All Exams >
BMAT >
Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2) >
All Questions
All questions of Chemical Bonding, Structure and Properties for BMAT Exam
The compound which contains both ionic and covalent bonds is(1979)- a)CH4
- b)H2
- c)KCN
- d)KCl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which contains both ionic and covalent bonds is(1979)
a)
CH4
b)
H2
c)
KCN
d)
KCl
|
|
Bhaskar Majumdar answered |
Explanation:
Ionic and covalent bonds are two types of chemical bonds.
Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal, where electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. These oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces.
Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals, where electrons are shared between the atoms. This sharing of electrons creates a bond between the atoms, resulting in the formation of a molecule.
Among the given options, the compound KCN (potassium cyanide) contains both ionic and covalent bonds.
- KCN consists of the metal potassium (K) and the non-metal cyanide (CN).
- The bond between potassium and cyanide is ionic because potassium is a metal and tends to lose one electron to form a cation, while cyanide is a non-metal and tends to gain one electron to form an anion.
- As a result, the potassium atom donates one electron to the cyanide ion, forming the ionic bond.
- However, the cyanide ion (CN-) contains a covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen.
- Carbon and nitrogen are both non-metals and share electrons to form a stable molecule.
Therefore, KCN contains both ionic and covalent bonds.
Ionic and covalent bonds are two types of chemical bonds.
Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal, where electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. These oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces.
Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals, where electrons are shared between the atoms. This sharing of electrons creates a bond between the atoms, resulting in the formation of a molecule.
Among the given options, the compound KCN (potassium cyanide) contains both ionic and covalent bonds.
- KCN consists of the metal potassium (K) and the non-metal cyanide (CN).
- The bond between potassium and cyanide is ionic because potassium is a metal and tends to lose one electron to form a cation, while cyanide is a non-metal and tends to gain one electron to form an anion.
- As a result, the potassium atom donates one electron to the cyanide ion, forming the ionic bond.
- However, the cyanide ion (CN-) contains a covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen.
- Carbon and nitrogen are both non-metals and share electrons to form a stable molecule.
Therefore, KCN contains both ionic and covalent bonds.
Which of the following is soluble in water (1980)- a)CS2
- b)C2H5OH
- c)CCl4
- d)CHCl3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is soluble in water (1980)
a)
CS2
b)
C2H5OH
c)
CCl4
d)
CHCl3
|
|
Harsh Singhal answered |
Alcohol are soluble in water due to h-bonding
Among the following species, identify the isostructural pairs. NF3, NO3- , BF3, H3O+, HN3 (1996 - 1 Mark)- a)[ NF3, NO3- ] and[BF3 , H3O+]
- b)[NF3, HN3] and[NO3-, BF3]
- c)[NF3, H3O+]and[NO3-, BF3
- d)[NF3, H3O+] and[HN3, BF3]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following species, identify the isostructural pairs. NF3, NO3- , BF3, H3O+, HN3 (1996 - 1 Mark)
a)
[ NF3, NO3- ] and[BF3 , H3O+]
b)
[NF3, HN3] and[NO3-, BF3]
c)
[NF3, H3O+]and[NO3-, BF3
d)
[NF3, H3O+] and[HN3, BF3]
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Structure of a molecule can be ascertained by knowing the number of hybrid bonds in the molecule. Thus
In NF3 : 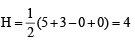
Thus N in NF3 is sp3 hybridized as 4 orbitals are involved in bonding.
In NO3– :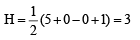
Thus N in NO3– is sp2 hybridized as 3 orbitals are involved in bonding
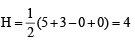
Thus N in NF3 is sp3 hybridized as 4 orbitals are involved in bonding.
In NO3– :
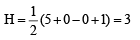
Thus N in NO3– is sp2 hybridized as 3 orbitals are involved in bonding
In BF3 : 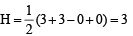
Thus B in BF3 is sp2 hybridized and 3 orbitals are involved in bonding
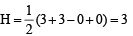
Thus B in BF3 is sp2 hybridized and 3 orbitals are involved in bonding
In H3O+ : 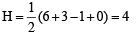
Thus O in H3O+ is sp3 hybridized as 4 orbitals are involved in bonding.
Thus, isostructural pairs are [NF3, H3O+] and [ NO3-, BF3]
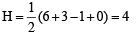
Thus O in H3O+ is sp3 hybridized as 4 orbitals are involved in bonding.
Thus, isostructural pairs are [NF3, H3O+] and [ NO3-, BF3]
The geometries of the ammonia complexes of Ni2+, Pt2+ and Zn2+ respectively, are (JEE Adv. 2016)- a)octah edral, square planar and tetrahedral
- b)square planar, octahedral and tetr ahedral
- c)tetrahedral, square planar an d octahedral
- d)octah edral, tetrahedral and square planar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The geometries of the ammonia complexes of Ni2+, Pt2+ and Zn2+ respectively, are (JEE Adv. 2016)
a)
octah edral, square planar and tetrahedral
b)
square planar, octahedral and tetr ahedral
c)
tetrahedral, square planar an d octahedral
d)
octah edral, tetrahedral and square planar
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Ni2+ with NH3 shows CN = 6 forming [Ni(NH3)6]2+ (Octahedral)
Pt2+ with NH3 shows CN = 4 forming [Pt(NH3)4]2+ (5d series CMA, square planner)
Zn2+ with NH3 shows CN = 4 forming [Zn(NH3)4]2+ (3d10 configuration, tetrahedral)
If a molecule MX3 has zero dipole moment, the sigma bonding orbitals used by M (atomic number < 21) are (1981 - 1 Mark)- a)pure p
- b)sp hybrid
- c)sp2 hybrid
- d)sp3 hybrid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a molecule MX3 has zero dipole moment, the sigma bonding orbitals used by M (atomic number < 21) are (1981 - 1 Mark)
a)
pure p
b)
sp hybrid
c)
sp2 hybrid
d)
sp3 hybrid

|
Shoaib Ali answered |
There is zero dipole moment, so no loan pair persent and three same group bonded with M, so s+p+p=sp2
The molecule having one unpaired electron is : (1985 - 1 Mark)- a)NO
- b)CO
- c)CN–
- d)O2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecule having one unpaired electron is : (1985 - 1 Mark)
a)
NO
b)
CO
c)
CN–
d)
O2

|
Sid Gupta answered |
Right configuration as given in ncert
The octet rule is not valid for the molecule (1979)- a)CO2
- b)H2O
- c)O2
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The octet rule is not valid for the molecule (1979)
a)
CO2
b)
H2O
c)
O2
d)
CO
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
∵ after forming the bonds, C has only 6 e– in its valence shell
The linear structure is assumed by : (1991 - 1 Mark)- a)SnCl2
- b)NCO–
- c)CS2
- d)NO+2
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The linear structure is assumed by : (1991 - 1 Mark)
a)
SnCl2
b)
NCO–
c)
CS2
d)
NO+2

|
Athira Datta answered |
[O = N = O]+; [N ≡ C – O]–; S = C = S
It can be seen from the structure shown above that CS2 being sp hybridized has a linear shape and other two molecules are isoelectronic to CS2, so they are also linear. SnCl2 and SO2 are sp2 hybridised and are not linear.
It can be seen from the structure shown above that CS2 being sp hybridized has a linear shape and other two molecules are isoelectronic to CS2, so they are also linear. SnCl2 and SO2 are sp2 hybridised and are not linear.
The types of bonds present in CuSO4.5H2O are only- a)electrovalent and covalent (1983 - 1 Mark)
- b)electrovalent and coordinate covalent
- c)electrovalent, covalent and coordinate covalent
- d)covalent and coordinate covalent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The types of bonds present in CuSO4.5H2O are only
a)
electrovalent and covalent (1983 - 1 Mark)
b)
electrovalent and coordinate covalent
c)
electrovalent, covalent and coordinate covalent
d)
covalent and coordinate covalent
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
All types of bonds present in this... also hydrogen bonding present..in this
Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is (2010)- a)1 and diamagnetic
- b)0 and dimagnetic
- c)1 and paramagnetic
- d)0 and paramagnetic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assuming that Hund’s rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is (2010)
a)
1 and diamagnetic
b)
0 and dimagnetic
c)
1 and paramagnetic
d)
0 and paramagnetic
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Molecular orbital configuration of B2(10) as per the condition will be
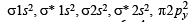
Bond order of B2 =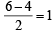 ,B2 will be diamagnetic.
,B2 will be diamagnetic.
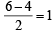 ,B2 will be diamagnetic.
,B2 will be diamagnetic.The correct order of hybridization of the central atom in the following species NH3, [PtCl4]2 –, PCl5 and BCl3 is (2001S)- a)dsp2, dsp3, sp2 and sp3
- b)sp3, dsp2, dsp3, sp2
- c)dsp2, sp2, sp3, dsp3
- d)dsp2, sp3, sp2, dsp3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of hybridization of the central atom in the following species NH3, [PtCl4]2 –, PCl5 and BCl3 is (2001S)
a)
dsp2, dsp3, sp2 and sp3
b)
sp3, dsp2, dsp3, sp2
c)
dsp2, sp2, sp3, dsp3
d)
dsp2, sp3, sp2, dsp3

|
Mudimadugula Raviteja answered |
In nh3 the central atom under goes s and p hybridization so u may choose b is correct
The species in which the central atom uses sp2 hybrid orbitals in its bonding is (1988 - 1 Mark)- a)PH3
- b)NH3
- c)CH3+
- d)SbH3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The species in which the central atom uses sp2 hybrid orbitals in its bonding is (1988 - 1 Mark)
a)
PH3
b)
NH3
c)
CH3+
d)
SbH3
|
|
Utkarsh Pandey answered |
(c) From amongst given species PH3, NH3 and SbH3 are all sp3 hybridised. Their central atom has both bond pair as well as lone pair of electrons. The lone pair occupy the fourth orbital. CH3+ has only three pairs of electrons so it is sp2 hybridised.
The geometry of H2S and its dipole moment are (1999 - 2 Marks)- a)angular and non-zero
- b)angular and zero
- c)linear and non-zero
- d)linear and zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The geometry of H2S and its dipole moment are (1999 - 2 Marks)
a)
angular and non-zero
b)
angular and zero
c)
linear and non-zero
d)
linear and zero
|
|
Sarthak Unni answered |
To determine the geometry of H2S, we need to look at the electron pair arrangement and the molecular shape.
1. Electron Pair Arrangement:
In H2S, there are two regions of electron density around the central sulfur atom. These regions can be occupied by either bonding pairs or lone pairs of electrons.
2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory:
The VSEPR theory states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves in a way that minimizes repulsion between them.
3. Molecular Shape:
Based on the VSEPR theory, the electron pair arrangement in H2S is determined to be bent/angular. This is because the two bonding pairs of electrons and the two lone pairs of electrons around the central sulfur atom repel each other, causing the molecule to adopt a bent shape.
4. Dipole Moment:
The dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a molecule. It is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved and the molecular geometry.
In the case of H2S, the sulfur atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. This means that the sulfur atom attracts the bonding electrons more strongly, resulting in a polar covalent bond.
The bent/angular geometry of H2S means that the dipole moments of the two S-H bonds do not cancel each other out. The dipole moment vectors do not have equal magnitude and are not directly opposite to each other. As a result, the molecule has a net dipole moment, making it polar.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - angular and non-zero.
1. Electron Pair Arrangement:
In H2S, there are two regions of electron density around the central sulfur atom. These regions can be occupied by either bonding pairs or lone pairs of electrons.
2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory:
The VSEPR theory states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves in a way that minimizes repulsion between them.
3. Molecular Shape:
Based on the VSEPR theory, the electron pair arrangement in H2S is determined to be bent/angular. This is because the two bonding pairs of electrons and the two lone pairs of electrons around the central sulfur atom repel each other, causing the molecule to adopt a bent shape.
4. Dipole Moment:
The dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a molecule. It is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved and the molecular geometry.
In the case of H2S, the sulfur atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms. This means that the sulfur atom attracts the bonding electrons more strongly, resulting in a polar covalent bond.
The bent/angular geometry of H2S means that the dipole moments of the two S-H bonds do not cancel each other out. The dipole moment vectors do not have equal magnitude and are not directly opposite to each other. As a result, the molecule has a net dipole moment, making it polar.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - angular and non-zero.
According to Molecular Orbital Theory, (JEE Adv. 2016)- a)C22- is expected to be diamagnetic
- b)O22+ is expected to have a longer bond length than O2
- c)N+2 an d N2- have th e same bond or der
- d)He+2 has the same ener gy as two isolated He atoms
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Molecular Orbital Theory, (JEE Adv. 2016)
a)
C22- is expected to be diamagnetic
b)
O22+ is expected to have a longer bond length than O2
c)
N+2 an d N2- have th e same bond or der
d)
He+2 has the same ener gy as two isolated He atoms
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
(A) The molecular orbital energy configuration of C22– is
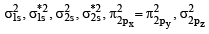
In the MO of C22– there is no unpaired electron hence it is diamagnetic
(B) Bond order of O22+ is 3 and O2 is 2 therefore bond length of O2 is greater than O22+
(C) The molecular orbital energy configuration of N+2 is
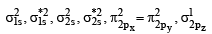
Bond order of 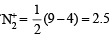
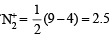
The molecular orbital energy configuration of N–2 is
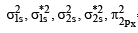
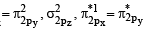
Bond order of 
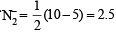
(D) He+2 has less energy in comparison to two isolated He atoms because some energy is released during the formation of He+2 from 2 He atoms.
Specify the coordination geometry around and hybridisation of N and B atoms in a 1 : 1 complex of BF3 and NH3- a)N : tetrahedral, sp3; B : tetrahedral, sp3 (2002S)
- b)N : pyramidal, sp3; B : pyramidal, sp3
- c)N : pyramidal, sp3; B : planar, sp2
- d)N : pyramidal, sp3; B : tetrahedral, sp3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Specify the coordination geometry around and hybridisation of N and B atoms in a 1 : 1 complex of BF3 and NH3
a)
N : tetrahedral, sp3; B : tetrahedral, sp3 (2002S)
b)
N : pyramidal, sp3; B : pyramidal, sp3
c)
N : pyramidal, sp3; B : planar, sp2
d)
N : pyramidal, sp3; B : tetrahedral, sp3
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
H3N → BF3 where both N, B are attaining tetrahedral geomerty.
According to molecular orbital theory which of the following statement about the magnetic character and bond order is correct regarding O+2 (2004S)- a)Paramagnetic and Bond order < O2
- b)Paramagnetic and Bond order > O2
- c)Diamagnetic and Bond order < O2
- d)Diamagnetic and Bond order > O2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to molecular orbital theory which of the following statement about the magnetic character and bond order is correct regarding O+2 (2004S)
a)
Paramagnetic and Bond order < O2
b)
Paramagnetic and Bond order > O2
c)
Diamagnetic and Bond order < O2
d)
Diamagnetic and Bond order > O2
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
O2 : σ1s2 , σ*1s2 , σ2s2, σ*2s2,σ2px2 ,
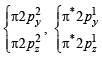
Bond order = 
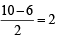
(two unpaired electrons in antibonding molecular orbital)
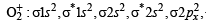
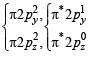
Bond order = 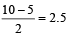
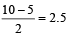
(One unpaired electron in antibonding molecular orbital) Hence O2 as well as O+2 is paramagnetic, and bond order of O+2 is greater than that of O2.
Assuming 2s-2p mixing is NOT operative, the paramagnetic species among the following is (JEE Adv. 2014)- a)Be2
- b)B2
- c)C2
- d)N2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assuming 2s-2p mixing is NOT operative, the paramagnetic species among the following is (JEE Adv. 2014)
a)
Be2
b)
B2
c)
C2
d)
N2

|
Avantika Joshi answered |
Be2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2
B2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2pz2
C2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2pz2 π2px1 π2py1
N2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2pz2 π2px2 π2py2
Thus only C2 will be paramagnetic
B2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2pz2
C2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2pz2 π2px1 π2py1
N2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2pz2 π2px2 π2py2
Thus only C2 will be paramagnetic
The critical temperature of water is higher than that of O2 because the H2O molecule has (1997 - 1 Mark)- a)fewer electrons than O2
- b)two covalent bonds
- c)V-shape
- d)dipole moment.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The critical temperature of water is higher than that of O2 because the H2O molecule has (1997 - 1 Mark)
a)
fewer electrons than O2
b)
two covalent bonds
c)
V-shape
d)
dipole moment.
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Critical temperature of water is higher than O2 because H2O molecule has dipole moment which is due to its V-shape.
Among the following, the paramagnetic compound is (2007)- a)Na2O2
- b)O3
- c)N2O
- d)KO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the paramagnetic compound is (2007)
a)
Na2O2
b)
O3
c)
N2O
d)
KO2
|
|
Pranavi Ahuja answered |
(i) In Na2O2, we have O22- ion. Number of valence elctrons of the two oxygen in O22- ion = 8 × 2 + 2 =18 which are present as follows
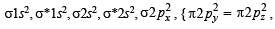
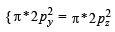
∴ Number of unpaired electrons = 0, hence, O22-is diamagnetic.
(ii) No. of valence electrons of all atoms in O3 = 6 × 3 = 18.
Thus, it also, does not have any unpaired electron, hence it is diamagnetic. (iii)
Thus, it also, does not have any unpaired electron, hence it is diamagnetic. (iii)
No. of valence electrons of all atom in N2O = 2 × 5 + 6 = 16.
Hence, here also all electrons are paired. So it is diamagnetic.
Hence, here also all electrons are paired. So it is diamagnetic.
(iv) In KO2, we have O2- No. of valence electrons of all atoms in O2- = 2 × 6 + 1 = 13,
Thus it has one unpaired electron, hence it is paramagnetic.
Thus it has one unpaired electron, hence it is paramagnetic.
Which one is most ionic : (1995S)- a)P2O5
- b)CrO3
- c)MnO
- d)Mn2O7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is most ionic : (1995S)
a)
P2O5
b)
CrO3
c)
MnO
d)
Mn2O7
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
P2O5 is a non- metallic oxide and so it must be more covalent than others which are metallic oxides.
More over the metallic oxide with metal in higher oxidation state is more covalent so Mn2O7(Mn=+7state) is most covalent and MnO(Mn=+2state) is most ionic amongst Mn2O7.
MnO and CrO3(Cr=+6state)
Hence C is the correct answer.
The compound with no dipole moment is (1982 - 1 Mark)- a)methyl chloride
- b)carbon tetrachloride
- c)methylene chloride
- d)chloroform
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound with no dipole moment is (1982 - 1 Mark)
a)
methyl chloride
b)
carbon tetrachloride
c)
methylene chloride
d)
chloroform
|
|
Navya Chakraborty answered |
TIPS/Formulae : (i) Dipole moment is vector quantity. When vector sum of all dipoles in molecule will be zero, then molecule will not have net dipole moment.
(ii) NOTE : For net dipole moment to be equal to zero, all the atoms attached to central atom must be identical and geometry must be regular.
(ii) NOTE : For net dipole moment to be equal to zero, all the atoms attached to central atom must be identical and geometry must be regular.
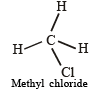
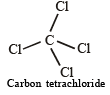

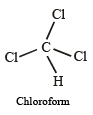
∴ Carbon tetrachloride having regular geometry and identical atoms attached to bonds has zero dipole moment.
Among the following, the molecule that is linear is- a)CO2
- b)NO2 (1982 - 1 Mark)
- c)SO2
- d)ClO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the molecule that is linear is
a)
CO2
b)
NO2 (1982 - 1 Mark)
c)
SO2
d)
ClO2
|
|
Saranya Choudhary answered |
The molecule that is linear among the given options is CO2.
Explanation:
CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a linear molecule because it consists of two oxygen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom in a straight line, with a bond angle of 180 degrees. This linear shape arises due to the arrangement of the atoms and the nature of the bonding.
Here is a detailed explanation of the molecular geometry of the given options:
a) CO2:
- Carbon dioxide consists of two oxygen atoms double bonded to a central carbon atom.
- The carbon-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the carbon and oxygen atoms.
- The carbon atom is sp hybridized, which means it has two sigma bonds and no lone pairs of electrons.
- As a result, the molecule has a linear shape, with the oxygen atoms on either side of the carbon atom.
- The bond angle between the carbon and oxygen atoms is 180 degrees.
b) NO2:
- Nitrogen dioxide consists of one nitrogen atom double bonded to an oxygen atom, and another oxygen atom single bonded to the nitrogen atom.
- The nitrogen-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms.
- The nitrogen atom has one lone pair of electrons.
- The molecule has a bent or V-shape, with the nitrogen atom at the apex of the V and the oxygen atoms on either side.
- The bond angle between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms is approximately 134 degrees.
c) SO2:
- Sulfur dioxide consists of one sulfur atom double bonded to an oxygen atom and single bonded to another oxygen atom.
- The sulfur-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
- The sulfur atom has one lone pair of electrons.
- The molecule has a bent or V-shape, with the sulfur atom at the apex of the V and the oxygen atoms on either side.
- The bond angle between the sulfur and oxygen atoms is approximately 119 degrees.
d) ClO2:
- Chlorine dioxide consists of one chlorine atom double bonded to an oxygen atom and single bonded to another oxygen atom.
- The chlorine-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the chlorine and oxygen atoms.
- The chlorine atom has two lone pairs of electrons.
- The molecule has a bent or V-shape, with the chlorine atom at the apex of the V and the oxygen atoms on either side.
- The bond angle between the chlorine and oxygen atoms is approximately 117 degrees.
In summary, among the given options, CO2 is the only molecule that is linear, with a bond angle of 180 degrees.
Explanation:
CO2, or carbon dioxide, is a linear molecule because it consists of two oxygen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom in a straight line, with a bond angle of 180 degrees. This linear shape arises due to the arrangement of the atoms and the nature of the bonding.
Here is a detailed explanation of the molecular geometry of the given options:
a) CO2:
- Carbon dioxide consists of two oxygen atoms double bonded to a central carbon atom.
- The carbon-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the carbon and oxygen atoms.
- The carbon atom is sp hybridized, which means it has two sigma bonds and no lone pairs of electrons.
- As a result, the molecule has a linear shape, with the oxygen atoms on either side of the carbon atom.
- The bond angle between the carbon and oxygen atoms is 180 degrees.
b) NO2:
- Nitrogen dioxide consists of one nitrogen atom double bonded to an oxygen atom, and another oxygen atom single bonded to the nitrogen atom.
- The nitrogen-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms.
- The nitrogen atom has one lone pair of electrons.
- The molecule has a bent or V-shape, with the nitrogen atom at the apex of the V and the oxygen atoms on either side.
- The bond angle between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms is approximately 134 degrees.
c) SO2:
- Sulfur dioxide consists of one sulfur atom double bonded to an oxygen atom and single bonded to another oxygen atom.
- The sulfur-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the sulfur and oxygen atoms.
- The sulfur atom has one lone pair of electrons.
- The molecule has a bent or V-shape, with the sulfur atom at the apex of the V and the oxygen atoms on either side.
- The bond angle between the sulfur and oxygen atoms is approximately 119 degrees.
d) ClO2:
- Chlorine dioxide consists of one chlorine atom double bonded to an oxygen atom and single bonded to another oxygen atom.
- The chlorine-oxygen bonds are formed by the sharing of electron pairs between the chlorine and oxygen atoms.
- The chlorine atom has two lone pairs of electrons.
- The molecule has a bent or V-shape, with the chlorine atom at the apex of the V and the oxygen atoms on either side.
- The bond angle between the chlorine and oxygen atoms is approximately 117 degrees.
In summary, among the given options, CO2 is the only molecule that is linear, with a bond angle of 180 degrees.
Geometrical shapes of the complexes formed by the reaction of Ni2+ with Cl– , CN– and H2O, respectively, are (2011)- a)octahedral, tetrahedral and square planar
- b)tetrahedral, square planar and octahedral
- c)square planar, tetrahedral and octahedral
- d)octahedral, square planar and octahedral
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Geometrical shapes of the complexes formed by the reaction of Ni2+ with Cl– , CN– and H2O, respectively, are (2011)
a)
octahedral, tetrahedral and square planar
b)
tetrahedral, square planar and octahedral
c)
square planar, tetrahedral and octahedral
d)
octahedral, square planar and octahedral
|
|
Arjun Sen answered |
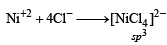
[NiCl4]2–. = 3d8 configuration with nickel in +2 oxidation state, Cl– being weak field ligand does not compel for pairing of electrons.
So,
[NiCl4]2–
So,
[NiCl4]2–
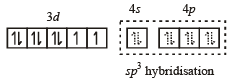
Hence, complex has tetrahedral geometry
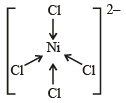
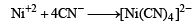
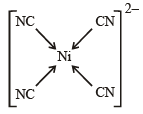
[Ni(CN)4]2– = 3d8 configuration with nickel in + 2 oxidation state, CN– being strong field ligand compels for pairing of electrons.
So,
So,
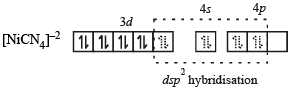
Hence, complex has square planar geometry.
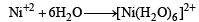
[Ni(H2O)6] = 3d8 configuration with nickel in +2 oxidation state. As with 3d8 configuration two dorbitals are not available for d2sp3 hybridisation. So, hybridisation of Ni (II) is sp3d2 and Ni (II) with six co-ordination will have octahedral geometry.
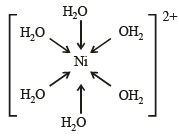
Note : With water as ligand, Ni (II) forms octahedral complexes.
The common features among the species CN–, CO and NO+ are (2001S)- a)bond order three and isoelectronic
- b)bond order three and weak field ligands
- c)bond order two and π-acceptors
- d)isoelectronic and weak field ligands
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The common features among the species CN–, CO and NO+ are (2001S)
a)
bond order three and isoelectronic
b)
bond order three and weak field ligands
c)
bond order two and π-acceptors
d)
isoelectronic and weak field ligands
|
|
Vivek answered |
Use MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY for finding the electronic configuration of the 3 molecules.
The number and type of bonds between two carbon atoms in CaC2 are : (1996 - 1 Mark)- a)one sigma (σ) and one pi(π) bonds
- b)one sigma (σ) and two pi(π) bonds
- c)one sigma (σ) and one and a half pi(π) bonds
- d)one sigma (σ) bond
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number and type of bonds between two carbon atoms in CaC2 are : (1996 - 1 Mark)
a)
one sigma (σ) and one pi(π) bonds
b)
one sigma (σ) and two pi(π) bonds
c)
one sigma (σ) and one and a half pi(π) bonds
d)
one sigma (σ) bond
|
|
Sneha Pillai answered |
Calcium carbide is an ionic compound (Ca2+ C2–) which produces acetylene on reacting with water. Thus the structure of C2– is [C ≡ C]2–. It has one s and two p bonds. [∵ A triple bond consists of one s and two p-bonds]
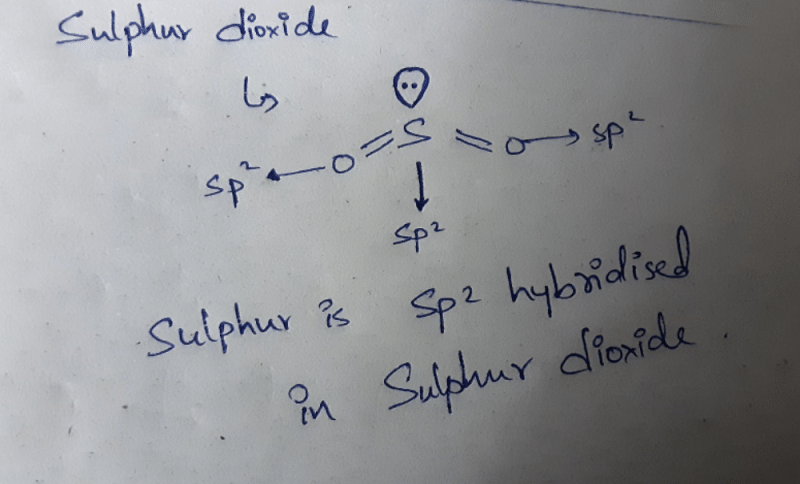
Which one of the following compounds has sp2 hydridization? (1997 - 1 Mark)- a)CO2
- b)SO2
- c)N2O
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following compounds has sp2 hydridization? (1997 - 1 Mark)
a)
CO2
b)
SO2
c)
N2O
d)
CO
|
|
Keerthana Bose answered |
TIPS/Formulae : H = 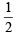 (V + M – C + A)
(V + M – C + A)
(i) CO2; H =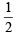 (4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2
(4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2
∴ sp hybridisation.
(ii) SO2; H =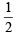 (6 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 3
(6 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 3
∴ sp2 hybridisation.
(iii) CO; H =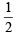 (4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2
(4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2
∴ sp hybridisation.
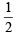 (V + M – C + A)
(V + M – C + A)(i) CO2; H =
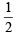 (4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2
(4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2∴ sp hybridisation.
(ii) SO2; H =
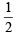 (6 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 3
(6 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 3∴ sp2 hybridisation.
(iii) CO; H =
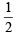 (4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2
(4 + 0 – 0 + 0) = 2∴ sp hybridisation.
On hybridization of one s and one p orbitals we get :- a)two mutually perpendicular orbitals (1984 - 1 Mark)
- b)two orbitals at 180º
- c)four orbitals directed tetrahedrally
- d)three orbitals in a plane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
On hybridization of one s and one p orbitals we get :
a)
two mutually perpendicular orbitals (1984 - 1 Mark)
b)
two orbitals at 180º
c)
four orbitals directed tetrahedrally
d)
three orbitals in a plane

|
Manisha Mehta answered |
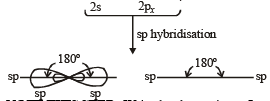
TIPS/Formulae : sp type of hybridization involves the intermixing of one s and one p (say px) orbitals to give two equivalent hybrid orbitals, known as sp hybrid orbitals.
The two sp hybrid orbitals are directed diagonally, i.e., in a straight line with an angle of 180º (collinear orbitals). The other two p orbitals (say py and pz) remain pure.
The two sp hybrid orbitals are directed diagonally, i.e., in a straight line with an angle of 180º (collinear orbitals). The other two p orbitals (say py and pz) remain pure.
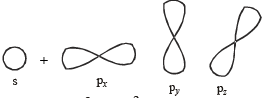
Hydrogen bonding is maximum in (1987 - 1 Mark)- a)Ethanol
- b)Diethyl ether
- c)Ethyl chloride
- d)Triethylamine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen bonding is maximum in (1987 - 1 Mark)
a)
Ethanol
b)
Diethyl ether
c)
Ethyl chloride
d)
Triethylamine
|
|
Khaja Moinuddin answered |
Write all the options in Newman's projection form you'll get your answer for the question
Which of the following are isoelectronic and isostructural?NO3–, CO32–, ClO3–, SO3 (2003S)- a)NO3–, CO32–
- b)SO3 ,NO3–
- c)ClO3–, CO32–
- d)CO32–, SO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are isoelectronic and isostructural?NO3–, CO32–, ClO3–, SO3 (2003S)
a)
NO3–, CO32–
b)
SO3 ,NO3–
c)
ClO3–, CO32–
d)
CO32–, SO3
|
|
Tanishq Singh answered |
NOTE : Isoelectronic species have same number of electrons and isostructural species have same type of hybridisation at central atom.
NO3– ; No. of e– = 7 + 8 × 3 + 1 = 32, hybridisation of N in NO3– is sp3
CO32– ; No. of e– = 6 + 8 × 3 + 2 = 32, hybridisation of C in
CO32– is sp3 ClO3– ; No. of e– = 17 + 8 × 3 + 1 = 42, hybridisation of Cl in
ClO3– is sp3 SO3; No. of e– = 16 + 8 × 3 = 40, hybridisation of S in
SO3 is sp2
∴ NO3– and CO32– are isostructural and isoelectronic.
NO3– ; No. of e– = 7 + 8 × 3 + 1 = 32, hybridisation of N in NO3– is sp3
CO32– ; No. of e– = 6 + 8 × 3 + 2 = 32, hybridisation of C in
CO32– is sp3 ClO3– ; No. of e– = 17 + 8 × 3 + 1 = 42, hybridisation of Cl in
ClO3– is sp3 SO3; No. of e– = 16 + 8 × 3 = 40, hybridisation of S in
SO3 is sp2
∴ NO3– and CO32– are isostructural and isoelectronic.
The correct order of increasing C — O bond length of CO, CO2-3, CO2, is (1999 - 2 Marks)- a)
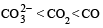
- b)
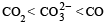
- c)
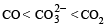
- d)
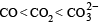
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing C — O bond length of CO, CO2-3, CO2, is (1999 - 2 Marks)
a)
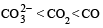
b)
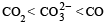
c)
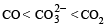
d)
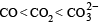

|
Anil Kumar answered |
D is the correct answer. It is true.
The hydrogen bond is strongest in : (1986 - 1 Mark)- a)O – H...........S
- b)S – H...........O
- c)F – H...........F
- d)F – H...........O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The hydrogen bond is strongest in : (1986 - 1 Mark)
a)
O – H...........S
b)
S – H...........O
c)
F – H...........F
d)
F – H...........O

|
Akshita Khandelwal answered |
The strength of an individual H bond depends on the polarity of the H-X bond and therefore on the electronegativity of X ( the more delta positive the H atom, the stronger the electrostatic force of attraction between it and a lone pair of electrons). Thus, on a per bond basis, HF H bonding is strongest.
The species having pyramidal shape is : (2010)- a)SO3
- b)BrF3
- c)SiO32–
- d)OSF2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The species having pyramidal shape is : (2010)
a)
SO3
b)
BrF3
c)
SiO32–
d)
OSF2
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
OSF2 : 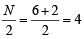 . It has 1 lone pair.
. It has 1 lone pair.
 . It has 1 lone pair.
. It has 1 lone pair.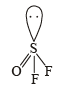 (Shape is trigonal pyramidal)
(Shape is trigonal pyramidal)The shapes of SO3, BrF3 and SiO32- are triangular planar respectively.
Identify the least stable ion amongst the following : (2002S)- a)Li–
- b)Be–
- c)B–
- d)C–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the least stable ion amongst the following : (2002S)
a)
Li–
b)
Be–
c)
B–
d)
C–

|
Sidharth Gupta answered |
Negative charge on metal is least stable so we have to choose from Li-and Be- so write their electron configuration so Li- achieving nobal gas confrigation so it is more stable then Be-
Pick out the isoelectronic structures from the following; (1993 - 1 Mark)I.CH+3 II.H3O+ III. NH3 IV CH3–- a)I and II
- b)III and IV
- c)I and III
- d)II, III and IV
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick out the isoelectronic structures from the following; (1993 - 1 Mark)
I.CH+3 II.H3O+ III. NH3 IV CH3–
a)
I and II
b)
III and IV
c)
I and III
d)
II, III and IV
|
|
Bhavana Gupta answered |
No. of e– in CH3+ = 6 + 3 – 1 = 8
No. of e– in H3O+ = 3 + 8 – 1 = 10
No. of e– in NH3 = 7 + 3 = 10
No. of e– in CH3– = 6 + 3 + 1 = 10
∴ H3O+, NH3 and CH3– are isoelectronic.
No. of e– in H3O+ = 3 + 8 – 1 = 10
No. of e– in NH3 = 7 + 3 = 10
No. of e– in CH3– = 6 + 3 + 1 = 10
∴ H3O+, NH3 and CH3– are isoelectronic.
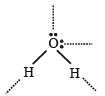
The maximum possible number of hydrogen bonds a water molecule can form is (1992 - 1 Mark)- a)2
- b)4
- c)3
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum possible number of hydrogen bonds a water molecule can form is (1992 - 1 Mark)
a)
2
b)
4
c)
3
d)
1
|
|
Krithika Choudhury answered |
H2O molecule can for m four hydr ogen bonds per molecule, two via lone pairs and two via hydrogen atoms.
The molecule which has zero dipole moment is :- a)CH2Cl2
- b)BF3 (1989 - 1 Mark)
- c)NF3
- d)ClO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecule which has zero dipole moment is :
a)
CH2Cl2
b)
BF3 (1989 - 1 Mark)
c)
NF3
d)
ClO2
|
|
Sanjana Sengupta answered |
TIPS/Formulae : Dipole moment of compound having regular geometry and same type of atoms is zero. It is vector quantity.
The zero dipole moment of BF3 is due to its symmetrical (triangular planar) structure. The three fluorine atoms lie at the corners of an equilateral triangle with boron at the centre.
NOTE : The vectorial addition of the dipole moments of the three bonds gives a net sum of zero because the resultant of any two dipole moments is equal and opposite to the third. The dipole moment of NH3 is 1.46 D indicating its unsymmetrical structure. The dipole moment of CH2Cl2 (the molecule uses sp3 hybridisation but is not symmetric) is 1.57D.
The zero dipole moment of BF3 is due to its symmetrical (triangular planar) structure. The three fluorine atoms lie at the corners of an equilateral triangle with boron at the centre.
NOTE : The vectorial addition of the dipole moments of the three bonds gives a net sum of zero because the resultant of any two dipole moments is equal and opposite to the third. The dipole moment of NH3 is 1.46 D indicating its unsymmetrical structure. The dipole moment of CH2Cl2 (the molecule uses sp3 hybridisation but is not symmetric) is 1.57D.
Which of the following is paramagnetic? (1989 - 1 Mark)- a)O-2
- b)CN–
- c)CO
- d)NO+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is paramagnetic? (1989 - 1 Mark)
a)
O-2
b)
CN–
c)
CO
d)
NO+

|
Amrutha Chaudhary answered |
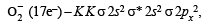
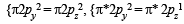
Thus, O-2 has one unpaired electron; hence it is paramagnetic. Other species have no unpaired electron.
All of them have 14 electrons.
All of them have 14 electrons.
Element X is strongly electropositive and element Y is strongly electronegative. Both are univalent. The compound formed would be (1980)- a)X+Y–
- b)X–X+
- c)X–Y
- d)X →Y
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Element X is strongly electropositive and element Y is strongly electronegative. Both are univalent. The compound formed would be (1980)
a)
X+Y–
b)
X–X+
c)
X–Y
d)
X →Y
|
|
Shreya Kumar answered |
X+ Y – ∵ Electropositive elements forms cation and electronegative elements forms anion.
Except this all compounds are ionic.
Except this all compounds are ionic.
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ? (2002S)- a)N2
- b)F2
- c)O-2
- d)O22-
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ? (2002S)
a)
N2
b)
F2
c)
O-2
d)
O22-

|
Abhishek Singh answered |
As in option c there are 17 electrons and when we write the molecular electronic configuration of these electrons we see that there is one unpaired electron present in (2pie antibonding molecular orbital ) ..
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemical Bonding, Structure and Properties - Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2) 2025 is part of BMAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BMAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BMAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemical Bonding, Structure and Properties - Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2) in English & Hindi are available as part of BMAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BMAT Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for BMAT (Section 2)
2 videos|143 docs|35 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup