All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Respiration in Plants for ACT Exam
The net gain of ATP in glycolysis is__________.
- a)4
- b)8
- c)2
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The net gain of ATP in glycolysis is__________.
a)
4
b)
8
c)
2
d)
6
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Glycolysis is the first stage of the breakdown of glucose in the cell.
During glycolysis 2 ATP molecules are used up and four ATP molecules are generated. In the entire process of glycolysis, two NADH₂ molecules are also generated. When these molecules undergo ETS they will form 3 ATP per NADH₂ which means 6 ATP.
Therefore the total ATP that are forming are 10 and as 2 ATP is used up the net gain will be 8.
So, the correct option is '8'
Respiration isa)Amphibolic processb)Catabolic processc)Anabolic processd)Both anabolic and catabolic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Because the respiratory pathway is involved in both anabolism and catabolism, it would hence be better to consider the respiratory pathway as an amphibolic pathway rather than as a catabolic one.
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles- a)a and b
- b)a and d
- c)b and d
- d)b and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a)
a and b
b)
a and d
c)
b and d
d)
b and c
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Plants unlike animals have no special systems for breathing or gaseous exchange. Stomata and lenticels allow gaseous exchange by diffusion.
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
- a)It starts with a six-carbon compound.
- b)It occurs in mitochondria.
- c)It is also called the citric acid cycle.
- d)The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
a)
It starts with a six-carbon compound.
b)
It occurs in mitochondria.
c)
It is also called the citric acid cycle.
d)
The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle because this reaction starts with the six-carbon compound which is citric acid. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs cycle is a closed-loop cycle. And each loop of the cycle generates a molecule of ATP. This cycle consists of eight steps which include redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. It is an aerobic pathway because NADH is produced and the electrons released are used up in the next cycle which uses oxygen.
- The process of the cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl- CoA with oxaloacetate.
- This reaction is controlled by the amount of ATP present.
- If the ATP level increases then the rate of the reaction decreases and vice versa. After glycolysis, the pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
- The Krebs cycle is the pathway that all organisms use to generate energy. The intermediate compound that links pyruvate to the Krebs cycle is Acetyl CoA.
- So, the answer is option (B) ‘the intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid’.
The first compound of TCA cycle is- a)Oxalo succinic acid
- b)Oxalo acetic acid
- c)Citric acid
- d)Cis aconitic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The first compound of TCA cycle is
a)
Oxalo succinic acid
b)
Oxalo acetic acid
c)
Citric acid
d)
Cis aconitic acid
|
|
Kaneez Fatima answered |
Citric acid is ist compound of TCA cycle ...
The site of glycolysis is- a)Chloroplast
- b)Cytoplasm
- c)Mitochondrial inner membrane
- d)Mitochondrial matrix
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The site of glycolysis is
a)
Chloroplast
b)
Cytoplasm
c)
Mitochondrial inner membrane
d)
Mitochondrial matrix
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell as the first step in cellular respiration of the Kreb’s cycle. When glycolysis occurs, it breaks down glucose into pyruvic acids in the cytoplasm.
How many netATP are produced in Glycolysis?- a)36 ATP
- b)8 ATP
- c)2 ATP
- d)16 ATP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many netATP are produced in Glycolysis?
a)
36 ATP
b)
8 ATP
c)
2 ATP
d)
16 ATP

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
At the end of glycolysis pathway, 2 net ATP molecules at step 6 and step 9 are produced.
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
- a)Respiratory products
- b)respiratory substrates
- c)ATP
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
a)
Respiratory products
b)
respiratory substrates
c)
ATP
d)
NADH

|
Shounak Nair answered |
The respiratory quotient depends upon the type of respiratory substrate used during respiration.
Fermentation is- a)Excretory process
- b)Aerobic respiration
- c)Incomplete oxidation
- d)Anaerobic respiration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Fermentation is
a)
Excretory process
b)
Aerobic respiration
c)
Incomplete oxidation
d)
Anaerobic respiration
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O2, NADH and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration. Some fermentation processes involve obligate anaerobes, which cannot tolerate oxygen.
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by- a)GTP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)GDP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by
a)
GTP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
GDP

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
During conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesised.
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because- a)Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
- b)It takes place is micrograms
- c)It takes place in inert medium
- d)Glucose is not available
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because
a)
Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
b)
It takes place is micrograms
c)
It takes place in inert medium
d)
Glucose is not available
|
|
Kuldeep Kuldeep answered |
Option a is correct. Because, in Anaerobic Respiration, respiration takes place on the absence of oxygen. Iteans, the oxidation of pyruvate takes place in the absence of oxygen to release CO2, Ethanol along with the release of Energy. Here, in Anaerobic Respiration, Water is not yet released due to the absence of oxygen. So, there will be incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place.
The TCA cycle is named after- a)Robert Emerson
- b)Melvin Calvin
- c)Embden
- d)Hans Krebs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle is named after
a)
Robert Emerson
b)
Melvin Calvin
c)
Embden
d)
Hans Krebs
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
*Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release the stored energy........ *It is a part of cellular respiration........ *It is also called as citric acid cycle or Krebs cycles which is named after it's discoverer Hans Krebs..... Thus, the correct answer is option 'D'.
R.Q. is less than one at the time of respiration of –- a)Starch
- b)Sugarcane
- c)Glucose
- d)Ground nut
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
R.Q. is less than one at the time of respiration of –
a)
Starch
b)
Sugarcane
c)
Glucose
d)
Ground nut
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
RQ value is less than 1 in case of ground nut
The process common to both aerobic and anaerobic organisms is- a)TCA cycle
- b)Krebs cycle
- c)Glycolysis
- d)Glyoxylate cycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The process common to both aerobic and anaerobic organisms is
a)
TCA cycle
b)
Krebs cycle
c)
Glycolysis
d)
Glyoxylate cycle
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Glycolysis ( process of break down of glucose into pyruvic acid ) is the process common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of- a)NADPH
- b)FADH2
- c)ADP
- d)ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of
a)
NADPH
b)
FADH2
c)
ADP
d)
ATP
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
- Oxysomes refer to small round structures present within the folds of the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is also known as F0-F1 particles.
- F0 and F1 particles are found in the inner mitochondrial region and are attached to the cristae and help in ATP production and oxidation.
Energy is stored in the form of- a)FAD
- b)NADH
- c)ATP
- d)ADP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy is stored in the form of
a)
FAD
b)
NADH
c)
ATP
d)
ADP

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
The energy stored to synthesise a larger number of ATP molecules.
Aerobic respiration is common in- a)Yeast
- b)Higher organisms
- c)Prokaryotes
- d)Unicellular eukaryotes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Aerobic respiration is common in
a)
Yeast
b)
Higher organisms
c)
Prokaryotes
d)
Unicellular eukaryotes
|
|
Rajesh Banerjee answered |
Aerobic respiration is a process in which organisms break down glucose to produce energy in the presence of oxygen. This process is common in higher organisms, which include animals and plants.
Reasons why aerobic respiration is common in higher organisms:
1. Energy production: Higher organisms require a lot of energy to carry out their daily activities, such as movement, reproduction, and growth. Aerobic respiration provides a large amount of energy in the form of ATP, which is used for these activities.
2. Efficiency: Aerobic respiration is a highly efficient process, producing a large amount of energy from each glucose molecule. This makes it an ideal process for higher organisms, which require a lot of energy to survive.
3. Oxygen availability: Higher organisms have complex respiratory systems that allow them to take in oxygen and distribute it throughout their bodies. This makes it possible for them to carry out aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen.
4. Evolution: Higher organisms have evolved to carry out aerobic respiration as a means of producing energy. This process has been refined over millions of years of evolution, making it an integral part of their biology.
In summary, aerobic respiration is common in higher organisms because it provides a large amount of energy, is highly efficient, requires oxygen, and has evolved as a means of energy production.
Reasons why aerobic respiration is common in higher organisms:
1. Energy production: Higher organisms require a lot of energy to carry out their daily activities, such as movement, reproduction, and growth. Aerobic respiration provides a large amount of energy in the form of ATP, which is used for these activities.
2. Efficiency: Aerobic respiration is a highly efficient process, producing a large amount of energy from each glucose molecule. This makes it an ideal process for higher organisms, which require a lot of energy to survive.
3. Oxygen availability: Higher organisms have complex respiratory systems that allow them to take in oxygen and distribute it throughout their bodies. This makes it possible for them to carry out aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen.
4. Evolution: Higher organisms have evolved to carry out aerobic respiration as a means of producing energy. This process has been refined over millions of years of evolution, making it an integral part of their biology.
In summary, aerobic respiration is common in higher organisms because it provides a large amount of energy, is highly efficient, requires oxygen, and has evolved as a means of energy production.
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in- a)Intermembrane space of mitochondria
- b)Mitochondrial matrix
- c)Inner membrane of mitochondria
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in
a)
Intermembrane space of mitochondria
b)
Mitochondrial matrix
c)
Inner membrane of mitochondria
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Mitochondrial matrix.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
When and where anaerobic respiration does occurs in man and yeast?- a)Muscle in man and submergence in sugary solution in yeast
- b)Bone in man and yeast in normal condition
- c)Muscle in man and salt solution in yeast
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When and where anaerobic respiration does occurs in man and yeast?
a)
Muscle in man and submergence in sugary solution in yeast
b)
Bone in man and yeast in normal condition
c)
Muscle in man and salt solution in yeast
d)
None of these.
|
|
Awantika Gupta answered |
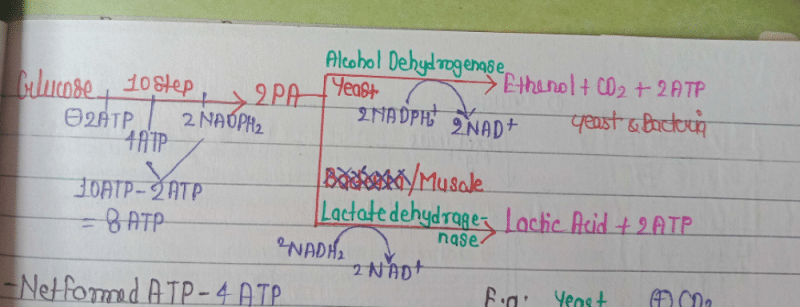
When fats are the respiratory substrate, the value of RQ would be- a)Approx. 0.7
- b)Approx. 1.0
- c)More than 1.0
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When fats are the respiratory substrate, the value of RQ would be
a)
Approx. 0.7
b)
Approx. 1.0
c)
More than 1.0
d)
None of the above

|
Surbhi Mishra answered |
Ans.
The respiratory quotient (or RQ or respiratory coefficient), is a dimensionless number used in calculations of basal metabolic rate (BMR) when estimated from carbon dioxide production. ... If metabolism consists solely of lipids, the Respiratory Quotient is 0.7, for proteins it is 0.8, and for carbohydrates it is 1.0.
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?- a)Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
- b)The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
- c)Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
- d)Mitochondria have a double membrane.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
a)
Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
b)
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
c)
Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
d)
Mitochondria have a double membrane.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mitochondria (singular - Mitochondrion) are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for the release of energy from food ,i.e, cellular respiration. This energy is released in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
While the cells release 2 ATP, mitochondria releases 34 ATP which adds up to 36 ATP. Since a major portion of the ATP is released by mitochondria, they are called the powerhouse of the cell.
Which one is not a preparatory phase or energy spending phase of Glycoloysis- a)Synthesis of fructose 6-phosphate
- b)Phosphorylation of glucose
- c)Formation of Pyruvate
- d)Isomerisation of DiHAP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a preparatory phase or energy spending phase of Glycoloysis
a)
Synthesis of fructose 6-phosphate
b)
Phosphorylation of glucose
c)
Formation of Pyruvate
d)
Isomerisation of DiHAP

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Formation of pyruvate is not a prerparatory phase or energy spending phase of Glycolysis. In this phase one ATP molecule is released.
The end products of respiration in plants are- a)CO2, H2O and energy
- b)Starch and O2
- c)Sugar and oxygen
- d)H2O and energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The end products of respiration in plants are
a)
CO2, H2O and energy
b)
Starch and O2
c)
Sugar and oxygen
d)
H2O and energy
|
|
Siddheshwar Kale answered |
Glucose + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy ( 686 Kcal.)
Energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reaction is stored immediately in the form of- a)Pyruvic acid
- b)Glucose
- c)ATP
- d)DNA
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reaction is stored immediately in the form of
a)
Pyruvic acid
b)
Glucose
c)
ATP
d)
DNA
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
The energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reactions is stored immediately in the form of ATP, as it is the energy currency of the cell.
Hence, option 'C' is correct.
Hence, option 'C' is correct.
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is- a)Oxalo acetic acid
- b)NADH
- c)Acetyl-CoA
- d)NADP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is
a)
Oxalo acetic acid
b)
NADH
c)
Acetyl-CoA
d)
NADP
|
|
Ashutosh Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and yields two molecules of ATP along with two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Interconnection:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Acetyl-CoA is then used in the Krebs cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces NADH, which is used in the electron transport chain to produce more ATP.
Therefore, Acetyl-CoA is the enzyme that interconnects glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and yields two molecules of ATP along with two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Interconnection:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Acetyl-CoA is then used in the Krebs cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces NADH, which is used in the electron transport chain to produce more ATP.
Therefore, Acetyl-CoA is the enzyme that interconnects glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
During which stage in the complete oxidation of glucose is the greatest number of ATP formed from ADP?- a)Glycolysis
- b)Electron transport chain
- c)During conversion of pyruvic acid to Acetyl Co A
- d)Krebs cycle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During which stage in the complete oxidation of glucose is the greatest number of ATP formed from ADP?
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Electron transport chain
c)
During conversion of pyruvic acid to Acetyl Co A
d)
Krebs cycle

|
Krish Khanna answered |
During electron transport chain stage of respiration of complete oxidation of glucose greatest number of ATP is formed from ADP in inner wall of mitochondria.
End-products of aerobic respiration are- a)Carbon dioxide and energy
- b)Sugar and oxygen
- c)Carbon dioxide, water and energy
- d)Water and energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
End-products of aerobic respiration are
a)
Carbon dioxide and energy
b)
Sugar and oxygen
c)
Carbon dioxide, water and energy
d)
Water and energy
|
|
Vartika Shukla answered |
Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of sugars in presence of oxygen.
The carbohydrates are broken down into CO₂ and H₂O and this releases energy. This energy is stored in the form of ATP and later used in the body.
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
The carbohydrates are broken down into CO₂ and H₂O and this releases energy. This energy is stored in the form of ATP and later used in the body.
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?- a)Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
- b)Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
- c)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
- d)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?
a)
Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
b)
Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
c)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
d)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
|
|
Akash Saini answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
Organism which depend on dead and decaying organic matter is- a)autotrophs
- b)saprophytes
- c)carnivores
- d)herbivorous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Organism which depend on dead and decaying organic matter is
a)
autotrophs
b)
saprophytes
c)
carnivores
d)
herbivorous

|
Anand Jain answered |
Saprophytes like fungi are dependent on dead and decaying matter.
Krebs cycle is both catabolic and anabolic because it provides- a)A number of intermediates
- b)Produce energy as well as use energy
- c)ATP is released as well as utilised
- d)A number of final products
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Krebs cycle is both catabolic and anabolic because it provides
a)
A number of intermediates
b)
Produce energy as well as use energy
c)
ATP is released as well as utilised
d)
A number of final products

|
Anand Jain answered |
During breakdown and synthesis of protein too, respiratory intermediates form the link. Breaking down processes within the living organism is catabolism, and synthesis is anabolism. Because the respiratory pathway (Kreb’s cycle) is involved in both anabolismand catabolism, it would hence be better to consider the respiratory pathway.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is used in converting –- a)Pyruvate to glucose
- b)Glucose to pyruvate
- c)Pyruvic acid to lactic acid
- d)Pyruvate to acetyl Co-A
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is used in converting –
a)
Pyruvate to glucose
b)
Glucose to pyruvate
c)
Pyruvic acid to lactic acid
d)
Pyruvate to acetyl Co-A
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is used in converting pyruvate to acetyl coA..this reaction is called link reaction
Oxidation of one molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration results in the production of- a)36 ATP molecules
- b)38 ATP molecules
- c)3 ATP molecules
- d)15 ATP molecules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation of one molecule of glucose in aerobic respiration results in the production of
a)
36 ATP molecules
b)
38 ATP molecules
c)
3 ATP molecules
d)
15 ATP molecules

|
User4284711 answered |
• Total ATP during aerobic glycolysis = 8ATP
• In pyruvic acid oxidation ATP produced = 6 ATP
• In Krebs cycle ATP produced =24 ATP
therefore total ATP produced is 38 ATP
• In pyruvic acid oxidation ATP produced = 6 ATP
• In Krebs cycle ATP produced =24 ATP
therefore total ATP produced is 38 ATP
Excess of ATP inhibits the enzyme –- a)Phosphofructokinase
- b)Hexokinase
- c)Aldolase (Lyases)
- d)Pyruvate decarboxylase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Excess of ATP inhibits the enzyme –
a)
Phosphofructokinase
b)
Hexokinase
c)
Aldolase (Lyases)
d)
Pyruvate decarboxylase
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) is one of the most important regulatory enzymes (EC 2.7.1.11) of glycolysis. It is an allosteric enzyme made of 4 subunits and controlled by many activators and inhibitors. For example, a high ratio of ATP to ADP will inhibit PFK and glycolysis.
Dough kept overnight in warm place becomes soft and spongy due to- a)Absorption of CO2
- b)Osmosis
- c)Fermentation
- d)Cohesion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dough kept overnight in warm place becomes soft and spongy due to
a)
Absorption of CO2
b)
Osmosis
c)
Fermentation
d)
Cohesion
|
|
Nitya Joshi answered |
Explanation:
When dough is kept overnight in a warm place, it undergoes a process called fermentation, which is responsible for the soft and spongy texture of the dough. Fermentation is a biological process in which yeast or bacteria convert sugars present in the dough into alcohol and carbon dioxide gas.
Importance of Fermentation:
Fermentation is an important step in the preparation of various food products like bread, beer, yogurt, cheese, and many others. It helps in improving the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of the food products.
How Fermentation Works in Dough:
When yeast is added to the dough, it starts feeding on the sugars present in the dough, and in the process, it produces carbon dioxide gas as a byproduct. This gas gets trapped in the dough and causes it to rise, making it soft and spongy.
Factors Affecting Fermentation:
The rate of fermentation is affected by several factors like temperature, pH, moisture content, and the type of yeast or bacteria used.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the soft and spongy texture of dough kept overnight in a warm place is due to the process of fermentation that occurs in the dough. Fermentation is an important process in the preparation of various food products and is influenced by several factors.
When dough is kept overnight in a warm place, it undergoes a process called fermentation, which is responsible for the soft and spongy texture of the dough. Fermentation is a biological process in which yeast or bacteria convert sugars present in the dough into alcohol and carbon dioxide gas.
Importance of Fermentation:
Fermentation is an important step in the preparation of various food products like bread, beer, yogurt, cheese, and many others. It helps in improving the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of the food products.
How Fermentation Works in Dough:
When yeast is added to the dough, it starts feeding on the sugars present in the dough, and in the process, it produces carbon dioxide gas as a byproduct. This gas gets trapped in the dough and causes it to rise, making it soft and spongy.
Factors Affecting Fermentation:
The rate of fermentation is affected by several factors like temperature, pH, moisture content, and the type of yeast or bacteria used.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the soft and spongy texture of dough kept overnight in a warm place is due to the process of fermentation that occurs in the dough. Fermentation is an important process in the preparation of various food products and is influenced by several factors.
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms- a)CO2
- b)CO2+ H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Acetyl CoA + CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms
a)
CO2
b)
CO2+ H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Acetyl CoA + CO2
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Pyruvate, the product obtained through glycolysis, gets oxidised with the loss of its carboxy group as CO2, to give acetyl Co-A, under aerobic condition. This acetyl Co-A is further oxidised completely to CO2 + H2O in citric acid cycle. Other options are incorrect as Lactic acid is formed in muscles under anaerobic conditions. Ethanol and CO2 are products of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells. CO2 and H2O are final and complete reaction products released at the end of cellular respiration.
Choose the correct statement.- a)There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
- b)Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
- c)During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
- d)Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement.
a)
There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
b)
Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
c)
During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
d)
Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- Oxygen sits at the end of the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons, hydrogen and picks up protons to form water.
- Pyruvate is formed in the cytoplasm.
- During fermentation glucose is partially broken down by glycolysis.
- During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesized.
So, the correct option is 'Oxygen is vital in respiration for removal of hydrogen'.
Which of the following is coenzyme - II ?- a)NAD
- b)NADP
- c)FAD
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is coenzyme - II ?
a)
NAD
b)
NADP
c)
FAD
d)
None of the above

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
Ans.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-phosphate (NMN) coupled by pyrophosphate linkage to the 5'-phosphate adenosine 2',5'-bisphosphate. It serves as an electron carrier in a number of reactions, being alternately oxidized (NADP+) and reduced (NADPH). (Dorland, 27th ed)
(Synonyms:
coenzyme II
NADP
NADP(+)
triphosphopyridine nucleotide
beta-NADP+)
The TCA cycle starts with- a)Condensation
- b)Dehydrogenation
- c)Phosphorylation
- d)Decarboxylation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle starts with
a)
Condensation
b)
Dehydrogenation
c)
Phosphorylation
d)
Decarboxylation

|
Anand Jain answered |
The TCA cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl group with oxaloacetic acid (OAA) and water to yield citric acid.
Energy equivalent of NADH is how many number of ATP molecules?- a)2
- b)3
- c)38
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy equivalent of NADH is how many number of ATP molecules?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
38
d)
6

|
Sougata Mukherjee answered |
NADH through electron trnasport system gives 3 ATP
The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport system is the formation of- a)Nucleic acids
- b)ATP in small stepwise units
- c)ATP in one large oxidation reaction
- d)Sugars
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport system is the formation of
a)
Nucleic acids
b)
ATP in small stepwise units
c)
ATP in one large oxidation reaction
d)
Sugars

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport system is the formation of ATP step-wise. The three processes are involved in cellular respiration of food to produce energy, which will be used for various cellular activities.
The universal hydrogen acceptor is- a)NAD
- b)ATP
- c)Co-A
- d)FMN
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The universal hydrogen acceptor is
a)
NAD
b)
ATP
c)
Co-A
d)
FMN
|
|
ภ๏๓คคภ answered |
The universal hydrogen acceptor is NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). It is knows as universal hydrogen acceptor because it gets easily reduced by combining with a hydrogen bond.
Most of the energy of the carbohydrates is released by oxidation when- a)Pyruvic acid is converted into CO2 and H2O
- b)Pyruvic acid is converted into acetyl Co-A
- c)Sugar is converted into pyruvic acid
- d)Glucose is converted into alcohol and CO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the energy of the carbohydrates is released by oxidation when
a)
Pyruvic acid is converted into CO2 and H2O
b)
Pyruvic acid is converted into acetyl Co-A
c)
Sugar is converted into pyruvic acid
d)
Glucose is converted into alcohol and CO2
|
|
Arushi Thakur answered |
Opt a is correct because in option A the process included to convert pyruvic acid to carbondioxide and water includes link rxn. + krebcycle in which maximum energy is formed or released.
In respiration pyruvic acid is- a)Formed only when oxygen is available
- b)One of product of Krebs cycle
- c)Broken down into Acetyl Co-A and CO2
- d)a result of protein break down
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In respiration pyruvic acid is
a)
Formed only when oxygen is available
b)
One of product of Krebs cycle
c)
Broken down into Acetyl Co-A and CO2
d)
a result of protein break down
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Respiration occurs in two stages. In the first stage called as glycolysis, which occurs in the absence of oxygen, one molecule of hexose glucose is broken down into two molecules of three carbon atom containing pyruvic acid. Each molecule of pyruvic acid is then oxidatively decarboxylated by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. The pyruvate dehydrogenase releases one molecule of carbon dioxide from each molecule of pyruvic acid during its conversion to Acetyl CoA. The Acetyl CoA is subsequently metabolised in Krebs cycle generating reduced coenzymes.
Arrange the following in descending order based upon number of carbon atoms in Kreb cycle
a) α-ketoglutaric acid
b) citric acid
c) Acetyl coA
d) Succinic acid- a)b, a, d, c
- b)a, d, b, c
- c)a, b, c, d
- d)b, c, d, a
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following in descending order based upon number of carbon atoms in Kreb cycle
a) α-ketoglutaric acid
b) citric acid
c) Acetyl coA
d) Succinic acid
a) α-ketoglutaric acid
b) citric acid
c) Acetyl coA
d) Succinic acid
a)
b, a, d, c
b)
a, d, b, c
c)
a, b, c, d
d)
b, c, d, a

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
In kerb cycle citric acid consists of 6C atoms ,α-ketoglutaric acid consist of 5C atoms, succinic acid consists of 4 C atoms and Acetyl co A consists of 2C atoms,
Aerobic respiration of glucose produces energy- a)637 K.Cal
- b)640 K.cal
- c)686 K.cal
- d)693 K.cal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Aerobic respiration of glucose produces energy
a)
637 K.Cal
b)
640 K.cal
c)
686 K.cal
d)
693 K.cal
|
|
Prerna Basu answered |
Aerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the presence of oxygen and involves the breakdown of glucose to produce energy. This process takes place in the mitochondria of cells and is the most efficient way to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The overall equation for aerobic respiration is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
The process of aerobic respiration involves several steps, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
1. Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the initial step of aerobic respiration that takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. In this step, glucose molecules are broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and reducing equivalents in the form of NADH.
2. Krebs cycle:
After glycolysis, the pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria, where they are further broken down in a series of reactions called the Krebs cycle. During this cycle, the carbon atoms from pyruvate are released as carbon dioxide, and reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and FADH2 are produced.
3. Electron transport chain:
The NADH and FADH2 molecules generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle enter the electron transport chain, which is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This chain consists of a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. As the electrons are transferred, energy is released and used to pump protons across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient is then used by ATP synthase to produce ATP.
The total energy produced during aerobic respiration can be calculated by considering the number of ATP molecules generated from each NADH and FADH2 molecule. On average, each NADH molecule yields around 2.5 ATP, while each FADH2 molecule yields around 1.5 ATP. Since glycolysis produces 2 NADH molecules and the Krebs cycle produces 8 NADH molecules and 2 FADH2 molecules per glucose molecule, we can calculate the total energy produced as follows:
(2 NADH x 2.5 ATP) + (8 NADH x 2.5 ATP) + (2 FADH2 x 1.5 ATP) = 5 ATP + 20 ATP + 3 ATP = 28 ATP
Since each ATP molecule carries around 7.6 K.Cal of energy, the total energy produced can be calculated as:
28 ATP x 7.6 K.Cal/ATP = 212.8 K.Cal
However, this calculation only accounts for the ATP produced through oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Additional ATP is also generated during glycolysis, resulting in a total energy production of around 686 K.Cal per glucose molecule.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
The process of aerobic respiration involves several steps, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
1. Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the initial step of aerobic respiration that takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. In this step, glucose molecules are broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and reducing equivalents in the form of NADH.
2. Krebs cycle:
After glycolysis, the pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria, where they are further broken down in a series of reactions called the Krebs cycle. During this cycle, the carbon atoms from pyruvate are released as carbon dioxide, and reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and FADH2 are produced.
3. Electron transport chain:
The NADH and FADH2 molecules generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle enter the electron transport chain, which is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This chain consists of a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. As the electrons are transferred, energy is released and used to pump protons across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient is then used by ATP synthase to produce ATP.
The total energy produced during aerobic respiration can be calculated by considering the number of ATP molecules generated from each NADH and FADH2 molecule. On average, each NADH molecule yields around 2.5 ATP, while each FADH2 molecule yields around 1.5 ATP. Since glycolysis produces 2 NADH molecules and the Krebs cycle produces 8 NADH molecules and 2 FADH2 molecules per glucose molecule, we can calculate the total energy produced as follows:
(2 NADH x 2.5 ATP) + (8 NADH x 2.5 ATP) + (2 FADH2 x 1.5 ATP) = 5 ATP + 20 ATP + 3 ATP = 28 ATP
Since each ATP molecule carries around 7.6 K.Cal of energy, the total energy produced can be calculated as:
28 ATP x 7.6 K.Cal/ATP = 212.8 K.Cal
However, this calculation only accounts for the ATP produced through oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Additional ATP is also generated during glycolysis, resulting in a total energy production of around 686 K.Cal per glucose molecule.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Which process makes direct use of oxygen- a)Fermentation
- b)Electron transport
- c)Glycolysis
- d)Krebs cycle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which process makes direct use of oxygen
a)
Fermentation
b)
Electron transport
c)
Glycolysis
d)
Krebs cycle

|
Anand Jain answered |
Electron transport process makes direct use of oxygen to produce ATP molecules in respiration process.
What is the importance of respiration in organisms?- a)It provides oxygen to plant
- b)It liberates CO2
- c)It liberates energy
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the importance of respiration in organisms?
a)
It provides oxygen to plant
b)
It liberates CO2
c)
It liberates energy
d)
All the above
|
|
Raza Great answered |
Respiration is a catabolic process, which oxidises reduced substrates, thus, resulting in the energy stored in reduced substrates. The reduced substrates are produced by the process of photosynthesis occurring in green plants and the reduced substrates are oxidised through respiration releasing CO2, water vapour and energy in the form of ATP.
Chapter doubts & questions for Respiration in Plants - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Respiration in Plants - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup