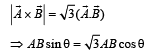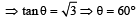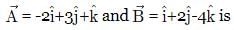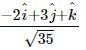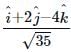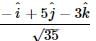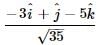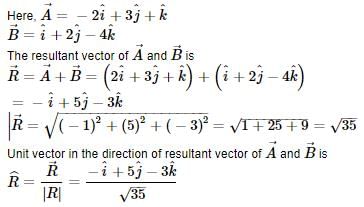All Exams >
NEET >
Physics Class 11 >
All Questions
All questions of Motion in a Plane for NEET Exam
If 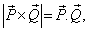 what is the angle between
what is the angle between 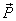 and
and 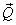
- a)900
- b)300
- c)600
- d)450
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 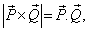 what is the angle between
what is the angle between 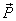 and
and 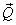
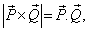 what is the angle between
what is the angle between 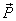 and
and 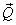
a)
900
b)
300
c)
600
d)
450
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
We know that for two vectors P and Q
P.Q = |P||Q| cos a
And PxQ = |P||Q| sin a
Where a is angle between them
When P.Q = PxQ
We get sin a = cos a
Thus a = 450
P.Q = |P||Q| cos a
And PxQ = |P||Q| sin a
Where a is angle between them
When P.Q = PxQ
We get sin a = cos a
Thus a = 450
A car travelling at 36km/h-1 due North turns West in 5 seconds and maintains the same speed. What is the acceleration of the car?
- a)2√2ms-2 South West
- b)√2ms-2 South West
- c)2ms-2 North West
- d)4ms-2 North West
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A car travelling at 36km/h-1 due North turns West in 5 seconds and maintains the same speed. What is the acceleration of the car?
a)
2√2ms-2 South West
b)
√2ms-2 South West
c)
2ms-2 North West
d)
4ms-2 North West
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Initial velocity of car = 36 km/hr due north
Final velocity of car = 36 km/hr due west
magnitude of change in velocity = root[(36)^2 + (36)^2] = 36 x √2
(since velocity is a vector, so direction has to be taken into account)
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time = [36√2 x 5/18]/5 m/s^2 = 2√2 m/s^2 = 2.828 m/s^2
A boat sails across a river with a velocity of 10 km/hr. If resultant boat velocity is 14 km/hr, then what is the velocity of river water?
- a) 17.20 km/hr
- b) 10 km/hr
- c) 9.79 km/hr
- d) 4.88 km/hr
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A boat sails across a river with a velocity of 10 km/hr. If resultant boat velocity is 14 km/hr, then what is the velocity of river water?
a)
17.20 km/hr
b)
10 km/hr
c)
9.79 km/hr
d)
4.88 km/hr
|
|
Om Desai answered |
We can use the Pythagorean theorem to solve this problem since the boat's velocity, river's velocity, and resultant velocity form a right triangle.
Let the boat's velocity be represented by A (10 km/hr), the river's velocity be represented by B, and the resultant velocity be represented by C (14 km/hr).
According to the Pythagorean theorem, A^2 + B^2 = C^2.
Now, we can plug in the given values and solve for B:
(10)^2 + B^2 = (14)^2
100 + B^2 = 196
Subtract 100 from both sides:
B^2 = 96
Now, take the square root of both sides:
B = sqrt(96) ≈ 9.79 km/hr
Let the boat's velocity be represented by A (10 km/hr), the river's velocity be represented by B, and the resultant velocity be represented by C (14 km/hr).
According to the Pythagorean theorem, A^2 + B^2 = C^2.
Now, we can plug in the given values and solve for B:
(10)^2 + B^2 = (14)^2
100 + B^2 = 196
Subtract 100 from both sides:
B^2 = 96
Now, take the square root of both sides:
B = sqrt(96) ≈ 9.79 km/hr
A particle moves in x-y plane starting from the origin in a direction making 30° angle with x-axis. Distance covered by it is 5 m. what is the position vector of the particle.- a)
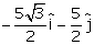
- b)
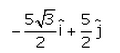
- c)
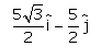
- d)
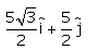
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves in x-y plane starting from the origin in a direction making 30° angle with x-axis. Distance covered by it is 5 m. what is the position vector of the particle.
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ankita Menon answered |
Initial velocity = u = 20 m/s
Final velocity = v = 0 [ at maximum height , v = 0 ]
Final velocity = v = 0 [ at maximum height , v = 0 ]
Acceleration due to gravity(g) in this case , is taken as negative.
This is because , when the direction of motion of object is opposite to "g" , then value of g is taken as -ve
This is because , when the direction of motion of object is opposite to "g" , then value of g is taken as -ve
hence ,
g = -9.8 m/s²
Let's use the formula :-
[h = height ]
v² -u² = 2gh
0² - 20² = 2*-9.8*h
-400 = -19.6h
h = -400/-19.6
= 20.408 m [ approximately ]
-400 = -19.6h
h = -400/-19.6
= 20.408 m [ approximately ]
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is- a)7 units
- b)8.5 units
- c)7√2 units
- d)10 units
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is
a)
7 units
b)
8.5 units
c)
7√2 units
d)
10 units
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Answer is C) 7 x (2)^1/2
Solution:
The initial velocity is given by
u = v - at
Where, v = Final Velocity, t = time taken, and a = acceleration
u = 3 i + 4 j
a = 0.4 i + 0.3 j
t = 10 s
Using initial velocity formula
3 i + 4 j = v - (0.4 i + 0.3 j) 10
v = 7 ( i + j)
Velocity is the vector quantity which is defined by both magnitude and direction but speed is scalar quantity which is defined by only magnitude.
The magnitude of v = (7^2+7^2)^1/2 = 7 x (2)^1/2
How many directions are possible for the same horizontal range?- a)4
- b)3
- c)2
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many directions are possible for the same horizontal range?
a)
4
b)
3
c)
2
d)
1
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
We know that the horizontal range for any projectile motion let say R = 2u2.sin 2a /g
Where u is initial speed, and a is the angle at which the particle is thrown, which is responsible for direction. So in between the possible range of a that is 0 - 90, there are maximum two equal values of sin 2a, thus the maximum number of directions for the same or equal range are 2.
Where u is initial speed, and a is the angle at which the particle is thrown, which is responsible for direction. So in between the possible range of a that is 0 - 90, there are maximum two equal values of sin 2a, thus the maximum number of directions for the same or equal range are 2.
The quantity which remains unchanged during the flight of an oblique projectile is- a)Horizontal component of acceleration
- b)Vertical component of acceleration
- c)Vertical component of velocity
- d)Horizontal component of velocity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The quantity which remains unchanged during the flight of an oblique projectile is
a)
Horizontal component of acceleration
b)
Vertical component of acceleration
c)
Vertical component of velocity
d)
Horizontal component of velocity

|
Sarthak Rajendra Bande answered |
As there is no horizontal acceleration is present in oblique projection horizontal component of velocity is constant
If an object is dropped through the window of a fast running train. Then- a)the object moves straight horizontally.
- b)to a man standing near the track, path of the object will be a part of parabola.
- c)the object falls down vertically.
- d)the object will follow an elliptical path
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If an object is dropped through the window of a fast running train. Then
a)
the object moves straight horizontally.
b)
to a man standing near the track, path of the object will be a part of parabola.
c)
the object falls down vertically.
d)
the object will follow an elliptical path
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
When an object is still held it is the part of a system in which the train is moving, once it is left it still has the same velocity as the train for a person from ground. Thus as the velocity is horizontal and acceleration is vertical, it would follow a parabolic trajectory.
Which statement is true for a ball thrown at 20 degrees with the horizontal, when it is at the highest point in its trajectory?- a)Its velocity is zero but its acceleration is nonzero
- b)Its velocity is nonzero but its acceleration is zero
- c)Its velocity and acceleration are both zero
- d)Its velocity is perpendicular to its acceleration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is true for a ball thrown at 20 degrees with the horizontal, when it is at the highest point in its trajectory?
a)
Its velocity is zero but its acceleration is nonzero
b)
Its velocity is nonzero but its acceleration is zero
c)
Its velocity and acceleration are both zero
d)
Its velocity is perpendicular to its acceleration
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
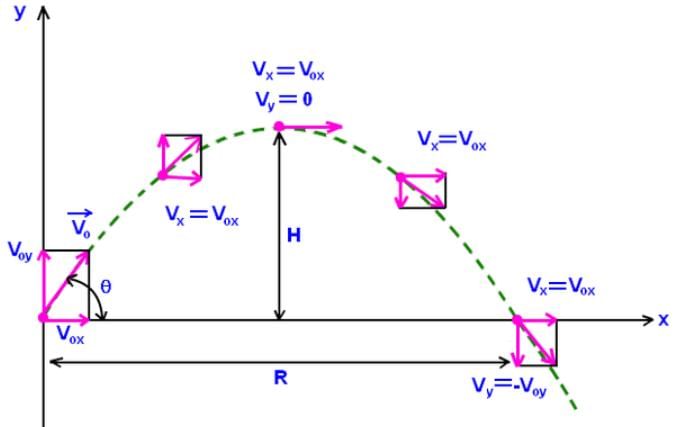
At the highest point in its trajectory, the acceleration (g) is acting in downward direction, whereas velocity of the projectile is only in the X (horizontal) direction.
Rain is falling vertically with the speed of 30 m/s. A man rides a bicycle with the speed of 10 m/s in east to west direction. What is the direction in which he should hold the umbrella?- a)cos-1 1/3
- b)sin-1 1/3
- c)tan-1 2/3
- d)tan-1 1/3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Rain is falling vertically with the speed of 30 m/s. A man rides a bicycle with the speed of 10 m/s in east to west direction. What is the direction in which he should hold the umbrella?
a)
cos-1 1/3
b)
sin-1 1/3
c)
tan-1 2/3
d)
tan-1 1/3
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
When the man rides, he should put an umbrella in the opposite direction to which the drops are falling with respect to him.
Hence wrt man, the speed of rain drop is
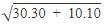 at an angle of tan-1 ⅓
at an angle of tan-1 ⅓
Hence he would put umbrella to the direction of tan-1 ⅓
Hence wrt man, the speed of rain drop is
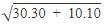 at an angle of tan-1 ⅓
at an angle of tan-1 ⅓Hence he would put umbrella to the direction of tan-1 ⅓
A body sliding on a smooth inclined plane requires 4 seconds to reach the bottom starting from rest at the top. How much time does it take to cover one-fourth distance starting from rest at the top- a)1 s
- b)2 s
- c)4 s
- d)16 s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body sliding on a smooth inclined plane requires 4 seconds to reach the bottom starting from rest at the top. How much time does it take to cover one-fourth distance starting from rest at the top
a)
1 s
b)
2 s
c)
4 s
d)
16 s
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
A body start from rest so, u = 0
Let total distance covered = s
Let a body moves with accerlation = a
► s = 1/2 × a× t2
► s = 1/2× a × 42
► s = 8a
The one-fourth of total distance, s' = 8a/4
= 2a
► s' = 1/2 × a × t2
► 2a / a = 1/2 × t2
► 4 = t2
► t = 2 s
Let total distance covered = s
Let a body moves with accerlation = a
► s = 1/2 × a× t2
► s = 1/2× a × 42
► s = 8a
The one-fourth of total distance, s' = 8a/4
= 2a
► s' = 1/2 × a × t2
► 2a / a = 1/2 × t2
► 4 = t2
► t = 2 s
A body is thrown with a velocity of 10m/s at an angle of 60 degrees with the horizontal. Its velocity at the highest point is: - a)5 m/s
- b)8.7 m/s
- c)10 mis
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A body is thrown with a velocity of 10m/s at an angle of 60 degrees with the horizontal. Its velocity at the highest point is:
a)
5 m/s
b)
8.7 m/s
c)
10 mis
d)
0
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
At the highest point, its vertical velocity will become zero. Hence the only left velocity is horizontal which remains unchanged and is equal to 10 cos 60 = 5m/s
A battle ship simultaneously fires two shells at enemy ships. Both are fired with the same speed but with different directions as shown. If the shells follow the parabolic trajectories shown, which ship gets hit first?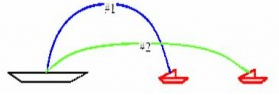
- a)they get hit at the same time.
- b)ship μ2
- c)need more information about the trajectories.
- d)ship μ1
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A battle ship simultaneously fires two shells at enemy ships. Both are fired with the same speed but with different directions as shown. If the shells follow the parabolic trajectories shown, which ship gets hit first?
a)
they get hit at the same time.
b)
ship μ2
c)
need more information about the trajectories.
d)
ship μ1
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Ship 2 gets hit first. The time of flight only depends on the y-component of motion, not the x-component. The higher you throw something up in the air, the more time it spends in the air. It can also be shown from equation-
y=v0y t – ½ g t2=0
v0y for projectile μ1 is greater than for μ2.
Vectors can be added by- a)adding the magnitudes of the vectors
- b)adding the angles of the vectors
- c)translating the two vectors
- d)parallelogram law of addition
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Vectors can be added by
a)
adding the magnitudes of the vectors
b)
adding the angles of the vectors
c)
translating the two vectors
d)
parallelogram law of addition

|
Puja Kaur answered |
Explanation:Parallelogram law of vector addition is,If two vectors are considered to be the adjacent sides of a Parallelogram, then the resultant of two vectors is given by the vector which is a diagonal passing through the point of contact of two vectors.
A monkey is running on the ground, next to a train, in the direction of the train. The speed of the monkey is 5km/h and the speed of the train is 100km/h. What is the velocity of the monkey with respect to the train?- a)105km/h in the direction opposite to the train
- b)95 km/h in the direction of the train
- c)105km/h in the direction of the train
- d)95 km/h in the direction opposite to the train.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A monkey is running on the ground, next to a train, in the direction of the train. The speed of the monkey is 5km/h and the speed of the train is 100km/h. What is the velocity of the monkey with respect to the train?
a)
105km/h in the direction opposite to the train
b)
95 km/h in the direction of the train
c)
105km/h in the direction of the train
d)
95 km/h in the direction opposite to the train.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Assuming the direction of velocity of train to be positive, wrt train the speed of monkey will be
-100 + 5 = -95 kmph
I.. 95 kmph in direction opposite to the train.
-100 + 5 = -95 kmph
I.. 95 kmph in direction opposite to the train.
Two boys are standing at the ends A and B of a ground where AB = a. The boy at B starts running in a direction perpendicular to AB with velocity v1. The boy at A starts running simultaneously with velocity v and catches the oth er boy in a time t, where t is [2005]- a)
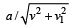 a /(v + v1)
a /(v + v1) - b)a /(v + v1)
- c)a /(v–v1)
- d)
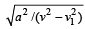
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two boys are standing at the ends A and B of a ground where AB = a. The boy at B starts running in a direction perpendicular to AB with velocity v1. The boy at A starts running simultaneously with velocity v and catches the oth er boy in a time t, where t is [2005]
a)
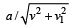 a /(v + v1)
a /(v + v1)b)
a /(v + v1)
c)
a /(v–v1)
d)
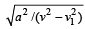
|
|
Vishal Kumar answered |

The vector which when added to the resultant of  and
and 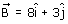 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.- a)
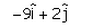
- b)
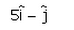
- c)
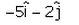
- d)
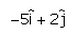
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The vector which when added to the resultant of  and
and 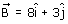 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.
 and
and 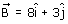 gives unit vector along x direction.
gives unit vector along x direction.a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Naveen Choudhary answered |
Time taken by first drop to cover 5 cm, u = 0
⇒ h = 1/2 gt2
⇒ 5 = 1/2 x 10 x t2
⇒ t = 1 sec
Hence interval is 0.5 sec for each drop.
Now distance fallen by second drop in 0.5 sec
⇒ h1 = 1/2 gt2
= 1/2 x 10 x (0.5)2
= 5 x 0.25
= 1.25 m
Height above the ground ( of 2nd drop) = 5 - 1.25
= 3.75 m
The angular speed of a wheel of radius 0.50 m moving with the speed of 20 m/s is:- a)40 radian/s
- b)10 radian/s
- c)30 radian/s
- d)20 radian/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angular speed of a wheel of radius 0.50 m moving with the speed of 20 m/s is:
a)
40 radian/s
b)
10 radian/s
c)
30 radian/s
d)
20 radian/s
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Radius r = 0.5 m
Speed, v = 20 m/s
We know,
v = r ω
where,
ω = angular velocity
20 = 0.5 x ω
ω = 20/0.5 = 40 rad/sec
When a projectile is thrown up at an angle θ to the ground, the time taken by it to rise and to fall are related as- a)time of rise can be less than or equal to time of fall
- b)they are equal
- c)time of rise < time of fall
- d)time of rise > time of fall
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a projectile is thrown up at an angle θ to the ground, the time taken by it to rise and to fall are related as
a)
time of rise can be less than or equal to time of fall
b)
they are equal
c)
time of rise < time of fall
d)
time of rise > time of fall
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The time of fall or rise for a projectile depends upon its vertical component of initial velocity and the vertical acceleration. As the acceleration does not change and the motion of path is identical for the rise phase and the fall phase, we can easily deduce that time taken is also the same.
At the point of maximum height, the acceleration is:- a)minimum
- b)g
- c)maximum
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At the point of maximum height, the acceleration is:
a)
minimum
b)
g
c)
maximum
d)
zero
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
At a point of maximum height, the derivative of displacement i.e. velocity is zero but as the gravitational acceleration is equal at all near points to the surface of earth, acceleration at maximum height is still equal to g.
Uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion mainly because its :- a)direction of motion changes
- b)speed remains the same
- c)velocity remains the same
- d)direction of motion does not change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion mainly because its :
a)
direction of motion changes
b)
speed remains the same
c)
velocity remains the same
d)
direction of motion does not change
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
An accelerating body is an object that is changing its velocity. And since velocity is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, a change in either the magnitude or the direction constitutes a change in the velocity.
Hence a uniform circular motion is a accelerated motion because direction of motion keeps on changing
Hence a uniform circular motion is a accelerated motion because direction of motion keeps on changing
In 5 seconds a body covers a distance of 50 m and in 10 seconds it covers 80 m with uniform acceleration. What is the distance traveled in 15 seconds?
- a) 100 m
- b) 110 m
- c) 1000 m
- d) None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In 5 seconds a body covers a distance of 50 m and in 10 seconds it covers 80 m with uniform acceleration. What is the distance traveled in 15 seconds?
a)
100 m
b)
110 m
c)
1000 m
d)
None of the above
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
ω = 2πT
where
T = Time period of revolution of earth around its own axis
= 24 hours
=24 x 60 x 60
=86400 s
Hence,
ω = 2π/86400
= π/43200 rad s^-1
A stone is tied to a string of length ℓ and is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string as the centre. At a certain instant of time, the stone is at its lowest position and has a speed u.
The magnitude of the change in velocity as it reaches a position where the string is horizontal (g being acceleration due to gravity) is [2004]- a)
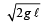
- b)
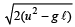
- c)
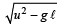
- d)
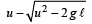
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone is tied to a string of length ℓ and is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string as the centre. At a certain instant of time, the stone is at its lowest position and has a speed u.
The magnitude of the change in velocity as it reaches a position where the string is horizontal (g being acceleration due to gravity) is [2004]
The magnitude of the change in velocity as it reaches a position where the string is horizontal (g being acceleration due to gravity) is [2004]
a)
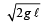
b)
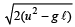
c)
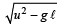
d)
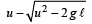

|
Adit Raj answered |
Are resultant vector nikal do..
DeltaV=Vf-Vi
option B aaega..
photo upload nhi ho rha hai warna me kr deta
The angle between two vectors of magnitude 12 and 18 units when their resultant is 24 units, is[1999]- a)63º 51´
- b)75º 52´
- c)82º 31´
- d)89º 16´
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle between two vectors of magnitude 12 and 18 units when their resultant is 24 units, is[1999]
a)
63º 51´
b)
75º 52´
c)
82º 31´
d)
89º 16´

|
Snehal Shah answered |
We know that, R2 = A2 + B2 + 2 AB cosθ
(24)2 = (12)2 + (18)2 + 2(12)(18) cos θ
(24)2 = (12)2 + (18)2 + 2(12)(18) cos θ
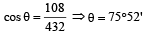
A boat is moving with a velocity 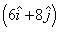 with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity
with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity 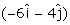 with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?- a)
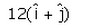
- b)
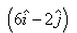
- c)
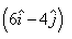
- d)
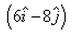
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A boat is moving with a velocity 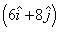 with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity
with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity 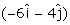 with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
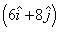 with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity
with respect to the ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity 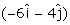 with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?
with respect to the ground. What is the relative velocity of boat with respect to river?a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Velocity of boat wrt river = velocity of boat wrt ground - velocity of river wrt ground
I.e. v = (6i + 8j) - (-6i - 4j)
= 12i + 12j
I.e. v = (6i + 8j) - (-6i - 4j)
= 12i + 12j
Which of the following statements not true?- a)The velocity vector of a particle at a point is always along the tangent to the path of the particle at that point
- b)The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector
- c)The net acceleration of a particle in uniform circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the centre
- d)The net acceleration of a particle in circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the centre
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements not true?
a)
The velocity vector of a particle at a point is always along the tangent to the path of the particle at that point
b)
The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector
c)
The net acceleration of a particle in uniform circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the centre
d)
The net acceleration of a particle in circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the centre
|
|
Jyoti Shah answered |
Understanding Circular Motion and Acceleration
In circular motion, it's crucial to differentiate between uniform and non-uniform circular motion. The statements provided touch on these concepts.
Analysis of Each Statement
- Statement A: The velocity vector of a particle at a point is always along the tangent to the path of the particle at that point.
This statement is true. In circular motion, the velocity is tangential to the circle.
- Statement B: The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector.
This statement is also true. Over one full cycle, the direction of the acceleration changes but the average vector sums to zero.
- Statement C: The net acceleration of a particle in uniform circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the center.
This statement is true. In uniform circular motion, the acceleration (centripetal) is directed inward toward the center.
- Statement D: The net acceleration of a particle in circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the center.
This statement is false. While centripetal acceleration is always directed towards the center in uniform circular motion, in non-uniform circular motion, tangential acceleration exists, which is not directed towards the center. Therefore, the net acceleration can have components both radial and tangential.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' as it incorrectly suggests that the net acceleration is always directed towards the center, ignoring the possibility of tangential acceleration in non-uniform circular motion.
In circular motion, it's crucial to differentiate between uniform and non-uniform circular motion. The statements provided touch on these concepts.
Analysis of Each Statement
- Statement A: The velocity vector of a particle at a point is always along the tangent to the path of the particle at that point.
This statement is true. In circular motion, the velocity is tangential to the circle.
- Statement B: The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector.
This statement is also true. Over one full cycle, the direction of the acceleration changes but the average vector sums to zero.
- Statement C: The net acceleration of a particle in uniform circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the center.
This statement is true. In uniform circular motion, the acceleration (centripetal) is directed inward toward the center.
- Statement D: The net acceleration of a particle in circular motion is always along the radius of the circle towards the center.
This statement is false. While centripetal acceleration is always directed towards the center in uniform circular motion, in non-uniform circular motion, tangential acceleration exists, which is not directed towards the center. Therefore, the net acceleration can have components both radial and tangential.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D' as it incorrectly suggests that the net acceleration is always directed towards the center, ignoring the possibility of tangential acceleration in non-uniform circular motion.
For angles of projection of a projectile (45° – θ) and (45° + θ), the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of [2006]- a)1: 3
- b)1 : 2
- c)2 : 1
- d)1 : 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For angles of projection of a projectile (45° – θ) and (45° + θ), the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of [2006]
a)
1: 3
b)
1 : 2
c)
2 : 1
d)
1 : 1

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
(45º – θ) & (45º + θ) are complementary angles as 45º – θ + 45º + θ = 90º. We know that if angle of projection of two projectiles make complementary angles, their ranges are equal.
In this case also, the range will be same. So the ratio is 1 : 1.
In this case also, the range will be same. So the ratio is 1 : 1.
The angular speed of a wheel of radius 0.50 m moving with the speed of 20 m/s is:- a)40 radian/s
- b)30 radins/s
- c)20 radians/s
- d)10 radians/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angular speed of a wheel of radius 0.50 m moving with the speed of 20 m/s is:
a)
40 radian/s
b)
30 radins/s
c)
20 radians/s
d)
10 radians/s
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Radius r = 0.5 m
Speed, v = 20 m/s
We know,
v = r ω
where,
ω = angular velocity
20 = 0.5 x ω
ω = 20/0.5 = 40 rad/sec
If a vector 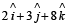 is perpendicular to the vector
is perpendicular to the vector 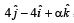 then the value of α is [2005]
then the value of α is [2005]- a)1/2
- b)–1/2
- c)1
- d)–1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a vector 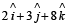 is perpendicular to the vector
is perpendicular to the vector 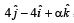 then the value of α is [2005]
then the value of α is [2005]
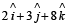 is perpendicular to the vector
is perpendicular to the vector 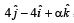 then the value of α is [2005]
then the value of α is [2005]a)
1/2
b)
–1/2
c)
1
d)
–1

|
Shounak Nair answered |
For two vectors to be perpendicular to each other
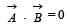
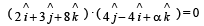
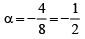
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is- a)7 units
- b)8.5 units
- c)7√2 units
- d)10 units
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle has an initial velocity 3 iˆ +4 jˆ and an acceleration 0.4 iˆ + 0.3 jˆ .Its speed after 10 s is
a)
7 units
b)
8.5 units
c)
7√2 units
d)
10 units
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Answer is C) 7 x (2)^1/2
Solution:
The initial velocity is given by
u = v - at
Where, v = Final Velocity, t = time taken, and a = acceleration
u = 3 i + 4 j
a = 0.4 i + 0.3 j
t = 10 s
Using initial velocity formula
3 i + 4 j = v - (0.4 i + 0.3 j) 10
v = 7 ( i + j)
Velocity is the vector quantity which is defined by both magnitude and direction but speed is scalar quantity which is defined by only magnitude.
The magnitude of v = (7^2+7^2)^1/2 = 7 x (2)^1/2
A projectile is fired a velocity of 150 meters per second at an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the vertical component of the velocity at the time the projectile is fired?- a)130 m/s
- b)75 m/s
- c)225 m/s
- d)150 m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A projectile is fired a velocity of 150 meters per second at an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the vertical component of the velocity at the time the projectile is fired?
a)
130 m/s
b)
75 m/s
c)
225 m/s
d)
150 m/s
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The vertical component of the velocity is given by 150sin(30 ) =150X0.5 =75 m/s.
The cir cular motion of a particle with constant speed is [2005]- a)periodic but not simple harmonic
- b)simple harmonic but not periodic
- c)periodic and simple harmonic
- d)neither periodic nor simple harmonic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cir cular motion of a particle with constant speed is [2005]
a)
periodic but not simple harmonic
b)
simple harmonic but not periodic
c)
periodic and simple harmonic
d)
neither periodic nor simple harmonic

|
Rajat Roy answered |
In circular motion of a particle with constant speed, particle repeats its motion after a regular interval of time but does not oscillate about a fixed point. So, motion of particle is periodic but not simple harmonic.
At what angle should a projectile with initial velocity ‘v’ be thrown, so that it achieves its maximum range?- a)450
- b)900
- c)600
- d)300
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what angle should a projectile with initial velocity ‘v’ be thrown, so that it achieves its maximum range?
a)
450
b)
900
c)
600
d)
300
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Sine of an angle has maximum value 1 when the angle is 90 degree Rmaxis obtained when 2ø = 90 degreeorø= 45 degree
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?- a)13 min, 700 m
- b)16 min, 650 m
- c)19 min, 500 m
- d)15 min, 750 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man can swim with a speed of 4.0 km/h in still water. How long does he take to cross a river 1.0 km wide if the river flows steadily at 3.0 km/h and he makes his strokes normal to the river current? How far down the river does he go when he reaches the other bank?
a)
13 min, 700 m
b)
16 min, 650 m
c)
19 min, 500 m
d)
15 min, 750 m

|
Stuti Kumar answered |
Explanation:
Speed of the man, vm = 4 km/h
Width of the river = 1 km
Width of the river = 1 km
The driver of a car moving towards a rocket launching pad with a speed of 6 ms−1 observed that the rocket is moving with a speed of 10 ms−1 the upward speed of the rocket as seen by the stationary observer is
- a)4 ms−1
- b)6 ms−1
- c)11 ms−1
- d)8 ms−1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The driver of a car moving towards a rocket launching pad with a speed of 6 ms−1 observed that the rocket is moving with a speed of 10 ms−1 the upward speed of the rocket as seen by the stationary observer is
a)
4 ms−1
b)
6 ms−1
c)
11 ms−1
d)
8 ms−1
|
|
Jithin Nair answered |
-1 suddenly sees a rocket launching vertically upwards with a velocity of 80ms-1. What is the relative velocity of the car with respect to the rocket?
The relative velocity of the car with respect to the rocket can be found by adding the velocity of the car and the velocity of the rocket.
Relative velocity = velocity of car + velocity of rocket
Relative velocity = 6 ms-1 + 80 ms-1
Relative velocity = 86 ms-1
Therefore, the relative velocity of the car with respect to the rocket is 86 ms-1.
The relative velocity of the car with respect to the rocket can be found by adding the velocity of the car and the velocity of the rocket.
Relative velocity = velocity of car + velocity of rocket
Relative velocity = 6 ms-1 + 80 ms-1
Relative velocity = 86 ms-1
Therefore, the relative velocity of the car with respect to the rocket is 86 ms-1.
The vector sum of two forces is perpendicular to their vector differences. In that case, the forces[2003]- a)can not be pr edicted
- b)are equal to each other
- c)are equal to each other in magnitude
- d)are not equal to each other in magnitude
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The vector sum of two forces is perpendicular to their vector differences. In that case, the forces[2003]
a)
can not be pr edicted
b)
are equal to each other
c)
are equal to each other in magnitude
d)
are not equal to each other in magnitude
|
|
Satakshi Kumari answered |

If the angle between the vectors 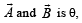 the value of the product
the value of the product 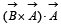 is equal to [2005]
is equal to [2005]- a)BA2 sinθ
- b)BA2 cosθ
- c)BA2 sinθ cosθ
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the angle between the vectors 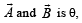 the value of the product
the value of the product 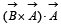 is equal to [2005]
is equal to [2005]
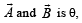 the value of the product
the value of the product 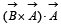 is equal to [2005]
is equal to [2005]a)
BA2 sinθ
b)
BA2 cosθ
c)
BA2 sinθ cosθ
d)
zero
|
|
Satakshi Kumari answered |
Direction of vector product of 2 vector is perpendicular to both vector
means if A×B=C then C is perpendicular to A as well as B .
now apply this concept on your question
let B×A=C ,
A.(B×C)=A.C
where C is perpendicular to both vector A&B
so angle b/w C and A is 90
A.C=0
means if A×B=C then C is perpendicular to A as well as B .
now apply this concept on your question
let B×A=C ,
A.(B×C)=A.C
where C is perpendicular to both vector A&B
so angle b/w C and A is 90
A.C=0
Which one of the following is not an example of projectile?- a)A bullet fired from a gun.
- b)A kicked football.
- c)Taking off of an aircraft.
- d)A javelin thrown by an athlete.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not an example of projectile?
a)
A bullet fired from a gun.
b)
A kicked football.
c)
Taking off of an aircraft.
d)
A javelin thrown by an athlete.

|
Top Rankers answered |
A projectile is any object thrown into space upon which the only acting force is gravity. A bullet fired from a gun, a kicked football, and a javelin thrown by an athlete are examples of projectiles once they are in motion and only gravity acts on them. Taking off of an aircraft is not a projectile because it involves continuous external force from the engines.
A particle moves in a circle of radius 5 cm with constant speed and time period 0.2πs. The acceleration of the particle is [2011]- a)15 m/s2
- b)25 m/s2
- c)36 m/s2
- d)5 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves in a circle of radius 5 cm with constant speed and time period 0.2πs. The acceleration of the particle is [2011]
a)
15 m/s2
b)
25 m/s2
c)
36 m/s2
d)
5 m/s2
|
|
Simran Nair answered |
To find the speed of the particle, we can use the formula:
speed = distance / time
Since the particle moves in a circle, the distance it travels in one complete revolution is the circumference of the circle, which is 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
Given that the radius is 5 cm, the distance the particle travels in one complete revolution is:
distance = 2π(5 cm) = 10π cm
Since the time period is 0.2 seconds, the time it takes for the particle to complete one revolution is 0.2 seconds.
Therefore, the speed of the particle is:
speed = distance / time = (10π cm) / (0.2 s) = 50π cm/s
So, the speed of the particle is 50π cm/s.
speed = distance / time
Since the particle moves in a circle, the distance it travels in one complete revolution is the circumference of the circle, which is 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
Given that the radius is 5 cm, the distance the particle travels in one complete revolution is:
distance = 2π(5 cm) = 10π cm
Since the time period is 0.2 seconds, the time it takes for the particle to complete one revolution is 0.2 seconds.
Therefore, the speed of the particle is:
speed = distance / time = (10π cm) / (0.2 s) = 50π cm/s
So, the speed of the particle is 50π cm/s.
A man standing on the roof of a house of height h throws one particle vertically downwards and another particle horizontally with the same velocity u. The ratio of their velocities when they reach the earth’s surface will be- a)
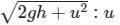
- b)1 : 2
- c)1 : 1
- d)
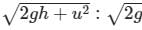
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A man standing on the roof of a house of height h throws one particle vertically downwards and another particle horizontally with the same velocity u. The ratio of their velocities when they reach the earth’s surface will be
a)
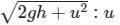
b)
1 : 2
c)
1 : 1
d)
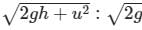

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Particle 1 (Thrown Vertically Downward):
Initial velocity (u) is downward.
Final velocity is affected by gravity. Using the equation of motion:
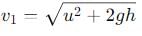
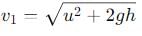
Particle 2 (Thrown Horizontally):
Horizontal velocity remains constant (u).
Vertical velocity due to free fall can be calculated as:
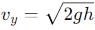
The resultant velocity (v2) at the Earth's surface is given by combining the horizontal and vertical velocities using the Pythagorean theorem:
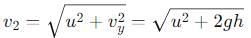
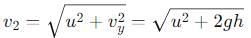
Velocity Ratio:
The magnitude of both velocities is the same:
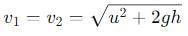
Thus, the ratio of their velocities is: 1 : 1
The magnitude of both velocities is the same:
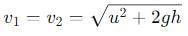
Thus, the ratio of their velocities is: 1 : 1
A passenger arriving in a new town wishes to go from the station to a hotel located 10 km away on a straight road from the station. A dishonest cabman takes him along a circuitous path 23 km long and reaches the hotel in 28 min. What is (a) the average speed of the taxi, (b) the magnitude of average velocity?- a)47.3 km/hr, 23.4 km/hr
- b)48.3 km/hr, 22.4 km/hr
- c)49.3 km/hr, 21.4 km/hr
- d)46.3 km/hr, 24.4 km/hr
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A passenger arriving in a new town wishes to go from the station to a hotel located 10 km away on a straight road from the station. A dishonest cabman takes him along a circuitous path 23 km long and reaches the hotel in 28 min. What is (a) the average speed of the taxi, (b) the magnitude of average velocity?
a)
47.3 km/hr, 23.4 km/hr
b)
48.3 km/hr, 22.4 km/hr
c)
49.3 km/hr, 21.4 km/hr
d)
46.3 km/hr, 24.4 km/hr
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Given,
Magnitude of displacement = 10 km
Total path length = 23 km
Time taken = 28 min = 7/15 hr.
Therefore,

Therefore, we can see that the average speed and magnitude of average velocity are not equal.
The vector that must be added to the vector  so that the resultant vector is a unit vector along the y-axis is
so that the resultant vector is a unit vector along the y-axis is
- a)
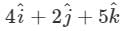
- b)
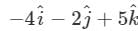
- c)
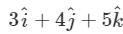
- d)Null vector
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The vector that must be added to the vector  so that the resultant vector is a unit vector along the y-axis is
so that the resultant vector is a unit vector along the y-axis is
 so that the resultant vector is a unit vector along the y-axis is
so that the resultant vector is a unit vector along the y-axis isa)
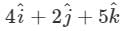
b)
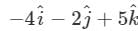
c)
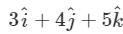
d)
Null vector

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Unit vector along y axis = 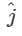 so the required vector =
so the required vector = 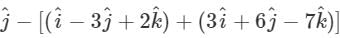
 so the required vector =
so the required vector = 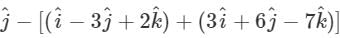
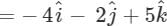
The resultant of 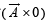 will be equal to [1992]
will be equal to [1992]- a)zero
- b)A
- c)zero vector
- d)unit vector
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The resultant of 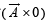 will be equal to [1992]
will be equal to [1992]
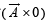 will be equal to [1992]
will be equal to [1992]a)
zero
b)
A
c)
zero vector
d)
unit vector

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
When a vector is multiplied with a scalar, the result is a vector.
A particle starting from the origin (0, 0) moves in a straight line in the (x, y) plane. Its coordinates at a later time are 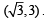 . The path of the particle makes with the x-axis an angle of [2007]
. The path of the particle makes with the x-axis an angle of [2007]- a)45o
- b)60o
- c)0o
- d)30o
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle starting from the origin (0, 0) moves in a straight line in the (x, y) plane. Its coordinates at a later time are 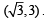 . The path of the particle makes with the x-axis an angle of [2007]
. The path of the particle makes with the x-axis an angle of [2007]
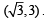 . The path of the particle makes with the x-axis an angle of [2007]
. The path of the particle makes with the x-axis an angle of [2007]a)
45o
b)
60o
c)
0o
d)
30o

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
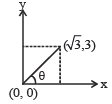
Let θ be the angle which the particle makes with x axis.
From figure,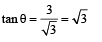
From figure,
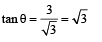
We can define the difference of two vectors A and B as the- a)sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by 0
- b)sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by -1
- c)sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by -2
- d)sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by 1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
We can define the difference of two vectors A and B as the
a)
sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by 0
b)
sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by -1
c)
sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by -2
d)
sum of two vectors A and B' such that B' is equal to B multiplied by 1

|
Surbhi Mishra answered |
Explanation:
Vector subtraction is defined in the following way.
- The difference of two vectors, A - B , is a vector C that is, C = A - B
- The addition of two vector such that C = A + (-B). B has been taken in opposite direction.
Thus vector subtraction can be represented as a vector addition.
Chapter doubts & questions for Motion in a Plane - Physics Class 11 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Motion in a Plane - Physics Class 11 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily

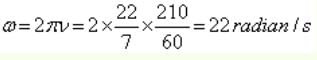
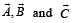 are such that
are such that 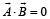 and
and 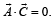 Then the vector parallel to
Then the vector parallel to 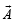 is [NEET Kar. 2013]
is [NEET Kar. 2013]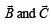
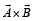
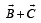
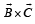

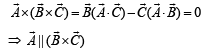
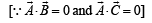
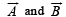 are two vectors and θ is the angle between them, if
are two vectors and θ is the angle between them, if 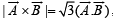 , the valueof θ is[2007]
, the valueof θ is[2007]