In addition to methane and carbon dioxide, biogas can also contain traces of other gases such as hydrogen, nitrogen, and hydrogen sulfide.
Therefore, all the given statements are correct, and the incorrect statement is option D: None of these.
The correct answer is option D: None of these.
Let's analyze each statement to understand why options A, B, and C are correct:
a) Word antibiotic is a misnomer. Anti Is a Greek word that means against, and bios means life, together they mean against life (in the context of disease-causing organisms); whereas with reference to human beings, they are pro life and not against
This statement is correct. The term "antibiotic" is derived from the Greek words "anti" meaning against and "bios" meaning life. Antibiotics are substances that are used to treat infections caused by bacteria or other microorganisms. They work by inhibiting the growth or killing the microorganisms. However, when it comes to human beings, antibiotics are actually pro-life as they help in fighting against harmful bacteria and improving health.
b) Flocs are masses of bacteria with interwoven fungal filaments which form mesh-like structures
This statement is also correct. Flocs are clusters or aggregates of microorganisms, typically bacteria, that are held together by a matrix of extracellular substances. Flocs can form in various environments such as wastewater treatment plants, natural water bodies, and soil. In some cases, these flocs can also contain fungal filaments, which contribute to the structure of the flocs.
c) Components of biogas are methane (50-70%); carbon dioxide (30-40%) and traces of hydrogen, nitrogen, and H2S
This statement is correct as well. Biogas is a mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. The main component of biogas is methane, which typically makes up around 50-70% of the gas composition. Carbon dioxide is another major component, accounting for 30-40% of the gas. In addition to methane and carbon dioxide, biogas can also contain traces of other gases such as hydrogen, nitrogen, and hydrogen sulfide.
Therefore, all the given statements are correct, and the incorrect statement is option D: None of these.
Which one of the following can be used as biofertiliser in cotton field?- a)Azolla-Anabaena
- b)Streptococcus
- c)Azosphillum
- d)Azotobacter chroocoocurn
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following can be used as biofertiliser in cotton field?
a)
Azolla-Anabaena
b)
Streptococcus
c)
Azosphillum
d)
Azotobacter chroocoocurn
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Cotton is a dicotyledonous crop. The best biofertiliser for cotton is Bacillus cereus and Azotobacter chroococcum. These are free-living N2 fixing bacteria and enhance the fertility of the soil.
Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil. Which of the following can be used as biofertilisers?- a)Nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria
- b)Nitrogen fixing bacteria
- c)Mycorrhizae
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil. Which of the following can be used as biofertilisers?
a)
Nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria
b)
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
c)
Mycorrhizae
d)
All of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to crops. Microorganisms which act as biofertilisers are bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycorrhizal fungi. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have the property of nitrogen fixation while mycorrhizal fungi preferentially withdraw minerals from organic matter for the plant with which they are associated. They maximize ecological benefits and minimize environmental hazards.
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strains have been used for designing novel- a)biofertilisers
- b)bio-metallurgical techniques
- c)bio-mineralisation process
- d)bio-insecticidal plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strains have been used for designing novel
a)
biofertilisers
b)
bio-metallurgical techniques
c)
bio-mineralisation process
d)
bio-insecticidal plants
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Bioinsecticides are those biological agents that are used to control harmful insects. Because of development of methods of genetic enginerring, B-Thuringiensis toxic genes are introduced into plants. Such plants are resistant to attack by insect pests. Bt cotton is one such example.
Cyanobacteria are:- a)heterotrophs
- b)chemotrophs
- c)autotrophs
- d)organotrophs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cyanobacteria are:
a)
heterotrophs
b)
chemotrophs
c)
autotrophs
d)
organotrophs
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic, Gram negative prokaryotes. They have chlorophyll a and are probably major primary producers in the world's oceans. Hence, they are autotrophs.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) discourages the excessive use of- a)biological methods
- b)chemical pesticides
- c)mechanical methods
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) discourages the excessive use of
a)
biological methods
b)
chemical pesticides
c)
mechanical methods
d)
all of the above
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an effective and environmental sensitive approach for pest management. IPM programs use current, comprehensive information on the life cycles of pest and their interaction with the environment. This information in combination with available pest control methods, is used to manage pest damage by the most economical means, and with the least possible hazard to people, property and the environment.
Which of the following is not used as a biopesticide?- a)Trichoderma harzianum
- b)Nucleopolyhedrovirus
- c)Xanthomonas campestris
- d)Bacillus thuringiensis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not used as a biopesticide?
a)
Trichoderma harzianum
b)
Nucleopolyhedrovirus
c)
Xanthomonas campestris
d)
Bacillus thuringiensis
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Xanthomonas campestris is not used as a biopesticide. Bacillus thuringiensis is used as a microbial biocontrol agent. Trichoderma harzianum is a free-living fungi, common in soil and root ecosystems. It is an effective biocontrol agent of several plant pathogens. viruses of the family Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack insecs and other arthropods. The majority of baculoviruses used as biological control agents belong to genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
The masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures are called as- a)primary sludge
- b)floces
- c)activated sludge
- d)anaerobic sludge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures are called as
a)
primary sludge
b)
floces
c)
activated sludge
d)
anaerobic sludge
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Flocs are masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures.
Chapter doubts & questions for Microbes in Human Welfare - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Microbes in Human Welfare - NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









