All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Biology for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Respiration for EmSAT Achieve Exam
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles- a)a and b
- b)a and d
- c)b and d
- d)b and c
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In plants, the gaseous exchange take place in
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a) Stomata
b) Roots
c) Stems
d) Lenticles
a)
a and b
b)
a and d
c)
b and d
d)
b and c
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Plants unlike animals have no special systems for breathing or gaseous exchange. Stomata and lenticels allow gaseous exchange by diffusion.
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
- a)It starts with a six-carbon compound.
- b)It occurs in mitochondria.
- c)It is also called the citric acid cycle.
- d)The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
a)
It starts with a six-carbon compound.
b)
It occurs in mitochondria.
c)
It is also called the citric acid cycle.
d)
The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle because this reaction starts with the six-carbon compound which is citric acid. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs cycle is a closed-loop cycle. And each loop of the cycle generates a molecule of ATP. This cycle consists of eight steps which include redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. It is an aerobic pathway because NADH is produced and the electrons released are used up in the next cycle which uses oxygen.
- The process of the cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl- CoA with oxaloacetate.
- This reaction is controlled by the amount of ATP present.
- If the ATP level increases then the rate of the reaction decreases and vice versa. After glycolysis, the pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
- The Krebs cycle is the pathway that all organisms use to generate energy. The intermediate compound that links pyruvate to the Krebs cycle is Acetyl CoA.
- So, the answer is option (B) ‘the intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid’.
How many netATP are produced in Glycolysis?- a)36 ATP
- b)8 ATP
- c)2 ATP
- d)16 ATP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many netATP are produced in Glycolysis?
a)
36 ATP
b)
8 ATP
c)
2 ATP
d)
16 ATP

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
At the end of glycolysis pathway, 2 net ATP molecules at step 6 and step 9 are produced.
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
- a)Respiratory products
- b)respiratory substrates
- c)ATP
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The respiratory quotient depends upon:
a)
Respiratory products
b)
respiratory substrates
c)
ATP
d)
NADH

|
Shounak Nair answered |
The respiratory quotient depends upon the type of respiratory substrate used during respiration.
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of- a)NADPH
- b)FADH2
- c)ADP
- d)ATP
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
F0−F1 particles participate in the synthesis of
a)
NADPH
b)
FADH2
c)
ADP
d)
ATP
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
- Oxysomes refer to small round structures present within the folds of the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is also known as F0-F1 particles.
- F0 and F1 particles are found in the inner mitochondrial region and are attached to the cristae and help in ATP production and oxidation.
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by- a)GTP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)GDP
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Kreb cycle conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid by
a)
GTP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
GDP

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
During conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesised.
The TCA cycle is named after- a)Robert Emerson
- b)Melvin Calvin
- c)Embden
- d)Hans Krebs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle is named after
a)
Robert Emerson
b)
Melvin Calvin
c)
Embden
d)
Hans Krebs
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
*Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release the stored energy........ *It is a part of cellular respiration........ *It is also called as citric acid cycle or Krebs cycles which is named after it's discoverer Hans Krebs..... Thus, the correct answer is option 'D'.
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because- a)Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
- b)It takes place is micrograms
- c)It takes place in inert medium
- d)Glucose is not available
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During anaerobic respiration less energy is produced than aerobic respiration because
a)
Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place
b)
It takes place is micrograms
c)
It takes place in inert medium
d)
Glucose is not available
|
|
Kuldeep Kuldeep answered |
Option a is correct. Because, in Anaerobic Respiration, respiration takes place on the absence of oxygen. Iteans, the oxidation of pyruvate takes place in the absence of oxygen to release CO2, Ethanol along with the release of Energy. Here, in Anaerobic Respiration, Water is not yet released due to the absence of oxygen. So, there will be incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place.
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in- a)Intermembrane space of mitochondria
- b)Mitochondrial matrix
- c)Inner membrane of mitochondria
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in
a)
Intermembrane space of mitochondria
b)
Mitochondrial matrix
c)
Inner membrane of mitochondria
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Mitochondrial matrix.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
When fats are the respiratory substrate, the value of RQ would be- a)Approx. 0.7
- b)Approx. 1.0
- c)More than 1.0
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When fats are the respiratory substrate, the value of RQ would be
a)
Approx. 0.7
b)
Approx. 1.0
c)
More than 1.0
d)
None of the above

|
Surbhi Mishra answered |
Ans.
The respiratory quotient (or RQ or respiratory coefficient), is a dimensionless number used in calculations of basal metabolic rate (BMR) when estimated from carbon dioxide production. ... If metabolism consists solely of lipids, the Respiratory Quotient is 0.7, for proteins it is 0.8, and for carbohydrates it is 1.0.
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?- a)Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
- b)The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
- c)Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
- d)Mitochondria have a double membrane.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
a)
Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
b)
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
c)
Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
d)
Mitochondria have a double membrane.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mitochondria (singular - Mitochondrion) are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for the release of energy from food ,i.e, cellular respiration. This energy is released in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
While the cells release 2 ATP, mitochondria releases 34 ATP which adds up to 36 ATP. Since a major portion of the ATP is released by mitochondria, they are called the powerhouse of the cell.
During which stage in the complete oxidation of glucose is the greatest number of ATP formed from ADP?- a)Glycolysis
- b)Electron transport chain
- c)During conversion of pyruvic acid to Acetyl Co A
- d)Krebs cycle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During which stage in the complete oxidation of glucose is the greatest number of ATP formed from ADP?
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Electron transport chain
c)
During conversion of pyruvic acid to Acetyl Co A
d)
Krebs cycle

|
Krish Khanna answered |
During electron transport chain stage of respiration of complete oxidation of glucose greatest number of ATP is formed from ADP in inner wall of mitochondria.
End-products of aerobic respiration are- a)Carbon dioxide and energy
- b)Sugar and oxygen
- c)Carbon dioxide, water and energy
- d)Water and energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
End-products of aerobic respiration are
a)
Carbon dioxide and energy
b)
Sugar and oxygen
c)
Carbon dioxide, water and energy
d)
Water and energy
|
|
Vartika Shukla answered |
Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of sugars in presence of oxygen.
The carbohydrates are broken down into CO₂ and H₂O and this releases energy. This energy is stored in the form of ATP and later used in the body.
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
The carbohydrates are broken down into CO₂ and H₂O and this releases energy. This energy is stored in the form of ATP and later used in the body.
So, the correct option is 'Carbon dioxide, water, and energy'
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms- a)CO2
- b)CO2+ H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Acetyl CoA + CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms
a)
CO2
b)
CO2+ H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Acetyl CoA + CO2
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Pyruvate, the product obtained through glycolysis, gets oxidised with the loss of its carboxy group as CO2, to give acetyl Co-A, under aerobic condition. This acetyl Co-A is further oxidised completely to CO2 + H2O in citric acid cycle. Other options are incorrect as Lactic acid is formed in muscles under anaerobic conditions. Ethanol and CO2 are products of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells. CO2 and H2O are final and complete reaction products released at the end of cellular respiration.
Energy equivalent of NADH is how many number of ATP molecules?- a)2
- b)3
- c)38
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy equivalent of NADH is how many number of ATP molecules?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
38
d)
6

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Each NADH molecule theoretically yields 3 ATP molecules during chemiosmosis. However, in some tissues, NADH requires more energy to cross the mitochondrial membrane and some of its potential is lost.
The TCA cycle starts with- a)Condensation
- b)Dehydrogenation
- c)Phosphorylation
- d)Decarboxylation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle starts with
a)
Condensation
b)
Dehydrogenation
c)
Phosphorylation
d)
Decarboxylation

|
Anand Jain answered |
The TCA cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl group with oxaloacetic acid (OAA) and water to yield citric acid.
The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport system is the formation of- a)Nucleic acids
- b)ATP in small stepwise units
- c)ATP in one large oxidation reaction
- d)Sugars
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport system is the formation of
a)
Nucleic acids
b)
ATP in small stepwise units
c)
ATP in one large oxidation reaction
d)
Sugars

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport system is the formation of ATP step-wise. The three processes are involved in cellular respiration of food to produce energy, which will be used for various cellular activities.
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is- a)Oxalo acetic acid
- b)NADH
- c)Acetyl-CoA
- d)NADP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme that interconnects the glycolysis and kreb cycle is
a)
Oxalo acetic acid
b)
NADH
c)
Acetyl-CoA
d)
NADP
|
|
Ashutosh Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and yields two molecules of ATP along with two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Interconnection:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Acetyl-CoA is then used in the Krebs cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces NADH, which is used in the electron transport chain to produce more ATP.
Therefore, Acetyl-CoA is the enzyme that interconnects glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA.
Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and yields two molecules of ATP along with two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle:
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. It involves the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Interconnection:
The interconnection between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle occurs through the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where it is converted to Acetyl-CoA by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Acetyl-CoA is then used in the Krebs cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The Krebs cycle produces NADH, which is used in the electron transport chain to produce more ATP.
Therefore, Acetyl-CoA is the enzyme that interconnects glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Choose the correct statement.- a)There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
- b)Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
- c)During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
- d)Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement.
a)
There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
b)
Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
c)
During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
d)
Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- Oxygen sits at the end of the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons, hydrogen and picks up protons to form water.
- Pyruvate is formed in the cytoplasm.
- During fermentation glucose is partially broken down by glycolysis.
- During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesized.
So, the correct option is 'Oxygen is vital in respiration for removal of hydrogen'.
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?- a)Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
- b)Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
- c)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
- d)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?
a)
Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
b)
Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
c)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
d)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
|
|
Akash Saini answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
Which process makes direct use of oxygen- a)Fermentation
- b)Electron transport
- c)Glycolysis
- d)Krebs cycle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which process makes direct use of oxygen
a)
Fermentation
b)
Electron transport
c)
Glycolysis
d)
Krebs cycle

|
Anand Jain answered |
Electron transport process makes direct use of oxygen to produce ATP molecules in respiration process.
R.Q is less than unity in case of- a)Protein
- b)Organic acid
- c)Carbohydrates
- d)Starch
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
R.Q is less than unity in case of
a)
Protein
b)
Organic acid
c)
Carbohydrates
d)
Starch

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
Respiratory quotient is the ratio of number of carbon dioxide molecules to the number of oxygen molecules during respiration. R.Q is less than one in case of protein
Arrange the following in descending order based upon number of carbon atoms in Kreb cycle
a) α-ketoglutaric acid
b) citric acid
c) Acetyl coA
d) Succinic acid- a)b, a, d, c
- b)a, d, b, c
- c)a, b, c, d
- d)b, c, d, a
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following in descending order based upon number of carbon atoms in Kreb cycle
a) α-ketoglutaric acid
b) citric acid
c) Acetyl coA
d) Succinic acid
a) α-ketoglutaric acid
b) citric acid
c) Acetyl coA
d) Succinic acid
a)
b, a, d, c
b)
a, d, b, c
c)
a, b, c, d
d)
b, c, d, a

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
In kerb cycle citric acid consists of 6C atoms ,α-ketoglutaric acid consist of 5C atoms, succinic acid consists of 4 C atoms and Acetyl co A consists of 2C atoms,
Which compound consists of 5 carbon atoms?- a)Oxalo acetic acid
- b)Malic acid
- c)Citric acid
- d)α –Ketoglutaric acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which compound consists of 5 carbon atoms?
a)
Oxalo acetic acid
b)
Malic acid
c)
Citric acid
d)
α –Ketoglutaric acid

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
In kreb cycle only one compound consists of 5 carbon atoms it is α –Ketoglutaric acid .
Which of the following conversions involve ATP synthesis during glycolysis?- a)Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate
- b)Fructose-6-phosphate → Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
- c)1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) → 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conversions involve ATP synthesis during glycolysis?
a)
Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate
b)
Fructose-6-phosphate → Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
c)
1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) → 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
d)
All of these
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
In the energy conserving phase of glycolysis, the conversion of BPGA to PGA is catalyzed by phosphoglycerate kinase. The phosphate on carbon 1 is transferred to a molecule of ADP, yielding ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate. This type of ATP synthesis, traditionally referred to as substrate-level phosphorylation, involves the direct transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP, to form ATP.
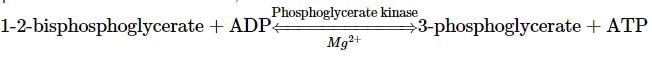
In Krebs cycle the FAD participates as electron acceptor during the conversion of- a)Succinyl CoA to succinic acid
- b)α− ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA
- c)Succinic acid to fumaric acid
- d)Fumaric acid to malic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Krebs cycle the FAD participates as electron acceptor during the conversion of
a)
Succinyl CoA to succinic acid
b)
α− ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA
c)
Succinic acid to fumaric acid
d)
Fumaric acid to malic acid
|
|
Bhavana Desai answered |
Conversion of Succinic acid to fumaric acid in Krebs cycle:
- Step in Krebs Cycle:
In the Krebs cycle, the conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid occurs as part of the overall process of generating energy from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- Role of FAD:
During this step, FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) acts as an electron acceptor. FAD accepts electrons from succinic acid, which is converted to fumaric acid in the process.
- Function of FAD:
FAD plays a crucial role in the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons and transports them to complex II of the respiratory chain. This helps in the generation of ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
- Overall Process:
The conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid is a key step in the Krebs cycle, as it helps in the production of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. This process is essential for the cell to generate energy for various cellular activities.
- Significance:
The involvement of FAD in this step highlights the importance of electron carriers in the Krebs cycle. These carriers help in transferring electrons from one molecule to another, ultimately leading to the production of ATP.
- Conclusion:
In conclusion, FAD participates as an electron acceptor during the conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid in the Krebs cycle. This process is vital for energy production and highlights the intricate mechanisms involved in cellular respiration.
- Step in Krebs Cycle:
In the Krebs cycle, the conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid occurs as part of the overall process of generating energy from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- Role of FAD:
During this step, FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) acts as an electron acceptor. FAD accepts electrons from succinic acid, which is converted to fumaric acid in the process.
- Function of FAD:
FAD plays a crucial role in the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons and transports them to complex II of the respiratory chain. This helps in the generation of ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
- Overall Process:
The conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid is a key step in the Krebs cycle, as it helps in the production of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. This process is essential for the cell to generate energy for various cellular activities.
- Significance:
The involvement of FAD in this step highlights the importance of electron carriers in the Krebs cycle. These carriers help in transferring electrons from one molecule to another, ultimately leading to the production of ATP.
- Conclusion:
In conclusion, FAD participates as an electron acceptor during the conversion of succinic acid to fumaric acid in the Krebs cycle. This process is vital for energy production and highlights the intricate mechanisms involved in cellular respiration.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Shreya Datta answered |
Explanation of Statements
The two statements provided about mitochondria and ATP synthesis are fundamental concepts in cell biology.
Statement 1: Mitochondria as the Powerhouse of the Cell
- Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouse of the cell."
- This term signifies their primary role in energy production through aerobic respiration.
Statement 2: ATP Synthesis Occurs in Mitochondria
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of the cell.
- The synthesis of ATP occurs in mitochondria through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements are accurate.
- Mitochondria are indeed responsible for generating ATP, which provides energy for various cellular functions.
Relationship Between the Statements
- Statement 2 serves as a direct explanation of why statement 1 is true.
- The ability of mitochondria to synthesize ATP is what qualifies them as the powerhouse of the cell.
Conclusion
- Therefore, both statements are correct, and statement 2 provides the correct explanation for statement 1.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'A': "Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1."
Understanding these concepts is crucial for NEET preparation, as they form the basis of cellular respiration and energy metabolism in biological systems.
The two statements provided about mitochondria and ATP synthesis are fundamental concepts in cell biology.
Statement 1: Mitochondria as the Powerhouse of the Cell
- Mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouse of the cell."
- This term signifies their primary role in energy production through aerobic respiration.
Statement 2: ATP Synthesis Occurs in Mitochondria
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of the cell.
- The synthesis of ATP occurs in mitochondria through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Correctness of the Statements
- Both statements are accurate.
- Mitochondria are indeed responsible for generating ATP, which provides energy for various cellular functions.
Relationship Between the Statements
- Statement 2 serves as a direct explanation of why statement 1 is true.
- The ability of mitochondria to synthesize ATP is what qualifies them as the powerhouse of the cell.
Conclusion
- Therefore, both statements are correct, and statement 2 provides the correct explanation for statement 1.
- This is why the correct answer is option 'A': "Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1."
Understanding these concepts is crucial for NEET preparation, as they form the basis of cellular respiration and energy metabolism in biological systems.
During complete metabolism of glucose, the number of ATP formed is- a)2
- b)12
- c)36
- d)44
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During complete metabolism of glucose, the number of ATP formed is
a)
2
b)
12
c)
36
d)
44
|
|
Anagha Sengupta answered |
Complete Metabolism of Glucose
The complete metabolism of glucose through cellular respiration involves several stages: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). Here’s a breakdown of ATP production in each stage.
1. Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm.
- Converts one glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Produces:
- 2 ATP (net gain).
- 2 NADH (which can yield additional ATP during oxidative phosphorylation).
2. Pyruvate Decarboxylation
- Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is converted to Acetyl-CoA.
- Produces:
- 2 NADH (one from each pyruvate).
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
- Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Each Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, producing:
- 2 ATP (1 ATP per cycle, and two cycles per glucose).
- 6 NADH (3 per cycle).
- 2 FADH2 (1 per cycle).
4. Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
- Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- NADH produces approximately 2.5 ATP each, and FADH2 produces about 1.5 ATP each.
- From the previous stages:
- 10 NADH = 10 x 2.5 = 25 ATP.
- 2 FADH2 = 2 x 1.5 = 3 ATP.
Total ATP Calculation
- Glycolysis: 2 ATP + 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Pyruvate Decarboxylation: 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP + 6 NADH (15 ATP) + 2 FADH2 (3 ATP).
- Total: 2 + 5 + 5 + 2 + 15 + 3 = 32 ATP.
However, due to the use of ATP for transport and other processes, the net yield is typically rounded to about 30-36 ATP, commonly cited as 36 ATP for simplicity.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C', with 36 ATP being formed during the complete metabolism of one glucose molecule.
The complete metabolism of glucose through cellular respiration involves several stages: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). Here’s a breakdown of ATP production in each stage.
1. Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm.
- Converts one glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Produces:
- 2 ATP (net gain).
- 2 NADH (which can yield additional ATP during oxidative phosphorylation).
2. Pyruvate Decarboxylation
- Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is converted to Acetyl-CoA.
- Produces:
- 2 NADH (one from each pyruvate).
3. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
- Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Each Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, producing:
- 2 ATP (1 ATP per cycle, and two cycles per glucose).
- 6 NADH (3 per cycle).
- 2 FADH2 (1 per cycle).
4. Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
- Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- NADH produces approximately 2.5 ATP each, and FADH2 produces about 1.5 ATP each.
- From the previous stages:
- 10 NADH = 10 x 2.5 = 25 ATP.
- 2 FADH2 = 2 x 1.5 = 3 ATP.
Total ATP Calculation
- Glycolysis: 2 ATP + 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Pyruvate Decarboxylation: 2 NADH (5 ATP).
- Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP + 6 NADH (15 ATP) + 2 FADH2 (3 ATP).
- Total: 2 + 5 + 5 + 2 + 15 + 3 = 32 ATP.
However, due to the use of ATP for transport and other processes, the net yield is typically rounded to about 30-36 ATP, commonly cited as 36 ATP for simplicity.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is option 'C', with 36 ATP being formed during the complete metabolism of one glucose molecule.
Which of the following steps of respiration is amphibolic?- a)Glycolysis
- b)Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
- c)TCA cycle
- d)Oxidative phosphorylation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following steps of respiration is amphibolic?
a)
Glycolysis
b)
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
c)
TCA cycle
d)
Oxidative phosphorylation
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
TCA or Krebs' cycle is amphibolic (both catabolic and anabolic) because it provides a number of intermediates for anabolic pathways.
Which of the following reactions is catalysed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase?- a)Fructose-1,6-bisphophate → Fructose-6-phosphate
- b)Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- c)G-3-P → Dihydroxy acetone phosphate
- d)Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions is catalysed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase?
a)
Fructose-1,6-bisphophate → Fructose-6-phosphate
b)
Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
c)
G-3-P → Dihydroxy acetone phosphate
d)
Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Phosphofructokinase is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose-6-phosphate in glycolysis. The enzyme catalysed transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP is an important reaction in a wide variety of biological processes.
Which of the following statements are correct?(A) The oxidation of pyruvic acid molecules formed in glycolysis occurs inside the mitochondria.(B) Acetyl CoA is a 3-carbon compound.(C) Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is reduced to either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.(D) Acetyl CoA molecules enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.- a)(A) and (B)
- b)(C) and (D)
- c)(A) and (C)
- d)(B) and (C)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The oxidation of pyruvic acid molecules formed in glycolysis occurs inside the mitochondria.
(B) Acetyl CoA is a 3-carbon compound.
(C) Under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is reduced to either ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
(D) Acetyl CoA molecules enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.
a)
(A) and (B)
b)
(C) and (D)
c)
(A) and (C)
d)
(B) and (C)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Acetyl CoA is a 2-carbon compound and 3-phosphoglycerate molecule enter into cyclic reactions during Calvin cycle.
At the end of citric acid cycle, most of the energy is transferred to- a)Oxaloacetic acid
- b)Citric acid
- c)NADH and FADH2
- d)ATP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At the end of citric acid cycle, most of the energy is transferred to
a)
Oxaloacetic acid
b)
Citric acid
c)
NADH and FADH2
d)
ATP
|
|
Sinjini Das answered |
Energy Transfer in the Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by generating energy-rich molecules.
Key Products of the Cycle
- At the end of the citric acid cycle, the majority of the energy derived from the oxidation of acetyl-CoA is captured in the form of high-energy electron carriers.
- The two main carriers involved are NADH and FADH2, which are produced at several steps during the cycle.
Why NADH and FADH2?
- Reduction Reactions: Throughout the cycle, NAD+ and FAD are reduced to form NADH and FADH2. This process captures energy from the oxidation of substrates.
- Energy Storage: NADH and FADH2 store energy in the form of high-energy electrons, which are essential for the subsequent production of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
Comparison with Other Products
- While ATP is produced directly during the cycle, the amount is relatively small compared to the energy stored in NADH and FADH2.
- Oxaloacetic acid and citric acid are intermediates in the cycle, but they do not serve as significant energy carriers like NADH and FADH2.
Conclusion
- In summary, the majority of energy at the end of the citric acid cycle is transferred to NADH and FADH2. These molecules are crucial for the electron transport chain, where most ATP is generated, highlighting their importance in energy metabolism.
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, plays a crucial role in cellular respiration by generating energy-rich molecules.
Key Products of the Cycle
- At the end of the citric acid cycle, the majority of the energy derived from the oxidation of acetyl-CoA is captured in the form of high-energy electron carriers.
- The two main carriers involved are NADH and FADH2, which are produced at several steps during the cycle.
Why NADH and FADH2?
- Reduction Reactions: Throughout the cycle, NAD+ and FAD are reduced to form NADH and FADH2. This process captures energy from the oxidation of substrates.
- Energy Storage: NADH and FADH2 store energy in the form of high-energy electrons, which are essential for the subsequent production of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
Comparison with Other Products
- While ATP is produced directly during the cycle, the amount is relatively small compared to the energy stored in NADH and FADH2.
- Oxaloacetic acid and citric acid are intermediates in the cycle, but they do not serve as significant energy carriers like NADH and FADH2.
Conclusion
- In summary, the majority of energy at the end of the citric acid cycle is transferred to NADH and FADH2. These molecules are crucial for the electron transport chain, where most ATP is generated, highlighting their importance in energy metabolism.
FAD + is produced during conversion of- a)Fumaric acid to Malic acid
- b)Isocitric acid Oxalosuccinic acid
- c)Citric acid to isocitric acid
- d)Succinic acid to Fumaric acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
FAD + is produced during conversion of
a)
Fumaric acid to Malic acid
b)
Isocitric acid Oxalosuccinic acid
c)
Citric acid to isocitric acid
d)
Succinic acid to Fumaric acid

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
During citric acid cycle, Succinic acid is converted into Fumaric acid during which FAD + FAD + molecules is produce that produce 2 ATP molecules.
Glycerol would enter the amphibolic pathway after being converted into- a)PGAL
- b)Fatty acids
- c)Acetyl co A
- d)Glucose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Glycerol would enter the amphibolic pathway after being converted into
a)
PGAL
b)
Fatty acids
c)
Acetyl co A
d)
Glucose
|
|
Hridoy Mehta answered |
Introduction to Glycerol Metabolism
Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule derived from the breakdown of triglycerides. It plays a significant role in both catabolic and anabolic pathways, making it an important intermediate in metabolism.
Conversion of Glycerol to PGAL
- Glycerol enters the amphibolic pathway by undergoing phosphorylation to form glycerol-3-phosphate.
- This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme glycerol kinase, utilizing ATP as the phosphate donor.
- Glycerol-3-phosphate can then be converted into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) through the action of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Connection with Glycolysis
- DHAP is an intermediate of glycolysis and can be further converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (PGAL).
- PGAL is a crucial substrate that can enter various metabolic pathways, including glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
- By converting glycerol into PGAL, it can be utilized for energy production or as a building block for glucose synthesis.
Importance of PGAL in Metabolism
- PGAL is a key player in energy metabolism, linking carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
- It can be further processed to produce ATP through glycolysis or be used to synthesize glucose when energy demands are low.
- This versatility makes PGAL an important intermediary in the amphibolic pathway, which integrates both anabolic and catabolic processes.
Conclusion
In summary, glycerol enters the amphibolic pathway after being converted into PGAL, enabling it to participate in various metabolic pathways and ensuring energy homeostasis in the body.
Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule derived from the breakdown of triglycerides. It plays a significant role in both catabolic and anabolic pathways, making it an important intermediate in metabolism.
Conversion of Glycerol to PGAL
- Glycerol enters the amphibolic pathway by undergoing phosphorylation to form glycerol-3-phosphate.
- This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme glycerol kinase, utilizing ATP as the phosphate donor.
- Glycerol-3-phosphate can then be converted into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) through the action of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Connection with Glycolysis
- DHAP is an intermediate of glycolysis and can be further converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (PGAL).
- PGAL is a crucial substrate that can enter various metabolic pathways, including glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
- By converting glycerol into PGAL, it can be utilized for energy production or as a building block for glucose synthesis.
Importance of PGAL in Metabolism
- PGAL is a key player in energy metabolism, linking carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
- It can be further processed to produce ATP through glycolysis or be used to synthesize glucose when energy demands are low.
- This versatility makes PGAL an important intermediary in the amphibolic pathway, which integrates both anabolic and catabolic processes.
Conclusion
In summary, glycerol enters the amphibolic pathway after being converted into PGAL, enabling it to participate in various metabolic pathways and ensuring energy homeostasis in the body.
End-product of citric acid/Krebs cycle is- a)Citric acid
- b)CO2 + H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Pyruvic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
End-product of citric acid/Krebs cycle is
a)
Citric acid
b)
CO2 + H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Pyruvic acid
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The eight steps of the citric acid cycle are a series of redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. Each turn of the cycle forms one GTP or ATP as well as three NADH molecules and one FADH2 molecule, which will be used in further steps of cellular respiration to produce ATP for the cell.
Which of the following is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?- a)ATP
- b)Malic acid
- c)Acetyl CoA
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?
a)
ATP
b)
Malic acid
c)
Acetyl CoA
d)
NADH
|
|
H2O answered |
Acetyl CoA is the key intermediate between the Krebs cycle of glycolysis. After glycolysis, the glucose converts to pyruvic acid which is a three-carbon molecule. It is converted into acetyl coenzyme a by oxidative decarboxylation This, Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and along with oxaloacetic acid forms the citric acid which is a 6C compound.
Which of the following is true about glycolysis?- a)It occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
- b)It requires oxygen for glucose breakdown.
- c)It occurs in the cytoplasm and is universal in all living organisms.
- d)It only occurs in prokaryotes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
b)
It requires oxygen for glucose breakdown.
c)
It occurs in the cytoplasm and is universal in all living organisms.
d)
It only occurs in prokaryotes.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Glycolysis is a universal pathway occurring in the cytoplasm of all living cells and does not require oxygen.
Substrate level phosphorylation occurs during which step of Krebs' cycle?- a)Succinyl - CoA → Succinicacid
- b)Isocitricacid → Oxalosuccinicacid
- c)Oxalosuccinicacid → α−ketoglutaricacid
- d)Malicacid → OAA
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Substrate level phosphorylation occurs during which step of Krebs' cycle?
a)
Succinyl - CoA → Succinicacid
b)
Isocitricacid → Oxalosuccinicacid
c)
Oxalosuccinicacid → α−ketoglutaricacid
d)
Malicacid → OAA
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
During Krebs' or citric acid cycle, succinyl-CoA is acted upon by enzyme succinyl-CoA synthetase to form succinate (a 4C compound). The reaction releases sufficient energy to form ATP (in plants) or GTP (in animals) by substrate-level phosphorylation. GTP can form ATP through a coupled reaction.
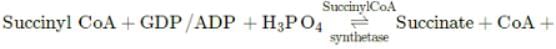 GTP/ATP
GTP/ATPWhich is true about the end products of glycolysis?- a)2 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
- b)2 pyruvicacid + 2NADH2
- c)1 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
- d)2 pyruvicacid + 1ATP + 1NADH2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about the end products of glycolysis?
a)
2 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
b)
2 pyruvicacid + 2NADH2
c)
1 pyruvicacid + 2ATP + 2NADH2
d)
2 pyruvicacid + 1ATP + 1NADH2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In glycolysis, two molecules of ATP are consumed during two phosphorylation reactions to form fructose 1, 6-biphosphate. In return four molecules of ATP are produced by substrate level phosphorylation (conversion of 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenol pyruvate to pyruvate). Two molecules of NADH2 are formed at the time of oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate. The net reaction of glycolysis is as follows :
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2H3PO4 → 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP
Each NADH is equivalent to 2 ATP, so the net gain in glycolysis is 8 ATP.
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP + 2H3PO4 → 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP
Each NADH is equivalent to 2 ATP, so the net gain in glycolysis is 8 ATP.
Electron transport chain (ETC) is a set of ______ electron carriers present in a specific sequence along ______ mitochondrial membrane.- a)seven, inner
- b)six, inner
- c)seven, outer
- d)six, outer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electron transport chain (ETC) is a set of ______ electron carriers present in a specific sequence along ______ mitochondrial membrane.
a)
seven, inner
b)
six, inner
c)
seven, outer
d)
six, outer
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In electron transport chain, there are 7 electron acceptors, which are as follows Co − Q → Cyt b → Cyt c1 → Cyt c → Cyt a → Cyt a3 → O2. Oxygen is the ultimate electron acceptor. These electron acceptors are present in a specific sequence along inner mitochondrial membrane.
Acetyl CoA forms a 6-C compound after combining with - a)Oxaloacetic acid
- b)Oxygen
- c)Pyruvic acid
- d)Citric acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acetyl CoA forms a 6-C compound after combining with
a)
Oxaloacetic acid
b)
Oxygen
c)
Pyruvic acid
d)
Citric acid

|
Karan answered |
Yes after combining with OAA , acetyl coA forms 6 -c compound citric acid in kreb cycle
Which of the following is performed by coenzyme A?- a)Oxidative phosphorylation
- b)Substrate level phosphorylation
- c)Breakdown of pyruvate
- d)Activation of acetyl group
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is performed by coenzyme A?
a)
Oxidative phosphorylation
b)
Substrate level phosphorylation
c)
Breakdown of pyruvate
d)
Activation of acetyl group
|
|
Ameya Mehta answered |
Activation of acetyl group
Coenzyme A plays a crucial role in the activation of acetyl groups, which is an essential step in various metabolic processes.
Formation of Acetyl-CoA
Coenzyme A binds to the acetyl group derived from pyruvate or fatty acids to form acetyl-CoA. This process is catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase in the case of pyruvate breakdown.
Role in Citric Acid Cycle
Acetyl-CoA is a key molecule in the citric acid cycle. It enters the cycle and undergoes a series of reactions to produce energy in the form of ATP. Coenzyme A facilitates the transfer of acetyl groups within the cycle.
Role in Fatty Acid Synthesis
In fatty acid synthesis, acetyl-CoA serves as a precursor for the synthesis of fatty acids. Coenzyme A is required for the activation of acetyl groups before they can be used in the fatty acid synthesis pathway.
Regulation of Metabolism
Coenzyme A is involved in regulating the balance of metabolic pathways by controlling the availability of acetyl groups. It acts as a carrier of acetyl units and facilitates their transfer between different metabolic reactions.
In summary, coenzyme A plays a crucial role in the activation of acetyl groups, which are essential for various metabolic processes including the breakdown of pyruvate, the citric acid cycle, and fatty acid synthesis.
Coenzyme A plays a crucial role in the activation of acetyl groups, which is an essential step in various metabolic processes.
Formation of Acetyl-CoA
Coenzyme A binds to the acetyl group derived from pyruvate or fatty acids to form acetyl-CoA. This process is catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase in the case of pyruvate breakdown.
Role in Citric Acid Cycle
Acetyl-CoA is a key molecule in the citric acid cycle. It enters the cycle and undergoes a series of reactions to produce energy in the form of ATP. Coenzyme A facilitates the transfer of acetyl groups within the cycle.
Role in Fatty Acid Synthesis
In fatty acid synthesis, acetyl-CoA serves as a precursor for the synthesis of fatty acids. Coenzyme A is required for the activation of acetyl groups before they can be used in the fatty acid synthesis pathway.
Regulation of Metabolism
Coenzyme A is involved in regulating the balance of metabolic pathways by controlling the availability of acetyl groups. It acts as a carrier of acetyl units and facilitates their transfer between different metabolic reactions.
In summary, coenzyme A plays a crucial role in the activation of acetyl groups, which are essential for various metabolic processes including the breakdown of pyruvate, the citric acid cycle, and fatty acid synthesis.
What is the number of ATP molecules that can be regarded as a net gain during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose? - a)2
- b)30
- c)36
- d)38
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the number of ATP molecules that can be regarded as a net gain during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose?
a)
2
b)
30
c)
36
d)
38

|
Stepway Academy answered |
There can be a net gain of 38 ATP molecules during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose.
Number of glucose molecule required to produce 38 ATP under anaerobic condition is- a)38
- b)4
- c)19
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of glucose molecule required to produce 38 ATP under anaerobic condition is
a)
38
b)
4
c)
19
d)
2

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
During anaerobic respiration only two molecules of ATP is produced by each molecules of glucose. So, 19 glucose molecules are required to produce 38 ATP molecules.
What is the final product of Glycolysis?- a)Malic acid
- b)Pyruvic acid
- c)Glucose
- d)Acetyl CoA
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the final product of Glycolysis?
a)
Malic acid
b)
Pyruvic acid
c)
Glucose
d)
Acetyl CoA

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
In glycolysis, glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid.
Respiratory substrates are the organic substances which are ________ during respiration to liberate energy.- a)Oxidised
- b)Reduced
- c)Synthesised
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiratory substrates are the organic substances which are ________ during respiration to liberate energy.
a)
Oxidised
b)
Reduced
c)
Synthesised
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Respiration is an oxidative process in which repiratory substrates are oxidised to liberate energy inside the living cells. The common respiratory substrates are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids. The most common respiratory substrates are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids. The most common respiratory substrate is glucose.
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants?- a)Hexokinase
- b)Invertase
- c)Phosphofructokinase
- d)Lactate dehydrogenase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Hexokinase
b)
Invertase
c)
Phosphofructokinase
d)
Lactate dehydrogenase
|
|
Sonal Reddy answered |
Enzyme Overview
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants is called invertase. This process is crucial for various physiological functions in plants, particularly in carbohydrate metabolism.
Function of Invertase
- Invertase, also known as sucrose-α-D-glucosidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose.
- It breaks the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose, resulting in free glucose and fructose.
Biological Importance
- Energy Source: The glucose produced serves as a primary energy source for plant cells.
- Sugar Transport: Fructose can also be utilized in energy production and serves as a precursor for other carbohydrates.
- Growth and Development: The availability of these simple sugars is essential for various metabolic processes, including growth and development.
Comparison with Other Enzymes
- Hexokinase: This enzyme phosphorylates glucose but does not convert sucrose.
- Phosphofructokinase: This enzyme is involved in glycolysis, acting on fructose-6-phosphate, not sucrose.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase: This enzyme is related to anaerobic respiration, specifically converting pyruvate to lactate.
Conclusion
In summary, invertase is the key enzyme that hydrolyzes sucrose into glucose and fructose, playing a vital role in plant metabolism and energy production. Understanding this enzyme's function is essential for comprehending how plants utilize carbohydrates effectively.
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of sucrose into glucose and fructose in plants is called invertase. This process is crucial for various physiological functions in plants, particularly in carbohydrate metabolism.
Function of Invertase
- Invertase, also known as sucrose-α-D-glucosidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose.
- It breaks the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose, resulting in free glucose and fructose.
Biological Importance
- Energy Source: The glucose produced serves as a primary energy source for plant cells.
- Sugar Transport: Fructose can also be utilized in energy production and serves as a precursor for other carbohydrates.
- Growth and Development: The availability of these simple sugars is essential for various metabolic processes, including growth and development.
Comparison with Other Enzymes
- Hexokinase: This enzyme phosphorylates glucose but does not convert sucrose.
- Phosphofructokinase: This enzyme is involved in glycolysis, acting on fructose-6-phosphate, not sucrose.
- Lactate Dehydrogenase: This enzyme is related to anaerobic respiration, specifically converting pyruvate to lactate.
Conclusion
In summary, invertase is the key enzyme that hydrolyzes sucrose into glucose and fructose, playing a vital role in plant metabolism and energy production. Understanding this enzyme's function is essential for comprehending how plants utilize carbohydrates effectively.
How many points are there in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Four
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many points are there in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Four
d)
Three

|
Lead Academy answered |
There are three points in the TCA cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+ and one point where FAD+ is reduced to FADH2. In a coupled reaction GTP is converted to GDP with the simultaneous synthesis of ATP from ADP.
Chapter doubts & questions for Respiration - Biology for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Respiration - Biology for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for EmSAT Achieve
157 videos|173 docs|136 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










