All questions of Communication System for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam
According to Carson’s rule, the bandwidth of FM wave is given by (Aω is the frequency deviation and ωm the modulating frequency)- a)(Δω + ωm)
- b)(Δω + 2ωm)
- c)2(Δω + ωm)
- d)(2Δω + ωm)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Carson’s rule, the bandwidth of FM wave is given by (Aω is the frequency deviation and ωm the modulating frequency)
a)
(Δω + ωm)
b)
(Δω + 2ωm)
c)
2(Δω + ωm)
d)
(2Δω + ωm)
|
|
Luminary Institute answered |
According to Carson’s rule, the bandwidth of a single-tone wideband FM is
BW = 2(Δω + ωm)
BW = 2(Δω + ωm)
What is the carrier frequency in an AM wave when its highest frequency component is 850Hz and the bandwidth of the signal is 50Hz?- a)80 Hz
- b)695 Hz
- c)625 Hz
- d)825 Hz
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the carrier frequency in an AM wave when its highest frequency component is 850Hz and the bandwidth of the signal is 50Hz?
a)
80 Hz
b)
695 Hz
c)
625 Hz
d)
825 Hz
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Upper frequency = 850Hz
Bandwidth = 50Hz
Therefore lower Frequency = 850 - 50= 800 Hz
Carrier Frequency = (850-800)/2
= 825 Hz
Bandwidth = 50Hz
Therefore lower Frequency = 850 - 50= 800 Hz
Carrier Frequency = (850-800)/2
= 825 Hz
Consider the following statements associated with angle modulations:
1. In FM, the frequency deviation is proportional to modulating frequency.
2. In PM, the frequency deviation is independent of modulating signal.
3. Amplitude of both FM and PM are constant.
4. It is possible to receive FM on a PM receiver and vice-versa.
5. Signal to noise ratio of PM is better than that of FM.
Which of the statements given above are correct?- a)2 and 5 only
- b)3 and 4 only
- c)1, 4 and 5
- d)2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements associated with angle modulations:
1. In FM, the frequency deviation is proportional to modulating frequency.
2. In PM, the frequency deviation is independent of modulating signal.
3. Amplitude of both FM and PM are constant.
4. It is possible to receive FM on a PM receiver and vice-versa.
5. Signal to noise ratio of PM is better than that of FM.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
1. In FM, the frequency deviation is proportional to modulating frequency.
2. In PM, the frequency deviation is independent of modulating signal.
3. Amplitude of both FM and PM are constant.
4. It is possible to receive FM on a PM receiver and vice-versa.
5. Signal to noise ratio of PM is better than that of FM.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
2 and 5 only
b)
3 and 4 only
c)
1, 4 and 5
d)
2, 3 and 4

|
Uday Kumar answered |
• In FM, the frequency deviation is proportional only to the amplitude variation of the modulating signal and it is independent of modulating frequency fm. Hence, statement-1 is not correct.
• In PM, the frequency deviation increases with increase in modulating frequency fm and decreases with decrease in modulating frequency. Thus, frequency deviation in PM is proportional to modulating frequency. Hence, statement-2 is false.
• Statement-3 is correct.
• it is possible to receive FM on a PM receiver and PM on a FM receiver. Hence, statement-4 is correct.
• Signal to noise ratio of PM is inferior to that in FM. Hence, statement-5 is not correct.
• In PM, the frequency deviation increases with increase in modulating frequency fm and decreases with decrease in modulating frequency. Thus, frequency deviation in PM is proportional to modulating frequency. Hence, statement-2 is false.
• Statement-3 is correct.
• it is possible to receive FM on a PM receiver and PM on a FM receiver. Hence, statement-4 is correct.
• Signal to noise ratio of PM is inferior to that in FM. Hence, statement-5 is not correct.
A 10 kW carrier is sinusoidally modulated by two carriers corresponding to a modulation index of 30% and 40% respectively. The total radiated power(is- a)11.25 kW
- b)12.5 kW
- c)15 kW
- d)17 kW
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A 10 kW carrier is sinusoidally modulated by two carriers corresponding to a modulation index of 30% and 40% respectively. The total radiated power(is
a)
11.25 kW
b)
12.5 kW
c)
15 kW
d)
17 kW

|
Baishali Bajaj answered |
The required answer is 1 (1 + 0.42 + 0.32) or 11.25 kW.
Determine the bandwidth required for an FM signal having frequency 2 kHz and maximum deviation 10 kHz. - a)16 kHz
- b)32 kHz
- c)24 kHz
- d)8 kHz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Determine the bandwidth required for an FM signal having frequency 2 kHz and maximum deviation 10 kHz.
a)
16 kHz
b)
32 kHz
c)
24 kHz
d)
8 kHz
|
|
Kavya Singhania answered |
To determine the bandwidth required for an FM signal, we need to consider the frequency of the signal and the maximum deviation. In frequency modulation (FM), the instantaneous frequency of the carrier signal is varied according to the modulating signal.
Frequency Modulation (FM):
FM is a modulation technique where the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. This modulation technique is widely used in applications such as radio broadcasting.
Maximum Deviation:
The maximum deviation represents the maximum change in frequency from the carrier frequency. In FM, it is the maximum frequency shift that occurs due to modulation. It is usually measured in kilohertz (kHz).
Given parameters:
Frequency of the FM signal = 2 kHz
Maximum deviation = 10 kHz
Calculation:
The bandwidth required for an FM signal can be calculated by using Carson's rule:
Bandwidth = 2 × (maximum deviation + modulating frequency)
In this case, the modulating frequency is 2 kHz and the maximum deviation is 10 kHz.
Bandwidth = 2 × (10 kHz + 2 kHz)
= 2 × 12 kHz
= 24 kHz
Therefore, the bandwidth required for the FM signal is 24 kHz.
Conclusion:
The correct answer is option 'C' - 24 kHz. The bandwidth required for an FM signal with a frequency of 2 kHz and a maximum deviation of 10 kHz is 24 kHz.
Frequency Modulation (FM):
FM is a modulation technique where the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. This modulation technique is widely used in applications such as radio broadcasting.
Maximum Deviation:
The maximum deviation represents the maximum change in frequency from the carrier frequency. In FM, it is the maximum frequency shift that occurs due to modulation. It is usually measured in kilohertz (kHz).
Given parameters:
Frequency of the FM signal = 2 kHz
Maximum deviation = 10 kHz
Calculation:
The bandwidth required for an FM signal can be calculated by using Carson's rule:
Bandwidth = 2 × (maximum deviation + modulating frequency)
In this case, the modulating frequency is 2 kHz and the maximum deviation is 10 kHz.
Bandwidth = 2 × (10 kHz + 2 kHz)
= 2 × 12 kHz
= 24 kHz
Therefore, the bandwidth required for the FM signal is 24 kHz.
Conclusion:
The correct answer is option 'C' - 24 kHz. The bandwidth required for an FM signal with a frequency of 2 kHz and a maximum deviation of 10 kHz is 24 kHz.
The autocorrelation of a wide-sense stationary random process is given by: e-2|τ| .The peak value of the spectral density is- a)2
- b)1
- c)e-1/2
- d)e
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The autocorrelation of a wide-sense stationary random process is given by: e-2|τ| .The peak value of the spectral density is
a)
2
b)
1
c)
e-1/2
d)
e
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Concept:
The power spectral density is basically the Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function of the power signal, i.e.
Sx(f) = F.T.{Rx(τ)}
Analysis:
Given, the autocorrelation function of the random signal X(t) as:
RX(τ) = e−2|τ|
So, its power spectral density is obtained as:
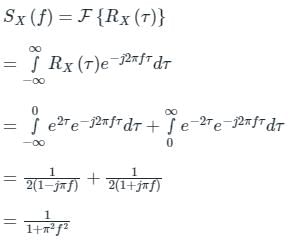 D is at f = 0,
D is at f = 0,SX(0) = 1
A phase modulated signal can be obtained from frequency modulator by passing the modulating signal through a- a)Differentiator
- b)Integrator
- c)High pass filter
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A phase modulated signal can be obtained from frequency modulator by passing the modulating signal through a
a)
Differentiator
b)
Integrator
c)
High pass filter
d)
None of these
|
|
Ojasvi Khurana answered |
Explanation:
Differentiator:
- A differentiator is a circuit that produces an output voltage proportional to the rate of change of the input voltage.
- When a modulating signal is passed through a differentiator, it enhances the high-frequency components in the signal.
- This results in the modulation index of the frequency modulated signal being directly proportional to the rate of change of the modulating signal.
Phase Modulated Signal:
- In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier signal is varied in accordance with the modulating signal.
- This results in a change in the phase of the carrier signal which carries the information.
Obtaining Phase Modulated Signal:
- By passing the modulating signal through a differentiator before feeding it to the frequency modulator, we can obtain a phase modulated signal.
- The differentiator enhances the high-frequency components in the modulating signal, which in turn affects the phase of the carrier signal in the frequency modulator.
Differentiator:
- A differentiator is a circuit that produces an output voltage proportional to the rate of change of the input voltage.
- When a modulating signal is passed through a differentiator, it enhances the high-frequency components in the signal.
- This results in the modulation index of the frequency modulated signal being directly proportional to the rate of change of the modulating signal.
Phase Modulated Signal:
- In phase modulation, the phase of the carrier signal is varied in accordance with the modulating signal.
- This results in a change in the phase of the carrier signal which carries the information.
Obtaining Phase Modulated Signal:
- By passing the modulating signal through a differentiator before feeding it to the frequency modulator, we can obtain a phase modulated signal.
- The differentiator enhances the high-frequency components in the modulating signal, which in turn affects the phase of the carrier signal in the frequency modulator.
Consider the FM signal xc(t) = 10 cos(2π × 108t + 0.5 sin(104 πt)). The bandwidth of xc(t) is approximately- a)2 kHz
- b)100 MHz
- c)15 kHz
- d)6 kHz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the FM signal xc(t) = 10 cos(2π × 108t + 0.5 sin(104 πt)). The bandwidth of xc(t) is approximately
a)
2 kHz
b)
100 MHz
c)
15 kHz
d)
6 kHz
|
|
Tanvi Ahuja answered |
Π(10^6)t + 2 cos(2π(10^3)t) + cos(2π(10^4)t).
To determine the bandwidth of this FM signal, we need to consider the highest frequency component present in the signal. In this case, the highest frequency component is 10^4 Hz.
The bandwidth of an FM signal can be approximated using Carson's rule, which states that the bandwidth is equal to 2 times the sum of the highest frequency component and the peak frequency deviation.
In this case, the peak frequency deviation can be determined by taking the difference between the highest frequency component and the carrier frequency. The carrier frequency is given as 10^6 Hz.
Therefore, the peak frequency deviation is 10^4 Hz - 10^6 Hz = -9 x 10^3 Hz.
Using Carson's rule, the bandwidth of the FM signal is approximately 2(10^4 Hz + 9 x 10^3 Hz) = 38 x 10^3 Hz or 38 kHz.
To determine the bandwidth of this FM signal, we need to consider the highest frequency component present in the signal. In this case, the highest frequency component is 10^4 Hz.
The bandwidth of an FM signal can be approximated using Carson's rule, which states that the bandwidth is equal to 2 times the sum of the highest frequency component and the peak frequency deviation.
In this case, the peak frequency deviation can be determined by taking the difference between the highest frequency component and the carrier frequency. The carrier frequency is given as 10^6 Hz.
Therefore, the peak frequency deviation is 10^4 Hz - 10^6 Hz = -9 x 10^3 Hz.
Using Carson's rule, the bandwidth of the FM signal is approximately 2(10^4 Hz + 9 x 10^3 Hz) = 38 x 10^3 Hz or 38 kHz.
The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 10 A when it is modulated to depth of 30% by an audio signal. It increases to 11 A when another signal modulates the carrier signal. The modulation index due to second signal is- a)62%
- b)66%
- c)67%
- d)64%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 10 A when it is modulated to depth of 30% by an audio signal. It increases to 11 A when another signal modulates the carrier signal. The modulation index due to second signal is
a)
62%
b)
66%
c)
67%
d)
64%

|
Ishita Patel answered |
Given,
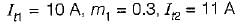
We know that, the overall modulation index is:
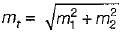
or,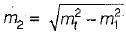
Now,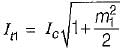
or,
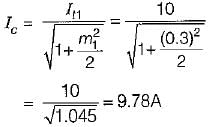
After modulating with the second signal, we have
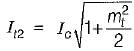
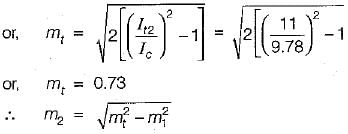
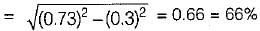
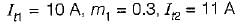
We know that, the overall modulation index is:
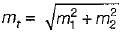
or,
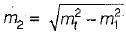
Now,
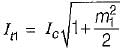
or,
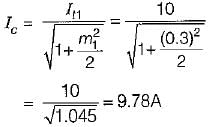
After modulating with the second signal, we have
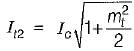
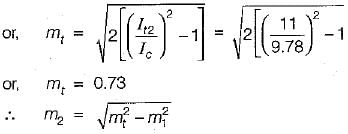
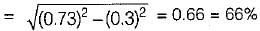
Which of the following Pulse time Modulation does not exist in practice?- a)PWM
- b)PAM
- c)PPM
- d)PFM
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following Pulse time Modulation does not exist in practice?
a)
PWM
b)
PAM
c)
PPM
d)
PFM
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
PFM does not exist in practice
Additional Information
PWM
The amplitude and position of pulses are constant in modulated signal (PWM), but the width (or duration) of pulses varies proportionally with the amplitude of an analog useful signal.
The carrier signal is produced by a clock.
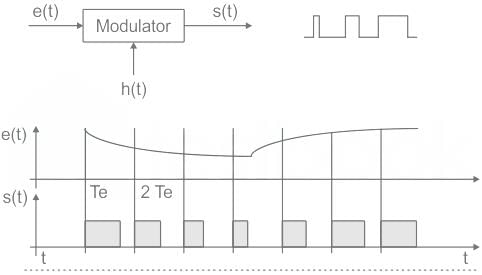
PWM
The amplitude and position of pulses are constant in modulated signal (PWM), but the width (or duration) of pulses varies proportionally with the amplitude of an analog useful signal.
The carrier signal is produced by a clock.

PPM
The amplitude and width of pulses are constant in a modulated signal (PPM), but the direction of pulses varies proportionally with the amplitude of analogical useful signal.
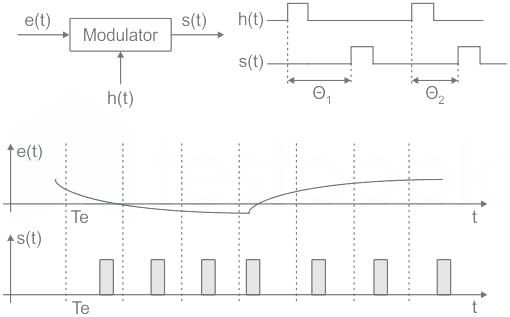
The amplitude and width of pulses are constant in a modulated signal (PPM), but the direction of pulses varies proportionally with the amplitude of analogical useful signal.

PAM
The width and location of pulses in a modulated signal (PAM) are constant, while the amplitude of pulses varies proportionally with the amplitude of an analogical useful signal.
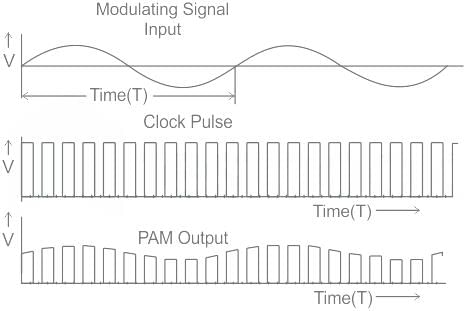
The width and location of pulses in a modulated signal (PAM) are constant, while the amplitude of pulses varies proportionally with the amplitude of an analogical useful signal.

