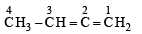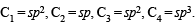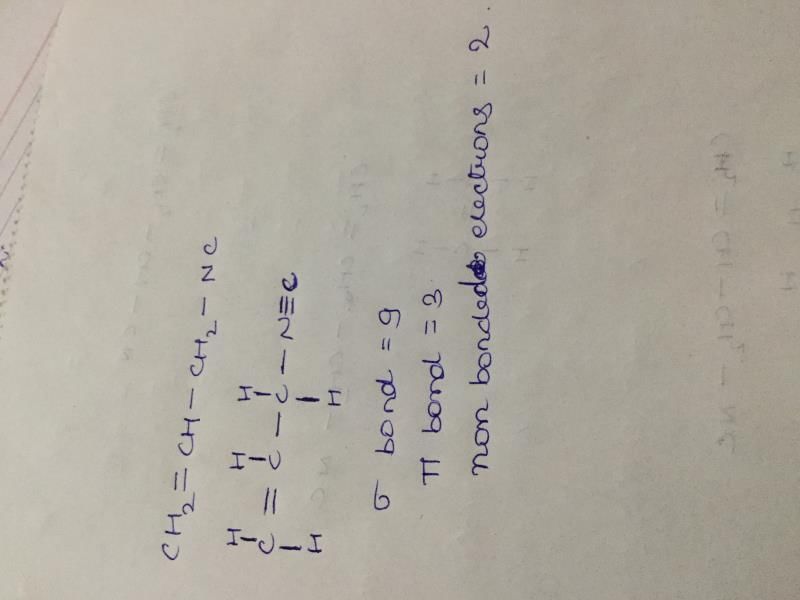All Exams >
JEE >
Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of General Organic Chemistry (GOC) for JEE Exam
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar - a)The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
- b)In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
- c)In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
- d)The most stable conformer is non-polar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a)
The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b)
In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c)
In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d)
The most stable conformer is non-polar
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option D
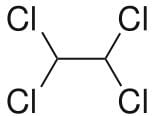
This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°

This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°
Pick the odd one out:- a)Napthalene
- b)Sodium chloride
- c)Ammonium chloride
- d)Camphor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick the odd one out:
a)
Napthalene
b)
Sodium chloride
c)
Ammonium chloride
d)
Camphor

|
Shrikrushna Mali answered |
Other 3 are sublimating substance except NaCl
The organic compound given below is one of the four options given below. Choose the most appropriate one. 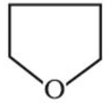
- a)aromatic heteroyclic compound
- b)aliphatic heteroyclic compound
- c)alicyclic compound
- d)ring compound
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The organic compound given below is one of the four options given below. Choose the most appropriate one.
a)
aromatic heteroyclic compound
b)
aliphatic heteroyclic compound
c)
alicyclic compound
d)
ring compound

|
Rohit Joshi answered |
this is aliphatic heterocyclic compound.
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds;CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH2COOH- a)1 > 2 > 3
- b)3 > 1 > 2
- c)1 > 3 > 2
- d)3 > 2 > 1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds;
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH2COOH
a)
1 > 2 > 3
b)
3 > 1 > 2
c)
1 > 3 > 2
d)
3 > 2 > 1

