All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Biology >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 6: Gene Expression for Grade 9 Exam
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16? - a)1
- b)4
- c)9
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16?
a)
1
b)
4
c)
9
d)
3

|
Vaibhav Kaushik answered |
Ratio is 9.3.3.1
where last 3.1 is drawf and green . drawf and yellow
4 answer
where last 3.1 is drawf and green . drawf and yellow
4 answer
XO type of sex determination is found in________.- a)Grasshopper
- b)Elephant
- c)Human beings
- d)Dog
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
XO type of sex determination is found in________.
a)
Grasshopper
b)
Elephant
c)
Human beings
d)
Dog
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
In grasshopper, sex determination is of XO type, in which the males have only one X-chromosome besides the autosomes whereas females have a pair of X-chromosomes.
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?- a)Mendel
- b)Morgan
- c)Watson
- d)Bateson
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?
a)
Mendel
b)
Morgan
c)
Watson
d)
Bateson
|
|
Riyα answered |
Option {A}
Gregor Johann Mandel...
cz it's gave the idea of heredity...
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?- a)Resemblance
- b)Heredity
- c)Variation
- d)Inheritance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?
a)
Resemblance
b)
Heredity
c)
Variation
d)
Inheritance
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called heredity. The offspring resembles to parent due to same genetic combination inherited from parents.
Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?- a)Skin pigmentation in humans
- b)Sex-linkage in humans
- c)Pink flowers of Snapdragon
- d)The ABO blood groups in human
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?
a)
Skin pigmentation in humans
b)
Sex-linkage in humans
c)
Pink flowers of Snapdragon
d)
The ABO blood groups in human
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Co-dominance is the phenomenon that deviates from Mendel’s law of inheritance. Both the alleles appear in offspring instead of one as in Mendel’s experiment. ABO blood grouping in human being is example of co-dominance in which both IA and IB appear simultaneously to form AB blood type.
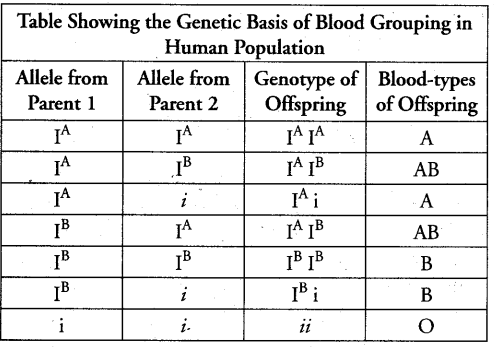
For ABO system of blood groups, allele IA produces N-acetylgalactosamine transferase enzyme which recognises H- antigen present in RBC membrane and adds N-acetylgalactosamine to sugar parts of H antigens to form A antigen.
The allele IB produces galactosyl transferase enzyme which recognized H antigen to form B antigens. Allele i does not produce any sugar or antigen.
IA and IB are completely dominant over i, in other words antigens A and B are produced. This is because of co-dominance. These antigens determine the type of blood group. Blood group A has antigens B have antigen, AB has both antigens while blood group. Blood group A have antigen A, group B have antigen B, AB has both antigens while blood group O do not carry any antigens.
Thus, six genotypes and four phenotypes are possible.
Dihybrid cross proves the law of________.- a)Segregation
- b)Purity of gametes
- c)Law of independent assortment
- d)Dominance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dihybrid cross proves the law of________.
a)
Segregation
b)
Purity of gametes
c)
Law of independent assortment
d)
Dominance

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Dihybrid cross proves the law of independent assortment. Mendel found that each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation. This is known as Law of independent assortment. Dihybrid cross - cross between two parents that differ by two pairs of alleles (AABB X aabb). The formation of gametes is an application of this law.
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into______.- a)Male
- b)Female
- c)Sterile
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into______.
a)
Male
b)
Female
c)
Sterile
d)
Any of the above

|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
In human male progeny contains XY chromosome
female progeny contains XX chromosome
female progeny contains XX chromosome
The term ‘Genetics’ was proposed by- a)Johannsen
- b)Morgan
- c)Mendel
- d)Bateson
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The term ‘Genetics’ was proposed by
a)
Johannsen
b)
Morgan
c)
Mendel
d)
Bateson
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Bateson co-discovered genetic linkage with Reginald Punnett and Edith Saunders, and he and Punnett founded the Journal of Genetics in 1910. Bateson also coined the term "epistasis" to describe the genetic interaction of two independent loci.
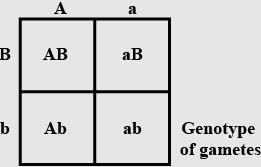
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?- a)AABB
- b)AaBb
- c)AABb
- d)AaBB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
a)
AABB
b)
AaBb
c)
AABb
d)
AaBB
|
|
Om Desai answered |
If the genotype is AaBb the alleles that will be produced will be AB, Ab, aB, ab, since there are two diallelic characters in the genotypes the person must be heterozygous for both genes. AABB is homozygous. So, the correct answer is "AaBb".

Sex determination in human being is______.- a)XY type
- b)XX type
- c)XXY type
- d)YY type
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sex determination in human being is______.
a)
XY type
b)
XX type
c)
XXY type
d)
YY type

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
- In humans, the males are heterogametic as they have XY sex chromosomes, so they make 50% sperms with X chromosome and 50% sperms with Y chromosome. Females are homogametic. All gametes made by them have X chromosomes. So, humans show XX-XY type of sex determination.
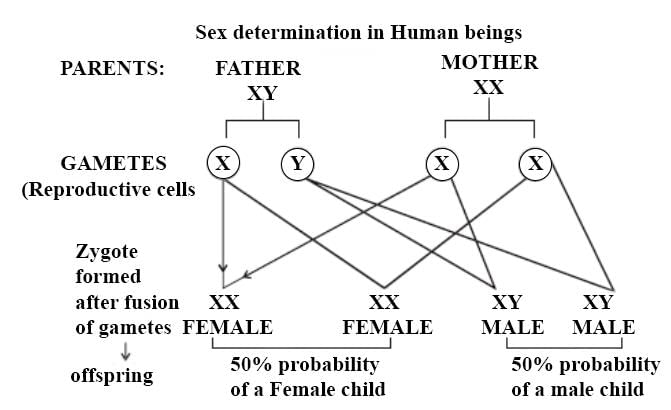
Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Topic SEX DETERMINATION of chapter "Principles of Inheritance and Variation" OF NCERT.
NCERT Reference: Topic SEX DETERMINATION of chapter "Principles of Inheritance and Variation" OF NCERT.
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was______.- a)Lathyrusodaratus
- b)Oryza sativa
- c)Pisumsativum
- d)Mirabilis jalappa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was______.
a)
Lathyrusodaratus
b)
Oryza sativa
c)
Pisumsativum
d)
Mirabilis jalappa
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option c is correct.. mendel conducted experiment's on pisumsativum (garden pea)...mirabilus jalapa is also called 4'o clock plant, oryza sativa (rice)...
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as? - a)Phenotype
- b)Morphology
- c)Ecotype
- d)Genotype
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as?
a)
Phenotype
b)
Morphology
c)
Ecotype
d)
Genotype

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The physical appearance of a character is called as phenotype. The genetic make of individual is called genotype. Tallness, round, wrinkled, yellow etc. are physical appearance.
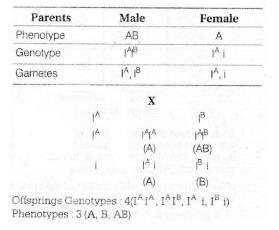
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?- a)3 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
- b)4 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
- c)3 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
- d)4 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?
a)
3 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
b)
4 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
c)
3 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
d)
4 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
A cross between two individuals, one with AB blood group and other with A blood group will produce four genotypes and three phenotypes.

In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plants, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?- a)9:1
- b)3:1
- c)50:50
- d)1:3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plants, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?
a)
9:1
b)
3:1
c)
50:50
d)
1:3

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with green seeded plants, the ratio of yellow and green seeded plants are 50:50 or 1:1 similar to test cross.
Which of the following conditions is called monosomic?- a)n + 1
- b)2n + 1
- c)2n + 2
- d)2n − 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conditions is called monosomic?
a)
n + 1
b)
2n + 1
c)
2n + 2
d)
2n − 1
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Monosomics (2n - 1) one chromosomes less then diploid set of somatic chromosome number.
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome________.- a)Hardly any cross-overs are produced
- b)The percentage of crossing over between them is very high
- c)No crossing over can take place
- d)Only double cross-over can occur between them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome________.
a)
Hardly any cross-overs are produced
b)
The percentage of crossing over between them is very high
c)
No crossing over can take place
d)
Only double cross-over can occur between them
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- When two genes are situated very close to one another on chromosome, hardly any cross-over are produced.
- Such genes are called linkage and do not separate from each other during gamete formation.
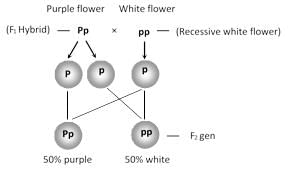
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower bearing snapdragon plants results into pink coloured flower.Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results into pink coloured flower.- a)Both assertion and reason are correct
- b)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
- c)Both assertion and reason are incorrect
- d)Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower bearing snapdragon plants results into pink coloured flower.
Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results into pink coloured flower.
a)
Both assertion and reason are correct
b)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
c)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect
d)
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
- In Snapdragon flower, cross between true-breeding white and red coloured flower produce pink coloured flower in the F1 generation.
- This happens due to the incomplete dominance of alleles over the other.
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed to produce offspring. Offspring were self-crossed. Find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf.- a)3:1
- b)1:1
- c)2:1
- d)1:2:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed to produce offspring. Offspring were self-crossed. Find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf.
a)
3:1
b)
1:1
c)
2:1
d)
1:2:1
|
|
Rajesh Chatterjee answered |
As true tall breeding and true dwarf breeding is seen only a single time in F2 generation, and the remaining are hybtid tall...so the ratio becomes 1:2:2:1.But 1:1 is the ratio for only true tall breeding nd true dwarf breeding in F2 generation.
F2 generation is obtained by______.- a)Crossing of F1 and F2
- b)Selfing of F1
- c)Selfing of F2
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
F2 generation is obtained by______.
a)
Crossing of F1 and F2
b)
Selfing of F1
c)
Selfing of F2
d)
None of these
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
F2 generation is obtained by selfing of F1 progeny..where F1 generation is obtained by crossing two parents..option B
The gene which controls many characters is called- a)Pleiotropic gene
- b)Co-dominant gene
- c)Multiple gene
- d)Polygene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The gene which controls many characters is called
a)
Pleiotropic gene
b)
Co-dominant gene
c)
Multiple gene
d)
Polygene
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A single gene may have two or more phenotypic expressions. The multiple phenotypic effect of a single gene is called pleiotropism. Hence the gene associated with this phenomenon is called Pleiotropic gene.
Klinefelter’s syndrome is due to- a)One Y only
- b)One X only
- c)Two X and one Y
- d)One X and two Y
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Klinefelter’s syndrome is due to
a)
One Y only
b)
One X only
c)
Two X and one Y
d)
One X and two Y