An AM broadcast station is found to be transmitting modulating frequencies up to 5 kHz and the station is allowed to transmit on a frequency of 950 kHz, then what will be the bandwidth (in kHz) allotted to the station?- a)5
- b)10
- c)20
- d)25
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An AM broadcast station is found to be transmitting modulating frequencies up to 5 kHz and the station is allowed to transmit on a frequency of 950 kHz, then what will be the bandwidth (in kHz) allotted to the station?
a)
5
b)
10
c)
20
d)
25
|
|
Tanay Singh answered |
To determine the bandwidth allotted to an AM broadcast station, we need to consider the modulating frequencies and the carrier frequency.
Given:
Modulating frequencies = 5 kHz
Carrier frequency = 950 kHz
The bandwidth allotted to the station can be determined using Carson's rule, which states that the bandwidth required for an AM signal is equal to twice the sum of the highest modulating frequency and the frequency deviation.
Formula:
Bandwidth = 2 * (Highest Modulating Frequency + Frequency Deviation)
1. Highest Modulating Frequency:
The given modulating frequencies go up to 5 kHz. Therefore, the highest modulating frequency is 5 kHz.
2. Frequency Deviation:
The frequency deviation is the maximum shift in frequency from the carrier frequency caused by the modulation. In AM, the frequency deviation is equal to the highest modulating frequency. So, the frequency deviation is also 5 kHz.
3. Calculate Bandwidth:
Using the formula,
Bandwidth = 2 * (5 kHz + 5 kHz)
= 2 * 10 kHz
= 20 kHz
Therefore, the bandwidth allotted to the AM broadcast station is 20 kHz.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'C' 20 kHz.
Given:
Modulating frequencies = 5 kHz
Carrier frequency = 950 kHz
The bandwidth allotted to the station can be determined using Carson's rule, which states that the bandwidth required for an AM signal is equal to twice the sum of the highest modulating frequency and the frequency deviation.
Formula:
Bandwidth = 2 * (Highest Modulating Frequency + Frequency Deviation)
1. Highest Modulating Frequency:
The given modulating frequencies go up to 5 kHz. Therefore, the highest modulating frequency is 5 kHz.
2. Frequency Deviation:
The frequency deviation is the maximum shift in frequency from the carrier frequency caused by the modulation. In AM, the frequency deviation is equal to the highest modulating frequency. So, the frequency deviation is also 5 kHz.
3. Calculate Bandwidth:
Using the formula,
Bandwidth = 2 * (5 kHz + 5 kHz)
= 2 * 10 kHz
= 20 kHz
Therefore, the bandwidth allotted to the AM broadcast station is 20 kHz.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'C' 20 kHz.
Which of the following is NOT one of the types of amplitude modulation?- a)Vestigial sideband
- b)Single-sideband with carrier
- c)Single-sideband suppressed carrier
- d)Double-sideband suppressed carrier
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT one of the types of amplitude modulation?
a)
Vestigial sideband
b)
Single-sideband with carrier
c)
Single-sideband suppressed carrier
d)
Double-sideband suppressed carrier
|
|
Harshit Thakkar answered |
Single-sideband with carrier
Single-sideband with carrier modulation is NOT one of the types of amplitude modulation. This type of modulation involves the transmission of only one of the sidebands along with the carrier signal, resulting in a more efficient use of bandwidth compared to double-sideband modulation.
Types of Amplitude Modulation:
- Vestigial sideband: In vestigial sideband modulation, one sideband is partially suppressed to reduce bandwidth while still retaining the necessary information for demodulation.
- Single-sideband suppressed carrier: Single-sideband suppressed carrier modulation involves the transmission of only one sideband without the carrier signal, which helps in reducing bandwidth requirements.
- Double-sideband suppressed carrier: In double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation, both sidebands are transmitted without the carrier signal, resulting in efficient use of bandwidth.
Explanation:
Single-sideband with carrier modulation is not a commonly used modulation technique in practice. It is not as efficient in terms of bandwidth utilization compared to other types of amplitude modulation. Therefore, it is important to understand the different types of modulation techniques available in order to choose the most suitable one for a particular application.
Single-sideband with carrier modulation is NOT one of the types of amplitude modulation. This type of modulation involves the transmission of only one of the sidebands along with the carrier signal, resulting in a more efficient use of bandwidth compared to double-sideband modulation.
Types of Amplitude Modulation:
- Vestigial sideband: In vestigial sideband modulation, one sideband is partially suppressed to reduce bandwidth while still retaining the necessary information for demodulation.
- Single-sideband suppressed carrier: Single-sideband suppressed carrier modulation involves the transmission of only one sideband without the carrier signal, which helps in reducing bandwidth requirements.
- Double-sideband suppressed carrier: In double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation, both sidebands are transmitted without the carrier signal, resulting in efficient use of bandwidth.
Explanation:
Single-sideband with carrier modulation is not a commonly used modulation technique in practice. It is not as efficient in terms of bandwidth utilization compared to other types of amplitude modulation. Therefore, it is important to understand the different types of modulation techniques available in order to choose the most suitable one for a particular application.
The types of distortions which can occur in the envelope detector output is/are
- a)only diagonal clipping.
- b)only negative peak clipping.
- c)both diagonal clipping and negative peak clipping.
- d)neither diagonal clipping nor negative peak clipping.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The types of distortions which can occur in the envelope detector output is/are
a)
only diagonal clipping.
b)
only negative peak clipping.
c)
both diagonal clipping and negative peak clipping.
d)
neither diagonal clipping nor negative peak clipping.
|
|
Aravind Sharma answered |
Envelope Detector Output Distortions
Distortions can occur in the output of an envelope detector, which can affect the accuracy of the envelope signal. The types of distortions that can occur are:
1. Diagonal Clipping: Diagonal clipping occurs when the input signal is too large for the diode to handle. This results in a loss of information in the envelope signal, which can cause distortion in the output signal.
2. Negative Peak Clipping: Negative peak clipping occurs when the negative peaks of the input signal are clipped by the diode. This results in a loss of information in the envelope signal, which can cause distortion in the output signal.
Both types of distortions can occur in the output of an envelope detector, leading to inaccurate envelope signals. Therefore, it is important to design the envelope detector circuitry carefully to avoid these types of distortions.
Distortions can occur in the output of an envelope detector, which can affect the accuracy of the envelope signal. The types of distortions that can occur are:
1. Diagonal Clipping: Diagonal clipping occurs when the input signal is too large for the diode to handle. This results in a loss of information in the envelope signal, which can cause distortion in the output signal.
2. Negative Peak Clipping: Negative peak clipping occurs when the negative peaks of the input signal are clipped by the diode. This results in a loss of information in the envelope signal, which can cause distortion in the output signal.
Both types of distortions can occur in the output of an envelope detector, leading to inaccurate envelope signals. Therefore, it is important to design the envelope detector circuitry carefully to avoid these types of distortions.
What is the percentage of power saved when an 80% modulated wave is transmitted over SSB-SC which was initially transmitted over AM?- a)0.8568
- b)0.8666
- c)0.8788
- d)0.8988
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the percentage of power saved when an 80% modulated wave is transmitted over SSB-SC which was initially transmitted over AM?
a)
0.8568
b)
0.8666
c)
0.8788
d)
0.8988
|
|
Luminary Institute answered |
Concept:
Power of a transmitted AM wave is given as:
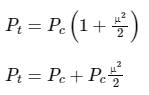
Power of a transmitted AM wave is given as:
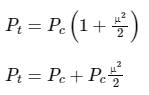
Power in the carrier = Pc
Power in both the sidebands is given by:
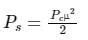
Since the power is distributed equally to the left and to the right side of the sideband, the power in one of the sidebands is given by:
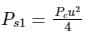
Analysis:
In SSB-SC, the carrier and one of the sidebands are suppressed, and when the carrier and 1 of the sideband are suppressed, the amount of power saving will be:
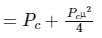
The percentage of power saved will be calculated as:
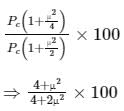
Given μ = 0.80, the amount of power saving will be
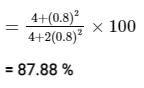
Power in both the sidebands is given by:
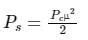
Since the power is distributed equally to the left and to the right side of the sideband, the power in one of the sidebands is given by:
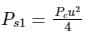
Analysis:
In SSB-SC, the carrier and one of the sidebands are suppressed, and when the carrier and 1 of the sideband are suppressed, the amount of power saving will be:
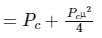
The percentage of power saved will be calculated as:
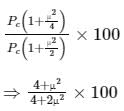
Given μ = 0.80, the amount of power saving will be
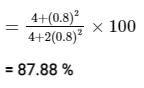
The error probability of QPSK is
- a)better than BPSK
- b)inferior to BPSK
- c)same as BPSK
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The error probability of QPSK is
a)
better than BPSK
b)
inferior to BPSK
c)
same as BPSK
d)
none of these

|
Manisha Chavan answered |
The error probability of QPSK is same as BPSK.
The bit error probability is determined when the signal interference and Gaussian noise are applied to the input of the QPSK receiver. The interference is approximated by a sum of sine waves with constant amplitudes and uniformly distributed phases.
The bit error probability is determined when the signal interference and Gaussian noise are applied to the input of the QPSK receiver. The interference is approximated by a sum of sine waves with constant amplitudes and uniformly distributed phases.
The signal m(t) = cos(ωmt) is SSB (single side-band) modulated with a carrier cos(ωct) to get s(t). The signal obtained by passing s(t) through an ideal envelope detector is- a)cos(ωmt)
- b)sin(ωmt)
- c)cos(ωmt) + sin(ωmt)
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The signal m(t) = cos(ωmt) is SSB (single side-band) modulated with a carrier cos(ωct) to get s(t). The signal obtained by passing s(t) through an ideal envelope detector is
a)
cos(ωmt)
b)
sin(ωmt)
c)
cos(ωmt) + sin(ωmt)
d)
1

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
1) General equation of SSB modulated wave:
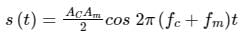
2) Output of envelope detector to signal
Acos ωct → A
Application:
Equation of SSB modulated signal
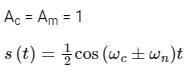
the output of envelope detector = ½
The output of the envelope detector is a constant voltage signal
Hence option (d) which represents a constant voltage is correct.
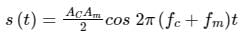
2) Output of envelope detector to signal
Acos ωct → A
Application:
Equation of SSB modulated signal
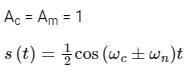
the output of envelope detector = ½
The output of the envelope detector is a constant voltage signal
Hence option (d) which represents a constant voltage is correct.
An angle modulated signal with carrier frequency ωc = 2π × 106 rad/s given by ϕm(t) = cos(ωct + 5 sin (1000πt) + 10 sin (2000πt)). The maximum deviation of the frequency in the angle modulated signal from that of the carrier is ___________ kHz.
Correct answer is between '12,13'. Can you explain this answer?
An angle modulated signal with carrier frequency ωc = 2π × 106 rad/s given by ϕm(t) = cos(ωct + 5 sin (1000πt) + 10 sin (2000πt)). The maximum deviation of the frequency in the angle modulated signal from that of the carrier is ___________ kHz.
|
|
Hiral Shah answered |
An angle modulated signal with carrier frequency refers to a type of signal where the frequency of the carrier wave is varied in accordance with the information being transmitted. This modulation technique is commonly used in frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM).
In FM, the frequency of the carrier wave is changed in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This means that as the amplitude of the modulating signal increases, the frequency of the carrier wave increases, and vice versa. This results in a signal that is resistant to noise and interference, making it ideal for applications such as radio broadcasting.
In PM, the phase of the carrier wave is changed in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This means that as the amplitude of the modulating signal increases, the phase of the carrier wave changes, and vice versa. PM is commonly used in applications where the phase information of the signal is important, such as in radar and telecommunications.
Both FM and PM are examples of angle modulation, where the phase or frequency of the carrier wave is modulated to carry the information being transmitted.
In FM, the frequency of the carrier wave is changed in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This means that as the amplitude of the modulating signal increases, the frequency of the carrier wave increases, and vice versa. This results in a signal that is resistant to noise and interference, making it ideal for applications such as radio broadcasting.
In PM, the phase of the carrier wave is changed in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. This means that as the amplitude of the modulating signal increases, the phase of the carrier wave changes, and vice versa. PM is commonly used in applications where the phase information of the signal is important, such as in radar and telecommunications.
Both FM and PM are examples of angle modulation, where the phase or frequency of the carrier wave is modulated to carry the information being transmitted.
In a digital continuous-time communication system, the bit rate of NRZ data stream is 1 Mbps and carrier frequency of transmission is 100 MHz. What is the bandwidth requirement of the channel in BPSK and QPSK systems respectively?- a)2 MHz and 4 MHz
- b)1 MHz and 2 MHz
- c)4 MHz and 2 MHz
- d)2 MHz and 1 MHz
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a digital continuous-time communication system, the bit rate of NRZ data stream is 1 Mbps and carrier frequency of transmission is 100 MHz. What is the bandwidth requirement of the channel in BPSK and QPSK systems respectively?
a)
2 MHz and 4 MHz
b)
1 MHz and 2 MHz
c)
4 MHz and 2 MHz
d)
2 MHz and 1 MHz

|
Diya Patel answered |
The bit period of NRZ data stream is
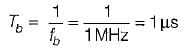
In BPSK, each binary bit is a symbol, therefore symbol duration Ts = Tb = 1 μs.
∴ The bandwidth required for BPSK system is
∴ The bandwidth required for BPSK system is
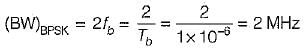
In QPSK, we group two successive bits to form one symbol, therefore symbol duration,
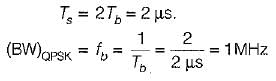
The bandwidth of TV video plus audio signal is 4.5 MHz. If this signal is converted into PCM bit stream with 1024 quantization levels and the signal is sampled at the rate 20% above Nyquist rate, then the number of bits/sec of the resulting signal is- a)196 M bits/sec
- b)108 M bits/sec
- c)88 M bits/sec
- d)216 M bits/sec
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The bandwidth of TV video plus audio signal is 4.5 MHz. If this signal is converted into PCM bit stream with 1024 quantization levels and the signal is sampled at the rate 20% above Nyquist rate, then the number of bits/sec of the resulting signal is
a)
196 M bits/sec
b)
108 M bits/sec
c)
88 M bits/sec
d)
216 M bits/sec
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Given,
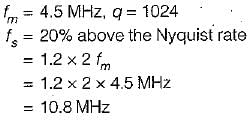
Now, quantization level, q = 2n
(n = No. of bits/sec)
∴ 2n = 1024 = 210
or, n = 10
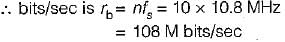
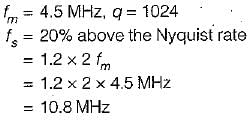
Now, quantization level, q = 2n
(n = No. of bits/sec)
∴ 2n = 1024 = 210
or, n = 10
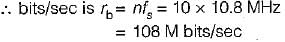
Fourier series analysis is a tool used to
1. analyse any periodic and non-periodic signal.
2. find how many frequency components are present in the signal.
3. find the relative phase difference between various frequency components.
4. represents a waveform in the form of sum of infinite number of exponential terms.
5. find the amplitude of various terms in the series.
Which of the statements given above are correct?- a)2, 5 and 3
- b)1, 3 and 4
- c)1, 2 and 3
- d)2, 3 and 5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Fourier series analysis is a tool used to
1. analyse any periodic and non-periodic signal.
2. find how many frequency components are present in the signal.
3. find the relative phase difference between various frequency components.
4. represents a waveform in the form of sum of infinite number of exponential terms.
5. find the amplitude of various terms in the series.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
1. analyse any periodic and non-periodic signal.
2. find how many frequency components are present in the signal.
3. find the relative phase difference between various frequency components.
4. represents a waveform in the form of sum of infinite number of exponential terms.
5. find the amplitude of various terms in the series.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a)
2, 5 and 3
b)
1, 3 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 3
d)
2, 3 and 5

|
Asha Deshpande answered |
Fourier series analysis is a tool used to
1. analyse any periodic signal only.
2. find how many frequency components are present in the signal.
3. find the relative phase difference between various frequency components.
4. represents a periodic waveform in the form of sum of infinite number of sine and cosine terms.
5. find the amplitude of various frequency components of the series.
Hence, statements 2, 3 and 5 are only correct.
1. analyse any periodic signal only.
2. find how many frequency components are present in the signal.
3. find the relative phase difference between various frequency components.
4. represents a periodic waveform in the form of sum of infinite number of sine and cosine terms.
5. find the amplitude of various frequency components of the series.
Hence, statements 2, 3 and 5 are only correct.
A carrier is simultaneously modulated by two sine waves with modulation indices of 0.4 and 0.3. The resultant modulation index will be- a)1.0
- b)0.7
- c)0.5
- d)0.35
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A carrier is simultaneously modulated by two sine waves with modulation indices of 0.4 and 0.3. The resultant modulation index will be
a)
1.0
b)
0.7
c)
0.5
d)
0.35
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Given: m1 = 0.4, m2 = 0.3
Resultant modulation index = α^2 = 0.3^2 + 0.4^2 = 0.5^2 or
α = 0.5.
Consider the following statements:
1. The figure of merit of DSB-SC and SSB receivers with coherent detection is 1.
2. The figure of merit of an AM receiver with envelope detection is more than 1.
3. If the average modulated signal power and the average noise power in the message bandwidth is same as that of DSB-SCreceiver then the output SNR and figure of merit of SSB coherent receiver is same as that of the DSB SC receiver.
4. A square-law demodulator operates above threshold on a weaker signal than with an envelope demodulator.
Which of the above statements are correct?- a)1, 3 and 4
- b)2 and 4
- c)1, 2 and 4
- d)2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. The figure of merit of DSB-SC and SSB receivers with coherent detection is 1.
2. The figure of merit of an AM receiver with envelope detection is more than 1.
3. If the average modulated signal power and the average noise power in the message bandwidth is same as that of DSB-SCreceiver then the output SNR and figure of merit of SSB coherent receiver is same as that of the DSB SC receiver.
4. A square-law demodulator operates above threshold on a weaker signal than with an envelope demodulator.
Which of the above statements are correct?
1. The figure of merit of DSB-SC and SSB receivers with coherent detection is 1.
2. The figure of merit of an AM receiver with envelope detection is more than 1.
3. If the average modulated signal power and the average noise power in the message bandwidth is same as that of DSB-SCreceiver then the output SNR and figure of merit of SSB coherent receiver is same as that of the DSB SC receiver.
4. A square-law demodulator operates above threshold on a weaker signal than with an envelope demodulator.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
1, 3 and 4
b)
2 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 4
d)
2 and 3

|
Subhankar Malik answered |
- Statement-1 is correct.
- The figure of merit of an AM receiver with envelope detection is less than 1.
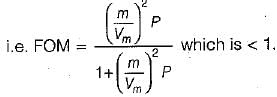
Hence, statement-2 is false. - Statement-3 and 4 are correct.
Which is true in a frequency modulated system ?- a)Variation of carrier amplitude does not affect quality of reception
- b)Amplitude of carrier is varied according to modulating signal
- c)The transmission does not require line of sight between transmitter and reciever
- d)Receiver uses diode detector
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true in a frequency modulated system ?
a)
Variation of carrier amplitude does not affect quality of reception
b)
Amplitude of carrier is varied according to modulating signal
c)
The transmission does not require line of sight between transmitter and reciever
d)
Receiver uses diode detector
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Variation of carrier amplitude does not affect quality of reception
Explanation:
Frequency modulation (FM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a carrier wave by varying the frequency of the carrier wave in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal.
In a frequency modulated system, the variation of the carrier amplitude does not affect the quality of reception. This is because FM is a form of angle modulation, where the information is encoded in the change of frequency, rather than the amplitude of the carrier wave.
Here are the key points explaining why the statement is true:
1. Amplitude vs Frequency Modulation:
- In amplitude modulation (AM), the amplitude of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. Changes in the carrier amplitude directly affect the quality of reception in AM systems.
- In frequency modulation (FM), on the other hand, the frequency of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. The amplitude of the carrier wave remains constant, and only the frequency changes.
2. Benefits of Frequency Modulation:
- FM has several advantages over AM, including better noise immunity, improved signal-to-noise ratio, and higher fidelity.
- The constant amplitude of the carrier wave in FM ensures that the received signal is less susceptible to amplitude variations caused by noise or interference.
3. Receiver Operation:
- In an FM system, the receiver uses a frequency discriminator to recover the modulating signal from the received frequency-modulated waveform.
- The receiver does not rely on variations in the carrier amplitude to extract the information. Instead, it focuses on detecting and measuring the changes in the carrier frequency.
- The diode detector mentioned in option 'D' is commonly used in amplitude demodulation (AM) systems, not frequency modulation (FM) systems.
Conclusion:
In summary, the statement that the variation of carrier amplitude does not affect the quality of reception in a frequency modulated system is true. FM systems rely on changes in frequency rather than amplitude, and the receiver uses a frequency discriminator to recover the modulating signal.
Explanation:
Frequency modulation (FM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a carrier wave by varying the frequency of the carrier wave in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal.
In a frequency modulated system, the variation of the carrier amplitude does not affect the quality of reception. This is because FM is a form of angle modulation, where the information is encoded in the change of frequency, rather than the amplitude of the carrier wave.
Here are the key points explaining why the statement is true:
1. Amplitude vs Frequency Modulation:
- In amplitude modulation (AM), the amplitude of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. Changes in the carrier amplitude directly affect the quality of reception in AM systems.
- In frequency modulation (FM), on the other hand, the frequency of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. The amplitude of the carrier wave remains constant, and only the frequency changes.
2. Benefits of Frequency Modulation:
- FM has several advantages over AM, including better noise immunity, improved signal-to-noise ratio, and higher fidelity.
- The constant amplitude of the carrier wave in FM ensures that the received signal is less susceptible to amplitude variations caused by noise or interference.
3. Receiver Operation:
- In an FM system, the receiver uses a frequency discriminator to recover the modulating signal from the received frequency-modulated waveform.
- The receiver does not rely on variations in the carrier amplitude to extract the information. Instead, it focuses on detecting and measuring the changes in the carrier frequency.
- The diode detector mentioned in option 'D' is commonly used in amplitude demodulation (AM) systems, not frequency modulation (FM) systems.
Conclusion:
In summary, the statement that the variation of carrier amplitude does not affect the quality of reception in a frequency modulated system is true. FM systems rely on changes in frequency rather than amplitude, and the receiver uses a frequency discriminator to recover the modulating signal.
A PAM source generates four symbols 3 V, 1 V, -1 V and -3 V with probability of p(3) = p(-3) = 0.2 and p(1) = p(-1) = 0.3 respectively. The variance for the source will be- a)4.2 V
- b)3.2 V
- c)3.6 V
- d)4.6 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A PAM source generates four symbols 3 V, 1 V, -1 V and -3 V with probability of p(3) = p(-3) = 0.2 and p(1) = p(-1) = 0.3 respectively. The variance for the source will be
a)
4.2 V
b)
3.2 V
c)
3.6 V
d)
4.6 V
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Concept:
For discrete random variable x:
Mean = E[x] = ∑I xi p (xi)
Mean square value (MSQ) = E[x2] = ∑I xi2 p (xi)
Variance (σ2) = E[x2] – {E(x)}2
Standard deviation (σ) =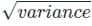
Calculation:
Given data: for the given PAM source
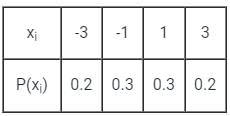
Mean = E[x] = ∑i xi p (xi)
= (-3)(0.2) + (-1)(0.3) + (1)(0.3) + (3)(0.2)
= 0
MSQ = E[x2] = ∑I xi2 p (xi)
= (-3)2(0.2) + (-1)2(0.3) + (1)2(0.3) + (3)2(0.2) V
= 4.2 V
Variance = E[x2] – {E[x]}2
= 4.2 – 0
= 4.2 V
For discrete random variable x:
Mean = E[x] = ∑I xi p (xi)
Mean square value (MSQ) = E[x2] = ∑I xi2 p (xi)
Variance (σ2) = E[x2] – {E(x)}2
Standard deviation (σ) =
Calculation:
Given data: for the given PAM source

Mean = E[x] = ∑i xi p (xi)
= (-3)(0.2) + (-1)(0.3) + (1)(0.3) + (3)(0.2)
= 0
MSQ = E[x2] = ∑I xi2 p (xi)
= (-3)2(0.2) + (-1)2(0.3) + (1)2(0.3) + (3)2(0.2) V
= 4.2 V
Variance = E[x2] – {E[x]}2
= 4.2 – 0
= 4.2 V
A rate 1/2 convolution code with dfrec = 10 is used to encode a data requeence occurring at a rate of 1 kbps. The modulation is binary PSK. The DS spread spectrum sequence has a chip rate of 10 MHzQue: The coding gain is- a)7 dB
- b)12 dB
- c)14 dB
- d)24 dB
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A rate 1/2 convolution code with dfrec = 10 is used to encode a data requeence occurring at a rate of 1 kbps. The modulation is binary PSK. The DS spread spectrum sequence has a chip rate of 10 MHz
Que: The coding gain is
a)
7 dB
b)
12 dB
c)
14 dB
d)
24 dB

|
Arjun Unni answered |
An amplifier has an operating spot noise figure of 10 dB when driven by a source of effective noise temperature 225 K.Que: In previous question what is the standard spot noisefigure of the cascade ?- a)10.3 dB
- b)12.2 dB
- c)14.9 dB
- d)17.6 dB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An amplifier has an operating spot noise figure of 10 dB when driven by a source of effective noise temperature 225 K.
Que: In previous question what is the standard spot noisefigure of the cascade ?
a)
10.3 dB
b)
12.2 dB
c)
14.9 dB
d)
17.6 dB

|
Subhankar Ghoshal answered |
Which of the following modulation scheme is most bandwidth efficient?- a)AM
- b)FM
- c)PM
- d)SSB-SC
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following modulation scheme is most bandwidth efficient?
a)
AM
b)
FM
c)
PM
d)
SSB-SC
|
|
Nakul Chauhan answered |
Bandwidth Efficiency of Modulation Schemes
The bandwidth efficiency of a modulation scheme refers to the amount of information that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth. In other words, it measures how efficiently the available bandwidth is utilized to transmit data. Among the given options (AM, FM, PM, SSB-SC), Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC) modulation scheme is the most bandwidth efficient. Let's understand why.
1. AM (Amplitude Modulation)
- In AM, the amplitude of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the message signal.
- The bandwidth required for AM is twice the frequency of the message signal.
- AM uses a lot of bandwidth to transmit the information and is not considered bandwidth efficient.
2. FM (Frequency Modulation)
- In FM, the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the message signal.
- The bandwidth required for FM is determined by the maximum frequency deviation and the highest frequency component in the message signal.
- FM requires a wider bandwidth compared to AM, but it provides better noise immunity.
3. PM (Phase Modulation)
- In PM, the phase of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the message signal.
- The bandwidth required for PM is also determined by the maximum frequency deviation and the highest frequency component in the message signal.
- PM requires a wider bandwidth compared to AM as well.
4. SSB-SC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier)
- SSB-SC is a modulation scheme that suppresses one of the sidebands and the carrier signal.
- By suppressing the carrier and one sideband, SSB-SC effectively reduces the required bandwidth.
- SSB-SC can achieve a bandwidth efficiency of 100%, meaning it utilizes the entire available bandwidth for transmission.
Conclusion
Among the given modulation schemes, Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC) is the most bandwidth efficient. It achieves this by suppressing the carrier and one sideband, effectively utilizing the entire available bandwidth for transmission. In contrast, AM, FM, and PM require wider bandwidths, making them less efficient in terms of bandwidth utilization.
The bandwidth efficiency of a modulation scheme refers to the amount of information that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth. In other words, it measures how efficiently the available bandwidth is utilized to transmit data. Among the given options (AM, FM, PM, SSB-SC), Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC) modulation scheme is the most bandwidth efficient. Let's understand why.
1. AM (Amplitude Modulation)
- In AM, the amplitude of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the message signal.
- The bandwidth required for AM is twice the frequency of the message signal.
- AM uses a lot of bandwidth to transmit the information and is not considered bandwidth efficient.
2. FM (Frequency Modulation)
- In FM, the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the message signal.
- The bandwidth required for FM is determined by the maximum frequency deviation and the highest frequency component in the message signal.
- FM requires a wider bandwidth compared to AM, but it provides better noise immunity.
3. PM (Phase Modulation)
- In PM, the phase of the carrier signal is varied in proportion to the message signal.
- The bandwidth required for PM is also determined by the maximum frequency deviation and the highest frequency component in the message signal.
- PM requires a wider bandwidth compared to AM as well.
4. SSB-SC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier)
- SSB-SC is a modulation scheme that suppresses one of the sidebands and the carrier signal.
- By suppressing the carrier and one sideband, SSB-SC effectively reduces the required bandwidth.
- SSB-SC can achieve a bandwidth efficiency of 100%, meaning it utilizes the entire available bandwidth for transmission.
Conclusion
Among the given modulation schemes, Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC) is the most bandwidth efficient. It achieves this by suppressing the carrier and one sideband, effectively utilizing the entire available bandwidth for transmission. In contrast, AM, FM, and PM require wider bandwidths, making them less efficient in terms of bandwidth utilization.
A DSB-SC signal is generated using the carrier signal cos (ωct + θ) and modulating signal m(t). What is the envelope detector output of this DSB-SC signal?- a)m(t) cos θ
- b)|m(t)|
- c)m(t) tan θ
- d)m(t) sin θ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A DSB-SC signal is generated using the carrier signal cos (ωct + θ) and modulating signal m(t). What is the envelope detector output of this DSB-SC signal?
a)
m(t) cos θ
b)
|m(t)|
c)
m(t) tan θ
d)
m(t) sin θ
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
s1(t) = Ac [1 + kam(t) ] cosωct
s2(t) = Ac [1 - kam(t) ] cosωct
s(t) = Ac [1 + kam(t) ] cosωct - Ac [ 1 - kam(t) ] cosωct
= 2 Ac ka m(t) cosωct
s(t) ∝ m(t) cosωct
Hence, Envelope of s(t) = |m(t)|
Which of the following circuits could NOT be used as demodulator of SSB?- a)Weaver Demodulator
- b)Phase Shift Method
- c)Phase discriminator
- d)Filter Method
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following circuits could NOT be used as demodulator of SSB?
a)
Weaver Demodulator
b)
Phase Shift Method
c)
Phase discriminator
d)
Filter Method
|
|
Luminary Institute answered |
Phase Discrimination is used for the demodulation of Frequency Modulate signals.
Direction: Two statements are given. Based on the given information, choose the correct answer.Statement-I: For the same message signal, the pre-detection SNR is double in the case of conventional practical AM modulation, than that in the case of SSB.
Statement-II: The AM signal bandwidth is double as compared to SSB signal bandwidth.- a)Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I.
- b)Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct, Statement II is false
- d)Statement I is false, Statement II is correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Two statements are given. Based on the given information, choose the correct answer.
Statement-I: For the same message signal, the pre-detection SNR is double in the case of conventional practical AM modulation, than that in the case of SSB.
Statement-II: The AM signal bandwidth is double as compared to SSB signal bandwidth.
Statement-II: The AM signal bandwidth is double as compared to SSB signal bandwidth.
a)
Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I.
b)
Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct, Statement II is false
d)
Statement I is false, Statement II is correct
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Let, the channel is practical having finite attenuation of 'A' dB, and the single-sided noise power spectral density is given as 'N' W/Hz
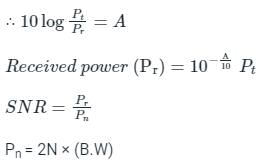
Let the message signal spectrum is given as:
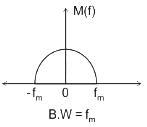
In the case of AM:-
B.W = 2fm kHz (twice of message signal bandwidth)
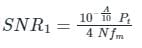
In the case of SSB:-
B.W = fm kHz (same as message signal bandwidth)
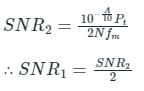
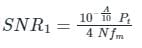
In the case of SSB:-
B.W = fm kHz (same as message signal bandwidth)
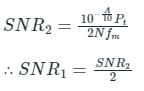
∴ SNR in the case of S.S.B is double that in the case of AM.
Statement-I is incorrect and Statement-II is correct.
Which of the following systems is analog?- a)PCM
- b)DM
- c)DPCM
- d)PAM
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following systems is analog?
a)
PCM
b)
DM
c)
DPCM
d)
PAM

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
- Analog modulation is a process in which analog low-frequency baseband signals (like an audio or TV signal) are transmitted over a larger distance without getting faded away, by superimposing over a higher frequency carrier signal such as a radio frequency band.
- Different modulation techniques are explained with the help of the following block diagram:
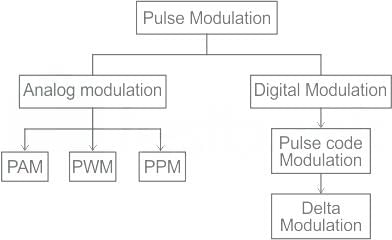
- If the amplitude of a pulse or duration of a pulse is varied according to the instantaneous values of the baseband modulating signal, then such a technique is called as Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM).
In a FM system, the modulating frequency fm = 1 kHz, the modulating voltage Vm= 2 volt and the deviation is 6 kHz. If the modulating voltage is raised to 4 volt then what is the new deviation?- a)4 kHz
- b)6 kHz
- c)8 kHz
- d)12 kHz
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a FM system, the modulating frequency fm = 1 kHz, the modulating voltage Vm= 2 volt and the deviation is 6 kHz. If the modulating voltage is raised to 4 volt then what is the new deviation?
a)
4 kHz
b)
6 kHz
c)
8 kHz
d)
12 kHz

|
Diya Chopra answered |
Given, 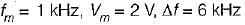
We know that,
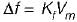
or,
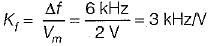
When, V'm = 4 V, the new deviation in frequency is
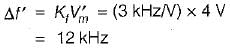
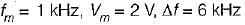
We know that,
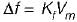
or,
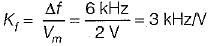
When, V'm = 4 V, the new deviation in frequency is
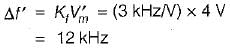
The bit rate of a digital communication system is 34 Mbps. The modulation scheme is QPSK. The baud rate of the system is- a)68 Mbps
- b)34 Mbps
- c)17 Mbps
- d)85 Mbps
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bit rate of a digital communication system is 34 Mbps. The modulation scheme is QPSK. The baud rate of the system is
a)
68 Mbps
b)
34 Mbps
c)
17 Mbps
d)
85 Mbps

|
Rounak Choudhary answered |
In BPSK, baud rate is half the bit rate due to which there is more effective utilization of the available bandwidth of the transmission channel. Given, bit rate = 34 Mbps


Assertion (A) : PCM has much better noise immunity as compared to PAM, PWM and PPM systems.
Reason (R) : PCM does not contain any information in the width or the position of the pulses.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A) : PCM has much better noise immunity as compared to PAM, PWM and PPM systems.
Reason (R) : PCM does not contain any information in the width or the position of the pulses.
Reason (R) : PCM does not contain any information in the width or the position of the pulses.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false but R is true.

|
Pankaj Rane answered |
In practice, the transmitted pulses usually have slightly sloping sides (edges). As the noise is superimposed on them, the width and the position of the regenerated pulses is changed. This distorts the information contents in the PWM and PPM signals. Since PCM does not contain any information in the width or the position of the pulses, therefore PCM has much better noise immunity as compared to PAM, PWM and PPM systems. Hence, both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
A super heterodyne receiver is designed to receive transmitted signals between 5 and 10 MHz. High-side tuning is to be used. The tuning range of the local oscillator for IF frequency 500 kHz would be- a)4.5 MHz - 9.5 MHz
- b)5.5 MHz - 10.5 MHz
- c)4.5 MHz - 10.5 MHz
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A super heterodyne receiver is designed to receive transmitted signals between 5 and 10 MHz. High-side tuning is to be used. The tuning range of the local oscillator for IF frequency 500 kHz would be
a)
4.5 MHz - 9.5 MHz
b)
5.5 MHz - 10.5 MHz
c)
4.5 MHz - 10.5 MHz
d)
None of the above

|
Varun Banerjee answered |
Since High-side tuning is used
Which of the following requires the least bandwidth?- a)DSB SC
- b)DSB
- c)VSB
- d)SSB
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following requires the least bandwidth?
a)
DSB SC
b)
DSB
c)
VSB
d)
SSB
|
|
Sakshi Chauhan answered |
Bandwidth Requirement for Different Modulation Techniques:
DSB SC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier):
- DSB SC modulation requires more bandwidth compared to other modulation techniques because it transmits both sidebands along with the carrier signal.
- It utilizes the full bandwidth available for transmission.
DSB (Double Sideband):
- DSB modulation also transmits both sidebands without the carrier signal.
- It requires more bandwidth than SSB but less than DSB SC.
VSB (Vestigial Sideband):
- VSB modulation transmits one complete sideband and a portion of the other sideband.
- It requires more bandwidth than SSB but less than DSB and DSB SC.
SSB (Single Sideband):
- SSB modulation transmits only one sideband while suppressing the other sideband and the carrier signal.
- It requires the least bandwidth among the listed modulation techniques.
- By eliminating redundant information, SSB modulation efficiently uses the available bandwidth.
In conclusion, SSB modulation requires the least bandwidth among DSB SC, DSB, VSB, and SSB modulation techniques. Its efficiency in utilizing bandwidth makes it a suitable choice for applications where bandwidth conservation is essential.
DSB SC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier):
- DSB SC modulation requires more bandwidth compared to other modulation techniques because it transmits both sidebands along with the carrier signal.
- It utilizes the full bandwidth available for transmission.
DSB (Double Sideband):
- DSB modulation also transmits both sidebands without the carrier signal.
- It requires more bandwidth than SSB but less than DSB SC.
VSB (Vestigial Sideband):
- VSB modulation transmits one complete sideband and a portion of the other sideband.
- It requires more bandwidth than SSB but less than DSB and DSB SC.
SSB (Single Sideband):
- SSB modulation transmits only one sideband while suppressing the other sideband and the carrier signal.
- It requires the least bandwidth among the listed modulation techniques.
- By eliminating redundant information, SSB modulation efficiently uses the available bandwidth.
In conclusion, SSB modulation requires the least bandwidth among DSB SC, DSB, VSB, and SSB modulation techniques. Its efficiency in utilizing bandwidth makes it a suitable choice for applications where bandwidth conservation is essential.
In a frequency modulation system, maximum frequency deviation allowed is 1000 and modulating frequency is 1 kHz. Determine modulation index β.- a)2
- b)2000
- c)1
- d)1000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a frequency modulation system, maximum frequency deviation allowed is 1000 and modulating frequency is 1 kHz. Determine modulation index β.
a)
2
b)
2000
c)
1
d)
1000
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Concept:
In FM (Frequency Modulation), the modulation index is defined as the ratio of frequency deviation to the modulating frequency.
Mathematically, this is defined as:
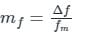
mf = Modulation index
Δf = Frequency deviation
fm = Modulating frequency
In FM (Frequency Modulation), the modulation index is defined as the ratio of frequency deviation to the modulating frequency.
Mathematically, this is defined as:
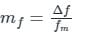
mf = Modulation index
Δf = Frequency deviation
fm = Modulating frequency
Calculation:
Given Δf = 1000 Hz = 1 kHz
fm = 1 kHz
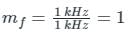
Given Δf = 1000 Hz = 1 kHz
fm = 1 kHz
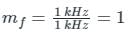
Modulation system used for video modulation in TV transmission is- a)DSB
- b)VSB
- c)SSB
- d)SSBBC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Modulation system used for video modulation in TV transmission is
a)
DSB
b)
VSB
c)
SSB
d)
SSBBC
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
In TV Transmission the use of FM is made for Audio transmission and AM for Video transmission.
Vestigial Sideband modulation (VSB) is used for video modulation in TV transmission due to the following reasons :
Vestigial Sideband modulation (VSB) is used for video modulation in TV transmission due to the following reasons :
- Video signal exhibits a large bandwidth and significant low-frequency content which suggests the use of VSB.
- VSB (vestigial side band) transmission transmits one side band fully and the other side band partially thus, reducing the bandwidth requirement.
- The circuitry for demodulation in the receiver should be simple and therefore cheap. VSB demodulation uses a simple envelope detection.
The four basic elements in a PLL are loop filter, loop amplifier, VCO and- a)Up converter
- b)Down converter
- c)Phase detector
- d)Frequency multiplier
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The four basic elements in a PLL are loop filter, loop amplifier, VCO and
a)
Up converter
b)
Down converter
c)
Phase detector
d)
Frequency multiplier
|
|
Luminary Institute answered |
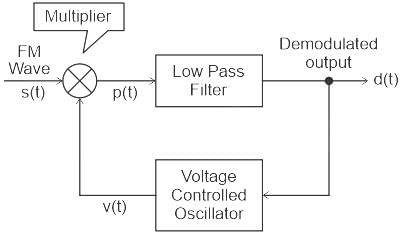
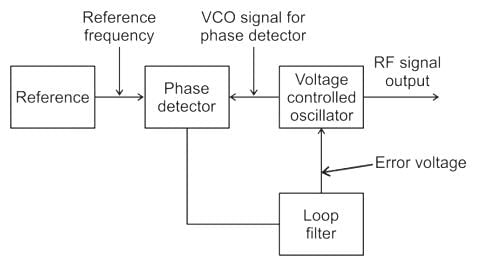
- A phase-locked loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal.
- The circuit can track an input frequency or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency.
- The basic elements of a PLL circuit are phase comparator/detector, a loop filter, voltage controlled oscillator (VCO).
The figure shows a schematic of a phase-locked loop:

In amplitude modulation, the modulation envelope has a peak value which is double the unmodulated carrier value. What is the value of the modulation index ?- a)25%
- b)50%
- c)75%
- d)100%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In amplitude modulation, the modulation envelope has a peak value which is double the unmodulated carrier value. What is the value of the modulation index ?
a)
25%
b)
50%
c)
75%
d)
100%

|
Pranavi Gupta answered |
The error probability of QPSK is- a)better than BPSK
- b)inferior to BPSK
- c)same as BPSK
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The error probability of QPSK is
a)
better than BPSK
b)
inferior to BPSK
c)
same as BPSK
d)
none of these

|
Arshiya Dasgupta answered |
The error probability of QPSK is better (or lower) than that of BPSK due to which QPSK is used for very high bit rate data transmission.
How much percentage power will be saved when the carrier and one of the sidebands are suppressed in an AM wave modulated to a depth of 50%?- a)83.3%
- b)94.4%
- c)47.2%
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How much percentage power will be saved when the carrier and one of the sidebands are suppressed in an AM wave modulated to a depth of 50%?
a)
83.3%
b)
94.4%
c)
47.2%
d)
None of the above

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
Concept:
Total power in AM (PT)= PC ( 1 + μ2/2 ) = PC + PCμ2/2
where;
PC → Carrier power
μ → modulation index
Power of single sideband = ( PCμ2/2)/2 = PCμ2/4
Calculation:
Given
μ = 50% = 0.5
After suppressing carrier and a single sideband :
PT = (PC + PCμ2/2) - (PC + PCμ2/4) = PCμ2/4
Percentage of power will be saved :
= [(PC + PCμ2/2 )- PCμ2/4 ]/PC ( 1 + μ2/2 ) × 100
= (1 + μ2/4)/( 1 + μ2/2 ) × 100
= (1 + (0.5)2/4)/( 1 + (0.5)2/2 ) × 100
= 94.44 %
Which of the following circuits could NOT be used as demodulator of SSB?- a)Weaver Demodulator
- b)Phase Shift Method
- c)Phase discriminator
- d)Filter Method
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following circuits could NOT be used as demodulator of SSB?
a)
Weaver Demodulator
b)
Phase Shift Method
c)
Phase discriminator
d)
Filter Method
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Phase Discrimination is used for the demodulation of Frequency Modulate signals.
Additional Information

Additional Information
- The following methods are used for the demodulation of Single Side Band (SSB) signals.
- The Filter Method
- The Phasing Shift Method
- The Weaver Demodulator
- Fourier based Demodulation.
- The following methods are used for the demodulation of Frequency Modulated (FM) signals.
- Frequency discrimination method
- Phase discrimination method.
Hence, phase discriminator is used as demodulator of SSB
Bandwidth of BPSK is ___ than that of BFSK.- a)higher
- b)equal
- c)lower
- d)either lower or higher
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bandwidth of BPSK is ___ than that of BFSK.
a)
higher
b)
equal
c)
lower
d)
either lower or higher

|
Anshu Kumar answered |
Minimum bandwidth required in BPSK = 2fb.
Minimum bandwidth required in BFSK = 4fb.
Hence, bandwidth of BPSK is lower than that of BFSK.
Minimum bandwidth required in BFSK = 4fb.
Hence, bandwidth of BPSK is lower than that of BFSK.
The amplitude of a random signal is uniformly distributed between –5V and 5V. If the signal to quantization noise ratio required in uniformly quantizing the signal is 43.5dB, the step size of the quantization is approximately-- a)0.0333V
- b)0.05V
- c)0.0667V
- d)0.10V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The amplitude of a random signal is uniformly distributed between –5V and 5V. If the signal to quantization noise ratio required in uniformly quantizing the signal is 43.5dB, the step size of the quantization is approximately-
a)
0.0333V
b)
0.05V
c)
0.0667V
d)
0.10V

|
Imtiaz Ahmad answered |
Given; Signal to quantization noise = 43.5 dB
The amplitude of a random signal is uniformly distributed between –5V and 5V.
The amplitude of a random signal is uniformly distributed between –5V and 5V.

E[X2] = 52/3 = 25/3
E[XQE2] = δ2/12
SNR = (25/3)/ (δ2/12) = 100/ δ2
SNR (dB) = 10log(SNR)
⇒ 43.5 = 10log(SNR)
⇒ log(SNR) = 43.5/10
⇒ SNR= 104.35
Therefore
100/ δ2 = 104.35
⇒ δ2 = 100/104.35
⇒ δ = 0.0667
signal is sampled at 8 kHz and is quantized using 8 bit uniform quantizer. Assuming SNRq for a sinusoidal signal, the correct statement for PCM signal with a bit rate of R is- a)R = 32 kbps, SNRq = 25.8 dB
- b)R = 64 kbps, SNRq = 49.8 dB
- c)R = 64 kbps, SNRq = 55.8 dB
- d)R = 32 kbps, SNRq = 49.8 dB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
signal is sampled at 8 kHz and is quantized using 8 bit uniform quantizer. Assuming SNRq for a sinusoidal signal, the correct statement for PCM signal with a bit rate of R is
a)
R = 32 kbps, SNRq = 25.8 dB
b)
R = 64 kbps, SNRq = 49.8 dB
c)
R = 64 kbps, SNRq = 55.8 dB
d)
R = 32 kbps, SNRq = 49.8 dB

|
Bhavya Rane answered |
Bit Rate = 8k x 8 = 64 kbps
Chapter doubts & questions for Communication System - GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Communication System - GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2026
26 docs|263 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup













