All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Biomolecules for NEET Exam
Select the right option regarding the given graph.
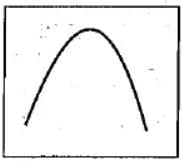
- a)X - axis = Rate of reaction
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
- b)X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Rate of reaction
- c)X - axis = pH/Temperature
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
- d)X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = pH/Temperature
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the right option regarding the given graph.

a)
X - axis = Rate of reaction
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
b)
X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Rate of reaction
Y - axis = Rate of reaction
c)
X - axis = pH/Temperature
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
d)
X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = pH/Temperature
Y - axis = pH/Temperature
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The variable with which we have to find the relation should always have to be on the y axis and the variable which does not show variation and will always increase will be on the x-axis.
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is- a)Cellulose
- b)Protein
- c)Steroids
- d)Lipid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is
a)
Cellulose
b)
Protein
c)
Steroids
d)
Lipid

|
Infinity Academy answered |
- Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth.
- Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes.
Chitin occurs in cell wall of- a)Bacteria
- b)Yeast
- c)Fungi
- d)Algae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Chitin occurs in cell wall of
a)
Bacteria
b)
Yeast
c)
Fungi
d)
Algae

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- Chitin is a polysaccharide. It is an important component of the cell wall of fungi.
- It is the main constituent of the exoskeleton of the arthropods.
- It is a long chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine.
- It is the second most abundant homopolysaccharide.
- The cell wall of bacteria is made up of peptidoglycan.
- Algae has the cell wall made up of cellulose.
- Yeast has the cell wall made up of beta-glucan and mannan sugar polymers), 15 - 30 % proteins, 5 - 20 % lipids and a small amount of chitin.
Which of the following is an example of isozyme?- a)α-amylase
- b)Glucokinase
- c)Lactate dehydrogenases
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of isozyme?
a)
α-amylase
b)
Glucokinase
c)
Lactate dehydrogenases
d)
All of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The multiple molecular forms of an enzyme occuring in the same organism and having a similar substrate activity are called isoenymes or isozymes. They have similar properties but different molecular weights and locations. Over 100 enzymes are known to have isoenzymes. α-amylase of wheat endosperm has 16 isozymes, lactate dehydrogenase has 5 isozymes. Glucokinase is an isozyme of hexokinase.
Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of- a)isomerases
- b)ligases
- c)lyases
- d)hydrolases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of
a)
isomerases
b)
ligases
c)
lyases
d)
hydrolases
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Isomerases catalyse the change of a substrate into a related isomeric form by rearrangement of molecules.
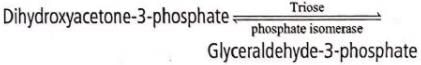
What is meant by feedback inhibition?- a)Inhibition of enzyme activity at an active site by an inhibitor, which is structurally similar to a substrate
- b)Inhibition of first step of biosynthesis by the end-product of reaction
- c)Inhibition by a structurally different inhibitor at a place other than active site
- d)Denaturation of enzyme
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is meant by feedback inhibition?
a)
Inhibition of enzyme activity at an active site by an inhibitor, which is structurally similar to a substrate
b)
Inhibition of first step of biosynthesis by the end-product of reaction
c)
Inhibition by a structurally different inhibitor at a place other than active site
d)
Denaturation of enzyme

|
Lead Academy answered |
Inhibition of an enzyme controlling an early stage of a series of biochemical reactions by the end product when it reaches a critical concentration.
How many carbon atoms are generally used in composition of monosaccharides?- a)3 to 7
- b)1 to 5
- c)5 to 10
- d)5 to 15
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many carbon atoms are generally used in composition of monosaccharides?
a)
3 to 7
b)
1 to 5
c)
5 to 10
d)
5 to 15
|
|
Anisha Dey answered |
Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller carbohydrate units. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates like disaccharides and polysaccharides. The composition of monosaccharides can vary, but they generally contain a carbon backbone of three to seven carbon atoms.
Explanation:
- Monosaccharides are carbohydrates that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The general formula for a monosaccharide is (CH2O)n, where n can range from 3 to 7.
- Monosaccharides are classified based on the number of carbon atoms they contain. Some examples include trioses (3 carbon atoms), tetroses (4 carbon atoms), pentoses (5 carbon atoms), hexoses (6 carbon atoms), and heptoses (7 carbon atoms).
- Trioses, such as glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone, have three carbon atoms. They are the simplest monosaccharides.
- Tetroses, like erythrose and threose, have four carbon atoms.
- Pentoses, such as ribose and deoxyribose, have five carbon atoms. They are important components of nucleic acids.
- Hexoses, like glucose and fructose, have six carbon atoms. Glucose is a primary source of energy for living organisms, while fructose is commonly found in fruits and honey.
- Heptoses, like sedoheptulose and mannoheptulose, have seven carbon atoms. They are less common than other monosaccharides.
- It is important to note that although monosaccharides generally contain three to seven carbon atoms, there are exceptions. For example, deoxyribose, a pentose, is an important component of DNA and RNA, but it only contains five carbon atoms.
- Overall, the correct answer is option 'A' (3 to 7), as monosaccharides typically have a carbon backbone consisting of three to seven carbon atoms.
Explanation:
- Monosaccharides are carbohydrates that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The general formula for a monosaccharide is (CH2O)n, where n can range from 3 to 7.
- Monosaccharides are classified based on the number of carbon atoms they contain. Some examples include trioses (3 carbon atoms), tetroses (4 carbon atoms), pentoses (5 carbon atoms), hexoses (6 carbon atoms), and heptoses (7 carbon atoms).
- Trioses, such as glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone, have three carbon atoms. They are the simplest monosaccharides.
- Tetroses, like erythrose and threose, have four carbon atoms.
- Pentoses, such as ribose and deoxyribose, have five carbon atoms. They are important components of nucleic acids.
- Hexoses, like glucose and fructose, have six carbon atoms. Glucose is a primary source of energy for living organisms, while fructose is commonly found in fruits and honey.
- Heptoses, like sedoheptulose and mannoheptulose, have seven carbon atoms. They are less common than other monosaccharides.
- It is important to note that although monosaccharides generally contain three to seven carbon atoms, there are exceptions. For example, deoxyribose, a pentose, is an important component of DNA and RNA, but it only contains five carbon atoms.
- Overall, the correct answer is option 'A' (3 to 7), as monosaccharides typically have a carbon backbone consisting of three to seven carbon atoms.
Which of the following carbohydrates is a disaccharide?- a)Sucrose
- b)Fructose
- c)Glucose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carbohydrates is a disaccharide?
a)
Sucrose
b)
Fructose
c)
Glucose
d)
Cellulose

|
Lead Academy answered |
Sucrose is a disaccharide.
Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Examples of carbohydrates having two monomers include Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose.
Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Examples of carbohydrates having two monomers include Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose.
Sources of Carbohydrates:
- Simple sugars are found in the form of fructose in many fruits.
- Galactose is present in all dairy products.
- Lactose is abundantly found in milk and other dairy products.
- Maltose is present in cereal, beer, potatoes, processed cheese, pasta, etc.
- Sucrose is naturally obtained from sugar and honey containing small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
An enzyme extract, when subjected to electric field, separates into two fractions, each catalysing the same reaction. These fractions are:- a)Allosteric enzymes
- b)Inducible enzymes
- c)Isoenzymes
- d)Coenzymes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An enzyme extract, when subjected to electric field, separates into two fractions, each catalysing the same reaction. These fractions are:
a)
Allosteric enzymes
b)
Inducible enzymes
c)
Isoenzymes
d)
Coenzymes

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Isoenzymes (also called isozymes) are alternative forms of the same enzyme activity that exist in different proportions in different tissues.
- Isoenzymes differ in amino acid composition and sequence and multimeric quaternary structure; mostly, but not always, they have similar (conserved) structures.
Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.- a)(i) and (v)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
a)
(i) and (v)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
All of these
|
|
Maitri Deshpande answered |
**Enzymes are biological catalysts that play a crucial role in speeding up chemical reactions in living organisms. Let's analyze each statement to determine which ones are correct:**
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes do not affect the overall change in free energy for a reaction. They only lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, but they do not change the energy difference between the reactants and products.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three-dimensional shape is key to their functions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are proteins, and their three-dimensional shape is critical for their proper functioning. The active site of an enzyme, where the substrate binds and the reaction takes place, is precisely shaped to accommodate specific substrates.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy is the energy input needed to start a reaction, and enzymes facilitate this process by providing an alternative pathway with a lower energy barrier.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are highly specific for particular reactions. Each enzyme is designed to catalyze a specific chemical reaction or a group of closely related reactions. This specificity is determined by the enzyme's active site and its ability to recognize and bind to specific substrates.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Activation energy refers to the energy input needed to initiate a chemical reaction. It is the energy required to break the bonds of the reactant molecules and reach the transition state, from which the reaction proceeds to form the products.
**In conclusion, all of the given statements are correct. Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy, their three-dimensional shape is crucial for their function, they lower activation energy, they are highly specific for reactions, and activation energy is the energy input needed to start a chemical reaction. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes do not affect the overall change in free energy for a reaction. They only lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, but they do not change the energy difference between the reactants and products.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three-dimensional shape is key to their functions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are proteins, and their three-dimensional shape is critical for their proper functioning. The active site of an enzyme, where the substrate binds and the reaction takes place, is precisely shaped to accommodate specific substrates.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy is the energy input needed to start a reaction, and enzymes facilitate this process by providing an alternative pathway with a lower energy barrier.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are highly specific for particular reactions. Each enzyme is designed to catalyze a specific chemical reaction or a group of closely related reactions. This specificity is determined by the enzyme's active site and its ability to recognize and bind to specific substrates.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Activation energy refers to the energy input needed to initiate a chemical reaction. It is the energy required to break the bonds of the reactant molecules and reach the transition state, from which the reaction proceeds to form the products.
**In conclusion, all of the given statements are correct. Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy, their three-dimensional shape is crucial for their function, they lower activation energy, they are highly specific for reactions, and activation energy is the energy input needed to start a chemical reaction. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
What percentage of the total cellular mass is made up of proteins?- a)Less than 1%
- b)About 2%
- c)Approximately 10-15%
- d)70-90%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Less than 1%
b)
About 2%
c)
Approximately 10-15%
d)
70-90%

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Proteins constitute a significant portion of the cellular mass, making up about 10-15% of it. This makes them vital for numerous cellular functions, including acting as enzymes, structural components, and signaling molecules.
An example of aromatic amino acid is- a)Tyrosine
- b)Phenylalanine
- c)Tryptophan
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of aromatic amino acid is
a)
Tyrosine
b)
Phenylalanine
c)
Tryptophan
d)
All of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Aromatic amino acids possess cyclic structure in the side chain, e.g., phenylalanine, tryptophan (actually heterocyclic) or tyrosine (having OH group).
Biological molecules are primarily joined by- a)Peptide bond
- b)Ionic bond
- c)Hydrogen bond
- d)Covalent bond
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biological molecules are primarily joined by
a)
Peptide bond
b)
Ionic bond
c)
Hydrogen bond
d)
Covalent bond
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Biological molecules, also known as biomolecules, are large structures that are responsible for the catalysis, structure and function of the cell. The molecules (C,H, O, N etc.) within the biomolecules are joined by covalent bond because it is strong bond that maintains structural integrity. The biomolecules will then combine to form a functional cell. The examples include peptide bond, glycosidic bond, phosphodiester bond etc.
A. Peptide bond is a type of covalent bond found in polypeptides. So only proteins will show peptide bonds.
B. Ionic bonds result in formation of cation and anion which could hamper the vital activities within the cells.
C. Hygrogen bonds are weak bonds and they do not confer structural integrity to the molecules.
D. Covalent bonds form the backbone of the structure of biomolecules.
Hence, the correct answer is 'covalent bond'.
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding triglycerides?- a)Liver cells can synthesise and store triglycerides.
- b)The process of lipolysis takes place in the intestine.
- c)Triglycerides form chylomicrons.
- d)In triglyceride form, lipids can be absorbed by the jejunum.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding triglycerides?
a)
Liver cells can synthesise and store triglycerides.
b)
The process of lipolysis takes place in the intestine.
c)
Triglycerides form chylomicrons.
d)
In triglyceride form, lipids can be absorbed by the jejunum.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- In triglyceride form, lipids can be absorbed by the jejunum is incorrect regarding triglycerides.
- Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) found in your blood. When you eat, your body converts any calories it doesn't need to use right away into triglycerides.
- The triglycerides are stored in your fat cells. Later, hormones release triglycerides for energy between meals.
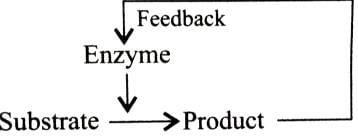
Feedback inhibition of enzyme is influenced by- a)Enzyme
- b)External factors
- c)End product
- d)Substrate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Feedback inhibition of enzyme is influenced by
a)
Enzyme
b)
External factors
c)
End product
d)
Substrate
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In feedback inhibition, product of a reaction inhibits the enzyme catalysing that reaction. It is a type of control mechanism at the enzyme level. If the product is produced in sufficient amount, in inhibits the enzyme to stop the further production.
Holoenzyme is the complete enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor. Select the option that correctly identifies the nature of apoenzyme and co-factor.- a)Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Non-Protein - b)Apoenzyme - Non - Protein
Co - factor - Protein - c)Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Protein - d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Holoenzyme is the complete enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor. Select the option that correctly identifies the nature of apoenzyme and co-factor.
a)
Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Non-Protein
Co - factor - Non-Protein
b)
Apoenzyme - Non - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
c)
Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
d)
None of the above
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Enzyme may be broadly classified into two types depending on their chemical composition-simple enzymes and conjugated enzymes are wholly made up of proteins and any additional substance or group is absent, e.g., pepsin, trypsin, etc. Conjugated enzymes (or holoenzymes) are formed of two parts -a protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named co-factor. The complete conjugated enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor is called holoenzyme. Holoenzyme is the functional unit of enzyme.
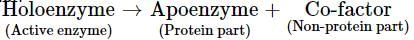
Co-factor may be inorgainc or roganic in nature. Catalytic activity is lost when co-factor is removed from the enzyme which indicates that it plays a crucial role in catalytic activity of enzymes.
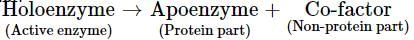
Co-factor may be inorgainc or roganic in nature. Catalytic activity is lost when co-factor is removed from the enzyme which indicates that it plays a crucial role in catalytic activity of enzymes.
Assertion (A): Lipids, despite their smaller molecular weights, are part of the acid insoluble fraction.
Reason (R): Lipids form structures like cell membranes that are not water soluble, leading to their inclusion in the macromolecular fraction.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Lipids, despite their smaller molecular weights, are part of the acid insoluble fraction.
Reason (R): Lipids form structures like cell membranes that are not water soluble, leading to their inclusion in the macromolecular fraction.
Reason (R): Lipids form structures like cell membranes that are not water soluble, leading to their inclusion in the macromolecular fraction.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Anisha Datta answered |
Assertion (A): Lipids, despite their smaller molecular weights, are part of the acid insoluble fraction.
The assertion is true. Lipids, which include fats, oils, and phospholipids, typically have lower molecular weights compared to proteins and carbohydrates. However, they are classified as part of the acid insoluble fraction due to their hydrophobic nature.
Reason (R): Lipids form structures like cell membranes that are not water soluble, leading to their inclusion in the macromolecular fraction.
The reason is also true. Lipids indeed play a crucial role in forming cell membranes, which are essential for maintaining cellular integrity and function. Their hydrophobic properties prevent them from dissolving in water, which is why they are categorized in the acid insoluble fraction.
Relationship between A and R:
- Both assertion and reason are true.
- The reason provides a correct explanation for the assertion. Lipids are included in the acid insoluble fraction not just because of their molecular weight but primarily due to their solubility characteristics.
Conclusion:
- Since both statements are true and R correctly explains A, the correct answer is option 'A': Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
This understanding is crucial in the context of biochemistry, especially for NEET aspirants, as it highlights the importance of lipid solubility and structure in biological systems.
The assertion is true. Lipids, which include fats, oils, and phospholipids, typically have lower molecular weights compared to proteins and carbohydrates. However, they are classified as part of the acid insoluble fraction due to their hydrophobic nature.
Reason (R): Lipids form structures like cell membranes that are not water soluble, leading to their inclusion in the macromolecular fraction.
The reason is also true. Lipids indeed play a crucial role in forming cell membranes, which are essential for maintaining cellular integrity and function. Their hydrophobic properties prevent them from dissolving in water, which is why they are categorized in the acid insoluble fraction.
Relationship between A and R:
- Both assertion and reason are true.
- The reason provides a correct explanation for the assertion. Lipids are included in the acid insoluble fraction not just because of their molecular weight but primarily due to their solubility characteristics.
Conclusion:
- Since both statements are true and R correctly explains A, the correct answer is option 'A': Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
This understanding is crucial in the context of biochemistry, especially for NEET aspirants, as it highlights the importance of lipid solubility and structure in biological systems.
The 20 different amino acids have different- a)R-groups
- b)Carboxylic groups
- c)Peptide bonds
- d)Amino groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The 20 different amino acids have different
a)
R-groups
b)
Carboxylic groups
c)
Peptide bonds
d)
Amino groups
|
|
Niti Bajaj answered |
The correct answer is option 'A': R-groups.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that can combine in various ways to form different proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom (called the alpha carbon) bonded to four different groups: an amino group, a carboxylic group, a hydrogen atom, and a unique side chain, also known as the R-group.
The R-group, or side chain, is what differentiates one amino acid from another. It can vary in size, shape, charge, polarity, and chemical properties. The R-group determines the unique characteristics and functions of each amino acid.
The side chain can be categorized into different groups based on its chemical properties. Some common categories of R-groups include:
1. Nonpolar side chains: These R-groups are hydrophobic, meaning they do not interact with water. Examples include glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, methionine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan.
2. Polar side chains: These R-groups are hydrophilic, meaning they interact with water. Examples include serine, threonine, cysteine, tyrosine, asparagine, and glutamine.
3. Charged side chains: These R-groups are either positively charged (basic) or negatively charged (acidic). Examples of basic side chains include lysine, arginine, and histidine. Examples of acidic side chains include aspartic acid and glutamic acid.
4. Specialized side chains: These R-groups have unique properties that do not fit into the above categories. For example, cysteine can form disulfide bonds, and glycine is the smallest amino acid.
The R-group determines how an amino acid interacts with its environment and other amino acids in a protein. It affects the protein's structure, stability, and function. The specific arrangement and composition of amino acids in a protein determine its three-dimensional structure and ultimately its biological activity.
In summary, the 20 different amino acids have different R-groups, which are responsible for their unique properties and functions. The R-group determines how amino acids interact with their environment and other amino acids in a protein, ultimately influencing the structure and function of the protein.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that can combine in various ways to form different proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom (called the alpha carbon) bonded to four different groups: an amino group, a carboxylic group, a hydrogen atom, and a unique side chain, also known as the R-group.
The R-group, or side chain, is what differentiates one amino acid from another. It can vary in size, shape, charge, polarity, and chemical properties. The R-group determines the unique characteristics and functions of each amino acid.
The side chain can be categorized into different groups based on its chemical properties. Some common categories of R-groups include:
1. Nonpolar side chains: These R-groups are hydrophobic, meaning they do not interact with water. Examples include glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, methionine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan.
2. Polar side chains: These R-groups are hydrophilic, meaning they interact with water. Examples include serine, threonine, cysteine, tyrosine, asparagine, and glutamine.
3. Charged side chains: These R-groups are either positively charged (basic) or negatively charged (acidic). Examples of basic side chains include lysine, arginine, and histidine. Examples of acidic side chains include aspartic acid and glutamic acid.
4. Specialized side chains: These R-groups have unique properties that do not fit into the above categories. For example, cysteine can form disulfide bonds, and glycine is the smallest amino acid.
The R-group determines how an amino acid interacts with its environment and other amino acids in a protein. It affects the protein's structure, stability, and function. The specific arrangement and composition of amino acids in a protein determine its three-dimensional structure and ultimately its biological activity.
In summary, the 20 different amino acids have different R-groups, which are responsible for their unique properties and functions. The R-group determines how amino acids interact with their environment and other amino acids in a protein, ultimately influencing the structure and function of the protein.
The component present in both nucleotides, and nucleosides is- a)Sugar
- b)Phosphate
- c)Nitrogenous base
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The component present in both nucleotides, and nucleosides is
a)
Sugar
b)
Phosphate
c)
Nitrogenous base
d)
Both (a) and (c)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Nucleoside is compound formed by the union of a nitrogen base with a pentose sugar. It is a component of nucleotide. Each nucleotide is composed of three units; a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate group.
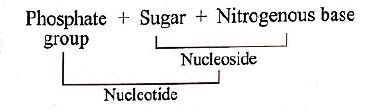
The nucleoside combines with a phosphate group at 5'position by an ester bond to form a nucleotide or nucleoside monophosphate.
So, the correct option is 'both (a) and (c)'
No cell could live without:- a)Enzymes
- b)Phytochrome
- c)Chloroplasts
- d)Protein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
No cell could live without:
a)
Enzymes
b)
Phytochrome
c)
Chloroplasts
d)
Protein
|
|
Anoushka Kaur answered |
Enzymes are essential for the survival of cells
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions within cells. Without enzymes, many essential cellular processes would occur too slowly to sustain life. Enzymes are involved in a wide range of functions within cells, including metabolism, growth, and repair.
Enzymes are needed for:
- Breaking down nutrients into smaller molecules that can be used by the cell for energy and building materials
- Facilitating the synthesis of important cellular molecules
- Helping cells respond to signals from their environment
- Repairing damage to cellular components
Importance of enzymes in cell survival
Enzymes are crucial for the functioning of cells because they lower the activation energy required for chemical reactions to occur. This allows cells to carry out essential processes at a much faster rate than would be possible without enzymes.
Enzymes are highly specific in their actions, meaning that each enzyme catalyzes a particular reaction. This specificity is essential for cells to regulate their metabolism and maintain homeostasis. Without enzymes, cells would not be able to efficiently carry out the chemical reactions necessary for their survival.
In conclusion, enzymes are indispensable for the survival of cells. They play a vital role in facilitating essential cellular processes and maintaining the overall function of the cell. Without enzymes, cells would not be able to function properly and would ultimately perish.
Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between the rate of an enzymatic activity and substrate concentration (S)?- a)
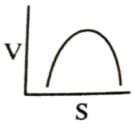
- b)
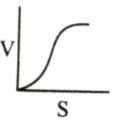
- c)
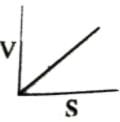
- d)
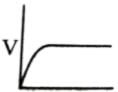
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between the rate of an enzymatic activity and substrate concentration (S)?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
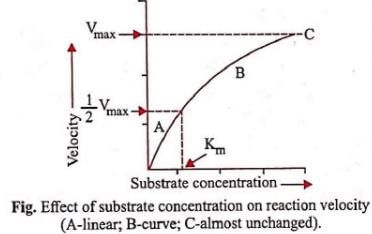
Increase in substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction due to two factors: (i) occupation of more and more active sites by the substrate molecules, (ii) higher number of collisions between substrate molecules. The rise in velocity is quite high in the beginning but it decreases progressively with the increase in substate concentration. If a graph is plotted for substrate concentration versus reaction velocity, it appears as a hyperbolic curve. A stage is reached where velocity is maximum. It does not increase further by increasing the substrate concentration. At this stage the anzyme molecule becomes fully saturated and no active site is left free to bind additional substrate molecules.
Michaelis Menten Constant (Km) is equal to- a)The rate of reaction
- b)The rate of enzymatic activity
- c)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
- d)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Michaelis Menten Constant (Km) is equal to
a)
The rate of reaction
b)
The rate of enzymatic activity
c)
Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
d)
Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximum
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Km or the Michaelis-Menten constant is defined as the substrate concentration (expressed in moles/l) at which half-maximum velocity in an enzyme catalysed reaction is achieved. It indicates that half of the enzyme molecules (i.e. 50%) are bound with the substrate molecules when the substrate concentration equals the Km value. It was given by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten (1913). Km value is a characteristic feature of a given enzyme. It is a representative for measuring the strength of ES complex. A low Km value indicates a strong affinity between enzyme and substrate, whereas a high Km value reflects a weak affinity between them. For majority of enzymes, the Km values are in the range of 10−5 to 10−2 moles.

A.
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: - a)B > C > D > A > E
- b)B > D > C > A > E
- c)B > D > A > E > C
- d)B > E > D > C > A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A.
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
B > C > D > A > E
b)
B > D > C > A > E
c)
B > D > A > E > C
d)
B > E > D > C > A

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Ans: 2
Sol: During the state where substrate is bound to the enzyme active site, a new structure of the substrate called transition state structure is formed. Very soon, after the expected bond breaking/making is completed, the product is released from the active site
Sol: During the state where substrate is bound to the enzyme active site, a new structure of the substrate called transition state structure is formed. Very soon, after the expected bond breaking/making is completed, the product is released from the active site
What is the primary role of the acid soluble pool within cells?- a)It serves as the structural framework of cells.
- b)It represents the cytoplasmic composition and includes a variety of small molecules.
- c)It stores genetic information.
- d)It is primarily involved in the storage of energy.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It serves as the structural framework of cells.
b)
It represents the cytoplasmic composition and includes a variety of small molecules.
c)
It stores genetic information.
d)
It is primarily involved in the storage of energy.
|
|
Shraddha Das answered |
Understanding the Acid Soluble Pool
The acid soluble pool within cells plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism and functionality. Here's a detailed explanation of its primary role:
Definition of the Acid Soluble Pool
- The acid soluble pool is a component of the cytoplasm, consisting largely of small molecules and metabolites.
- It includes various organic compounds such as amino acids, nucleotides, and intermediary metabolites.
Composition and Functions
- Cytoplasmic Composition:
- The acid soluble pool represents the diverse array of small molecules found within the cytoplasm, crucial for metabolic activities.
- Metabolic Pathways:
- These small molecules act as substrates and cofactors in various metabolic pathways, facilitating biochemical reactions necessary for cell survival and function.
- Cellular Signaling:
- Components of the acid soluble pool are involved in signaling pathways, helping cells respond to environmental changes and maintain homeostasis.
Importance in Cellular Processes
- Energy Production:
- While not primarily an energy storage reservoir, the acid soluble pool contains key metabolites involved in the energy production processes, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
- Biosynthesis:
- It provides the building blocks for synthesizing larger biomolecules, including proteins and nucleic acids, essential for growth and repair.
Conclusion
In summary, the acid soluble pool is integral to cellular function as it reflects the cytoplasmic composition of small molecules that support various metabolic activities, making option 'B' the correct choice.
The acid soluble pool within cells plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism and functionality. Here's a detailed explanation of its primary role:
Definition of the Acid Soluble Pool
- The acid soluble pool is a component of the cytoplasm, consisting largely of small molecules and metabolites.
- It includes various organic compounds such as amino acids, nucleotides, and intermediary metabolites.
Composition and Functions
- Cytoplasmic Composition:
- The acid soluble pool represents the diverse array of small molecules found within the cytoplasm, crucial for metabolic activities.
- Metabolic Pathways:
- These small molecules act as substrates and cofactors in various metabolic pathways, facilitating biochemical reactions necessary for cell survival and function.
- Cellular Signaling:
- Components of the acid soluble pool are involved in signaling pathways, helping cells respond to environmental changes and maintain homeostasis.
Importance in Cellular Processes
- Energy Production:
- While not primarily an energy storage reservoir, the acid soluble pool contains key metabolites involved in the energy production processes, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
- Biosynthesis:
- It provides the building blocks for synthesizing larger biomolecules, including proteins and nucleic acids, essential for growth and repair.
Conclusion
In summary, the acid soluble pool is integral to cellular function as it reflects the cytoplasmic composition of small molecules that support various metabolic activities, making option 'B' the correct choice.
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.- a)Both Statements 1 and 2 are correct
- b)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
- d)Both Statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.
a)
Both Statements 1 and 2 are correct
b)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
d)
Both Statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Low temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive state. Therefore it is used in preservation of foods inside cold storage. Low temperature present inside cold storage prevents spoilage of food.
High temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation, This occurs at 50oC or so. In between the minimum and maximum temperature the reaction velocity doubles for every 10oC in temperature (general rule of thumb).
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called- a)Competitive inhibitor
- b)Non-competitive inhibitor
- c)Activator
- d)Substrate analogue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called
a)
Competitive inhibitor
b)
Non-competitive inhibitor
c)
Activator
d)
Substrate analogue
|
|
Juhi Bose answered |
Non-competitive inhibitor:
Non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. They do not resemble the substrate in structure. These inhibitors inhibit enzyme activity by changing the shape of the enzyme, making it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.
Mechanism of action:
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme at an allosteric site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme.
- This conformational change may prevent the substrate from binding to the active site or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
- Since non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for the active site, increasing substrate concentration will not overcome their inhibitory effect.
Characteristics:
- Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding to the enzyme.
- They can bind to the enzyme-substrate complex as well as the free enzyme.
- The inhibition by non-competitive inhibitors is not easily reversible.
- These inhibitors are not affected by changes in substrate concentration.
Examples:
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and lead are examples of non-competitive inhibitors.
- Drugs like aspirin and certain antibiotics also act as non-competitive inhibitors of specific enzymes.
In conclusion, non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that inhibits enzyme activity.
Non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. They do not resemble the substrate in structure. These inhibitors inhibit enzyme activity by changing the shape of the enzyme, making it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.
Mechanism of action:
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme at an allosteric site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme.
- This conformational change may prevent the substrate from binding to the active site or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
- Since non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for the active site, increasing substrate concentration will not overcome their inhibitory effect.
Characteristics:
- Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding to the enzyme.
- They can bind to the enzyme-substrate complex as well as the free enzyme.
- The inhibition by non-competitive inhibitors is not easily reversible.
- These inhibitors are not affected by changes in substrate concentration.
Examples:
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and lead are examples of non-competitive inhibitors.
- Drugs like aspirin and certain antibiotics also act as non-competitive inhibitors of specific enzymes.
In conclusion, non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that inhibits enzyme activity.
In maltose, two glucose units are linked by a- a)Peptide bond
- b)Hydrogen bond
- c)Glycosidic bond
- d)Phosphodiester bond
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In maltose, two glucose units are linked by a
a)
Peptide bond
b)
Hydrogen bond
c)
Glycosidic bond
d)
Phosphodiester bond

|
Infinity Academy answered |
- Maltose is a disaccharide made up of two units each of glucose.
- The two units of glucose are joined together covalently by an O-glycosidic bond which is formed when a hydroxyl group on one sugar reacts with the anomeric carbon on another.
What is denoted by X and Y in the given graph?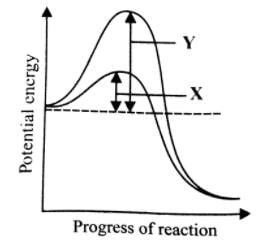
- a)X-Activation energy without enzyme; Y-Activation energy with enzyme
- b)X-Activation energy with enzyme; Y-Activation energy without enzyme
- c)X-Substrate concentration with enzyme; Y- Substrate concentration without enzyme
- d)X-Substrate concentration without enzyme; Y-Substrate concentration with enzyme
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is denoted by X and Y in the given graph?

a)
X-Activation energy without enzyme; Y-Activation energy with enzyme
b)
X-Activation energy with enzyme; Y-Activation energy without enzyme
c)
X-Substrate concentration with enzyme; Y- Substrate concentration without enzyme
d)
X-Substrate concentration without enzyme; Y-Substrate concentration with enzyme
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Most reactions do not start automatically because the reactions have an energy barrier which may be due to hydrogen bonding, absence of precise collisions due to small reactive site, mutual repulsion, etc. External supply of energy needed to overcome this barrier is known as activation energy. The enzyme lowers the activation energy of the reaction and allows a large number of molecules to react at a time.
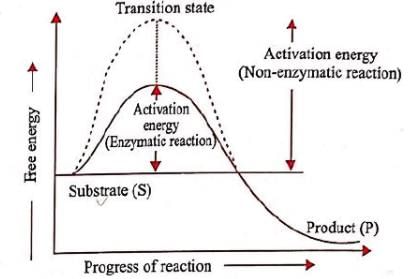
Fig. Lowering of activation energy by enzyme in the energy relations of a chemical reaction
Match the Following

- a)1-A, 2-D
- b)1-B, 2-A
- c)1-A, 2-B
- d)1-D, 2-C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the Following


a)
1-A, 2-D
b)
1-B, 2-A
c)
1-A, 2-B
d)
1-D, 2-C

|
Ambition Institute answered |

The acid soluble pool is characterized by having lower molecular weight compounds ranging from 18 to around 800 daltons and typically includes water and small ions, matching with Option B in Column II. The acid insoluble fraction includes macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides, which generally have molecular weights above ten thousand daltons, aligning with Option A in Column II. Thus, the correct match is 1-B, 2-A.
Topic in NCERT: Nature of enzyme action
Line in NCERT: Error occcured while getting response from embedding
Identify the given structural formulae and select the correct option.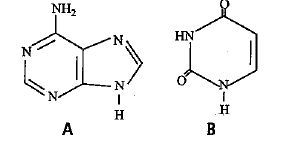
- a)A - Adenine
B - Uracil - b)A - Guanine
B - Thymine - c)A - Adenine
B - Guanine - d)A - Cytosine
B - Thymine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the given structural formulae and select the correct option.
a)
A - Adenine
B - Uracil
B - Uracil
b)
A - Guanine
B - Thymine
B - Thymine
c)
A - Adenine
B - Guanine
B - Guanine
d)
A - Cytosine
B - Thymine
B - Thymine
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Nitrogen bases are heterocyclic compounds. They are of two types, substituted purines and substituted pyrimidines. Purines are larger-sized nitrogen containing biomolecules. They have 9−9-membered double rings. A purine has imidazole ring joined to pyrimidine ring at 44 and 55 positions. It has nitrogens at 1, 3, 7 and 9 positions. There are two types of purines- adenine (A) and guanine (G). Pyrimidines are 6−6- membered rings. A pyrimidine ring has nitrogen at 11 and 33 positions. Pyrimidine bases are of three types-cytosine (C), thymine (T) and uracil (U).
Which of the following options correctly identifies the structural formulae shown in figure?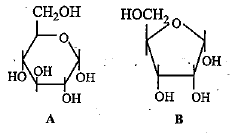
- a)A - Fructose
B - Ribose - b)A - Glucose
B - Deoxyribose - c)A - Glucose
B - Ribose - d)A - Glucose
B - Fructose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options correctly identifies the structural formulae shown in figure?
a)
A - Fructose
B - Ribose
B - Ribose
b)
A - Glucose
B - Deoxyribose
B - Deoxyribose
c)
A - Glucose
B - Ribose
B - Ribose
d)
A - Glucose
B - Fructose
B - Fructose
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Glucose ans ribose both are carbohydrates. Ribose sugar constitutes RNA nucleotides. Glucose is a hexose sugar while ribose is a pentose sugar.
Identify the amino acids given below and select the correct option.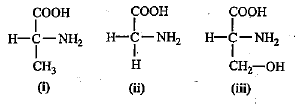
- a)i - Glycine, ii - Serine, iii - Alanine
- b)i - Alanine, ii - Glycine, iii - Serine
- c)i - Alanine, ii - Serine, iii - Glycine
- d)i - Serine, ii - Alanine, iii - Glycine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the amino acids given below and select the correct option.
a)
i - Glycine, ii - Serine, iii - Alanine
b)
i - Alanine, ii - Glycine, iii - Serine
c)
i - Alanine, ii - Serine, iii - Glycine
d)
i - Serine, ii - Alanine, iii - Glycine
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
(i) The amino acid is the basic units of proteins and is formed by one carboxyl bond plus one amine group on the side chain.
(ii) On the basis of the compound present, they are divided into various types, for example, simple amino acid, sulphur containing amino acids, basic amino acids, an aromatic amino acid.
(iii) On the given structure CH3 is present on the side chain, and here the amino acid is alanine and in the second image hydrogen is present as the side chain and so it is the simplest amino acid that is glycine.
(iv) On the third chain, CH₂OH is present and the amino acid is serine.
So, the correct option is 'i - Alanine, ii - Glycine, iii - Serine'
(ii) On the basis of the compound present, they are divided into various types, for example, simple amino acid, sulphur containing amino acids, basic amino acids, an aromatic amino acid.
(iii) On the given structure CH3 is present on the side chain, and here the amino acid is alanine and in the second image hydrogen is present as the side chain and so it is the simplest amino acid that is glycine.
(iv) On the third chain, CH₂OH is present and the amino acid is serine.
So, the correct option is 'i - Alanine, ii - Glycine, iii - Serine'
Given, molecular formula belongs to which of the following groups of biomolecules?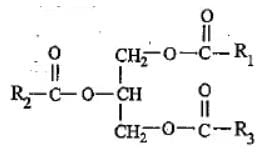
- a)Carbohydrates
- b)Proteins
- c)Nucleic acids
- d)Triglycerides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Given, molecular formula belongs to which of the following groups of biomolecules?

a)
Carbohydrates
b)
Proteins
c)
Nucleic acids
d)
Triglycerides
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Lipids are estres of fatty acids and alcohol. These are hydrophobic in nature and they are insoluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents like benzene, ether and chloroform.
Simple lipids are the esters of fatty acid and glycerol. Fats and oils are the triglycerides of fatty acid and glycerol.
Simple lipids are the esters of fatty acid and glycerol. Fats and oils are the triglycerides of fatty acid and glycerol.
Enzymes which catalyse reactions involving changes in structure of a molecule (inter conversion of geometrical/positional isomers) are:- a)Ligase
- b)Lyase
- c)Isomerase
- d)Hydrolase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes which catalyse reactions involving changes in structure of a molecule (inter conversion of geometrical/positional isomers) are:
a)
Ligase
b)
Lyase
c)
Isomerase
d)
Hydrolase

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Hydrolases: Enzymes catalysing hydrolysis of ester, ether, peptide, glycosidic, C-C, C-halide or P-N bonds.
Lyases: Enzymes that catalyse removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds.
Isomerases: Includes all enzymes catalysing inter-conversion of optical, geometric or positional isomers.
Ligases: Enzymes catalysing the linking together of 2 compounds, e.g., enzymes which catalyse joining of C-O, C-S, C-N, P-O etc. bonds.
Lyases: Enzymes that catalyse removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds.
Isomerases: Includes all enzymes catalysing inter-conversion of optical, geometric or positional isomers.
Ligases: Enzymes catalysing the linking together of 2 compounds, e.g., enzymes which catalyse joining of C-O, C-S, C-N, P-O etc. bonds.
The combination of apoenzyme and coenzyme producesenzyme substrate complex- a)Prosthetic group
- b)Enzyme product complex
- c)Enzyme substrate complex
- d)Holoenzyme
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The combination of apoenzyme and coenzyme producesenzyme substrate complex
a)
Prosthetic group
b)
Enzyme product complex
c)
Enzyme substrate complex
d)
Holoenzyme

|
Lead Academy answered |
- The apoenzyme is the protein part of a conjugated enzyme, and the coenzyme is the non-protein part.
- The combination of the apoenzyme and the coenzyme results in the formation of a functional enzyme which is called holoenzyme. Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the human body.
- They are essential for digesting food, nerve function, muscle, respiration, and among thousands of other roles.
- Conjugation of enzymes to antibodies involves the formation of a stable, covalent linkage between an enzyme.
- Coenzymes, support the functions of enzymes.
- The coenzymes share electrons with the enzymes, rather than lose or gain electrons.
Enzymes are regarded as the:- a)Messengers
- b)Activators
- c)Biocatalysts
- d)Anti bodies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes are regarded as the:
a)
Messengers
b)
Activators
c)
Biocatalysts
d)
Anti bodies

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Enzymes are regarded as the biocatalysts.
- Enzymes are proteins made from amino acids.
- It is made up of hundreds and thousands of amino acids stringed together in a very specific and unique order.
- Any chemical reaction inside a cell or any work that goes on inside a cell is the handiwork of enzymes inside the cell.
Cytidine is a- a)Nitrogenous base
- b)Nucleoside
- c)Nucleotide
- d)Nucleic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cytidine is a
a)
Nitrogenous base
b)
Nucleoside
c)
Nucleotide
d)
Nucleic acid
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Cytosine (C) is a pyrimidine i.e, a nitrogenous base. A combination of a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) with a pentose sugar is known as a nucleoside. Thus the combination of cytosine with ribose sugar results in the formation of a nucleoside called as cytidine, Similarly, The combination of cytosine with deoxyribose sugar is called as deoxycytidine.
Which of the following statements about amino acids is incorrect?- a)Essential amino acids are not synthesised in the body, therefore have to be provided in the diet
- b)Leucine, isoleucine, lysine, valine are essential amino acids
- c)Cysteine and methionine are sulphur containing amino acids
- d)Lysine and arginine are acidic amino acids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about amino acids is incorrect?
a)
Essential amino acids are not synthesised in the body, therefore have to be provided in the diet
b)
Leucine, isoleucine, lysine, valine are essential amino acids
c)
Cysteine and methionine are sulphur containing amino acids
d)
Lysine and arginine are acidic amino acids
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Acidic amino acids have an extra carboxylic group (mono-amino dicarboxylic), e.g., glutamate (glutamic acid or Glu), asparate (aspartic acid or Asp).
Basic amino acids have an additional amino group without forming amides (diamino monocarboxylic), e.g., arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys).
Why are lipids categorized under the acid insoluble fraction despite not having high molecular weights like other macromolecules?- a)Lipids form large polymeric structures similar to proteins.
- b)Lipids are hydrophilic, making them soluble in acidic solutions.
- c)Lipids arrange into cell membrane structures which form vesicles that are not water-soluble when tissues are disrupted.
- d)Lipids have molecular weights above ten thousand daltons.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Lipids form large polymeric structures similar to proteins.
b)
Lipids are hydrophilic, making them soluble in acidic solutions.
c)
Lipids arrange into cell membrane structures which form vesicles that are not water-soluble when tissues are disrupted.
d)
Lipids have molecular weights above ten thousand daltons.

|
Lead Academy answered |
Lipids, though they do not have high molecular weights like other macromolecules, are part of the acid insoluble fraction because they arrange into structures like cell membranes. When tissues are ground up, these membranes break into vesicles that are not water-soluble, leading to their categorization as part of the acid insoluble fraction despite their smaller size.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biomolecules - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biomolecules - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









