All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Natural Habitats for JAMB Exam
Ecosystem follows:- a)only first law of thermodynamics
- b)only second law of thermodynamics
- c)both first and second laws of thermodynamics
- d)only third law of thermodynamics
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ecosystem follows:
a)
only first law of thermodynamics
b)
only second law of thermodynamics
c)
both first and second laws of thermodynamics
d)
only third law of thermodynamics
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The first law, also known as Law of Conservation of Energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system. The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches absolute zero.
Correct sequence for decomposition process is:
- a)fragmentation -> leaching -> catabolism -> mineralisation
- b)fragmentation -> leaching -> mineralisation -> humification
- c)leaching -> fragmentation -> humification -> mineralisation
- d)fragmentation -> catabolism -> leaching -> mineralisation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct sequence for decomposition process is:
a)
fragmentation -> leaching -> catabolism -> mineralisation
b)
fragmentation -> leaching -> mineralisation -> humification
c)
leaching -> fragmentation -> humification -> mineralisation
d)
fragmentation -> catabolism -> leaching -> mineralisation
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Decomposition is the process that involves the breakdown of complex organic matter or biomass from the body of dead plants and animals with the help of decomposers into inorganic raw materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and other nutrients.
The various processes involved in decomposition are as follows:
➢ Fragmentation
➢ Fragmentation
- It is the first step in the process of decomposition.
- It involves the breakdown of detritus into smaller pieces by the action of detritivores such as earthworms.
➢ Leaching
- It is a process where the water soluble nutrients go down into the soil layers and get locked as unavailable salts.
➢ Catabolism
- It is a process in which bacteria and fungi degrade detritus through various enzymes into smaller pieces.
➢ Humification
- The next step is humification which leads to the formation of a dark-coloured colloidal substance called humus, which acts as reservoir of nutrients for plants.
➢ Mineralization
- The humus is further degraded by the action of microbes, which finally leads to the release of inorganic nutrients into the soil.
- This process of releasing inorganic nutrients from the humus is known as mineralization.
Which of the following is correct?a)GPP + NPP = Rb)NPP – R = GPPc)GPP – R = NPPd)NPP – GPP = RCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Net primary productivity (NPP) is equal to Gross primary productivity (GPP) minus Respiration loss (R). NPP is the available biomass for the consumption of heterotrophs in the ecosystem.
A detritus food chain will start with which of the following?- a)Protozoans
- b)Rhizophora species
- c)Bacteria & fungi
- d)Earthworm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A detritus food chain will start with which of the following?
a)
Protozoans
b)
Rhizophora species
c)
Bacteria & fungi
d)
Earthworm

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
A detritus food chain begins with dead organic matter. It is made of decomposers which are heterotrophic organism fungi and bacteria.Rhizophora species is a saprophyticheterotrophs.
Which one of the following is the most important service provided by ecosystems?- a)soil formation
- b)aesthetic values
- c)pollination
- d)water purification
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the most important service provided by ecosystems?
a)
soil formation
b)
aesthetic values
c)
pollination
d)
water purification

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
Ecosystem services includes all activities performed by nature to benefits of human beings. The most important ecological service includes soil formation. Soil is essential for growth of plants that provide food to all living forms.
Humus will never be:
- a)Good for plant growth.
- b)Resistant to microbial action.
- c)Reservoir of nutrients.
- d)all of these
- e)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Humus will never be:
a)
Good for plant growth.
b)
Resistant to microbial action.
c)
Reservoir of nutrients.
d)
all of these
e)
None of these.
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
- Humus is a dark brown amorphous gummy substance formed by partial decomposition of plant and animal matter.
- It is not good for plant growth.
- Humus is quite resistant to microbial action.
- It is a reservoir of nutrients and is helpful in the maintenance of soil moisture as well as aeration.
Hence, None of these statements is correct about Humus.
There are only 4 or 5 trophic levels in food chain of an ecosystem due to :- a)Limited number of members in biotic community
- b)Loss of energy at successive levels
- c)Carrying capacity
- d)Environmental resistance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are only 4 or 5 trophic levels in food chain of an ecosystem due to :
a)
Limited number of members in biotic community
b)
Loss of energy at successive levels
c)
Carrying capacity
d)
Environmental resistance

|
Krish Saha answered |
In most of the food chain of ecosystem only 4 to 5 trophic levels are present because loss of energy at successive levels is very high. Only 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level.
Which of the following is not an ecological parameter?- a)Stratification
- b)Number
- c)Energy
- d)Biomass
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an ecological parameter?
a)
Stratification
b)
Number
c)
Energy
d)
Biomass

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Ecological parameter includes, biomass, energy and number of individual in the ecosystem. Stratification is not a part of ecological parameter.
Conditions favouring decomposition are :- a)high temperature and intermediate humidity
- b)low temperature and low humidity
- c)low temperature and high humidity
- d)high temperature and low humidity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Conditions favouring decomposition are :
a)
high temperature and intermediate humidity
b)
low temperature and low humidity
c)
low temperature and high humidity
d)
high temperature and low humidity
|
|
Tarun Saha answered |
**Explanation:**
Decomposition is the process by which organic matter breaks down into simpler substances, such as carbon dioxide, water, and minerals. It is a natural process that is essential for nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
Conditions that favor decomposition are important to understand because they can determine the rate at which organic matter decomposes and the types of organisms involved in the process.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'A', which states that high temperature and intermediate humidity favor decomposition. Let's understand why this is the case:
**1. High Temperature:**
- Decomposition is an enzymatic process, meaning it is facilitated by the action of enzymes produced by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi.
- Enzymatic reactions are generally more efficient at higher temperatures because they increase the rate of biochemical reactions.
- High temperatures accelerate the metabolic activity of decomposer organisms, leading to faster decomposition rates.
**2. Intermediate Humidity:**
- Decomposer organisms require a certain level of moisture to carry out their metabolic processes effectively.
- If the humidity is too high, the excessive moisture can create an anaerobic environment (lack of oxygen) that is unfavorable for many decomposer organisms.
- If the humidity is too low, the lack of moisture restricts the activity of decomposer organisms.
- Intermediate humidity provides the ideal conditions for decomposer organisms to thrive and efficiently decompose organic matter.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the correct answer to the given question is option 'A' (high temperature and intermediate humidity) because these conditions provide the ideal environment for the activity of decomposer organisms, leading to faster and more efficient decomposition of organic matter.
Decomposition is the process by which organic matter breaks down into simpler substances, such as carbon dioxide, water, and minerals. It is a natural process that is essential for nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
Conditions that favor decomposition are important to understand because they can determine the rate at which organic matter decomposes and the types of organisms involved in the process.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'A', which states that high temperature and intermediate humidity favor decomposition. Let's understand why this is the case:
**1. High Temperature:**
- Decomposition is an enzymatic process, meaning it is facilitated by the action of enzymes produced by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi.
- Enzymatic reactions are generally more efficient at higher temperatures because they increase the rate of biochemical reactions.
- High temperatures accelerate the metabolic activity of decomposer organisms, leading to faster decomposition rates.
**2. Intermediate Humidity:**
- Decomposer organisms require a certain level of moisture to carry out their metabolic processes effectively.
- If the humidity is too high, the excessive moisture can create an anaerobic environment (lack of oxygen) that is unfavorable for many decomposer organisms.
- If the humidity is too low, the lack of moisture restricts the activity of decomposer organisms.
- Intermediate humidity provides the ideal conditions for decomposer organisms to thrive and efficiently decompose organic matter.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the correct answer to the given question is option 'A' (high temperature and intermediate humidity) because these conditions provide the ideal environment for the activity of decomposer organisms, leading to faster and more efficient decomposition of organic matter.
Available organic matter for herbivores is represented by:- a)Secondary productivity
- b)GPP
- c)NPP
- d)All the these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Available organic matter for herbivores is represented by:
a)
Secondary productivity
b)
GPP
c)
NPP
d)
All the these

|
Charvi Shah answered |
The organic matter available for herbivores is called net primary productivity (NPP). Total amount of organic matter fix during photosynthesis is called Gross primary productivity (GPP).
Which of the following pyramid/s is/are inverted?- a)pyramid of number in an aquatic system
- b)pyramid of biomass in a grassland system
- c)pyramid of biomass in an aquatic system
- d)pyramid of number in a grassland system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pyramid/s is/are inverted?
a)
pyramid of number in an aquatic system
b)
pyramid of biomass in a grassland system
c)
pyramid of biomass in an aquatic system
d)
pyramid of number in a grassland system

|
Snehal Shah answered |
The pyramid of biomass in an aquatic system is always inverted. Sharp decrease in biomass results into inverted pyramids.
Flow of energy in our ecosystem takes place :- a)only in one direction
- b)possible in two directions
- c)in three dimensions
- d)may occur in multiple directions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Flow of energy in our ecosystem takes place :
a)
only in one direction
b)
possible in two directions
c)
in three dimensions
d)
may occur in multiple directions

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
In ecosystem, flow of energy takes place in only one direction. The flow of energy takes place from producers to final consumers. Energy present in one trophic levels neversreturn back to producer.
Forest controls drought through- a)Functioning as water shed.
- b)Lot of water plant
- c)Retention of water and prevention of soil erosion.
- d) Increasing rainfall
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Forest controls drought through
a)
Functioning as water shed.
b)
Lot of water plant
c)
Retention of water and prevention of soil erosion.
d)
Increasing rainfall
|
|
Akshat Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' i.e., retention of water and prevention of soil erosion.
Explanation:
Forests are essential for the survival of life on earth. They are responsible for various ecological, environmental, and social benefits. Forests play a crucial role in controlling drought by retaining water and preventing soil erosion. Let's discuss how forests control drought through water retention and soil erosion prevention:
Retention of water:
Forests help in retaining water in the following ways:
1. Watershed: Forests act as a water catchment area and function as a natural watershed. They store and release water gradually, reducing the risk of floods and droughts.
2. Groundwater recharge: Forests help in recharging groundwater by allowing rainwater to seep into the soil, thus replenishing underground water resources.
3. Transpiration: Trees in the forest transpire water, which helps in the formation of clouds and precipitation, leading to increased rainfall.
Prevention of soil erosion:
Forests help in preventing soil erosion in the following ways:
1. Root systems: Trees in the forest have deep root systems that hold the soil in place and prevent it from eroding.
2. Canopy cover: The canopy cover of trees in the forest acts as a barrier, reducing the impact of raindrops on the soil surface and preventing soil erosion.
3. Organic matter: Forests are rich in organic matter, which helps in improving soil structure, reducing soil erosion, and retaining water.
Conclusion:
Forests play a crucial role in controlling drought by retaining water and preventing soil erosion. Therefore, it is important to conserve and protect forests to ensure a sustainable future for all.
Explanation:
Forests are essential for the survival of life on earth. They are responsible for various ecological, environmental, and social benefits. Forests play a crucial role in controlling drought by retaining water and preventing soil erosion. Let's discuss how forests control drought through water retention and soil erosion prevention:
Retention of water:
Forests help in retaining water in the following ways:
1. Watershed: Forests act as a water catchment area and function as a natural watershed. They store and release water gradually, reducing the risk of floods and droughts.
2. Groundwater recharge: Forests help in recharging groundwater by allowing rainwater to seep into the soil, thus replenishing underground water resources.
3. Transpiration: Trees in the forest transpire water, which helps in the formation of clouds and precipitation, leading to increased rainfall.
Prevention of soil erosion:
Forests help in preventing soil erosion in the following ways:
1. Root systems: Trees in the forest have deep root systems that hold the soil in place and prevent it from eroding.
2. Canopy cover: The canopy cover of trees in the forest acts as a barrier, reducing the impact of raindrops on the soil surface and preventing soil erosion.
3. Organic matter: Forests are rich in organic matter, which helps in improving soil structure, reducing soil erosion, and retaining water.
Conclusion:
Forests play a crucial role in controlling drought by retaining water and preventing soil erosion. Therefore, it is important to conserve and protect forests to ensure a sustainable future for all.
Producers in the aquatic ecosystem are :- a)Shrubs
- b)Herbacious plants
- c)Phytoplanktons
- d)Zooplanktons
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Producers in the aquatic ecosystem are :
a)
Shrubs
b)
Herbacious plants
c)
Phytoplanktons
d)
Zooplanktons

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Phytoplanktons are small floating photosynthetic unicellular plant. In the aquatic ecosystem phytoplankton are producers that fix solar energy by the process of photosynthesis.
Which of the following ecological pyramid is always erect and upright?- a)pyramid of biomass
- b)pyramid of energy
- c)pyramid of number
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ecological pyramid is always erect and upright?
a)
pyramid of biomass
b)
pyramid of energy
c)
pyramid of number
d)
none of these

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Pyramid of energy is always erect and upright because the amount of energy get reduce at each trophic level from prouder to consumers.
Amount of biomass produced per unit area by green plants is called?- a)Respiration
- b)Primary productivity
- c)Secondary productivity
- d)Tertiary productivity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Amount of biomass produced per unit area by green plants is called?
a)
Respiration
b)
Primary productivity
c)
Secondary productivity
d)
Tertiary productivity

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Primary productivity is the amount of biomass produced per unit area by green plants in an ecosystem. Producers fix the solar energy by the process of photosynthesis.
Speed of decomposition will be:- a)fast if detritus is rich in simple sugars
- b)slow if detritus contains water soluble substances like sugars
- c)fast if detritus is rich in lignin
- d)slow if detritus lacks chitin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Speed of decomposition will be:
a)
fast if detritus is rich in simple sugars
b)
slow if detritus contains water soluble substances like sugars
c)
fast if detritus is rich in lignin
d)
slow if detritus lacks chitin

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
In detritus food chain, speed of decomposition will be fast if detritus is rich in simple sugar that can be easily decomposed into glucose by saprophytes that includes bacteria and fungi.
What is the rate at which solar energy is converted and stored by the producers per unit area over a time period called?- a)Tertiary productivity
- b)Primary productivity
- c)Gross primary productivity
- d)Net productivity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the rate at which solar energy is converted and stored by the producers per unit area over a time period called?
a)
Tertiary productivity
b)
Primary productivity
c)
Gross primary productivity
d)
Net productivity

|
Top Rankers answered |
The rate at which solar energy is converted and stored by the producers per unit area over a time period is called primary productivity. The solar energy is converted into usable form by plants with the help of photosynthesis.
If the number of producers in a pond ecosystem is approx 10 million then the number of top carnivore (in million) which it can support may be:- a)20
- b)2
- c)11
- d)50
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the number of producers in a pond ecosystem is approx 10 million then the number of top carnivore (in million) which it can support may be:
a)
20
b)
2
c)
11
d)
50

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
In a food chain, number of organisms reduce from producer to carnivores at each trophic levels. So, the number of carnivores will be less than the prouder which is less than 10 million.
If 20000J energy is present in transducers then 3°consumers will get:- a)20J
- b)200J
- c)10000J
- d)2000J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 20000J energy is present in transducers then 3°consumers will get:
a)
20J
b)
200J
c)
10000J
d)
2000J
|
|
Anuj Pillai answered |
Explanation:
To understand the answer to this question, we need to consider the concept of energy distribution among multiple consumers.
Energy Distribution:
When energy is distributed among multiple consumers, the total energy remains constant. In this case, we have a total of 20,000 J of energy available. We need to distribute this energy among 3 consumers.
Calculation:
To find out how much energy each consumer will receive, we divide the total energy by the number of consumers.
Total energy = 20,000 J
Number of consumers = 3
Energy per consumer = Total energy / Number of consumers
Energy per consumer = 20,000 J / 3
Energy per consumer ≈ 6,666.67 J
Answer:
According to the options provided, the closest answer to 6,666.67 J is option 'A' which is 20 J. Therefore, each consumer will receive approximately 20 J of energy.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Option 'A' states that each consumer will get 20 J of energy. This means that when the total energy of 20,000 J is distributed among 3 consumers, each consumer will receive approximately 20 J of energy.
Reasoning:
To find the correct answer, we need to divide the total energy by the number of consumers (20,000 J / 3). This calculation results in approximately 6,666.67 J per consumer. Since option 'A' is the closest answer to this value, it is the correct answer.
Summary:
In summary, when 20,000 J of energy is distributed among 3 consumers, each consumer will receive approximately 20 J of energy. This is calculated by dividing the total energy by the number of consumers.
To understand the answer to this question, we need to consider the concept of energy distribution among multiple consumers.
Energy Distribution:
When energy is distributed among multiple consumers, the total energy remains constant. In this case, we have a total of 20,000 J of energy available. We need to distribute this energy among 3 consumers.
Calculation:
To find out how much energy each consumer will receive, we divide the total energy by the number of consumers.
Total energy = 20,000 J
Number of consumers = 3
Energy per consumer = Total energy / Number of consumers
Energy per consumer = 20,000 J / 3
Energy per consumer ≈ 6,666.67 J
Answer:
According to the options provided, the closest answer to 6,666.67 J is option 'A' which is 20 J. Therefore, each consumer will receive approximately 20 J of energy.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Option 'A' states that each consumer will get 20 J of energy. This means that when the total energy of 20,000 J is distributed among 3 consumers, each consumer will receive approximately 20 J of energy.
Reasoning:
To find the correct answer, we need to divide the total energy by the number of consumers (20,000 J / 3). This calculation results in approximately 6,666.67 J per consumer. Since option 'A' is the closest answer to this value, it is the correct answer.
Summary:
In summary, when 20,000 J of energy is distributed among 3 consumers, each consumer will receive approximately 20 J of energy. This is calculated by dividing the total energy by the number of consumers.
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is- a)1 - 5%
- b)2 - 10%
- c)less than 50%
- d)approx 100%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is
a)
1 - 5%
b)
2 - 10%
c)
less than 50%
d)
approx 100%
|
|
Lakshmi Deshpande answered |
The percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is less than 50%. PAR refers to the portion of sunlight that is within the wavelength range of 400 to 700 nanometers, which is the range most effectively used by plants for photosynthesis.
Here is a detailed explanation:
1. Definition of PAR:
- PAR is the range of light wavelengths that are absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in plants, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis.
- PAR is typically measured in micromoles per square meter per second (µmol/m²/s).
2. Components of solar radiation:
- Solar radiation is composed of various wavelengths, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light.
- Only a small portion of solar radiation falls within the PAR range.
3. Wavelengths of PAR:
- The PAR range is defined as 400 to 700 nanometers (nm), which corresponds to the visible light spectrum.
- Within this range, different wavelengths of light have varying effects on plant growth and development.
4. Importance of PAR for photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, using water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll, the primary pigment in plants, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue (400-500 nm) and red (600-700 nm) regions of the spectrum.
- Therefore, light within the PAR range is crucial for driving photosynthesis.
5. Percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation:
- While the exact percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation varies depending on factors such as atmospheric conditions and time of day, it is generally accepted to be less than 50%.
- This means that more than half of the solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface falls outside the PAR range.
6. Utilization of non-PAR wavelengths:
- Plants can also utilize certain wavelengths of light outside the PAR range, such as UV and IR light, for various physiological processes.
- UV light, for example, can stimulate the production of protective compounds in plants, while IR light can affect plant growth and development.
In conclusion, the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is less than 50%. This indicates that a significant portion of solar radiation falls outside the PAR range, highlighting the importance of considering the entire spectrum of light when studying plant responses to sunlight.
Here is a detailed explanation:
1. Definition of PAR:
- PAR is the range of light wavelengths that are absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in plants, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis.
- PAR is typically measured in micromoles per square meter per second (µmol/m²/s).
2. Components of solar radiation:
- Solar radiation is composed of various wavelengths, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light.
- Only a small portion of solar radiation falls within the PAR range.
3. Wavelengths of PAR:
- The PAR range is defined as 400 to 700 nanometers (nm), which corresponds to the visible light spectrum.
- Within this range, different wavelengths of light have varying effects on plant growth and development.
4. Importance of PAR for photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, using water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll, the primary pigment in plants, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue (400-500 nm) and red (600-700 nm) regions of the spectrum.
- Therefore, light within the PAR range is crucial for driving photosynthesis.
5. Percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation:
- While the exact percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation varies depending on factors such as atmospheric conditions and time of day, it is generally accepted to be less than 50%.
- This means that more than half of the solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface falls outside the PAR range.
6. Utilization of non-PAR wavelengths:
- Plants can also utilize certain wavelengths of light outside the PAR range, such as UV and IR light, for various physiological processes.
- UV light, for example, can stimulate the production of protective compounds in plants, while IR light can affect plant growth and development.
In conclusion, the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is less than 50%. This indicates that a significant portion of solar radiation falls outside the PAR range, highlighting the importance of considering the entire spectrum of light when studying plant responses to sunlight.
Which food chain is the major conduit for energy flow in an aquatic ecosystem?- a)Grazing food chain (GFC)
- b)Detritus food chain (DFC)
- c)Both GFC and DFC
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Grazing food chain (GFC)
b)
Detritus food chain (DFC)
c)
Both GFC and DFC
d)
None of the above

|
EduRev NEET answered |
In an aquatic ecosystem, the grazing food chain (GFC) is the major pathway for energy flow, whereas the detritus food chain plays a smaller role compared to terrestrial ecosystems.
In an aquatic ecosystem, the organism present at the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands is?- a)Phytolanktons
- b)Large fishes
- c)Sea gulls
- d)Zooplanktons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an aquatic ecosystem, the organism present at the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands is?
a)
Phytolanktons
b)
Large fishes
c)
Sea gulls
d)
Zooplanktons
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In an aquatic ecosystem, the important herbivores are zooplankton, larvae, tadpoles, etc. Cows in grasslands also act as herbivores as these feed on producers. Thus, both cows and zooplankton occupy second trophic level in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem respectively.
Functional and dynamic unit of nature where living and non-living components interact with each-other is:- a)Biome
- b)Community
- c)Tropic structure
- d)Ecosystem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Functional and dynamic unit of nature where living and non-living components interact with each-other is:
a)
Biome
b)
Community
c)
Tropic structure
d)
Ecosystem

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
Ecosystem is the functional and dynamic unit of nature where living and non-living components interact with each other for flow of energy and biomass from producer to consumers.
Assertion (A): Nutrient cycling includes both gaseous and sedimentary cycles, which play crucial roles in ecosystem health.Reason (R): The gaseous cycle relies solely on the atmosphere as its reservoir, while the sedimentary cycle depends on the Earth's crust.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Nutrient cycling includes both gaseous and sedimentary cycles, which play crucial roles in ecosystem health.
Reason (R): The gaseous cycle relies solely on the atmosphere as its reservoir, while the sedimentary cycle depends on the Earth's crust.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false
|
|
Dipanjan Choudhary answered |
Understanding Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling is essential for maintaining ecosystem health and can be categorized into two main types: gaseous cycles and sedimentary cycles.
Assertion (A): Nutrient Cycling Types
- Nutrient cycling encompasses both gaseous and sedimentary cycles.
- These cycles are crucial for ecosystem health as they facilitate the movement of essential nutrients.
Reason (R): Reservoirs of Nutrient Cycles
- The gaseous cycle primarily relies on the atmosphere as its reservoir.
- The sedimentary cycle is dependent on the Earth’s crust for its reservoirs.
Evaluating the Assertion and Reason
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true statements.
- However, the Reason (R) does not serve as the correct explanation for the Assertion (A).
Why Option B is Correct?
- While it is accurate that nutrient cycling involves both gaseous and sedimentary cycles, the explanation provided in Reason (R) does not directly clarify why these cycles are important for ecosystem health.
- The reason only describes the reservoirs of the cycles but fails to connect this information to the overall significance of nutrient cycling in supporting life and maintaining ecosystem balance.
Conclusion
Thus, the answer is option 'B': both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. Understanding the distinction between these cycles and their roles enhances our comprehension of ecosystem dynamics.
Nutrient cycling is essential for maintaining ecosystem health and can be categorized into two main types: gaseous cycles and sedimentary cycles.
Assertion (A): Nutrient Cycling Types
- Nutrient cycling encompasses both gaseous and sedimentary cycles.
- These cycles are crucial for ecosystem health as they facilitate the movement of essential nutrients.
Reason (R): Reservoirs of Nutrient Cycles
- The gaseous cycle primarily relies on the atmosphere as its reservoir.
- The sedimentary cycle is dependent on the Earth’s crust for its reservoirs.
Evaluating the Assertion and Reason
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true statements.
- However, the Reason (R) does not serve as the correct explanation for the Assertion (A).
Why Option B is Correct?
- While it is accurate that nutrient cycling involves both gaseous and sedimentary cycles, the explanation provided in Reason (R) does not directly clarify why these cycles are important for ecosystem health.
- The reason only describes the reservoirs of the cycles but fails to connect this information to the overall significance of nutrient cycling in supporting life and maintaining ecosystem balance.
Conclusion
Thus, the answer is option 'B': both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. Understanding the distinction between these cycles and their roles enhances our comprehension of ecosystem dynamics.
Ecological pyramids does not give any place to :- a)Saprophytes
- b)Transducers
- c)Predators
- d)Parasites
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ecological pyramids does not give any place to :
a)
Saprophytes
b)
Transducers
c)
Predators
d)
Parasites

|
Krish Saha answered |
In ecological pyramids, saprophytes do not have any place even though they play very vital role in ecosystem. This is because ecological pyramids does not take into account same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
Which of the following organisms are primary consumers in a grazing food chain?- a)Phytoplankton
- b)Zooplankton
- c)Carnivores
- d)Decomposers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Phytoplankton
b)
Zooplankton
c)
Carnivores
d)
Decomposers
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Understanding Primary Consumers in a Grazing Food Chain
In a grazing food chain, primary consumers play a crucial role by feeding on primary producers. Let's break down the organisms listed in the question to understand why the correct answer is zooplankton.
What Are Primary Consumers?
- Primary consumers are organisms that eat primary producers (plants and phytoplankton) to obtain energy.
- They are usually herbivores or omnivores, and their main role is to convert the energy stored in producers into a form that can be consumed by higher trophic levels.
Analysis of the Options
- Phytoplankton: These are primary producers, not consumers. They convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis.
- Zooplankton: These organisms are primary consumers. They feed on phytoplankton and other small organisms, thus playing a vital role in the food chain by transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels.
- Carnivores: These are secondary or tertiary consumers that feed on other animals. They do not consume primary producers directly.
- Decomposers: Organisms like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, but they are not considered consumers in the grazing food chain.
Conclusion
In summary, zooplankton are classified as primary consumers because they directly consume phytoplankton, which are the primary producers in aquatic ecosystems. Their role is essential for energy transfer in the food chain, making them a key component of the grazing food web.
In a grazing food chain, primary consumers play a crucial role by feeding on primary producers. Let's break down the organisms listed in the question to understand why the correct answer is zooplankton.
What Are Primary Consumers?
- Primary consumers are organisms that eat primary producers (plants and phytoplankton) to obtain energy.
- They are usually herbivores or omnivores, and their main role is to convert the energy stored in producers into a form that can be consumed by higher trophic levels.
Analysis of the Options
- Phytoplankton: These are primary producers, not consumers. They convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis.
- Zooplankton: These organisms are primary consumers. They feed on phytoplankton and other small organisms, thus playing a vital role in the food chain by transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels.
- Carnivores: These are secondary or tertiary consumers that feed on other animals. They do not consume primary producers directly.
- Decomposers: Organisms like fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, but they are not considered consumers in the grazing food chain.
Conclusion
In summary, zooplankton are classified as primary consumers because they directly consume phytoplankton, which are the primary producers in aquatic ecosystems. Their role is essential for energy transfer in the food chain, making them a key component of the grazing food web.
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Decomposers and detritivores constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
For greater efficiency a food chain must be:- a)without transducers
- b)shorter
- c)longer
- d)without microconsumers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For greater efficiency a food chain must be:
a)
without transducers
b)
shorter
c)
longer
d)
without microconsumers

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
For greater efficiency a food chain must have three to four trophic levels. At each trophic levels loss of energy is very high so very small amount of energy is left after there trophic level.
Assertion: If a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then prey might become extinct.
Reason: The predator will also become extinct for lack of food.- a)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
- b)Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
- c)Both assertion and reason are correct.
- d)Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: If a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then prey might become extinct.
Reason: The predator will also become extinct for lack of food.
Reason: The predator will also become extinct for lack of food.
a)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
b)
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
c)
Both assertion and reason are correct.
d)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
If a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then prey might become extinct. The predator will also become extinct for lack of food. Therefore, predators in nature are prudent.
Which of the following is an example of catabolism?- a)Breaking down of stones into smaller parts.
- b)Decrease in size of mountain.
- c)Breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes.
- d)All of the these.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of catabolism?
a)
Breaking down of stones into smaller parts.
b)
Decrease in size of mountain.
c)
Breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes.
d)
All of the these.

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
Breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes into simple forms is called catabolism in which mass of the organisms decrease without any external reduction is size of the organisms.
Stability will be provided to the ecosystem by:- a)Ecological pyramids
- b)Food webs
- c)Decomposition
- d)Food chains
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Stability will be provided to the ecosystem by:
a)
Ecological pyramids
b)
Food webs
c)
Decomposition
d)
Food chains

|
Krish Saha answered |
Food web is formed by interaction between a numbers of food chains having common members. Stability of ecosystem largely depends upon the kinds of food web exists in it for proper flow of energy.
Breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes into simple forms is called?- a)Mineralization
- b)Catabolism
- c)Fragmentation
- d)Leaching
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes into simple forms is called?
a)
Mineralization
b)
Catabolism
c)
Fragmentation
d)
Leaching
|
|
Naina Dey answered |
Catabolism - Breakdown of Detritus by Microbial Enzymes
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler compounds by the action of microbial enzymes. In the process of catabolism, detritus is decomposed and transformed into various forms that are readily available for use by other living organisms. This process is important for the maintenance of the ecosystem as it cycles nutrients and energy from dead organic matter back into the living world.
Mechanism of Catabolism
The process of catabolism involves the following steps:
1. Fragmentation: The detritus is fragmented into smaller particles by the action of physical and chemical forces.
2. Leaching: The soluble compounds are leached out of the detritus and are transported to other parts of the ecosystem.
3. Mineralization: The remaining organic matter is decomposed by the action of microbial enzymes into simpler forms such as carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus.
4. Catabolism: The simpler compounds are further broken down into energy and essential nutrients by the action of microbial enzymes.
Significance of Catabolism
Catabolism plays a crucial role in the cycling of nutrients and energy in the ecosystem. The breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes releases essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus into the soil, which can be taken up by plants for growth. The energy released during catabolism is also utilized by other living organisms in the ecosystem, thereby sustaining the food web. In addition, catabolism also helps in the removal of waste materials from the ecosystem.
Conclusion
Catabolism is a complex process that involves the breakdown of detritus into simpler forms by the action of microbial enzymes. This process is essential for the cycling of nutrients and energy in the ecosystem and helps in sustaining the food web. The significance of catabolism in the maintenance of the ecosystem cannot be overemphasized as it plays a crucial role in the removal of waste materials and the release of essential nutrients into the environment.
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler compounds by the action of microbial enzymes. In the process of catabolism, detritus is decomposed and transformed into various forms that are readily available for use by other living organisms. This process is important for the maintenance of the ecosystem as it cycles nutrients and energy from dead organic matter back into the living world.
Mechanism of Catabolism
The process of catabolism involves the following steps:
1. Fragmentation: The detritus is fragmented into smaller particles by the action of physical and chemical forces.
2. Leaching: The soluble compounds are leached out of the detritus and are transported to other parts of the ecosystem.
3. Mineralization: The remaining organic matter is decomposed by the action of microbial enzymes into simpler forms such as carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus.
4. Catabolism: The simpler compounds are further broken down into energy and essential nutrients by the action of microbial enzymes.
Significance of Catabolism
Catabolism plays a crucial role in the cycling of nutrients and energy in the ecosystem. The breakdown of detritus by microbial enzymes releases essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus into the soil, which can be taken up by plants for growth. The energy released during catabolism is also utilized by other living organisms in the ecosystem, thereby sustaining the food web. In addition, catabolism also helps in the removal of waste materials from the ecosystem.
Conclusion
Catabolism is a complex process that involves the breakdown of detritus into simpler forms by the action of microbial enzymes. This process is essential for the cycling of nutrients and energy in the ecosystem and helps in sustaining the food web. The significance of catabolism in the maintenance of the ecosystem cannot be overemphasized as it plays a crucial role in the removal of waste materials and the release of essential nutrients into the environment.
In an aquatic ecosystem, which of the following is a limiting factor for productivity?- a)Carbon dioxide
- b)Nutrient availability
- c)Oxygen
- d)Soil composition
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Carbon dioxide
b)
Nutrient availability
c)
Oxygen
d)
Soil composition
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Nutrient Availability as a Limiting Factor
In aquatic ecosystems, productivity is primarily influenced by the availability of nutrients. Here’s a breakdown of why nutrient availability is crucial:
1. Definition of Productivity
- Productivity refers to the rate at which energy is produced in an ecosystem, particularly through photosynthesis in plants and phytoplankton.
2. Role of Nutrients
- Aquatic organisms, especially primary producers like phytoplankton, need nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to grow and reproduce.
- These nutrients are essential for various biological processes, including the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll.
3. Limiting Nutrients
- In many aquatic environments, one or more nutrients can be in short supply, which limits growth and productivity.
- For instance, in oceanic regions, nitrogen is often a limiting nutrient, while in freshwater systems, phosphorus may be more limiting.
4. Impact on Ecosystem
- When nutrient levels are low, the growth of primary producers decreases, leading to a reduction in the overall biomass of the ecosystem.
- This decrease affects the entire food web, as fewer producers mean less energy is available for herbivores and, consequently, for higher trophic levels.
5. Other Factors Considered
- While carbon dioxide, oxygen, and soil composition play roles in aquatic systems, they do not limit productivity to the same extent as nutrient availability does.
- For example, carbon dioxide is typically abundant in water, and oxygen levels can vary but are not usually the primary limiting factor for productivity.
In summary, nutrient availability is the critical limiting factor for productivity in aquatic ecosystems, as it directly influences the growth and reproduction of primary producers, thereby affecting the entire ecosystem's health and energy flow.
In aquatic ecosystems, productivity is primarily influenced by the availability of nutrients. Here’s a breakdown of why nutrient availability is crucial:
1. Definition of Productivity
- Productivity refers to the rate at which energy is produced in an ecosystem, particularly through photosynthesis in plants and phytoplankton.
2. Role of Nutrients
- Aquatic organisms, especially primary producers like phytoplankton, need nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to grow and reproduce.
- These nutrients are essential for various biological processes, including the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll.
3. Limiting Nutrients
- In many aquatic environments, one or more nutrients can be in short supply, which limits growth and productivity.
- For instance, in oceanic regions, nitrogen is often a limiting nutrient, while in freshwater systems, phosphorus may be more limiting.
4. Impact on Ecosystem
- When nutrient levels are low, the growth of primary producers decreases, leading to a reduction in the overall biomass of the ecosystem.
- This decrease affects the entire food web, as fewer producers mean less energy is available for herbivores and, consequently, for higher trophic levels.
5. Other Factors Considered
- While carbon dioxide, oxygen, and soil composition play roles in aquatic systems, they do not limit productivity to the same extent as nutrient availability does.
- For example, carbon dioxide is typically abundant in water, and oxygen levels can vary but are not usually the primary limiting factor for productivity.
In summary, nutrient availability is the critical limiting factor for productivity in aquatic ecosystems, as it directly influences the growth and reproduction of primary producers, thereby affecting the entire ecosystem's health and energy flow.
What type of pyramid is generally inverted in an aquatic ecosystem?- a)Pyramid of numbers
- b)Pyramid of energy
- c)Pyramid of biomass
- d)All pyramids
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Pyramid of numbers
b)
Pyramid of energy
c)
Pyramid of biomass
d)
All pyramids
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Understanding the Inverted Pyramid of Biomass
In aquatic ecosystems, the pyramid of biomass is often inverted, which is distinct from the typical structure seen in terrestrial ecosystems. Here’s why:
1. Definition of Biomass Pyramid
- The biomass pyramid represents the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level.
- In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, it decreases as you move from producers to top consumers.
2. Aquatic Ecosystems Characteristics
- In aquatic environments, producers such as phytoplankton have a low biomass compared to the organisms that feed on them, like zooplankton and small fish.
- The rapid reproduction and turnover rates of phytoplankton lead to a situation where the total weight of consumers can exceed that of the producers.
3. Reasons for Inversion
- High Reproduction Rates: Phytoplankton reproduce quickly, but their biomass is low at any given time.
- Efficiency of Energy Transfer: In aquatic systems, energy transfer from producers to consumers is highly efficient, allowing a larger biomass of consumers.
- Size Difference: Small primary producers can support larger consumers, leading to an inverted biomass pyramid.
4. Implications
- This structure challenges the traditional understanding of food webs and energy flow.
- It highlights the unique dynamics of aquatic ecosystems where even small organisms can support a diverse and larger community of consumers.
In conclusion, the pyramid of biomass is inverted in aquatic ecosystems due to the high productivity and turnover of phytoplankton, resulting in greater biomass of consumers compared to producers.
In aquatic ecosystems, the pyramid of biomass is often inverted, which is distinct from the typical structure seen in terrestrial ecosystems. Here’s why:
1. Definition of Biomass Pyramid
- The biomass pyramid represents the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level.
- In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, it decreases as you move from producers to top consumers.
2. Aquatic Ecosystems Characteristics
- In aquatic environments, producers such as phytoplankton have a low biomass compared to the organisms that feed on them, like zooplankton and small fish.
- The rapid reproduction and turnover rates of phytoplankton lead to a situation where the total weight of consumers can exceed that of the producers.
3. Reasons for Inversion
- High Reproduction Rates: Phytoplankton reproduce quickly, but their biomass is low at any given time.
- Efficiency of Energy Transfer: In aquatic systems, energy transfer from producers to consumers is highly efficient, allowing a larger biomass of consumers.
- Size Difference: Small primary producers can support larger consumers, leading to an inverted biomass pyramid.
4. Implications
- This structure challenges the traditional understanding of food webs and energy flow.
- It highlights the unique dynamics of aquatic ecosystems where even small organisms can support a diverse and larger community of consumers.
In conclusion, the pyramid of biomass is inverted in aquatic ecosystems due to the high productivity and turnover of phytoplankton, resulting in greater biomass of consumers compared to producers.
Which of the following best describes primary productivity?- a)The rate of organic matter formation by consumers
- b)The total biomass available for herbivores
- c)The rate of biomass production by producers
- d)The decomposition of dead organic matter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The rate of organic matter formation by consumers
b)
The total biomass available for herbivores
c)
The rate of biomass production by producers
d)
The decomposition of dead organic matter
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Understanding Primary Productivity
Primary productivity refers to the process by which producers, such as plants and phytoplankton, convert inorganic substances (like carbon dioxide and water) into organic matter through photosynthesis. This process is fundamental to ecosystems, as it forms the base of the food web.
Key Points about Primary Productivity:
- Definition: It is the rate at which biomass is produced by autotrophs (producers) in a given area over a specific time period.
- Significance: Primary productivity is crucial because it determines the energy available for all other trophic levels, including herbivores and carnivores.
- Measurement: It is often measured in terms of biomass (grams of carbon per square meter per year) and can be categorized into gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP).
- Gross Primary Productivity (GPP): The total amount of organic matter produced.
- Net Primary Productivity (NPP): The amount of organic matter available after subtracting the energy used by producers for respiration.
Why Option C is Correct:
- The correct answer, option 'C', states that primary productivity is "the rate of biomass production by producers." This definition accurately captures the essence of primary productivity, highlighting the role of producers in generating organic matter.
- Other options do not correctly describe primary productivity:
- Option 'A' refers to consumers, which do not produce organic matter.
- Option 'B' pertains to biomass available for herbivores, which is a result of primary productivity but not the definition itself.
- Option 'D' discusses decomposition, which is a separate ecological process and not related to the generation of new biomass.
In summary, primary productivity is essential for understanding energy flow in ecosystems and is fundamentally about the production of biomass by producers.
Primary productivity refers to the process by which producers, such as plants and phytoplankton, convert inorganic substances (like carbon dioxide and water) into organic matter through photosynthesis. This process is fundamental to ecosystems, as it forms the base of the food web.
Key Points about Primary Productivity:
- Definition: It is the rate at which biomass is produced by autotrophs (producers) in a given area over a specific time period.
- Significance: Primary productivity is crucial because it determines the energy available for all other trophic levels, including herbivores and carnivores.
- Measurement: It is often measured in terms of biomass (grams of carbon per square meter per year) and can be categorized into gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP).
- Gross Primary Productivity (GPP): The total amount of organic matter produced.
- Net Primary Productivity (NPP): The amount of organic matter available after subtracting the energy used by producers for respiration.
Why Option C is Correct:
- The correct answer, option 'C', states that primary productivity is "the rate of biomass production by producers." This definition accurately captures the essence of primary productivity, highlighting the role of producers in generating organic matter.
- Other options do not correctly describe primary productivity:
- Option 'A' refers to consumers, which do not produce organic matter.
- Option 'B' pertains to biomass available for herbivores, which is a result of primary productivity but not the definition itself.
- Option 'D' discusses decomposition, which is a separate ecological process and not related to the generation of new biomass.
In summary, primary productivity is essential for understanding energy flow in ecosystems and is fundamentally about the production of biomass by producers.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.- a)Both statement 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statement 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.
a)
Both statement 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statement 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
First-order consumers are animals that eat plants called herbivores. They are the first step in the food chain.
Organisms which are associated with first as well as third trophic level are- a)macrophytes
- b)phytoplanktons
- c)chemoautotrophs
- d)insectivorous plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms which are associated with first as well as third trophic level are
a)
macrophytes
b)
phytoplanktons
c)
chemoautotrophs
d)
insectivorous plants
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Trophic level is a functional level. A single species may occupy more than one trophic level. Insectivorous plants are producers, occupying first trophic level. They also eat insects and thus, occupy third trophic level also.
If 10 joules of energy is available at the producer level, then amount of energy present at the level of secondary consumer is- a)10 J
- b)1 J
- c)0.1 J
- d)0.01 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If 10 joules of energy is available at the producer level, then amount of energy present at the level of secondary consumer is
a)
10 J
b)
1 J
c)
0.1 J
d)
0.01 J
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Only 10 % of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next trophic level of a food chain (ten percent law, given by Linderman). In present case, energy available at producer level is 10 J. Hence energy at primary consumer level would be 1 H (10% of 10 J). Similarly, at secondary consumer level, energy present will be 0.1 J (100 % of 1 J).
In a grassland ecosystem, if the number of primary producers is approximately 6 million plants, the number of the top carnivores (in million), which may be supported by it may be ________ million.- a)3
- b)30
- c)6
- d)60
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a grassland ecosystem, if the number of primary producers is approximately 6 million plants, the number of the top carnivores (in million), which may be supported by it may be ________ million.
a)
3
b)
30
c)
6
d)
60
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
In a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of numbers is upright. If primary producers are approximately 6 million plants, then number of top carnivores must be less than 6 milliion. Hecne, according to the option given, there would be 3 million top carnivores.
What is the correct formula for net primary productivity (NPP)?- a)NPP = GPP + R
- b)NPP = GPP - R
- c)NPP = R - GPP
- d)NPP = GPP × R
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
NPP = GPP + R
b)
NPP = GPP - R
c)
NPP = R - GPP
d)
NPP = GPP × R

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Net primary productivity (NPP) is calculated by subtracting the respiration losses (R) from gross primary productivity (GPP). Hence, NPP = GPP - R.
Which of the following is a decomposer?- a)Earthworm
- b)Grasshopper
- c)Fungi
- d)Eagle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Earthworm
b)
Grasshopper
c)
Fungi
d)
Eagle

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Fungi are decomposers that break down dead organic matter into simpler substances. Earthworms are detritivores, not decomposers.
Which of the following components are abiotic in an ecosystem?- a)Plants and animals
- b)Soil, water, and air
- c)Bacteria and fungi
- d)Herbivores and carnivores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Plants and animals
b)
Soil, water, and air
c)
Bacteria and fungi
d)
Herbivores and carnivores
|
|
Mrinalini Basak answered |
Understanding Abiotic Components
In an ecosystem, components are classified into two main categories: abiotic and biotic.
Abiotic Components Defined
Abiotic components are the non-living parts of an ecosystem that influence living organisms and the functioning of the ecosystem itself. They include:
- Soil: Provides nutrients and a medium for plants to grow.
- Water: Essential for all living organisms, involved in various biological processes.
- Air: Contains gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, which are crucial for respiration and photosynthesis.
Biotic Components vs. Abiotic Components
In contrast, biotic components are the living organisms in an ecosystem, including:
- Plants: Producers that convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- Animals: Consumers that depend on plants and other animals for food.
- Bacteria and Fungi: Decomposers that break down organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Why Option B is Correct
The correct answer, option 'B', identifies soil, water, and air as abiotic components of an ecosystem:
- They are non-living elements that play significant roles in sustaining life.
- They provide the necessary conditions for biotic components to thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between abiotic and biotic components is crucial for studying ecosystems. Option 'B', which includes soil, water, and air, accurately represents the abiotic factors that are foundational to the existence and health of ecosystems.
In an ecosystem, components are classified into two main categories: abiotic and biotic.
Abiotic Components Defined
Abiotic components are the non-living parts of an ecosystem that influence living organisms and the functioning of the ecosystem itself. They include:
- Soil: Provides nutrients and a medium for plants to grow.
- Water: Essential for all living organisms, involved in various biological processes.
- Air: Contains gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, which are crucial for respiration and photosynthesis.
Biotic Components vs. Abiotic Components
In contrast, biotic components are the living organisms in an ecosystem, including:
- Plants: Producers that convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- Animals: Consumers that depend on plants and other animals for food.
- Bacteria and Fungi: Decomposers that break down organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Why Option B is Correct
The correct answer, option 'B', identifies soil, water, and air as abiotic components of an ecosystem:
- They are non-living elements that play significant roles in sustaining life.
- They provide the necessary conditions for biotic components to thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between abiotic and biotic components is crucial for studying ecosystems. Option 'B', which includes soil, water, and air, accurately represents the abiotic factors that are foundational to the existence and health of ecosystems.
In the given food web, an increase in the population of hawks will not result in
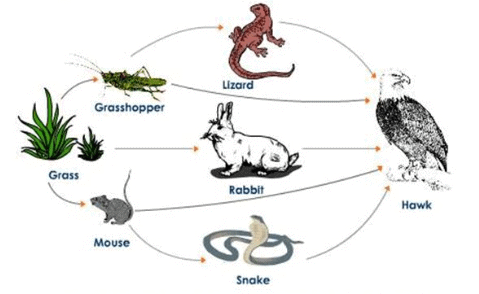
- a)decrease in the population of rabbits and snakes
- b)increase in the population of producers
- c)increase in the population of grasshoppers
- d)decrease in the population of lizards
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given food web, an increase in the population of hawks will not result in
a)
decrease in the population of rabbits and snakes
b)
increase in the population of producers
c)
increase in the population of grasshoppers
d)
decrease in the population of lizards
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
If population of hawks would increase, they would feed on more lizards which will result in decrease of lizard population.
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that is captured by plants in synthesis of organic matter is?- a)50-70%
- b)30-40%
- c)80-100%
- d)2-10%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that is captured by plants in synthesis of organic matter is?
a)
50-70%
b)
30-40%
c)
80-100%
d)
2-10%
|
|
Mohd Parvez answered |
According to NCERT page number 245 chapter ecosystems incident solar radiation less than 50% of its photosynthetically active radiation Then option D will correct.
Less than 50% Aisa ek hi option h jisme kam hai
Less than 50% Aisa ek hi option h jisme kam hai
Primary consumer category in aquatic &/or terrestrial ecosystem will include :- a)Zooplanktons, frog tadpole, snails and tortoise
- b)Zooplanktons, frog, grasshoppers and hydra
- c)Frog tadpole, goat, bacteria and fungi
- d)Water insects, rabbits, frogs and snails
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Primary consumer category in aquatic &/or terrestrial ecosystem will include :
a)
Zooplanktons, frog tadpole, snails and tortoise
b)
Zooplanktons, frog, grasshoppers and hydra
c)
Frog tadpole, goat, bacteria and fungi
d)
Water insects, rabbits, frogs and snails

|
Krish Patel answered |
Primary consumers obtain food from producers or autotrophs. In aquatic ecosystem phytoplankton are main prouder and zooplankton are primary consumers along with frog tadpole , snail and tortoise.
What does the 10% law of energy transfer imply?- a)Only 10% of the energy is utilized by producers.
- b)Only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
- c)10% of energy is lost during respiration at each trophic level.
- d)10% of energy is lost as heat at each trophic level.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Only 10% of the energy is utilized by producers.
b)
Only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
c)
10% of energy is lost during respiration at each trophic level.
d)
10% of energy is lost as heat at each trophic level.
|
|
Pooja Desai answered |
Understanding the 10% Law of Energy Transfer
The 10% law of energy transfer is a key concept in ecology that describes how energy flows through an ecosystem. This law provides insight into the efficiency of energy transfer between different trophic levels.
What is the 10% Law?
- The 10% law states that, on average, only about 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level.
- This implies that when energy is passed from producers (like plants) to primary consumers (herbivores), and then to secondary consumers (carnivores), a significant portion of energy is lost at each step.
Energy Transfer Efficiency
- When producers convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, they capture a large amount of energy. However, not all of this energy is available to the next level.
- Factors such as metabolic processes, movement, and energy lost as heat during respiration account for the energy that is not passed on.
Reasons for Energy Loss
- Metabolic Processes: Organisms use energy for growth, reproduction, and maintenance.
- Heat Loss: A considerable amount of energy is lost as heat during cellular respiration.
- Waste Production: Not all consumed energy is absorbed; some is lost in waste products.
Implications of the 10% Law
- This law illustrates the inefficiency of energy transfer and highlights the limitations on the number of trophic levels in an ecosystem.
- It also shows the importance of primary producers for sustaining the energy needs of higher trophic levels.
In summary, the 10% law emphasizes that only about 10% of energy is effectively transferred from one trophic level to the next, making it essential for understanding the dynamics of ecosystems.
The 10% law of energy transfer is a key concept in ecology that describes how energy flows through an ecosystem. This law provides insight into the efficiency of energy transfer between different trophic levels.
What is the 10% Law?
- The 10% law states that, on average, only about 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level.
- This implies that when energy is passed from producers (like plants) to primary consumers (herbivores), and then to secondary consumers (carnivores), a significant portion of energy is lost at each step.
Energy Transfer Efficiency
- When producers convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, they capture a large amount of energy. However, not all of this energy is available to the next level.
- Factors such as metabolic processes, movement, and energy lost as heat during respiration account for the energy that is not passed on.
Reasons for Energy Loss
- Metabolic Processes: Organisms use energy for growth, reproduction, and maintenance.
- Heat Loss: A considerable amount of energy is lost as heat during cellular respiration.
- Waste Production: Not all consumed energy is absorbed; some is lost in waste products.
Implications of the 10% Law
- This law illustrates the inefficiency of energy transfer and highlights the limitations on the number of trophic levels in an ecosystem.
- It also shows the importance of primary producers for sustaining the energy needs of higher trophic levels.
In summary, the 10% law emphasizes that only about 10% of energy is effectively transferred from one trophic level to the next, making it essential for understanding the dynamics of ecosystems.
Study the food web given below and answer the questions that follow.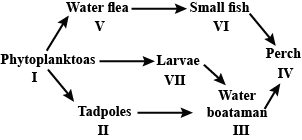 Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?
Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?- a)II and V
- b)III and VI
- c)VII only
- d)IV only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the food web given below and answer the questions that follow.

Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?
a)
II and V
b)
III and VI
c)
VII only
d)
IV only
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In the given food web, organisms I (phytoplanktons) act as producers, organisms II, V and VII act as primary consumers as they feed on producers, organisms III and VI act as secondary consumers as they upon primary consumers, and organism IV acts as a tertiary consumer.
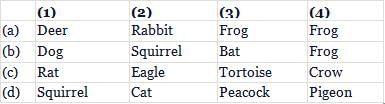
Given food web contains some missing organisms, (1), (2), (3) and (4). Identify these organisms and select the correct answer.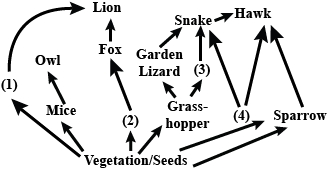
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given food web contains some missing organisms, (1), (2), (3) and (4). Identify these organisms and select the correct answer.


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
A lion feeds on a deer.
Deer are the primary consumer.
Fox acts a secondary consumer and feeds on a primary consumer such as Rabbit.
Frog feeds on a grasshopper and acts as a primary consumer.
Rat acts as prey for both Snake and a hawk.
Deer are the primary consumer.
Fox acts a secondary consumer and feeds on a primary consumer such as Rabbit.
Frog feeds on a grasshopper and acts as a primary consumer.
Rat acts as prey for both Snake and a hawk.
What is the process of breaking down complex organic matter into inorganic substances called?- a)Productivity
- b)Energy Flow
- c)Decomposition
- d)Nutrient Cycling
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Productivity
b)
Energy Flow
c)
Decomposition
d)
Nutrient Cycling

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Decomposition is the process by which decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down complex organic matter into simpler inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients.
Chapter doubts & questions for Natural Habitats - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Natural Habitats - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









