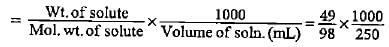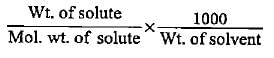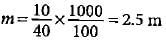All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Stoichiometry for EmSAT Achieve Exam
What volume of 5 M Na2SO4 must be added to 25 mL of 1 M BaCl2 to produce 10 g of BaSO4?- a)8.58 mL
- b)7.2 mL
- c)10 mL
- d)12 mL
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What volume of 5 M Na2SO4 must be added to 25 mL of 1 M BaCl2 to produce 10 g of BaSO4?
a)
8.58 mL
b)
7.2 mL
c)
10 mL
d)
12 mL
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Na2SO4 + BaCI2 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
No. of moles of BaSO4 = w/M = 10/233 = 0.0429
∴ No. of moles of Na2SO4 needed = M x V/1000
Or 0.0429 = 5 x V/1000
V = 8.58 mL
No. of moles of BaSO4 = w/M = 10/233 = 0.0429
∴ No. of moles of Na2SO4 needed = M x V/1000
Or 0.0429 = 5 x V/1000
V = 8.58 mL
What volume of water is to be added to 100 cm3 of 0.5 M NaOH solution to make it 0.1 M solution?- a)200 cm3
- b)400 cm3
- c)500 cm3
- d)100 cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What volume of water is to be added to 100 cm3 of 0.5 M NaOH solution to make it 0.1 M solution?
a)
200 cm3
b)
400 cm3
c)
500 cm3
d)
100 cm3

|
Siddhi Sonakshi answered |
N1=n2
M1V1=M2(V1+V H20)
.5×100=.1(100+VH20)
500=(100+VH20)
400=VH20
M1V1=M2(V1+V H20)
.5×100=.1(100+VH20)
500=(100+VH20)
400=VH20
1 g of Mg is burnt in a closed vessel containing 0.5 g of O2. Which reactant is limiting reagent and how much of the excess reactant will be left?- a)O2 is a limiting reagent and Mg is in excess by 0.25 g
- b)Mg is a limiting reagent and is in excess by 0.5 g
- c)O2 is a limiting reagent and is in excess by 0.25 g
- d)O2 is a limiting reagent and Mg is in excess by 0.75 g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 g of Mg is burnt in a closed vessel containing 0.5 g of O2. Which reactant is limiting reagent and how much of the excess reactant will be left?
a)
O2 is a limiting reagent and Mg is in excess by 0.25 g
b)
Mg is a limiting reagent and is in excess by 0.5 g
c)
O2 is a limiting reagent and is in excess by 0.25 g
d)
O2 is a limiting reagent and Mg is in excess by 0.75 g
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
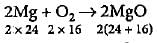
48 g of Mg requires 32 g of O2
1 g of Mg requires 32/48 = 0.66 g of O2
Oxygen available = 0.5 g
Hence, O2 is limiting reagent.
32 g of O2 reacts with 48 g of Mg
0.5 g of O2 will react with 48/32 x 0.5 = 0.75 g of Mg
Excess of Mg = (1.0 - 0.75) = 0.25 g
If 40 g of CaCO3 is treated with 40 g of HCl, which of the reactants will act as limiting reagent?- a)CaCO3
- b)HCl
- c)Both are equal
- d)Cannot be calculated
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If 40 g of CaCO3 is treated with 40 g of HCl, which of the reactants will act as limiting reagent?
a)
CaCO3
b)
HCl
c)
Both are equal
d)
Cannot be calculated
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
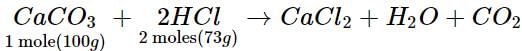
100 g of CaCO3 reacts with 73 g of HCl
40 g of CaCO3 will react with 73/100 x 40 = 29.2 g of HCl
Since CaCO3 is completely consumed and some amount (40 - 29.2 = 10.8g) of HCl remains unreacted and hence, CaCO3 is limiting reagent.
How much copper is present in 50 g of CuSO4?- a)19.90 g
- b)39.81 g
- c)63.5 g
- d)31.71 g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How much copper is present in 50 g of CuSO4?
a)
19.90 g
b)
39.81 g
c)
63.5 g
d)
31.71 g
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Molar mass of CuSO4 = 63.5 + 32 + 4 x 16 = 159.5 g
Mass of copper present in 159.5 g of CuSO4 = 63.5 g
∴ Mass of copper present in 50 g of CuSO4
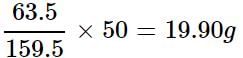
Mass of copper present in 159.5 g of CuSO4 = 63.5 g
∴ Mass of copper present in 50 g of CuSO4
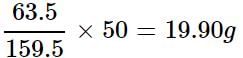
The final molarity of a solution made by mixing 50 mL of 0.5 M HCl, 150 mL of 0.25 M HCl and water to make the volume 250 mL is- a)0.5 M
- b)1 M
- c)0.75 M
- d)0.25 M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The final molarity of a solution made by mixing 50 mL of 0.5 M HCl, 150 mL of 0.25 M HCl and water to make the volume 250 mL is
a)
0.5 M
b)
1 M
c)
0.75 M
d)
0.25 M
|
|
Swara Dey answered |
To find the final molarity of the solution, we need to consider the principle of conservation of moles. This principle states that the total number of moles of solute before and after mixing should remain the same.
- Initial moles of HCl in 50 mL of 0.5 M HCl:
Moles = Molarity x Volume
Moles = 0.5 M x 0.050 L = 0.025 moles
- Initial moles of HCl in 150 mL of 0.25 M HCl:
Moles = Molarity x Volume
Moles = 0.25 M x 0.150 L = 0.0375 moles
- Total moles of HCl before mixing:
Total moles = 0.025 moles + 0.0375 moles = 0.0625 moles
- Final volume of the solution = 250 mL = 0.250 L
- Final molarity of the solution:
Molarity = Total moles / Final volume
Molarity = 0.0625 moles / 0.250 L = 0.25 M
Therefore, the final molarity of the solution is 0.25 M.
- Initial moles of HCl in 50 mL of 0.5 M HCl:
Moles = Molarity x Volume
Moles = 0.5 M x 0.050 L = 0.025 moles
- Initial moles of HCl in 150 mL of 0.25 M HCl:
Moles = Molarity x Volume
Moles = 0.25 M x 0.150 L = 0.0375 moles
- Total moles of HCl before mixing:
Total moles = 0.025 moles + 0.0375 moles = 0.0625 moles
- Final volume of the solution = 250 mL = 0.250 L
- Final molarity of the solution:
Molarity = Total moles / Final volume
Molarity = 0.0625 moles / 0.250 L = 0.25 M
Therefore, the final molarity of the solution is 0.25 M.
An impure sample of silver (1.5 g) is heated with S to form 0.124 g of Ag2S. What was the per cent yield of Ag2S?- a)21.6%
- b)7.2%
- c)1.7%
- d)24.8%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An impure sample of silver (1.5 g) is heated with S to form 0.124 g of Ag2S. What was the per cent yield of Ag2S?
a)
21.6%
b)
7.2%
c)
1.7%
d)
24.8%
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
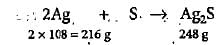
216 g of Ag forms 248 g of Ag2S
1.5 g of Ag forms 248/216 x 1.5 = 1.722 g of Ag2S
% yield of Ag2S = 0.124/1.722 x 100 = 7.2%
1.5 g of Ag forms 248/216 x 1.5 = 1.722 g of Ag2S
% yield of Ag2S = 0.124/1.722 x 100 = 7.2%
The weight of AgCl precipitated when a solution containing 5.85 g of NaCl is added to a solution containing 3.4 g of AgNO3 is- a)28 g
- b)9.25 g
- c)2.870 g
- d)58 g
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The weight of AgCl precipitated when a solution containing 5.85 g of NaCl is added to a solution containing 3.4 g of AgNO3 is
a)
28 g
b)
9.25 g
c)
2.870 g
d)
58 g
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
No. of moles of AgNO3 = 3.4/170 = 0.02
No, of moles of NaCl = 5.85/58.5 = 0.1
Limiting reagent = AgNO3
1 mole of AgNO3 produces 1 mole of AgCl
0.02 mole of AgNO3 will produce 0.02 mole of AgCl
Weight of AgCl produced = 0.02 x 143.5 = 2.870 g.
No. of moles of AgNO3 = 3.4/170 = 0.02
No, of moles of NaCl = 5.85/58.5 = 0.1
Limiting reagent = AgNO3
1 mole of AgNO3 produces 1 mole of AgCl
0.02 mole of AgNO3 will produce 0.02 mole of AgCl
Weight of AgCl produced = 0.02 x 143.5 = 2.870 g.
How much oxygen is required for complete combustion of 560 g of ethene?- a)6.4 kg
- b)1.92 kg
- c)2.8 kg
- d)9.6 kg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How much oxygen is required for complete combustion of 560 g of ethene?
a)
6.4 kg
b)
1.92 kg
c)
2.8 kg
d)
9.6 kg
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
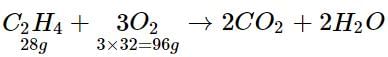
28 g of C2H4 requires 96 g of O2
560 g of C2H4 requires 96/28 x 560
= 1920 g or 1.92 kg of O2
What is the concentration of copper sulphate (in mol L-1) if 80 g of it is dissolved in enough water to make a final volume of 3 L?- a)0.0167
- b)0.167
- c)1.067
- d)10.67
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the concentration of copper sulphate (in mol L-1) if 80 g of it is dissolved in enough water to make a final volume of 3 L?
a)
0.0167
b)
0.167
c)
1.067
d)
10.67
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Molar mass of CUSO4 = 63.5 + 32 + 64 = 159.5
Moles of CUSO4 = 80/159.5 = O.50
Volume of solution = 3 L
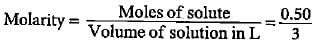
= 0.167 mol L-1
Moles of CUSO4 = 80/159.5 = O.50
Volume of solution = 3 L
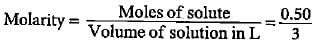
= 0.167 mol L-1
What is the mass percent of oxygen in ethanol?- a)52.14%
- b)13.13%
- c)16%
- d)34.73%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the mass percent of oxygen in ethanol?
a)
52.14%
b)
13.13%
c)
16%
d)
34.73%
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Molecular formula of ethanol = C2H5OH
Molar mass of ethanol of 2 x 12.01 + 6 x 1.008 + 16 = 46.068g
Mass percent of oxygen = 16/46.068 x 100 = 34.73%
Molar mass of ethanol of 2 x 12.01 + 6 x 1.008 + 16 = 46.068g
Mass percent of oxygen = 16/46.068 x 100 = 34.73%
How much mass of sodium acetate is required to make 250 mL of 0.575 molar aqueous solution?- a)11.79 g
- b)15.38 g
- c)10.81 g
- d)25.35 g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How much mass of sodium acetate is required to make 250 mL of 0.575 molar aqueous solution?
a)
11.79 g
b)
15.38 g
c)
10.81 g
d)
25.35 g
|
|
Saanvi Nair answered |
To calculate the mass of sodium acetate required to make a 0.575 M aqueous solution, we can use the formula:
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters
First, we need to convert the volume of the solution from milliliters to liters:
250 mL = 250/1000 = 0.25 L
Next, we rearrange the formula to solve for moles of solute:
moles of solute = Molarity (M) x volume of solution in liters
Given that the molarity is 0.575 M and the volume is 0.25 L, we can substitute these values into the formula:
moles of solute = 0.575 M x 0.25 L = 0.14375 moles
The molar mass of sodium acetate (NaC2H3O2) is calculated as follows:
Na: 1 atom x 22.99 g/mol = 22.99 g/mol
C: 2 atoms x 12.01 g/mol = 24.02 g/mol
H: 3 atoms x 1.01 g/mol = 3.03 g/mol
O: 2 atoms x 16.00 g/mol = 32.00 g/mol
Total molar mass = 22.99 + 24.02 + 3.03 + 32.00 = 82.04 g/mol
Finally, we can calculate the mass of sodium acetate required using the moles of solute and the molar mass:
mass of sodium acetate = moles of solute x molar mass
mass of sodium acetate = 0.14375 moles x 82.04 g/mol = 11.79 g
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 11.79 g.
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters
First, we need to convert the volume of the solution from milliliters to liters:
250 mL = 250/1000 = 0.25 L
Next, we rearrange the formula to solve for moles of solute:
moles of solute = Molarity (M) x volume of solution in liters
Given that the molarity is 0.575 M and the volume is 0.25 L, we can substitute these values into the formula:
moles of solute = 0.575 M x 0.25 L = 0.14375 moles
The molar mass of sodium acetate (NaC2H3O2) is calculated as follows:
Na: 1 atom x 22.99 g/mol = 22.99 g/mol
C: 2 atoms x 12.01 g/mol = 24.02 g/mol
H: 3 atoms x 1.01 g/mol = 3.03 g/mol
O: 2 atoms x 16.00 g/mol = 32.00 g/mol
Total molar mass = 22.99 + 24.02 + 3.03 + 32.00 = 82.04 g/mol
Finally, we can calculate the mass of sodium acetate required using the moles of solute and the molar mass:
mass of sodium acetate = moles of solute x molar mass
mass of sodium acetate = 0.14375 moles x 82.04 g/mol = 11.79 g
Therefore, the correct answer is option A) 11.79 g.
4.28 g of NaOH is dissolved inwater and the solution is made to 250 cc. What will be the molarity of the solution?- a)0.615 mol L-1
- b)0.428 mol L-1
- c)0.99 mol L-1
- d)0.301 mol L-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
4.28 g of NaOH is dissolved inwater and the solution is made to 250 cc. What will be the molarity of the solution?
a)
0.615 mol L-1
b)
0.428 mol L-1
c)
0.99 mol L-1
d)
0.301 mol L-1
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
No. of moles of NaOH = 4.28/40 = 0.107 Volume of solution = 250 cm3
M = n/V(in L) = 0.107/250 x 1000 = 0.428 mol L-1
M = n/V(in L) = 0.107/250 x 1000 = 0.428 mol L-1
What will be the molality of chloroform in the water sample which contains 15 ppm chloroform by mass?- a)1.25 x 10-4 m
- b)2.5 x 10-4 m
- c)1.5 x 10-3 m
- d)1.25 X 10-5 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the molality of chloroform in the water sample which contains 15 ppm chloroform by mass?
a)
1.25 x 10-4 m
b)
2.5 x 10-4 m
c)
1.5 x 10-3 m
d)
1.25 X 10-5 m
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
15 ppm = 15/106 x 102 = 1.5 x 10-3g
Molality of CHCl3 solution = 1.5 x 10-3/100 x 1000/119.5
= 1.25 x 10-4 m
Molality of CHCl3 solution = 1.5 x 10-3/100 x 1000/119.5
= 1.25 x 10-4 m
What will be the molarity of the solution in which 0.365 g of HCl gas is dissolved in 100 mL of solution?- a)2 M
- b)0.2 M
- c)1 M
- d)0.1 M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the molarity of the solution in which 0.365 g of HCl gas is dissolved in 100 mL of solution?
a)
2 M
b)
0.2 M
c)
1 M
d)
0.1 M
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
No. of moles in 0.365 g of HCl = 0.365/36.5 = 0.01
Volume of solution in L = 100/1000 = 0.1 L
Molarity = n/V (in L) = 0.01/0.1 = 0.1 M
Volume of solution in L = 100/1000 = 0.1 L
Molarity = n/V (in L) = 0.01/0.1 = 0.1 M
2.82 g of glucose is dissolved in 30 g of water. The mole fraction of glucose in the solution is- a)0.01
- b)0.99
- c)0.52
- d)1.66
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
2.82 g of glucose is dissolved in 30 g of water. The mole fraction of glucose in the solution is
a)
0.01
b)
0.99
c)
0.52
d)
1.66
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
No. of moles of glucose = 2.82/180 = 0.01567
No. of moles of water = 30/18 = 1.667
Total no. of moles of solution = 0.01567 + 1.667 = 1.683
Mole fraction of glucose = 0.01567/1.683 = 0.0093 = 0.01
No. of moles of water = 30/18 = 1.667
Total no. of moles of solution = 0.01567 + 1.667 = 1.683
Mole fraction of glucose = 0.01567/1.683 = 0.0093 = 0.01
In a reaction container, 100 g of hydrogen and 100 g of CI2 are mixed for the formation of HCl gas. What is the limiting reagent and how much HCl is formed in the reaction?- a)H2 is limiting reagent and 36.5 g of HCl are formed
- b)CI2 is limiting reagent and 102.8 g of HCl are formed
- c)H2 is limiting reagent and 142 g of HCl are formed
- d)CI2 is limiting reagent and 73 g HCl are formed
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a reaction container, 100 g of hydrogen and 100 g of CI2 are mixed for the formation of HCl gas. What is the limiting reagent and how much HCl is formed in the reaction?
a)
H2 is limiting reagent and 36.5 g of HCl are formed
b)
CI2 is limiting reagent and 102.8 g of HCl are formed
c)
H2 is limiting reagent and 142 g of HCl are formed
d)
CI2 is limiting reagent and 73 g HCl are formed
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
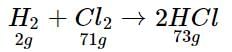
2 g of H2 reacts with 71 g of CI2
100 g of H2 will react with 71/2 x 100 = 3550g of CI2
Hence, CI2 is the limiting reagent.
71 g of CI2 produces 73 g of HCl
100g of CI2 will produce 73/71 x 100 = 102.8 g of HCl
Chapter doubts & questions for Stoichiometry - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Stoichiometry - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup