All Exams >
UPSC >
Lucent For GK >
All Questions
All questions of The Revolt of 1857 for UPSC CSE Exam
Match the following:
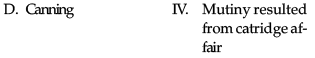
- a)(A-III) (B-II) (C-I) (D-IV)
- b)(A-IV) (B-III) (C-II) (D-I)
- c)(A-I) (B-II) (C-III) (D-IV)
- d)(A-IV) (B-III) (C-I) (D-II)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following:
a)
(A-III) (B-II) (C-I) (D-IV)
b)
(A-IV) (B-III) (C-II) (D-I)
c)
(A-I) (B-II) (C-III) (D-IV)
d)
(A-IV) (B-III) (C-I) (D-II)

|
K.L Institute answered |
B is the correct option.
- Sir John Lawrence, the Chief Commissioner mutiny resulted from cartridge affair
- Sir James Outram, 1st Baronet, English general and political officer in India ... At the outbreak of the Indian Mutiny of 1857 he was recalled from Iran, given ... The British military commander Sir James Outram thought it was a Muslim conspiracy.
- In 1876, at the prompting of Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli when rebellion was formed by Brahmans on religious pretences.
- Charles Canning, the Governor-General of India during the rebellion of 1857.
Who among the following analysed the causes of the uprising of 1857 advocating a reconciliation between the British and the Muslims?- a)Syed Ahmed Khan
- b)Syed Amir Ali
- c)Shah Wali-Ullah
- d)Syed Ahmed Bardvi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who among the following analysed the causes of the uprising of 1857 advocating a reconciliation between the British and the Muslims?
a)
Syed Ahmed Khan
b)
Syed Amir Ali
c)
Shah Wali-Ullah
d)
Syed Ahmed Bardvi

|
Palak Yadav answered |
Sir Sayyed Ahmad khan analysed the cause of uprising of 1857 advocating a reconciliation between the British and Muslims.
Which factor was not responsible for the failure of the Revolt of 1857?
- a)Indians lacked a developed political consciousness.
- b)The educated middle classes did not support the rebels.
- c)There was infighting in the ranks of the rebels.
- d)The rebels had a strong leadership.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which factor was not responsible for the failure of the Revolt of 1857?
a)
Indians lacked a developed political consciousness.
b)
The educated middle classes did not support the rebels.
c)
There was infighting in the ranks of the rebels.
d)
The rebels had a strong leadership.

|
Ikbal Hussain answered |
A and b will be Answer
Who said “Without own hands we shall not our Azadshahi (independent rule) bury”?- a)Rani Lakshmibai
- b)Kunwar Singh
- c)Nana Sahib
- d)Maulavi Ahmadullah
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who said “Without own hands we shall not our Azadshahi (independent rule) bury”?
a)
Rani Lakshmibai
b)
Kunwar Singh
c)
Nana Sahib
d)
Maulavi Ahmadullah
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Answer: A. Rani LakshmibaiRani Lakshmibai, the Queen of Jhansi, is known to have said, "Without own hands we shall not our Azadshahi (independent rule) bury." This quote highlights her determination and courage to fight against the British forces during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Explanation:- Rani Lakshmibai was a prominent figure in the Indian Rebellion of 1857, also known as the First War of Indian Independence.- She led the revolt against British rule in the state of Jhansi, which was annexed by the British East India Company under the Doctrine of Lapse.- The quote showcases her strong belief in self-reliance and the importance of active participation in the struggle for independence.- Rani Lakshmibai's fierce resistance against the British forces earned her a legendary status as a symbol of resistance to British rule in India.
What is the correct chronological order of the following revolts?I. Kacha Nagas revolt of CacharII. Thadoe Kukis revolt of ManipurIII. Munda revolt of Chotanagpur- a)I, II, III
- b)II, I, III
- c)III, II, I
- d)I, III, II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct chronological order of the following revolts?
I. Kacha Nagas revolt of Cachar
II. Thadoe Kukis revolt of Manipur
III. Munda revolt of Chotanagpur
a)
I, II, III
b)
II, I, III
c)
III, II, I
d)
I, III, II
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
Kachnagas revolt took place in Cachar region of Assam in 1882,. The leader of this revolt was Sambudhan. The revolt was crushed brutally by the British
The Munda revolt led by Birsa, called Ulgulan or the great tumult, started in 1899. A series of concerted attacks were unleashed on the British using guerrilla warfare tactics
The Great Kuki Rebellion took place in 1917.
The Munda revolt led by Birsa, called Ulgulan or the great tumult, started in 1899. A series of concerted attacks were unleashed on the British using guerrilla warfare tactics
The Great Kuki Rebellion took place in 1917.
Which one of the following was not a consequence of the Revolt of 1857? The British Raj:- a)Promised to respect the ancient rights, usages and customs of India to abstain from any interference with Indian religion.
- b)Confirmed the treaties of East India Company with the Indian princes, promised to respect their rights and privileges and disclaimed all desire for British territorial expansion at their cost.
- c)Proclaimed that all these found eligible by education, ability and integrity would be truly amditted to offices in the service of the British Raj irrespective of race or creed.
- d)Promised to ensure a minimum surplus in the hands of the Indian peasants, guarantee freedom of religion and customs of India and introduction of Indians in the Administration.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following was not a consequence of the Revolt of 1857? The British Raj:
a)
Promised to respect the ancient rights, usages and customs of India to abstain from any interference with Indian religion.
b)
Confirmed the treaties of East India Company with the Indian princes, promised to respect their rights and privileges and disclaimed all desire for British territorial expansion at their cost.
c)
Proclaimed that all these found eligible by education, ability and integrity would be truly amditted to offices in the service of the British Raj irrespective of race or creed.
d)
Promised to ensure a minimum surplus in the hands of the Indian peasants, guarantee freedom of religion and customs of India and introduction of Indians in the Administration.

|
Manish Ranjan answered |
No
The Scindia of Gwalior, the Raja of Jodhpur and the Nizam of Hyderabad, besides others, helped the British in crushing the Revolt. Who remarked that these rulers and chiefs “acted as the breakwaters to the storm which would have otherwise swept us in once great wave?”- a)Lord Canning
- b)Sir John Lawrence
- c)Lord Curzon
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Scindia of Gwalior, the Raja of Jodhpur and the Nizam of Hyderabad, besides others, helped the British in crushing the Revolt. Who remarked that these rulers and chiefs “acted as the breakwaters to the storm which would have otherwise swept us in once great wave?”
a)
Lord Canning
b)
Sir John Lawrence
c)
Lord Curzon
d)
None of these
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
Answer: A: Lord Canning
Explanation:
- The remark that these rulers and chiefs “acted as the breakwaters to the storm which would have otherwise swept us in one great wave” was made by Lord Canning, who was the Governor-General of India during the 1857 Revolt.
- The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising against the rule of the British East India Company in India.
- The Scindia of Gwalior, the Raja of Jodhpur, and the Nizam of Hyderabad played significant roles in supporting the British during the Revolt.
- Their support was crucial for the British in suppressing the rebellion and maintaining their control over India.
- Lord Canning's statement highlights the importance of these rulers and chiefs in preventing the rebellion from becoming a more significant threat to British rule in India.
Explanation:
- The remark that these rulers and chiefs “acted as the breakwaters to the storm which would have otherwise swept us in one great wave” was made by Lord Canning, who was the Governor-General of India during the 1857 Revolt.
- The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising against the rule of the British East India Company in India.
- The Scindia of Gwalior, the Raja of Jodhpur, and the Nizam of Hyderabad played significant roles in supporting the British during the Revolt.
- Their support was crucial for the British in suppressing the rebellion and maintaining their control over India.
- Lord Canning's statement highlights the importance of these rulers and chiefs in preventing the rebellion from becoming a more significant threat to British rule in India.
A sepoy mutiny had broken out in Bengal as early as- a)1757
- b)1764
- c)1773
- d)1784
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A sepoy mutiny had broken out in Bengal as early as
a)
1757
b)
1764
c)
1773
d)
1784
|
|
Bhargavi Dasgupta answered |
The Sepoy Mutiny, also known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857, was a significant event in Indian history. However, the question states that a sepoy mutiny had broken out in Bengal much earlier. Let's explore this in detail.
The correct answer to the question is option 'B,' which states that the sepoy mutiny had broken out in Bengal in 1764. Here's why:
1. Background: Before we delve into the events of 1764, it's essential to understand the context leading up to it. The British East India Company had established its presence in India since the early 1600s. By the mid-1700s, they had gained significant control over various parts of India, including Bengal, through a combination of diplomacy, trade, and military conquest.
2. Bengal Army: The East India Company recruited Indian soldiers, known as sepoys, to serve in its army. The Bengal Army was the largest and most crucial component of the Company's military establishment. However, the sepoys were treated poorly, with low pay, long hours, and discriminatory practices.
3. The Mutiny: In 1764, the Bengal Army was engaged in a war against the Nawab of Bengal, Siraj-ud-Daula. However, the East India Company had made an alliance with Mir Jafar, one of Siraj-ud-Daula's generals, to overthrow him. When the sepoys discovered this, they were outraged, as Siraj-ud-Daula was their legitimate ruler. They began to mutiny and refused to fight for the British.
4. Consequences: The mutiny was eventually suppressed by the British, but it had significant consequences. The East India Company realized that it could not rely entirely on Indian soldiers and began to recruit more British soldiers. It also introduced various reforms to improve the conditions of the sepoys, such as higher pay and better treatment.
In conclusion, the sepoy mutiny did indeed break out in Bengal in 1764. While it may not have been as significant as the rebellion of 1857, it was a crucial event in Indian history that highlighted the tensions between the Indian soldiers and their British masters.
The correct answer to the question is option 'B,' which states that the sepoy mutiny had broken out in Bengal in 1764. Here's why:
1. Background: Before we delve into the events of 1764, it's essential to understand the context leading up to it. The British East India Company had established its presence in India since the early 1600s. By the mid-1700s, they had gained significant control over various parts of India, including Bengal, through a combination of diplomacy, trade, and military conquest.
2. Bengal Army: The East India Company recruited Indian soldiers, known as sepoys, to serve in its army. The Bengal Army was the largest and most crucial component of the Company's military establishment. However, the sepoys were treated poorly, with low pay, long hours, and discriminatory practices.
3. The Mutiny: In 1764, the Bengal Army was engaged in a war against the Nawab of Bengal, Siraj-ud-Daula. However, the East India Company had made an alliance with Mir Jafar, one of Siraj-ud-Daula's generals, to overthrow him. When the sepoys discovered this, they were outraged, as Siraj-ud-Daula was their legitimate ruler. They began to mutiny and refused to fight for the British.
4. Consequences: The mutiny was eventually suppressed by the British, but it had significant consequences. The East India Company realized that it could not rely entirely on Indian soldiers and began to recruit more British soldiers. It also introduced various reforms to improve the conditions of the sepoys, such as higher pay and better treatment.
In conclusion, the sepoy mutiny did indeed break out in Bengal in 1764. While it may not have been as significant as the rebellion of 1857, it was a crucial event in Indian history that highlighted the tensions between the Indian soldiers and their British masters.
Which social legislation was disliked by many Hindus which made them dislike the British?- a)Abolition to sati
- b)Legislation of widow remarriage
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)Abolition of slavery
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which social legislation was disliked by many Hindus which made them dislike the British?
a)
Abolition to sati
b)
Legislation of widow remarriage
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
Abolition of slavery
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
The correct answer is option (C). Abolition to Sati and Legislation of widow marriage were disliked by hindus and made them dislike the British.
Due to fierce campaign and lobbying of Raja Rammohan Roy and others,Sati practice was formally banned in all the lands under Bengal Presidency by Lord William Bentinck on 4 December 1829. By this regulation, the people who abetted sati were declared guilty of “culpable homicide.”
The Hindu Widows' Remarriage Act, 1856, also Act XV, 1856, enacted on 26 July 1856, legalised the remarriage of Hindu widows in all jurisdictions of India under East India Company rule. It was drafted by Lord Dalhousie and passed by Lord Dalhousie before the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Due to fierce campaign and lobbying of Raja Rammohan Roy and others,Sati practice was formally banned in all the lands under Bengal Presidency by Lord William Bentinck on 4 December 1829. By this regulation, the people who abetted sati were declared guilty of “culpable homicide.”
The Hindu Widows' Remarriage Act, 1856, also Act XV, 1856, enacted on 26 July 1856, legalised the remarriage of Hindu widows in all jurisdictions of India under East India Company rule. It was drafted by Lord Dalhousie and passed by Lord Dalhousie before the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
The privilege of the postage so long enjoyed by the sepoys in the Company’s army was withdrawn with the passing of the Post Office Act of- a)1850
- b)1852
- c)1854
- d)1856
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The privilege of the postage so long enjoyed by the sepoys in the Company’s army was withdrawn with the passing of the Post Office Act of
a)
1850
b)
1852
c)
1854
d)
1856

|
Mainak Mukherjee answered |
The privilege of free postage so long enjoyed by the scpoys was withdrawn with the passing of the Post Office Act of 1854 Besides, the disparity in numbers between European and Indian troops had lately been growing greater. In 1856, the Company's army consisted of 238,000 native and 45,322 British soldiers.
With which single act, did the sepoys transform a mutiny of soldiers into a revolutionary war in 1857- a)By killing officers stationed at Meerut.
- b)When Bahadur Shah II was proclaimed the Emperor of India.
- c)When the Meerut soldiers joined the local infantry in Delhi which had killed their own European officers.
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
With which single act, did the sepoys transform a mutiny of soldiers into a revolutionary war in 1857
a)
By killing officers stationed at Meerut.
b)
When Bahadur Shah II was proclaimed the Emperor of India.
c)
When the Meerut soldiers joined the local infantry in Delhi which had killed their own European officers.
d)
None of these.
|
|
Mrittunjoy Ghosh answered |
B
What causes were responsible for the failure of the Revolt of 1857?I. The rebels lacked a supreme head.I. Most vested interests in India remained firm in their loyalty to the British.III. The rebels had negligible financial resources.IV. Modern scientific means of communication were under the control of the British.- a)I, II, III, IV
- b)I, III, IV
- c)III and IV
- d)II, III, IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What causes were responsible for the failure of the Revolt of 1857?
I. The rebels lacked a supreme head.
I. Most vested interests in India remained firm in their loyalty to the British.
III. The rebels had negligible financial resources.
IV. Modern scientific means of communication were under the control of the British.
a)
I, II, III, IV
b)
I, III, IV
c)
III and IV
d)
II, III, IV
|
|
Ravi Sharma answered |
The main reasons behind the failure of the Revolt of 1857 were :
- Lack of Planning and Co-ordination.
- Weak Leadership of the 1857 Mutiny.
- Superior British Army.
- Limited Supplies and Lack of Modern Communication.
- Lack of Societal Alternative.
- The Princes and Educated Classes did not participate.
- Limited Spread of the Revolt.
Which of the following not only kept aloof from the tremendous political upsurge, but also rendered memorable service to the British in 1857?- a)The middle class
- b)The backward castes
- c)The feudatory princes
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following not only kept aloof from the tremendous political upsurge, but also rendered memorable service to the British in 1857?
a)
The middle class
b)
The backward castes
c)
The feudatory princes
d)
All of these
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
When the British arrived India, they saw rivalry among Indian kings because of land so they use this rivalry against Indian kings as tool of success and they simply help one king to defend or defeat another king and in return British ask for money to maintain army and weapons, if king give them money they help him otherwise they attack him because he/she broke the treaty this is how British empire setup in India.
The first Indian who found a place in GovernorGeneral’s Executive Council was- a)S.P. Sinha
- b)M.M. Malviya
- c)Sir Tegbahadur Sapru
- d)Dr.B.R. Ambedkar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The first Indian who found a place in GovernorGeneral’s Executive Council was
a)
S.P. Sinha
b)
M.M. Malviya
c)
Sir Tegbahadur Sapru
d)
Dr.B.R. Ambedkar

|
Meera Chopra answered |
Historical Context
The inclusion of Indians in the Governor-General's Executive Council marked a significant moment in colonial history. The British administration in India was largely dominated by British officials, but gradual political changes led to increased Indian representation.
S.P. Sinha's Appointment
- Who was S.P. Sinha?
Satyendra Prasad Sinha, popularly known as S.P. Sinha, was a prominent Indian politician and lawyer. His contributions lay in advocating for Indian representation in governance.
- Significance of His Appointment:
In 1919, S.P. Sinha became the first Indian to be appointed to the Governor-General’s Executive Council under the Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms. This was a crucial step in recognizing the role of Indians in the administrative framework of British India.
Impact on Indian Politics
- Paving the Way for Future Leaders:
Sinha's inclusion set a precedent that encouraged other Indian leaders to strive for positions of power within the British administration.
- Catalyst for Political Change:
His appointment symbolized the beginning of a shift towards a more inclusive governance model, which would eventually lead to the demand for greater self-governance and independence.
Conclusion
S.P. Sinha’s appointment as the first Indian in the Governor-General’s Executive Council was a landmark achievement in Indian political history, representing the aspirations of Indian leaders for participation in governance and laying the groundwork for future political advancements.
The inclusion of Indians in the Governor-General's Executive Council marked a significant moment in colonial history. The British administration in India was largely dominated by British officials, but gradual political changes led to increased Indian representation.
S.P. Sinha's Appointment
- Who was S.P. Sinha?
Satyendra Prasad Sinha, popularly known as S.P. Sinha, was a prominent Indian politician and lawyer. His contributions lay in advocating for Indian representation in governance.
- Significance of His Appointment:
In 1919, S.P. Sinha became the first Indian to be appointed to the Governor-General’s Executive Council under the Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms. This was a crucial step in recognizing the role of Indians in the administrative framework of British India.
Impact on Indian Politics
- Paving the Way for Future Leaders:
Sinha's inclusion set a precedent that encouraged other Indian leaders to strive for positions of power within the British administration.
- Catalyst for Political Change:
His appointment symbolized the beginning of a shift towards a more inclusive governance model, which would eventually lead to the demand for greater self-governance and independence.
Conclusion
S.P. Sinha’s appointment as the first Indian in the Governor-General’s Executive Council was a landmark achievement in Indian political history, representing the aspirations of Indian leaders for participation in governance and laying the groundwork for future political advancements.
Khan Bahadur Khan took part in the Revolt of 1857 by leading a rebellion in- a)Allahabad
- b)Bereilly
- c)Satara
- d)Indore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Khan Bahadur Khan took part in the Revolt of 1857 by leading a rebellion in
a)
Allahabad
b)
Bereilly
c)
Satara
d)
Indore
|
|
Tarun Datta answered |
Khan Bahadur Khan Rohilla
(1823 – 24 February 1860) was the grandson of
Hafiz Rahmat Khan
, who was the Nawab of R
hilkhando in Uttar Pradesh. He formed his own government in
Bareilly
in the 1857 Indian revolt against the British. When the
Indian Rebellion of 1857
failed, Bareilly, too, was subjugated by the British. He escaped to
Nepal
where the Nepalese captured him and turned him over to the British. Khan Bahadur Khan Rohilla was sentenced to death and hanged in the Kotwali (Police Station, Dhaka) on 24 February 1860
Before the outbreak of the revolt of 1857 at Meerut Mangal Pandey had become a martyr on 29 March 1857(he was hanged) at- a)Lucknow
- b)Faizabad
- c)Bhagalpur
- d)Barrackpore
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Before the outbreak of the revolt of 1857 at Meerut Mangal Pandey had become a martyr on 29 March 1857(he was hanged) at
a)
Lucknow
b)
Faizabad
c)
Bhagalpur
d)
Barrackpore
|
|
Dishani Choudhary answered |
D is the correct option.Mangal Pandey was arrested and sentenced to death after he attacked British officers in Barrackpore on March 29, 1857. Anticipating a revolt, British authorities moved up his initial execution date from April 18 to April 8, when he was hanged.
Azimullah was an expert political propagandist.He was a Ioyal follower of- a)Rani Lakshmibai
- b)Nana Sahib
- c)Kunwar Singh
- d)Bahadur Shah II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Azimullah was an expert political propagandist.He was a Ioyal follower of
a)
Rani Lakshmibai
b)
Nana Sahib
c)
Kunwar Singh
d)
Bahadur Shah II
|
|
Sahana Menon answered |
Explanation:
Rani Lakshmibai:
Rani Lakshmibai, also known as the Rani of Jhansi, was a prominent figure in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 against British colonial rule. She was a warrior queen and played an active role in the uprising. However, there is no evidence or historical record suggesting that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Rani Lakshmibai.
Nana Sahib:
Nana Sahib, born as Dhondu Pant, was one of the prominent leaders of the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He played a crucial role in the revolt and was considered a symbol of resistance against the British Raj. Nana Sahib was known for his political acumen and military leadership. It is unlikely that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Nana Sahib because there is no historical evidence supporting this claim.
Kunwar Singh:
Kunwar Singh, also known as Veer Kunwar Singh, was a notable freedom fighter from Bihar. He actively participated in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and led a rebellion against the British forces. While Kunwar Singh was a respected leader, there is no mention of Azimullah being his loyal follower in historical records.
Bahadur Shah II:
Bahadur Shah II, also known as Zafar, was the last Mughal emperor of India. He was a figurehead during the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and was widely seen as a symbol of the uprising. Azimullah, being an expert political propagandist, was likely to support and be a loyal follower of Bahadur Shah II, as he would have recognized the symbolic power and influence the emperor held over the masses.
Conclusion:
Based on historical records and the roles of various leaders during the Indian Rebellion of 1857, it can be concluded that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Bahadur Shah II. The emperor's position as a figurehead and symbol of the uprising would have made him an attractive leader for a political propagandist like Azimullah. However, there is no evidence to suggest that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Rani Lakshmibai, Nana Sahib, or Kunwar Singh.
Rani Lakshmibai:
Rani Lakshmibai, also known as the Rani of Jhansi, was a prominent figure in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 against British colonial rule. She was a warrior queen and played an active role in the uprising. However, there is no evidence or historical record suggesting that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Rani Lakshmibai.
Nana Sahib:
Nana Sahib, born as Dhondu Pant, was one of the prominent leaders of the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He played a crucial role in the revolt and was considered a symbol of resistance against the British Raj. Nana Sahib was known for his political acumen and military leadership. It is unlikely that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Nana Sahib because there is no historical evidence supporting this claim.
Kunwar Singh:
Kunwar Singh, also known as Veer Kunwar Singh, was a notable freedom fighter from Bihar. He actively participated in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and led a rebellion against the British forces. While Kunwar Singh was a respected leader, there is no mention of Azimullah being his loyal follower in historical records.
Bahadur Shah II:
Bahadur Shah II, also known as Zafar, was the last Mughal emperor of India. He was a figurehead during the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and was widely seen as a symbol of the uprising. Azimullah, being an expert political propagandist, was likely to support and be a loyal follower of Bahadur Shah II, as he would have recognized the symbolic power and influence the emperor held over the masses.
Conclusion:
Based on historical records and the roles of various leaders during the Indian Rebellion of 1857, it can be concluded that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Bahadur Shah II. The emperor's position as a figurehead and symbol of the uprising would have made him an attractive leader for a political propagandist like Azimullah. However, there is no evidence to suggest that Azimullah was a loyal follower of Rani Lakshmibai, Nana Sahib, or Kunwar Singh.
Which of the following has been accused by some historians of carrying on intrigues with the British during the Revolt of 1857?- a)Zeenat Mahal
- b)Tantia Tope
- c)Kunwar Singh
- d)Maulavi Ahmadullah
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has been accused by some historians of carrying on intrigues with the British during the Revolt of 1857?
a)
Zeenat Mahal
b)
Tantia Tope
c)
Kunwar Singh
d)
Maulavi Ahmadullah
|
|
Shilpa Yadav answered |
Zeenat Mahal has been accused by some historians of carrying on intrigues with the British during the Revolt of 1857.
The Revolt of 1857, also known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857 or the First War of Independence, was a major uprising against British rule in India. It began in Meerut on May 10, 1857, and quickly spread to other parts of the country. The revolt was a result of various grievances, including political, economic, social, and religious factors.
During the revolt, several leaders emerged who played significant roles in organizing and leading the rebellion against British rule. One of these leaders was Zeenat Mahal, who was the wife of the last Mughal Emperor, Bahadur Shah II.
Zeenat Mahal, also known as Begum Zeenat Mahal, was accused by some historians of secretly communicating and collaborating with the British during the revolt. It is believed that she was in contact with British officials and provided them with information about the rebel activities and plans.
However, it is important to note that these accusations are controversial and not universally accepted by all historians. Some argue that Zeenat Mahal was merely trying to protect her family and ensure their safety in a tumultuous time. Others believe that she may have been coerced or manipulated by the British.
Regardless of the truth behind these accusations, Zeenat Mahal's role during the revolt remains a subject of debate among historians. The complexities of her position as the wife of the Mughal Emperor and the political circumstances of the time make it difficult to ascertain her true motivations and actions.
In conclusion, Zeenat Mahal has been accused by some historians of carrying on intrigues with the British during the Revolt of 1857. However, the veracity of these accusations is a matter of historical debate and interpretation.
The Revolt of 1857, also known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857 or the First War of Independence, was a major uprising against British rule in India. It began in Meerut on May 10, 1857, and quickly spread to other parts of the country. The revolt was a result of various grievances, including political, economic, social, and religious factors.
During the revolt, several leaders emerged who played significant roles in organizing and leading the rebellion against British rule. One of these leaders was Zeenat Mahal, who was the wife of the last Mughal Emperor, Bahadur Shah II.
Zeenat Mahal, also known as Begum Zeenat Mahal, was accused by some historians of secretly communicating and collaborating with the British during the revolt. It is believed that she was in contact with British officials and provided them with information about the rebel activities and plans.
However, it is important to note that these accusations are controversial and not universally accepted by all historians. Some argue that Zeenat Mahal was merely trying to protect her family and ensure their safety in a tumultuous time. Others believe that she may have been coerced or manipulated by the British.
Regardless of the truth behind these accusations, Zeenat Mahal's role during the revolt remains a subject of debate among historians. The complexities of her position as the wife of the Mughal Emperor and the political circumstances of the time make it difficult to ascertain her true motivations and actions.
In conclusion, Zeenat Mahal has been accused by some historians of carrying on intrigues with the British during the Revolt of 1857. However, the veracity of these accusations is a matter of historical debate and interpretation.
The troops of which of the following deserted and joined the ranks of Rani Lakshmibai?- a)The Raja of Puwain
- b)The Nizam of Hyderabad
- c)Maharaja Scindia
- d)The Rana of Nepal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The troops of which of the following deserted and joined the ranks of Rani Lakshmibai?
a)
The Raja of Puwain
b)
The Nizam of Hyderabad
c)
Maharaja Scindia
d)
The Rana of Nepal
|
|
Dhruv Yadav answered |
On 1 June 1858 Jayajirao led his forces to Morar to fight a rebel army led by Tatya Tope, Rani Lakshmibai and Rao Sahib. This army had 7,000 infantry, 4,000 cavalry and 12 guns while he had only 1,500 cavalry, his bodyguard of 600 men and 8 guns. He waited for their attack which came at 7 o'clock in the morning; in this attack the rebel cavalry took the guns and most of the Gwalior forces except the bodyguard went over to the rebels. The Maharaja and the remainder fled without stopping until they reached Agra.
Which of the following act abolished all laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste? - a)Abolition of Sati (1829)
- b)Hindu Widow Remarriage Act (1856)
- c)Religious Disabilities Act of 1850
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following act abolished all laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste?
a)
Abolition of Sati (1829)
b)
Hindu Widow Remarriage Act (1856)
c)
Religious Disabilities Act of 1850
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rhea Mehta answered |
Religious Disabilities Act of 1850
The Religious Disabilities Act of 1850 was a significant legislation introduced by the British government in India during the colonial period. The act abolished all laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste. Let's discuss the act in detail:
Background
Before the enactment of the Religious Disabilities Act, there were various laws that affected the rights of people converting to another religion or caste. For instance, the Hindu law did not recognize the conversion of a Hindu to another religion. It declared that a person who renounced Hinduism lost his or her rights to ancestral property. Similarly, the Muslim law did not permit a Muslim to convert to another religion. The converted person was considered an apostate and was liable to be punished.
Provisions of the Act
The Religious Disabilities Act, 1850, was introduced to remove these discriminatory laws. The main provisions of the act were as follows:
- The act declared that no person shall be disqualified from holding any office or employment under the government, or from being an executor, trustee, or legatee, on account of religion.
- It abolished all laws and customs which prevented any person from inheriting property or succeeding to any title, office, or employment on the ground of religion.
- The act also declared that any person who converts to another religion shall not forfeit any property, rights, or privileges that he or she had before the conversion.
- The act further declared that any marriage contracted between persons of different religions shall be valid in law.
Significance of the Act
The Religious Disabilities Act, 1850, was a significant legislation that abolished discriminatory laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste. The act paved the way for religious freedom and equality in India. It recognized the rights of individuals to choose their religion and to practice it freely. The act was a major step towards the secularization of the Indian society and paved the way for other reforms like the Hindu Widow Remarriage Act and the Abolition of Sati Act.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Religious Disabilities Act, 1850, was a landmark legislation that abolished all laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste. The act was a major step towards religious freedom and equality in India. It recognized the rights of individuals to choose their religion and to practice it freely. The act paved the way for the secularization of Indian society and was a major milestone in the history of Indian reforms.
The Religious Disabilities Act of 1850 was a significant legislation introduced by the British government in India during the colonial period. The act abolished all laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste. Let's discuss the act in detail:
Background
Before the enactment of the Religious Disabilities Act, there were various laws that affected the rights of people converting to another religion or caste. For instance, the Hindu law did not recognize the conversion of a Hindu to another religion. It declared that a person who renounced Hinduism lost his or her rights to ancestral property. Similarly, the Muslim law did not permit a Muslim to convert to another religion. The converted person was considered an apostate and was liable to be punished.
Provisions of the Act
The Religious Disabilities Act, 1850, was introduced to remove these discriminatory laws. The main provisions of the act were as follows:
- The act declared that no person shall be disqualified from holding any office or employment under the government, or from being an executor, trustee, or legatee, on account of religion.
- It abolished all laws and customs which prevented any person from inheriting property or succeeding to any title, office, or employment on the ground of religion.
- The act also declared that any person who converts to another religion shall not forfeit any property, rights, or privileges that he or she had before the conversion.
- The act further declared that any marriage contracted between persons of different religions shall be valid in law.
Significance of the Act
The Religious Disabilities Act, 1850, was a significant legislation that abolished discriminatory laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste. The act paved the way for religious freedom and equality in India. It recognized the rights of individuals to choose their religion and to practice it freely. The act was a major step towards the secularization of the Indian society and paved the way for other reforms like the Hindu Widow Remarriage Act and the Abolition of Sati Act.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Religious Disabilities Act, 1850, was a landmark legislation that abolished all laws affecting the rights of persons converting to another religion or caste. The act was a major step towards religious freedom and equality in India. It recognized the rights of individuals to choose their religion and to practice it freely. The act paved the way for the secularization of Indian society and was a major milestone in the history of Indian reforms.
Who openly declared that “the Christianization of India was to be the ultimate end of one continued possession of it”- a)Major Edwards
- b)Colonel Malleson
- c)Lord Curzon
- d)Lord Canning
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who openly declared that “the Christianization of India was to be the ultimate end of one continued possession of it”
a)
Major Edwards
b)
Colonel Malleson
c)
Lord Curzon
d)
Lord Canning

|
Amar Menon answered |
In 1857 Mr. Mangles, the Chairman of the Directors of the East India Company, in the House of Commons said that Providence has entrusted the extensive empire of Hindustan to England in order that the banner of Christ should wave triumphant from one end of India to the other. Everyone must exert all his strength that there may be no dilatoriness on any account in continuing in the country the grand work of making all Indians Christians. Major Edwards also openly declared that the Christianization of India was to be the ultimate end of our continued possession of it. Lord Shaftsbury believed that the failure to Christianize India was the cause of the whole trouble.
The religious sentiments of many Indians were hurt when the Government enacted a law which enabled a convert to Christianity to inherit his ancestral property. This law was enacted in- a)1850
- b)1853
- c)1855
- d)1856
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The religious sentiments of many Indians were hurt when the Government enacted a law which enabled a convert to Christianity to inherit his ancestral property. This law was enacted in
a)
1850
b)
1853
c)
1855
d)
1856
|
|
Nandita Kumar answered |
Background:
The law enabling a convert to Christianity to inherit his ancestral property was enacted in 1850 in India. This law caused a stir among many Indians, particularly those with strong religious sentiments.
Reason for Hurt Sentiments:
1. Religious Beliefs: Many Indians held strong religious beliefs and traditions regarding inheritance and property rights. The idea of a convert to Christianity being able to inherit ancestral property went against these beliefs.
2. Cultural Norms: In Indian society, inheritance rules were often deeply rooted in cultural norms and traditions. The new law disrupted these norms and caused discomfort among those who valued tradition.
3. Perception of Conversion: The provision allowing converts to Christianity to inherit property may have been seen as incentivizing conversion, which could have been viewed as a threat to the dominant religion and culture.
Impact on Society:
1. Protests: The enactment of this law led to protests from various religious groups and individuals who felt that it undermined their beliefs and traditions.
2. Social Unrest: The discontent caused by the law could have contributed to social unrest and tensions within communities that held differing beliefs.
3. Legal Challenges: The law may have faced legal challenges from groups or individuals who believed it was unconstitutional or discriminatory.
In conclusion, the law enacted in 1850 allowing converts to Christianity to inherit ancestral property in India stirred religious sentiments and caused unrest among those who held traditional beliefs and values. It highlighted the complex interplay between religious beliefs, cultural norms, and legal provisions in a diverse and multicultural society like India.
Match the following leaders of the Revolt of 1857 with their centres of activity:
- a)[A-I], [B-III]
- b)[A-II], [B-I]
- c)[A-III], [B-II]
- d)[A-I], [B-II]
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following leaders of the Revolt of 1857 with their centres of activity:
a)
[A-I], [B-III]
b)
[A-II], [B-I]
c)
[A-III], [B-II]
d)
[A-I], [B-II]

|
Arshiya Mehta answered |
The revolt spread over the entire area from the neighborhood of Patna to the borders of Rajasthan. The main centers of revolt in these regions namely Kanpur, Lucknow, Bareilly, Jhansi, Gwalior, and Arrah in Bihar. Following is a list of important leaders who took part in the revolt from different parts of the country:
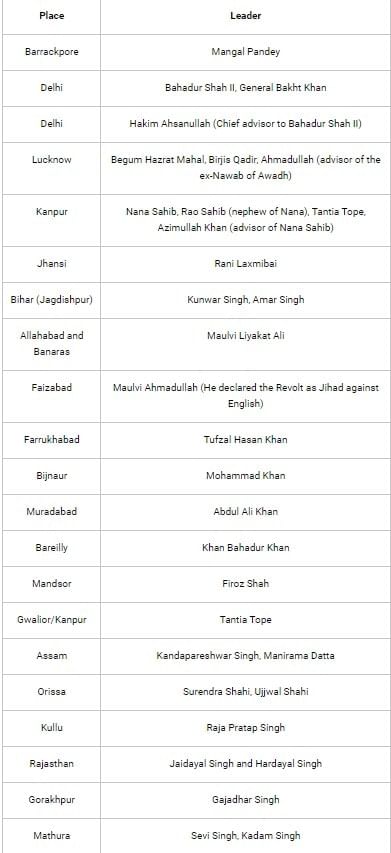
The revolt of 1857 was an unprecedented event in the history of British rule in India. It united, though in a limited way, many sections of Indian society for a common cause. Though the revolt failed to achieve the desired goal, it sowed the seeds of Indian nationalism.
Which of the following was not a major cause of the Revolt of 1857?- a)Pitiabie living conditions of Indian soldiers.
- b)Fear of the princes and zamindars that they would lose their possessions to the British.
- c)Fear of the masses that their religion would be interfered by the British.
- d)A strong patriotic fervour among Indian soldiers and the common people.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was not a major cause of the Revolt of 1857?
a)
Pitiabie living conditions of Indian soldiers.
b)
Fear of the princes and zamindars that they would lose their possessions to the British.
c)
Fear of the masses that their religion would be interfered by the British.
d)
A strong patriotic fervour among Indian soldiers and the common people.

|
Anshika Singh answered |
Ill-treatment of Indian soldiers: The East India Company discriminated against their Indian sepoys. They were poorly paid, ill-fed and badly housed. They were forbidden from wearing any caste or sectarian marks, beads or turbans. As a result, there was resentment among the Indian troops.
Decay of Cottage Industries and Handicrafts: Because of the British policy of preferential treatment to British businesses, Indian industries were gradually destroyed. By the middle of the 19th century, export of cotton and silk goods had practically ceased. The misery of the unemployed artisans was further complemented by the disappearance of their traditional patrons and buyers, i.e. the princes, chieftains and zamindars.
Decay of Cottage Industries and Handicrafts: Because of the British policy of preferential treatment to British businesses, Indian industries were gradually destroyed. By the middle of the 19th century, export of cotton and silk goods had practically ceased. The misery of the unemployed artisans was further complemented by the disappearance of their traditional patrons and buyers, i.e. the princes, chieftains and zamindars.
Why did the taluqdars (zamindars) of Avadh become the most dangerous opponents of British rule?- a)Their revenue from land was drastically reduced by the British.
- b)A few of them were killed by the Company’s soldiers.
- c)The estates of a majority of the taluqdars were confiscated by the British.
- d)Both (a) and (b).
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Why did the taluqdars (zamindars) of Avadh become the most dangerous opponents of British rule?
a)
Their revenue from land was drastically reduced by the British.
b)
A few of them were killed by the Company’s soldiers.
c)
The estates of a majority of the taluqdars were confiscated by the British.
d)
Both (a) and (b).

|
Anshika Singh answered |
The British confiscated the estates of a majority of the taluqdars or zamindars. These dispossessed taluqdars, numbering nearly 21,000, anxious to regain their lost estates and position, became the most dangerous opponents of the British rule.
Match the following:
- a)[A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
- b)[A-II], [B-I], [C-III]
- c)[A-III], [B-II], [C-I]
- d)[A-III], [B-I], [C-II]
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following:
a)
[A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
b)
[A-II], [B-I], [C-III]
c)
[A-III], [B-II], [C-I]
d)
[A-III], [B-I], [C-II]
|
|
Anshul Saini answered |
The IPC was enacted in 1860, while
The Indian Divorce Act, 1869
and The Criminal Procedure Code, 1861 was passed by the British parliament. The CrPC was created for the first time ever in 1882 and then amended in 1898, then according to the 41st Law Commission report in 1973.
The selfishness and the tendency on the part of the leaders to form cliques made the Revolt loss its vitality. Azimullah asked his leader not to visit Delhi lest he be overshadowed by the Emperor Bahadur Shah II. Azimullah was the political advisor of- a)Tantia Tope
- b)Nana Sahib
- c)Sir John Kaye
- d)Khan Bahadur Khan
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The selfishness and the tendency on the part of the leaders to form cliques made the Revolt loss its vitality. Azimullah asked his leader not to visit Delhi lest he be overshadowed by the Emperor Bahadur Shah II. Azimullah was the political advisor of
a)
Tantia Tope
b)
Nana Sahib
c)
Sir John Kaye
d)
Khan Bahadur Khan
|
|
Asha Kulkarni answered |
The correct answer is B as The selfishness and the tendency on the part of the leaders to form cliques made the Revolt loss its vitality. Azimullah asked his leader not to visit Delhi lest he be overshadowed by the Emperor Bahadur Shah II. Azimullah was the political advisor of NANA SAHIB.
Which of the following had warned the British Government in 1857 that if it did not suppress the Revolt in time, it would “find other characters on the state, with whom to contend, besides the princes of India”?- a)Benjamin Disraelie
- b)Sir John Lawrence
- c)Sir John Kaye
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following had warned the British Government in 1857 that if it did not suppress the Revolt in time, it would “find other characters on the state, with whom to contend, besides the princes of India”?
a)
Benjamin Disraelie
b)
Sir John Lawrence
c)
Sir John Kaye
d)
None of these
|
|
Pallavi Rane answered |
Benjamin Disraelie had warned the British Government in 1857 that if it did not suppress the Revolt in time, it would “find other characters on the state, with whom to contend, besides the princes of India”.
Which of the following was probably the weakest link in the chain of leadership of the Revolt of 1857?- a)Bahadur Shah II
- b)Kunwar Singh
- c)Nana Sahib
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was probably the weakest link in the chain of leadership of the Revolt of 1857?
a)
Bahadur Shah II
b)
Kunwar Singh
c)
Nana Sahib
d)
None of these
|
|
Nidhi Shah answered |
Weakness in the Chain of Leadership in the Revolt of 1857
Introduction:
The Revolt of 1857 was a significant event in the history of India, which marked the beginning of the end of British rule. The rebellion was led by a group of Indian leaders who fought against the British East India Company's exploitative policies. However, the chain of leadership during the revolt was not strong enough, and there were some weak links that affected the outcome of the rebellion.
Weakest Link in the Chain of Leadership:
Out of the three options given, Bahadur Shah II was probably the weakest link in the chain of leadership during the revolt of 1857. He was the last Mughal emperor, who was declared the leader of the rebellion but lacked the necessary leadership qualities to lead an armed rebellion against the British.
Reasons for Bahadur Shah II's Weakness:
1. Lack of military experience: Bahadur Shah II had no military experience, and he was more interested in poetry and music than warfare. This lack of experience made it difficult for him to lead the armed rebellion effectively.
2. Age and Health Issues: Bahadur Shah II was 82 years old during the revolt, and his health was not good. He suffered from various ailments, which made it difficult for him to take active part in the rebellion.
3. Lack of Political Support: Bahadur Shah II did not have the support of most of the Indian leaders who participated in the rebellion. Many of them saw him as a figurehead, and it was difficult for him to assert his authority over them.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Bahadur Shah II was probably the weakest link in the chain of leadership during the revolt of 1857. His lack of military experience, age and health issues, and lack of political support affected the outcome of the rebellion. However, it is essential to acknowledge the contributions of all the Indian leaders who participated in the revolt and fought against the British East India Company's oppressive policies.
Introduction:
The Revolt of 1857 was a significant event in the history of India, which marked the beginning of the end of British rule. The rebellion was led by a group of Indian leaders who fought against the British East India Company's exploitative policies. However, the chain of leadership during the revolt was not strong enough, and there were some weak links that affected the outcome of the rebellion.
Weakest Link in the Chain of Leadership:
Out of the three options given, Bahadur Shah II was probably the weakest link in the chain of leadership during the revolt of 1857. He was the last Mughal emperor, who was declared the leader of the rebellion but lacked the necessary leadership qualities to lead an armed rebellion against the British.
Reasons for Bahadur Shah II's Weakness:
1. Lack of military experience: Bahadur Shah II had no military experience, and he was more interested in poetry and music than warfare. This lack of experience made it difficult for him to lead the armed rebellion effectively.
2. Age and Health Issues: Bahadur Shah II was 82 years old during the revolt, and his health was not good. He suffered from various ailments, which made it difficult for him to take active part in the rebellion.
3. Lack of Political Support: Bahadur Shah II did not have the support of most of the Indian leaders who participated in the rebellion. Many of them saw him as a figurehead, and it was difficult for him to assert his authority over them.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Bahadur Shah II was probably the weakest link in the chain of leadership during the revolt of 1857. His lack of military experience, age and health issues, and lack of political support affected the outcome of the rebellion. However, it is essential to acknowledge the contributions of all the Indian leaders who participated in the revolt and fought against the British East India Company's oppressive policies.
Match the following according to the founder of the departments:A. Public Works DepartmentI. DalhousieB. Department of Commerce & IndustryII. CurzonC. Income-taxIII.Canning- a)IA-II], [B-I], [C-III]
- b)[A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
- c)[A-III], |B-I], [C-II]
- d)[A-I], IB-III]. [C-II]
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following according to the founder of the departments:
A. Public Works Department
I. Dalhousie
B. Department of Commerce & Industry
II. Curzon
C. Income-tax
III.Canning
a)
IA-II], [B-I], [C-III]
b)
[A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
c)
[A-III], |B-I], [C-II]
d)
[A-I], IB-III]. [C-II]
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The correct match is:
B: [A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
Explanation:
- Public Works Department was founded by Dalhousie (A-I). Lord Dalhousie established the Public Works Department in 1854 to improve the infrastructure and development of the country.
- Department of Commerce & Industry was founded by Curzon (B-II). Lord Curzon established the Department of Commerce & Industry in 1900 to promote trade and commerce in India.
- Income-tax was introduced by Canning (C-III). Lord Canning introduced Income-tax in 1860 as a financial measure to support the British administration in India.
B: [A-I], [B-II], [C-III]
Explanation:
- Public Works Department was founded by Dalhousie (A-I). Lord Dalhousie established the Public Works Department in 1854 to improve the infrastructure and development of the country.
- Department of Commerce & Industry was founded by Curzon (B-II). Lord Curzon established the Department of Commerce & Industry in 1900 to promote trade and commerce in India.
- Income-tax was introduced by Canning (C-III). Lord Canning introduced Income-tax in 1860 as a financial measure to support the British administration in India.
20,000 troops of which state went over to Tantia Tope and Rani Lakshmi Bai?- a)Gwalior
- b)Hyderabad
- c)Bengal
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
20,000 troops of which state went over to Tantia Tope and Rani Lakshmi Bai?
a)
Gwalior
b)
Hyderabad
c)
Bengal
d)
None of these
|
|
Samarth Unni answered |
Tantia Tope
came to the relief of
Rani Lakshmibai of Jhansi and with her seized the city of Gwalior.
The simmering discontent among the masses in India culminated in a violent outburst in 1857. The most important causes of the popular discontent was- a)The British land revenue policies.
- b)The British systems of law administration.
- c)The economic exploitation of India by the British.
- d)The foreignness of the British rule.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The simmering discontent among the masses in India culminated in a violent outburst in 1857. The most important causes of the popular discontent was
a)
The British land revenue policies.
b)
The British systems of law administration.
c)
The economic exploitation of India by the British.
d)
The foreignness of the British rule.

|
Rajat Mukherjee answered |
The most important cause of popular discontent was the British policy of economically exploiting India. This hurt all sections of society. The peasants suffered due to high revenue demands and the strict revenue collection policy. Artisans and craftsmen were ruined by the large-scale influx of cheap British manufactured goods into India which, in turn, made their hand-made goods uneconomical to produce. People who made a living by following religious and cultural pursuits lost their source of livelihood due to the withdrawal of royal patronage caused by the displacement of the old ruling classes. A corrupt and unresponsive administration added to the miseries of the people.
What is the correct sequence of the following events?I. Annexation of OudhII. Abolition of Peshwa’s PensionIII. Pensioning off the Rani of Jhansi- a)II, III, I
- b)I, II, III
- c)III, I, II
- d)II, I, III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct sequence of the following events?
I. Annexation of Oudh
II. Abolition of Peshwa’s Pension
III. Pensioning off the Rani of Jhansi
a)
II, III, I
b)
I, II, III
c)
III, I, II
d)
II, I, III
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
The correct sequence of the following events is:
II. Abolition of Peshwa’s Pension
III. Pensioning off the Rani of Jhansi
I. Annexation of Oudh
The abolition of Peshwa's pension took place in 1818, while the pensioning off of the Rani of Jhansi happened in 1854. The annexation of Oudh took place in 1856. Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
What was the main weakness of the Revolt of 1857?
- a)The Revolt lacked mass support.
- b)All of these
- c)The lack of common ideal among sepoys was the cause of the failure.
- d)The sepoys didn’t have any support from the ruling prince.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the main weakness of the Revolt of 1857?
a)
The Revolt lacked mass support.
b)
All of these
c)
The lack of common ideal among sepoys was the cause of the failure.
d)
The sepoys didn’t have any support from the ruling prince.

|
Anshika Singh answered |
The following were the causes of the failure of 1857 Revolt:
- The Revolt was a failure due to localized and poorly organized.
- The Revolt lacked mass support.
- The lack of common ideal among sepoys was the cause of the failure.
- It was hard to find a leader who has the military capability and political skills.
- The sepoys didn’t have any support from the ruling prince.
Where was an entire garrison wiped out after being assured of safe conduct?- a)Kanpur
- b)Meerut
- c)Satara
- d)Faizabad
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where was an entire garrison wiped out after being assured of safe conduct?
a)
Kanpur
b)
Meerut
c)
Satara
d)
Faizabad
|
|
Bhavya Bajaj answered |
The correct answer is option 'A' i.e. Kanpur.
Kanpur is located in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It was the site of a significant event during India's struggle for independence from British rule.
The Incident:
In 1857, Indian soldiers in the British army, known as sepoys, revolted against their British officers. This rebellion, which spread throughout northern India, is known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857 or the First War of Indian Independence.
In June 1857, a group of sepoys in Kanpur rebelled against their British officers and captured the city. They were led by Nana Sahib, the adopted son of the last Peshwa (ruler) of the Maratha Empire. The British garrison in Kanpur, consisting of around 900 soldiers, was taken captive by the rebels.
Assured of Safe Conduct:
Nana Sahib assured the British garrison that they would be provided safe passage to the nearest British outpost if they surrendered their weapons. The British soldiers, who were running low on supplies and ammunition, agreed to the offer.
However, Nana Sahib did not keep his promise. Instead of providing safe passage, he and his followers massacred the British soldiers in a brutal manner. The exact number of casualties is disputed, but it is believed that around 120 women and children were killed.
Impact:
The massacre at Kanpur was a turning point in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. It led to a brutal crackdown by the British, who were determined to suppress the rebellion. The British eventually recaptured Kanpur and executed many of the rebels, including Nana Sahib. The rebellion was finally crushed in 1858, and India remained under British rule until 1947.
Conclusion:
The massacre at Kanpur is a reminder of the brutality of colonialism and the sacrifices made by Indians in their struggle for freedom. It is also a cautionary tale about the dangers of trusting one's enemy, as the British soldiers in Kanpur learned to their cost.
Kanpur is located in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It was the site of a significant event during India's struggle for independence from British rule.
The Incident:
In 1857, Indian soldiers in the British army, known as sepoys, revolted against their British officers. This rebellion, which spread throughout northern India, is known as the Indian Rebellion of 1857 or the First War of Indian Independence.
In June 1857, a group of sepoys in Kanpur rebelled against their British officers and captured the city. They were led by Nana Sahib, the adopted son of the last Peshwa (ruler) of the Maratha Empire. The British garrison in Kanpur, consisting of around 900 soldiers, was taken captive by the rebels.
Assured of Safe Conduct:
Nana Sahib assured the British garrison that they would be provided safe passage to the nearest British outpost if they surrendered their weapons. The British soldiers, who were running low on supplies and ammunition, agreed to the offer.
However, Nana Sahib did not keep his promise. Instead of providing safe passage, he and his followers massacred the British soldiers in a brutal manner. The exact number of casualties is disputed, but it is believed that around 120 women and children were killed.
Impact:
The massacre at Kanpur was a turning point in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. It led to a brutal crackdown by the British, who were determined to suppress the rebellion. The British eventually recaptured Kanpur and executed many of the rebels, including Nana Sahib. The rebellion was finally crushed in 1858, and India remained under British rule until 1947.
Conclusion:
The massacre at Kanpur is a reminder of the brutality of colonialism and the sacrifices made by Indians in their struggle for freedom. It is also a cautionary tale about the dangers of trusting one's enemy, as the British soldiers in Kanpur learned to their cost.
Though nearly 80 years old, which leader was perhaps the best military leader and strategist of the Revolt of 1857?- a)Nana Sahib
- b)Khan Bahadur Khan
- c)Kunwar Singh
- d)Bahadur Shah II
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Though nearly 80 years old, which leader was perhaps the best military leader and strategist of the Revolt of 1857?
a)
Nana Sahib
b)
Khan Bahadur Khan
c)
Kunwar Singh
d)
Bahadur Shah II
|
|
Anoushka Reddy answered |
Kunwar Singh, a ruined and discontented zamindar of Jagdishpur near Arrah, was the chief organiser of the revolt in Bihar. Though nearly 80 year old, he was perhaps the most outstanding military leader and strategist of the Revolt.
Who can be called the greatest heroes of the Revolt of 1857?- a)The peasants
- b)The sepoys
- c)Rani Lakshmibai
- d)Nana Sahib
- e)Both (c) and (d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who can be called the greatest heroes of the Revolt of 1857?
a)
The peasants
b)
The sepoys
c)
Rani Lakshmibai
d)
Nana Sahib
e)
Both (c) and (d
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 occurred as the result of an accumulation of factors over time, rather than any single event. The sepoys were Indian soldiers who were recruited into the Company's army. Just before the rebellion, there were over 300,000 sepoys in the army, compared to about 50,000 British.
Before 1857, Christian missionaries tried to convert Indians to their faith. The right of unrestricted entry of Christian missionaries into India was conceded by- a)The Regulating Act, 1773
- b)Pitt’s India Act, 1784
- c)Charter Act of 1813
- d)Charter Act of 1833
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Before 1857, Christian missionaries tried to convert Indians to their faith. The right of unrestricted entry of Christian missionaries into India was conceded by
a)
The Regulating Act, 1773
b)
Pitt’s India Act, 1784
c)
Charter Act of 1813
d)
Charter Act of 1833

|
Anshika Singh answered |
The Character Act of 1813 was the first parliamentary approval for propagation of Christianity in India.
The policy of modernising Indian society and culture was also encouraged by the Christian missionaries and religious minded persons such as William Wilberforce and Charles Grant, the Chairman of the Court of Directors of the East India Company, who wanted to spread Christianity in India. They too adopted a critical attitude towards Indian society but on religious grounds. They passionately believed that Christianity alone was the true
The English language played an important role in this respect. It became the medium for the spread of modern ideas. It also became the medium of communication and exchange of ideas between educated Indians from different linguistic regions of the country.
The fear of the greased cartridge can be accepted as a temporary, accidental and immediate cause. Why can’t it be regarded as a major political cause responsible for the outbreak of the revolt of 1857?
- a)Nana Sahib and Rani of Jhansi were never going to serve in the company’s army.
- b)If the revolt had been wholly or chiefly due to the cartridges, it would have been stopped suddenly as soon as the English GovernorGeneral issued a proclamation that they wouldn’t be used anymore.
- c)Both (a) and (b).
- d)Historians are vague about this incident.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The fear of the greased cartridge can be accepted as a temporary, accidental and immediate cause. Why can’t it be regarded as a major political cause responsible for the outbreak of the revolt of 1857?
a)
Nana Sahib and Rani of Jhansi were never going to serve in the company’s army.
b)
If the revolt had been wholly or chiefly due to the cartridges, it would have been stopped suddenly as soon as the English GovernorGeneral issued a proclamation that they wouldn’t be used anymore.
c)
Both (a) and (b).
d)
Historians are vague about this incident.
|
|
Muskaan Dey answered |
The political causes for the First War of Independence (1857) include:
(a) British policy of expansion
(b) Disrespect shown to Bahadur Shah
(c) Treatment given to Nana Saheb and Rani Laxmi Bai
(d) Absentee sovereignty of the British
(a) British policy of expansion
(b) Disrespect shown to Bahadur Shah
(c) Treatment given to Nana Saheb and Rani Laxmi Bai
(d) Absentee sovereignty of the British
How did the British hurt the sentiments of the Muslims before the Mutiny of 1857?I. They did not recognise the successor of Bahadur Shah, Faqir-ud-din.II. In 1849, Dalhousie announced that the successor to Bahadur will have to leave Red Fort and move to the Qutab.III. In 1856, Canning announced that after Bahadur Shah’s death the Mughals would lose the title of kings and would be known as mere princes.IV. A son of Bahadur Shah was killed by the British.- a)I, II, III, IV
- b)II and III
- c)II, III, IV
- d)I, II, III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How did the British hurt the sentiments of the Muslims before the Mutiny of 1857?
I. They did not recognise the successor of Bahadur Shah, Faqir-ud-din.
II. In 1849, Dalhousie announced that the successor to Bahadur will have to leave Red Fort and move to the Qutab.
III. In 1856, Canning announced that after Bahadur Shah’s death the Mughals would lose the title of kings and would be known as mere princes.
IV. A son of Bahadur Shah was killed by the British.
a)
I, II, III, IV
b)
II and III
c)
II, III, IV
d)
I, II, III
|
|
Dipika Sen answered |
The correct option is C.
As the third statement is not related to the given topic.
In 1856 Lord Canning announced that after the death of Bahadur Shah his successors would not be allowed to use the imperial titles and dignities with their names, this announcement adversely affected the Mughal Dynasty in India.
As the third statement is not related to the given topic.
In 1856 Lord Canning announced that after the death of Bahadur Shah his successors would not be allowed to use the imperial titles and dignities with their names, this announcement adversely affected the Mughal Dynasty in India.
After the revolt was crushed, Begum Hazrat Mahal of Avadh was compelled to hide in Nepal.Many leaders died. One such guerilla who waged a warfare in the jungles of central India was being betrayed and hanged in 1859. Who was this leader?- a)Tantia Tope
- b)Kunwar Singh
- c)Rani Lakshmibai
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
After the revolt was crushed, Begum Hazrat Mahal of Avadh was compelled to hide in Nepal.Many leaders died. One such guerilla who waged a warfare in the jungles of central India was being betrayed and hanged in 1859. Who was this leader?
a)
Tantia Tope
b)
Kunwar Singh
c)
Rani Lakshmibai
d)
None of these
|
|
Anjali Tiwari answered |
**Answer:**
**A) Tantia Tope**
Tatya Tope, also known as Tantia Tope, was one of the key leaders of the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He was born as Ramachandra Pandurang Tope in 1814 in Pune, Maharashtra. Tantia Tope played a crucial role in organizing and leading the rebellion against the British East India Company.
**Role in the Rebellion:**
1. **Leadership in Central India:** After the revolt was crushed in Avadh (Awadh) and many leaders were either killed or forced into hiding, Tantia Tope emerged as one of the prominent leaders of the rebellion in Central India. He organized and led guerilla warfare against the British forces.
2. **Jungle Warfare:** Tantia Tope and his followers took refuge in the jungles of Central India, where they continued to resist British rule. They employed guerilla tactics, using the dense forest cover to their advantage. This strategy allowed them to launch surprise attacks on British forces and then retreat quickly into the forests, making it difficult for the British to capture them.
3. **Betrayal and Capture:** Despite his efforts to evade capture, Tantia Tope was eventually betrayed by a fellow rebel. In 1859, he was captured by the British near the town of Shivpuri in present-day Madhya Pradesh. The British forces, led by General Napier, arrested Tantia Tope and his loyalists.
4. **Trial and Execution:** Tantia Tope was put on trial by the British for his role in the rebellion. He was charged with waging war against the British East India Company. In April 1859, Tantia Tope was convicted and sentenced to death by hanging. On April 18, 1859, he was executed in Shivpuri.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, Tantia Tope was a prominent leader during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He played a crucial role in leading guerilla warfare in the jungles of Central India. However, he was eventually betrayed and captured by the British, leading to his trial and execution in 1859.
**A) Tantia Tope**
Tatya Tope, also known as Tantia Tope, was one of the key leaders of the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He was born as Ramachandra Pandurang Tope in 1814 in Pune, Maharashtra. Tantia Tope played a crucial role in organizing and leading the rebellion against the British East India Company.
**Role in the Rebellion:**
1. **Leadership in Central India:** After the revolt was crushed in Avadh (Awadh) and many leaders were either killed or forced into hiding, Tantia Tope emerged as one of the prominent leaders of the rebellion in Central India. He organized and led guerilla warfare against the British forces.
2. **Jungle Warfare:** Tantia Tope and his followers took refuge in the jungles of Central India, where they continued to resist British rule. They employed guerilla tactics, using the dense forest cover to their advantage. This strategy allowed them to launch surprise attacks on British forces and then retreat quickly into the forests, making it difficult for the British to capture them.
3. **Betrayal and Capture:** Despite his efforts to evade capture, Tantia Tope was eventually betrayed by a fellow rebel. In 1859, he was captured by the British near the town of Shivpuri in present-day Madhya Pradesh. The British forces, led by General Napier, arrested Tantia Tope and his loyalists.
4. **Trial and Execution:** Tantia Tope was put on trial by the British for his role in the rebellion. He was charged with waging war against the British East India Company. In April 1859, Tantia Tope was convicted and sentenced to death by hanging. On April 18, 1859, he was executed in Shivpuri.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, Tantia Tope was a prominent leader during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He played a crucial role in leading guerilla warfare in the jungles of Central India. However, he was eventually betrayed and captured by the British, leading to his trial and execution in 1859.
Before the Revolt of 1857, the Inam Commission at Bombay, appointed by Lord Dalhousie, investigated the titles of landowners. What was the result of this investigation?- a)Some land-owners were arrested and put to death.
- b)There were many rebellions led by land-owners in the Deccan and parts of Bihar and Bengal.
- c)20,000 estates in the Deccan were confiscated.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Before the Revolt of 1857, the Inam Commission at Bombay, appointed by Lord Dalhousie, investigated the titles of landowners. What was the result of this investigation?
a)
Some land-owners were arrested and put to death.
b)
There were many rebellions led by land-owners in the Deccan and parts of Bihar and Bengal.
c)
20,000 estates in the Deccan were confiscated.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Madhurima Deshpande answered |
The result of the investigation conducted by the Inam Commission at Bombay, appointed by Lord Dalhousie, before the Revolt of 1857 was that 20,000 estates in the Deccan were confiscated. This decision had significant implications for the landowners and the overall socio-political landscape of the region.
The Inam Commission was established to investigate the titles of landowners, particularly in the Deccan region. The commission aimed to determine the legitimacy of land grants, known as inams, which were given to individuals or institutions by the Mughal and Maratha rulers. These land grants exempted the owners from paying land revenue.
The investigation revealed that many of these land grants were either fraudulent or invalid. The commission found numerous instances where landowners had obtained inams unlawfully or through forged documents. As a result, the commission recommended the confiscation of approximately 20,000 estates in the Deccan.
This decision had a profound impact on the affected landowners. The confiscation of their estates meant that they lost their traditional source of income and livelihood. Many of them were also stripped of their social status and influence. This created a sense of deep resentment and anger among the landowners, who felt that their rights and privileges were being violated.
Additionally, the confiscation of the estates led to a significant redistribution of land and wealth. The confiscated estates were brought under direct control of the British administration, which further strengthened their grip on the region. This move also disrupted the existing power dynamics and social structures, as the British favored certain individuals and communities over others in the allocation of land.
It is important to note that while the investigation by the Inam Commission and the subsequent confiscation of estates contributed to the underlying discontent that eventually led to the Revolt of 1857, it was not the sole cause of the rebellion. The revolt had multiple factors, including economic, political, and social grievances, which were exacerbated by British policies and actions.
In conclusion, the result of the investigation conducted by the Inam Commission at Bombay, appointed by Lord Dalhousie, before the Revolt of 1857 was the confiscation of approximately 20,000 estates in the Deccan. This decision had far-reaching consequences for the affected landowners and the overall socio-political landscape of the region.
The Inam Commission was established to investigate the titles of landowners, particularly in the Deccan region. The commission aimed to determine the legitimacy of land grants, known as inams, which were given to individuals or institutions by the Mughal and Maratha rulers. These land grants exempted the owners from paying land revenue.
The investigation revealed that many of these land grants were either fraudulent or invalid. The commission found numerous instances where landowners had obtained inams unlawfully or through forged documents. As a result, the commission recommended the confiscation of approximately 20,000 estates in the Deccan.
This decision had a profound impact on the affected landowners. The confiscation of their estates meant that they lost their traditional source of income and livelihood. Many of them were also stripped of their social status and influence. This created a sense of deep resentment and anger among the landowners, who felt that their rights and privileges were being violated.
Additionally, the confiscation of the estates led to a significant redistribution of land and wealth. The confiscated estates were brought under direct control of the British administration, which further strengthened their grip on the region. This move also disrupted the existing power dynamics and social structures, as the British favored certain individuals and communities over others in the allocation of land.
It is important to note that while the investigation by the Inam Commission and the subsequent confiscation of estates contributed to the underlying discontent that eventually led to the Revolt of 1857, it was not the sole cause of the rebellion. The revolt had multiple factors, including economic, political, and social grievances, which were exacerbated by British policies and actions.
In conclusion, the result of the investigation conducted by the Inam Commission at Bombay, appointed by Lord Dalhousie, before the Revolt of 1857 was the confiscation of approximately 20,000 estates in the Deccan. This decision had far-reaching consequences for the affected landowners and the overall socio-political landscape of the region.
Lord Dalhousie’s annexations had caused suspicion and uneasiness in the minds of most ruling princes in India. Which one of the following states was not annexed by the British under Dalhousie’s Doctrine of Lapse?- a)The Punjab
- b)Sambalpur
- c)Satara
- d)Nagpur
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lord Dalhousie’s annexations had caused suspicion and uneasiness in the minds of most ruling princes in India. Which one of the following states was not annexed by the British under Dalhousie’s Doctrine of Lapse?
a)
The Punjab
b)
Sambalpur
c)
Satara
d)
Nagpur
|
|
Amrita Saha answered |
Lord Dalhousie, whose full name was James Andrew Broun-Ramsay, was a British statesman and colonial administrator who served as the Governor-General of India from 1848 to 1856. He is known for his ambitious modernization and reform policies, which greatly transformed India during his tenure.
Dalhousie introduced several significant reforms in various fields, including infrastructure, education, communication, and administration. He initiated the construction of railways, bridges, and roads, which helped connect different parts of India and facilitated trade and commerce. He also established the telegraph network in India, improving communication and connecting the country with the outside world.
In the field of education, Dalhousie established numerous schools and colleges, including the renowned Indian Engineering College (now known as the Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur) and the Roorkee College (now known as the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee). He also laid the foundation for the modern postal system in India.
Dalhousie is controversially remembered for his policies of annexation, also known as the Doctrine of Lapse. Under this policy, he annexed several princely states that did not have a direct male heir, claiming that they had lapsed to the British East India Company. This policy was met with resistance and opposition from many Indian rulers and was seen as a violation of the sovereignty of the princely states.
Despite his reforms and modernization efforts, Dalhousie's tenure also witnessed the outbreak of the Indian Rebellion of 1857, also known as the Sepoy Mutiny. The rebellion, which began as a result of various grievances against British rule, marked a turning point in India's struggle for independence.
Lord Dalhousie left India in 1856 and returned to Britain, where he continued to play a role in politics and public life. He passed away in 1860 at the age of 57.
Dalhousie introduced several significant reforms in various fields, including infrastructure, education, communication, and administration. He initiated the construction of railways, bridges, and roads, which helped connect different parts of India and facilitated trade and commerce. He also established the telegraph network in India, improving communication and connecting the country with the outside world.
In the field of education, Dalhousie established numerous schools and colleges, including the renowned Indian Engineering College (now known as the Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur) and the Roorkee College (now known as the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee). He also laid the foundation for the modern postal system in India.
Dalhousie is controversially remembered for his policies of annexation, also known as the Doctrine of Lapse. Under this policy, he annexed several princely states that did not have a direct male heir, claiming that they had lapsed to the British East India Company. This policy was met with resistance and opposition from many Indian rulers and was seen as a violation of the sovereignty of the princely states.
Despite his reforms and modernization efforts, Dalhousie's tenure also witnessed the outbreak of the Indian Rebellion of 1857, also known as the Sepoy Mutiny. The rebellion, which began as a result of various grievances against British rule, marked a turning point in India's struggle for independence.
Lord Dalhousie left India in 1856 and returned to Britain, where he continued to play a role in politics and public life. He passed away in 1860 at the age of 57.
Which of the following was paid Rs. 50,000 as reward money by the British for treacherously killing Maulavi Ahmadullah?- a)The Raja of Puwain
- b)The Nizam of Hyderabad
- c)The Ruler of Nobha
- d)Maharaja Scindia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was paid Rs. 50,000 as reward money by the British for treacherously killing Maulavi Ahmadullah?
a)
The Raja of Puwain
b)
The Nizam of Hyderabad
c)
The Ruler of Nobha
d)
Maharaja Scindia
|
|
Maya Desai answered |
The Raja of Puwain was paid Rs. 50,000 as reward money by the British for treacherously killing Maulavi Ahmadullah. This incident took place during the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Background:
Maulavi Ahmadullah was a prominent figure in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He was a Muslim cleric who had actively participated in the rebellion against the British rule. He had organized a movement in Awadh and Rohilkhand to overthrow the British rule and establish a free and independent India. He had even formed an army of his own and had fought several battles against the British forces.
The role of the Raja of Puwain:
The Raja of Puwain was a local chieftain who had initially supported the rebellion. However, he later switched sides and joined hands with the British forces. He was promised a huge sum of money as a reward for his treachery. The British wanted to eliminate Maulavi Ahmadullah, who was seen as a major threat to their rule, and they saw the Raja of Puwain as the perfect tool to do so.
The killing of Maulavi Ahmadullah:
The Raja of Puwain invited Maulavi Ahmadullah to his palace under the pretext of holding peace talks. However, he had already made a secret deal with the British forces to betray the Maulavi. When Maulavi Ahmadullah arrived at the palace, he was ambushed by the British forces and the Raja of Puwain's men. He was killed in the ensuing battle.
The aftermath:
The killing of Maulavi Ahmadullah was a major blow to the rebellion. It demoralized the rebels and boosted the morale of the British forces. The Raja of Puwain was given the promised reward money of Rs. 50,000 by the British. However, he was later assassinated by his own people who were angered by his treachery.
Conclusion:
The killing of Maulavi Ahmadullah by the Raja of Puwain was a shameful act of treachery. It was a clear example of how the British used local chieftains and rulers to suppress the rebellion and maintain their hold over India. It is a dark chapter in India's history and serves as a reminder of the atrocities committed by the British during their rule.
Background:
Maulavi Ahmadullah was a prominent figure in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. He was a Muslim cleric who had actively participated in the rebellion against the British rule. He had organized a movement in Awadh and Rohilkhand to overthrow the British rule and establish a free and independent India. He had even formed an army of his own and had fought several battles against the British forces.
The role of the Raja of Puwain:
The Raja of Puwain was a local chieftain who had initially supported the rebellion. However, he later switched sides and joined hands with the British forces. He was promised a huge sum of money as a reward for his treachery. The British wanted to eliminate Maulavi Ahmadullah, who was seen as a major threat to their rule, and they saw the Raja of Puwain as the perfect tool to do so.
The killing of Maulavi Ahmadullah:
The Raja of Puwain invited Maulavi Ahmadullah to his palace under the pretext of holding peace talks. However, he had already made a secret deal with the British forces to betray the Maulavi. When Maulavi Ahmadullah arrived at the palace, he was ambushed by the British forces and the Raja of Puwain's men. He was killed in the ensuing battle.
The aftermath:
The killing of Maulavi Ahmadullah was a major blow to the rebellion. It demoralized the rebels and boosted the morale of the British forces. The Raja of Puwain was given the promised reward money of Rs. 50,000 by the British. However, he was later assassinated by his own people who were angered by his treachery.
Conclusion:
The killing of Maulavi Ahmadullah by the Raja of Puwain was a shameful act of treachery. It was a clear example of how the British used local chieftains and rulers to suppress the rebellion and maintain their hold over India. It is a dark chapter in India's history and serves as a reminder of the atrocities committed by the British during their rule.
How did the international situation favour the British during the Revolt of 1857?- a)The Crimean War and the trouble in Persia were over.
- b)The British could delay the war in China.
- c)The Indian Army sent for service abroad was called back quickly by the British.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How did the international situation favour the British during the Revolt of 1857?
a)
The Crimean War and the trouble in Persia were over.
b)
The British could delay the war in China.
c)
The Indian Army sent for service abroad was called back quickly by the British.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Deepika Dey answered |
The international situation during the Revolt of 1857 favoured the British in multiple ways, as mentioned below:
End of Crimean War and Trouble in Persia:
• The Crimean War ended in 1856, and the trouble in Persia was also resolved.
• This meant that the British could divert their attention and resources towards suppressing the revolt in India.
Delay in War with China:
• The British were also able to delay the Second Opium War with China, which was scheduled to begin in 1857.
• This allowed them to focus on the situation in India without having to worry about another front.
Recall of Indian Army:
• The British were able to recall the Indian Army, which was deployed in various parts of the world for service abroad.
• This was crucial as the Indian soldiers were well-trained and experienced, and their absence would have weakened the British forces in India.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the combination of these factors worked in favour of the British during the Revolt of 1857, and enabled them to quell the rebellion and reassert their control over India.
End of Crimean War and Trouble in Persia:
• The Crimean War ended in 1856, and the trouble in Persia was also resolved.
• This meant that the British could divert their attention and resources towards suppressing the revolt in India.
Delay in War with China:
• The British were also able to delay the Second Opium War with China, which was scheduled to begin in 1857.
• This allowed them to focus on the situation in India without having to worry about another front.
Recall of Indian Army:
• The British were able to recall the Indian Army, which was deployed in various parts of the world for service abroad.
• This was crucial as the Indian soldiers were well-trained and experienced, and their absence would have weakened the British forces in India.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the combination of these factors worked in favour of the British during the Revolt of 1857, and enabled them to quell the rebellion and reassert their control over India.
Which of the following wrote letters to all the chiefs and rulers of India urging them to organise a confederacy of Indian states to fight and replace the British regime?- a)Bahadur Shah II
- b)Tantia Tope
- c)Rani Lakshmi Bai
- d)Maulavi Ahmadullah
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following wrote letters to all the chiefs and rulers of India urging them to organise a confederacy of Indian states to fight and replace the British regime?
a)
Bahadur Shah II
b)
Tantia Tope
c)
Rani Lakshmi Bai
d)
Maulavi Ahmadullah

|
UPSC Achievers answered |
Bahadur Shah, after initial vacillation, wrote letters to all the chiefs and rulers of India urging them to organise a confederacy of Indian states to fight and replace the British regime. The entire Bengal Army soon rose in revolt which spread quickly. Awadh, Rohilkhand, the Doab, the Bundelkhand, central India, large parts of Bihar and East Punjab shook off British authority.
Who was the 'Agent to Governor-General' (AGG) in 'Rajputana Residency' at the time of the demise of 1857 AD?- a)Captain Shovers
- b)William Eden
- c)Major Burton
- d)Patrick Lawrence
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was the 'Agent to Governor-General' (AGG) in 'Rajputana Residency' at the time of the demise of 1857 AD?
a)
Captain Shovers
b)
William Eden
c)
Major Burton
d)
Patrick Lawrence
|
|
Arun Khatri answered |
The correct answer is Patrick Lawrence.
Key Points: Patrick Lawrence was the 'Agent to Governor-General' (AGG) in 'Rajputana Residency' at the time of the demise of 1857 AD.
Key Points: Patrick Lawrence was the 'Agent to Governor-General' (AGG) in 'Rajputana Residency' at the time of the demise of 1857 AD.
He emerged as one of the leaders of the Revolt of 1857 in Avadh. He also led the rebellion in Rohilkhand. Who is being talked about?- a)Nana Sahib
- b)Khan Bahadur Khan
- c)Maulavi Ahmadullah
- d)Ali Rizvi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
He emerged as one of the leaders of the Revolt of 1857 in Avadh. He also led the rebellion in Rohilkhand. Who is being talked about?
a)
Nana Sahib
b)
Khan Bahadur Khan
c)
Maulavi Ahmadullah
d)
Ali Rizvi
|
|
Divya Mukherjee answered |
Ahmadullah Shah, born in 1787, more famously known as Maulavi of Faizabad, was one of the leading figures of the great Indian revolt of 1857. In the Awadh region, Maulavi Ahmadullah Shah was known as the 'Lighthouse of Rebellion'.Jun 5, 2018
Some historians opine that some military causes were responsible for the outbreak of the revolt of 1857. The General Service Enlistment Act provided that all fresh recruits for the Bengal Army would have to serve any where including abroad. According to current religious beliefs of the Hindus, travel across the sea was forbidden and led to loss of caste. This Act hurt the sepoys’ sentiments. It was passed in- a)1849
- b)1852
- c)1855
- d)1856
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Some historians opine that some military causes were responsible for the outbreak of the revolt of 1857. The General Service Enlistment Act provided that all fresh recruits for the Bengal Army would have to serve any where including abroad. According to current religious beliefs of the Hindus, travel across the sea was forbidden and led to loss of caste. This Act hurt the sepoys’ sentiments. It was passed in
a)
1849
b)
1852
c)
1855
d)
1856

|
Manasa Datta answered |
General Service Enlistment Act of 25 July 1856 espoused that the Bengal Army shall take upon the responsibility of serving overseas, if need be. Out if the three Presidencies, only the armies of Bombay and Madras had the obligation of serving overseas, as such they faced immense strain for deployment at Burma and China fronts. The General Services Enlistment Act called for the same from Bengal Army as well that faced great resentment because they were initially exempted from overseas operations.
The New Enlistment Act of 1856 entailed that every unit of the Bengal Army was accountable for servings overseas, if asked to do so. Though this was applicable to only the new recruits of the Bengal Army, the older recruits feared that they too would be asked to do so and hence they resented.
Chapter doubts & questions for The Revolt of 1857 - Lucent For GK 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The Revolt of 1857 - Lucent For GK in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










