All Exams >
Grade 9 >
Biology for Grade 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Human Nutrition for Grade 9 Exam
Amoeba obtain the food using finger-like projection calledA: PseudopodiaB: SpiraclesC: DiaphragmD: MouthCorrect answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amoeba obtain the food using finger-like projection called
A: Pseudopodia
B: Spiracles
C: Diaphragm
D: Mouth
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Abhay Menon answered |
The finger-like projections are called “pseudopodia“. They not only help in engulfing food molecules but also help the organism in movement.
Grass is rich in ________ a special kind of carbohydrate which can only be digested by ruminants.- a)Glucose
- b)Cellulose
- c)Sucrose
- d)Fructose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Grass is rich in ________ a special kind of carbohydrate which can only be digested by ruminants.
a)
Glucose
b)
Cellulose
c)
Sucrose
d)
Fructose
|
|
Aarav Sen answered |
Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants and not by humans.
Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called rumen between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called rumen between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
1) What process allows digested food to pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine?- a)Excretion
- b)Digestion
- c)Assimilation
- d)Absorption
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
1) What process allows digested food to pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine?
a)
Excretion
b)
Digestion
c)
Assimilation
d)
Absorption
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The process of digested food passing into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine is called absorption.
Mode of nutrition in amoeba is- a)Herbivores
- b)Holozoic
- c)Omnivores
- d)Autotrophic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mode of nutrition in amoeba is
a)
Herbivores
b)
Holozoic
c)
Omnivores
d)
Autotrophic

|
Anmol Iyer answered |
Nutrition in amoeba is holozoic. Thus, solid food particles are ingested which are then acted upon by enzymes and digested. It is an omnivore, feeding on both plants and animals. Its diet includes bacteria, microscopic plants like the diatoms, minute algae, microscopic animals like other protozoa, nematodes and even dead organic matter.
Absorption of water in alimentary canal takes place in
- a)Small intestine
- b)Large intestine
- c)Rectum
- d)Stomach
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Absorption of water in alimentary canal takes place in
a)
Small intestine
b)
Large intestine
c)
Rectum
d)
Stomach

