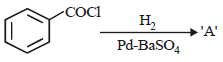All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids for NEET Exam
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is:- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Ethanal
- c)Formaldehyde
- d)Methanal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is:
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Ethanal
c)
Formaldehyde
d)
Methanal

|
Ambition Institute answered |
- The functional group is an aldehyde; −CHO and the given compound has two carbon atoms.
- Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is ethanal.
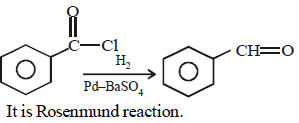
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO?- a)2,2-Dimethylpropanal
- b)3-Hydroxypropanal
- c)But-3-en-2-one
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO?
a)
2,2-Dimethylpropanal
b)
3-Hydroxypropanal
c)
But-3-en-2-one
d)
None of these
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
The IUPAC name of (CH3)2CHCHO is 2-methylpropanal and its chemical name is Isobutyraldehyde.
Which of the following statements are correct in case of the carbonyl bond between carbon and oxygen?- a)Carbon is the nucleophilic centre and Oxygen is the electrophilic centre.
- b)Oxygen is the nucleophilic centre and Carbon is the electrophilic centre.
- c)Carbon and Oxygen double bond is polarised.
- d)Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ are correct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct in case of the carbonyl bond between carbon and oxygen?
a)
Carbon is the nucleophilic centre and Oxygen is the electrophilic centre.
b)
Oxygen is the nucleophilic centre and Carbon is the electrophilic centre.
c)
Carbon and Oxygen double bond is polarised.
d)
Both ‘b’ and ‘c’ are correct
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The double bonds in alkenes and double bonds in carbonyl groups are VERY different in terms of reactivity. The C=C is less reactive due to C=O electronegativity attributed to the oxygen and its two lone pairs of electrons. One pair of the oxygen lone pairs are located in 2s while the other pair are in 2p orbital where its axis is directed perpendicular to the direction of the pi orbitals. The Carbonyl groups properties are directly tied to its electronic structure as well as geometric positioning. For example, the electronegativity of oxygen also polarizes the pi bond allowing the single bonded substituent connected to become electron withdrawing.
Which of the following statement about C=O and C=C is correct?- a)Both consist of a sigma and pi bond
- b)C=O is polar but C=C is non-polar
- c)Both a and b are correct
- d)Both C=O and C=C undergo nucleophilic addition reactions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement about C=O and C=C is correct?
a)
Both consist of a sigma and pi bond
b)
C=O is polar but C=C is non-polar
c)
Both a and b are correct
d)
Both C=O and C=C undergo nucleophilic addition reactions

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
- The first bond formed is a sigma bind and the second one is a pi bond.
- O has a higher electronegativity than C and hence the electron cloud will be shifted towards the O atom, making the compound polar.
- This is not possible in C=C.
Among the following functional groups, which of these is not a carbonyl compound?- a)alcohols
- b)aldehydes
- c)Carboxylic acid
- d)ketones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following functional groups, which of these is not a carbonyl compound?
a)
alcohols
b)
aldehydes
c)
Carboxylic acid
d)
ketones
|
|
Pari answered |
In carbonyl compound C=O is present bt in alchol OH is present. So alchol is not a carbonyl compound
Acetone is isomeric to:- a)n-propyl alcohol
- b)propanal
- c)ethyl methyl ether
- d)isopropyl alcohol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acetone is isomeric to:
a)
n-propyl alcohol
b)
propanal
c)
ethyl methyl ether
d)
isopropyl alcohol
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
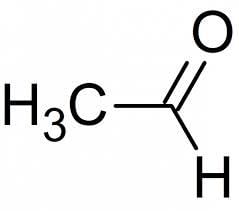
Acetone (CH3COCH3) and Propanal (CH3CH2CHO) are functional isomers.
- Acetone:
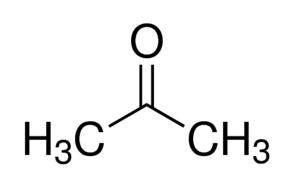
- Propanal:

Propanone and prop-2-en-1-ol are examples of which type of isomerism?
- a)Functional isomers
- b)Chain isomers
- c)Tautomers
- d)Position isomers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Propanone and prop-2-en-1-ol are examples of which type of isomerism?
a)
Functional isomers
b)
Chain isomers
c)
Tautomers
d)
Position isomers
|
|
Gayatri Banerjee answered |
Functional isomers
Explanation: Propanone (CH3COCH3) and prop-2-en-1-ol (CH2=CHCH2OH) are examples of functional isomers because they have the same molecular formula (C3H6O) but different functional groups. Propanone has a carbonyl group (C=O) while prop-2-en-1-ol has an alcohol group (OH) and a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Explanation: Propanone (CH3COCH3) and prop-2-en-1-ol (CH2=CHCH2OH) are examples of functional isomers because they have the same molecular formula (C3H6O) but different functional groups. Propanone has a carbonyl group (C=O) while prop-2-en-1-ol has an alcohol group (OH) and a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
How many structural isomers can compound with molecular formula ‘C3H6O’ have?- a)6
- b)4
- c)5
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many structural isomers can compound with molecular formula ‘C3H6O’ have?
a)
6
b)
4
c)
5
d)
11
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The Isomers of C3H6O include:
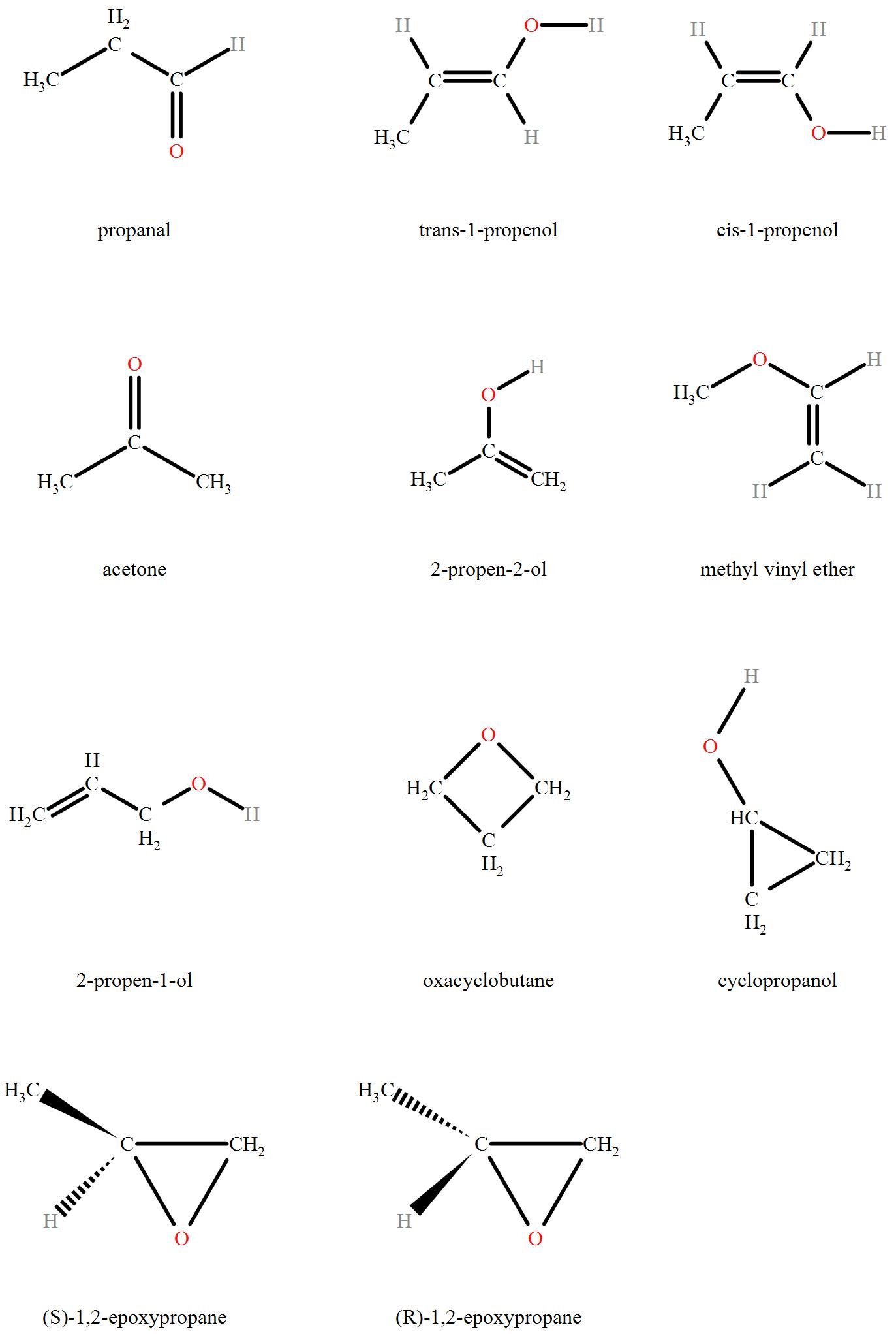
Hence we can see that a total of 11 isomers of C3H6O are possible.
What is the common name of 2-methyl-propanal?- a)formaldehyde
- b)Isobutyraldehyde
- c)carbaldehyde
- d)acetaldehyde
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the common name of 2-methyl-propanal?
a)
formaldehyde
b)
Isobutyraldehyde
c)
carbaldehyde
d)
acetaldehyde
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- Isobutyraldehyde is the chemical compound with the formula (CH₃)₂CHCHO.

- It is an aldehyde, isomeric with n-butyraldehyde.
- Isobutyraldehyde is manufactured, often as a side-product, by the hydroformylation of propene. Its odour is described as that of wet cereal or straw.
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by: [2012]
- a)Benedict test
- b)Iodoform test
- c)Tollen’s reagent test
- d)Fehling solution test
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by: [2012]
a)
Benedict test
b)
Iodoform test
c)
Tollen’s reagent test
d)
Fehling solution test

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO both are aldehydes so they can give the test of Tollen’s reagent, Fehling's solution and Benedict’s solution.
The carbonyl compounds with the structure R-CO-CH3 can only give the Iodoform test.
CH3CHO is the only aldehyde which reacts with NaOH and I2 to give yellow crystals of Iodoform while C6H5CH2CHO doesn’t react with it.
So, the iodoform test is used to distinguish between CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO compounds.
CH3CHO + 3I2 + 4NaOH ⟶ CHI3 + HCOONa + 3NaI +3H2O
C6H5CH2CHO + I2 + 4NaOH⟶ No reaction.
Propionic acid with Br2|P yields a dibromo product. Its structure would be: [2009]- a)
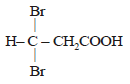
- b)CH2Br – CH2 – COBr
- c)
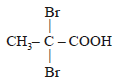
- d)CH2 Br – CHBr – COOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Propionic acid with Br2|P yields a dibromo product. Its structure would be: [2009]
a)
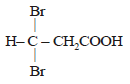
b)
CH2Br – CH2 – COBr
c)
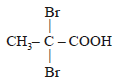
d)
CH2 Br – CHBr – COOH

|
Anand Jain answered |
This reaction is an example of Hell - Volhard
Zelinsky reaction. In this reaction acids
containing α– H on treatment with X2 /P
give di-halo substituted acid.
Zelinsky reaction. In this reaction acids
containing α– H on treatment with X2 /P
give di-halo substituted acid.
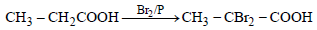
Self condensation of two moles of ethyl acetatein presence of sodium ethoxide yields [2006]- a)acetoacetic ester
- b)methyl acetoacetate
- c)ethyl propionate
- d)ethyl butyrate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Self condensation of two moles of ethyl acetatein presence of sodium ethoxide yields [2006]
a)
acetoacetic ester
b)
methyl acetoacetate
c)
ethyl propionate
d)
ethyl butyrate

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
It is an example of Claisen condensation. The
product is acetoacetic ester.
product is acetoacetic ester.

CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by:- a)Benedict test
- b)Iodoform test
- c)Tollen's reagent test
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by:
a)
Benedict test
b)
Iodoform test
c)
Tollen's reagent test
d)
None of these

|
Samridhi Bajaj answered |
CH3CHO will give iodoform test and C6H5CH2CHO will not give iodoform test.
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,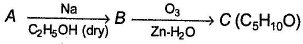 C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.
C can also be obtained as one of the product in the following reaction.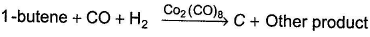 Consider the reaction given below,
Consider the reaction given below,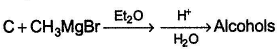 Q. How many different alcohols are expected?
Q. How many different alcohols are expected?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrocarbon A (C10H18) is capable of showing both enantiomerism as well as diastereomerism. Treatment of A either with HgSO4 / H2SO4 or B2H6 / H2O2 -NaOH results in the same carbonyl compound B. Also,
Consider the reaction given below,
Q.
How many different alcohols are expected?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Yoganand Pendem answered |
C can be pentanal or 2- Me butanal .Both on rxn with CH3MgBr followed by hydrolysis yield enantiomeric pair of secondary alcohols.So a total of 2+2=4 different alcohols are formed.
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q, Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following will give a racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4 followed by acid work-up?- a)
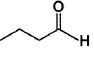
- b)
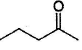
- c)
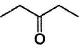
- d)
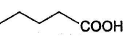
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q, Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following will give a racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4 followed by acid work-up?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Amisha answered |
The ans is B . coz after the action of NaBH4 ,chiral carbon is present only in the product of B.And hence it can give both R and S configuration.
Which of the following could result as a product in the aldol condensation reaction?- a)4-methyl-3-penten-2-on
- b)4-methyl-4-penten-2-one
- c)4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one
- d)3-methyl-4-hexen-2-one
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following could result as a product in the aldol condensation reaction?
a)
4-methyl-3-penten-2-on
b)
4-methyl-4-penten-2-one
c)
4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one
d)
3-methyl-4-hexen-2-one

|
Maulik Verma answered |
It is an α, β-unsaturated ketone which can be formed in an aldol condensation followed by dehydration.
The incorrect statement regarding oxo process for synthesis of an aldehyde is- a)Mixture of CO and H2 is allowed to react with an alkene
- b)Co2(CO)8 may be used as a catalyst
- c)[Co(CO)4H] may act as a catalyst
- d)This process can also be used in the same manner for the synthesis of ketone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The incorrect statement regarding oxo process for synthesis of an aldehyde is
a)
Mixture of CO and H2 is allowed to react with an alkene
b)
Co2(CO)8 may be used as a catalyst
c)
[Co(CO)4H] may act as a catalyst
d)
This process can also be used in the same manner for the synthesis of ketone

|
Yoganand Pendem answered |
Oxo process involves formulation of alkene to form aldehyde only not ketone
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage. The reaction is called?- a)Etard reaction
- b)Stephen reaction
- c)Friedel – crafts reaction
- d)Gatterman – Koch reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage. The reaction is called?
a)
Etard reaction
b)
Stephen reaction
c)
Friedel – crafts reaction
d)
Gatterman – Koch reaction

|
Aryan Sen answered |
Etard reaction
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage by using the Etard reaction. The Etard reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons using chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) as the oxidizing agent. This reaction is commonly used to convert alkylbenzenes, such as toluene, into their corresponding aldehydes.
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction proceeds through several steps:
1. Formation of the chromyl chloride complex: Chromyl chloride is formed by the reaction of chromic acid (H2CrO4) with sodium chloride (NaCl). The chromyl chloride complex acts as the oxidizing agent in the Etard reaction.
2. Activation of the aromatic ring: The aromatic ring of toluene is activated through the coordination of the chromyl chloride complex with the electron-rich aromatic system. This coordination weakens the carbon-hydrogen bonds adjacent to the aromatic ring, making them more susceptible to oxidation.
3. Oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde: The activated toluene undergoes oxidation by the chromyl chloride complex, resulting in the formation of benzaldehyde. The chromyl chloride complex acts as a strong electrophile, attacking the activated carbon-hydrogen bond and forming a carbocation intermediate. This intermediate is then hydrolyzed to yield benzaldehyde.
4. Further oxidation to benzoic acid: If the reaction is allowed to continue, benzaldehyde can undergo further oxidation to form benzoic acid. However, to stop the reaction at the aldehyde stage, the reaction conditions can be carefully controlled, such as by adjusting the reaction temperature or using a milder oxidizing agent.
Applications
The Etard reaction has several applications in organic synthesis. It is commonly used for the selective oxidation of alkylbenzenes to their corresponding aldehydes, as demonstrated in the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde. This reaction is useful for the synthesis of various aromatic aldehydes, which are important intermediates in the preparation of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other organic compounds.
Conclusion
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage by using the Etard reaction. This reaction involves the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride as the oxidizing agent. By carefully controlling the reaction conditions, it is possible to halt the reaction at the aldehyde stage and prevent further oxidation to benzoic acid. The Etard reaction has important applications in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of aromatic aldehydes.
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage by using the Etard reaction. The Etard reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons using chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) as the oxidizing agent. This reaction is commonly used to convert alkylbenzenes, such as toluene, into their corresponding aldehydes.
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction proceeds through several steps:
1. Formation of the chromyl chloride complex: Chromyl chloride is formed by the reaction of chromic acid (H2CrO4) with sodium chloride (NaCl). The chromyl chloride complex acts as the oxidizing agent in the Etard reaction.
2. Activation of the aromatic ring: The aromatic ring of toluene is activated through the coordination of the chromyl chloride complex with the electron-rich aromatic system. This coordination weakens the carbon-hydrogen bonds adjacent to the aromatic ring, making them more susceptible to oxidation.
3. Oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde: The activated toluene undergoes oxidation by the chromyl chloride complex, resulting in the formation of benzaldehyde. The chromyl chloride complex acts as a strong electrophile, attacking the activated carbon-hydrogen bond and forming a carbocation intermediate. This intermediate is then hydrolyzed to yield benzaldehyde.
4. Further oxidation to benzoic acid: If the reaction is allowed to continue, benzaldehyde can undergo further oxidation to form benzoic acid. However, to stop the reaction at the aldehyde stage, the reaction conditions can be carefully controlled, such as by adjusting the reaction temperature or using a milder oxidizing agent.
Applications
The Etard reaction has several applications in organic synthesis. It is commonly used for the selective oxidation of alkylbenzenes to their corresponding aldehydes, as demonstrated in the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde. This reaction is useful for the synthesis of various aromatic aldehydes, which are important intermediates in the preparation of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other organic compounds.
Conclusion
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage by using the Etard reaction. This reaction involves the oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride as the oxidizing agent. By carefully controlling the reaction conditions, it is possible to halt the reaction at the aldehyde stage and prevent further oxidation to benzoic acid. The Etard reaction has important applications in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of aromatic aldehydes.
In the propanoate ion- a)both the carbon – oxygen bonds are the same length.
- b)the carbon atom bears a – 1 charge.
- c)one of the oxygen atoms bears a – 1 charge
- d)the carbon – oxygen double bond is shorter.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the propanoate ion
a)
both the carbon – oxygen bonds are the same length.
b)
the carbon atom bears a – 1 charge.
c)
one of the oxygen atoms bears a – 1 charge
d)
the carbon – oxygen double bond is shorter.
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
This is because of Resonance.
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?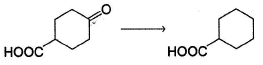
- a)Zn(Hg)-HCI
- b)N2H4/NaOH/Heat
- c)LiAIH4
- d)NaBH4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following transformation?
a)
Zn(Hg)-HCI
b)
N2H4/NaOH/Heat
c)
LiAIH4
d)
NaBH4
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Clemmensen reduction is suitable for reductio n of carbonyls containing additional acidic functional group.
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of their acid strength: i) trichloroacetic acid ii) trifluoroacetic acid iii) acetic acid and iv) formic acid- a)trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, formic acid and acetic acid
- b)formic acid., trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, and acetic acid
- c)trichloroacetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, acetic acid and formic acid.
- d)trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid acetic acid and Propan – 1 – ol, 4 – methylphenol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of their acid strength: i) trichloroacetic acid ii) trifluoroacetic acid iii) acetic acid and iv) formic acid
a)
trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, formic acid and acetic acid
b)
formic acid., trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, and acetic acid
c)
trichloroacetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, acetic acid and formic acid.
d)
trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid acetic acid and Propan – 1 – ol, 4 – methylphenol
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Acidic strength of carboxylic acid -
– More acidic than phenols or alcohols.
– Acidity increase with the presence of a group with -I effect in the alkyl group.Whereas it decreases with the presence of +I group.
– Acidity increases with increase in the number of halogen atoms on  - position.
- position.
 - position.
- position.– It decreases with increasing distance of halogen from 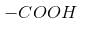
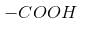
– It increases with increase in the electronegativity of halogen.
- CF3COOH > CCl3COOH > HCOOH > CH3 COOH
Iodoform test is not given by [1999]- a)2-Pentanone
- b)Ethanol
- c)Ethanal
- d)3-Pentanone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Iodoform test is not given by [1999]
a)
2-Pentanone
b)
Ethanol
c)
Ethanal
d)
3-Pentanone

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Iodoform test is exhibited by ethyl alcohol acetaldehyde, acetone methyl ketones and those alcohols which possess CH3CH(OH)- group. As 3-pentanone does not contain
CH3CO-group as therefore it does not give iodoform test.
CH3CO-group as therefore it does not give iodoform test.
Which of the following is incorrect? [2001]- a)NaHSO3 is used in detection of carbonylcompound
- b)FeCl3 is used in detection of phenolic group
- c)Tollen reagent is used in detection ofunsaturation
- d)Fehling solution is used in detection ofglucose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect? [2001]
a)
NaHSO3 is used in detection of carbonylcompound
b)
FeCl3 is used in detection of phenolic group
c)
Tollen reagent is used in detection ofunsaturation
d)
Fehling solution is used in detection ofglucose

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Tollen's reagent is used to detect of
aldehydes. Tollen's reagent is an ammonical
solution of silver nitrate. When aldehyde is
added to Tollen's reagent, silver oxide is
reduced to metallic silver which deposits as
mirror.
aldehydes. Tollen's reagent is an ammonical
solution of silver nitrate. When aldehyde is
added to Tollen's reagent, silver oxide is
reduced to metallic silver which deposits as
mirror.
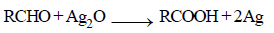
Consider the following reaction,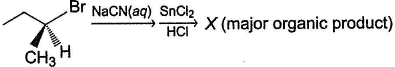
(A pure enantiomer)Q. The incorrect statement regarding X is- a)It is an aldehyde
- b)Product has inverted configuration at the α-carbon
- c)X is a racemic mixture
- d)Product can be either laevorotatory or dextrorotatory isomer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction,
(A pure enantiomer)
Q.
The incorrect statement regarding X is
a)
It is an aldehyde
b)
Product has inverted configuration at the α-carbon
c)
X is a racemic mixture
d)
Product can be either laevorotatory or dextrorotatory isomer
|
|
Om Desai answered |
X will be a pure enantiomer of aldehyde.
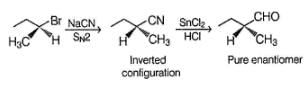

An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.Q. If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will give- a)a pure enantiomer
- b)a racemic mixture
- c)a pair of diastereomers
- d)an achiral alcohol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic compound A (C7H16O) shows both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Treatment of a pure enantiomer of A with Na2CrO4 /Dil. H2SO4 gives B (C7H14O) - Also A on dehydration with concentrated H2SO4 gives a single alkene C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by work-up with Zn-H2O gives D (C5H10O) as one of the product which gives racemic mixture on reduction with NaBH4.
Q.
If B is reduced with LiAIH4 followed by acid hydrolysis will give
a)
a pure enantiomer
b)
a racemic mixture
c)
a pair of diastereomers
d)
an achiral alcohol
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Since, A is completely saturated, it must contain more than one chiral carbon atoms in order to show both enantiomerism and diastereomerism. Also, C on ozonolysis gives D (C5H10O) as one product, other product must be CH3SHO. Hence, C must be 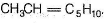
B is enantiomeric. If a pure enantiomer of B is reduced with LiAIH4, pair of diastereomers would be formed.
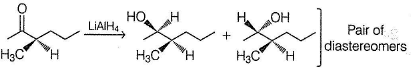
B is enantiomeric. If a pure enantiomer of B is reduced with LiAIH4, pair of diastereomers would be formed.
A strong base can abstract an α – hydrogen from- a)Alkane.
- b)Amine
- c)Ketone
- d)Alkene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A strong base can abstract an α – hydrogen from
a)
Alkane.
b)
Amine
c)
Ketone
d)
Alkene
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
After deprotonation the negative charge will be in conjugation with the pi orbital of carbonyl..so base will prefer to abstract alpha hydrogen from ketone.
In which of the following reactions, ketone is formed as the major organic product?- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions, ketone is formed as the major organic product?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Infinity Academy answered |
If acid derivatives like nitrile, acid chlorid e or ester is taken in excess in Grignard synthesis, second addition of Grignard’s reagent on carbonyl product does not succeed and carbonyls are obtained as major products.
In option (b), carboxylic acids and in option (d), an aldehyde is formed.
In option (b), carboxylic acids and in option (d), an aldehyde is formed.
All of the following reaction gives atleast one ketone as a significant organic product except- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
All of the following reaction gives atleast one ketone as a significant organic product except
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
It gives aldehydes as major product.
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?- a)adipic acid
- b)succinic acid
- c)hexanoic acid
- d)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?
a)
adipic acid
b)
succinic acid
c)
hexanoic acid
d)
cyclohexanecarboxylic acid

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
Conc KMnO4 will cause oxidation and ring opening forming adipic acid.
Which one of the following compounds will be most readily dehydrated? [2010]- a)
- b)
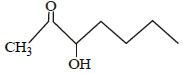
- c)
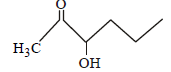
- d)
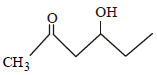
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following compounds will be most readily dehydrated? [2010]
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Raghav Khanna answered |
The intermediate is carbocation which is
destabilised by C = O group (present on ��-
carbon to the –OH group) in the first three
cases. In (d), α–hydrogen is more acidic which
can be removed as water. Moreover, the
positive charge on the intermediate carbocation
is relatively away from the C = O group.
destabilised by C = O group (present on ��-
carbon to the –OH group) in the first three
cases. In (d), α–hydrogen is more acidic which
can be removed as water. Moreover, the
positive charge on the intermediate carbocation
is relatively away from the C = O group.
∴ Correct choice : (d)
Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried outin the presence of which of the following ? [2011]- a)Glycol with KOH
- b)Zn-Hg with HCl
- c)Li Al H4
- d)H2 and Pt as catalyst
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried outin the presence of which of the following ? [2011]
a)
Glycol with KOH
b)
Zn-Hg with HCl
c)
Li Al H4
d)
H2 and Pt as catalyst
|
|
Sankar Banerjee answered |
Clemmensen Reduction and Its Mechanism:
The Clemmensen reduction is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group in a ketone to a methylene group using zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid. This process is particularly effective for reducing ketones to alkanes.
Role of Zn-Hg with HCl:
- In the Clemmensen reduction, zinc amalgam (Zn-Hg) serves as the reducing agent while hydrochloric acid (HCl) acts as a catalyst.
- The reaction occurs at high temperatures, typically refluxing conditions, to facilitate the reduction of the carbonyl group.
- The zinc amalgam reacts with the carbonyl group in the ketone, leading to the formation of an alkyl zinc intermediate.
- The alkyl zinc intermediate is unstable and undergoes protonation by HCl to form the corresponding alkane.
Comparison with Other Reagents:
- Glycol with KOH is commonly used for cleaving ethers, not for the Clemmensen reduction of ketones.
- LiAlH4 is a powerful reducing agent that can reduce ketones to alcohols, but it is not typically used in the Clemmensen reduction.
- H2 and Pt as a catalyst are commonly used for hydrogenation reactions, not for the Clemmensen reduction.
In conclusion, the Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried out in the presence of zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid. These reagents work together to reduce the carbonyl group in the ketone to a methylene group, producing the desired alkane product.
The cyanohydrin of a compound on hydrolysisgives an optically active α-hydroxy acid. Thecompound is [1999]- a)Diethyl ketone
- b)Formaldehyde
- c)Acetaldehyde
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cyanohydrin of a compound on hydrolysisgives an optically active α-hydroxy acid. Thecompound is [1999]
a)
Diethyl ketone
b)
Formaldehyde
c)
Acetaldehyde
d)
Acetone

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
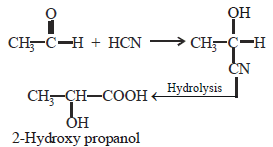
(As it has a chiral C-atom thus it is optically active)
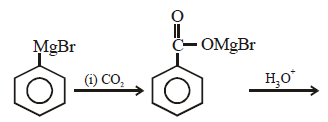
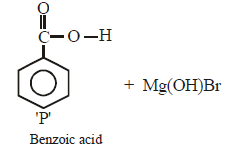
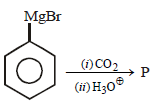 In the above reaction product 'P' is [2002]
In the above reaction product 'P' is [2002]- a)
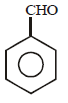
- b)
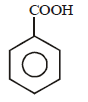
- c)
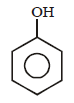
- d)
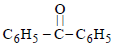
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
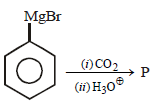
In the above reaction product 'P' is [2002]
a)

b)

c)

d)
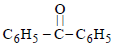

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Grignard reagent forms addition product with
bubbled carbondioxide which on hydrolysis
with HCl yields benzoic acid.
bubbled carbondioxide which on hydrolysis
with HCl yields benzoic acid.
 A is optically active and C is one of the several aldol possible in the above reaction.Q. The product B is stereomeric. If a mixture containing all stereoisomers of B is treated with excess of LiAIH4 followed by the acidification will give how many different isomeric diols ?
A is optically active and C is one of the several aldol possible in the above reaction.Q. The product B is stereomeric. If a mixture containing all stereoisomers of B is treated with excess of LiAIH4 followed by the acidification will give how many different isomeric diols ?- a)2
- b)4
- c)6
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

A is optically active and C is one of the several aldol possible in the above reaction.
Q.
The product B is stereomeric. If a mixture containing all stereoisomers of B is treated with excess of LiAIH4 followed by the acidification will give how many different isomeric diols ?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
6
d)
8

|
Niti Saha answered |
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?- a)Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]
- b)Cannizaro reaction
- c)Wurtz reaction
- d)Friedel-Crafts acylation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions will not resultin the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?
a)
Reimer-Tieman reaction [2010]
b)
Cannizaro reaction
c)
Wurtz reaction
d)
Friedel-Crafts acylation

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
Note that new C–C bond is formed is a, c and d.
Which one of the following can be oxidised tothe corresponding carbonyl compound? [2004]- a)2-hydroxy-propane
- b)Ortho-nitro-phenol
- c)Phenol
- d)2-methyl-2 hydroxy-propane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following can be oxidised tothe corresponding carbonyl compound? [2004]
a)
2-hydroxy-propane
b)
Ortho-nitro-phenol
c)
Phenol
d)
2-methyl-2 hydroxy-propane

|
Bhavana Das answered |
2-hydroxy-propane can be oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compound
- Explanation:
- 2-hydroxy-propane: Also known as acetone, it has a hydroxyl group attached to a carbon atom. This hydroxyl group can be oxidized to a carbonyl group (C=O) through the process of dehydrogenation.
- Oxidation: Oxidation involves the loss of electrons or the gain of oxygen. In this case, the hydroxyl group in 2-hydroxy-propane can be oxidized to a carbonyl group by removing hydrogen atoms.
- Carbonyl compound: The resulting product after oxidation of 2-hydroxy-propane would be a carbonyl compound, specifically acetone. The carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Importance: The oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds is an important reaction in organic chemistry as it allows for the conversion of one functional group to another, expanding the range of compounds that can be synthesized.
In conclusion, 2-hydroxy-propane can be oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compound through the removal of hydrogen atoms from the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of acetone.
- Explanation:
- 2-hydroxy-propane: Also known as acetone, it has a hydroxyl group attached to a carbon atom. This hydroxyl group can be oxidized to a carbonyl group (C=O) through the process of dehydrogenation.
- Oxidation: Oxidation involves the loss of electrons or the gain of oxygen. In this case, the hydroxyl group in 2-hydroxy-propane can be oxidized to a carbonyl group by removing hydrogen atoms.
- Carbonyl compound: The resulting product after oxidation of 2-hydroxy-propane would be a carbonyl compound, specifically acetone. The carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Importance: The oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds is an important reaction in organic chemistry as it allows for the conversion of one functional group to another, expanding the range of compounds that can be synthesized.
In conclusion, 2-hydroxy-propane can be oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compound through the removal of hydrogen atoms from the hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of acetone.
The OH group of an alcohol or the –COOH groupof a carboxylic acid can be replaced by–Cl using [2004]- a)phosphorus pentachloride
- b)hypochlorous acid
- c)chlorine
- d)hydrochloric acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The OH group of an alcohol or the –COOH groupof a carboxylic acid can be replaced by–Cl using [2004]
a)
phosphorus pentachloride
b)
hypochlorous acid
c)
chlorine
d)
hydrochloric acid

|
Pragati Dey answered |
Phosphorus Pentachloride as a Reagent for Substitution Reactions
Phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is commonly used as a reagent for substitution reactions involving the replacement of hydroxyl (-OH) groups with chlorine. This reaction is especially common in the conversion of alcohols to alkyl chlorides.
Mechanism of the Reaction
- In the presence of PCl5, the lone pairs on the oxygen atom of the alcohol or carboxylic acid attack the electrophilic phosphorus atom in PCl5.
- This leads to the formation of an intermediate complex which then undergoes elimination of HCl to form the desired alkyl chloride or acyl chloride product.
Advantages of Using Phosphorus Pentachloride
- Phosphorus pentachloride is a cost-effective and readily available reagent.
- It allows for a rapid and efficient conversion of alcohols and carboxylic acids to their corresponding chlorides.
- The reaction conditions are relatively mild compared to other chlorinating agents.
Alternative Reagents
- Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is not a suitable reagent for this type of substitution reaction as it is more commonly used as a bleaching agent.
- Chlorine gas and hydrochloric acid are not typically used for the direct substitution of hydroxyl groups with chlorine due to the harsh reaction conditions and potential side reactions that may occur.
In conclusion, phosphorus pentachloride is the most suitable reagent for replacing the -OH group of an alcohol or the -COOH group of a carboxylic acid with chlorine due to its efficiency, mild reaction conditions, and availability.
Phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) is commonly used as a reagent for substitution reactions involving the replacement of hydroxyl (-OH) groups with chlorine. This reaction is especially common in the conversion of alcohols to alkyl chlorides.
Mechanism of the Reaction
- In the presence of PCl5, the lone pairs on the oxygen atom of the alcohol or carboxylic acid attack the electrophilic phosphorus atom in PCl5.
- This leads to the formation of an intermediate complex which then undergoes elimination of HCl to form the desired alkyl chloride or acyl chloride product.
Advantages of Using Phosphorus Pentachloride
- Phosphorus pentachloride is a cost-effective and readily available reagent.
- It allows for a rapid and efficient conversion of alcohols and carboxylic acids to their corresponding chlorides.
- The reaction conditions are relatively mild compared to other chlorinating agents.
Alternative Reagents
- Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is not a suitable reagent for this type of substitution reaction as it is more commonly used as a bleaching agent.
- Chlorine gas and hydrochloric acid are not typically used for the direct substitution of hydroxyl groups with chlorine due to the harsh reaction conditions and potential side reactions that may occur.
In conclusion, phosphorus pentachloride is the most suitable reagent for replacing the -OH group of an alcohol or the -COOH group of a carboxylic acid with chlorine due to its efficiency, mild reaction conditions, and availability.
Ketones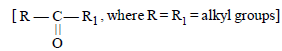 can be obtained in one step by [1998]
can be obtained in one step by [1998]- a)oxidation of primary alcohols
- b)hydrolysis of esters
- c)oxidation of tertiary alcohols
- d)reaction of acid halides with alcohols
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ketones
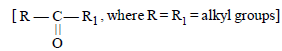 can be obtained in one step by [1998]
can be obtained in one step by [1998]a)
oxidation of primary alcohols
b)
hydrolysis of esters
c)
oxidation of tertiary alcohols
d)
reaction of acid halides with alcohols

|
Roshni Chavan answered |
By oxidation of tertiary alcohol with stronger oxidising agents ketones may be formed along with carboxylic acid.
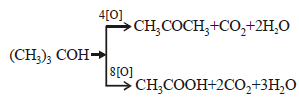
In which of the following compounds, enol form exist? - a)C6H5COCH3
- b)C6H5CHO
- c)
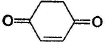
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following compounds, enol form exist?
a)
C6H5COCH3
b)
C6H5CHO
c)
d)
Both (a) and (c)
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Both option (a) and option (c) forms enol but option (b) does not form enol.
The common name for pentanedioic acid is:- a)succinic acid
- b)oxalic acid
- c)glutaric acid
- d)pimelic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The common name for pentanedioic acid is:
a)
succinic acid
b)
oxalic acid
c)
glutaric acid
d)
pimelic acid

|
Aryan Sen answered |
Pentanedioic acid is glutaric acid.
The compound obtained when acetaldehyde reacts with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide exhibits:- a)geometrical isomerism
- b)both optical and geometrical isomerism
- c)optical isomerism.
- d)neither optical nor geometrical isomerism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound obtained when acetaldehyde reacts with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide exhibits:
a)
geometrical isomerism
b)
both optical and geometrical isomerism
c)
optical isomerism.
d)
neither optical nor geometrical isomerism

|
Amrutha Pillai answered |
CH3CH=CHCHO is the product which is suitably substituted so will show geometrical isomer.
If glyoxal glycol is treated with a mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr in diethyl ether followed by acid hydrolysis, how many different diols would be formed, which are simultaneously optically active?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
If glyoxal glycol is treated with a mixture of CH3MgBr and C2H5MgBr in diethyl ether followed by acid hydrolysis, how many different diols would be formed, which are simultaneously optically active?

|
Ishani Yadav answered |
One pair of enantiomers for each (I) and (II) while two pairs of enantiomers for (III).
Which of the following is correct? [2001]- a)Diastase is an enzyme
- b)Acetophenone is an ether
- c)Cycloheptane is an aromatic compound
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct? [2001]
a)
Diastase is an enzyme
b)
Acetophenone is an ether
c)
Cycloheptane is an aromatic compound
d)
All the above

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
Acetophenone is a ketone, cyclopentane
doesn’t contain (4n + 2)π electron hence is
not aromatic. Diastase is an enzyme used in
the preparation of Maltose (Malt sugar, C12
H22 O11) through hydrolysis of starch.
doesn’t contain (4n + 2)π electron hence is
not aromatic. Diastase is an enzyme used in
the preparation of Maltose (Malt sugar, C12
H22 O11) through hydrolysis of starch.
Chapter doubts & questions for Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup