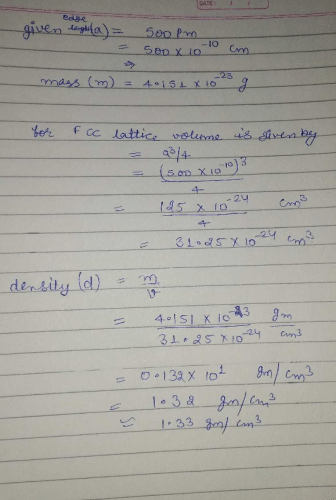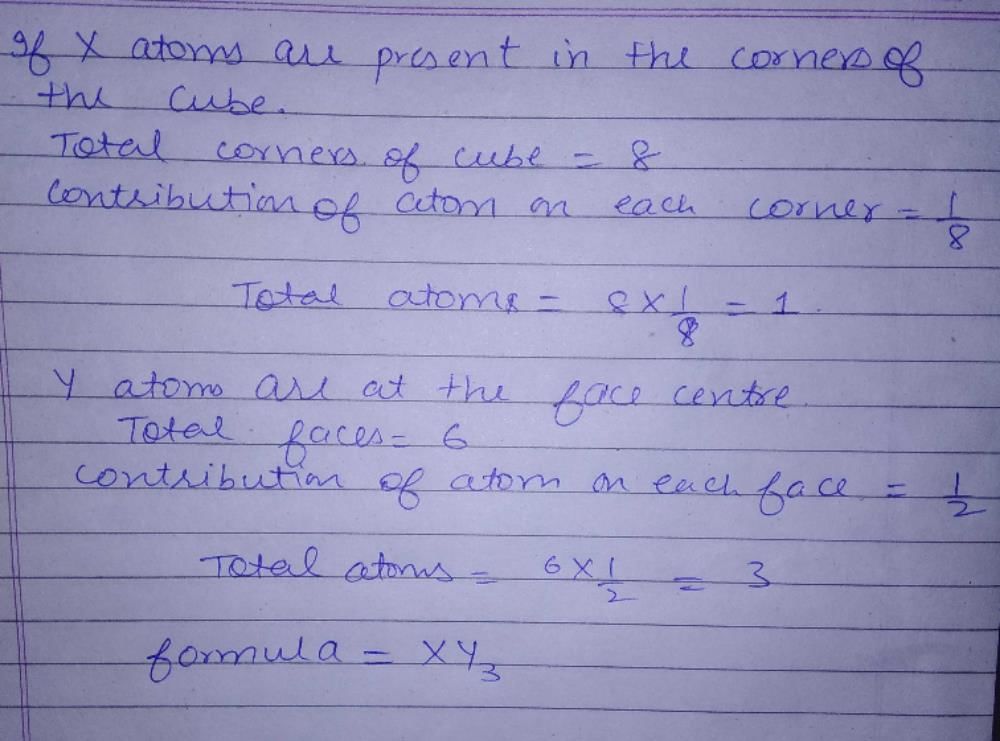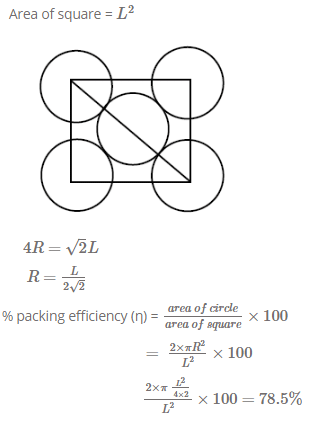All Exams >
Chemistry >
Physical Chemistry >
All Questions
All questions of Solid State for Chemistry Exam
In a crystalline solid, anion B are arranged in CCP lattice and cations A occupy 50% of the octahedral voids and 50% of the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the solid:- a)AB
- b)A3B2
- c)A2B2
- d)A2B3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a crystalline solid, anion B are arranged in CCP lattice and cations A occupy 50% of the octahedral voids and 50% of the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the solid:
a)
AB
b)
A3B2
c)
A2B2
d)
A2B3

|
Akanksha Choudhary answered |
No of atoms in a CCP unit cell=similar to FCC=4
Therefore no of B atoms present=4
No of A atom=tetrahedral void and octohedral void(4+2)=6
The formula of the compound =A3B2
Which of the units given can be used to build the structure of covalent crystal, diamond:- a)Tetrahedral
- b)Octahedral
- c)Hexagonal
- d)Cubic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the units given can be used to build the structure of covalent crystal, diamond:
a)
Tetrahedral
b)
Octahedral
c)
Hexagonal
d)
Cubic

|
Swara Dasgupta answered |
Diamond and Graphite, Two allotropes of carbon are covalent network solids which differ in the bonding geometry of the carbon atoms.
In diamond, the bonding occurs in the tetrahedral geometry, while in graphite the carbons bond with each other in the trigonal planar arrangement. This difference accounts for the drastically different appearance and properties of these two forms of carbon.
Diamond is also an allotrope of carbon. Diamond is the hardest material known, defining the upper end of the 1-10 scale known as Moh’s hardness scale. Diamond cannot be melted; above 1700 deg C it is converted to graphite, the more stable form of carbon. The diamond unit cell is face-centered cubic and contains eight carbon atoms.
For a simple cubic crystal lattice, the angle between the [201] plane and the xy plane is:- a)Less than 300
- b)Between 300 and 450
- c)Between 450 and 600
- d)Greater than 600
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For a simple cubic crystal lattice, the angle between the [201] plane and the xy plane is:
a)
Less than 300
b)
Between 300 and 450
c)
Between 450 and 600
d)
Greater than 600

|
Sarthak Chavan answered |
Explanation:
- A simple cubic lattice is a type of crystal lattice where the lattice points form a cube and are located at the corners of the cube.
- The [201] plane is a crystallographic plane that passes through the lattice points at (2, 0, 1), (-2, 0, 1), (0, 2, 1) and (0, -2, 1).
- The xy plane is a plane that is parallel to the x and y axes of the lattice.
- The angle between the [201] plane and the xy plane can be determined by finding the dot product of the normal vectors to each plane and using the formula:
cosθ = (a . b) / (|a| |b|)
where a and b are the normal vectors to the two planes.
- The normal vector to the [201] plane can be found by taking the cross product of two vectors that lie in the plane, such as (2, 0, 1) and (0, 2, 1), which gives the vector (-2, -2, 4).
- The normal vector to the xy plane is simply the z-axis vector, (0, 0, 1).
- Taking the dot product of these two vectors gives:
(-2, -2, 4) . (0, 0, 1) = 4
- The magnitude of each vector is:
|(2, 0, 1) × (0, 2, 1)| = 4
|(0, 0, 1)| = 1
- Substituting these values into the formula gives:
cosθ = (4) / (4 * 1) = 1
- Therefore, the angle θ between the [201] plane and the xy plane is:
θ = cos-1(1) = 0
- Since the angle is zero, it means that the two planes are parallel to each other, and therefore never intersect. Therefore, the angle between the [201] plane and the xy plane is greater than 600 degrees.
- A simple cubic lattice is a type of crystal lattice where the lattice points form a cube and are located at the corners of the cube.
- The [201] plane is a crystallographic plane that passes through the lattice points at (2, 0, 1), (-2, 0, 1), (0, 2, 1) and (0, -2, 1).
- The xy plane is a plane that is parallel to the x and y axes of the lattice.
- The angle between the [201] plane and the xy plane can be determined by finding the dot product of the normal vectors to each plane and using the formula:
cosθ = (a . b) / (|a| |b|)
where a and b are the normal vectors to the two planes.
- The normal vector to the [201] plane can be found by taking the cross product of two vectors that lie in the plane, such as (2, 0, 1) and (0, 2, 1), which gives the vector (-2, -2, 4).
- The normal vector to the xy plane is simply the z-axis vector, (0, 0, 1).
- Taking the dot product of these two vectors gives:
(-2, -2, 4) . (0, 0, 1) = 4
- The magnitude of each vector is:
|(2, 0, 1) × (0, 2, 1)| = 4
|(0, 0, 1)| = 1
- Substituting these values into the formula gives:
cosθ = (4) / (4 * 1) = 1
- Therefore, the angle θ between the [201] plane and the xy plane is:
θ = cos-1(1) = 0
- Since the angle is zero, it means that the two planes are parallel to each other, and therefore never intersect. Therefore, the angle between the [201] plane and the xy plane is greater than 600 degrees.
The molar volume of KCl and NaCl are 37.46 ml and 27.94 ml. The ratio of unit cell edges of the two crystals is:- a)1.296
- b)1.116
- c)1.341
- d)0.950
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar volume of KCl and NaCl are 37.46 ml and 27.94 ml. The ratio of unit cell edges of the two crystals is:
a)
1.296
b)
1.116
c)
1.341
d)
0.950

|
Anagha Chauhan answered |
Molar volume =N4/3πr³ where N is Avogadro number ,
Now Molar volume of KCl is 37.46cm³ So N4/3πR³ = 37.46 cm³
On solving this gives R=2.458 x 10-8 cm
And for NaCl by using the same formula it gives R=2.22 x 10-8 cm
Now the ratio of edge length must be equal to ratio of radii as both belong to same crystal system so KCl/NaCl = 2.458/2.22 = 1.108
A solid has a structure in which W atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, O atom of the centre of the edges and Na atom at centre of the cubic. The formula for the compound is:- a)NaWO2
- b)NaWO3
- c)Na2WO3
- d)NaWO4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A solid has a structure in which W atoms are located at the corners of a cubic lattice, O atom of the centre of the edges and Na atom at centre of the cubic. The formula for the compound is:
a)
NaWO2
b)
NaWO3
c)
Na2WO3
d)
NaWO4

|
Sagarika Patel answered |
In a unit cell W atoms at the corner
= 1/8 x 8 = 1
0-atoms at the centre of edges = 1/4 x 12 = 3
Na-atoms at the centre of the cube = 1
W: 0: Na = 1:3:1
Hence, formula is NaW03
Na2SeO4 and Na2SO4 show:- a)Isomorphism
- b)Polymorphism
- c)Allotropism
- d)Ferromagnetism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Na2SeO4 and Na2SO4 show:
a)
Isomorphism
b)
Polymorphism
c)
Allotropism
d)
Ferromagnetism

|
Saanvi Roy answered |
Na2SO4 and Na2SeO4 are different substances possessing similar formula, they are called isomorphous systems
The density of CaF2 (fluorite structure) is 3.18 g/cm3. The length of the side of the unit cell is:- a)253 pm
- b)344 pm
- c)546 pm
- d)273 pm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The density of CaF2 (fluorite structure) is 3.18 g/cm3. The length of the side of the unit cell is:
a)
253 pm
b)
344 pm
c)
546 pm
d)
273 pm
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
d = zM/NA × V
For flourite structure, z = 4 and M = 78
3.18 = (4 × 78)/6.023 × 1023 × a3
a3 = 312/(6.023×1023 × 3.18)
a3 = 16.28 × 10-23
a = 546 pm
For flourite structure, z = 4 and M = 78
3.18 = (4 × 78)/6.023 × 1023 × a3
a3 = 312/(6.023×1023 × 3.18)
a3 = 16.28 × 10-23
a = 546 pm
Solid CO2 is an example of the crystal type:- a)Ionic
- b)Covalent
- c)Metallic
- d)Molecular
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Solid CO2 is an example of the crystal type:
a)
Ionic
b)
Covalent
c)
Metallic
d)
Molecular
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
Solid CO₂ is an example of Molecular Crystal.
Extra information - Basically molecular crystalline solids are held by dipole-dipole , hydrogen-bond inter-particle forces and dispersion forces i.e. London forces. Molecular crystalline solids are soft , melting point is low and also poor conductors of heat and electricity. Forces found in molecular crystalline solid which are mentioned above are collectively known as intermolecular forces which are weaker than intramolecular forces.
Which of the following expressions is true in case of sodium chloride unit cell:- a)rc + ra = a
- b)rc + ra = a/2
- c)rc + ra = 2a
- d)
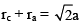
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expressions is true in case of sodium chloride unit cell:
a)
rc + ra = a
b)
rc + ra = a/2
c)
rc + ra = 2a
d)

|
Nandini Das answered |
In face-centered cubic system, the inter ionic distance is given by rc + ra = a/2
rc = Radius of the cation
ra = Radius of the Anion.
The radius of an atom of an element is 55 pm. What is the edge length of the unit cell if it is body-centred cubic?- a)144.6 pm
- b)163.4 pm
- c)127.0 pm
- d)123.5 pm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The radius of an atom of an element is 55 pm. What is the edge length of the unit cell if it is body-centred cubic?
a)
144.6 pm
b)
163.4 pm
c)
127.0 pm
d)
123.5 pm

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Explanation: Given,
Interionic radius (r) = 55 pm
Edge length (a) =?
For BCC, r =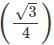 x a
x a
Or a =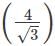 x r= 4 x 55/1.732 = 127 pm.
x r= 4 x 55/1.732 = 127 pm.
Interionic radius (r) = 55 pm
Edge length (a) =?
For BCC, r =
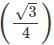 x a
x aOr a =
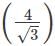 x r= 4 x 55/1.732 = 127 pm.
x r= 4 x 55/1.732 = 127 pm.An element exists as hexagonal close packed structure as well as cubic closed packed structure. In which case the element would have higher density:- a)ccp
- b)hcp
- c)Same in both
- d)Unpredictable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An element exists as hexagonal close packed structure as well as cubic closed packed structure. In which case the element would have higher density:
a)
ccp
b)
hcp
c)
Same in both
d)
Unpredictable

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
The packing efficiency of both hcp and ccp is aprrox. same i.e. 74%. This means there is same mass for given same volume for both packing and hence density will be same for both packing, given the element is same.
X-rays of wKa (wavelength 154 pm) are diffracted by a set of atomic planes in a crystals in the following manner. The separation of the la yers in the crystals in 404 Pm. Find the angle a along which the first order reflection will occur: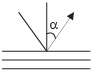
- a)79º
- b)45º
- c)11º
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
X-rays of wKa (wavelength 154 pm) are diffracted by a set of atomic planes in a crystals in the following manner. The separation of the la yers in the crystals in 404 Pm. Find the angle a along which the first order reflection will occur:
a)
79º
b)
45º
c)
11º
d)
None of these
|
|
Ram Kumar answered |
Keep in mind that θ=90-α in Bragg's law, where α is angle of incidence and θ is angle of glancing, which is also called sometimes angle of incidence of X-ray, not to be confused.
An element exists in two crystallographic modifications with FCC and BCC structures. The ratio of the densities of the FCC and BCC modifications in terms of the volumes of their unit cells (VFCC and VBCC) is:- a)VBCC: VFCC
- b)2VBCC: VFCC
- c)VBCC: 2VFCC
- d)
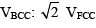
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An element exists in two crystallographic modifications with FCC and BCC structures. The ratio of the densities of the FCC and BCC modifications in terms of the volumes of their unit cells (VFCC and VBCC) is:
a)
VBCC: VFCC
b)
2VBCC: VFCC
c)
VBCC: 2VFCC
d)
|
|
Ram Kumar answered |
The game is of z, total number of atoms in a unit cell. Now you can play the game easily.
Schottky defect generally appears in:- a)NaCl
- b)CsCl
- c)KCl
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Schottky defect generally appears in:
a)
NaCl
b)
CsCl
c)
KCl
d)
All of these

|
Rahul Chatterjee answered |
Schottky defects occurs in highly ionic compounds which have high co-ordination number, e.g., NaCl, KCl, CsCl.
In Rocksalt structure:a)Cation is present at corners as well face centre and anion is present in octahedral void.b)Anion is present in corners as well as face centre whereas cation in octahedral voidc)Cation in fcc and anion in alternate tetrahedral voidd)Anion at fcc and cation in all the tetrahedral void.Correct answer is option 'b'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Azarudeen answered |
Answer is option B but iam unable to post that picture so I keep that solution in my profile photo
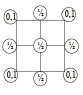
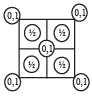
2D representation of the fcc unit cell is:
- a)
- b)
- c)
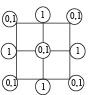
- d)
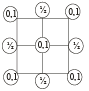
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
2D representation of the fcc unit cell is:
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Tanuja Srivastava answered |
Here we are taking 2D side of a 3D shape so first cut the FCC crystal such that x and y axis 2D remains with you.
Now we know that FCC have an atom in center of face, and rest are at the four corners, assuming ball the atoms to be of equal size solve it for the remaining spaces of a square.
Now we know that FCC have an atom in center of face, and rest are at the four corners, assuming ball the atoms to be of equal size solve it for the remaining spaces of a square.
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.- a)0.1
- b)0.4
- c)0.8
- d)1.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If an X-ray tube operates at the voltage of 10 kV, find the ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X-rays produced. The specific charge of an electron is 1.8 × 1011 C / kg.
a)
0.1
b)
0.4
c)
0.8
d)
1.0

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
CONCEPT:
The wavelength of any charged particle due to its motion is called the de-Broglie wavelength.
When a charged particle is accelerated in a potential difference the energy gained by the particle is given by:
Energy (E) = e × V
Where V is the potential difference and q is a charge.
The de-Broglie wavelength of charge particle (λd) is given by:
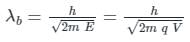
Where E is energy, h is Planck constant, m is the mass of the charged particle
EXPLANATION:
De-Broglie wavelength when a charge q is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts is
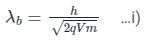
For cut off wavele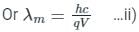 ngth of X-rays, we have
ngth of X-rays, we have
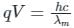
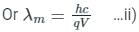
From Eqs, i) and ii), we get
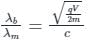
For electron q/m = 1.8 x 1011C/kg (given).
Substituting the values the desired ratio is

The wavelength of any charged particle due to its motion is called the de-Broglie wavelength.
When a charged particle is accelerated in a potential difference the energy gained by the particle is given by:
Energy (E) = e × V
Where V is the potential difference and q is a charge.
The de-Broglie wavelength of charge particle (λd) is given by:
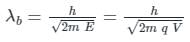
Where E is energy, h is Planck constant, m is the mass of the charged particle
EXPLANATION:
De-Broglie wavelength when a charge q is accelerated by a potential difference of V volts is
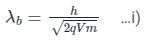
For cut off wavele
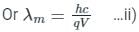 ngth of X-rays, we have
ngth of X-rays, we have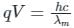
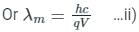
From Eqs, i) and ii), we get
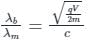
For electron q/m = 1.8 x 1011C/kg (given).
Substituting the values the desired ratio is

If the anions(A) form hexagonal closest packing and cations (C) occupy only 2/3 octahedral voids in it, then the general formula of the compound is:- a)CA
- b)CA2
- c)C2A3
- d)C3A2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the anions(A) form hexagonal closest packing and cations (C) occupy only 2/3 octahedral voids in it, then the general formula of the compound is:
a)
CA
b)
CA2
c)
C2A3
d)
C3A2

|
Kaavya Sengupta answered |
Number of A atoms per unit cell in hcp lattice=6. Number of octahedral voids=6 Number of octahedral voids occupied by C = (2/3)*6 = 4 Therefore formula of compound = C4A6 = C2A3
A crystal has the lattice parameters a ≠ b ≠ c and α = β = γ = 900. The crystal system is:- a)Tetragonal
- b)Monoclinic
- c)Cubic
- d)Orthorhombic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A crystal has the lattice parameters a ≠ b ≠ c and α = β = γ = 900. The crystal system is:
a)
Tetragonal
b)
Monoclinic
c)
Cubic
d)
Orthorhombic

|
Shivam Khanna answered |
Crystal System Identification
Explanation:
The crystal system of a crystal can be identified by its lattice parameters and angles between them. The lattice parameters are the lengths of the edges of the unit cell and the angles between them are the angles formed by the edges.
Orthorhombic Crystal System:
In an orthorhombic crystal system, all three lattice parameters, a, b, and c, are different and the angles between them are all 90 degrees. This means that the crystal is not cubic or tetragonal since all edges are not the same length. Additionally, since all angles are right angles, it is not monoclinic or triclinic.
Therefore, the crystal in question has lattice parameters a, b, and c, and angles between them of 90 degrees, indicating that it is in the orthorhombic crystal system.
Explanation:
The crystal system of a crystal can be identified by its lattice parameters and angles between them. The lattice parameters are the lengths of the edges of the unit cell and the angles between them are the angles formed by the edges.
Orthorhombic Crystal System:
In an orthorhombic crystal system, all three lattice parameters, a, b, and c, are different and the angles between them are all 90 degrees. This means that the crystal is not cubic or tetragonal since all edges are not the same length. Additionally, since all angles are right angles, it is not monoclinic or triclinic.
Therefore, the crystal in question has lattice parameters a, b, and c, and angles between them of 90 degrees, indicating that it is in the orthorhombic crystal system.
The characteristic of light used in X-Ray crystallography is-- a)Interference
- b)Diffraction
- c)Reflection
- d)Refraction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The characteristic of light used in X-Ray crystallography is-
a)
Interference
b)
Diffraction
c)
Reflection
d)
Refraction

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
CONCEPT:
- X-ray crystallography: It is the technique of determining the molecular and atomic structure of a crystal.
- X-ray beams are used to determine the structure of the crystal.
- The crystal diffracts the X-ray beams and the intensities and angle of diffraction of these diffracted beams are studied to estimate the structure of the crystal.
EXPLANATION:
- The diffraction of light is used in X-ray crystallography.
- X-rays diffracted from the crystal are studied to determine the structure of the crystal.
X-rays can be deflected by:- a)electric field
- b)none of the fields
- c)magnetic field
- d)electromagnetic field
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
X-rays can be deflected by:
a)
electric field
b)
none of the fields
c)
magnetic field
d)
electromagnetic field

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
X-rays aren't deflected by electrons and magnetic fields because x-rays do not carry and charge. They are electro-magnetic radiations and therefore cannot be deflected by electronic or any magnetic fields.
EXTRA POINTS:
1. X-rays: An electromagnetic wave with wavelengths from 0.1 Å to 100 Å called X-rays.
2. X-rays were discovered by WC Roentgen in 1895 and he was later awarded with Nobel Prize in 1901. So option 4 is correct.
3. He named that new unknown type of radiation as X-rays.
4. X-rays are the second most energetic radiations in the Electromagnetic Spectrum following Gamma rays.
5. The wavelength of these rays ranges from 10-11 to 10-8 m and the frequency is around 3 x 1016 - 3 x 1019.
6. Therefore these are very shortwave and high energy EM radiations (travelling with the speed of light).
7. X-rays are widely used in medical diagnosis and Astronomy.
EXTRA POINTS:
1. X-rays: An electromagnetic wave with wavelengths from 0.1 Å to 100 Å called X-rays.
2. X-rays were discovered by WC Roentgen in 1895 and he was later awarded with Nobel Prize in 1901. So option 4 is correct.
3. He named that new unknown type of radiation as X-rays.
4. X-rays are the second most energetic radiations in the Electromagnetic Spectrum following Gamma rays.
5. The wavelength of these rays ranges from 10-11 to 10-8 m and the frequency is around 3 x 1016 - 3 x 1019.
6. Therefore these are very shortwave and high energy EM radiations (travelling with the speed of light).
7. X-rays are widely used in medical diagnosis and Astronomy.

If metallic atoms of mass 197 and radius 166 pm are arranged in ABCABC fashion then what is the surface area of each unit cell?- a)1.32 × 106 pm2
- b)1.32 × 10-18pm2
- c)2.20 × 105 pm2
- d)2.20 × 10-19 pm2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If metallic atoms of mass 197 and radius 166 pm are arranged in ABCABC fashion then what is the surface area of each unit cell?
a)
1.32 × 106 pm2
b)
1.32 × 10-18pm2
c)
2.20 × 105 pm2
d)
2.20 × 10-19 pm2
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
ABCABC arrangement is found in CCP.
In closed cubic packing, relation between edge length of unit cell, a, and radius of particle, r, is given as a=2√2r.
Surface area (S.A.) = 6a2
From the relationship,
a2 = 8r2
S.A. = 6a2 = 48r2
When r = 166 pm, S.A. = 48(166pm) = 1.32 x 106 pm2.
In closed cubic packing, relation between edge length of unit cell, a, and radius of particle, r, is given as a=2√2r.
Surface area (S.A.) = 6a2
From the relationship,
a2 = 8r2
S.A. = 6a2 = 48r2
When r = 166 pm, S.A. = 48(166pm) = 1.32 x 106 pm2.
Which of the following crystals have 8:8 coordination:- a)NH4Cl
- b)AlFe
- c)MnO
- d)NH4Br
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following crystals have 8:8 coordination:
a)
NH4Cl
b)
AlFe
c)
MnO
d)
NH4Br

|
Sparsh Menon answered |
Explanation:
Coordination number refers to the number of neighboring ions or molecules that a central ion or molecule is surrounded by. The coordination number of a crystal is determined by the size and charge of the ions in the crystal lattice. In this case, we are looking for crystals with 8:8 coordination.
Crystals with 8:8 coordination:
Therefore, the crystals with 8:8 coordination are NH4Cl, AlF3, and NH4Br.
Coordination number refers to the number of neighboring ions or molecules that a central ion or molecule is surrounded by. The coordination number of a crystal is determined by the size and charge of the ions in the crystal lattice. In this case, we are looking for crystals with 8:8 coordination.
Crystals with 8:8 coordination:
- NH4Cl: Ammonium chloride contains NH4+ and Cl- ions. The NH4+ ion is tetrahedral in shape and is surrounded by four Cl- ions, while each Cl- ion is surrounded by four NH4+ ions. Therefore, NH4Cl has 8:8 coordination.
- AlFe: Aluminium fluoride has a crystal structure where each Al3+ ion is surrounded by six F- ions and each F- ion is surrounded by six Al3+ ions. Therefore, AlF3 has 6:6 coordination. Iron is not present in this crystal.
- MnO: Manganese oxide has a rock salt crystal structure where each Mn2+ ion is surrounded by six O2- ions and each O2- ion is surrounded by six Mn2+ ions. Therefore, MnO has 6:6 coordination.
- NH4Br: Ammonium bromide has a crystal structure similar to NH4Cl, where each NH4+ ion is surrounded by four Br- ions and each Br- ion is surrounded by four NH4+ ions. Therefore, NH4Br has 8:8 coordination.
Therefore, the crystals with 8:8 coordination are NH4Cl, AlF3, and NH4Br.
If edge length of the unit cell is 356 pm, then radius of carbon atom in diamond:- a)77.07 pm
- b)154.14 pm
- c)251.7 pm
- d)89 pm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If edge length of the unit cell is 356 pm, then radius of carbon atom in diamond:
a)
77.07 pm
b)
154.14 pm
c)
251.7 pm
d)
89 pm

|
Kaavya Sengupta answered |
In a diamond structure, there are atoms at each corner and alternate tetrahedral voids. Consider the body diagonal of unit cell (cube with side a). It corresponds to 8R, and length of body diagonal is √3xa.
Thus R = √3xa/8 = 356 x 1.732/8 = 77.07 pm
Name of the crystal class for which all the four types of unit cells are possible:- a)Hexagonal
- b)Tetragonal
- c)Monoclinic
- d)Orthorhombic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Name of the crystal class for which all the four types of unit cells are possible:
a)
Hexagonal
b)
Tetragonal
c)
Monoclinic
d)
Orthorhombic

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
Every crystal system does not have all the four types of unit cells (simples, face centered, end centered and body centered). But orthorhombic crystal class has all four types of unit cells - primitive, face-centered, body-centered and end-centered.
Lithium forms a BCC lattice with an edge length of 350 pm. The experimental density of lithium is 0.53 g cm-3. What is the percentage of missing lithium atoms? (Atomic mass of Lithium = 7 amu)- a)97.7%
- b)95.4%
- c)4.6%
- d)2.3%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Lithium forms a BCC lattice with an edge length of 350 pm. The experimental density of lithium is 0.53 g cm-3. What is the percentage of missing lithium atoms? (Atomic mass of Lithium = 7 amu)
a)
97.7%
b)
95.4%
c)
4.6%
d)
2.3%

|
Abhishek Nambiar answered |
Given:
- Lithium forms a BCC lattice with an edge length of 350 pm.
- Experimental density of lithium is 0.53 g cm-3.
- Atomic mass of Lithium = 7 amu.
To Find:
- The percentage of missing lithium atoms.
Concepts Used:
- BCC lattice structure.
- Calculation of the number of atoms in a BCC unit cell.
- Calculation of the density of a substance.
- Calculation of the percentage of missing atoms.
Explanation:
Step 1: Calculate the number of atoms in a BCC unit cell:
- In a BCC lattice, there are 2 atoms per unit cell.
- Each corner atom is shared by 8 unit cells, and each unit cell contributes 1/8th of an atom.
- There is 1 atom at the center of the unit cell, which is not shared.
- Therefore, the total number of atoms in a BCC unit cell is (1/8) * 8 + 1 = 2.
Step 2: Calculate the volume of the unit cell:
- The edge length of the BCC unit cell is given as 350 pm.
- The volume of a cube is calculated by multiplying the edge length by itself three times.
- Therefore, the volume of the unit cell is (350 pm)^3.
Step 3: Calculate the mass of the unit cell:
- The density of lithium is given as 0.53 g cm-3.
- Density is defined as mass divided by volume.
- Therefore, the mass of the unit cell is the product of the density and the volume of the unit cell.
Step 4: Calculate the molar mass of the unit cell:
- The atomic mass of lithium is given as 7 amu.
- Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance.
- Therefore, the molar mass of the unit cell is the product of the atomic mass of lithium and the number of atoms in the unit cell.
Step 5: Calculate the number of moles of lithium in the unit cell:
- The number of moles is calculated by dividing the mass of the unit cell by the molar mass of the unit cell.
Step 6: Calculate the number of missing lithium atoms:
- The number of missing lithium atoms is calculated by subtracting the number of moles of lithium in the unit cell from the number of atoms in the unit cell.
Step 7: Calculate the percentage of missing lithium atoms:
- The percentage of missing lithium atoms is calculated by dividing the number of missing lithium atoms by the total number of atoms in the unit cell and multiplying by 100.
Answer:
The percentage of missing lithium atoms is 2.3%.
- Lithium forms a BCC lattice with an edge length of 350 pm.
- Experimental density of lithium is 0.53 g cm-3.
- Atomic mass of Lithium = 7 amu.
To Find:
- The percentage of missing lithium atoms.
Concepts Used:
- BCC lattice structure.
- Calculation of the number of atoms in a BCC unit cell.
- Calculation of the density of a substance.
- Calculation of the percentage of missing atoms.
Explanation:
Step 1: Calculate the number of atoms in a BCC unit cell:
- In a BCC lattice, there are 2 atoms per unit cell.
- Each corner atom is shared by 8 unit cells, and each unit cell contributes 1/8th of an atom.
- There is 1 atom at the center of the unit cell, which is not shared.
- Therefore, the total number of atoms in a BCC unit cell is (1/8) * 8 + 1 = 2.
Step 2: Calculate the volume of the unit cell:
- The edge length of the BCC unit cell is given as 350 pm.
- The volume of a cube is calculated by multiplying the edge length by itself three times.
- Therefore, the volume of the unit cell is (350 pm)^3.
Step 3: Calculate the mass of the unit cell:
- The density of lithium is given as 0.53 g cm-3.
- Density is defined as mass divided by volume.
- Therefore, the mass of the unit cell is the product of the density and the volume of the unit cell.
Step 4: Calculate the molar mass of the unit cell:
- The atomic mass of lithium is given as 7 amu.
- Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance.
- Therefore, the molar mass of the unit cell is the product of the atomic mass of lithium and the number of atoms in the unit cell.
Step 5: Calculate the number of moles of lithium in the unit cell:
- The number of moles is calculated by dividing the mass of the unit cell by the molar mass of the unit cell.
Step 6: Calculate the number of missing lithium atoms:
- The number of missing lithium atoms is calculated by subtracting the number of moles of lithium in the unit cell from the number of atoms in the unit cell.
Step 7: Calculate the percentage of missing lithium atoms:
- The percentage of missing lithium atoms is calculated by dividing the number of missing lithium atoms by the total number of atoms in the unit cell and multiplying by 100.
Answer:
The percentage of missing lithium atoms is 2.3%.
An element with cell edge of 288 pm has a density of 7.2 g cm-3. What type of structure does the element have if it’s atomic mass M=51.8 g mol-1?- a)Body-Centred Cubic (BCC)
- b)Face-Centred Cubic (FCC)
- c)Simple Cubic
- d)Hexagonal Closed Packing (HCP)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An element with cell edge of 288 pm has a density of 7.2 g cm-3. What type of structure does the element have if it’s atomic mass M=51.8 g mol-1?
a)
Body-Centred Cubic (BCC)
b)
Face-Centred Cubic (FCC)
c)
Simple Cubic
d)
Hexagonal Closed Packing (HCP)
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
Given,
Edge length (a) = 288 pm
Density (ρ) = 7.2 g cm-3
Atomic mass (M) = 51.8 g mol-1
Avogadro’s number (N0) = 6.02 x 1023
We know, (ρ) = (Z x M)/(a3 x N0)
Or Z =(ρ x a3 x N0)/M = (7.2 x (288 x 10-10) 3 x 6.02 x 1023)/51.8
Z = 2
Therefore, the element has Body-Centred Cubic (BCC) type of structure.
Edge length (a) = 288 pm
Density (ρ) = 7.2 g cm-3
Atomic mass (M) = 51.8 g mol-1
Avogadro’s number (N0) = 6.02 x 1023
We know, (ρ) = (Z x M)/(a3 x N0)
Or Z =(ρ x a3 x N0)/M = (7.2 x (288 x 10-10) 3 x 6.02 x 1023)/51.8
Z = 2
Therefore, the element has Body-Centred Cubic (BCC) type of structure.
An alloy of copper, silver and gold is found to have copper constituting the ccp lattice. If silver atoms occupy the edge centres and gold is present at body centre, the alloy has a formula:
- a) Cu4Ag2Au
- b) Cu4Ag4Au
- c) Cu4Ag3Au
- d) CuAgAu
Correct answer is option `C`. Can you explain this answer?
An alloy of copper, silver and gold is found to have copper constituting the ccp lattice. If silver atoms occupy the edge centres and gold is present at body centre, the alloy has a formula:
a) Cu4Ag2Au
b) Cu4Ag4Au
c) Cu4Ag3Au
d) CuAgAu
|
|
Rajeev Menon answered |
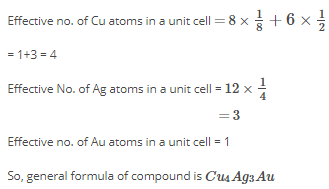
The melting point of RbBr is 682°C, while that of NaF is 988°C. The principal reason that melting point of NaF is much higher than that of RbBr is that:- a)The two crystals are not Isomorphous.
- b)The molar mass of NaF is smaller than that of RbBr
- c)The inter-nuclear distance rc + ra is lesser for NaF than for RbBr
- d)The bond in RbBr has more covalent character than the bond in NaF
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The melting point of RbBr is 682°C, while that of NaF is 988°C. The principal reason that melting point of NaF is much higher than that of RbBr is that:
a)
The two crystals are not Isomorphous.
b)
The molar mass of NaF is smaller than that of RbBr
c)
The inter-nuclear distance rc + ra is lesser for NaF than for RbBr
d)
The bond in RbBr has more covalent character than the bond in NaF

|
Shivam Sharma answered |
In ionic compounds as internuclear distance incrreases, melting point decreases so as we move down the group, melting point decreases. So, as rc+ra is greater for RbBr than for NaF so NaF have higher melting point.
The atomic radius (in cm) of an element with a body centred cubit unit cell of molecular weight 137.3 and density 3.62 g cm–3 is:- a)1.5 × 10–8
- b)1.6 × 10–8
- c)2.2 × 10–8
- d)2.0 × 10–8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomic radius (in cm) of an element with a body centred cubit unit cell of molecular weight 137.3 and density 3.62 g cm–3 is:
a)
1.5 × 10–8
b)
1.6 × 10–8
c)
2.2 × 10–8
d)
2.0 × 10–8

|
Abhijeet Majumdar answered |
First, we need to find the edge length (a) of the body centred cubic unit cell using the density and molecular weight of the element.
Density = mass/volume
Volume of unit cell = a^3
Mass of unit cell = molecular weight/Avogadro's number
Combining these equations:
density = (molecular weight/Avogadro's number) / a^3
a^3 = (molecular weight/Avogadro's number) / density
a^3 = (137.3 g/mol / 6.022 x 10^23 mol^-1) / 3.62 g cm^-3
a^3 = 6.036 x 10^-23 cm^3
a = (6.036 x 10^-23 cm^3)^(1/3)
a = 3.184 x 10^-8 cm
Now, we can find the radius (r) of the atom using the edge length (a) and the geometry of the body centred cubic unit cell.
r = a * sqrt(3) / 4
r = (3.184 x 10^-8 cm) * sqrt(3) / 4
r = 1.386 x 10^-8 cm
Therefore, the atomic radius of the element is approximately 1.386 x 10^-8 cm.
Density = mass/volume
Volume of unit cell = a^3
Mass of unit cell = molecular weight/Avogadro's number
Combining these equations:
density = (molecular weight/Avogadro's number) / a^3
a^3 = (molecular weight/Avogadro's number) / density
a^3 = (137.3 g/mol / 6.022 x 10^23 mol^-1) / 3.62 g cm^-3
a^3 = 6.036 x 10^-23 cm^3
a = (6.036 x 10^-23 cm^3)^(1/3)
a = 3.184 x 10^-8 cm
Now, we can find the radius (r) of the atom using the edge length (a) and the geometry of the body centred cubic unit cell.
r = a * sqrt(3) / 4
r = (3.184 x 10^-8 cm) * sqrt(3) / 4
r = 1.386 x 10^-8 cm
Therefore, the atomic radius of the element is approximately 1.386 x 10^-8 cm.
The edge length of a face centred cubic cell of an ionic substance is 508 pm. If the radius of the cation is 110 pm, the radius of the anion is- a)288 pm
- b)144 pm
- c)618 pm
- d)398 pm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The edge length of a face centred cubic cell of an ionic substance is 508 pm. If the radius of the cation is 110 pm, the radius of the anion is
a)
288 pm
b)
144 pm
c)
618 pm
d)
398 pm

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
Given:
Edge length of a face-centred cubic cell = 508 pm
Radius of cation = 110 pm
To find: Radius of anion
Formula used:
In a face-centred cubic cell, the cation is present at the corners of the cube and the face-centred positions, while the anion is present at the centre of each face of the cube.
Let the radius of the anion be 'r'.
The edge length of the face-centred cubic cell (a) can be given as:
a = 4r/sqrt(2)
Calculation:
Given, edge length of the face-centred cubic cell = 508 pm
Therefore, a = 508 pm
Substituting the value of 'a' in the above equation, we get:
508 = 4r/sqrt(2)
r = 508 x sqrt(2)/4
r = 254 x sqrt(2) pm
r = 254 x 1.414 pm
r = 359 pm
Therefore, the radius of the anion is 359 pm.
Answer:
The correct option is not given in the question. The calculated value of the radius of the anion is 359 pm.
Edge length of a face-centred cubic cell = 508 pm
Radius of cation = 110 pm
To find: Radius of anion
Formula used:
In a face-centred cubic cell, the cation is present at the corners of the cube and the face-centred positions, while the anion is present at the centre of each face of the cube.
Let the radius of the anion be 'r'.
The edge length of the face-centred cubic cell (a) can be given as:
a = 4r/sqrt(2)
Calculation:
Given, edge length of the face-centred cubic cell = 508 pm
Therefore, a = 508 pm
Substituting the value of 'a' in the above equation, we get:
508 = 4r/sqrt(2)
r = 508 x sqrt(2)/4
r = 254 x sqrt(2) pm
r = 254 x 1.414 pm
r = 359 pm
Therefore, the radius of the anion is 359 pm.
Answer:
The correct option is not given in the question. The calculated value of the radius of the anion is 359 pm.
The angle at which the first order Bragg reflection is observed from (110) plane in a simple cubic unit cell of side 3.238 Å when chromium Ka radiation of wavelength 2.29 Å is used, is:- a)300
- b)450
- c)600
- d)900
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle at which the first order Bragg reflection is observed from (110) plane in a simple cubic unit cell of side 3.238 Å when chromium Ka radiation of wavelength 2.29 Å is used, is:
a)
300
b)
450
c)
600
d)
900

|
Sid Gupta answered |
Hey use 2dsin theta = n *lemda
When Frenkel defects are created in an otherwise perfect ionic crystal, the density of the ionic crystal:- a)Increases
- b)Decreases
- c)Remains same
- d)Oscillates with the number of defects
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When Frenkel defects are created in an otherwise perfect ionic crystal, the density of the ionic crystal:
a)
Increases
b)
Decreases
c)
Remains same
d)
Oscillates with the number of defects

|
Priya Mehar answered |
In ionic solids cations are smaller than anions and sometimes due to mechanical disruption or change in temperature or pressure cations leave their position and occupy interstial site ....which doesnt affect density of crystal as cations still remain in crystal lattice
Two lines, A and B, of an X-ray beam, give second-order reflection maximum at a glancing angle of 60° and third-order reflection maximum at an angle of 30° respectively from the face of the same crystal. If the wavelength of line B is 0.25 nm, then the wavelength of line A will be:- a)0.65 nm
- b)0.35 nm
- c)0.95 nm
- d)0.15 nm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two lines, A and B, of an X-ray beam, give second-order reflection maximum at a glancing angle of 60° and third-order reflection maximum at an angle of 30° respectively from the face of the same crystal. If the wavelength of line B is 0.25 nm, then the wavelength of line A will be:
a)
0.65 nm
b)
0.35 nm
c)
0.95 nm
d)
0.15 nm

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Concept:
In X-ray scattering
nλ = 2d sin θ
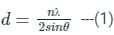
where d = distance between atomic planes, θ = glancing angle, λ = wavelength
Calculation:
Given:
For line A:
n1 = 2, θ1 = 60o, λ1 = ?
For line B;
n2 = 3, θ2 = 30o, λ2 = 0.25 nm
Distance between atomic planes d1 and d2 is equal for same crystal i.e.;
d1 = d2 = d
From equation (1);
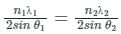
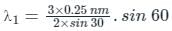
On solving we'll get;
λ1 = 0.649 nm ≈ 0.65 nm
In X-ray scattering
nλ = 2d sin θ
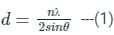
where d = distance between atomic planes, θ = glancing angle, λ = wavelength
Calculation:
Given:
For line A:
n1 = 2, θ1 = 60o, λ1 = ?
For line B;
n2 = 3, θ2 = 30o, λ2 = 0.25 nm
Distance between atomic planes d1 and d2 is equal for same crystal i.e.;
d1 = d2 = d
From equation (1);
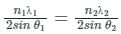
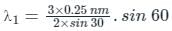
On solving we'll get;
λ1 = 0.649 nm ≈ 0.65 nm
If a metal forms a FCC lattice with unit edge length 500 pm. Calculate the density of the metal if its atomic mass is 110.- a)2923 kg/m3
- b)5846 kg/m3
- c)8768 kg/m3
- d)1750 kg/m3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a metal forms a FCC lattice with unit edge length 500 pm. Calculate the density of the metal if its atomic mass is 110.
a)
2923 kg/m3
b)
5846 kg/m3
c)
8768 kg/m3
d)
1750 kg/m3

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Given,
Edge length (a) = 500 pm = 500 x 10-12 m
Atomic mass (M) = 110 g/mole = 110 x 10-3 kg/mole
Avogadro’s number (NA) = 6.022 x 1023/mole
z = 4 atoms/cell
The density, d of a metal is given as d=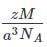
On substitution, d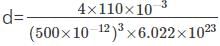 =5846 kg/m3.
=5846 kg/m3.
Edge length (a) = 500 pm = 500 x 10-12 m
Atomic mass (M) = 110 g/mole = 110 x 10-3 kg/mole
Avogadro’s number (NA) = 6.022 x 1023/mole
z = 4 atoms/cell
The density, d of a metal is given as d=
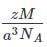
On substitution, d
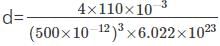 =5846 kg/m3.
=5846 kg/m3.What is each point (position of particle) in a crystal lattice termed as?
- a)Lattice point
- b)Lattice index
- c)Lattice lines
- d)Lattice spot
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is each point (position of particle) in a crystal lattice termed as?
a)
Lattice point
b)
Lattice index
c)
Lattice lines
d)
Lattice spot

|
Abhishek Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option 'B', not 'A'.
Explanation:
A crystal lattice is a regular arrangement of atoms or molecules in a three-dimensional pattern. Each point in this pattern represents the position of a particle in the crystal lattice. These points are known as lattice points.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', lattice point.
Explanation:
A crystal lattice is a regular arrangement of atoms or molecules in a three-dimensional pattern. Each point in this pattern represents the position of a particle in the crystal lattice. These points are known as lattice points.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', lattice point.
The angle between the two planes represented by the Miller indices (110) and (111) in a simple cubic:- a)300
- b)450
- c)600
- d)900
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle between the two planes represented by the Miller indices (110) and (111) in a simple cubic:
a)
300
b)
450
c)
600
d)
900
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
cosθ = (h1h2 + k1k2 + l1l2)/(h12 + k12 + l12)1/2(h22+ k22 + l22)1/2
=> (1+1+0)/[(12 + 12 + 02)1/2(12 + 12 + 02)½]
=> 2/(6)1/2
=> cos-1 2/(6)1/2
=> 30o approx.
A metal X has a BCC structure with nearest neighbor distance 365.9 pm. What is metal X if its density is 1.0016 g cm-3?- a)Aluminum
- b)Magnesium
- c)Sodium
- d)Potassium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal X has a BCC structure with nearest neighbor distance 365.9 pm. What is metal X if its density is 1.0016 g cm-3?
a)
Aluminum
b)
Magnesium
c)
Sodium
d)
Potassium

|
Asf Institute answered |
Given,
Nearest neighbor distance (d) = 365.9 pm
Density (ρ) = 1.51 g cm-3
For the BCC structure, nearest neighbor distance (d) is related to the edge length (a) as d=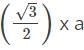
Or a=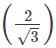 x d = 2/1.732 x 365.9 = 422.5 pm
x d = 2/1.732 x 365.9 = 422.5 pm
For BCC structure, Z=2
We know, (ρ) = (Z x M)/(a3 x N0)
Or M = (ρ x a3 x N0)/Z
= (1.0016 x 106 x (422.5 x 10-12)3 x 6.02 x 1023)/2
= 23 amu
Therefore, the given metal X is Sodium.
Nearest neighbor distance (d) = 365.9 pm
Density (ρ) = 1.51 g cm-3
For the BCC structure, nearest neighbor distance (d) is related to the edge length (a) as d=
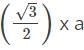
Or a=
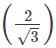 x d = 2/1.732 x 365.9 = 422.5 pm
x d = 2/1.732 x 365.9 = 422.5 pmFor BCC structure, Z=2
We know, (ρ) = (Z x M)/(a3 x N0)
Or M = (ρ x a3 x N0)/Z
= (1.0016 x 106 x (422.5 x 10-12)3 x 6.02 x 1023)/2
= 23 amu
Therefore, the given metal X is Sodium.
Aluminium crystallises in a face-centred cubic lattice. The edge length of the unit cell of aluminium is 4.05 x 10-10m. What is the density of aluminium? (Atomic mass of Al=27)- a)2700 kg m-3
- b)3000 kg m-3
- c)2400 kg m-3
- d)2100 kg m-3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aluminium crystallises in a face-centred cubic lattice. The edge length of the unit cell of aluminium is 4.05 x 10-10m. What is the density of aluminium? (Atomic mass of Al=27)
a)
2700 kg m-3
b)
3000 kg m-3
c)
2400 kg m-3
d)
2100 kg m-3

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
Given,
Atomic mass (M)=27 amu
For FCC structure, Z=4
Avogadro’s number (N0) = 6.02 x 1023
Edge length of the Al unit cell (a)= 4.05 x 10-10m
The density of aluminium (ρ) = (Z x M)/(a3 X N0)
= (4 x 27)/((4.05 x 10-10) 3 x 6.02 x 1023)
= 2700 kg m-3.
Atomic mass (M)=27 amu
For FCC structure, Z=4
Avogadro’s number (N0) = 6.02 x 1023
Edge length of the Al unit cell (a)= 4.05 x 10-10m
The density of aluminium (ρ) = (Z x M)/(a3 X N0)
= (4 x 27)/((4.05 x 10-10) 3 x 6.02 x 1023)
= 2700 kg m-3.
Number of rotational symmetry axes for triclinic crystal system is:- a)4
- b)3
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of rotational symmetry axes for triclinic crystal system is:
a)
4
b)
3
c)
1
d)
0

|
Srishti Khanna answered |
Triclinic Crystal System and Rotational Symmetry Axes
The triclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems in which crystalline materials can be classified. It is the least symmetrical crystal system and has the lowest symmetry among all crystal systems. In the triclinic system, the crystal lattice is characterized by three unequal axes (a, b, and c) that intersect at oblique angles.
Rotational Symmetry Axes
Rotational symmetry is a property of a crystal that describes how the crystal appears the same when rotated about an axis by a certain angle. The rotational symmetry axes are imaginary lines or directions along which a crystal can be rotated to match its original appearance.
In the triclinic crystal system, the rotational symmetry is very limited due to the lack of symmetry elements. The crystal does not possess any rotational symmetry axes other than the identity axis (no rotation). This means that the crystal does not exhibit any rotational symmetry about any axis.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer to the question is option 'D' - 0. This means that the triclinic crystal system does not have any rotational symmetry axes.
The absence of rotational symmetry axes in the triclinic crystal system is due to its lack of symmetry elements. Unlike other crystal systems such as cubic, tetragonal, or hexagonal, which possess multiple symmetry elements, the triclinic system lacks any significant symmetry elements. This lack of symmetry leads to the absence of rotational symmetry axes.
Without rotational symmetry axes, the crystal structure of triclinic materials appears different when rotated about any axis. This lack of symmetry also affects the physical properties of triclinic crystals, such as their thermal expansion characteristics or optical properties.
Overall, the triclinic crystal system is characterized by its low symmetry and absence of rotational symmetry axes. This makes it distinct from other crystal systems and highlights its unique structural and physical properties.
The triclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems in which crystalline materials can be classified. It is the least symmetrical crystal system and has the lowest symmetry among all crystal systems. In the triclinic system, the crystal lattice is characterized by three unequal axes (a, b, and c) that intersect at oblique angles.
Rotational Symmetry Axes
Rotational symmetry is a property of a crystal that describes how the crystal appears the same when rotated about an axis by a certain angle. The rotational symmetry axes are imaginary lines or directions along which a crystal can be rotated to match its original appearance.
In the triclinic crystal system, the rotational symmetry is very limited due to the lack of symmetry elements. The crystal does not possess any rotational symmetry axes other than the identity axis (no rotation). This means that the crystal does not exhibit any rotational symmetry about any axis.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer to the question is option 'D' - 0. This means that the triclinic crystal system does not have any rotational symmetry axes.
The absence of rotational symmetry axes in the triclinic crystal system is due to its lack of symmetry elements. Unlike other crystal systems such as cubic, tetragonal, or hexagonal, which possess multiple symmetry elements, the triclinic system lacks any significant symmetry elements. This lack of symmetry leads to the absence of rotational symmetry axes.
Without rotational symmetry axes, the crystal structure of triclinic materials appears different when rotated about any axis. This lack of symmetry also affects the physical properties of triclinic crystals, such as their thermal expansion characteristics or optical properties.
Overall, the triclinic crystal system is characterized by its low symmetry and absence of rotational symmetry axes. This makes it distinct from other crystal systems and highlights its unique structural and physical properties.
The coordinate number for an atom in a primitive cubic unit cell is- a)6
- b)8
- c)10
- d)12
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The coordinate number for an atom in a primitive cubic unit cell is
a)
6
b)
8
c)
10
d)
12
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
The coordination number for an atom in a primitive cubic unit cell is 6. Each sphere present at a corner of the unit cell is surrounded by 6 neighboring spheres present at 6 other corners.
Molybdenum crystallizes in a bcc-structure with unit cell dimensions of 0.314 nm. Considering the atomic mass of molybdenum to be 96, its density (in kg m–3) is in the range of:- a)8000-10000
- b)10000-10200
- c)10000-10300
- d)10000-10500
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Molybdenum crystallizes in a bcc-structure with unit cell dimensions of 0.314 nm. Considering the atomic mass of molybdenum to be 96, its density (in kg m–3) is in the range of:
a)
8000-10000
b)
10000-10200
c)
10000-10300
d)
10000-10500
|
|
Study Sesh answered |
We know that d = (zM) /(Na)*(a³) and
z = 2 for bcc
Substituting for M (96 g/mol), Na (Avogadro number), and a (0.314nm),
We get d = 10298 kg/m³
Hence, option c is correct.
A metal crystallizes in face-centered cubic lattice with a lattice parameter of 4.20 Å. The shortest atom to atom contact distance in the lattice is:- a)4.20 Å
- b)2.97 Å
- c)2.42 Å
- d)2.10 Å
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal crystallizes in face-centered cubic lattice with a lattice parameter of 4.20 Å. The shortest atom to atom contact distance in the lattice is:
a)
4.20 Å
b)
2.97 Å
c)
2.42 Å
d)
2.10 Å

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
In a face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice, atoms touch along the face diagonal. The face diagonal is equal to √2 times the lattice parameter. Therefore, the shortest atom-to-atom contact distance is calculated as follows: 4.20 Å / √2 = 2.97 Å. Hence, the correct answer is option b.
Gold (atomic mass 197 u) crystallises in a face-centred unit cell. What is its atomic radius if the edge length of the gold unit cell is 0.407 x 10-9m?- a)0.115 nm
- b)0.144 nm
- c)0.235 nm
- d)0.156 nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gold (atomic mass 197 u) crystallises in a face-centred unit cell. What is its atomic radius if the edge length of the gold unit cell is 0.407 x 10-9m?
a)
0.115 nm
b)
0.144 nm
c)
0.235 nm
d)
0.156 nm

|
Bhavana Pillai answered |
Given:
- Atomic mass of gold = 197 u
- Edge length of the gold unit cell = 0.407 x 10^(-9) m
To find:
The atomic radius of gold.
Solution:
The face-centered unit cell of gold consists of atoms located at the corners and the face centers of the unit cell.
Step 1: Calculate the number of atoms in the unit cell:
In a face-centered unit cell, there are:
- 8 corner atoms, where each atom contributes 1/8th to the unit cell
- 6 face-centered atoms, where each atom contributes 1/2 to the unit cell
Total number of atoms in the unit cell = (8 x 1/8) + (6 x 1/2) = 4
Step 2: Calculate the volume of the unit cell:
The volume of a unit cell can be calculated using the formula:
Volume = (edge length)^3
Given:
Edge length of the unit cell = 0.407 x 10^(-9) m
Volume of the unit cell = (0.407 x 10^(-9))^3 = 6.835 x 10^(-29) m^3
Step 3: Calculate the volume occupied by each atom:
Since there are 4 atoms in the unit cell, the volume occupied by each atom can be calculated by dividing the total volume of the unit cell by the number of atoms:
Volume occupied by each atom = Volume of unit cell / Number of atoms = 6.835 x 10^(-29) / 4 = 1.70875 x 10^(-29) m^3
Step 4: Calculate the radius of each atom:
The volume occupied by each atom can also be calculated using the formula for the volume of a sphere:
Volume of a sphere = (4/3) x π x (radius)^3
Given:
Mass of gold atom = 197 u
Avogadro's number = 6.022 x 10^23
The mass of one gold atom can be converted to grams:
Mass of one gold atom = (197 u) x (1.66 x 10^(-27) kg/u) = 3.26 x 10^(-25) kg
The volume occupied by one gold atom can be calculated using its mass and the density of gold:
Density of gold = Mass / Volume
Volume = Mass / Density = (3.26 x 10^(-25) kg) / (19.3 x 10^3 kg/m^3) = 1.69 x 10^(-29) m^3
Equating the two expressions for the volume occupied by each atom:
1.70875 x 10^(-29) m^3 = (4/3) x π x (radius)^3
Simplifying the equation:
(radius)^3 = (1.70875 x 10^(-29) m^3) x (3/4π)
(radius)^3 = 3.226 x 10^(-29) m^3
Taking the cube root of both sides:
radius = (3.226 x 10^(-29))^(1/3) m
radius ≈
- Atomic mass of gold = 197 u
- Edge length of the gold unit cell = 0.407 x 10^(-9) m
To find:
The atomic radius of gold.
Solution:
The face-centered unit cell of gold consists of atoms located at the corners and the face centers of the unit cell.
Step 1: Calculate the number of atoms in the unit cell:
In a face-centered unit cell, there are:
- 8 corner atoms, where each atom contributes 1/8th to the unit cell
- 6 face-centered atoms, where each atom contributes 1/2 to the unit cell
Total number of atoms in the unit cell = (8 x 1/8) + (6 x 1/2) = 4
Step 2: Calculate the volume of the unit cell:
The volume of a unit cell can be calculated using the formula:
Volume = (edge length)^3
Given:
Edge length of the unit cell = 0.407 x 10^(-9) m
Volume of the unit cell = (0.407 x 10^(-9))^3 = 6.835 x 10^(-29) m^3
Step 3: Calculate the volume occupied by each atom:
Since there are 4 atoms in the unit cell, the volume occupied by each atom can be calculated by dividing the total volume of the unit cell by the number of atoms:
Volume occupied by each atom = Volume of unit cell / Number of atoms = 6.835 x 10^(-29) / 4 = 1.70875 x 10^(-29) m^3
Step 4: Calculate the radius of each atom:
The volume occupied by each atom can also be calculated using the formula for the volume of a sphere:
Volume of a sphere = (4/3) x π x (radius)^3
Given:
Mass of gold atom = 197 u
Avogadro's number = 6.022 x 10^23
The mass of one gold atom can be converted to grams:
Mass of one gold atom = (197 u) x (1.66 x 10^(-27) kg/u) = 3.26 x 10^(-25) kg
The volume occupied by one gold atom can be calculated using its mass and the density of gold:
Density of gold = Mass / Volume
Volume = Mass / Density = (3.26 x 10^(-25) kg) / (19.3 x 10^3 kg/m^3) = 1.69 x 10^(-29) m^3
Equating the two expressions for the volume occupied by each atom:
1.70875 x 10^(-29) m^3 = (4/3) x π x (radius)^3
Simplifying the equation:
(radius)^3 = (1.70875 x 10^(-29) m^3) x (3/4π)
(radius)^3 = 3.226 x 10^(-29) m^3
Taking the cube root of both sides:
radius = (3.226 x 10^(-29))^(1/3) m
radius ≈
A metal has a fcc lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 404 pm. The density of the metal is 2.72 g cm-3. The molar mass of the metal is (NA Avogadro's constant= 6.02 x 1023 mol-1)- a)40 g mol-1
- b)30 g mol-1
- c)27 g mol-1
- d)20 g mol-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal has a fcc lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 404 pm. The density of the metal is 2.72 g cm-3. The molar mass of the metal is (NA Avogadro's constant= 6.02 x 1023 mol-1)
a)
40 g mol-1
b)
30 g mol-1
c)
27 g mol-1
d)
20 g mol-1

|
Nilotpal Basu answered |
Given, cell is fcc, So Z =4
Edge length, a = 404 pm = 4.04 x 10-8 cm
Density of metal, d = 2.72 g cm-3
NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
Molar mass ofg the metal, M =?
We know that
Edge length, a = 404 pm = 4.04 x 10-8 cm
Density of metal, d = 2.72 g cm-3
NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-1
Molar mass ofg the metal, M =?
We know that
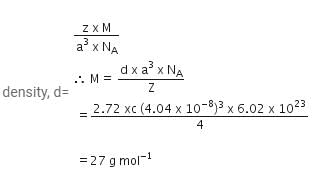
Chapter doubts & questions for Solid State - Physical Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Solid State - Physical Chemistry in English & Hindi are available as part of Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Physical Chemistry
83 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup