All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Respiration in Plants for JAMB Exam
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles- a)a and b
- b)a and d
- c)b and d
- d)b and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a)
a and b
b)
a and d
c)
b and d
d)
b and c
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Plants unlike animals have no special systems for breathing or gaseous exchange. Stomata and lenticels allow gaseous exchange by diffusion.
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
- a)It starts with a six-carbon compound.
- b)It occurs in mitochondria.
- c)It is also called the citric acid cycle.
- d)The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
a)
It starts with a six-carbon compound.
b)
It occurs in mitochondria.
c)
It is also called the citric acid cycle.
d)
The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle because this reaction starts with the six-carbon compound which is citric acid. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs cycle is a closed-loop cycle. And each loop of the cycle generates a molecule of ATP. This cycle consists of eight steps which include redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. It is an aerobic pathway because NADH is produced and the electrons released are used up in the next cycle which uses oxygen.
- The process of the cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl- CoA with oxaloacetate.
- This reaction is controlled by the amount of ATP present.
- If the ATP level increases then the rate of the reaction decreases and vice versa. After glycolysis, the pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
- The Krebs cycle is the pathway that all organisms use to generate energy. The intermediate compound that links pyruvate to the Krebs cycle is Acetyl CoA.
- So, the answer is option (B) ‘the intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid’.
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
- a)Respiratory products
- b)respiratory substrates
- c)ATP
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
a)
Respiratory products
b)
respiratory substrates
c)
ATP
d)
NADH

|
Shounak Nair answered |
The respiratory quotient depends upon the type of respiratory substrate used during respiration.
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of- a)NADPH
- b)FADH2
- c)ADP
- d)ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of
a)
NADPH
b)
FADH2
c)
ADP
d)
ATP
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
- Oxysomes refer to small round structures present within the folds of the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is also known as F0-F1 particles.
- F0 and F1 particles are found in the inner mitochondrial region and are attached to the cristae and help in ATP production and oxidation.
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by- a)GTP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)GDP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by
a)
GTP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
GDP

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
During conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesised.
The TCA cycle is named after- a)Robert Emerson
- b)Melvin Calvin
- c)Embden
- d)Hans Krebs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle is named after
a)
Robert Emerson
b)
Melvin Calvin
c)
Embden
d)
Hans Krebs
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
*Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release the stored energy........ *It is a part of cellular respiration........ *It is also called as citric acid cycle or Krebs cycles which is named after it's discoverer Hans Krebs..... Thus, the correct answer is option 'D'.
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because- a)Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
- b)It takes place is micrograms
- c)It takes place in inert medium
- d)Glucose is not available
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because
a)
Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
b)
It takes place is micrograms
c)
It takes place in inert medium
d)
Glucose is not available
|
|
Kuldeep Kuldeep answered |
Option a is correct. Because, in Anaerobic Respiration, respiration takes place on the absence of oxygen. Iteans, the oxidation of pyruvate takes place in the absence of oxygen to release CO2, Ethanol along with the release of Energy. Here, in Anaerobic Respiration, Water is not yet released due to the absence of oxygen. So, there will be incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place.
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in- a)Intermembrane space of mitochondria
- b)Mitochondrial matrix
- c)Inner membrane of mitochondria
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in
a)
Intermembrane space of mitochondria
b)
Mitochondrial matrix
c)
Inner membrane of mitochondria
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Mitochondrial matrix.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?- a)Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
- b)The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
- c)Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
- d)Mitochondria have a double membrane.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
a)
Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
b)
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
c)
Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
d)
Mitochondria have a double membrane.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mitochondria (singular - Mitochondrion) are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for the release of energy from food ,i.e, cellular respiration. This energy is released in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
While the cells release 2 ATP, mitochondria releases 34 ATP which adds up to 36 ATP. Since a major portion of the ATP is released by mitochondria, they are called the powerhouse of the cell.
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms- a)CO2
- b)CO2+ H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Acetyl CoA + CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms
a)
CO2
b)
CO2+ H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Acetyl CoA + CO2
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Pyruvate, the product obtained through glycolysis, gets oxidised with the loss of its carboxy group as CO2, to give acetyl Co-A, under aerobic condition. This acetyl Co-A is further oxidised completely to CO2 + H2O in citric acid cycle. Other options are incorrect as Lactic acid is formed in muscles under anaerobic conditions. Ethanol and CO2 are products of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells. CO2 and H2O are final and complete reaction products released at the end of cellular respiration.
The TCA cycle starts with- a)Condensation
- b)Dehydrogenation
- c)Phosphorylation
- d)Decarboxylation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle starts with
a)
Condensation
b)
Dehydrogenation
c)
Phosphorylation
d)
Decarboxylation

|
Anand Jain answered |
The TCA cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl group with oxaloacetic acid (OAA) and water to yield citric acid.
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is- a)Oxalo acetic acid
- b)NADH
- c)Acetyl-CoA
- d)NADP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is
a)
Oxalo acetic acid
b)
NADH
c)
Acetyl-CoA
d)
NADP
|
|
Ashutosh Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and yields two molecules of ATP along with two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Interconnection:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Acetyl-CoA is then used in the Krebs cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces NADH, which is used in the electron transport chain to produce more ATP.
Therefore, Acetyl-CoA is the enzyme that interconnects glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and yields two molecules of ATP along with two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Interconnection:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Acetyl-CoA is then used in the Krebs cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces NADH, which is used in the electron transport chain to produce more ATP.
Therefore, Acetyl-CoA is the enzyme that interconnects glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Choose the correct statement.- a)There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
- b)Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
- c)During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
- d)Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement.
a)
There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
b)
Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
c)
During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
d)
Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- Oxygen sits at the end of the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons, hydrogen and picks up protons to form water.
- Pyruvate is formed in the cytoplasm.
- During fermentation glucose is partially broken down by glycolysis.
- During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesized.
So, the correct option is 'Oxygen is vital in respiration for removal of hydrogen'.
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?- a)Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
- b)Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
- c)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
- d)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?
a)
Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
b)
Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
c)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
d)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
|
|
Akash Saini answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
Dough kept overnight in warm weather becomes soft and spongy due to- a)Absorption of CO2 from atmosphere
- b)Imbibition
- c)Fermentation
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dough kept overnight in warm weather becomes soft and spongy due to
a)
Absorption of CO2 from atmosphere
b)
Imbibition
c)
Fermentation
d)
All of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Fermentation can be described as an enzyme-catalyzed process in which one substrate is usually broken down by the enzymes produced by bacteria, yeast, and other microorganisms.
- Fermentation of glucose results in the formation of ethanol and carbon monoxide. This is an exothermic reaction and results in the release of energy. The changes observed in dough after keeping it overnight in warm weather is an example of fermentation.
________ is an obligate anaerobe.- a)Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- b)Clostridium tetani
- c)Azotobacter
- d)Beijerinckia
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
________ is an obligate anaerobe.
a)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
b)
Clostridium tetani
c)
Azotobacter
d)
Beijerinckia
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
- According to the mode of respiration, bacteria can be aerobic or anaerobic. Each of them is further of two types, obligate and facultative.
- Obligate anaerobic bacteria respire only anaerobically. They generally get killed under aerobic conditions, e.g., Clostridium tetani, C. botulinum etc.
- Facultative anaerobes are bacteria which generally respire aerobically but switch over to anaerobic mode of respiration, if oxygen becomes deficient, e.g., Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Mercury (Hg) is generally used in anaerobic respiration experiments because it does not react with ___________.- a)O2
- b)CO2
- c)H2O
- d)air
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mercury (Hg) is generally used in anaerobic respiration experiments because it does not react with ___________.
a)
O2
b)
CO2
c)
H2O
d)
air
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Mercury is very reactive towards oxygen. It reacts with the oxygen in the air and also reacts with dilute acids containing oxygen. However, mercury is comparatively non-reactive in water. This is why it is used in anaerobic respiration experiments.
Which of the following conversions involve ATP synthesis during glycolysis?- a)Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate
- b)Fructose-6-phosphate → Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
- c)1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) → 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conversions involve ATP synthesis during glycolysis?
a)
Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate
b)
Fructose-6-phosphate → Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
c)
1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) → 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
d)
All of these
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
In the energy conserving phase of glycolysis, the conversion of BPGA to PGA is catalyzed by phosphoglycerate kinase. The phosphate on carbon 1 is transferred to a molecule of ADP, yielding ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate. This type of ATP synthesis, traditionally referred to as substrate-level phosphorylation, involves the direct transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP, to form ATP.
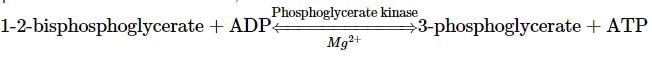
In Krebs cycle the FAD participates as electron acceptor during the conversion of- a)Succinyl CoA to succinic acid
- b)α− ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA
- c)Succinic acid to fumaric acid
- d)Fumaric acid to malic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Krebs cycle the FAD participates as electron acceptor during the conversion of
a)
Succinyl CoA to succinic acid
b)
α− ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA
c)
Succinic acid to fumaric acid
d)
Fumaric acid to malic acid
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Succinate undergoes dehydrogenation to form fumarate with the help of a membrane based enzyme succinate dehydrogenase. FADH2 (reduced flavin adenine dinucleotide) is produced.
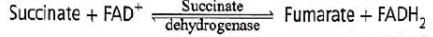
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Shreya Datta answered |
Explanation of Statements
The two statements provided about mitochondria and ATP synthesis are fundamental concepts in cell biology.
Statement 1: Mitochondria as the Powerhouse of the Cell
- Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouse of the cell."
- This term signifies their primary role in energy production through aerobic respiration.
Statement 2: ATP Synthesis Occurs in Mitochondria
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of the cell.
- The synthesis of ATP occurs in mitochondria through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements are accurate.
- Mitochondria are indeed responsible for generating ATP, which provides energy for various cellular functions.
Relationship Between the Statements
- Statement 2 serves as a direct explanation of why statement 1 is true.
- The ability of mitochondria to synthesize ATP is what qualifies them as the powerhouse of the cell.
Conclusion
- Therefore, both statements are correct, and statement 2 provides the correct explanation for statement 1.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'A': "Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1."
Understanding these concepts is crucial for NEET preparation, as they form the basis of cellular respiration and energy metabolism in biological systems.
The two statements provided about mitochondria and ATP synthesis are fundamental concepts in cell biology.
Statement 1: Mitochondria as the Powerhouse of the Cell
- Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouse of the cell."
- This term signifies their primary role in energy production through aerobic respiration.
Statement 2: ATP Synthesis Occurs in Mitochondria
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of the cell.
- The synthesis of ATP occurs in mitochondria through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements are accurate.
- Mitochondria are indeed responsible for generating ATP, which provides energy for various cellular functions.
Relationship Between the Statements
- Statement 2 serves as a direct explanation of why statement 1 is true.
- The ability of mitochondria to synthesize ATP is what qualifies them as the powerhouse of the cell.
Conclusion
- Therefore, both statements are correct, and statement 2 provides the correct explanation for statement 1.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'A': "Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1."
Understanding these concepts is crucial for NEET preparation, as they form the basis of cellular respiration and energy metabolism in biological systems.
During complete metabolism of glucose, the number of ATP formed is- a)2
- b)12
- c)36
- d)44
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During complete metabolism of glucose, the number of ATP formed is
a)
2
b)
12
c)
36
d)
44
|
|
Anagha Sengupta answered |
Complete Metabolism of Glucose
The complete metabolism of glucose through cellular respiration involves several stages: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). Here’s a breakdown of ATP production in each stage.
1. Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm.
- Converts one glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Produces:
- 2 ATP (net gain).
- 2 NADH (which can yield additional ATP during oxidative phosphorylation).
2. Pyruvate Decarboxylation
- Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is converted to Acetyl-CoA.
- Produces:
- 2 NADH (one from each pyruvate).
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
- Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Each Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, producing:
- 2 ATP (1 ATP per cycle, and two cycles per glucose).
- 6 NADH (3 per cycle).
- 2 FADH2 (1 per cycle).
4. Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
- Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- NADH produces approximately 2.5 ATP each, and FADH2 produces about 1.5 ATP each.
- From the previous stages:
- 10 NADH = 10 x 2.5 = 25 ATP.
- 2 FADH2 = 2 x 1.5 = 3 ATP.
Total ATP Calculation
- Glycolysis: 2 ATP + 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Pyruvate Decarboxylation: 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP + 6 NADH (15 ATP) + 2 FADH2 (3 ATP).
- Total: 2 + 5 + 5 + 2 + 15 + 3 = 32 ATP.
However, due to the use of ATP for transport and other processes, the net yield is typically rounded to about 30-36 ATP, commonly cited as 36 ATP for simplicity.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C', with 36 ATP being formed during the complete metabolism of one glucose molecule.
The complete metabolism of glucose through cellular respiration involves several stages: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). Here’s a breakdown of ATP production in each stage.
1. Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm.
- Converts one glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Produces:
- 2 ATP (net gain).
- 2 NADH (which can yield additional ATP during oxidative phosphorylation).
2. Pyruvate Decarboxylation
- Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is converted to Acetyl-CoA.
- Produces:
- 2 NADH (one from each pyruvate).
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
- Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Each Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, producing:
- 2 ATP (1 ATP per cycle, and two cycles per glucose).
- 6 NADH (3 per cycle).
- 2 FADH2 (1 per cycle).
4. Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
- Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- NADH produces approximately 2.5 ATP each, and FADH2 produces about 1.5 ATP each.
- From the previous stages:
- 10 NADH = 10 x 2.5 = 25 ATP.
- 2 FADH2 = 2 x 1.5 = 3 ATP.
Total ATP Calculation
- Glycolysis: 2 ATP + 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Pyruvate Decarboxylation: 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP + 6 NADH (15 ATP) + 2 FADH2 (3 ATP).
- Total: 2 + 5 + 5 + 2 + 15 + 3 = 32 ATP.
However, due to the use of ATP for transport and other processes, the net yield is typically rounded to about 30-36 ATP, commonly cited as 36 ATP for simplicity.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C', with 36 ATP being formed during the complete metabolism of one glucose molecule.
Which of the following steps of respiration is amphibolic?- a)Glycolysis
- b)Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
- c)TCA cycle
- d)Oxidative phosphorylation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following steps of respiration is amphibolic?
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
c)
TCA cycle
d)
Oxidative phosphorylation
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
TCA or Krebs' cycle is amphibolic (both catabolic and anabolic) because it provides a number of intermediates for anabolic pathways.
Which of the following reactions is catalysed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase?- a)Fructose-1,6-bisphophate → Fructose-6-phosphate
- b)Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- c)G-3-P → Dihydroxy acetone phosphate
- d)Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions is catalysed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase?
a)
Fructose-1,6-bisphophate → Fructose-6-phosphate
b)
Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
c)
G-3-P → Dihydroxy acetone phosphate
d)
Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Phosphofructokinase is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose-6-phosphate in glycolysis. The enzyme catalysed transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP is an important reaction in a wide variety of biological processes.
Which of the following statements are correct?(A) The oxidation of pyruvic acid molecules formed in glycolysis occurs inside the mitochondria.(B) Acetyl CoA is a 3-carbon compound.(C) Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is reduced to either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.(D) Acetyl CoA molecules enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.- a)(A) and (B)
- b)(C) and (D)
- c)(A) and (C)
- d)(B) and (C)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The oxidation of pyruvic acid molecules formed in glycolysis occurs inside the mitochondria.
(B) Acetyl CoA is a 3-carbon compound.
(C) Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is reduced to either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
(D) Acetyl CoA molecules enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.
a)
(A) and (B)
b)
(C) and (D)
c)
(A) and (C)
d)
(B) and (C)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Acetyl CoA is a 2-carbon compound and 3-phosphoglycerate molecule enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.
End-product of citric acid/Krebs cycle is- a)Citric acid
- b)CO2 + H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Pyruvic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
End-product of citric acid/Krebs cycle is
a)
Citric acid
b)
CO2 + H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Pyruvic acid
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The eight steps of the citric acid cycle are a series of redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. Each turn of the cycle forms one GTP or ATP as well as three NADH molecules and one FADH2 molecule, which will be used in further steps of cellular respiration to produce ATP for the cell.
Which of the following is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?- a)ATP
- b)Malic acid
- c)Acetyl CoA
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?
a)
ATP
b)
Malic acid
c)
Acetyl CoA
d)
NADH
|
|
H2O answered |
Acetyl CoA is the key intermediate between the Krebs cycle of glycolysis. After glycolysis, the glucose converts to pyruvic acid which is a three-carbon molecule. It is converted into acetyl coenzyme a by oxidative decarboxylation This, Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and along with oxaloacetic acid forms the citric acid which is a 6C compound.
Which of the following is true about glycolysis?- a)It occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
- b)It requires oxygen for glucose breakdown.
- c)It occurs in the cytoplasm and is universal in all living organisms.
- d)It only occurs in prokaryotes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
b)
It requires oxygen for glucose breakdown.
c)
It occurs in the cytoplasm and is universal in all living organisms.
d)
It only occurs in prokaryotes.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Glycolysis is a universal pathway occurring in the cytoplasm of all living cells and does not require oxygen.
Select the incorrectly matched pair.- a)End products of alcoholic fermentation - Ethanol + CO2
- b)End products of lactic acid fermentation - Lactic acid + CO2
- c)Obligate anaerobe - Clostridium tetani
- d)RQ of carbohydrates - One
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrectly matched pair.
a)
End products of alcoholic fermentation - Ethanol + CO2
b)
End products of lactic acid fermentation - Lactic acid + CO2
c)
Obligate anaerobe - Clostridium tetani
d)
RQ of carbohydrates - One
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in lactic acid bacteria (e.g., Lactobacillus), some fungi and muscles. In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis is directly reduced by NADH to form lactic acid. NoCO2 is produced. The enzyme is lactate dehydrogenase which requires FMN and Zn2+.

A test tube containing molasses solution and yeast is kept in a warm place overnight. The gas collected from this mixture- a)Extinguishes the flame
- b)Bursts into flame when ignited
- c)Turns lime water milky
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A test tube containing molasses solution and yeast is kept in a warm place overnight. The gas collected from this mixture
a)
Extinguishes the flame
b)
Bursts into flame when ignited
c)
Turns lime water milky
d)
Both (a) and (c)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The given process is an example of alcoholic fermentation, thus the gas produced is CO2.
Substrate level phosphorylation occurs during which step of Krebs' cycle?- a)Succinyl - CoA → Succinicacid
- b)Isocitricacid → Oxalosuccinicacid
- c)Oxalosuccinicacid → α−ketoglutaricacid
- d)Malicacid → OAA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Substrate level phosphorylation occurs during which step of Krebs' cycle?
a)
Succinyl - CoA → Succinicacid
b)
Isocitricacid → Oxalosuccinicacid
c)
Oxalosuccinicacid → α−ketoglutaricacid
d)
Malicacid → OAA
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
During Krebs' or citric acid cycle, succinyl-CoA is acted upon by enzyme succinyl-CoA synthetase to form succinate (a 4C compound). The reaction releases sufficient energy to form ATP (in plants) or GTP (in animals) by substrate-level phosphorylation. GTP can form ATP through a coupled reaction.
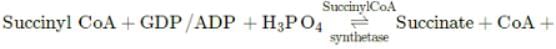 GTP/ATP
GTP/ATPWhich is true about the end products of glycolysis?- a)2 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
- b)2 pyruvicacid + 2NADH2
- c)1 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
- d)2 pyruvicacid + 1ATP + 1NADH2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about the end products of glycolysis?
a)
2 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
b)
2 pyruvicacid + 2NADH2
c)
1 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
d)
2 pyruvicacid + 1ATP + 1NADH2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In glycolysis, two molecules of ATP are consumed during two phosphorylation reactions to form fructose 1, 6-biphosphate. In return four molecules of ATP are produced by substrate level phosphorylation (conversion of 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenol pyruvate to pyruvate). Two molecules of NADH2 are formed at the time of oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate. The net reaction of glycolysis is as follows :
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2H3PO4 → 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP
Each NADH is equivalent to 2 ATP, so the net gain in glycolysis is 8 ATP.
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2H3PO4 → 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP
Each NADH is equivalent to 2 ATP, so the net gain in glycolysis is 8 ATP.
Electron transport chain (ETC) is a set of ______ electron carriers present in a specific sequence along ______ mitochondrial membrane.- a)seven, inner
- b)six, inner
- c)seven, outer
- d)six, outer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electron transport chain (ETC) is a set of ______ electron carriers present in a specific sequence along ______ mitochondrial membrane.
a)
seven, inner
b)
six, inner
c)
seven, outer
d)
six, outer
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In electron transport chain, there are 7 electron acceptors, which are as follows Co − Q → Cyt b → Cyt c1 → Cyt c → Cyt a → Cyt a3 → O2. Oxygen is the ultimate electron acceptor. These electron acceptors are present in a specific sequence along inner mitochondrial membrane.
Acetyl CoA forms a 6-C compound after combining with - a)Oxaloacetic acid
- b)Oxygen
- c)Pyruvic acid
- d)Citric acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acetyl CoA forms a 6-C compound after combining with
a)
Oxaloacetic acid
b)
Oxygen
c)
Pyruvic acid
d)
Citric acid

|
Karan answered |
Yes after combining with OAA , acetyl coA forms 6 -c compound citric acid in kreb cycle
Which of the following is performed by coenzyme A?- a)Oxidative phosphorylation
- b)Substrate level phosphorylation
- c)Breakdown of pyruvate
- d)Activation of acetyl group
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is performed by coenzyme A?
a)
Oxidative phosphorylation
b)
Substrate level phosphorylation
c)
Breakdown of pyruvate
d)
Activation of acetyl group

|
Lead Academy answered |
CoA is acetylated to acetyl CoA by the breakdown of carbohydrates through glycolysis and by the breakdown of fatty acids through β-oxidation.
What is the number of ATP molecules that can be regarded as a net gain during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose? - a)2
- b)30
- c)36
- d)38
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the number of ATP molecules that can be regarded as a net gain during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose?
a)
2
b)
30
c)
36
d)
38

|
Stepway Academy answered |
There can be a net gain of 38 ATP molecules during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose.
Respiratory substrates are the organic substances which are ________ during respiration to liberate energy.- a)Oxidised
- b)Reduced
- c)Synthesised
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiratory substrates are the organic substances which are ________ during respiration to liberate energy.
a)
Oxidised
b)
Reduced
c)
Synthesised
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Respiration is an oxidative process in which repiratory substrates are oxidised to liberate energy inside the living cells. The common respiratory substrates are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids. The most common respiratory substrates are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids. The most common respiratory substrate is glucose.
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants?- a)Hexokinase
- b)Invertase
- c)Phosphofructokinase
- d)Lactate dehydrogenase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Hexokinase
b)
Invertase
c)
Phosphofructokinase
d)
Lactate dehydrogenase
|
|
Sonal Reddy answered |
Enzyme Overview
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants is called invertase. This process is crucial for various physiological functions in plants, particularly in carbohydrate metabolism.
Function of Invertase
- Invertase, also known as sucrose-α-D-glucosidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose.
- It breaks the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose, resulting in free glucose and fructose.
Biological Importance
- Energy Source: The glucose produced serves as a primary energy source for plant cells.
- Sugar Transport: Fructose can also be utilized in energy production and serves as a precursor for other carbohydrates.
- Growth and Development: The availability of these simple sugars is essential for various metabolic processes, including growth and development.
Comparison with Other Enzymes
- Hexokinase: This enzyme phosphorylates glucose but does not convert sucrose.
- Phosphofructokinase: This enzyme is involved in glycolysis, acting on fructose-6-phosphate, not sucrose.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase: This enzyme is related to anaerobic respiration, specifically converting pyruvate to lactate.
Conclusion
In summary, invertase is the key enzyme that hydrolyzes sucrose into glucose and fructose, playing a vital role in plant metabolism and energy production. Understanding this enzyme's function is essential for comprehending how plants utilize carbohydrates effectively.
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants is called invertase. This process is crucial for various physiological functions in plants, particularly in carbohydrate metabolism.
Function of Invertase
- Invertase, also known as sucrose-α-D-glucosidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose.
- It breaks the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose, resulting in free glucose and fructose.
Biological Importance
- Energy Source: The glucose produced serves as a primary energy source for plant cells.
- Sugar Transport: Fructose can also be utilized in energy production and serves as a precursor for other carbohydrates.
- Growth and Development: The availability of these simple sugars is essential for various metabolic processes, including growth and development.
Comparison with Other Enzymes
- Hexokinase: This enzyme phosphorylates glucose but does not convert sucrose.
- Phosphofructokinase: This enzyme is involved in glycolysis, acting on fructose-6-phosphate, not sucrose.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase: This enzyme is related to anaerobic respiration, specifically converting pyruvate to lactate.
Conclusion
In summary, invertase is the key enzyme that hydrolyzes sucrose into glucose and fructose, playing a vital role in plant metabolism and energy production. Understanding this enzyme's function is essential for comprehending how plants utilize carbohydrates effectively.
Which of the following options does not hold good regarding anaerobic respiration of fermentation?- a)Occurs inside the mitochondria
- b)Partial breakdown of glucose occurs
- c)Net gain of only 2 ATP molecules
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options does not hold good regarding anaerobic respiration of fermentation?
a)
Occurs inside the mitochondria
b)
Partial breakdown of glucose occurs
c)
Net gain of only 2 ATP molecules
d)
None of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Fermentation is the incomplete oxidation of glucose under anaerobic conditions by sets of reactions where pyruvic acid is converted to CO2 and ethanol (alcoholic fermentation) or lactic acid (lactic acid fermentation). In fermentation, there is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules for each molecule of glucose degraded to pyruvic acid.
How many points are there in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Four
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many points are there in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Four
d)
Three
|
|
Niti Kumar answered |
Explanation:
Points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced:
- The TCA cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme that plays a crucial role in the TCA cycle by accepting electrons and protons to become NADH.
- There are three points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH:
1. Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Reaction: In this step, isocitrate is oxidized to alpha-ketoglutarate, and NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
2. Alpha-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex Reaction: Alpha-ketoglutarate is oxidized to succinyl-CoA, and NAD+ is again reduced to NADH.
3. Malate Dehydrogenase Reaction: Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate, and NAD+ is once more reduced to NADH.
- Therefore, there are a total of three points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH. This reduction of NAD+ to NADH is essential for the generation of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain.
Points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced:
- The TCA cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme that plays a crucial role in the TCA cycle by accepting electrons and protons to become NADH.
- There are three points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH:
1. Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Reaction: In this step, isocitrate is oxidized to alpha-ketoglutarate, and NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
2. Alpha-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex Reaction: Alpha-ketoglutarate is oxidized to succinyl-CoA, and NAD+ is again reduced to NADH.
3. Malate Dehydrogenase Reaction: Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate, and NAD+ is once more reduced to NADH.
- Therefore, there are a total of three points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH. This reduction of NAD+ to NADH is essential for the generation of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain.
Seeds respire in the- a)Presence of O2
- b)Presence of CO2
- c)Absence of O2
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Seeds respire in the
a)
Presence of O2
b)
Presence of CO2
c)
Absence of O2
d)
Both (a) and (c)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Oxygen is required by the germinating seed during aerobic respiration, it is the main source of energy for the seedlings until the formation of leaves. Oxygen is an atmospheric gas that is found in soil pore spaces. If a seed is buried too deeply within the soil or’the soil is water logged, the seed can be oxygen starved. If germinating seeds do not get air for respiration, they are still capable of respiration in absence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the seeds in the absence of free oxygen.
The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organism is- a) cytochrome
- b) oxygen
- c) hydrogen
- d) glucose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organism is
a)
cytochrome
b)
oxygen
c)
hydrogen
d)
glucose

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Oxygen is the ultimate hydrogen acceptor in aerobic respiration because at the end of electron transport chain it accepts a pair of electron and combines with hydrogen atom to form water molecule.
When two molecules of acetyl CoA enter the TCA cycle, net gain at the end of the cycle is- a)2NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 1GTP
- b)3NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 2GTP
- c)6NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 2GTP
- d)3NADH2 + 1FADH2 + 4GTP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When two molecules of acetyl CoA enter the TCA cycle, net gain at the end of the cycle is
a)
2NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 1GTP
b)
3NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 2GTP
c)
6NADH2 + 2FADH2 + 2GTP
d)
3NADH2 + 1FADH2 + 4GTP
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Krebs' cycle produces 2 GTP (or 2 ATP) through substrate level phosphorylation. Six molecules of NADH2 and 2 molecules of FADH2 for every two molecules of Acetyl CoA oxidised by it.
Which of the following cellular metabolic processes can occur both in the presence or absence of O2?- a)Glycolysis
- b)Fermentation
- c)TCA cycle
- d)Electron transport coupled with chemiosmosis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cellular metabolic processes can occur both in the presence or absence of O2?
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Fermentation
c)
TCA cycle
d)
Electron transport coupled with chemiosmosis
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Glycolysis is an oxidative process in which one molecule of glucose partially oxidised into two molecules of pyruvate on a series of enzyme catalysed reactions. Glycolysis, the major pathway for glucose metabolism, occurs in the cytosol of all cells. It is a unique pathway that occurs aerobically as well as anaerobically and does not involve molecular oxygen.
Match the pathway with its characteristics Column I (Pathway) Column II (Characteristic) a. Glycolysis i. Occurs in cytoplasm; partial oxidation of glucose b. Alcoholic fermentation ii. Produces lactic acid under anaerobic conditions c. Lactic acid fermentation iii. Produces ethanol and CO2 in anaerobic organisms d. Aerobic respiration iv. Complete oxidation of glucose in mitochondria
- a)a-iii, b-ii, c-iv, d-i
- b)a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
- c)a-ii, b-iv, c-i, d-iii
- d) a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the pathway with its characteristics
| Column I (Pathway) | Column II (Characteristic) |
|---|---|
| a. Glycolysis | i. Occurs in cytoplasm; partial oxidation of glucose |
| b. Alcoholic fermentation | ii. Produces lactic acid under anaerobic conditions |
| c. Lactic acid fermentation | iii. Produces ethanol and CO2 in anaerobic organisms |
| d. Aerobic respiration | iv. Complete oxidation of glucose in mitochondria |
a)
a-iii, b-ii, c-iv, d-i
b)
a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
c)
a-ii, b-iv, c-i, d-iii
d)
a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv

|
Top Rankers answered |
Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm, alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol, lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid, and aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria.
In animal cells, the first stage of glucose break down is- a)Glycolysis
- b)Kreb cycle
- c)Oxidative phosphorylation
- d)ETS cycle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In animal cells, the first stage of glucose break down is
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Kreb cycle
c)
Oxidative phosphorylation
d)
ETS cycle
|
|
Ashutosh Nair answered |
The first stage of glucose break down in animal cells is Glycolysis.
Glycolysis:
- Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is broken down into pyruvate.
- It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- It is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not require oxygen.
- The process produces a small amount of ATP (energy) and NADH (a molecule that carries energy).
Steps of Glycolysis:
1. Glucose is phosphorylated by ATP to form glucose-6-phosphate.
2. Glucose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose-6-phosphate.
3. Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated by ATP to form fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
4. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is split into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
5. Each G3P molecule is oxidized and phosphorylated to form two molecules of pyruvate.
6. The process produces a small amount of ATP and NADH.
Overall, glycolysis is an important process in the breakdown of glucose in animal cells, as it produces a small amount of energy and precursor molecules for further energy production pathways.
Glycolysis:
- Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is broken down into pyruvate.
- It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- It is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not require oxygen.
- The process produces a small amount of ATP (energy) and NADH (a molecule that carries energy).
Steps of Glycolysis:
1. Glucose is phosphorylated by ATP to form glucose-6-phosphate.
2. Glucose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose-6-phosphate.
3. Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated by ATP to form fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
4. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is split into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
5. Each G3P molecule is oxidized and phosphorylated to form two molecules of pyruvate.
6. The process produces a small amount of ATP and NADH.
Overall, glycolysis is an important process in the breakdown of glucose in animal cells, as it produces a small amount of energy and precursor molecules for further energy production pathways.
RQ in anaerobic respiration is?- a)0.7
- b)0.9
- c)Unity
- d)Infinity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
RQ in anaerobic respiration is?
a)
0.7
b)
0.9
c)
Unity
d)
Infinity
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In anaerobic respiration, there is no consumption of oxygen and carbon dioxide is produced in most of the cases. Therefore, respiratory quotient is infinity. Carb the usual substarte.

Identify the step in tricarboxylic acid cycle, which does not involve oxidation of substrate?- a)
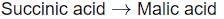
- b)
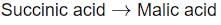
- c)
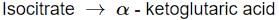
- d)
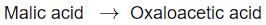
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the step in tricarboxylic acid cycle, which does not involve oxidation of substrate?
a)
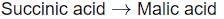
b)
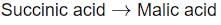
c)
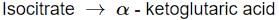
d)
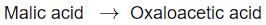
|
|
Sravya Sarkar answered |
Understanding the TCA Cycle Step
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a crucial metabolic pathway involved in cellular respiration. Among its various steps, one specific reaction does not involve the oxidation of the substrate.
Step Analysis
In the context of the options provided, we analyze each step:
- a) Succinic acid → Malic Acid
- This step involves the oxidation of succinic acid to fumaric acid, followed by hydration to malic acid.
- b) Succinyl-CoA → Succinic acid
- This step is a substrate-level phosphorylation. Here, succinyl-CoA is converted to succinic acid, resulting in the production of GTP (or ATP). Importantly, there is no transfer of electrons or oxidation occurring in this step.
- c) Isocitrate → α-Ketoglutaric acid
- This reaction involves the oxidation of isocitrate, resulting in the production of α-ketoglutaric acid and the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.
- d) Malic acid → Oxaloacetic Acid
- In this step, malic acid is oxidized to oxaloacetic acid, generating NADH in the process.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option B: Succinyl-CoA → Succinic acid. This step is unique as it does not involve oxidation but rather a direct conversion facilitated by substrate-level phosphorylation, making it a key differentiator from the other steps in the TCA cycle.
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a crucial metabolic pathway involved in cellular respiration. Among its various steps, one specific reaction does not involve the oxidation of the substrate.
Step Analysis
In the context of the options provided, we analyze each step:
- a) Succinic acid → Malic Acid
- This step involves the oxidation of succinic acid to fumaric acid, followed by hydration to malic acid.
- b) Succinyl-CoA → Succinic acid
- This step is a substrate-level phosphorylation. Here, succinyl-CoA is converted to succinic acid, resulting in the production of GTP (or ATP). Importantly, there is no transfer of electrons or oxidation occurring in this step.
- c) Isocitrate → α-Ketoglutaric acid
- This reaction involves the oxidation of isocitrate, resulting in the production of α-ketoglutaric acid and the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.
- d) Malic acid → Oxaloacetic Acid
- In this step, malic acid is oxidized to oxaloacetic acid, generating NADH in the process.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option B: Succinyl-CoA → Succinic acid. This step is unique as it does not involve oxidation but rather a direct conversion facilitated by substrate-level phosphorylation, making it a key differentiator from the other steps in the TCA cycle.
Which of the following describes the significance of fermentation?
(i) Production of alcohol in the brewing industry
(ii) Making of dough in the baking industry
(iii) Curing of tea and tobacco
(iv) Production of vinegar by acetic acid bacteria- a)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- b)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- c)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following describes the significance of fermentation?
(i) Production of alcohol in the brewing industry
(ii) Making of dough in the baking industry
(iii) Curing of tea and tobacco
(iv) Production of vinegar by acetic acid bacteria
(i) Production of alcohol in the brewing industry
(ii) Making of dough in the baking industry
(iii) Curing of tea and tobacco
(iv) Production of vinegar by acetic acid bacteria
a)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
b)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
c)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
(i) Alcoholic fermentation is used is brewing industry for the productin of various types of beer, whisky and other wines.
(ii) Carbon dioxide of alcoholic fermentation is used in baking indutry for making the bread spongy.
(iii) Tea and tobacco leaves are cured (or removed of their bitterness) and provided with a fine falvour through fermentation Vinegar is obtained by the fermentation activity if acetic acid bacteria.
(ii) Carbon dioxide of alcoholic fermentation is used in baking indutry for making the bread spongy.
(iii) Tea and tobacco leaves are cured (or removed of their bitterness) and provided with a fine falvour through fermentation Vinegar is obtained by the fermentation activity if acetic acid bacteria.
Chapter doubts & questions for Respiration in Plants - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Respiration in Plants - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










