All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Cell - The Unit of Life for NEET Exam
Which cell organelle is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- a)Mitochondria
- b)Endoplasmic reticulum
- c)Nucleus
- d)Ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which cell organelle is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Endoplasmic reticulum
c)
Nucleus
d)
Ribosomes
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the two different types of cells.
- Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria while prokaryotic cells do not but the ribosome is the only organelle that can be seen in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes perform the same functions that is protein synthesis, however, eukaryotic ribosomes are much larger than prokaryotic ones.
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:- a)Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion
- b)Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
- c)Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
- d)Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
a)
Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion
b)
Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
c)
Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
d)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
|
|
Prasenjit Chavan answered |
Explanation:
• Prokaryotic cells, which are found in bacteria and archaea, lack the membrane-bound organelles that are present in eukaryotic cells. These organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
• The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement, which is a characteristic of eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasmic streaming is driven by motor proteins that move along actin filaments and microtubules.
• The absence of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotic cells is related to their small size and simpler structure. They are able to carry out all their necessary functions within the cytoplasm without the need for specialized compartments.
• The lack of cytoplasmic streaming in prokaryotic cells is also related to their small size, as diffusion is sufficient for most of their metabolic processes.
Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
The correct answer is option 'A'. Both the assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
• Prokaryotic cells, which are found in bacteria and archaea, lack the membrane-bound organelles that are present in eukaryotic cells. These organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
• The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement, which is a characteristic of eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasmic streaming is driven by motor proteins that move along actin filaments and microtubules.
• The absence of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotic cells is related to their small size and simpler structure. They are able to carry out all their necessary functions within the cytoplasm without the need for specialized compartments.
• The lack of cytoplasmic streaming in prokaryotic cells is also related to their small size, as diffusion is sufficient for most of their metabolic processes.
Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
The correct answer is option 'A'. Both the assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
The largest subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes is- a)40S
- b)60S
- c)30S
- d)50S
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The largest subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes is
a)
40S
b)
60S
c)
30S
d)
50S
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
50S, roughly equivalent to the 60S ribosomal subunit in eukaryotic cells, is the larger subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes. The 50S subunit is primarily composed of proteins but also contains single-stranded RNA known as ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Glycocalyx is associated with ___________
- a)Nucleosome
- b)Nucleus
- c)Plasma membrane
- d)Nucleolus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glycocalyx is associated with ___________
a)
Nucleosome
b)
Nucleus
c)
Plasma membrane
d)
Nucleolus
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The glycocalyx is a thick outer covering of the plasma membrane. It is composed of strands of sugars and proteins bound together. The result is a thick, sticky layer that helps cells stay put in environments with lots of physical stress.
Which of the following is a prokaryote?- a)Bacteria
- b)Amoeba
- c)Chlamydomonas
- d)Spirogyra
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a prokaryote?
a)
Bacteria
b)
Amoeba
c)
Chlamydomonas
d)
Spirogyra
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have a true nucleus or most other cell organelles. Organisms that have prokaryotic cells are unicellular and called prokaryotes. Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes.
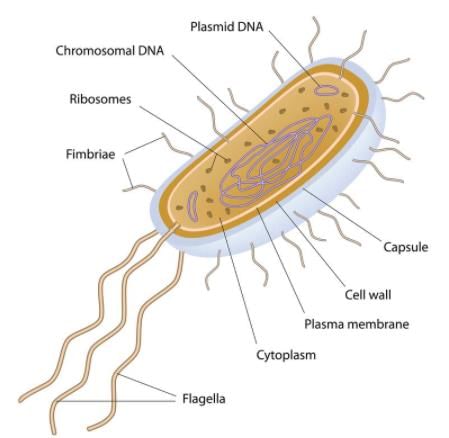
Cell organelles with single membrane is- a)Lysosomes
- b)Chloroplast
- c)Plastids
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell organelles with single membrane is
a)
Lysosomes
b)
Chloroplast
c)
Plastids
d)
Mitochondria

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Lysosomes are single membrane structures containing enzymes for digestion of all types of macromolecules.
Which is common in plant and animal cells- a)Mitochondria
- b)Plastids
- c)Centrioles
- d)Central vacuoles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is common in plant and animal cells
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Plastids
c)
Centrioles
d)
Central vacuoles

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Mitochondria are present in both plant as well as animal cells. Plastids and central vacuoles are present in plant cells and centrioles are present in only animal cells.
The process of movement of few ions or molecules across the membrane against a concentration gradient from lower to higher concentration, it is called
a) Diffusionb)Passive transportc)Active transportd) OsmosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Passive transport, also known as passive diffusion, is a process by which an ion or molecule passes through a cell wall via a concentration gradient, or from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It’s like moving from the train to the platform of a subway station, or stepping out of a crowded room. Basically, passive transport gives an ion or molecule “room to breathe.”
Smallest cell organelle is :-- a)Lysosome
- b)Centrosome
- c)Ribosome
- d)Golgibody
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Smallest cell organelle is :-
a)
Lysosome
b)
Centrosome
c)
Ribosome
d)
Golgibody
|
|
Akshat Majumdar answered |
Smallest cell organelle is:
The correct answer is option 'C', which is Ribosome.
Explanation:
Ribosomes are the smallest cell organelles found in all living cells. They are responsible for protein synthesis, which is a vital process for the growth and functioning of cells. Ribosomes are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins.
Importance of Ribosomes:
Ribosomes play a crucial role in protein synthesis, and proteins are essential for various cellular processes. Here are some key points about the importance of ribosomes:
1. Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes are responsible for translating the genetic information stored in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins. This process is called translation and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomes help in the assembly of amino acids in the correct sequence to form a polypeptide chain, which ultimately folds into a functional protein.
2. Cellular Growth and Repair: Proteins are the building blocks of cells and are required for cell growth and repair. Ribosomes are involved in the production of new proteins, which are necessary for the synthesis of new cell components during growth and repair processes.
3. Enzyme Production: Many enzymes, which are essential for various metabolic reactions in the cell, are synthesized by ribosomes. Enzymes act as catalysts and help in speeding up biochemical reactions in the cell.
4. Antibiotic Targets: Ribosomes are the targets of many antibiotics. Antibiotics inhibit the function of ribosomes in bacterial cells, which disrupts protein synthesis and ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria.
5. Different Types of Ribosomes: Ribosomes can be found in two locations within the cell - free ribosomes in the cytoplasm and bound ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Free ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used within the cell, while bound ribosomes produce proteins that are transported outside the cell or inserted into the cell membrane.
In conclusion, ribosomes are the smallest cell organelles and are critical for protein synthesis and various cellular processes.
The correct answer is option 'C', which is Ribosome.
Explanation:
Ribosomes are the smallest cell organelles found in all living cells. They are responsible for protein synthesis, which is a vital process for the growth and functioning of cells. Ribosomes are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins.
Importance of Ribosomes:
Ribosomes play a crucial role in protein synthesis, and proteins are essential for various cellular processes. Here are some key points about the importance of ribosomes:
1. Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes are responsible for translating the genetic information stored in the form of messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins. This process is called translation and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomes help in the assembly of amino acids in the correct sequence to form a polypeptide chain, which ultimately folds into a functional protein.
2. Cellular Growth and Repair: Proteins are the building blocks of cells and are required for cell growth and repair. Ribosomes are involved in the production of new proteins, which are necessary for the synthesis of new cell components during growth and repair processes.
3. Enzyme Production: Many enzymes, which are essential for various metabolic reactions in the cell, are synthesized by ribosomes. Enzymes act as catalysts and help in speeding up biochemical reactions in the cell.
4. Antibiotic Targets: Ribosomes are the targets of many antibiotics. Antibiotics inhibit the function of ribosomes in bacterial cells, which disrupts protein synthesis and ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria.
5. Different Types of Ribosomes: Ribosomes can be found in two locations within the cell - free ribosomes in the cytoplasm and bound ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Free ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used within the cell, while bound ribosomes produce proteins that are transported outside the cell or inserted into the cell membrane.
In conclusion, ribosomes are the smallest cell organelles and are critical for protein synthesis and various cellular processes.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Organisms which lack mitosis division and use binary fission method for cell division are known as
- A:
prokaryotes
- B:
eukaryotes
- C:
yeast
- D:
fungi
The answer is a.
Organisms which lack mitosis division and use binary fission method for cell division are known as
prokaryotes
eukaryotes
yeast
fungi
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
- As in prokaryotes, centrioles are absent.
- Centrioles play an important part in mitosis during spindle fibre formation. so mitosis is not seen in them, thus they use binary fission.
Which of following is not common in chloroplasts and mitochondria?
a)Both are present in animal cellsb)Both contain their own genetic materialc)Both are present in eukaryotic cellsd)Both are present in plant cellsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Chloroplast is an organelle which is present in plant cells and green algae and carries out photosynthesis that converts light energy to chemical energy. It contains a pigment called chlorophyll and hence is green in color. This organelle is exclusively present in plant cells.
On the other hand, mitochondria are organelles present in both plant and animal cells and their primary function is to regulate cellular metabolism and cellular respiration to provide the organism with energy.
Hence, the correct answer is 'Both are present in animal cells'.
On the other hand, mitochondria are organelles present in both plant and animal cells and their primary function is to regulate cellular metabolism and cellular respiration to provide the organism with energy.
Hence, the correct answer is 'Both are present in animal cells'.
Nuclear membrane is absent in- a)Nostoc
- b)Penicillium
- c)Volvox
- d)Agaricus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nuclear membrane is absent in
a)
Nostoc
b)
Penicillium
c)
Volvox
d)
Agaricus
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Nostoc, genus of blue-green algae with cells arranged in beadlike chains that are grouped together in a gelatinous mass. Ranging from microscopic to walnut-sized, masses of Nostoc may be found on soil and floating in quiet water. Reproduction is by fragmentation. A special thick-walled cell (akinete) has the ability to withstand desiccation for long periods of time. After 70 years of dry storage, the akinete of one species germinates into a filament when moistened. Like most blue-green algae, Nostoc contains two pigments, blue phycocyanin and red phycoerythrin, as well as chlorophyll, and has the ability to fix nitrogen in specialized cells called heterocysts. A terrestrial species has been used as a supplementary food source in Asia.
Who was the first to explain that cells divide?
- a)Schwann
- b)Robert Brown
- c)Rudolf Virchow
- d)Anton von LeeuwenHoek
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was the first to explain that cells divide?
a)
Schwann
b)
Robert Brown
c)
Rudolf Virchow
d)
Anton von LeeuwenHoek

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Rudolf Virchow(1855) first explained that cells divided and new cells are formed .
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The cisternae in Golgi complex have cis face and trans face.
Statement 2: The cis face is also called forming face and trans face is also called maturing face.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The cisternae in Golgi complex have cis face and trans face.
Statement 2: The cis face is also called forming face and trans face is also called maturing face.
Statement 1: The cisternae in Golgi complex have cis face and trans face.
Statement 2: The cis face is also called forming face and trans face is also called maturing face.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Golgi complex consists of a stack of cisternae which are curved to give definite polarity to the Golgi apparatus. The convex side (forming/cis face) receives vesicles from endoplasmic reticulum. The concave side (maturing /transface) buds off vesicles as secretion.
Smallest free living organism are- a)PPLOs
- b)Bacteria
- c)Viroids
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Smallest free living organism are
a)
PPLOs
b)
Bacteria
c)
Viroids
d)
Virus

|
Shounak Nair answered |
PleuroPneumonia Like Organisms (PPLOs) are considered as smallest free living organism. It do not contain cell membrane or cell wall and present as fluid. It causes disease in plants.
Which of the following is known as "System of membrane" :–- a)Lysosome
- b)E.R.
- c)Mitochondria
- d)Chloroplast
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is known as "System of membrane" :–
a)
Lysosome
b)
E.R.
c)
Mitochondria
d)
Chloroplast
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Mitochondria are surrounded by a double-membrane system, consisting of inner and outer mitochondrial membranes separated by an intermembrane space. The inner membrane forms numerous folds (cristae), which extend into the interior (or matrix) of the organelle.
Amphipathic molecule in plasma membrane is :-- a)Protein
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Phospholipids
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Amphipathic molecule in plasma membrane is :-
a)
Protein
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Phospholipids
d)
All the above
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer arranged back-to-back. The membrane is also covered in places with cholesterol molecules and proteins. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and regulates which molecules are allowed to enter and exit the cell.
The chlorophyll pigment is readily soluble in:-- a)Water
- b)Acids
- c)Alkalies
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The chlorophyll pigment is readily soluble in:-
a)
Water
b)
Acids
c)
Alkalies
d)
Acetone
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The chlorophyll pigment is readily soluble in acetone. Chlorophylls possess a phytyl chain which is bound to a porphyrin ring system. The possession of the phytyl side chain, which is esterified to the carboxyl group of the ring, gives the chlorophylls their lipid character. Moreover, chlorophylls are fat-soluble compounds that can be extracted from water-containing living plant tissue by organic solvents such as acetone, methanol, or ethanol, which can take up water.
Semiautonomous cell organelle is :–- a)Mitochondria
- b)Ribosome
- c)Plasma membrane
- d)Peroxysome
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Semiautonomous cell organelle is :–
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Ribosome
c)
Plasma membrane
d)
Peroxysome
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
A eukaryotic cell has DNA in nucleus as well as cell organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. The DNA in cell organelles resembles prokaryotic DNA. These organelles (mitochondria and chloroplasts) not only have DNA but also their own protein synthesis machinery. These organelles are double membrane bound and can divide through fission independent of nuclear division. Thus these cell organelles are semi-autonomous.
The smooth E.R. is generally made up of :–- a)Cisternae
- b)Tubules
- c)Vesicle
- d)All the above
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The smooth E.R. is generally made up of :–
a)
Cisternae
b)
Tubules
c)
Vesicle
d)
All the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Endoplasmic reticulum are made up of three kinds of structure, cisternae, tubules and vesicles.
Cisternae are found in cells actively involved in protein synthesis.Tubules are common in cells involved in lipid and sterol syntheis.Vesicles are found in pancreatic cells and spermatocytes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum when observed under a microscope give the apperance of smooth tubular structure.Smooth ER are function in the synthesis of lipids and steriods.
Cisternae are found in cells actively involved in protein synthesis.Tubules are common in cells involved in lipid and sterol syntheis.Vesicles are found in pancreatic cells and spermatocytes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum when observed under a microscope give the apperance of smooth tubular structure.Smooth ER are function in the synthesis of lipids and steriods.
Rough E.R. mainly responsible for:-- a)Protein synthesis
- b)Cell wall formation
- c)Lipid synthesis
- d)Cholesterol synthesis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rough E.R. mainly responsible for:-
a)
Protein synthesis
b)
Cell wall formation
c)
Lipid synthesis
d)
Cholesterol synthesis
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Rough endoplasmic reticulum carry ribosomes on their surface. The ribosomes present on rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesize secretory proteins. The proteins required for internal use of cell are synthesized on cytoplasmic ribosomes.
A single unit membrane surrounds the organelle:- a)Chloroplast
- b)Nucleus
- c)Lysosome
- d)Microsome
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A single unit membrane surrounds the organelle:
a)
Chloroplast
b)
Nucleus
c)
Lysosome
d)
Microsome
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Single membrane-bound: Some organelles are bounded by a single membrane. For example, vacuole, lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum etc. They are present only in a eukaryotic cell.
Non pigmented part of chloroplast is called :-- a)Thylakoids
- b)Grana
- c)Stroma
- d)Lamellae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Non pigmented part of chloroplast is called :-
a)
Thylakoids
b)
Grana
c)
Stroma
d)
Lamellae
|
|
Anuj Singh answered |
Non-pigmented part of chloroplast is called Stroma.
Stroma is the aqueous matrix present in chloroplasts. It is the non-pigmented part of chloroplasts and fills the space between the thylakoid membranes and the inner membrane of the chloroplast. It is a gel-like fluid that contains several enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and other soluble proteins. The stroma is enclosed by a double membrane, which separates the chloroplast from the cytoplasm.
Functions of Stromal Enzymes:
1. Calvin Cycle: The stromal enzymes play a crucial role in the carbon fixation process (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis. The enzymes present in the stroma are responsible for converting CO2 into carbohydrates.
2. Fatty Acid Synthesis: Stromal enzymes also play a role in the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, which is generated during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
3. Amino Acid Synthesis: The stromal enzymes are involved in the synthesis of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
4. Nitrogen Assimilation: The stromal enzymes are responsible for the assimilation of nitrogen from the atmosphere into the chloroplast.
Conclusion:
Thus, stroma is an important part of chloroplasts that contains several enzymes and other soluble proteins which are important for the functioning of the chloroplast. The stromal enzymes play a crucial role in the carbon fixation process, fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and nitrogen assimilation. Therefore, stroma is an essential component of the photosynthetic machinery of plants.
Stroma is the aqueous matrix present in chloroplasts. It is the non-pigmented part of chloroplasts and fills the space between the thylakoid membranes and the inner membrane of the chloroplast. It is a gel-like fluid that contains several enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and other soluble proteins. The stroma is enclosed by a double membrane, which separates the chloroplast from the cytoplasm.
Functions of Stromal Enzymes:
1. Calvin Cycle: The stromal enzymes play a crucial role in the carbon fixation process (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis. The enzymes present in the stroma are responsible for converting CO2 into carbohydrates.
2. Fatty Acid Synthesis: Stromal enzymes also play a role in the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, which is generated during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
3. Amino Acid Synthesis: The stromal enzymes are involved in the synthesis of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
4. Nitrogen Assimilation: The stromal enzymes are responsible for the assimilation of nitrogen from the atmosphere into the chloroplast.
Conclusion:
Thus, stroma is an important part of chloroplasts that contains several enzymes and other soluble proteins which are important for the functioning of the chloroplast. The stromal enzymes play a crucial role in the carbon fixation process, fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and nitrogen assimilation. Therefore, stroma is an essential component of the photosynthetic machinery of plants.
Plasma membrane is :–- a)Selectively permeable
- b)Permeable
- c)Impermeable
- d)Semipermeable
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasma membrane is :–
a)
Selectively permeable
b)
Permeable
c)
Impermeable
d)
Semipermeable
|
|
Priya Mahale answered |
It allows hydrophobic molecules and small polar molecules diffuse through the lipid layer, but does not allow ions and large polar molecules cannot diffuse through the membrane.
Plasmodesmata are:-- a)Pores in cell wall
- b)Pores in cell membrane
- c)Protoplasmic connections
- d)1 and 2 both
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmodesmata are:-
a)
Pores in cell wall
b)
Pores in cell membrane
c)
Protoplasmic connections
d)
1 and 2 both

|
S. G. answered |
It's simple Plasmodesmata are protoplasmic connect... moreions between adjacent cells.These R threads like structure of protoplasms which travel from protoplasm of one cell to protoplasm of nearest adjacent cell crossing cell wall.These Plasmodesmata connects the protoplasm of adjacent cells.These are charastically found out only in plant cells and ABSENT IN ANIMAL CELLS ..
The rod shaped bacteria is called as- a)Bacillus
- b)Vibrio
- c)Spiral
- d)Spherical
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The rod shaped bacteria is called as
a)
Bacillus
b)
Vibrio
c)
Spiral
d)
Spherical

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The shapes of bacteria are bacillus (rod like), coccus (spherical), vibrio (comma shaped) and spirillum (spiral).
The structure of plasma membrane fluid mosaic model is proposed by- a)Gram
- b)Singer and Nicolson
- c)Schwann and Schleiden
- d)Robert brown
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure of plasma membrane fluid mosaic model is proposed by
a)
Gram
b)
Singer and Nicolson
c)
Schwann and Schleiden
d)
Robert brown
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
An improved model of the structure of cell membrane was proposed by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson (1972) widely accepted as fluid mosaic model.CORRECT OPTION IS B.
Plasma membrane is fluid structure due to presence of :–- a)Carbohydrate
- b)Lipid
- c)Glyco protein
- d)Poly saccharide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasma membrane is fluid structure due to presence of :–
a)
Carbohydrate
b)
Lipid
c)
Glyco protein
d)
Poly saccharide
|
|
Sanjana Singh answered |
See-
composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded peoteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells. The plasma membrane is fluid structure due to composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded peoteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells. The plasma membrane is fluid structure due to composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
Who first saw and described a live cell?- a)T. Schwann
- b)R. Virchow
- c)A.V. Leeuwenhoek
- d)M. Schleiden
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who first saw and described a live cell?
a)
T. Schwann
b)
R. Virchow
c)
A.V. Leeuwenhoek
d)
M. Schleiden

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek first saw and described a live cell.
Mitochondria are present in the :–- a)Aerobic organism only
- b)Obligate anaerobic organism
- c)Aerobic and obligate anaerobic organism
- d)Angiosperm only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitochondria are present in the :–
a)
Aerobic organism only
b)
Obligate anaerobic organism
c)
Aerobic and obligate anaerobic organism
d)
Angiosperm only
|
|
Amir Raza answered |
Mitochondria is involved in aerobic respiration. It generates ATP by utilizing the protein complexes present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The two major process like TCA cycle and electron transport system majorly take place in mitochondria.
Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic cells in having:
- a)
True nucleus
- b)Mitochondria in mesosome form
- c)Only smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- d)70S ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic cells in having:
a)
True nucleus
b)
Mitochondria in mesosome form
c)
Only smooth endoplasmic reticulum
d)
70S ribosomes
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Correct option is A)
- Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus whereas prokaryotic cells have a primitive nucleus.
- The true nucleus of eukaryotes is a double membrane-covered protoplasmic body that contains hereditary information.
- A true nucleus is made up of five parts- nuclear envelope, nucleoplasm, nuclear matrix, chromatin, and nucleolus.
- The primitive nucleus of a prokaryote is also called as nucleoid as it lacks these parts. It is comprised of only the genetic material. So, option A is correct.
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in- a)Pyrenoid
- b)Both grana and stroma
- c)Grana
- d)Stroma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in
a)
Pyrenoid
b)
Both grana and stroma
c)
Grana
d)
Stroma
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Correct Answer :- c
Explanation : Chloroplasts are structurally made up of two components- thylakoids (internal membrane structures) and stroma. Some of the thylakoid membranes are stacked one above the other and are called as grana. The grana contain light trapping pigment chlorophyll and are thus the site of light reaction.
Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on Earth, are produced by- a)Viruses, fungi and bacteria
- b)Fungi, algae and green plant cells
- c)Some bacteria, algae and green plant cells
- d)All bacteria, fungi and algae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on Earth, are produced by
a)
Viruses, fungi and bacteria
b)
Fungi, algae and green plant cells
c)
Some bacteria, algae and green plant cells
d)
All bacteria, fungi and algae

|
Rocky Handsome answered |
Carbohydrates are organic compounds synthesized in the chlorophyll containing cells of some bacteria,-algae and green plant cells, during photosynthesis. Certain photoautotrophic bacteria eg. Green sulphur bacteria and purple sulphur bacteria contain pigments like chlorobium chlorophyll and bacteriochlorophyll respectively that helps them in photosynthesis. During photosynthesis carbon dioxide is reduced into carbohydrates by water and oxygen is liberated.
so option C ) is correct
( . __ .)
Lysosomes are produced by- a)Leucoplast
- b)Golgi bodies
- c)Mitochondria
- d)Endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lysosomes are produced by
a)
Leucoplast
b)
Golgi bodies
c)
Mitochondria
d)
Endoplasmic reticulum

|
Rohan Unni answered |
These are membrane bound vesicular structures formed by the process of packaging in the Golgi apparatus.
The prokaryotic cells are characterised by- a)Presence of a distinct chromosome
- b)Absence of chromatin material
- c)Absence of a nuclear membrane
- d)Presence of a distinct nuclear membrane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The prokaryotic cells are characterised by
a)
Presence of a distinct chromosome
b)
Absence of chromatin material
c)
Absence of a nuclear membrane
d)
Presence of a distinct nuclear membrane
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Prokaryotes lack an organized nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. The cell wall of a prokaryote acts as an extra layer of protection, helps maintain cell shape, and prevents dehydration.prokaryotic cells are those that do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. In fact "pro-karyotic" is Greek for "before nucleus". Besides bacteria, the cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) are a major group of prokaryotes.
Protoplasm found inside the nucleus is known as- a)Amyloplast
- b)Nucleoplasm
- c)cytoplasm
- d)Elaioplast
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Protoplasm found inside the nucleus is known as
a)
Amyloplast
b)
Nucleoplasm
c)
cytoplasm
d)
Elaioplast
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Protoplasm is the living content of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a general term for the cytoplasm. Protoplasm is composed of a mixture of small molecules such as ions, amino acids, monosaccharides and water, and macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and polysaccharides.Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains 'nucleoplasm' (nucleus sap) or karyoplasm. The nucleoplasm is one of the types of protoplasm, and it is enveloped by the nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope. The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleoli.
Which of the following cell organelles store hydrolytic enzymes?- a)Chloroplasts
- b)Centrioles
- c)Chromoplasts
- d)Lysosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cell organelles store hydrolytic enzymes?
a)
Chloroplasts
b)
Centrioles
c)
Chromoplasts
d)
Lysosomes
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
Lysosomes are spherical bodies, or vacuoles that are enclosed by a single membrane (membrane- bound organelles). It contains different hydrolytic enzymes, such as proteases, lipases, and nucleases that are capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers (e.g., proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids) that enter the cell or are no longer useful to the cell. So, the correct answer is 'Lysosome'.
Cell wall is :–- a)Dead and impermeable
- b)Dead and permeable
- c)Living and impermeable
- d)Living and selective
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall is :–
a)
Dead and impermeable
b)
Dead and permeable
c)
Living and impermeable
d)
Living and selective
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. ... In bacteria, the cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan.
Synthesis of cell wall material takes place in :–- a)Dictyosome
- b)Mitochondria
- c)Lysosome
- d)E.R.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Synthesis of cell wall material takes place in :–
a)
Dictyosome
b)
Mitochondria
c)
Lysosome
d)
E.R.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In plant cells, Golgi apparatus consists of a number of isolated units called as dictyosomes while in animal cells it occurs as single compact or loose complex. The dictyosomes are engaged in secretory activities (because secretory materials are produced in dictyosomes) and rapid divisions (because wall materials are synthesized in dictyosomes).
Which element mainly occurs in middle lamella:-- a)Ca
- b)Mg
- c)Na
- d)K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which element mainly occurs in middle lamella:-
a)
Ca
b)
Mg
c)
Na
d)
K

|
Manvi Bansal answered |
Ca and mg pectate are present in middle lamella
The organelle involved in respiration is- a)Mitochondria
- b)Endoplasmic reticulum
- c)Chloroplast
- d)Golgi complex
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The organelle involved in respiration is
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Endoplasmic reticulum
c)
Chloroplast
d)
Golgi complex

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration. They producecellular energy in the form of ATP
DNA of chloroplast discovered by :–- a)Randad and Disprey
- b)Nash and Margit
- c)Ris and Plaut
- d)Benda
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA of chloroplast discovered by :–
a)
Randad and Disprey
b)
Nash and Margit
c)
Ris and Plaut
d)
Benda
|
|
꧁༒gundagi༒꧂ ꧁༒विरेश༒꧂ answered |
Masahiro R. Ishida-
In 1963, Masahiro R. Ishida, together with Ruth Sager, was acknowledged for being the first to extract the chloroplast DNA.
So may be all options are wrong....
In which types of cell lysosomes are abundantly found :–- a)Storage cell
- b)Glandular cell
- c)Phagocytic cell
- d)Vascular cell
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which types of cell lysosomes are abundantly found :–
a)
Storage cell
b)
Glandular cell
c)
Phagocytic cell
d)
Vascular cell
|
|
Rhythm answered |
Lysosomes are abundantly found in the phagocytic cell. Phagocytosis is the process of taking in particles such as bacteria, parasites, dead host cells, and cellular and foreign debris by a cell. A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle found in most animal cells.
Percentage of intrinsic proteins in the total proteins of plasma membrane :–- a)70%
- b)20%
- c)10%
- d)90%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of intrinsic proteins in the total proteins of plasma membrane :–
a)
70%
b)
20%
c)
10%
d)
90%
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is the outer covering of all cells but in a plant cell, it is present below the cell wall. It is mainly composed of phospholipid bilayer structure with the embedded proteins. The membrane proteins are extrinsic (on the surface of the membrane) and intrinsic (across the membrane i.e., cross the bilipid layer). About 70% of the proteins of the plasma membrane are intrinsic proteins. The intrinsic proteins, as their name implies, are firmly embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. Almost all intrinsic proteins contain special amino acid sequences.
Carbohydrates which present in the cell membrane take part in :–- a)Transport of substance
- b)Cell recognition
- c)Attachment to microfilament
- d)Attachment to microtubules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates which present in the cell membrane take part in :–
a)
Transport of substance
b)
Cell recognition
c)
Attachment to microfilament
d)
Attachment to microtubules
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Carbohydrates which are present in the cell membrane take part in cell recognition. Cell recognition is defined as an active process giving rise to a specific response.
Cell adhesion is a good example of cell recognition when it can be demonstrated that the adhesion is mediated by molecules having specific binding properties. Such cell adhesion molecules have now been identified in several cellular systems. Carbohydrates, or sugars, are sometimes found attached to proteins or lipids on the outside of a cell membrane. That is, they are only found on the extracellular side of a cell membrane. Together these carbohydrates form the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx of a cell has many functions. It can provide cushioning and protection for the plasma membrane, and it is also important in cell recognition. Based on the structure and types of carbohydrates in the glycocalyx, your body can recognize cells and determine if they should be there or not.
Cell adhesion is a good example of cell recognition when it can be demonstrated that the adhesion is mediated by molecules having specific binding properties. Such cell adhesion molecules have now been identified in several cellular systems. Carbohydrates, or sugars, are sometimes found attached to proteins or lipids on the outside of a cell membrane. That is, they are only found on the extracellular side of a cell membrane. Together these carbohydrates form the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx of a cell has many functions. It can provide cushioning and protection for the plasma membrane, and it is also important in cell recognition. Based on the structure and types of carbohydrates in the glycocalyx, your body can recognize cells and determine if they should be there or not.
Chlorophyll is located inside- a)Stroma
- b)Plasma lemma
- c)Chromatophores
- d)Thylakoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll is located inside
a)
Stroma
b)
Plasma lemma
c)
Chromatophores
d)
Thylakoids

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
The chloroplast consists of a number of organised flattened membranous sacs called the thylakoids,Chlorophyll pigments are present in the thylakoids.
In prokaryotes, the reserved food material is stored in- a)Cytoplasm
- b)Vacuole
- c)Centrosome
- d)Endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In prokaryotes, the reserved food material is stored in
a)
Cytoplasm
b)
Vacuole
c)
Centrosome
d)
Endoplasmic reticulum

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Reserve material in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies.
During spermatogenesis golgi is thought to be responsible for the formation of :–
- a)Tail
- b)Myeloid piece
- c)Head
- d)Acrosome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During spermatogenesis golgi is thought to be responsible for the formation of :–
a)
Tail
b)
Myeloid piece
c)
Head
d)
Acrosome
|
|
Ruchi Iyer answered |
During spermatogenesis, the Golgi apparatus is responsible for the formation of the acrosome in sperm cells. The Golgi apparatus synthesizes and packages enzymes and proteins that make up the acrosome, a specialized structure located at the tip of the sperm head. The acrosome contains enzymes that help the sperm penetrate and fertilize the egg.
Carbohydrates are present in the plasmalemma in the form of :–- a)Hemicellulose
- b)Cellulose
- c)Starch
- d)Glycoprotein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates are present in the plasmalemma in the form of :–
a)
Hemicellulose
b)
Cellulose
c)
Starch
d)
Glycoprotein
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Chemically, cell membrane or plasma lemma is composed of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and water. Carbohydrates of cell membrane are small unbranched or branched chains called as oligosaccharides. They are attached to both lipids and protein molecules found on outer surface of the membrane producing glycolipids and glycoproteins respectively.
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell - The Unit of Life - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell - The Unit of Life - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