|
Pooja Banerjee answered |
Absorption of water in alimentary canal takes place in the Large intestine.
The process of absorption refers to the movement of water, nutrients, and other substances from the digestive system into the bloodstream. In the case of water absorption, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and preventing dehydration. The absorption of water in the alimentary canal specifically occurs in the large intestine.
Here is a detailed explanation of water absorption in the large intestine:
Anatomy of the Large Intestine:
- The large intestine is the final section of the digestive tract, following the small intestine.
- It is a wider and shorter tube that measures about 1.5 meters in length.
- The major parts of the large intestine include the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal.
Process of Water Absorption in the Large Intestine:
1. Residue from the small intestine enters the large intestine through the ileocecal valve.
2. In the large intestine, the residue passes through the ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and finally reaches the rectum.
3. The large intestine mainly functions to reabsorb water and electrolytes from this residue before it is eliminated as feces.
4. The walls of the large intestine are lined with specialized cells called colonocytes that facilitate water absorption.
5. The colonocytes actively transport sodium ions out of the lumen of the large intestine and into the interstitial fluid.
6. The movement of sodium ions creates an osmotic gradient, causing water to follow passively through osmosis.
7. As a result, water is absorbed from the residue and into the bloodstream, helping to maintain the body's hydration levels.
8. The remaining residue, which is now more solid, continues to move through the large intestine and eventually reaches the rectum for elimination.
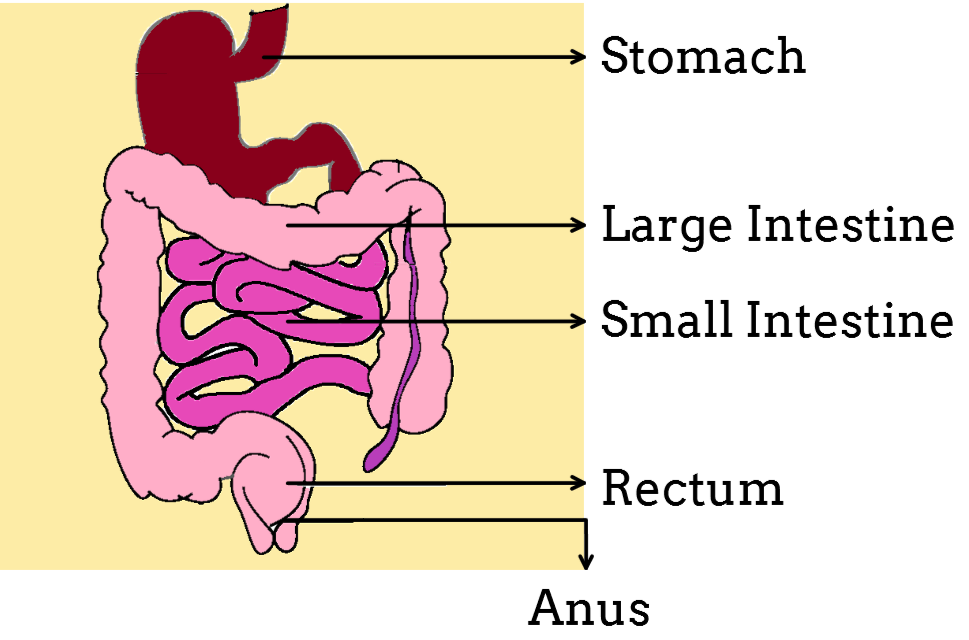
Significance of Water Absorption in the Large Intestine:
- The large intestine plays a crucial role in maintaining water balance in the body.
- It helps prevent dehydration by reabsorbing water from the residue, which would otherwise be lost as feces.
- The absorbed water is then transported to the bloodstream, where it can be distributed to various parts of the body.
- Adequate water absorption in the large intestine is essential for maintaining normal bowel movements and preventing constipation.
In conclusion, the absorption of water in the alimentary canal takes place in the large intestine. The walls of the large intestine, particularly the colonocytes, actively transport sodium ions, creating an osmotic gradient that facilitates water absorption through osmosis. This process helps maintain the body's fluid balance and prevents dehydration.
The process of absorption refers to the movement of water, nutrients, and other substances from the digestive system into the bloodstream. In the case of water absorption, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and preventing dehydration. The absorption of water in the alimentary canal specifically occurs in the large intestine.
Here is a detailed explanation of water absorption in the large intestine:
Anatomy of the Large Intestine:
- The large intestine is the final section of the digestive tract, following the small intestine.
- It is a wider and shorter tube that measures about 1.5 meters in length.
- The major parts of the large intestine include the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal.
Process of Water Absorption in the Large Intestine:
1. Residue from the small intestine enters the large intestine through the ileocecal valve.
2. In the large intestine, the residue passes through the ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and finally reaches the rectum.
3. The large intestine mainly functions to reabsorb water and electrolytes from this residue before it is eliminated as feces.
4. The walls of the large intestine are lined with specialized cells called colonocytes that facilitate water absorption.
5. The colonocytes actively transport sodium ions out of the lumen of the large intestine and into the interstitial fluid.
6. The movement of sodium ions creates an osmotic gradient, causing water to follow passively through osmosis.
7. As a result, water is absorbed from the residue and into the bloodstream, helping to maintain the body's hydration levels.
8. The remaining residue, which is now more solid, continues to move through the large intestine and eventually reaches the rectum for elimination.

Significance of Water Absorption in the Large Intestine:
- The large intestine plays a crucial role in maintaining water balance in the body.
- It helps prevent dehydration by reabsorbing water from the residue, which would otherwise be lost as feces.
- The absorbed water is then transported to the bloodstream, where it can be distributed to various parts of the body.
- Adequate water absorption in the large intestine is essential for maintaining normal bowel movements and preventing constipation.
In conclusion, the absorption of water in the alimentary canal takes place in the large intestine. The walls of the large intestine, particularly the colonocytes, actively transport sodium ions, creating an osmotic gradient that facilitates water absorption through osmosis. This process helps maintain the body's fluid balance and prevents dehydration.
Small intestine contain small finger-like projections to absorb digested food is called- a)Pseudopodia
- b)Cilia
- c)Villi
- d)Flagella
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Small intestine contain small finger-like projections to absorb digested food is called
a)
Pseudopodia
b)
Cilia
c)
Villi
d)
Flagella

|
Madhurima Kulkarni answered |
The mucosa is a mucous membrane. It is the innermost lining of the small intestine. It is made up of a:
- the layer of epithelial cells (called the epithelium)
- a layer of loose connective tissue (called the lamina propria)
- the very thin layer of muscle (called the muscularis mucosa)
The inner surface of the mucosa has many finger-like projections called villi. The villi increase the surface area of the small intestine, which helps it absorb digested food.
The process of chewing of food is called- a)Digestion
- b)Ingestion
- c)Mastication
- d)Emulsification
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of chewing of food is called
a)
Digestion
b)
Ingestion
c)
Mastication
d)
Emulsification

|
Snehal Basak answered |
The process of chewing food is called mastication. Teeth and tongue help in mastication of food.
Bile juice is stored in- a)Stomach
- b)Gall bladder
- c)Liver
- d)Urinary bladder
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bile juice is stored in
a)
Stomach
b)
Gall bladder
c)
Liver
d)
Urinary bladder
|
|
Divya Joshi answered |
Bile salts are one of the primary components of bile. Bile is a greenish-yellow fluid made by the liver and stored in our gallbladder.
Which of the following component of food do not provide energy of body building?- a)Roughage
- b)Proteins
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)Fats
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following component of food do not provide energy of body building?
a)
Roughage
b)
Proteins
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
Fats
|
|
Nandini Sengupta answered |
Roughage is a component of food which do not provides energy or help in body building. Roughage helps in movement of food in alimentary canal.
Bile is secreted from- a)Pancreas
- b)Small intestine
- c)Stomach
- d)Liver
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bile is secreted from
a)
Pancreas
b)
Small intestine
c)
Stomach
d)
Liver
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Bile is secreted from liver that contain bile salt. Bile salt helps in emulsification of fat.
In amoeba, digestion of food takes place inside- a)Food pipe
- b)Gizzard
- c)Food vacuole
- d)Stomach
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In amoeba, digestion of food takes place inside
a)
Food pipe
b)
Gizzard
c)
Food vacuole
d)
Stomach
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The mode of nutrition in amoeba is holozoic. Amoeba digests the food inside food vacuole that contain enzyme for digestion.
Ingestion is the process in which organisma)intake of food inside the body b)Nutrient are utilisedc)Digest the bodyd)Undigested food are removedCorrect answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Kavya Rane answered |
While ingestion refers to the taking in of a substance, there are a multitude of mechanisms by which various organisms do this. Everything from the tiny cells of your body, single-celled organisms, such as amoebas and paramecium, bacteria, and yeasts to animals and humans ingest nutritive substances.
What does animal nutrition include?- a)Nutrient requirement
- b)Mode of intake of food
- c)Utilization of food in the body
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does animal nutrition include?
a)
Nutrient requirement
b)
Mode of intake of food
c)
Utilization of food in the body
d)
All of the above
|
|
Academic Studio answered |
Production of Bile in the Liver
- The liver is the primary organ responsible for the production of bile in the human body.
- Bile is a yellow-green fluid that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine.
- Hepatocytes, the main functional cells of the liver, synthesize bile by extracting waste products, cholesterol, and other substances from the blood.
- Bile is then stored and concentrated in the gallbladder before being released into the small intestine to help with the digestion of fats.
- The liver is the primary organ responsible for the production of bile in the human body.
- Bile is a yellow-green fluid that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine.
- Hepatocytes, the main functional cells of the liver, synthesize bile by extracting waste products, cholesterol, and other substances from the blood.
- Bile is then stored and concentrated in the gallbladder before being released into the small intestine to help with the digestion of fats.
Which one is the largest gland in the human body?- a)Pancreas
- b)Pituitary gland
- c)Liver
- d)Gall bladder
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is the largest gland in the human body?
a)
Pancreas
b)
Pituitary gland
c)
Liver
d)
Gall bladder

|
Gauri Basak answered |
Liver is the largest gland in the human body. Liver secretes bile juice that contains bile salt. Emulsification of fat occurs by the action of bile salt.
What is the primary characteristic of diarrhoea?- a) Frequent urination
- b) Watery stool
- c) Headaches
- d) Fever
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary characteristic of diarrhoea?
a)
Frequent urination
b)
Watery stool
c)
Headaches
d)
Fever
|
|
Mansi rane answered |
Understanding Diarrhoea
Diarrhoea is primarily characterized by the frequent passage of watery stool. This condition can affect individuals of all ages and can arise from various causes, including infections, dietary changes, or underlying health issues.
Key Characteristics of Diarrhoea:
- Watery Stool: The hallmark of diarrhoea is the consistency of the stool. It is often loose or watery, which differentiates it from normal bowel movements.
- Frequency: Individuals may experience an increased frequency of bowel movements, often more than three times a day.
- Causes: Diarrhoea can result from viral infections (like norovirus), bacterial infections (like E. coli), parasites, or even food intolerances.
- Dehydration Risk: One of the significant concerns associated with diarrhoea is dehydration. The body loses fluids and electrolytes rapidly, making it essential to stay hydrated.
Other Symptoms that May Accompany Diarrhoea:
- Fever: While fever can be present, it is not a defining characteristic of diarrhoea itself.
- Abdominal Pain: Cramping and discomfort in the abdomen may occur alongside diarrhoea.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may also experience nausea or vomiting, but these are not defining symptoms.
Conclusion:
In summary, while other symptoms can accompany diarrhoea, the primary characteristic is the presence of watery stool. Understanding this can help in identifying the condition and seeking appropriate treatment.
Diarrhoea is primarily characterized by the frequent passage of watery stool. This condition can affect individuals of all ages and can arise from various causes, including infections, dietary changes, or underlying health issues.
Key Characteristics of Diarrhoea:
- Watery Stool: The hallmark of diarrhoea is the consistency of the stool. It is often loose or watery, which differentiates it from normal bowel movements.
- Frequency: Individuals may experience an increased frequency of bowel movements, often more than three times a day.
- Causes: Diarrhoea can result from viral infections (like norovirus), bacterial infections (like E. coli), parasites, or even food intolerances.
- Dehydration Risk: One of the significant concerns associated with diarrhoea is dehydration. The body loses fluids and electrolytes rapidly, making it essential to stay hydrated.
Other Symptoms that May Accompany Diarrhoea:
- Fever: While fever can be present, it is not a defining characteristic of diarrhoea itself.
- Abdominal Pain: Cramping and discomfort in the abdomen may occur alongside diarrhoea.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may also experience nausea or vomiting, but these are not defining symptoms.
Conclusion:
In summary, while other symptoms can accompany diarrhoea, the primary characteristic is the presence of watery stool. Understanding this can help in identifying the condition and seeking appropriate treatment.
The type of digestion which takes place within the cell is termed as- a)Extra cellular digestion
- b)Intra tissue digestion
- c)Inter cellular digestion
- d)Intracellular digestion
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The type of digestion which takes place within the cell is termed as
a)
Extra cellular digestion
b)
Intra tissue digestion
c)
Inter cellular digestion
d)
Intracellular digestion

|
Anagha Choudhury answered |
Intracellular digestion, or cellular digestion, is the process in which large molecules, from outside or from a cell’s own metabolism, are broken down into smaller molecules within the cell. Products and wastes of intracellular digestion are either used by the cell or excreted.
Intracellular digestion is classified into two types: heterophagic intracellular digestion and autophagic intracellular digestion.
The sharp teeth used for tearing food is called- a)Molars
- b)Premolars
- c)Incisors
- d)Canines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The sharp teeth used for tearing food is called
a)
Molars
b)
Premolars
c)
Incisors
d)
Canines
|
|
Anshika Saha answered |
Canines are sharp teeth used for tearing food. Canine is more prominent in carnivores to tear the meat.
Which one is a unicellular organism?- a)Frog
- b)Hydra
- c)Amoeba
- d)Ant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is a unicellular organism?
a)
Frog
b)
Hydra
c)
Amoeba
d)
Ant

|
Anand Ghoshal answered |
Those organisms whose body is made up of only one cell is called unicellular organism. Amoeba is a unicellular organism.
Peristalsis is theA: Slow movement of foodB: Contraction and expansion of muscles of oesophagusC: Downward movement of digested foodD: Assimilation of foodCorrect answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Peristalsis is the
A: Slow movement of food
B: Contraction and expansion of muscles of oesophagus
C: Downward movement of digested food
D: Assimilation of food

|
Prisha Banerjee answered |
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the oesophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed. The strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle in the oesophagus carry the food to the stomach, where it is churned into a liquid mixture called chyme.
Our mouth has __________ glands which secrete saliva.- a)
- Salivary
- b)
- Muscular
- c)
- Digestive
- d)
- Respiratory
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Our mouth has __________ glands which secrete saliva.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Keystone Instructors answered |
Salivary glands in our mouth produce saliva. Saliva helps in breaking down food while chewing and swallowing. It also contains enzymes that start the digestion process.
Which juice is released by the stomach to aid digestion?
- a)Pancreatic juice
- b)Bile juice
- c)Gastric juice
- d)Intestinal juice
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which juice is released by the stomach to aid digestion?
a)
Pancreatic juice
b)
Bile juice
c)
Gastric juice
d)
Intestinal juice

|
Rainbow Rise Classes answered |
The stomach releases digestive juices, including hydrochloric acid and enzymes, to break down food into simpler substances for easier digestion.
What is the role of villi in the intestine?- a)To make the stomach wider
- b)To absorb food in the small intestine
- c)To help in swallowing food
- d)To produce bile juice
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the role of villi in the intestine?
a)
To make the stomach wider
b)
To absorb food in the small intestine
c)
To help in swallowing food
d)
To produce bile juice