|
Kritika Singh answered |
In klinefelter syndrome One X chromosome increases... show the situation is XXY
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?- a)Back cross
- b)F1 cross
- c)Test cross
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?
a)
Back cross
b)
F1 cross
c)
Test cross
d)
All of these
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called back cross. It is used to check the purity of individual. When F1 is crossed with recessive parent, it is called test cross.
Down’s syndrome is due to- a)Linkage
- b)Non-disjunction of chromosome
- c)Crossing over
- d)Sex-linked inheritance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Down’s syndrome is due to
a)
Linkage
b)
Non-disjunction of chromosome
c)
Crossing over
d)
Sex-linked inheritance
|
|
Lakshmi Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristic features of Down syndrome.
Non-disjunction of chromosome:
The most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. Non-disjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division, resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells. In the case of Down syndrome, non-disjunction of chromosome 21 occurs either during the formation of the egg or sperm, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg.
Key Points:
- Non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis is the most common cause of Down syndrome.
- Non-disjunction can occur during the formation of the egg or sperm.
- Non-disjunction leads to an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Other Causes:
While non-disjunction is the primary cause of Down syndrome, there are other rare genetic variations that can also result in the condition. These include translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy.
- Translocation: In some cases, a piece of chromosome 21 breaks off and attaches to another chromosome, typically chromosome 14. This is called a translocation. If a person has a translocation involving chromosome 21, they may have a higher risk of having a child with Down syndrome.
- Mosaicism: Mosaicism occurs when there is a mixture of cells with a normal number of chromosomes and cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21. This can result in milder symptoms or features of Down syndrome.
- Partial Trisomy: In rare cases, a person may have only a portion of chromosome 21 duplicated, leading to a condition known as partial trisomy. This can result in a milder form of Down syndrome, as only a subset of genes on chromosome 21 is affected.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. This results in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg, leading to the characteristic features of Down syndrome. Other rare genetic variations, such as translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy, can also result in Down syndrome but are less common.
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristic features of Down syndrome.
Non-disjunction of chromosome:
The most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. Non-disjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division, resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells. In the case of Down syndrome, non-disjunction of chromosome 21 occurs either during the formation of the egg or sperm, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg.
Key Points:
- Non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis is the most common cause of Down syndrome.
- Non-disjunction can occur during the formation of the egg or sperm.
- Non-disjunction leads to an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the resulting cells, resulting in an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Other Causes:
While non-disjunction is the primary cause of Down syndrome, there are other rare genetic variations that can also result in the condition. These include translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy.
- Translocation: In some cases, a piece of chromosome 21 breaks off and attaches to another chromosome, typically chromosome 14. This is called a translocation. If a person has a translocation involving chromosome 21, they may have a higher risk of having a child with Down syndrome.
- Mosaicism: Mosaicism occurs when there is a mixture of cells with a normal number of chromosomes and cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21. This can result in milder symptoms or features of Down syndrome.
- Partial Trisomy: In rare cases, a person may have only a portion of chromosome 21 duplicated, leading to a condition known as partial trisomy. This can result in a milder form of Down syndrome, as only a subset of genes on chromosome 21 is affected.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the most common cause of Down syndrome is non-disjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis. This results in an extra copy of chromosome 21 in the fertilized egg, leading to the characteristic features of Down syndrome. Other rare genetic variations, such as translocation, mosaicism, and partial trisomy, can also result in Down syndrome but are less common.
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?- a)Haemophilia
- b)Turner’s syndrome
- c)Cystic fibrosis
- d)Colour blindness
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?
a)
Haemophilia
b)
Turner’s syndrome
c)
Cystic fibrosis
d)
Colour blindness
|
|
Devanshi Mehta answered |
All humans have 46 chromosomes, which determine who and what we are genetically. Boys have an X and Y chromosome. Girls have 2 X chromosomes. Turner Syndrome is a chromosomal disorder in girls in which part or all of one of the X-chromosomes is missing.
This loss of genetic material causes 2 primary features: namely, short stature and underdeveloped ovaries causing delayed or absent puberty. It is usually diagnosed when a girl is noted to be very short and a chromosome blood test is obtained. It should also be suspected if a girl has not developed breasts by 13-14 years of age or had her menstrual period by 15-16 years of age. Effective hormonal treatment is available for both the short stature and to stimulate normal pubertal changes.
This loss of genetic material causes 2 primary features: namely, short stature and underdeveloped ovaries causing delayed or absent puberty. It is usually diagnosed when a girl is noted to be very short and a chromosome blood test is obtained. It should also be suspected if a girl has not developed breasts by 13-14 years of age or had her menstrual period by 15-16 years of age. Effective hormonal treatment is available for both the short stature and to stimulate normal pubertal changes.
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?- a)Insects
- b)Human beings
- c)Lizards
- d)Birds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?
a)
Insects
b)
Human beings
c)
Lizards
d)
Birds
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
In birds male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes while female contain one Z and one W chromosome.
In a given plant, red colour (R) of fruits is dominant over white fruit (r); and tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfness (t). If a plant with genotype RrTt is crossed with a plant of genotype rrtt, what will be the percentage of tall plants with red fruits in the next generation?- a)20%
- b)40%
- c)50%
- d)60%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a given plant, red colour (R) of fruits is dominant over white fruit (r); and tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfness (t). If a plant with genotype RrTt is crossed with a plant of genotype rrtt, what will be the percentage of tall plants with red fruits in the next generation?
a)
20%
b)
40%
c)
50%
d)
60%

|
Universal Academy answered |
According to question, tallness (T) is dominant over dwarfism (t) and red colour (R) is dominant over white (r) fruit colour.
Parent Generation; P1 : RRTt x rrtt
F1 generation :
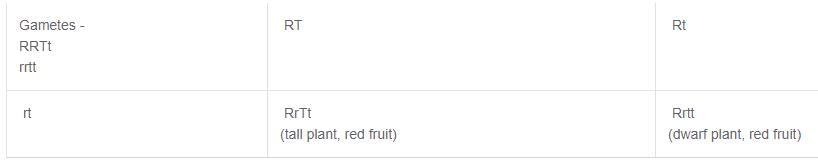
Phenotypic ratio = 1 (tall plant, red fruit)
: 1 (dwarf plant, red fruit)
; thus, percent of tall plant with red fruit is 50%.

Phenotypic ratio = 1 (tall plant, red fruit)
: 1 (dwarf plant, red fruit)
; thus, percent of tall plant with red fruit is 50%.
What will be expected blood groups in the off spring when there is a cross between AB blood group mother and heterozygous B blood group father?- a)25% AB, 25% A, 50%B
- b)50% AB, 25% A, 25%B
- c)25% AB, 50% O, 25%A
- d)25% O, 25% A, 50%B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be expected blood groups in the off spring when there is a cross between AB blood group mother and heterozygous B blood group father?
a)
25% AB, 25% A, 50%B
b)
50% AB, 25% A, 25%B
c)
25% AB, 50% O, 25%A
d)
25% O, 25% A, 50%B
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Given;
Mother is with "AB" blood group....i.e. it means the genotypes are 'IAIB' ..
For "B" blood group genotypes are:-'IBIB'(homozygous condition);'IBIO'(Heterozygous condition)..
In question it is said that Father is with "B" heterozygous blood group...So;the genotypes are 'IBIO' ...
When cross is done between Mother with 'IAIB' & father with 'IBIO'..
the possible genotypes of the progeny are :-
'IAIB'(i.e."AB" blood group);'IAIO'(i.e."A" blood group);'IBIB'(i.e."B" blood group);'IBIO'(i.e."B" blood group)..
% of "AB" blood group=>1×100/4 =>25% of progeny with "AB" blood group..
% of "A" blood group=>1×100/4 =>25% of progeny with "A" blood group..
% of "B" blood group =>2×100/4 =>50% of progeny with "B" blood group....
Hence;option _'A'_holds true here...
Mutations which arise suddenly in nature are called- a)Spontaneous mutations
- b)Gene mutations
- c)Induced mutations
- d)Chromosomal mutations
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mutations which arise suddenly in nature are called
a)
Spontaneous mutations
b)
Gene mutations
c)
Induced mutations
d)
Chromosomal mutations
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Gene mutation is defined as a sudden discrete change in the genetic material of gene which is heritable. Mutations when they arise suddenly in nature are called spontaneous mutations.
The test cross is used to determine the________.- a)Genotype of the plant
- b)Phenotype of the plant
- c)Both a and b
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The test cross is used to determine the________.
a)
Genotype of the plant
b)
Phenotype of the plant
c)
Both a and b
d)
None of these

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
The test cross is used to determine the genotype of the plant in which F1 plant is crossed with homozygous recessive plants. If the ratio is 1:1 the plant is homozygous.
Monohybrid ratio is_____.- a)9:3:1
- b)3:1
- c)9:3:3:1
- d)9:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Monohybrid ratio is_____.
a)
9:3:1
b)
3:1
c)
9:3:3:1
d)
9:1

|
Dipika Das answered |
Monohybrid ratio is the ratio of different phenotypic traits obtained on hybridizing single pair of trait. It is 3:1. When tall pea plant is crossed with dwarf, the offspring obtained are in ¾ tall and ¼ dwarf.
Turner syndrome is- a)XYY
- b)XO
- c)XXX
- d)XXY
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Turner syndrome is
a)
XYY
b)
XO
c)
XXX
d)
XXY

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Turner syndrome (TS), also known 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partly or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected.
In a plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with RRTt genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt:- a)25% will be tall with red fruit
- b)75% will be tall with red fruit
- c)50% will be tall with red fruit
- d)All the offspring will be tall with red fruit
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with RRTt genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt:
a)
25% will be tall with red fruit
b)
75% will be tall with red fruit
c)
50% will be tall with red fruit
d)
All the offspring will be tall with red fruit

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
If a plant with RRTt genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt 50% of the offspring will be tall with red fruit.
If two pea plants having red (dominant) coloured flowers with unknown genotypes are crossed, 75% of the flowers are red and 25% are white. The genotypic constitution of the parents having red coloured flowers will be- a)Both heterozygous
- b)One homozygous and other heterozygous
- c)Both homozygous
- d)Both hemizygous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If two pea plants having red (dominant) coloured flowers with unknown genotypes are crossed, 75% of the flowers are red and 25% are white. The genotypic constitution of the parents having red coloured flowers will be
a)
Both heterozygous
b)
One homozygous and other heterozygous
c)
Both homozygous
d)
Both hemizygous
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
Yeah...the parents are heterozygous ...as in this case in F2 generation we obtain 3:1(i.e.,75:25) phenotypic ratio ...
In Mirabilis jalapa when two F1pink flowered plants were crossed with each other, the F2 generation produced 40 red, 80 pink and 40 white flowering plants. This a case of:- a)Duplicate genes
- b)Epistatis
- c)Incomplete dominance
- d)Lethal genes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Mirabilis jalapa when two F1pink flowered plants were crossed with each other, the F2 generation produced 40 red, 80 pink and 40 white flowering plants. This a case of:
a)
Duplicate genes
b)
Epistatis
c)
Incomplete dominance
d)
Lethal genes

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
F1pink flowered plants are heterozygous. When selfing is done the genotype and phenotype develops as 1:2:1 as 40 red, 80 pink and 40 white flowering plants.
Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character under consideration is called- a)Back cross
- b)Dihybrid cross
- c)Reciprocal cross
- d)Test cross
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character under consideration is called
a)
Back cross
b)
Dihybrid cross
c)
Reciprocal cross
d)
Test cross

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Test cross is the cross of the individuals with its homozygous recessive parent. In other words, we can say that it is a specialized back cross of F1 hybrid with it's homozygous recessive parent in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character. Reciprocal cross is the cross that could be made either way or independent of the sex of the parents. Dihybrid cross is the cross of the hybrids of F1 generations with either of its parents.
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is- a)1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
- b)9:3:3:1
- c)7:1:1:7
- d)12:3:4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is
a)
1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
b)
9:3:3:1
c)
7:1:1:7
d)
12:3:4
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Because it produces produced nine plants with round, yellow seeds, three plants with round, green seeds, three plants with wrinkled, yellow seeds and one plant with wrinkled, green seeds.therefore the ratio is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is
- A:
1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
- B:
9:3:3:1
- C:
7:1:1:7
- D:
12:3:4
The answer is b.
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is
1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
9:3:3:1
7:1:1:7
12:3:4
|
|
Ashish Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
In a dihybrid cross, two traits are considered simultaneously. The F1 generation produced after crossing two pure breeding lines will all be heterozygous for both traits.
For example, if two pure breeding plants with yellow round seeds (YYRR) are crossed with plants with green wrinkled seeds (yyrr), the F1 generation will all be heterozygous for both traits (YyRr).
When the F1 generation is crossed with itself or another F1 individual, the resulting F2 generation will exhibit all possible combinations of the two traits.
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is determined by the number of possible combinations of the two traits.
The possible combinations of the two traits can be determined using a Punnett square or the FOIL method.
For example, using the FOIL method:
(YyRr) x (YyRr)
YYRr YyRR YyRr yyRR
YYRr YyRR YyRr yyRR
YyRr yyRR YyRr yyrr
yyRR yyRR yyrr yyrr
In this example, there are 9 individuals with both dominant traits (yellow and round seeds), 3 individuals with one dominant and one recessive trait (yellow and wrinkled seeds, green and round seeds), and 1 individual with both recessive traits (green and wrinkled seeds).
Therefore, the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of this dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1, which is option B.
In a dihybrid cross, two traits are considered simultaneously. The F1 generation produced after crossing two pure breeding lines will all be heterozygous for both traits.
For example, if two pure breeding plants with yellow round seeds (YYRR) are crossed with plants with green wrinkled seeds (yyrr), the F1 generation will all be heterozygous for both traits (YyRr).
When the F1 generation is crossed with itself or another F1 individual, the resulting F2 generation will exhibit all possible combinations of the two traits.
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is determined by the number of possible combinations of the two traits.
The possible combinations of the two traits can be determined using a Punnett square or the FOIL method.
For example, using the FOIL method:
(YyRr) x (YyRr)
YYRr YyRR YyRr yyRR
YYRr YyRR YyRr yyRR
YyRr yyRR YyRr yyrr
yyRR yyRR yyrr yyrr
In this example, there are 9 individuals with both dominant traits (yellow and round seeds), 3 individuals with one dominant and one recessive trait (yellow and wrinkled seeds, green and round seeds), and 1 individual with both recessive traits (green and wrinkled seeds).
Therefore, the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of this dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1, which is option B.
Chromosome theory of XY sex determination was proposed by:- a)Wilson and Stevens
- b)Sutton and Boveri
- c)Johannsen
- d)Henking
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chromosome theory of XY sex determination was proposed by:
a)
Wilson and Stevens
b)
Sutton and Boveri
c)
Johannsen
d)
Henking

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
Chromosome theory of XY sex determination was proposed by Wilson and Stevens.
Two genes p and q showing 1.3% of recombination while other two genes x and y show 37.2 percent of recombination. Which pair of genes is close to each other?- a)p and q
- b)x and y
- c)Both pairs are equally placed
- d)There is no relation between them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two genes p and q showing 1.3% of recombination while other two genes x and y show 37.2 percent of recombination. Which pair of genes is close to each other?
a)
p and q
b)
x and y
c)
Both pairs are equally placed
d)
There is no relation between them

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
Two genes p and q showing 1.3% of recombination while other two genes x and y show 37.2 percent of recombination. p and q genes are present close to each other as they show less recombination percentage.
With green pods as a dominant trait over yellow, which of the following crosses will result in all progeny having yellow pods?- a)Homozygous green and homozygous yellow
- b)Heterozygous green and heterozygous green
- c)Homozygous yellow and homozygous yellow
- d)Homozygous green and homozygous green
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
With green pods as a dominant trait over yellow, which of the following crosses will result in all progeny having yellow pods?
a)
Homozygous green and homozygous yellow
b)
Heterozygous green and heterozygous green
c)
Homozygous yellow and homozygous yellow
d)
Homozygous green and homozygous green
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Yellow being recessive will express only when both alleles are present. That occurs only when both parents can contribute an allele encoding for the yellow pod. For all progeny to have yellow pods, both parents have to be homozygous for yellow pods.
Which of the following statements is true regarding the “law of independent assortment”?- a)Independent assortment leads to variation.
- b)Independent assortment leads to formation of new combinations of characters.
- c)Factors assort independent of each other when more than one pair of characters are present together.
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the “law of independent assortment”?
a)
Independent assortment leads to variation.
b)
Independent assortment leads to formation of new combinations of characters.
c)
Factors assort independent of each other when more than one pair of characters are present together.
d)
All of these
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. Independent assortment of genes and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel. Recombination occurs during meiosis and is a process that breaks and recombines pieces of DNA to produce new combinations of genes. Recombination scrambles pieces of maternal and paternal genes, which ensures that genes assort independently from one another.
The pure line round-seeded pea plant was crossed with a wrinkled-seeded pea plant. The F1 generation is ____ and it can be explained by _____.- a)Wrinkled : Law of segregation
- b)Round : Law of dominance
- c)Round : Co-dominance
- d)Wrinkled : Law of dominance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Wrinkled : Law of segregation
b)
Round : Law of dominance
c)
Round : Co-dominance
d)
Wrinkled : Law of dominance

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The F1 generation from crossing a pure line round-seeded pea plant with a wrinkled-seeded pea plant will be round-seeded. This can be explained by the Law of Dominance, where round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds.
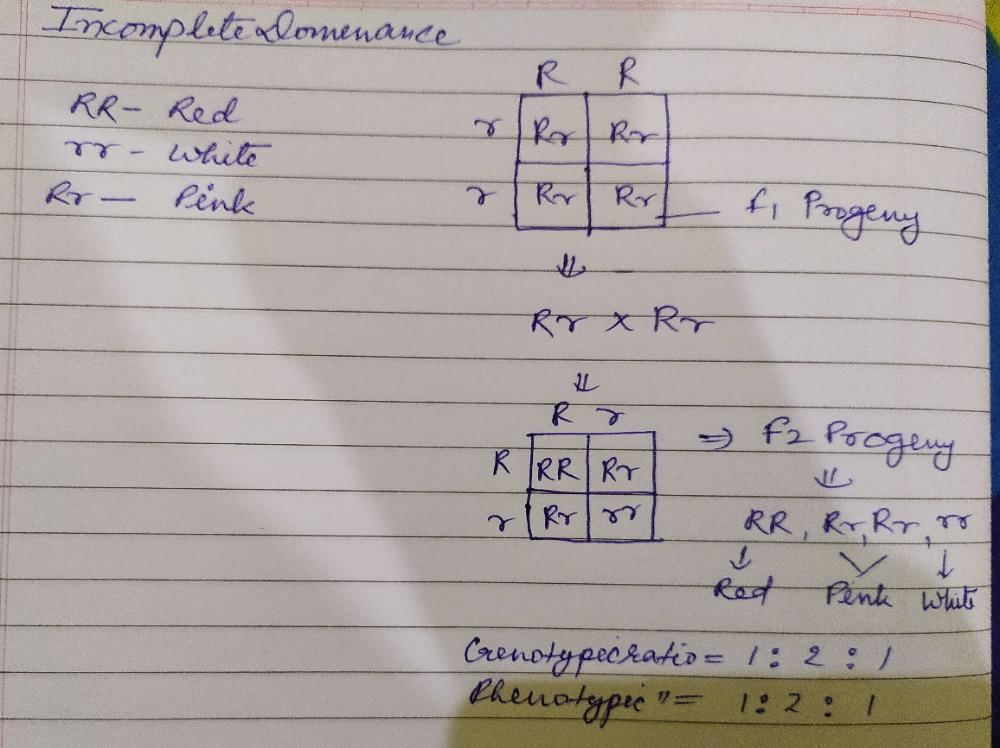
F2 generation in a Mendelian cross showed that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are same as 1 : 2 : 1. It represents in case of- a)Monohybrid cross with complete dominance
- b)Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance
- c)Dihybrid Cross
- d)Co – Dominance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
F2 generation in a Mendelian cross showed that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are same as 1 : 2 : 1. It represents in case of
a)
Monohybrid cross with complete dominance
b)
Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance
c)
Dihybrid Cross
d)
Co – Dominance

