All Exams >
Grade 12 >
Biology for Grade 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Population Dynamics for Grade 12 Exam
Biological organisation starts witha) Cellular levelb) Atomic levelc) Submicroscopic molecular leveld) Organismic levelCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Correct option is (c)
Biological organisation starts with submicroscopic molecular level, where four types of molecules, i.e. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acid are organised into organelles of cell.
Biological organisation starts with submicroscopic molecular level, where four types of molecules, i.e. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acid are organised into organelles of cell.
Animals undergo an inactive stage during the winter known as- a)Adaptation
- b)Hibernation
- c)Aestivation
- d)Acclimatisation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals undergo an inactive stage during the winter known as
a)
Adaptation
b)
Hibernation
c)
Aestivation
d)
Acclimatisation
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Aestivation: Aestivation is summer sleep and during aestivation, animals usually tend to rest in a shady and cool place. ... In aestivation, usually cold blooded animals like reptiles maintain their body temperature by reducing their metabolic activities and protecting themselves from very high temperature.
Organisms capable of maintaining constant body temperature are- a)Poikilothermal
- b)Conformers
- c)Stenothermal
- d)Homeothermal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms capable of maintaining constant body temperature are
a)
Poikilothermal
b)
Conformers
c)
Stenothermal
d)
Homeothermal
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Homeotherms: animals who maintain a constant internal body temperature across a wide range of environmental conditions. Most mammals and birds are homeotherms.
In which of the following interactions both partners are adversely affected ?[2015 RS]- a)Predation
- b)Parasitism
- c)Mutualism
- d)Competition
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following interactions both partners are adversely affected ?
[2015 RS]
a)
Predation
b)
Parasitism
c)
Mutualism
d)
Competition

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
(d) Competition occurs for light, food and space among organisms in which all partners are adversely affected in an ecosystom.
Which of the following is/are poikilotherm:?- a)Tapeworm and rabbits
- b)Elephants
- c)Humans and fishes
- d)Tapeworm and naked mole rat
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are poikilotherm:?
a)
Tapeworm and rabbits
b)
Elephants
c)
Humans and fishes
d)
Tapeworm and naked mole rat

|
Divey Sethi answered |
In the given scenario, the laboratory population of fruit flies consists of 40 fruit flies, and during a specified time interval, 4 individuals died. To calculate the death rate, we divide the number of deaths by the total population.
Number of deaths = 4
Total population = 40
Total population = 40
Death rate = Number of deaths / Total population
= 4 / 40
= 0.1 individuals per fruitfly per week
= 4 / 40
= 0.1 individuals per fruitfly per week
Option a) "0.1 individuals per fruitfly per week" is the correct answer because it accurately represents the death rate calculated based on the given information.
Xerophytes are mostly- a)Succulents
- b)Water related
- c)Mesophytes
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Xerophytes are mostly
a)
Succulents
b)
Water related
c)
Mesophytes
d)
None of the above
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Plants adapted to living in dry environments such as succulents are termed xerophytes. However, not all xerophytes are succulents, since there are other ways of adapting to a shortage of water, e.g., by developing small leaves which may roll up or having leathery rather than succulent leaves.
Cold-blooded animals fall under the category of- a)Psychotherms
- b)Ectotherms
- c)Thermophiles
- d)Endotherms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cold-blooded animals fall under the category of
a)
Psychotherms
b)
Ectotherms
c)
Thermophiles
d)
Endotherms
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
An ectotherm "outside" and "hot"), is an organism in which internal physiological sources of heat are of relatively small or quite negligible importance in controlling body temperature.] Such organisms (for example frogs) rely on environmental heat sources,which permit them to operate at very economical metabolic rates. Colloquially, some refer to these organisms as "cold blooded" though such a term is not technically correct, as the blood temperature of the organism varies with ambient environmental temperature. Some of these animals live in environments where temperatures are practically constant, as is typical of regions of the abyssal ocean and hence can be regarded as homeothermic ectotherms. In contrast, in places where temperature varies so widely as to limit the physiological activities of other kinds of ectotherms, many species habitually seek out external sources of heat or shelter from heat; for example, many reptiles regulate their body temperature by basking in the sun, or seeking shade when necessary in addition to a whole host of other behavioral thermoregulation mechanisms. For home captivity as pet, reptile owners can use a UVB/UVA light system to assist the animals' basking behaviour.
The birth and death rates of four counteries are given below. which one will have the least population growth rate?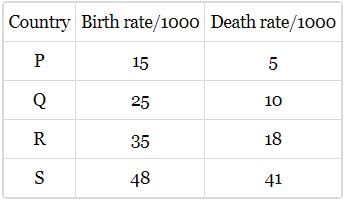
- a)P
- b)Q
- c)R
- d)S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The birth and death rates of four counteries are given below. which one will have the least population growth rate?

a)
P
b)
Q
c)
R
d)
S

|
Top Rankers answered |
Growth rate = Birth rate - death rate
For country P, it is 10/1000. For country Q, It is 15/1000
For country R, it is 17/1000. For country S, It is 7/1000
Hence, country S has the least population growth rate
For country P, it is 10/1000. For country Q, It is 15/1000
For country R, it is 17/1000. For country S, It is 7/1000
Hence, country S has the least population growth rate
Orchid shows commensalism as interaction with:- a)bee
- b)mango tree
- c)both mango tree and bee
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Orchid shows commensalism as interaction with:
a)
bee
b)
mango tree
c)
both mango tree and bee
d)
none of these

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Commensalism is interaction in which one species is benefited by other is neither benefited nor harmed. Orchids growing on mango tree do not harm the mango plants but get shelter.
A statement 933 females per 1000 males depict:- a)ecological ages
- b)generation time
- c)sex ratio
- d)biotic potential
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A statement 933 females per 1000 males depict:
a)
ecological ages
b)
generation time
c)
sex ratio
d)
biotic potential

|
Aman Sharma answered |
Sex ratio is the no of female available per thousands of male in a population. Sex ratio is decline due to female feticides alarmingly in some part of India.
Cuscuta is an example of[2012M]- a)ectoparasitism
- b)brood parasitism
- c)predation
- d)endoparasitism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cuscuta is an example of
[2012M]
a)
ectoparasitism
b)
brood parasitism
c)
predation
d)
endoparasitism

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Cuscuta, or Dodder plant, is a parasitic plant that wraps around other plants for nourishment. Cuscuta is found on outer side of the host and is total stem parasite. Cuscuta a parasite of Acacia.
Small fish get stuck near the bottom of a shark and derive their nutrition from it? This kind of association is called- a)Parasitism
- b)Symbiosis
- c)Predation
- d)Commensalism
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Small fish get stuck near the bottom of a shark and derive their nutrition from it? This kind of association is called
a)
Parasitism
b)
Symbiosis
c)
Predation
d)
Commensalism
|
|
Sonal Chakraborty answered |
Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits from the association, while the other is neither harmed nor helped. In this type of association, one species derives benefits from the other without causing any harm to the host.
Explanation:
In the given scenario, the small fish gets stuck near the bottom of a shark and derives its nutrition from it. The small fish is not harming the shark, nor is it providing any benefits to the shark. Therefore, this is an example of commensalism.
The small fish is using the shark as a shelter and also gets access to food particles that are present near the shark's mouth. The shark is not affected by the presence of the small fish, and it does not derive any benefit from it either.
In summary, commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits from the association, while the other is neither harmed nor helped. The small fish getting stuck near the bottom of a shark and deriving its nutrition from it is an example of commensalism.
Explanation:
In the given scenario, the small fish gets stuck near the bottom of a shark and derives its nutrition from it. The small fish is not harming the shark, nor is it providing any benefits to the shark. Therefore, this is an example of commensalism.
The small fish is using the shark as a shelter and also gets access to food particles that are present near the shark's mouth. The shark is not affected by the presence of the small fish, and it does not derive any benefit from it either.
In summary, commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one species benefits from the association, while the other is neither harmed nor helped. The small fish getting stuck near the bottom of a shark and deriving its nutrition from it is an example of commensalism.
Homeostasis is[1991]- a)tendency of biological systems to change with change in environment
- b)tendency of biological systems to resist change
- c)disturbance of self regulatory system and natural controls
- d)biotic materials used in homeopathic medicines.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Homeostasis is
[1991]
a)
tendency of biological systems to change with change in environment
b)
tendency of biological systems to resist change
c)
disturbance of self regulatory system and natural controls
d)
biotic materials used in homeopathic medicines.

|
Pankaj Kulkarni answered |
Homeostasis is the property of an open system, especially living organisms, to regulate its internal environment to maintain a stable, constant condition, by means of multiple dynamic equilibrium adjustments, controlled by interrelated regulation mechanisms.
A large regional unit characterised by a major vegetation type and associated fauna found in a specific climate zone constitutes- a)Biological community
- b)Ecosystem
- c)Biome
- d)Habitat
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A large regional unit characterised by a major vegetation type and associated fauna found in a specific climate zone constitutes
a)
Biological community
b)
Ecosystem
c)
Biome
d)
Habitat
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
A biome is a community of plants and animals that have common characteristics for the environment they exist in. They can be found over a range of continents. Biomes are distinct biological communities that have formed in response to a shared physical climate."Biome" is a broader term than "habitat"; any biome can comprise a variety of habitats.
While a biome can cover large areas, a microbiome is a mix of organisms that coexist in a defined space on a much smaller scale. For example, the human microbiome is the collection of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that are present on or in a human body.
A 'biota' is the total collection of organisms of a geographic region or a time period, from local geographic scales and instantaneous temporal scales all the way up to whole-planet and whole-timescale spatiotemporal scales. The biotas of the Earth make up the biosphere.
The birth rate if 7 new plants are added to previous year plant population of 23 Salvinia plants will be:- a)0.3
- b)0.25
- c)0.4
- d)0.5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The birth rate if 7 new plants are added to previous year plant population of 23 Salvinia plants will be:
a)
0.3
b)
0.25
c)
0.4
d)
0.5

|
Rohan Unni answered |
The birth rate of a population = new individual added / previous population. Here birth rate= 7/23=0.3043. Hence, birth rate of Salvinia plants is equal to 0.3.
Gause's principle of competitive exclusion states that :[2016]- a)more abundant species will exclude the less abundant species through competition.
- b)competition for the same resources excludes species having different food preferences.
- c)no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources.
- d)larger organisms exclude smaller ones through competition.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gause's principle of competitive exclusion states that :
[2016]
a)
more abundant species will exclude the less abundant species through competition.
b)
competition for the same resources excludes species having different food preferences.
c)
no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources.
d)
larger organisms exclude smaller ones through competition.

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
(c) Gause's principle of competitive exclusion can be restated to say that no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely when resources are limiting. Certainly species can and do coexist while competing for some of the same resources. Nevertheless, Gause's theory predicts that when two species coexist on a long-term basis, either resources must not be limited or their niches will always differ in one or more features; otherwise, one species will outcompete the other and the extinction of the second species will inevitably result, a process referred to as competitive exclusion
When does the growth rate of a population following the logistic model equal zero ? The logistic model is given as dN/dt = rN(1–N/K)[2016]- a)when N/K is exactly one.
- b)when N nears the carrying capacity of the habitat.
- c)when N/K equals zero.
- d)when death rate is greater than birth rate.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When does the growth rate of a population following the logistic model equal zero ? The logistic model is given as dN/dt = rN(1–N/K)
[2016]
a)
when N/K is exactly one.
b)
when N nears the carrying capacity of the habitat.
c)
when N/K equals zero.
d)
when death rate is greater than birth rate.

|
Pallabi Reddy answered |
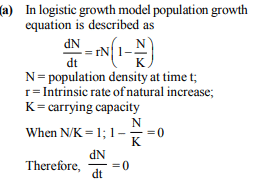
Carnivorous animals lions and leopards, occupy the same niche but lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take smaller ones. This mechanism of competition is referred to as [2019]- a)Character displacement
- b)Altruism
- c)Resource partitioning
- d)Competitive exclusion.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Carnivorous animals lions and leopards, occupy the same niche but lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take smaller ones. This mechanism of competition is referred to as [2019]
a)
Character displacement
b)
Altruism
c)
Resource partitioning
d)
Competitive exclusion.
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Species facing competition might evolve mechanism that promotes co-existence rather exclusion. One such mechanism is resource partitioning.
Resource partitioning is the division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche. Example - carnivorous animals like lions, leopards occupy the same niche but lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take smaller ones.
So, correct answer is option C.
Interacting members of species live close to each other in following interaction/s:- a)parasitism
- b)competition
- c)commensalism, predation and parasitism
- d)commensalism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Interacting members of species live close to each other in following interaction/s:
a)
parasitism
b)
competition
c)
commensalism, predation and parasitism
d)
commensalism

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
Interacting members of species live close to each other in commensalism, predation and parasitism.
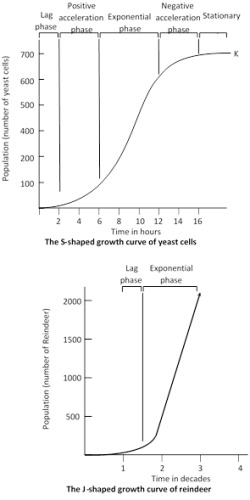
Human population follows the- a)J-shaped growth curve
- b)Z-shaped growth curve
- c)S-shaped growth curve
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Human population follows the
a)
J-shaped growth curve
b)
Z-shaped growth curve
c)
S-shaped growth curve
d)
All of the above

|
Harshitha Chavan answered |
Logarithmic or Exponential phase : It is characterized by rapid growth in population which continues till enough food is available. But with the increase in reindeer population, there is corresponding decrease in the availability of food and space, which finally become exhausted, which leads to mass starvation and mortality. This sudden increase in mortality is called population crash. Lemming of Tundra, some insect, algal blooms and annual plants also show J-shaped curves. The population growth curve is S- shaped in most of the organisms, Human population also shows S-shaped curve.

Mycorrhiza represents - a)symbiotic association between a fungus and liverworts
- b)parasitic association between a fungus and an alga
- c)parasitic association between a fungus and roots of plants
- d)symbiotic association between a fungus and roots of higher plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mycorrhiza represents
a)
symbiotic association between a fungus and liverworts
b)
parasitic association between a fungus and an alga
c)
parasitic association between a fungus and roots of plants
d)
symbiotic association between a fungus and roots of higher plants

|
Sonal Kulkarni answered |
A nutrient depletion zone can develop when there is rapid soil solution uptake, low nutrient concentration, low diffusion rate, or low soil moisture. These conditions are very common; therefore, most plants rely on fungi to facilitate the uptake of minerals from the soil. Mycorrhizae, known as root fungi, form symbiotic associations with plant roots. In these associations, the fungi are actually integrated into the physical structure of the root. The fungi colonize the living root tissue during active plant growth.
In a pond, last year there were 30 lotus plants. Through reproduction, 25 new lotus plants were added in one year while 8 plants died. The birth and death rates for the lotus population respectively are ___ and ____ individuals per lotus per year.- a)0.83 , 0.26
- b)0.26, 0.83
- c)0.25 , 0.80
- d)0.80, 0.25
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a pond, last year there were 30 lotus plants. Through reproduction, 25 new lotus plants were added in one year while 8 plants died. The birth and death rates for the lotus population respectively are ___ and ____ individuals per lotus per year.
a)
0.83 , 0.26
b)
0.26, 0.83
c)
0.25 , 0.80
d)
0.80, 0.25
|
|
Pallavi Pillai answered |
Understanding the Lotus Population Dynamics
To solve the problem, we need to calculate the birth and death rates for the lotus plants based on the given data.
Initial Population
- Last year, there were 30 lotus plants.
New Plants Added
- In one year, 25 new lotus plants were added due to reproduction.
Plants that Died
- During the same year, 8 plants died.
Calculating the Birth Rate
- Formula for Birth Rate:
Birth Rate = (Number of New Plants / Initial Population)
- Calculation:
- Birth Rate = 25 new plants / 30 initial plants = 0.8333 (approximately 0.83)
Calculating the Death Rate
- Formula for Death Rate:
Death Rate = (Number of Deaths / Initial Population)
- Calculation:
- Death Rate = 8 plants died / 30 initial plants = 0.2667 (approximately 0.27)
Final Rates
- Therefore, the birth rate is approximately 0.83 individuals per lotus per year.
- The death rate is approximately 0.27 individuals per lotus per year.
Conclusion
The birth and death rates for the lotus population are:
- Birth Rate: 0.83
- Death Rate: 0.27
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': 0.83 and 0.26 individuals per lotus per year.
To solve the problem, we need to calculate the birth and death rates for the lotus plants based on the given data.
Initial Population
- Last year, there were 30 lotus plants.
New Plants Added
- In one year, 25 new lotus plants were added due to reproduction.
Plants that Died
- During the same year, 8 plants died.
Calculating the Birth Rate
- Formula for Birth Rate:
Birth Rate = (Number of New Plants / Initial Population)
- Calculation:
- Birth Rate = 25 new plants / 30 initial plants = 0.8333 (approximately 0.83)
Calculating the Death Rate
- Formula for Death Rate:
Death Rate = (Number of Deaths / Initial Population)
- Calculation:
- Death Rate = 8 plants died / 30 initial plants = 0.2667 (approximately 0.27)
Final Rates
- Therefore, the birth rate is approximately 0.83 individuals per lotus per year.
- The death rate is approximately 0.27 individuals per lotus per year.
Conclusion
The birth and death rates for the lotus population are:
- Birth Rate: 0.83
- Death Rate: 0.27
Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': 0.83 and 0.26 individuals per lotus per year.
Exponential growth pattern in a population results into:- a)Sigmoid curve
- b)U-shaped curve
- c)J-shaped curve
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Exponential growth pattern in a population results into:
a)
Sigmoid curve
b)
U-shaped curve
c)
J-shaped curve
d)
None of these

|
Shalini Saha answered |
Exponential growth pattern in population results into j-shaped curve. During exponential growth faster growth occurs and j-shaped curve is formed when time v/s growth is drawn.
A mutually beneficial association necessary for survival of both partners is[1988]- a)mutualism/symbiosis
- b)commensalism
- c)amensalism
- d)both A and B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A mutually beneficial association necessary for survival of both partners is
[1988]
a)
mutualism/symbiosis
b)
commensalism
c)
amensalism
d)
both A and B

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Symbiosis or mutualism is a mutually beneficial association necessary for the survival of both the partners.
The formula for exponential population growth is- a)dN/rN = dt
- b)r N/dN = dt
- c)dt/dN = r N
- d)dN/dt = r N
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for exponential population growth is
a)
dN/rN = dt
b)
r N/dN = dt
c)
dt/dN = r N
d)
dN/dt = r N

|
Abhiram Nair answered |
Ans.
Formula = the rate of change in population size) = (the contribution of each individual to population growth) x (the number of individuals in the population

In a population per capita birth rate is 0.15 and per capita death rate is 0.08 during a unit time period. What is the value of r (intrinsic rate of natural increase) for the given population ?- a)0.023
- b)0.07
- c)0.05
- d)0.25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a population per capita birth rate is 0.15 and per capita death rate is 0.08 during a unit time period. What is the value of r (intrinsic rate of natural increase) for the given population ?
a)
0.023
b)
0.07
c)
0.05
d)
0.25

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Intrinsic rate of natural increase (r)
= Birth rate − death rate
=0.15−0.08=0.07
In which of the following interaction/s one species is benefitted while other is harmed?- a)parasitism only
- b)competition only
- c)predation and parasitism
- d)competition and amensalism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following interaction/s one species is benefitted while other is harmed?
a)
parasitism only
b)
competition only
c)
predation and parasitism
d)
competition and amensalism

|
Nayanika Dasgupta answered |
In predation and parasitism one species is benefitted while other is harmed. Parasite obtain food from host by harming them.
In a population unrestricted reproductive capacity is called as[2002]- a)biotic potential
- b)fertility
- c)carrying capacity
- d)birth rate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a population unrestricted reproductive capacity is called as
[2002]
a)
biotic potential
b)
fertility
c)
carrying capacity
d)
birth rate

|
Charvi Shah answered |
Carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of individuals that can be sustained by the environment. Birth rate refers to number of births per unit population.
Soil particles determine its[1992]- a)texture
- b)field capacity
- c)water holding capacity
- d)soil flora
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Soil particles determine its
[1992]
a)
texture
b)
field capacity
c)
water holding capacity
d)
soil flora

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Soil particles size defines its texture. The mineral particles present in soil, vary enosmously in size the fire fiagments. (consisting of sand, silt and clay particles) and coarse fiagments (gravel, copples and stones). The relative proportion's of sand, silt and clay in a soil is referred as soil texture. Fine textured soil have more of clay particles.
Water holding capacity-Larger soil particles like sand, gravel have large pores. This have high less holding capacity and higher percolotion rate field capacity is the of soil moisture or water content held in soil after excess water has drained away.
Water holding capacity-Larger soil particles like sand, gravel have large pores. This have high less holding capacity and higher percolotion rate field capacity is the of soil moisture or water content held in soil after excess water has drained away.
For which of the following would you expect distribution range to be badly affected if average Global temperature keeps increasing:- a)Stenothermal species
- b)Euryhaline species
- c)Both Stenothermal species and Euryhaline species
- d)Eurythermal species
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For which of the following would you expect distribution range to be badly affected if average Global temperature keeps increasing:
a)
Stenothermal species
b)
Euryhaline species
c)
Both Stenothermal species and Euryhaline species
d)
Eurythermal species

|
Diya Datta answered |
A majority of organisms are restricted to narrow range of temperature. Such organisms are called stenothermal species. The distribution range of these species will be adversely affected if average global temperature keeps increasing.
Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms and:- a)Abiotic and biotic components
- b)Biotic components only
- c)Abiotic components only
- d)Non-living components only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms and:
a)
Abiotic and biotic components
b)
Biotic components only
c)
Abiotic components only
d)
Non-living components only
|
|
Milan Unni answered |
Ecology is the branch of biology that studies the relationships between living organisms and their environment. It is concerned with understanding how organisms interact with both the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of their surroundings.
An example of predation is :- a)Cuckoo laying eggs in crow’s nest
- b)Biological control of pest population
- c)Penicilliumwhose toxins kill bacteria
- d)None of the these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of predation is :
a)
Cuckoo laying eggs in crow’s nest
b)
Biological control of pest population
c)
Penicilliumwhose toxins kill bacteria
d)
None of the these

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
Biological control method adopted in agricultural pest control are based on the ability of predator to regulate prey population.
“In Competition, the superior competitor eliminates the inferior one”, this statement is called?- a)Gause’s principle
- b)Allen’s rule
- c)Darwinian fitness
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
“In Competition, the superior competitor eliminates the inferior one”, this statement is called?
a)
Gause’s principle
b)
Allen’s rule
c)
Darwinian fitness
d)
All of these

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
E In competition, superior competitor eliminates the inferior one. This statement is called Gause’s competitive exclusion principle. Two closely related competing for same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and inferior will be eliminated.
Species facing competition might evolve mechanism that promotes co-existence rather than exclusion and that mechanism can be- a)Interspecific competition
- b)Intraspecific competition
- c)Competitive release
- d)Resource partitioning
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Species facing competition might evolve mechanism that promotes co-existence rather than exclusion and that mechanism can be
a)
Interspecific competition
b)
Intraspecific competition
c)
Competitive release
d)
Resource partitioning

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Species facing completion might evolve mechanism that promotes co-existence rather than exclusion that mechanism is called resource partitioning. In which they avoid completion by choosing different times of feeding or different foraging patterns.
_____ biomes are abundant in regions of hot and wet climate, while _____ biomes are found in hot and dry climate.- a)Desert, temperate
- b)Tropical, desert
- c)Tundra, savannah
- d)Desert, chapparal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
_____ biomes are abundant in regions of hot and wet climate, while _____ biomes are found in hot and dry climate.
a)
Desert, temperate
b)
Tropical, desert
c)
Tundra, savannah
d)
Desert, chapparal
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In tropical biome, the climate is warm with alternate wet dry periods. Rainfall is 90-160 cm. The climate in desert biome is hot and dry. The air, having little water vapour, is a poor insulator. The temperature rises considerably during the day and falls greatly at night because the ground radiates heat rapidly.
An age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top indicates a population that is:- a)Changing
- b)Stable
- c)Declining
- d)Growing rapidly
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top indicates a population that is:
a)
Changing
b)
Stable
c)
Declining
d)
Growing rapidly
|
|
Akshay Chavan answered |
Age Pyramid
An age pyramid, also known as an age distribution graph or population pyramid, is a graphical representation of the age and sex distribution of a population. The pyramid is divided into male and female populations, with age cohorts represented on the horizontal axis and the percentage of the population represented on the vertical axis.
Interpreting an Age Pyramid
The shape of an age pyramid provides valuable insights into the demographic characteristics of a population. By examining the width of the base and the narrowness of the top, we can determine the growth rate and age structure of the population.
Wide Base
A wide base on an age pyramid indicates a large proportion of young individuals in the population. This suggests a high birth rate and a growing population. The wider the base, the higher the number of children and young adults, indicating a significant proportion of the population is in the reproductive age group.
Narrow Top
A narrow top on an age pyramid indicates a smaller proportion of elderly individuals in the population. This suggests a lower life expectancy and a lower proportion of older adults. A narrow top indicates a lower percentage of the population in the older age groups.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer, option 'D' (Growing rapidly), is inferred from the description of an age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top. This pyramid shape indicates a population that has a high birth rate and a large proportion of young individuals. The narrower top suggests a lower life expectancy and a smaller proportion of older individuals.
When a population has a wide base and a narrow top, it indicates that the birth rate is higher than the death rate, leading to a rapid increase in population size. The large number of young individuals suggests a growing population with a high potential for future growth.
Therefore, an age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top indicates a population that is growing rapidly.
An age pyramid, also known as an age distribution graph or population pyramid, is a graphical representation of the age and sex distribution of a population. The pyramid is divided into male and female populations, with age cohorts represented on the horizontal axis and the percentage of the population represented on the vertical axis.
Interpreting an Age Pyramid
The shape of an age pyramid provides valuable insights into the demographic characteristics of a population. By examining the width of the base and the narrowness of the top, we can determine the growth rate and age structure of the population.
Wide Base
A wide base on an age pyramid indicates a large proportion of young individuals in the population. This suggests a high birth rate and a growing population. The wider the base, the higher the number of children and young adults, indicating a significant proportion of the population is in the reproductive age group.
Narrow Top
A narrow top on an age pyramid indicates a smaller proportion of elderly individuals in the population. This suggests a lower life expectancy and a lower proportion of older adults. A narrow top indicates a lower percentage of the population in the older age groups.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer, option 'D' (Growing rapidly), is inferred from the description of an age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top. This pyramid shape indicates a population that has a high birth rate and a large proportion of young individuals. The narrower top suggests a lower life expectancy and a smaller proportion of older individuals.
When a population has a wide base and a narrow top, it indicates that the birth rate is higher than the death rate, leading to a rapid increase in population size. The large number of young individuals suggests a growing population with a high potential for future growth.
Therefore, an age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top indicates a population that is growing rapidly.
If N population density at time t, then population density at time t+1 can be written asNt +1=Nt +[(A+B)−(C+D)]
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation. - a)A can be mortality and B can be natality
- b)B can be immigration and C can be natality
- c)C can be mortality and D can be immigration
- d)A can be natality and D can be emigration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If N population density at time t, then population density at time t+1 can be written as
Nt +1=Nt +[(A+B)−(C+D)]
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation.
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation.
a)
A can be mortality and B can be natality
b)
B can be immigration and C can be natality
c)
C can be mortality and D can be immigration
d)
A can be natality and D can be emigration
|
|
Anuj Singh answered |
Understanding Population Density Dynamics
Population density at any given time is influenced by various factors such as births, deaths, immigration, and emigration. The equation provided,
Nt+1 = Nt + [(A + B) - (C + D)],
helps in understanding how these factors affect population density over time.
Key Terminology Explained
- A (Natality): Refers to the birth rate in the population. An increase in natality contributes positively to population density.
- B (Immigration): This is the influx of individuals into a population from other areas. Immigration increases population density.
- C (Mortality): This term represents the death rate. An increase in mortality leads to a decrease in population density.
- D (Emigration): Emigration is the movement of individuals out of a population. Like mortality, it reduces population density.
Analyzing the Correct Option
The equation states that the population density at time t+1 is equal to the density at time t plus the net change from births and immigration, minus deaths and emigration.
- In this context, if we assign:
- A = Natality (births)
- B = Immigration (influx)
- C = Mortality (deaths)
- D = Emigration (outflux)
This fits perfectly into the equation as it correctly reflects the contributions of each factor to population density changes over time.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', where A is natality and D is emigration, as it accurately represents how these factors influence population density:
Nt+1 = Nt + [(Natality + Immigration) - (Mortality + Emigration)].
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for studies in ecology and population biology, especially in the context of NEET.
Population density at any given time is influenced by various factors such as births, deaths, immigration, and emigration. The equation provided,
Nt+1 = Nt + [(A + B) - (C + D)],
helps in understanding how these factors affect population density over time.
Key Terminology Explained
- A (Natality): Refers to the birth rate in the population. An increase in natality contributes positively to population density.
- B (Immigration): This is the influx of individuals into a population from other areas. Immigration increases population density.
- C (Mortality): This term represents the death rate. An increase in mortality leads to a decrease in population density.
- D (Emigration): Emigration is the movement of individuals out of a population. Like mortality, it reduces population density.
Analyzing the Correct Option
The equation states that the population density at time t+1 is equal to the density at time t plus the net change from births and immigration, minus deaths and emigration.
- In this context, if we assign:
- A = Natality (births)
- B = Immigration (influx)
- C = Mortality (deaths)
- D = Emigration (outflux)
This fits perfectly into the equation as it correctly reflects the contributions of each factor to population density changes over time.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', where A is natality and D is emigration, as it accurately represents how these factors influence population density:
Nt+1 = Nt + [(Natality + Immigration) - (Mortality + Emigration)].
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for studies in ecology and population biology, especially in the context of NEET.
Statement I: Age pyramid of expanding population is broader at base and thin upwards.
Statement II: Number of individuals in pre-reproductive age is more than post reproductive age.
Statement III: population size is technically called as population density.- a)Only statement II and III are correct.
- b)Only statement I and II are correct.
- c)All statements are correct.
- d)All statements are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I: Age pyramid of expanding population is broader at base and thin upwards.
Statement II: Number of individuals in pre-reproductive age is more than post reproductive age.
Statement III: population size is technically called as population density.
Statement II: Number of individuals in pre-reproductive age is more than post reproductive age.
Statement III: population size is technically called as population density.
a)
Only statement II and III are correct.
b)
Only statement I and II are correct.
c)
All statements are correct.
d)
All statements are incorrect.

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
Age pyramid of expanding population is broader at base and thin upwards. Number of individuals in pre-reproductive age is more than post reproductive age. Population size is technically called as population density.
Which growth pattern occurs when resources become progressively limiting in a population?- a)Logistic growth
- b)Exponential growth
- c)Constant growth
- d)Declining growth
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which growth pattern occurs when resources become progressively limiting in a population?
a)
Logistic growth
b)
Exponential growth
c)
Constant growth
d)
Declining growth
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Populations grow through births and immigration and decline through deaths and emigration.
When resources become progressively limiting for a population, the growth pattern turns logistic. This means that initially, the population may experience exponential growth when resources are abundant and unlimited.
However, as resources start to become scarce and limiting, the growth rate of the population slows down and eventually levels off. This pattern is known as logistic growth.
- Exponential growth (option b) refers to a rapid and unrestricted increase in population size without resource limitations.
- Constant growth (option c) implies a steady and consistent growth rate over time, regardless of resource availability.
- Declining growth (option d) suggests a decrease in population size over time, often due to factors like limited resources or environmental disturbances.
Which of the following is not an attribute of a population? [2020]- a)Mortality
- b)Species interaction
- c)Sex ratio
- d)Natality
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an attribute of a population? [2020]
a)
Mortality
b)
Species interaction
c)
Sex ratio
d)
Natality
|
|
Hrishikesh Rane answered |
Attributes of a Population:
A population is a group of individuals of the same species occupying a particular geographical area. The attributes of a population are:
1. Mortality: The death rate of a population is an important attribute. It is the number of deaths per unit time in a population.
2. Natality: The birth rate of a population is the number of individuals born per unit time in a population. It is an important attribute that determines the growth of a population.
3. Sex ratio: The proportion of males and females in a population is an important attribute. It affects the breeding patterns and reproductive success of a population.
4. Age structure: The proportion of individuals of different age groups in a population is an important attribute. It affects the growth rate and survival of a population.
5. Density: The number of individuals per unit area is an important attribute. It affects the resource availability and competition for resources.
6. Distribution: The spatial arrangement of individuals in a population is an important attribute. It affects the interactions between individuals and their environment.
Explanation:
Species interaction is not an attribute of a population because it involves the interactions between different species, not just individuals of the same species in a population. Population attributes are specific to a particular species occupying a particular geographical area.
A population is a group of individuals of the same species occupying a particular geographical area. The attributes of a population are:
1. Mortality: The death rate of a population is an important attribute. It is the number of deaths per unit time in a population.
2. Natality: The birth rate of a population is the number of individuals born per unit time in a population. It is an important attribute that determines the growth of a population.
3. Sex ratio: The proportion of males and females in a population is an important attribute. It affects the breeding patterns and reproductive success of a population.
4. Age structure: The proportion of individuals of different age groups in a population is an important attribute. It affects the growth rate and survival of a population.
5. Density: The number of individuals per unit area is an important attribute. It affects the resource availability and competition for resources.
6. Distribution: The spatial arrangement of individuals in a population is an important attribute. It affects the interactions between individuals and their environment.
Explanation:
Species interaction is not an attribute of a population because it involves the interactions between different species, not just individuals of the same species in a population. Population attributes are specific to a particular species occupying a particular geographical area.
Which of the following adaptations are examples of plant defenses against herbivores?- a)Thorns on Acacia trees.
- b)High reproductive rate of a parasitic plant.
- c)Chemical production in Calotropis that harms herbivores.
- d)Camouflage in insects like the Monarch butterfly.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Thorns on Acacia trees.
b)
High reproductive rate of a parasitic plant.
c)
Chemical production in Calotropis that harms herbivores.
d)
Camouflage in insects like the Monarch butterfly.

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Thorns on Acacia trees (A) and chemical production in Calotropis (C) are direct plant defenses against herbivores. The other options do not describe plant adaptations.
Topic in NCERT: Defenses Against Herbivory
Line in NCERT: "Plants therefore have evolved an astonishing variety of morphological and chemical defences against herbivores. Thorns (Acacia, Cactus) are the most common morphological means of defence. Many plants produce and store chemicals that make the herbivore sick when they are eaten, inhibit feeding or digestion, disrupt its reproduction or even kill it."
What does the carrying capacity (K) of a habitat refer to?- a)The maximum growth rate a population can achieve
- b)The maximum number of individuals an environment can support
- c)The rate of immigration into a population
- d)The total biomass of a population
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The maximum growth rate a population can achieve
b)
The maximum number of individuals an environment can support
c)
The rate of immigration into a population
d)
The total biomass of a population

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Carrying capacity (K) refers to the maximum number of individuals a habitat can support given the available resources. Beyond this limit, the population will stop growing or may even decline due to resource depletion.
Topic in NCERT: Carrying Capacity
Line in NCERT: "In nature, a given habitat has enough resources to support a maximum possible number, beyond which no further growth is possible. Let us call this limit as nature's carrying capacity (K) for that species in that habitat."
Which of the following is not a factor that would limit the growth of a population ?- a)Food shortage
- b)Immigration
- c)Disease
- d)Famine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a factor that would limit the growth of a population ?
a)
Food shortage
b)
Immigration
c)
Disease
d)
Famine
|
|
Kirti Khanna answered |
Introduction:
The growth of a population is influenced by various factors. While some factors can limit population growth, others can promote it. This question asks which of the given options is not a factor that would limit population growth.
Explanation:
Immigration:
Immigration refers to the movement of individuals into a population from another area. It can contribute to an increase in the population size and counteract the limiting factors. When individuals immigrate into a population, they bring their genetic diversity, which can help the population adapt to changing environments and increase its resilience. Immigration can also introduce new individuals that may increase the available workforce, stimulate economic growth, and contribute to the overall development of the population. Therefore, immigration does not limit population growth but rather facilitates it.
Food Shortage:
Food shortage is a significant limiting factor for population growth. When there is a scarcity of food resources in a population, individuals may struggle to obtain adequate nutrition for survival and reproduction. This can lead to decreased birth rates, increased mortality rates, and overall population decline. Food shortage can be caused by various factors such as environmental changes, overexploitation of resources, or competition among individuals within the population. It is a crucial factor that can limit the carrying capacity of an ecosystem and, consequently, the growth of the population.
Disease:
Diseases can exert a significant impact on population growth. When a population is affected by diseases, it can lead to increased mortality rates and decreased reproductive success. Infectious diseases, for example, can spread rapidly within a population and cause widespread illness and death. This can result in a decrease in population size and limit population growth. Additionally, diseases can also affect the health and well-being of individuals, leading to reduced fertility and birth rates. Therefore, disease is a limiting factor for population growth.
Famine:
Famine refers to a widespread scarcity of food in a population, often caused by factors such as drought, crop failure, or political instability. Like food shortage, famine can lead to a lack of adequate nutrition, increased mortality rates, and reduced reproductive success. It can have severe consequences on population growth, causing population decline and impacting the overall health and survival of individuals. Therefore, famine is a limiting factor for population growth.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, immigration is not a factor that would limit the growth of a population. On the contrary, immigration can contribute to population growth by introducing new individuals, genetic diversity, and enhancing the workforce and overall development of the population.
The growth of a population is influenced by various factors. While some factors can limit population growth, others can promote it. This question asks which of the given options is not a factor that would limit population growth.
Explanation:
Immigration:
Immigration refers to the movement of individuals into a population from another area. It can contribute to an increase in the population size and counteract the limiting factors. When individuals immigrate into a population, they bring their genetic diversity, which can help the population adapt to changing environments and increase its resilience. Immigration can also introduce new individuals that may increase the available workforce, stimulate economic growth, and contribute to the overall development of the population. Therefore, immigration does not limit population growth but rather facilitates it.
Food Shortage:
Food shortage is a significant limiting factor for population growth. When there is a scarcity of food resources in a population, individuals may struggle to obtain adequate nutrition for survival and reproduction. This can lead to decreased birth rates, increased mortality rates, and overall population decline. Food shortage can be caused by various factors such as environmental changes, overexploitation of resources, or competition among individuals within the population. It is a crucial factor that can limit the carrying capacity of an ecosystem and, consequently, the growth of the population.
Disease:
Diseases can exert a significant impact on population growth. When a population is affected by diseases, it can lead to increased mortality rates and decreased reproductive success. Infectious diseases, for example, can spread rapidly within a population and cause widespread illness and death. This can result in a decrease in population size and limit population growth. Additionally, diseases can also affect the health and well-being of individuals, leading to reduced fertility and birth rates. Therefore, disease is a limiting factor for population growth.
Famine:
Famine refers to a widespread scarcity of food in a population, often caused by factors such as drought, crop failure, or political instability. Like food shortage, famine can lead to a lack of adequate nutrition, increased mortality rates, and reduced reproductive success. It can have severe consequences on population growth, causing population decline and impacting the overall health and survival of individuals. Therefore, famine is a limiting factor for population growth.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, immigration is not a factor that would limit the growth of a population. On the contrary, immigration can contribute to population growth by introducing new individuals, genetic diversity, and enhancing the workforce and overall development of the population.
Mediterranean orchid Ophrysensures pollination by :- a)Pseudocopulation only
- b)Sexual deceit and co-evolution
- c)Brood parasitism
- d)Co-evolution, sexual deceit and pseudo-copulation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mediterranean orchid Ophrysensures pollination by :
a)
Pseudocopulation only
b)
Sexual deceit and co-evolution
c)
Brood parasitism
d)
Co-evolution, sexual deceit and pseudo-copulation

|
Yash Saha answered |
Mediterranean orchid Ophrys ensures pollination by co-evolution, sexual deceit and pseudo-copulation. One petal of flower bears an uncanny resemblance to female of bee in size, colour and markings.
It can be said that some animals in their evolutionary development preferred to be conformers than regulators. Which of the following can be the best suited reason for it?- a)The metabolic reactions of these organisms can occur at a very wide range of temperature
- b)Maintaining homeostasis is an energetically expensive process
- c)The enzymes of these organisms are functional at high temperatures
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
It can be said that some animals in their evolutionary development preferred to be conformers than regulators. Which of the following can be the best suited reason for it?
a)
The metabolic reactions of these organisms can occur at a very wide range of temperature
b)
Maintaining homeostasis is an energetically expensive process
c)
The enzymes of these organisms are functional at high temperatures
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Maintainig homeostasis, especially thermoregulation is energetically expensive for many organisms. During the course of evolution, the costs and benefits of maintaining a constant internal environment were taken into consideration and thus some species preferred to be conformers.
Chapter doubts & questions for Population Dynamics - Biology for Grade 12 2025 is part of Grade 12 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 12 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Population Dynamics - Biology for Grade 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 12 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 12
97 videos|151 docs|108 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily