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
- Villi in the intestine help to absorb the food that has been digested. They are like tiny fingers that take in the good parts of the food and send them to different parts of the body to help us grow and stay healthy.
- So, villi are like little helpers in our body that take the good stuff from our food and bring it where it's needed.
Mechanism in which amoeba takes in O2 and gives out CO2 is called _______.
- a)Respiration
- b)Diffusion
- c)Assimilation
- d)Absorption
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mechanism in which amoeba takes in O2 and gives out CO2 is called _______.
a)
Respiration
b)
Diffusion
c)
Assimilation
d)
Absorption
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Amoeba gets oxygen gas dissolved in surrounding water through its plasma membrane by the process of diffusion.The carbon dioxide gas is also liberated in the surrounding water through the same process of diffusion.
Cellulose digestion in ruminants occurs in ________.
- a)Omasum
- b)Rumen
- c)Abomasum
- d)Reticulum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellulose digestion in ruminants occurs in ________.
a)
Omasum
b)
Rumen
c)
Abomasum
d)
Reticulum
|
|
Freak Artworks answered |
Cellulose digestion in ruminants like cattle occurs in the rumen or foregut that harbors bacteria that bring about breakdown of cellulose through fermentation. Here, mechanical digestion also occurs by converting ingested food into cud.
So, the correct answer is option A
So, the correct answer is option A
What does saliva do to food?- a)Makes it sweeter
- b)Breaks down starch into sugars
- c)Changes its color
- d)Turns it into liquid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What does saliva do to food?
a)
Makes it sweeter
b)
Breaks down starch into sugars
c)
Changes its color
d)
Turns it into liquid

|
Tutorpedia Coaching answered |
Saliva helps in breaking down the starch in food into sugars. This makes it easier for our bodies to digest the food we eat. So, saliva plays an important role in making food easier for our bodies to use for energy.
The movement of food in food pipe is called- a)Linear movement
- b)Rectilinear movement
- c)Smooth movement
- d)Peristaltic movement
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The movement of food in food pipe is called
a)
Linear movement
b)
Rectilinear movement
c)
Smooth movement
d)
Peristaltic movement

|
Prisha Banerjee answered |
The digestion starts in the mouth where the food mixes which saliva. Saliva is produced by the salivary glands which makes the food slimy and makes it easy to be swallowed. Once the food is salllowed then it enters to a long tube like structure called Oesophagus. The walls of the oesophagus contract and relax to produce wave like movements called Peristaltic movements. These movements help to move the food down into a big sack like structure called stomach.
Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function?- a)Canines and incisors
- b)Molars and premolars
- c)Incisors and molars
- d)Premolars and canines
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function?
a)
Canines and incisors
b)
Molars and premolars
c)
Incisors and molars
d)
Premolars and canines
|
|
Rhea Reddy answered |
The molars (12 in number) are the largest teeth of all whereas the premolars (8 in number) present next to molars.
The function of these types of teeth is similar, i.e. crushing and grinding of food.
The function of these types of teeth is similar, i.e. crushing and grinding of food.
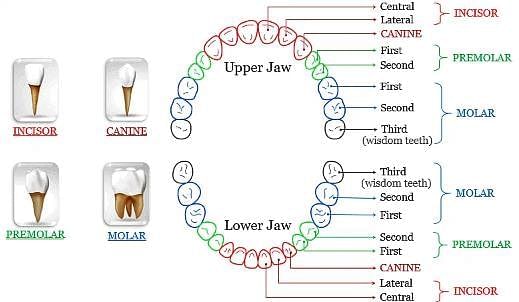
Biological catalyst that breakdown the food into simpler form is called- a)Acids
- b)Bases
- c)Alkalies
- d)Enzyme
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biological catalyst that breakdown the food into simpler form is called
a)
Acids
b)
Bases
c)
Alkalies
d)
Enzyme
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Enzymes are biological catalyst that breakdown the complex food into simple form. Enzymes are released from exocrine glands.
The semi-solid mass which is produced after thoroughly mix up of food and gastric juice is called- a)bolus
- b)chyme
- c)bile
- d)villus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The semi-solid mass which is produced after thoroughly mix up of food and gastric juice is called
a)
bolus
b)
chyme
c)
bile
d)
villus

|
Diya Chavan answered |
The stomach stores the food for 4-5 hours. The food mixes thoroughly with the acidic gastric juice of the stomach by the churning movements of its muscular wall and is called the chyme. The proenzyme pepsinogen, on exposure to hydrochloric acid gets converted into the active enzyme pepsin, the proteolytic enzyme of the stomach. Pepsin converts proteins into proteoses and peptones (peptides).
Which part of the digestive canal is responsible for the formation of feces?- a)Stomach
- b)Small intestine
- c)Large intestine
- d)Esophagus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Stomach
b)
Small intestine
c)
Large intestine
d)
Esophagus
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
The large intestine absorbs water and salts from the undigested food, converting it into solid waste or feces, which is then stored in the rectum until it is excreted.
Peristalsis is the- a)Slow movement of food
- b)Contraction and expansion of muscles of oesophagus
- c)Downward movement of digested food
- d)Assimilation of food
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Peristalsis is the
a)
Slow movement of food
b)
Contraction and expansion of muscles of oesophagus
c)
Downward movement of digested food
d)
Assimilation of food