|
Lalita Jha answered |
Indentify the incorrect statement:- a)Tall plant produce gametes by meiosis and the dwarf plants by mitosis.
- b)Only one allele is transmitted to a gamete.
- c)The segregation of alleles is a random process.
- d)Gametes will always be pure for the trait.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Indentify the incorrect statement:
a)
Tall plant produce gametes by meiosis and the dwarf plants by mitosis.
b)
Only one allele is transmitted to a gamete.
c)
The segregation of alleles is a random process.
d)
Gametes will always be pure for the trait.
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Both tall and dwarf plants produce gametes by mitosis. Plants use meiosis only to produce spores that develop into multicellular haploid gametophytes which produce gametes by mitosis.
Therefore, gamete formation in both tall and dwarf plants is by mitosis.
Therefore, gamete formation in both tall and dwarf plants is by mitosis.
Match the items of Column - I with Column - II:
Column-I Column-II
(a) XX-XO method of sex determination (i) Turner's syndrome
(b) XX-XY method of sex determination (ii) Female heterogametic
(c) Karyotype-45 (iii) Grasshopper
(d) ZW-ZZ method of sex determination (iv) Female homogametic
Select the correct option from the following:- a)(a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
- b)(a) - (i), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iii)
- c)(a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
- d)(a) - (iv), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the items of Column - I with Column - II:
Column-I Column-II
(a) XX-XO method of sex determination (i) Turner's syndrome
(b) XX-XY method of sex determination (ii) Female heterogametic
(c) Karyotype-45 (iii) Grasshopper
(d) ZW-ZZ method of sex determination (iv) Female homogametic
Select the correct option from the following:
Column-I Column-II
(a) XX-XO method of sex determination (i) Turner's syndrome
(b) XX-XY method of sex determination (ii) Female heterogametic
(c) Karyotype-45 (iii) Grasshopper
(d) ZW-ZZ method of sex determination (iv) Female homogametic
Select the correct option from the following:
a)
(a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
b)
(a) - (i), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iii)
c)
(a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii)
d)
(a) - (iv), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii)
|
|
Ritika Sain answered |
(c) is correct option
Gene for colour blindness is located on- a)13th chromosome
- b)Y chromosome
- c)21st chromosome
- d)X chromosome
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gene for colour blindness is located on
a)
13th chromosome
b)
Y chromosome
c)
21st chromosome
d)
X chromosome
|
|
Asha Chauhan answered |
Introduction:
Color blindness is a genetic disorder that impairs a person's ability to perceive certain colors, usually red and green. It is caused by a genetic mutation that affects the cones in the retina of the eye, which are responsible for color vision. This mutation is located on the X chromosome.
Explanation:
1. Genetic Basis of Color Blindness:
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder. This means that the gene responsible for color blindness is located on the X chromosome. The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes, with females having two X chromosomes (XX) and males having one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Since the gene for color blindness is located on the X chromosome, it primarily affects males.
2. X Chromosome and Inheritance:
The X chromosome carries many genes that are responsible for various traits and characteristics. In males, the Y chromosome does not have a corresponding allele for the genes on the X chromosome. Therefore, if a male inherits a mutated gene on the X chromosome, he will express the trait associated with that gene, as there is no second copy of the gene to mask its effects.
3. Inheritance Pattern of Color Blindness:
When a female carries a mutated gene on one of her X chromosomes, she is considered a carrier. As carriers have a normal copy of the gene on their other X chromosome, they do not exhibit color blindness themselves but can pass the mutated gene to their offspring. If a carrier female has a son, there is a 50% chance that he will inherit the mutated gene and be color blind.
4. Higher Prevalence in Males:
Since males have only one X chromosome, they are more susceptible to color blindness. If a male inherits the mutated gene on his X chromosome, he will be color blind. On the other hand, females need to inherit the mutated gene on both of their X chromosomes to be color blind. This is why color blindness is more commonly seen in males.
Conclusion:
The gene for color blindness is located on the X chromosome. This genetic disorder primarily affects males due to the inheritance pattern of the X chromosome. Understanding the genetic basis of color blindness helps in diagnosing and managing the condition effectively.
Color blindness is a genetic disorder that impairs a person's ability to perceive certain colors, usually red and green. It is caused by a genetic mutation that affects the cones in the retina of the eye, which are responsible for color vision. This mutation is located on the X chromosome.
Explanation:
1. Genetic Basis of Color Blindness:
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder. This means that the gene responsible for color blindness is located on the X chromosome. The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes, with females having two X chromosomes (XX) and males having one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Since the gene for color blindness is located on the X chromosome, it primarily affects males.
2. X Chromosome and Inheritance:
The X chromosome carries many genes that are responsible for various traits and characteristics. In males, the Y chromosome does not have a corresponding allele for the genes on the X chromosome. Therefore, if a male inherits a mutated gene on the X chromosome, he will express the trait associated with that gene, as there is no second copy of the gene to mask its effects.
3. Inheritance Pattern of Color Blindness:
When a female carries a mutated gene on one of her X chromosomes, she is considered a carrier. As carriers have a normal copy of the gene on their other X chromosome, they do not exhibit color blindness themselves but can pass the mutated gene to their offspring. If a carrier female has a son, there is a 50% chance that he will inherit the mutated gene and be color blind.
4. Higher Prevalence in Males:
Since males have only one X chromosome, they are more susceptible to color blindness. If a male inherits the mutated gene on his X chromosome, he will be color blind. On the other hand, females need to inherit the mutated gene on both of their X chromosomes to be color blind. This is why color blindness is more commonly seen in males.
Conclusion:
The gene for color blindness is located on the X chromosome. This genetic disorder primarily affects males due to the inheritance pattern of the X chromosome. Understanding the genetic basis of color blindness helps in diagnosing and managing the condition effectively.
The ultimate source of allelic variation is:- a)Recombination
- b)Natural selection
- c)Mutation
- d)Drift
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ultimate source of allelic variation is:
a)
Recombination
b)
Natural selection
c)
Mutation
d)
Drift
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Gene is a segment of DNA and new alleles arise by mutation - a sudden inheritable change in DNA.
What are the possible phenotypes that can be observed after self-crossing violet flowered pea plants?- a)All violet
- b)All white
- c)25% violet and 75% white
- d)25% white and 75% violet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the possible phenotypes that can be observed after self-crossing violet flowered pea plants?
a)
All violet
b)
All white
c)
25% violet and 75% white
d)
25% white and 75% violet
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Violet is dominant over white. Self-crossing of violet flowered plants will produce 25% recessive plants, which will have white-flowers.
A plant that exhibits two alleles for only one trait is called ________- a)monohybrid
- b)dihybrid
- c)monogamous
- d)digamous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A plant that exhibits two alleles for only one trait is called ________
a)
monohybrid
b)
dihybrid
c)
monogamous
d)
digamous
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Monohybrid refers to a hybrid that differs at only one gene. Thus, a plant that exhibits two alleles for one trait is a monohybrid.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 6: Gene Expression - AP Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 6: Gene Expression - AP Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Biology
130 videos|198 docs|114 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup