All Exams >
Grade 11 >
Biology for Grade 11 >
All Questions
All questions of Enzymes for Grade 11 Exam
Select the right option regarding the given graph.
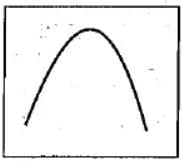
- a)X - axis = Rate of reaction
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
- b)X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Rate of reaction
- c)X - axis = pH/Temperature
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
- d)X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = pH/Temperature
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the right option regarding the given graph.

a)
X - axis = Rate of reaction
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
b)
X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Rate of reaction
Y - axis = Rate of reaction
c)
X - axis = pH/Temperature
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = Enzymatic activity
d)
X - axis = Enzymatic activity
Y - axis = pH/Temperature
Y - axis = pH/Temperature
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
The variable with which we have to find the relation should always have to be on the y axis and the variable which does not show variation and will always increase will be on the x-axis.
Which of the following is an example of isozyme?- a)α-amylase
- b)Glucokinase
- c)Lactate dehydrogenases
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of isozyme?
a)
α-amylase
b)
Glucokinase
c)
Lactate dehydrogenases
d)
All of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The multiple molecular forms of an enzyme occuring in the same organism and having a similar substrate activity are called isoenymes or isozymes. They have similar properties but different molecular weights and locations. Over 100 enzymes are known to have isoenzymes. α-amylase of wheat endosperm has 16 isozymes, lactate dehydrogenase has 5 isozymes. Glucokinase is an isozyme of hexokinase.
Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of- a)isomerases
- b)ligases
- c)lyases
- d)hydrolases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of
a)
isomerases
b)
ligases
c)
lyases
d)
hydrolases
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Isomerases catalyse the change of a substrate into a related isomeric form by rearrangement of molecules.
What is meant by feedback inhibition?- a)Inhibition of enzyme activity at an active site by an inhibitor, which is structurally similar to a substrate
- b)Inhibition of first step of biosynthesis by the end-product of reaction
- c)Inhibition by a structurally different inhibitor at a place other than active site
- d)Denaturation of enzyme
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is meant by feedback inhibition?
a)
Inhibition of enzyme activity at an active site by an inhibitor, which is structurally similar to a substrate
b)
Inhibition of first step of biosynthesis by the end-product of reaction
c)
Inhibition by a structurally different inhibitor at a place other than active site
d)
Denaturation of enzyme

|
Lead Academy answered |
Inhibition of an enzyme controlling an early stage of a series of biochemical reactions by the end product when it reaches a critical concentration.
An enzyme extract, when subjected to electric field, separates into two fractions, each catalysing the same reaction. These fractions are:- a)Allosteric enzymes
- b)Inducible enzymes
- c)Isoenzymes
- d)Coenzymes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An enzyme extract, when subjected to electric field, separates into two fractions, each catalysing the same reaction. These fractions are:
a)
Allosteric enzymes
b)
Inducible enzymes
c)
Isoenzymes
d)
Coenzymes

|
EduRev NEET answered |
- Isoenzymes (also called isozymes) are alternative forms of the same enzyme activity that exist in different proportions in different tissues.
- Isoenzymes differ in amino acid composition and sequence and multimeric quaternary structure; mostly, but not always, they have similar (conserved) structures.
Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.- a)(i) and (v)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iv)
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three dimensional shape is key to their functions.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
a)
(i) and (v)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
d)
All of these
|
|
Maitri Deshpande answered |
**Enzymes are biological catalysts that play a crucial role in speeding up chemical reactions in living organisms. Let's analyze each statement to determine which ones are correct:**
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes do not affect the overall change in free energy for a reaction. They only lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, but they do not change the energy difference between the reactants and products.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three-dimensional shape is key to their functions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are proteins, and their three-dimensional shape is critical for their proper functioning. The active site of an enzyme, where the substrate binds and the reaction takes place, is precisely shaped to accommodate specific substrates.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy is the energy input needed to start a reaction, and enzymes facilitate this process by providing an alternative pathway with a lower energy barrier.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are highly specific for particular reactions. Each enzyme is designed to catalyze a specific chemical reaction or a group of closely related reactions. This specificity is determined by the enzyme's active site and its ability to recognize and bind to specific substrates.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Activation energy refers to the energy input needed to initiate a chemical reaction. It is the energy required to break the bonds of the reactant molecules and reach the transition state, from which the reaction proceeds to form the products.
**In conclusion, all of the given statements are correct. Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy, their three-dimensional shape is crucial for their function, they lower activation energy, they are highly specific for reactions, and activation energy is the energy input needed to start a chemical reaction. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
(i) Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy for a reaction.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes do not affect the overall change in free energy for a reaction. They only lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, but they do not change the energy difference between the reactants and products.
(ii) Enzymes are proteins whose three-dimensional shape is key to their functions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are proteins, and their three-dimensional shape is critical for their proper functioning. The active site of an enzyme, where the substrate binds and the reaction takes place, is precisely shaped to accommodate specific substrates.
(iii) Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy is the energy input needed to start a reaction, and enzymes facilitate this process by providing an alternative pathway with a lower energy barrier.
(iv) Enzymes are highly specific for reactions.
- This statement is correct. Enzymes are highly specific for particular reactions. Each enzyme is designed to catalyze a specific chemical reaction or a group of closely related reactions. This specificity is determined by the enzyme's active site and its ability to recognize and bind to specific substrates.
(v) The energy input needed to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
- This statement is correct. Activation energy refers to the energy input needed to initiate a chemical reaction. It is the energy required to break the bonds of the reactant molecules and reach the transition state, from which the reaction proceeds to form the products.
**In conclusion, all of the given statements are correct. Enzymes do not alter the overall change in free energy, their three-dimensional shape is crucial for their function, they lower activation energy, they are highly specific for reactions, and activation energy is the energy input needed to start a chemical reaction. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Feedback inhibition of enzyme is influenced by- a)Enzyme
- b)External factors
- c)End product
- d)Substrate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Feedback inhibition of enzyme is influenced by
a)
Enzyme
b)
External factors
c)
End product
d)
Substrate
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
In feedback inhibition, product of a reaction inhibits the enzyme catalysing that reaction. It is a type of control mechanism at the enzyme level. If the product is produced in sufficient amount, in inhibits the enzyme to stop the further production.
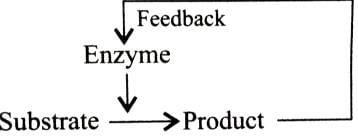
Holoenzyme is the complete enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor. Select the option that correctly identifies the nature of apoenzyme and co-factor.- a)Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Non-Protein - b)Apoenzyme - Non - Protein
Co - factor - Protein - c)Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Protein - d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Holoenzyme is the complete enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor. Select the option that correctly identifies the nature of apoenzyme and co-factor.
a)
Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Non-Protein
Co - factor - Non-Protein
b)
Apoenzyme - Non - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
c)
Apoenzyme - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
Co - factor - Protein
d)
None of the above
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Enzyme may be broadly classified into two types depending on their chemical composition-simple enzymes and conjugated enzymes are wholly made up of proteins and any additional substance or group is absent, e.g., pepsin, trypsin, etc. Conjugated enzymes (or holoenzymes) are formed of two parts -a protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named co-factor. The complete conjugated enzyme consisting of an apoenzyme and a co-factor is called holoenzyme. Holoenzyme is the functional unit of enzyme.
Co-factor may be inorgainc or roganic in nature. Catalytic activity is lost when co-factor is removed from the enzyme which indicates that it plays a crucial role in catalytic activity of enzymes.
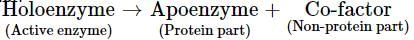
Co-factor may be inorgainc or roganic in nature. Catalytic activity is lost when co-factor is removed from the enzyme which indicates that it plays a crucial role in catalytic activity of enzymes.
Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between the rate of an enzymatic activity and substrate concentration (S)?- a)
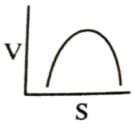
- b)
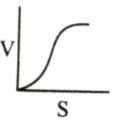
- c)
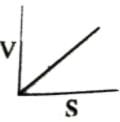
- d)
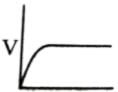
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between the rate of an enzymatic activity and substrate concentration (S)?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Increase in substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction due to two factors: (i) occupation of more and more active sites by the substrate molecules, (ii) higher number of collisions between substrate molecules. The rise in velocity is quite high in the beginning but it decreases progressively with the increase in substate concentration. If a graph is plotted for substrate concentration versus reaction velocity, it appears as a hyperbolic curve. A stage is reached where velocity is maximum. It does not increase further by increasing the substrate concentration. At this stage the anzyme molecule becomes fully saturated and no active site is left free to bind additional substrate molecules.
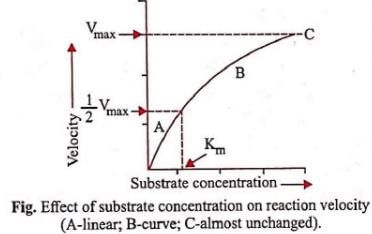
Michaelis Menten Constant (Km) is equal to- a)The rate of reaction
- b)The rate of enzymatic activity
- c)Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
- d)Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Michaelis Menten Constant (Km) is equal to
a)
The rate of reaction
b)
The rate of enzymatic activity
c)
Substrate concentration at which the reaction attains half of its maximum velocity
d)
Substrate concentration at which the rate of reaction is maximum
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Km or the Michaelis-Menten constant is defined as the substrate concentration (expressed in moles/l) at which half-maximum velocity in an enzyme catalysed reaction is achieved. It indicates that half of the enzyme molecules (i.e. 50%) are bound with the substrate molecules when the substrate concentration equals the Km value. It was given by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten (1913). Km value is a characteristic feature of a given enzyme. It is a representative for measuring the strength of ES complex. A low Km value indicates a strong affinity between enzyme and substrate, whereas a high Km value reflects a weak affinity between them. For majority of enzymes, the Km values are in the range of 10−5 to 10−2 moles.

A.
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: - a)B > C > D > A > E
- b)B > D > C > A > E
- c)B > D > A > E > C
- d)B > E > D > C > A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A.
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Release of products of the reaction
B.
Binding of substrate to the active site of the enzyme
C.
Formation of enzyme-substrate complex
D.
Alteration in the shape of the enzyme
E.
Enzyme free to bind another molecule of substrate
Given above are the steps involved in the catalytic cycle of enzyme action. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
B > C > D > A > E
b)
B > D > C > A > E
c)
B > D > A > E > C
d)
B > E > D > C > A

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Ans: 2
Sol: During the state where substrate is bound to the enzyme active site, a new structure of the substrate called transition state structure is formed. Very soon, after the expected bond breaking/making is completed, the product is released from the active site
Sol: During the state where substrate is bound to the enzyme active site, a new structure of the substrate called transition state structure is formed. Very soon, after the expected bond breaking/making is completed, the product is released from the active site
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.- a)Both Statements 1 and 2 are correct
- b)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
- d)Both Statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.
a)
Both Statements 1 and 2 are correct
b)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
d)
Both Statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Low temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive state. Therefore it is used in preservation of foods inside cold storage. Low temperature present inside cold storage prevents spoilage of food.
High temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation, This occurs at 50oC or so. In between the minimum and maximum temperature the reaction velocity doubles for every 10oC in temperature (general rule of thumb).
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called- a)Competitive inhibitor
- b)Non-competitive inhibitor
- c)Activator
- d)Substrate analogue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called
a)
Competitive inhibitor
b)
Non-competitive inhibitor
c)
Activator
d)
Substrate analogue
|
|
Juhi Bose answered |
Non-competitive inhibitor:
Non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. They do not resemble the substrate in structure. These inhibitors inhibit enzyme activity by changing the shape of the enzyme, making it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.
Mechanism of action:
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme at an allosteric site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme.
- This conformational change may prevent the substrate from binding to the active site or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
- Since non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for the active site, increasing substrate concentration will not overcome their inhibitory effect.
Characteristics:
- Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding to the enzyme.
- They can bind to the enzyme-substrate complex as well as the free enzyme.
- The inhibition by non-competitive inhibitors is not easily reversible.
- These inhibitors are not affected by changes in substrate concentration.
Examples:
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and lead are examples of non-competitive inhibitors.
- Drugs like aspirin and certain antibiotics also act as non-competitive inhibitors of specific enzymes.
In conclusion, non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that inhibits enzyme activity.
Non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site. They do not resemble the substrate in structure. These inhibitors inhibit enzyme activity by changing the shape of the enzyme, making it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.
Mechanism of action:
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme at an allosteric site, causing a conformational change in the enzyme.
- This conformational change may prevent the substrate from binding to the active site or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
- Since non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for the active site, increasing substrate concentration will not overcome their inhibitory effect.
Characteristics:
- Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding to the enzyme.
- They can bind to the enzyme-substrate complex as well as the free enzyme.
- The inhibition by non-competitive inhibitors is not easily reversible.
- These inhibitors are not affected by changes in substrate concentration.
Examples:
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and lead are examples of non-competitive inhibitors.
- Drugs like aspirin and certain antibiotics also act as non-competitive inhibitors of specific enzymes.
In conclusion, non-competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change that inhibits enzyme activity.
What is denoted by X and Y in the given graph?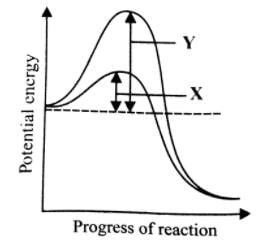
- a)X-Activation energy without enzyme; Y-Activation energy with enzyme
- b)X-Activation energy with enzyme; Y-Activation energy without enzyme
- c)X-Substrate concentration with enzyme; Y- Substrate concentration without enzyme
- d)X-Substrate concentration without enzyme; Y-Substrate concentration with enzyme
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is denoted by X and Y in the given graph?

a)
X-Activation energy without enzyme; Y-Activation energy with enzyme
b)
X-Activation energy with enzyme; Y-Activation energy without enzyme
c)
X-Substrate concentration with enzyme; Y- Substrate concentration without enzyme
d)
X-Substrate concentration without enzyme; Y-Substrate concentration with enzyme
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Most reactions do not start automatically because the reactions have an energy barrier which may be due to hydrogen bonding, absence of precise collisions due to small reactive site, mutual repulsion, etc. External supply of energy needed to overcome this barrier is known as activation energy. The enzyme lowers the activation energy of the reaction and allows a large number of molecules to react at a time.
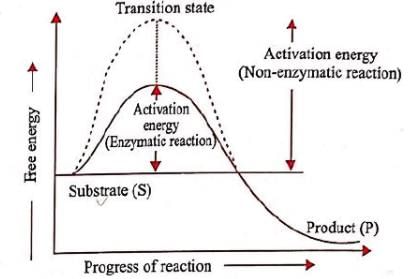
Fig. Lowering of activation energy by enzyme in the energy relations of a chemical reaction
Enzymes are regarded as the:- a)Messengers
- b)Activators
- c)Biocatalysts
- d)Anti bodies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes are regarded as the:
a)
Messengers
b)
Activators
c)
Biocatalysts
d)
Anti bodies

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- Enzymes are regarded as the biocatalysts.
- Enzymes are proteins made from amino acids.
- It is made up of hundreds and thousands of amino acids stringed together in a very specific and unique order.
- Any chemical reaction inside a cell or any work that goes on inside a cell is the handiwork of enzymes inside the cell.
Chapter doubts & questions for Enzymes - Biology for Grade 11 2025 is part of Grade 11 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 11 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Enzymes - Biology for Grade 11 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 11 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 11
26 docs|12 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