|
Ishita Reddy answered |
In car boxylic acids, molecules ar e more str ongly associated followed by alcohols.
The compound which is not isomeric with diethyl ether is - a)n-propyl methyl ether
- b)butan-1-ol
- c)2-methylpropan-2-ol
- d)butan on e
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which is not isomeric with diethyl ether is
a)
n-propyl methyl ether
b)
butan-1-ol
c)
2-methylpropan-2-ol
d)
butan on e
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The first three are isomers of diethyl ether, C2H5OC2H5 (C4H10O).
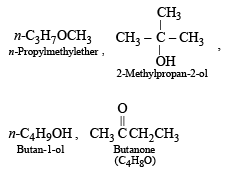
Write the state of hybridisation of carbon in H2C=O.- a)sp3 hybridised carbon, trigonal
- b)sp2 hybridised carbon, trigonal planar
- c)sp3 hybridised carbon, tetrahedral
- d)sp hybridised carbon, linear
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Write the state of hybridisation of carbon in H2C=O.
a)
sp3 hybridised carbon, trigonal
b)
sp2 hybridised carbon, trigonal planar
c)
sp3 hybridised carbon, tetrahedral
d)
sp hybridised carbon, linear
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
C in H2C=O is sp2 hybridised and geometry is planar.
Among the following, the molecule with the highest dipole moment is:- a)CH3Cl
- b)CH2Cl2
- c)CHCl3
- d)CCl4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the molecule with the highest dipole moment is:
a)
CH3Cl
b)
CH2Cl2
c)
CHCl3
d)
CCl4
|
|
Nandita Chopra answered |
NOTE : Dipole moment is a vector quantity.
Methane molecule being symmetrical, has zero dipole moment. Replacement of one of the H– atoms by Cl atom increases the dipole moment. The increase in dipole moment is rather more than what can be expected because of the fact that the bond dipole moment of C – H bond and that of C – Cl bond reinforce one another.
Replacement of another H atom by Cl increases the bond angle due to lone pair – lone pair repulsion between two Cl–atoms thereby reducing the dipole moment of the molecule. Increase in angle is again caused by the the introduction of the third Cl–atom.
When the fourth Cl–atom is introduced, the molecule (CCl4) again becomes symmetrical and dipole moment reduces to zero. So, CH3Cl will have the maximum dipole moment.
Methane molecule being symmetrical, has zero dipole moment. Replacement of one of the H– atoms by Cl atom increases the dipole moment. The increase in dipole moment is rather more than what can be expected because of the fact that the bond dipole moment of C – H bond and that of C – Cl bond reinforce one another.
Replacement of another H atom by Cl increases the bond angle due to lone pair – lone pair repulsion between two Cl–atoms thereby reducing the dipole moment of the molecule. Increase in angle is again caused by the the introduction of the third Cl–atom.
When the fourth Cl–atom is introduced, the molecule (CCl4) again becomes symmetrical and dipole moment reduces to zero. So, CH3Cl will have the maximum dipole moment.
Nitration of benzene is:- a)Free radical substitution reaction
- b)Nucleophilic addition reaction
- c)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)Electrophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitration of benzene is:
a)
Free radical substitution reaction
b)
Nucleophilic addition reaction
c)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
d)
Electrophilic substitution reaction
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Nitration and sulfonation of benzene are two examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution. The nitronium ion (NO2+) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) are the electrophiles and individually react with benzene to give nitrobenzene and benzenesulfonic acid respectively.
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name?
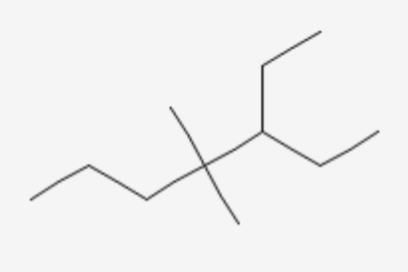
- a)5-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
- b)4, 4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
- c)3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
- d)4, 4-Bis(methyl)-3-ethylheptane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name?


a)
5-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
b)
4, 4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
c)
3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane
d)
4, 4-Bis(methyl)-3-ethylheptane
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
While writing IUPAC name, the alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order. Thus lower locant 3 is assigned to ethyl. Prefix, di, tri, and tetra are not included in alphabetical order.
Statement -1: Phenol is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution reactions.Statement-2:In the case of phenol, the intermediate carbocation is more resonance stabilized.- a)If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, and Statement -2 is the correct explanation of the Statement -2.
- b)If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, but Statement -2 is not the cor rect explanation of the Statement -1.
- c)If Statement -1 is correct but Statement -2 is incorrect.
- d)If Statement -1 is incorrect but Statement -2 is correct.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement -1: Phenol is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution reactions.
Statement-2:In the case of phenol, the intermediate carbocation is more resonance stabilized.
a)
If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, and Statement -2 is the correct explanation of the Statement -2.
b)
If both Statement -1 and Statement -2 are correct, but Statement -2 is not the cor rect explanation of the Statement -1.
c)
If Statement -1 is correct but Statement -2 is incorrect.
d)
If Statement -1 is incorrect but Statement -2 is correct.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
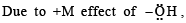 its in termediate carbocation is more stable than the one in benzene.
its in termediate carbocation is more stable than the one in benzene.Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)- a)Naphthalene
- b)Aniline
- c)Pyridine
- d)Tropolone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)
a)
Naphthalene
b)
Aniline
c)
Pyridine
d)
Tropolone

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Pyridine is heterocyclic aromatic compound. Whereas naphthalene and aniline are benzenoid aromatic compounds and tropolone is a non-benzenoid aromatic compound.
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by:- a)Distillation
- b)Chromatography
- c)Crystallisation
- d)Sublimation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by:
a)
Distillation
b)
Chromatography
c)
Crystallisation
d)
Sublimation
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by Sublimation.
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
- a)alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
- b)Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
- c)Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
- d)Open chain compounds and closed compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
a)
alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
b)
Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
c)
Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
d)
Open chain compounds and closed compounds

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option D
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?- a)Theoretically infinite conformers exist
- b)Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
- c)Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
- d)By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?
a)
Theoretically infinite conformers exist
b)
Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
c)
Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
d)
By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
The IUPAC name of C6H5COCl is- a)Benzene chloro ketone
- b)Benzoyl chloride
- c)Chloro phenyl ketone
- d)Benzene carbonyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of C6H5COCl is
a)
Benzene chloro ketone
b)
Benzoyl chloride
c)
Chloro phenyl ketone
d)
Benzene carbonyl chloride
|
|
Nikhil Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
The IUPAC name of the compound C6H5COCl is benzoyl chloride.
Reasoning:
To determine the IUPAC name of a compound, we need to follow the guidelines provided by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Let's break down the name and analyze it:
- The compound contains a benzene ring, which is represented by the prefix "benzene" in the name.
- The functional group attached to the benzene ring is a carbonyl group (-CO-), which is represented by the suffix "oyl" in the name.
- The carbonyl group is attached to a chlorine atom, which is represented by the prefix "chloride" in the name.
Putting it all together, we have "benzoyl chloride" as the IUPAC name for the compound C6H5COCl.
Summary:
The IUPAC name of the compound C6H5COCl is benzoyl chloride. The name is derived from the presence of a benzene ring and a carbonyl group attached to a chlorine atom.
The IUPAC name of the compound C6H5COCl is benzoyl chloride.
Reasoning:
To determine the IUPAC name of a compound, we need to follow the guidelines provided by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Let's break down the name and analyze it:
- The compound contains a benzene ring, which is represented by the prefix "benzene" in the name.
- The functional group attached to the benzene ring is a carbonyl group (-CO-), which is represented by the suffix "oyl" in the name.
- The carbonyl group is attached to a chlorine atom, which is represented by the prefix "chloride" in the name.
Putting it all together, we have "benzoyl chloride" as the IUPAC name for the compound C6H5COCl.
Summary:
The IUPAC name of the compound C6H5COCl is benzoyl chloride. The name is derived from the presence of a benzene ring and a carbonyl group attached to a chlorine atom.
In Carius method of estimation of halogens, 250 mg of an organic compound gave 141 mg of AgBr. The percentage of bromine in the compound is :(at. mass Ag =108; Br = 80)- a)48
- b)60
- c)24
- d)36
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Carius method of estimation of halogens, 250 mg of an organic compound gave 141 mg of AgBr. The percentage of bromine in the compound is :
(at. mass Ag =108; Br = 80)
a)
48
b)
60
c)
24
d)
36
|
|
Harsh Singhal answered |
First we have to find moles of br in rex. as 141/188
now mass of br in compound is 141*80/188
so %br=141*80*100/188*250=24
now mass of br in compound is 141*80/188
so %br=141*80*100/188*250=24
In the given conformation, if C2 is rotated about C2 – C3 bond anticlockwise by an angle of 120º then the conformation obtained is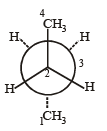
- a)fully eclipsed conformation
- b)partially eclipsed conformation
- c)gauche conformation
- d)staggered conformation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given conformation, if C2 is rotated about C2 – C3 bond anticlockwise by an angle of 120º then the conformation obtained is

a)
fully eclipsed conformation
b)
partially eclipsed conformation
c)
gauche conformation
d)
staggered conformation
|
|
Anand Kumar answered |
Option C is correct.
once go through some examples of gauche isomers.
once go through some examples of gauche isomers.
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is :- a)
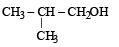
- b)
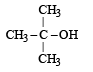
- c)
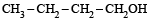
- d)
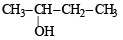
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is :
a)
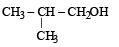
b)

c)
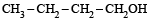
d)
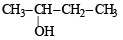
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
NOTE : The order of stability of carbonium ion is
tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl
Tertiary carbonium ions (formed in b) are more stable because of electron repelling (+I effect) nature of CH3 group due to which the +ve charge gets dispersed and also due to hyperconjugation.
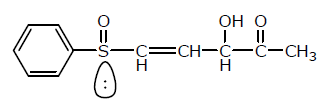 Number of chiral centers are:
Number of chiral centers are:- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of chiral centers are:
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Number of chiral centers = 2
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group? - a)Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
- b)Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
- c)Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
- d)Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group?
a)
Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
b)
Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
c)
Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
d)
Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
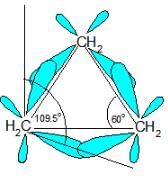
The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.

The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.
Process of separation of mixtures into their components and to purify the compounds by using adsorption is known as:- a)Sublimation
- b)Differential extraction
- c)Distillation
- d)Chromatography
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Process of separation of mixtures into their components and to purify the compounds by using adsorption is known as:
a)
Sublimation
b)
Differential extraction
c)
Distillation
d)
Chromatography
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Chromatography is an important separation technique used to separate constituent particles of a mixture of substances, to purify the compounds and check the purity of organic compounds. In this technique on a stationary phase (solid or a liquid) a mixture of substances is applied. The mixture of gas or the pure solvent is allowed to move slowly on the stationary phase. Due to which the components of the mixture start separating from one another.
Chromatography is an important separation technique used to separate constituent particles of a mixture of substances, to purify the compounds and check the purity of organic compounds. In this technique on a stationary phase (solid or a liquid) a mixture of substances is applied. The mixture of gas or the pure solvent is allowed to move slowly on the stationary phase. Due to which the components of the mixture start separating from one another.
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?- a)Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
- b)Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
- c)Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
- d)Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?
a)
Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
b)
Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
c)
Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
d)
Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Correct answer is option D
Chair >Twist boat > Boat > Half-chair
above is the stability order of
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
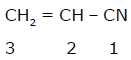 C1 - C2 bond of this molecules is formed by:
C1 - C2 bond of this molecules is formed by:- a)sp3-sp2 overlap
- b)sp2-sp3 overlap
- c)sp2-sp overlap
- d)sp2-sp2 overlap
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
C1 - C2 bond of this molecules is formed by:
a)
sp3-sp2 overlap
b)
sp2-sp3 overlap
c)
sp2-sp overlap
d)
sp2-sp2 overlap

|
Snehal answered |
I draw Actual structure For U=> CH2 = CH-C=_ N u can see between C & N there are three bonds (1 sigma & 2 π bonds) NOTE FOR U ==>
(1) if carbon is singly bonded only then sp^3 hybridisation
(2) if there is one π bond only then sp^2 hybridisation
(3) if there is 2 π bonds then there is sp hybridisation ________ So now u use this given information and conclude answer by ur own self
😄😄😄😃
Aliphatic compound is the other name for- a)Acyclic compounds
- b)Alicyclic compounds
- c)Ring compounds
- d)Closed chain compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aliphatic compound is the other name for
a)
Acyclic compounds
b)
Alicyclic compounds
c)
Ring compounds
d)
Closed chain compounds

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
During estimation of nitrogen present in an organic compound by Kjeldahl’s method, the ammonia evolved from 0.5 g of the compound, neutralized 10 mL of 1 M H2SO4.Find out the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.- a)56 %
- b)51%
- c) 46%
- d) 2 %
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During estimation of nitrogen present in an organic compound by Kjeldahl’s method, the ammonia evolved from 0.5 g of the compound, neutralized 10 mL of 1 M H2SO4.Find out the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.
a)
56 %
b)
51%
c)
46%
d)
2 %

|
Jay Chakraborty answered |
moles of NH3= moles of N= 2 × 10 ×1/1000 = 0.02 moles Mass of N = 0.02 × 14 % = 0.02 x 14 × 100/0.5 = 56%
The number of isomers of C6H14 is - a)4
- b)5
- c)6
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of isomers of C6H14 is
a)
4
b)
5
c)
6
d)
7
|
|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
1) N-hexane
2)2 ,Methyl pentane
3)2,2 dimethyl butane
4)2,3 dimethyl butane
5)3 methyl pentane
In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is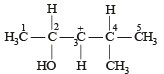
- a)CH3 at C-4
- b)H at C-4
- c)CH3 at C-2
- d)H at C-2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is

a)
CH3 at C-4
b)
H at C-4
c)
CH3 at C-2
d)
H at C-2
|
|
Akash Kumar answered |
As we know that the migratory aptitude of H-ion is more than CH3- ion.And we always have to form the most stable carbocation in case of rearrangement. Hence if we remove H-Ion form C4 linkage we will gate a +ve charge in the vicinity of a lone pair which is very stable due to back bonding.So option D is correct.
I hope u get it.
Among the following, the compound that can be most readily sulphonated is- a)benzene
- b)nitrobenzene
- c)toluene
- d)chlorobenzene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the compound that can be most readily sulphonated is
a)
benzene
b)
nitrobenzene
c)
toluene
d)
chlorobenzene

|
Sagar Mukherjee answered |
TIPS/FORMULAE :
–NO2, –Cl and –OH are electron-attracting or withdrawing group due to –M, –E and/or –I effects where as –CH3 show, +I effect (electron releasing).
Because of the + I effect of the CH3 group, toluene has the highest electron density in the o- and p- positions and hence can be most readily sulphonated.
Because of the + I effect of the CH3 group, toluene has the highest electron density in the o- and p- positions and hence can be most readily sulphonated.
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group- a)Isocyanide
- b)Isocyano
- c)Carboxyl
- d)Carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
a)
Isocyanide
b)
Isocyano
c)
Carboxyl
d)
Carbonyl

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Isocyanide is a compound and it is not a functional group.
Which of the following structures represents a chiral compound ?- a)
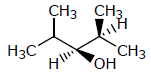
- b)
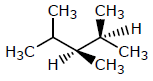
- c)
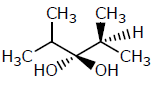
- d)
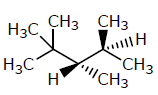
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structures represents a chiral compound ?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
All four substituent are different so it is chiral compound.
The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is:- a)2- methyl propene
- b)2-butene
- c)2- methyl -2- butene
- d)pr open e
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The alkene that exhibits geometrical isomerism is:
a)
2- methyl propene
b)
2-butene
c)
2- methyl -2- butene
d)
pr open e

|
Sahana Joshi answered |
Correct answer is option (B) : 2-butene
When two groups attached to a double bonded carbon atom are same, the compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Compounds in which the two groups attached to a double bonded carbon are different, exhibit geometrical isomerism, thus, only 2-butene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
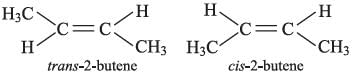
When two groups attached to a double bonded carbon atom are same, the compound does not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Compounds in which the two groups attached to a double bonded carbon are different, exhibit geometrical isomerism, thus, only 2-butene exhibits cis-trans isomerism.
The Cl—C—Cl angle in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about - a)120º and 109.5º
- b)90º and 109.5º
- c)109.5º and 90º
- d)109.5º and 120º
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Cl—C—Cl angle in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about
a)
120º and 109.5º
b)
90º and 109.5º
c)
109.5º and 90º
d)
109.5º and 120º
|
|
Jyoti Tiwari answered |
The Cl is a fictional character and also the main antagonist in the novel and film adaptation of "Gone Girl" by Gillian Flynn. The Cl, short for "Cool Girl," is a term used to describe a woman who is low-maintenance, easygoing, and effortlessly attractive. In the story, the Cl is the alter ego of the protagonist, Amy Dunne. Amy invents the persona of the Cl to please her husband, Nick, and mold herself into the perfect wife. However, as the story unfolds, it is revealed that the Cl is a facade and Amy is actually a manipulative and calculating individual. The Cl represents the societal pressures on women to conform to a specific ideal and the consequences of trying to live up to those expectations.
This apparatus provides many surfaces for heat exchange between the ascending vapours and the descending condensed liquid.
- a)Round bottom flask
- b)Pipette
- c)Burette
- d)Fractionating column
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
This apparatus provides many surfaces for heat exchange between the ascending vapours and the descending condensed liquid.
a)
Round bottom flask
b)
Pipette
c)
Burette
d)
Fractionating column
|
|
Anand Kapoor answered |
**Explanation:**
The correct answer is option D, the fractionating column. Let's break down the explanation:
**1. Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus mentioned in the question is designed to facilitate heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid. Heat exchange is an essential process that occurs in various applications, such as distillation, where it helps in separating mixtures based on differences in boiling points.
**2. Surfaces for Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus should provide multiple surfaces or stages where heat exchange can occur. This means that the ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid should come into close contact with each other, allowing thermal energy transfer.
**3. Round Bottom Flask, Pipette, and Burette:**
The options A (round bottom flask), B (pipette), and C (burette) do not meet the criteria for providing multiple surfaces for heat exchange. Let's briefly explain why:
- **Round Bottom Flask (Option A):** A round bottom flask is a commonly used laboratory glassware that is primarily used for holding liquids and conducting chemical reactions. It does not provide multiple surfaces for heat exchange as required in the question.
- **Pipette (Option B):** A pipette is a laboratory tool used for accurately measuring and transferring small volumes of liquids. It is not designed for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
- **Burette (Option C):** A burette is a long, graduated glass tube with a stopcock at the bottom. It is commonly used in titrations for precise volume measurements but does not provide the required surfaces for heat exchange.
**4. Fractionating Column (Option D):**
The fractionating column is a specially designed apparatus used in distillation processes to achieve separation of liquid mixtures based on differences in boiling points. It consists of multiple stages or trays, providing numerous surfaces for heat exchange.
- **Heat Exchange in the Fractionating Column:** As the vapor rises through the fractionating column, it comes into contact with the descending condensed liquid. Heat is exchanged between the ascending vapors and the descending liquid, allowing the separation of components with different boiling points.
- **Multiple Surfaces for Heat Exchange:** The fractionating column contains several trays or stages, each acting as a surface for heat exchange. The vapors and condensed liquid interact on these trays, promoting efficient heat transfer between the two phases.
Therefore, the fractionating column is the apparatus that best fits the description provided in the question, offering multiple surfaces for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
The correct answer is option D, the fractionating column. Let's break down the explanation:
**1. Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus mentioned in the question is designed to facilitate heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid. Heat exchange is an essential process that occurs in various applications, such as distillation, where it helps in separating mixtures based on differences in boiling points.
**2. Surfaces for Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus should provide multiple surfaces or stages where heat exchange can occur. This means that the ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid should come into close contact with each other, allowing thermal energy transfer.
**3. Round Bottom Flask, Pipette, and Burette:**
The options A (round bottom flask), B (pipette), and C (burette) do not meet the criteria for providing multiple surfaces for heat exchange. Let's briefly explain why:
- **Round Bottom Flask (Option A):** A round bottom flask is a commonly used laboratory glassware that is primarily used for holding liquids and conducting chemical reactions. It does not provide multiple surfaces for heat exchange as required in the question.
- **Pipette (Option B):** A pipette is a laboratory tool used for accurately measuring and transferring small volumes of liquids. It is not designed for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
- **Burette (Option C):** A burette is a long, graduated glass tube with a stopcock at the bottom. It is commonly used in titrations for precise volume measurements but does not provide the required surfaces for heat exchange.
**4. Fractionating Column (Option D):**
The fractionating column is a specially designed apparatus used in distillation processes to achieve separation of liquid mixtures based on differences in boiling points. It consists of multiple stages or trays, providing numerous surfaces for heat exchange.
- **Heat Exchange in the Fractionating Column:** As the vapor rises through the fractionating column, it comes into contact with the descending condensed liquid. Heat is exchanged between the ascending vapors and the descending liquid, allowing the separation of components with different boiling points.
- **Multiple Surfaces for Heat Exchange:** The fractionating column contains several trays or stages, each acting as a surface for heat exchange. The vapors and condensed liquid interact on these trays, promoting efficient heat transfer between the two phases.
Therefore, the fractionating column is the apparatus that best fits the description provided in the question, offering multiple surfaces for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
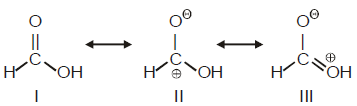 Among these canonical structures, the correct order of stability is
Among these canonical structures, the correct order of stability is- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I
- c)I > III > II
- d)II > I > III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among these canonical structures, the correct order of stability is
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I
c)
I > III > II
d)
II > I > III

|
Armaan Sharma answered |
In structure no 1 no charge is present.in third one positive charge is on "OH" which sjows negative I effect and also "O" atom is more electronegative than C so 3rd is more stable than 2
Rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is:- a)Br2> I2>F2>Cl2
- b)Cl2> Br2> I2>F2
- c)F2>Cl2> Br2> I2
- d)Cl2> Br2>F2> I2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is:
a)
Br2> I2>F2>Cl2
b)
Cl2> Br2> I2>F2
c)
F2>Cl2> Br2> I2
d)
Cl2> Br2>F2> I2
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option C
The reactivity of the halogens decreases in the following order: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
fluorine is so explosively reactive it is difficult to control, and iodine is generally unreactive. Chlorination and bromination are normally exothermic.
The reactivity of the halogens decreases in the following order: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
fluorine is so explosively reactive it is difficult to control, and iodine is generally unreactive. Chlorination and bromination are normally exothermic.
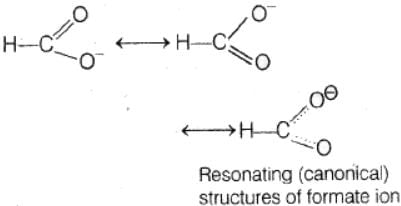
In the anion HCOO– the two carbon-oxygen bonds are found to be of equal length. what is the reason for it ?
- a)The C = O bond is weaker than the C — O bond
- b)The anion is obtained by removal of a proton from the acid molecule
- c)Electronic orbitals of carbon atom are hybridised
- d)The anion HCOO– has two resonating structures
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the anion HCOO– the two carbon-oxygen bonds are found to be of equal length. what is the reason for it ?
a)
The C = O bond is weaker than the C — O bond
b)
The anion is obtained by removal of a proton from the acid molecule
c)
Electronic orbitals of carbon atom are hybridised
d)
The anion HCOO– has two resonating structures

|
Nandita Basak answered |
The anion HCOO− has two resonating structures in which double bond occurs on both xygen atoms. So, the bond length of both the CO bonds is equal.

Addition of dihydrogen to propyne forms:- a)Ethanal
- b)Carbocation
- c)Propene
- d)carbanion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Addition of dihydrogen to propyne forms:
a)
Ethanal
b)
Carbocation
c)
Propene
d)
carbanion
|
|
Ashish Roy answered |
The addition of dihydrogen to propyne is a type of hydrogenation reaction, where the double bond in propyne is broken and replaced with two hydrogen atoms. This leads to the formation of a new compound, propene.
Explanation:
Propyne has the chemical formula C3H4, containing a triple bond between the second and third carbon atoms. When dihydrogen (H2) is added to propyne, it reacts with the triple bond and leads to the formation of a new compound, propene (C3H6). The reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
C3H4 + H2 → C3H6
This reaction is an example of an addition reaction, where the reactants combine to form a single product. The addition of dihydrogen to propyne breaks the triple bond between the carbon atoms and forms a single bond between them. The remaining carbon-carbon double bond in propene is more stable than the triple bond in propyne, making it a more favorable product.
Option (C) is the correct answer, as propene is the product formed when dihydrogen is added to propyne.
In summary, the addition of dihydrogen to propyne leads to the formation of propene, where the triple bond in propyne is broken and replaced with a carbon-carbon double bond.
Explanation:
Propyne has the chemical formula C3H4, containing a triple bond between the second and third carbon atoms. When dihydrogen (H2) is added to propyne, it reacts with the triple bond and leads to the formation of a new compound, propene (C3H6). The reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
C3H4 + H2 → C3H6
This reaction is an example of an addition reaction, where the reactants combine to form a single product. The addition of dihydrogen to propyne breaks the triple bond between the carbon atoms and forms a single bond between them. The remaining carbon-carbon double bond in propene is more stable than the triple bond in propyne, making it a more favorable product.
Option (C) is the correct answer, as propene is the product formed when dihydrogen is added to propyne.
In summary, the addition of dihydrogen to propyne leads to the formation of propene, where the triple bond in propyne is broken and replaced with a carbon-carbon double bond.
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?- a)Alcohols
- b)Aldehydes
- c)Alkyl halides
- d)Cyanides
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?
a)
Alcohols
b)
Aldehydes
c)
Alkyl halides
d)
Cyanides

|
Naina Menon answered |
Alkyl halides do not show functional isomerism. Alcohols and ethers, aldehydes and ketones, cyanides and isocyanides are functional isomers.
Identify the odd one among the following- a)Indene
- b)Anthracene
- c)o,m,p-xylene
- d)Azulene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the odd one among the following
a)
Indene
b)
Anthracene
c)
o,m,p-xylene
d)
Azulene

|
Saumya Ahuja answered |
Azulene is a non- benzenoid compound. Whereas, Indene, anthracene, and o,m,p-Xylene are examples of benzenoid aromatic compounds.
Arrangement of (CH3)3C –, (CH3)2CH –, CH3 – CH2 – when attached to benzyl or an unsaturated group in increasing order of inductive effect is- a)(CH3)3C – < (CH3)2CH – < CH3 – CH2
- b)CH3 –CH2– < (CH3)2 CH – < (CH3)3C –
- c)(CH3)2CH– <(CH3)3C –< CH3, –CH2
- d)(CH3)3C– < CH3 –CH2 –(CH3)2CH –
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrangement of (CH3)3C –, (CH3)2CH –, CH3 – CH2 – when attached to benzyl or an unsaturated group in increasing order of inductive effect is
a)
(CH3)3C – < (CH3)2CH – < CH3 – CH2
b)
CH3 –CH2– < (CH3)2 CH – < (CH3)3C –
c)
(CH3)2CH– <(CH3)3C –< CH3, –CH2
d)
(CH3)3C– < CH3 –CH2 –(CH3)2CH –

|
Anisha Deshpande answered |
Hyperconjugation effect increases in the order :
(CH3)3C−<(CH3)2CH−<CH3CH2−
The σ electrons of C—H bond of the alkyl group enter into partial conjugation with the attached unsaturated system or with the unshared p orbital.
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
(CH3)3C−<(CH3)2CH−<CH3CH2−
The σ electrons of C—H bond of the alkyl group enter into partial conjugation with the attached unsaturated system or with the unshared p orbital.
Hence (B) is the correct answer.
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ?- a)Cl3CCOOH
- b)ClCH2 COOH
- c)Cl2CH COOH
- d)CH3 COOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ?
a)
Cl3CCOOH
b)
ClCH2 COOH
c)
Cl2CH COOH
d)
CH3 COOH
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
For Cl and other halogen, we prioritise -I effect over +M effect because of their electron withdrawing nature.
In firstcase, we have 3 -Cl which exerts maximum electron withdrawing nature, thus decreasing electron density on carboxylate which in turn, breaks O-H bond. With decrease in no. of Cl atoms, acidic strength decreases.
So, a is the strongest acid.
In firstcase, we have 3 -Cl which exerts maximum electron withdrawing nature, thus decreasing electron density on carboxylate which in turn, breaks O-H bond. With decrease in no. of Cl atoms, acidic strength decreases.
So, a is the strongest acid.
Which of the following represents the given mode of hybridisation sp2 – sp2 – sp – sp from left to right?- a)H2C = CH – C ≡ N
- b)HC ≡ C – C ≡ CH
- c)H2C = C = C = CH2
- d)
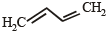
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the given mode of hybridisation sp2 – sp2 – sp – sp from left to right?
a)
H2C = CH – C ≡ N
b)
HC ≡ C – C ≡ CH
c)
H2C = C = C = CH2
d)

|
Notes Wala answered |
A has the following hybridization order:
Nitrogen atom has an sp hybridization because it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
Note: lone pair and negative charge on an atom can be converted to a bond while considering the hybridization.
B has the following hybridization order:
C has the following hybridization order:
D has the following hybridization order:
Hence A is the correct answer.
In a π (pi) bond formation, is necessary for one of the below criteria. Choose the appropriate one.- a)trigonal orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
- b)parallel orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
- c)pentagonal orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
- d)planar orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a π (pi) bond formation, is necessary for one of the below criteria. Choose the appropriate one.
a)
trigonal orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
b)
parallel orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
c)
pentagonal orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms
d)
planar orientation of the two p orbitals on adjacent atoms

|
Aniket Basu answered |
parallel orientataion of p orbitals are necessary for proper overlapping and formation of pie bond.
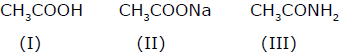 Among these compounds, the correct order of resonance energy is
Among these compounds, the correct order of resonance energy is- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I
- c)II > III > I
- d)II > I > III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among these compounds, the correct order of resonance energy is
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I
c)
II > III > I
d)
II > I > III
|
|
Shiva Reddy answered |
Resonance energy is directly proportional to stability
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives- a)an enantiomer of the substrate
- b)a product with opposite optical rotation
- c)a mixture of diastereomers
- d)a single stereoisomer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives
a)
an enantiomer of the substrate
b)
a product with opposite optical rotation
c)
a mixture of diastereomers
d)
a single stereoisomer

|
Manisha Mehta answered |
SN2 reactions proceed with inversion of configuration.
Since the attacking nucleophile is not necessarily the same as that of leaving group, the product cannot be enantiomer of the substrate and thus necessarily will not have opposite optical rotation. Moreover since only one product is obtained, we can not obtain diastereomers.
Since the attacking nucleophile is not necessarily the same as that of leaving group, the product cannot be enantiomer of the substrate and thus necessarily will not have opposite optical rotation. Moreover since only one product is obtained, we can not obtain diastereomers.
Chapter doubts & questions for General Organic Chemistry (GOC) - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of General Organic Chemistry (GOC) - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup