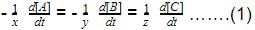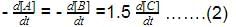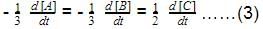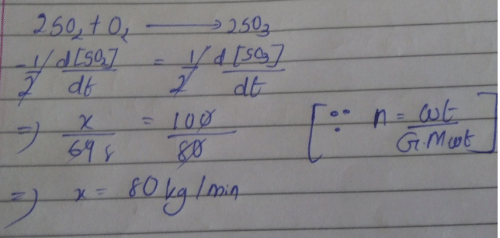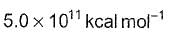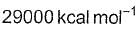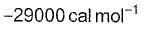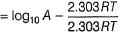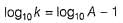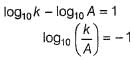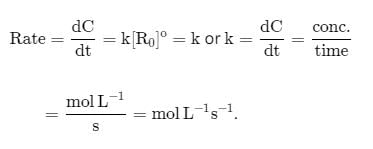All Exams >
JAMB >
Chemistry for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Rates of Chemical Reaction for JAMB Exam
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
- a)k[NO2]
- b)k[NO2]0
- c)k[NO2]3
- d)k[NO2]2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
a)
k[NO2]
b)
k[NO2]0
c)
k[NO2]3
d)
k[NO2]2
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Given unit of rate = mol L-1 s-1
General formula for unit of rate = mol n-1 Ln-1 s -1
On equating,
1-n = 1 ⇒ n = 0
n-1 = -1 ⇒ n = 0
General formula for unit of rate = mol n-1 Ln-1 s -1
On equating,
1-n = 1 ⇒ n = 0
n-1 = -1 ⇒ n = 0
Hence, it is a zero order reaction.
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by __________0C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.- a)2
- b)10
- c)100
- d)50
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by __________0C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.
a)
2
b)
10
c)
100
d)
50

|
Devika Banerjee answered |
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by 100C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants. Thus, rate law is equal to
Thus, rate law is equal to- a)k[A][B]
- b)k[A][B]2
- c) k[A]
- d) k[B]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.
Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants.
Thus, rate law is equal to
a)
k[A][B]
b)
k[A][B]2
c)
k[A]
d)
k[B]
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Let order w.r.t. A = a, order w.r.t. B = b
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by about [AIEEE 2011]a)64 timesb)32 timesc)24 timesd)10 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Rate at 50 degree C/(Rate at T1 degree C)
= (2)^(ΔT/T1)
= (2)^(50/10)
= 2^5
= 32
Hence, the rate of the reaction increases by 32 times.
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by- a)Arrhenius equation
- b)Kirchoff’s Equation
- c)Clauius Claperyron equation
- d)Gibb’s Helmholtz equation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by
a)
Arrhenius equation
b)
Kirchoff’s Equation
c)
Clauius Claperyron equation
d)
Gibb’s Helmholtz equation
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
Increasing the temperature increasesreaction rates because of the disproportionately large increase in the number of high energy collisions. It is only these collisions (possessing at least the activation energy for the reaction) which result in a reaction.
The reactions with low activation energy are- a)Slow
- b)Non-spontaneous
- c)Fast
- d)Always spontaneous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reactions with low activation energy are
a)
Slow
b)
Non-spontaneous
c)
Fast
d)
Always spontaneous
|
|
Vivek Godara answered |
Low activation energy mean energy reguire for reaction to occur is low so product making is fast
A foreign substance that increase the speed of a chemical reaction is called- a)promotor
- b)catalyst
- c)moderator
- d)inhibitor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A foreign substance that increase the speed of a chemical reaction is called
a)
promotor
b)
catalyst
c)
moderator
d)
inhibitor
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Catalyst: Substances which alter the rate of a chemical reaction and themselves remain chemically and quantitatively unchanged after the reaction are known as catalysts and the phenomenon is known as catalysis.
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given byrate = k[A]n [B]mIf concentration of A is doubled and that of 8 is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be - a)
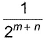
- b)(m + n)
- c)(n - m)
- d)2(n-m)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given by
rate = k[A]n [B]m
If concentration of A is doubled and that of 8 is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be
a)
b)
(m + n)
c)
(n - m)
d)
2(n-m)

|
Top Rankers answered |
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O- a)O2
- b)NO
- c)H2O
- d)Equal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
a)
O2
b)
NO
c)
H2O
d)
Equal

|
Nabanita Basu answered |
Understanding the Reaction
The given reaction is:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
This reaction involves the disappearance of ammonia (NH3) and the appearance of the products NO and H2O.
Rate of Reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction can be expressed in terms of the rate of disappearance of reactants or the rate of appearance of products.
Stoichiometry of the Reaction
- According to the stoichiometry:
- 4 moles of NH3 produce 4 moles of NO and 6 moles of H2O.
- The coefficients in the balanced equation indicate the relative rates of disappearance and appearance.
Rate of Disappearance
- The rate of disappearance of NH3 is given by:
Rate = - (1/4) * d[NH3]/dt
- The rates for O2, NO, and H2O can be expressed similarly:
- O2: Rate = - (1/5) * d[O2]/dt
- NO: Rate = (1/4) * d[NO]/dt
- H2O: Rate = (1/6) * d[H2O]/dt
Comparison of Rates
To find the maximum rate of disappearance, we can compare the rates derived from the balanced equation:
- NH3: - (1/4) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- O2: - (1/5) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- NO: (1/4) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
- H2O: (1/6) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
The fractions reveal how many moles of each substance are involved in the reaction. The lower the denominator, the higher the rate of disappearance or appearance.
Conclusion
- Among the reactants and products, H2O has the highest coefficient when considering the rate of disappearance of NH3.
- Therefore, the maximum rate of disappearance is related to H2O's formation.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' (H2O).
The given reaction is:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
This reaction involves the disappearance of ammonia (NH3) and the appearance of the products NO and H2O.
Rate of Reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction can be expressed in terms of the rate of disappearance of reactants or the rate of appearance of products.
Stoichiometry of the Reaction
- According to the stoichiometry:
- 4 moles of NH3 produce 4 moles of NO and 6 moles of H2O.
- The coefficients in the balanced equation indicate the relative rates of disappearance and appearance.
Rate of Disappearance
- The rate of disappearance of NH3 is given by:
Rate = - (1/4) * d[NH3]/dt
- The rates for O2, NO, and H2O can be expressed similarly:
- O2: Rate = - (1/5) * d[O2]/dt
- NO: Rate = (1/4) * d[NO]/dt
- H2O: Rate = (1/6) * d[H2O]/dt
Comparison of Rates
To find the maximum rate of disappearance, we can compare the rates derived from the balanced equation:
- NH3: - (1/4) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- O2: - (1/5) (for every 1 mole of disappearance)
- NO: (1/4) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
- H2O: (1/6) (for every 1 mole of appearance)
The fractions reveal how many moles of each substance are involved in the reaction. The lower the denominator, the higher the rate of disappearance or appearance.
Conclusion
- Among the reactants and products, H2O has the highest coefficient when considering the rate of disappearance of NH3.
- Therefore, the maximum rate of disappearance is related to H2O's formation.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C' (H2O).
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of- a)Rate of reaction
- b)Mechanism of reaction
- c)Factors which affects the rate of reaction
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of
a)
Rate of reaction
b)
Mechanism of reaction
c)
Factors which affects the rate of reaction
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of rate of reaction, their mechanism and the factors which affects the rate of reaction. It specifies all the general characteristics of a chemical reaction.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O- a)O2
- b)NO
- c)H2O
- d)Equal
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
a)
O2
b)
NO
c)
H2O
d)
Equal
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
By stoichiometry of the reaction

similarly,
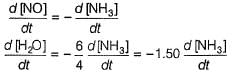
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?- a)The reaction with the greater activation energy will be faster
- b)The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster
- c)The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature also
- d)Temperature range is also required
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two reactions with different activation energies have the same rate at room temperature. Which statement correctly describes the rates of these two reactions at the same higher temperature?
a)
The reaction with the greater activation energy will be faster
b)
The reaction with the smaller activation energy will be faster
c)
The two reactions will have the same rate at higher temperature also
d)
Temperature range is also required

|
Pranjal Pillai answered |
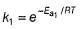

If temperature is increased to T`,
If 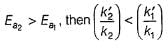
Thus, reaction with smaller activation energy will be faster on increasing temperature.
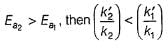
Thus, reaction with smaller activation energy will be faster on increasing temperature.
For the reaction, 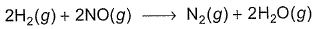
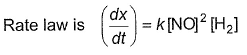 Mechanism is given by
Mechanism is given by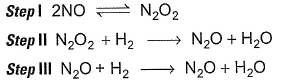 Rate law is true, if
Rate law is true, if - a)step I is the slow step
- b)step II is the slow step
- c)step III is the slow step
- d)step I and step II are the slow steps
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction, 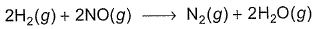
Mechanism is given by
Rate law is true, if
a)
step I is the slow step
b)
step II is the slow step
c)
step III is the slow step
d)
step I and step II are the slow steps

|
Thedot Starry answered |
Yes b is correct because the rate law is written using the slowest step and it matches with second option.
. What will be the value of instantaneous rate of reaction from the graph?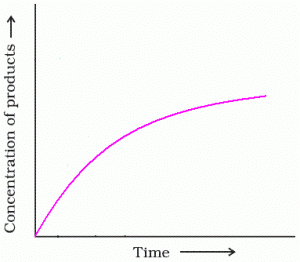
- a)rinst = 1/ Slope
- b)rinst = Slope
- c)rinst = – Slope
- d)rinst = – 1/ Slope
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
. What will be the value of instantaneous rate of reaction from the graph?

a)
rinst = 1/ Slope
b)
rinst = Slope
c)
rinst = – Slope
d)
rinst = – 1/ Slope
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
If you make a graph of concentration of reactant vs time, the instantaneous reaction rate at a given time is the slope of the tangent line at that point in time. It is also the value of the rate law at a specific concentration (dA/dt is rate = k [A]).
The activation energies of two reactions are given as Ea1= 40 J and Ea2= 80 J, then the relation between their rate constants can be written as:- a)k1 > k2
- b)k1 < k2
- c)k1 = k2
- d)k1 + k2 = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The activation energies of two reactions are given as Ea1= 40 J and Ea2= 80 J, then the relation between their rate constants can be written as:
a)
k1 > k2
b)
k1 < k2
c)
k1 = k2
d)
k1 + k2 = 0
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
As the value of activation energy, Ea increases, the value of rate constant, k decreases.
So, k1 > k2 since E1 < E2
For the reaction,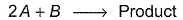 The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is
The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is- a)L mol-1s-1
- b)mol L-1s-1
- c)unitless
- d)S-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
The half-life period was independent of concentration of B. On doubling the concentration A, rate increases two times. Thus, unit of rate constant for this reaction is
a)
L mol-1s-1
b)
mol L-1s-1
c)
unitless
d)
S-1
|
|
Shanaya Choudhary answered |
I apologize, but your question about the reaction is incomplete. Could you provide more information or detail about the reaction you are referring to?
The rate equation for the reaction,2A + B → Cis found to be, rate = k[A] [B]Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the- a)unit of k must be s-1
- b)t1/2 is constant
- c)rate of formation of C is half of the rate of disappearance of A
- d)value of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and 8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate equation for the reaction,
2A + B → C
is found to be, rate = k[A] [B]
Q. The correct statement in relation to this reaction is that the
a)
unit of k must be s-1
b)
t1/2 is constant
c)
rate of formation of C is half of the rate of disappearance of A
d)
value of k is independent of the initial concentration of A and 8

|
Amar Jain answered |
Rate = k (A)[B]
The given reaction is first order in A and first order is B.
Thus, total order = 2
Thus, total order = 2
(a) Unit of k = cone 1 - n time -1 = conc-1 time-1 Thus, (a) is false.
(b) of second-order reaction, thus (b) is false.
of second-order reaction, thus (b) is false.
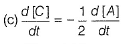
(b)
Thus, (c) is correct.
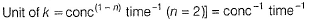
Thus, value of k is dependent on the concentration of A and B. Thus, (d) is false.
Thus, value of k is dependent on the concentration of A and B. Thus, (d) is false.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)In the following reaction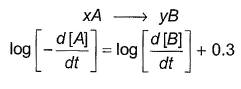 Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?- a)2
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
In the following reaction
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Praveen Reddy answered |
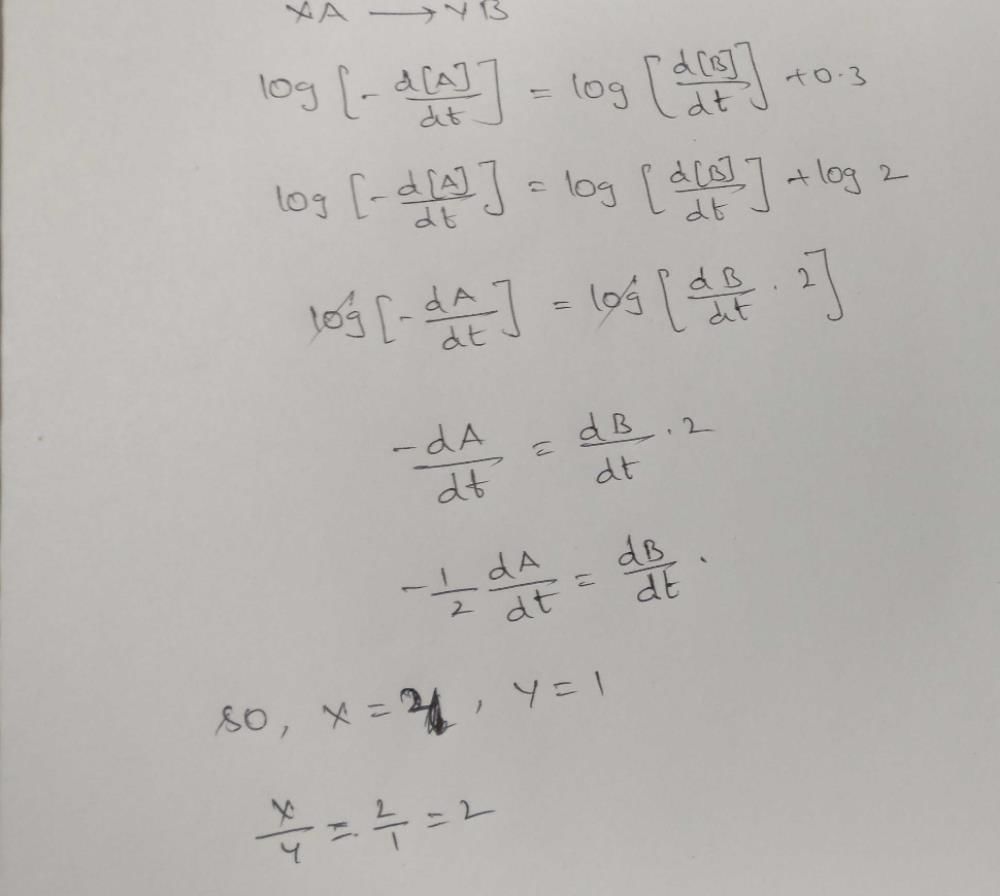
The rate constant, activation energy and Arrhenius parameter of a chemical reaction at 25°C are 3.0 x 10-4 s-1, 104.4 kJ mol-1 and 6.0 x 1014 s-1 respectively. The value of the rate constant at infinite temperature is is- a)6.0 x 1030 s-1
- b)2 x 1018 s-1
- c)6.0 x 1014s-1
- d) Infinity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate constant, activation energy and Arrhenius parameter of a chemical reaction at 25°C are 3.0 x 10-4 s-1, 104.4 kJ mol-1 and 6.0 x 1014 s-1 respectively. The value of the rate constant at infinite temperature is is
a)
6.0 x 1030 s-1
b)
2 x 1018 s-1
c)
6.0 x 1014s-1
d)
Infinity
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option C
Arrhenius equation
⇒ K = Ae−Ea/RT
As T → ∞,
RT → ∞
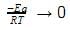
e−Ea/RT → 1
Hence K → A as T→∞
∴ Value of K as T → ∞ = 6.0×1014S−1
Arrhenius equation
⇒ K = Ae−Ea/RT
As T → ∞,
RT → ∞
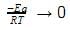
e−Ea/RT → 1
Hence K → A as T→∞
∴ Value of K as T → ∞ = 6.0×1014S−1
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants __________ with time or the concentration of products ___________ with time.- a)Increase, increase
- b)Decrease, decrease
- c)Decrease, increase
- d)Increase, decrease
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants __________ with time or the concentration of products ___________ with time.
a)
Increase, increase
b)
Decrease, decrease
c)
Decrease, increase
d)
Increase, decrease
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants decreases with time or the concentration of products increases with time.
For the reaction,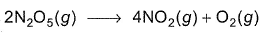
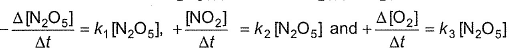 Thus,
Thus,- a)k1 = k2 = k3
- b)2k1 = k2 = 4k3
- c)2k1 = 4k2 = k3
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
Thus,
a)
k1 = k2 = k3
b)
2k1 = k2 = 4k3
c)
2k1 = 4k2 = k3
d)
None of these

|
Chetu Bola answered |
V hav a formula. I. E For a reaction aA-----bB+cC Rate of reaction is [A] /[t]. a AC to given, 1/2[N205]/[t]=k1[N205]/2------eq(1) 1/4[N02]/[t]=k2[N205]/4------eq(2) 1/1[02]/[t]=k3[02]------eq(3) On diving all d 3 equations, v get K1/2=k2/4=k3 Multiply vit 4 to all d ratios V get 2k1=k2=4k3
Direction (Q. No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.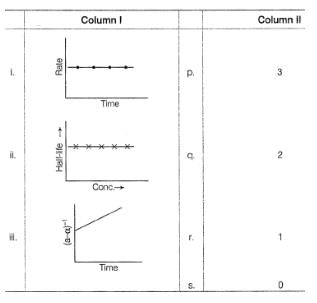

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 14) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Harsh Singhal answered |
For 2nd graph half live is cons.on increasing conc.so it is of 1st order
for 1st graph rate remains cons.with time means independent on conc.so it is of 0 order
so ans.is c
for 1st graph rate remains cons.with time means independent on conc.so it is of 0 order
so ans.is c
For a reaction, time of 75% reaction is thrice of time of 50% reaction. Thus, order of the reaction is- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For a reaction, time of 75% reaction is thrice of time of 50% reaction. Thus, order of the reaction is
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Anuj Unni answered |
For n th order reaction (n > 1)
This equation is true, if n = 2
Identify the incorrect statement- a)ftp stands for file transfer protocol
- b)ftp uses two parallel TCP connections
- c)ftp sends its control information in band
- d)ftp sends exactly one file over the data connection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement
a)
ftp stands for file transfer protocol
b)
ftp uses two parallel TCP connections
c)
ftp sends its control information in band
d)
ftp sends exactly one file over the data connection
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Out-of-band controlis a characteristic of network protocols with which data control is regulated. Out-of-band control passes control data on a separate connection from main data. Protocols such asFTPuse out-of-band control. FTP uses two parallel TCP connections, one connection for sending control information (such as a request to transfer a file) and another connection foractually transferring the file. Because the control information is not sent over the same connection that the file is sent over, FTP sends control information out of band
For the reaction, 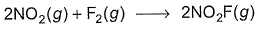 Steps are
Steps are 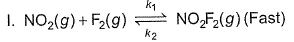
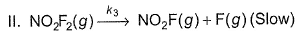
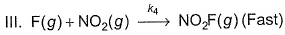
- a)Rate law is in agreement with net stoichiometry of the reaction
- b)Rate law is in agreement with slow step
- c)Rate law is in agreement with net stoichiometry of the reaction as well as with slow step
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction, 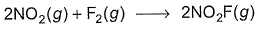
Steps are
a)
Rate law is in agreement with net stoichiometry of the reaction
b)
Rate law is in agreement with slow step
c)
Rate law is in agreement with net stoichiometry of the reaction as well as with slow step
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ananya Singh answered |
Because slow step is the rate determining step
Chemical substances speeding up the rate of chemical reaction is called as
- a)pressure
- b)concentration
- c)catalysts
- d)inhibitors
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Chemical substances speeding up the rate of chemical reaction is called as
a)
pressure
b)
concentration
c)
catalysts
d)
inhibitors
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of the reaction without being consumed by the reaction itself. When a catalyst is added, the activation energy is lowered because the catalyst provides a new reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
Passage IIIA reaction between substances A and B is represented as: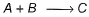 Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :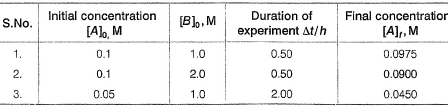 Q.Rate constant of the overall reaction is
Q.Rate constant of the overall reaction is- a)5.0 * 10-2 M-1 h-1
- b)5.0 * 10-2 M-2 h-1
- c)5.0 * 10-2 h-1
- d)5.0 * 10-2 mh-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage III
A reaction between substances A and B is represented as:
Observations on the rate of this reaction are obtained as :
Q.
Rate constant of the overall reaction is
a)
5.0 * 10-2 M-1 h-1
b)
5.0 * 10-2 M-2 h-1
c)
5.0 * 10-2 h-1
d)
5.0 * 10-2 mh-1

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
where, a == order w.r.t. A, 6 = order w.r.t. B
(i) 5.0 x 10-3 = K [0.1]a [1.0]b
(ii) 2.0 x 10-2 = k [ 0.1]a[2.0]b
(iii) 2.5 x 10-3 = k [0.05]a[1.0]b
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
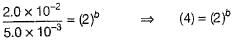
(2)2 = (2)b
∴ b = 2
Order w.r.t.B = 2
From Eqs. (i) and (iii), we get
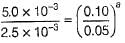
(2) = (2)a
a = 1
Order w.r.t.A
From Eq. (ii),
5.0 x 10-3 = k (0.1) (1.0)2
∴ k = 5.0 x 10-2m-2h-1
Rate of a reaction can be expressed by Arrhenius equation as k = Ae-EalRT. In this equation, Ea represents.- a)the energy above which all the colliding molecules will react
- b)the energy below which colliding molecules will not react
- c)the total energy of the reacting molecules at a temperature T
- d)the fraction of molecules with energy greater than the activation energy of the reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of a reaction can be expressed by Arrhenius equation as k = Ae-EalRT. In this equation, Ea represents.
a)
the energy above which all the colliding molecules will react
b)
the energy below which colliding molecules will not react
c)
the total energy of the reacting molecules at a temperature T
d)
the fraction of molecules with energy greater than the activation energy of the reaction

|
Amar Pillai answered |
Ea (activation energy) is the energy required to activate the reactant so that they may collide and give the final product. Below point B, the reactants will not react at all.
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-21) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).At room temperature (27°C) milk turns sour in about 64 h. In a refrigerator at -3°C, milk can be stored x times as long before it sours. The activation energy of the reaction that causes the souring of milk is 11.231 kcal mol-1.
What is the value of x?
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-21) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
At room temperature (27°C) milk turns sour in about 64 h. In a refrigerator at -3°C, milk can be stored x times as long before it sours. The activation energy of the reaction that causes the souring of milk is 11.231 kcal mol-1.
What is the value of x?
What is the value of x?

|
Rajdeep Saini answered |
Rate of souring of milk at 27°C (300 K) is  times faster than at-3°C(270K).
times faster than at-3°C(270K).
∴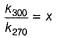
∴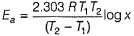
11.231 kcal mol-1 = 2.303 x 2 x10-3 kcal mol-1k-1
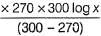
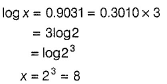
∴
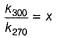
∴
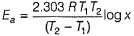
11.231 kcal mol-1 = 2.303 x 2 x10-3 kcal mol-1k-1
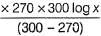
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.A chemical reaction proceeds through the following steps :Step I, 2A ⇌ X fast
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fastQ. The rate law for the overall reaction is- a)K'[A]2
- b)K'[B]2
- c)K'[A][B]
- d)K'[A]2[B]
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
A chemical reaction proceeds through the following steps :
Step I, 2A ⇌ X fast
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fast
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fast
Q. The rate law for the overall reaction is
a)
K'[A]2
b)
K'[B]2
c)
K'[A][B]
d)
K'[A]2[B]
|
|
Chirag Joshi answered |
By slow step II,
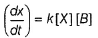
By reversible fast step

∴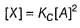
∴
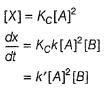
By reversible fast step

∴
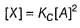
∴
If in the fermentation of sugar in an enzymatic solution that is 0.12 M, the concentration of sugar is reduced to 0.06 M in 10 h and to 0.03 M in 20 h. Thus, order of the reaction is - a)3
- b)2
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If in the fermentation of sugar in an enzymatic solution that is 0.12 M, the concentration of sugar is reduced to 0.06 M in 10 h and to 0.03 M in 20 h. Thus, order of the reaction is
a)
3
b)
2
c)
1
d)
0

|
Ashish Nambiar answered |

We find that, t75 = 2 x t50
Thus, given reaction is of first-order.
Kinetics of the following reaction,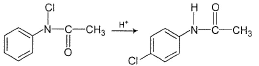 can be studied by
can be studied by- a)measurement of pH
- b)titration with hypo after adding Kl
- c)titration with AgNO3 solution
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Kinetics of the following reaction,
can be studied by
a)
measurement of pH
b)
titration with hypo after adding Kl
c)
titration with AgNO3 solution
d)
All of the above

|
Aditya Sen answered |
Cl-atom attached to N-atom, is an oxidising agent and can oxidise Kl to l2.
l2 can be titrated using hypo in iodometric titration.
Cl-atom attached to benzene nucleus is not an oxidising agent.
Rate law cannot be determined from balanced chemical equation if _______.- a)reverse reaction is involved.
- b) it is an elementary reaction.
- c) it is a sequence of elementary reactions.
- d)any of the reactants is in excess.
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate law cannot be determined from balanced chemical equation if _______.
a)
reverse reaction is involved.
b)
it is an elementary reaction.
c)
it is a sequence of elementary reactions.
d)
any of the reactants is in excess.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of the reaction without being consumed by the reaction itself. When a catalyst is added, the activation energy is lowered because the catalyst provides a new reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-12 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).Q. Rate constant of the reaction will be - a)0.54 L mol-1 s-1
- b)0.54 x 10-3 L mol-1 s-1
- c)5.4 s-1
- d)0.54s-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. Rate constant of the reaction will be
a)
0.54 L mol-1 s-1
b)
0.54 x 10-3 L mol-1 s-1
c)
5.4 s-1
d)
0.54s-1
|
|
Simran Patel answered |
Understanding the Reaction Rate
The given reaction is:
2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g)
The rate of the reaction is expressed as:
Rate = - (1/2) d[NO2]/dt
Given:
- Rate = 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1
- [NO2] = 0.01 mol L^-1
Rate Law Expression
For this reaction, the rate law can be expressed as:
Rate = k [NO2]^n
Where:
- k = rate constant
- n = order of the reaction
Assuming the reaction is first-order with respect to NO2 (n = 1):
Calculating the Rate Constant (k)
1. Substitute the given values into the rate law:
- Rate = k [NO2]
- 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1 = k (0.01 mol L^-1)
2. Rearranging the equation to solve for k:
- k = (5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1) / (0.01 mol L^-1)
- k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1
3. Converting to appropriate units:
- Since k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1 can also be expressed as:
- k = 0.54 x 10^-2 s^-1 = 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1 (taking into account the units of rate and concentration)
Conclusion
Thus, the rate constant k is 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1. The correct answer is option 'A'.
The given reaction is:
2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g)
The rate of the reaction is expressed as:
Rate = - (1/2) d[NO2]/dt
Given:
- Rate = 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1
- [NO2] = 0.01 mol L^-1
Rate Law Expression
For this reaction, the rate law can be expressed as:
Rate = k [NO2]^n
Where:
- k = rate constant
- n = order of the reaction
Assuming the reaction is first-order with respect to NO2 (n = 1):
Calculating the Rate Constant (k)
1. Substitute the given values into the rate law:
- Rate = k [NO2]
- 5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1 = k (0.01 mol L^-1)
2. Rearranging the equation to solve for k:
- k = (5.4 x 10^-5 mol L^-1 s^-1) / (0.01 mol L^-1)
- k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1
3. Converting to appropriate units:
- Since k = 5.4 x 10^-3 s^-1 can also be expressed as:
- k = 0.54 x 10^-2 s^-1 = 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1 (taking into account the units of rate and concentration)
Conclusion
Thus, the rate constant k is 0.54 L mol^-1 s^-1. The correct answer is option 'A'.
Chapter doubts & questions for Rates of Chemical Reaction - Chemistry for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Rates of Chemical Reaction - Chemistry for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for JAMB
213 videos|209 docs|162 tests
|