|
Pranavi Roy answered |
Peristalsis is the contraction and expansion of muscles of oesophagus for passage of food towards stomach. As the food passes through oesophagus the wall of it expand to allow passage of food.
The inner walls of the small intestine have millions of small finger like projections called- a)villi
- b)trachae
- c)appendix
- d)oesophagus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The inner walls of the small intestine have millions of small finger like projections called
a)
villi
b)
trachae
c)
appendix
d)
oesophagus
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The interior walls of the small intestine are tightly wrinkled into projections called circular folds that greatly increase their surface area. Microscopic examination of the mucosa reveals that the mucosal cells are organized into finger-like projections known as villi, which further increase the surface area.
Saliva is released from- a)Pinus gland
- b)Thyroid gland
- c)Adrenal gland
- d)Salivary gland
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Saliva is released from
a)
Pinus gland
b)
Thyroid gland
c)
Adrenal gland
d)
Salivary gland

|
Vandana Mukherjee answered |
Saliva is produced in and secreted from salivary glands. The basic secretory units of salivary glands are clusters of cells called an acini. These cells secrete a fluid that contains water, electrolytes, mucus and enzymes, all of which flow out of the acinus into collecting ducts.
The acid present in the stomach:- a)Protects the stomach lining from harmful substances.
- b)Kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food.
- c)Digests starch into simpler sugars.
- d)Makes the medium alkaline.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The acid present in the stomach:
a)
Protects the stomach lining from harmful substances.
b)
Kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food.
c)
Digests starch into simpler sugars.
d)
Makes the medium alkaline.
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
'Hydrochloric acid' is an acid that is secreted in the stomach. It helps to kill the harmful bacteria that may enter the food.
Longest part of human alimentary canal is- a)Liver
- b)Large intestine
- c)Stomach
- d)Small intestine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Longest part of human alimentary canal is
a)
Liver
b)
Large intestine
c)
Stomach
d)
Small intestine

|
Abhay Menon answered |
Human alimentary canal is about 9 meter long. Small intestine forms the largest part of meet. Most of digestion takes place in small intestine.
Wall of stomach contains- a)Neural glands
- b)Lymph nodes
- c)Gastric glands
- d)Absorptive glands
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Wall of stomach contains
a)
Neural glands
b)
Lymph nodes
c)
Gastric glands
d)
Absorptive glands

|
Kavya Rane answered |
Fundic glands found in the fundus and also in the body have another two cell types–gastric chief cells and parietal cells (oxyntic)). The chief cells are found in the basal regions of the gland and release a zymogen – pepsinogen, a precursor to pepsin.
In digestion the unused parts of the food are________.- a)utilised
- b)defecated
- c)converted
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In digestion the unused parts of the food are________.
a)
utilised
b)
defecated
c)
converted
d)
None of the above
|
|
Meghana verma answered |
Understanding Digestion and Waste Removal
Digestion is a complex process that involves breaking down food into smaller, absorbable components. However, not all parts of the food are utilized by the body. The unused parts must be properly eliminated, and this is where the process of defecation comes in.
Unused Parts of Food
- The human digestive system efficiently extracts essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals from the food we consume.
- After the nutrients are absorbed by the intestines, the remaining components that are indigestible or not required by the body remain.
Defecation Process
- The indigestible parts, including fiber, certain minerals, and other waste products, are compacted in the large intestine.
- This waste material is formed into feces, which is stored in the rectum until it is expelled from the body through the anus.
Importance of Defecation
- Defecation is crucial for maintaining health, as it removes toxins and waste products that could lead to illness if retained.
- Regular elimination helps prevent constipation and promotes overall digestive health.
In summary, the correct answer to the question is option 'B' - defecated. The unused parts of the food are not utilized or converted; instead, they are expelled from the body through defecation, ensuring the digestive system functions effectively and healthily.
Digestion is a complex process that involves breaking down food into smaller, absorbable components. However, not all parts of the food are utilized by the body. The unused parts must be properly eliminated, and this is where the process of defecation comes in.
Unused Parts of Food
- The human digestive system efficiently extracts essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals from the food we consume.
- After the nutrients are absorbed by the intestines, the remaining components that are indigestible or not required by the body remain.
Defecation Process
- The indigestible parts, including fiber, certain minerals, and other waste products, are compacted in the large intestine.
- This waste material is formed into feces, which is stored in the rectum until it is expelled from the body through the anus.
Importance of Defecation
- Defecation is crucial for maintaining health, as it removes toxins and waste products that could lead to illness if retained.
- Regular elimination helps prevent constipation and promotes overall digestive health.
In summary, the correct answer to the question is option 'B' - defecated. The unused parts of the food are not utilized or converted; instead, they are expelled from the body through defecation, ensuring the digestive system functions effectively and healthily.
Amoeba obtain the food using finger-like projection called- a)Pseudopodia
- b)Spiracles
- c)Diaphragm
- d)Mouth
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Amoeba obtain the food using finger-like projection called
a)
Pseudopodia
b)
Spiracles
c)
Diaphragm
d)
Mouth

|
Pooja Banerjee answered |
Amoeba obtains its food by a process called as endocytosis. It extends finger like projections called as pseudopodia around the food particle through the flexibility of its cell membrane and cytoplasm, and then engulfs the food particle. Once engulfed, it is stored in small vacuoles which contains enzymes to break the food into simpler forms which can be easily taken up by the amoeba.
What is the largest gland in the human body?
- a)Pancreas
- b)Liver
- c)Thyroid
- d)Adrenal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the largest gland in the human body?
a)
Pancreas
b)
Liver
c)
Thyroid
d)
Adrenal

|
Tutorpedia Coaching answered |
The liver is the largest gland in the human body and performs many vital functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
In which part of the human digestive system does most digestion and absorption of nutrients take place?
- a)Stomach
- b)Small intestine
- c)Mouth
- d)Large intestine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which part of the human digestive system does most digestion and absorption of nutrients take place?
a)
Stomach
b)
Small intestine
c)
Mouth
d)
Large intestine
|
|
Eduskill Classes answered |
The digestion of starch begins in the mouth where the enzyme amylase, present in saliva, breaks down starch into simpler sugars.
The stomach is a thick-walled bag that receives food from the food pipe at one end and opens into the ____ at the other.- a)large intestine
- b)small intestine
- c)liver
- d)pancreas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The stomach is a thick-walled bag that receives food from the food pipe at one end and opens into the ____ at the other.
a)
large intestine
b)
small intestine
c)
liver
d)
pancreas

|
Tutorpedia Coaching answered |
The stomach receives food from the food pipe and opens into the small intestine at the other end for further digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Where does the complete digestion of food occur?- a)Stomach
- b)Large intestine
- c)Small intestine
- d)Mouth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Stomach
b)
Large intestine
c)
Small intestine
d)
Mouth

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
The small intestine is the primary site for the complete digestion of food. Here, digestive enzymes break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into their absorbable units.
What is the primary organelle in Amoeba responsible for regulating its movement and maintaining its shape?
- a)Cell membrane
- b)Nucleus
- c)Vacuoles
- d)Pseudopodia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary organelle in Amoeba responsible for regulating its movement and maintaining its shape?
a)
Cell membrane
b)
Nucleus
c)
Vacuoles
d)
Pseudopodia
|
|
Eduskill Classes answered |
Pseudopodia, also known as false feet, are finger-like projections that Amoeba extends and retracts for movement and capturing food. These structures allow Amoeba to constantly change its shape and position.
Which of the following are the main steps of nutrition in humans?- a)Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
- b)Ingestion, absorption, egestion, digestion, assimilation
- c)Absorption, ingestion, digestion, egestion, assimilation
- d)Digestion, ingestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are the main steps of nutrition in humans?
a)
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
b)
Ingestion, absorption, egestion, digestion, assimilation
c)
Absorption, ingestion, digestion, egestion, assimilation
d)
Digestion, ingestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
|
|
Eduskill Classes answered |
The correct sequence of the main steps of nutrition in humans is:
- Ingestion: Intake of food
- Digestion: Breakdown of food into smaller molecules
- Absorption: Passage of digested food molecules into the bloodstream
- Assimilation: Utilization of absorbed nutrients by cells
- Egestion: Elimination of undigested waste
This order ensures that nutrients are extracted from food, absorbed, utilized by the body, and waste is removed efficiently.
- Ingestion: Intake of food
- Digestion: Breakdown of food into smaller molecules
- Absorption: Passage of digested food molecules into the bloodstream
- Assimilation: Utilization of absorbed nutrients by cells
- Egestion: Elimination of undigested waste
This order ensures that nutrients are extracted from food, absorbed, utilized by the body, and waste is removed efficiently.
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for chapter Nutrition in Animals, Class 7, Science. You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic. Q. Mode of nutrition in animal is- a)Saprophytic
- b)Heterotrophic
- c)Omnivores
- d)Autotrophic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for chapter Nutrition in Animals, Class 7, Science. You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic.
Q. Mode of nutrition in animal is
a)
Saprophytic
b)
Heterotrophic
c)
Omnivores
d)
Autotrophic
|
|
Shobha dasgupta answered |
Understanding Modes of Nutrition in Animals
In the context of Chapter Nutrition in Animals from Class 7 Science, it's essential to explore the different modes of nutrition employed by various organisms. Among the given options, the correct answer is Heterotrophic nutrition (option B).
What is Heterotrophic Nutrition?
- Heterotrophic nutrition refers to the way animals obtain their food by consuming other living organisms or organic matter.
- Animals cannot produce their own food through photosynthesis like plants; instead, they rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Herbivores: Animals that primarily eat plants (e.g., cows, deer).
- Carnivores: Animals that primarily consume other animals (e.g., lions, eagles).
- Omnivores: Animals that eat both plants and animals (e.g., humans, bears).
- Saprophytic: While some organisms like fungi exhibit saprophytic nutrition, animals do not fall into this category.
Why Not Other Options?
- Saprophytic (Option A): This mode of nutrition involves organisms that feed on dead and decaying matter. It does not apply to animals as a whole.
- Omnivores (Option C): While omnivores are a category of heterotrophs, the term "heterotrophic" encompasses all animals, making it a broader and more accurate classification.
- Autotrophic (Option D): Autotrophic organisms, like plants, produce their own food through photosynthesis, which is not applicable to animals.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is Heterotrophic (Option B) as it accurately describes the mode of nutrition prevalent in animals, highlighting their dependence on other organisms for food. Understanding this concept is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of nutrition in biology.
In the context of Chapter Nutrition in Animals from Class 7 Science, it's essential to explore the different modes of nutrition employed by various organisms. Among the given options, the correct answer is Heterotrophic nutrition (option B).
What is Heterotrophic Nutrition?
- Heterotrophic nutrition refers to the way animals obtain their food by consuming other living organisms or organic matter.
- Animals cannot produce their own food through photosynthesis like plants; instead, they rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Herbivores: Animals that primarily eat plants (e.g., cows, deer).
- Carnivores: Animals that primarily consume other animals (e.g., lions, eagles).
- Omnivores: Animals that eat both plants and animals (e.g., humans, bears).
- Saprophytic: While some organisms like fungi exhibit saprophytic nutrition, animals do not fall into this category.
Why Not Other Options?
- Saprophytic (Option A): This mode of nutrition involves organisms that feed on dead and decaying matter. It does not apply to animals as a whole.
- Omnivores (Option C): While omnivores are a category of heterotrophs, the term "heterotrophic" encompasses all animals, making it a broader and more accurate classification.
- Autotrophic (Option D): Autotrophic organisms, like plants, produce their own food through photosynthesis, which is not applicable to animals.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is Heterotrophic (Option B) as it accurately describes the mode of nutrition prevalent in animals, highlighting their dependence on other organisms for food. Understanding this concept is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of nutrition in biology.
What is the function of the rectum in the human digestive system?- a)Digesting proteins
- b)Storing bile
- c)Absorbing nutrients
- d)Storing feces
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Digesting proteins
b)
Storing bile
c)
Absorbing nutrients
d)
Storing feces

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
The rectum stores feces temporarily before they are expelled from the body through the anus. This storage allows for controlled defecation.
Where is bile stored temporarily before being released into the small intestine?- a)Liver
- b)Pancreas
- c)Gallbladder
- d)Stomach
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Liver
b)
Pancreas
c)
Gallbladder
d)
Stomach

|
Rainbow Rise Classes answered |
Bile is stored temporarily in the gallbladder before being released into the small intestine to aid in the digestion and emulsification of fats.
Which are cutting teeth in humans?- a)Canines
- b)Incisors
- c)Premolars
- d) Molars
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which are cutting teeth in humans?
a)
Canines
b)
Incisors
c)
Premolars
d)
Molars

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
The incisors are called cutting teeth because they present a sharp cutting edge, adapted for biting the food. They are eight in number, and form the four front teeth in each dental unit.
So, option B is the correct option.
So, option B is the correct option.
Where do amoebas digest their food?- a)Cytoplasm
- b)Nucleus
- c)Food vacuole
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Cytoplasm
b)
Nucleus
c)
Food vacuole
d)
Mitochondria
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
Amoebas digest their food in food vacuoles, where enzymes break down the food particles into simpler substances that can be absorbed by the cell.
Chapter doubts & questions for Human Nutrition - Biology for Grade 9 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Human Nutrition - Biology for Grade 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 9
50 videos|96 docs|27 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









