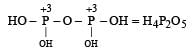All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of P-block elements for NEET Exam
The correct statements among the given are
- a)Antimony belongs to 15th group and 5th period
- b)electron gain enthalpy of P > N > S > O
- c)Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus is -3 and +6
- d)Fluoroapatite, formula is Ca6(PO4)6 CaF2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statements among the given are
a)
Antimony belongs to 15th group and 5th period
b)
electron gain enthalpy of P > N > S > O
c)
Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus is -3 and +6
d)
Fluoroapatite, formula is Ca6(PO4)6 CaF2

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Option A: Group 5A (or VA) of the periodic table are the pnictogens: the nonmetals nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), the metalloids arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb), and the metal bismuth (Bi).
Option B: The electron gain enthalpy of P< N< S< O.
Option C: Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus are -3 and +5 respectively.
Option D: Fluorapatite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F .
Option B: The electron gain enthalpy of P< N< S< O.
Option C: Minimum and maximum oxidation number of phosphorus are -3 and +5 respectively.
Option D: Fluorapatite is a phosphate mineral with the formula Ca5(PO4)3F .
Hence, option A is correct.
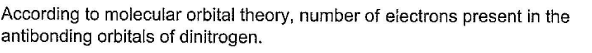
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Subhankar Choudhary answered |
Molecular Orbital Theory and Antibonding Orbitals in Nitrogen
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is a theoretical model that describes the behavior of electrons in molecules based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is used to explain and predict the properties of molecules, including their electronic and magnetic properties, bond lengths, bond angles, and so on.
In MOT, the electrons in a molecule are treated as waves that are described by molecular orbitals (MOs), which are mathematical functions that represent the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space. These MOs are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the atoms in the molecule.
Antibonding orbitals are MOs that have a higher energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed. When electrons occupy these orbitals, they weaken the bond between the atoms in the molecule, making it more likely to break apart.
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, which are represented by the atomic orbitals s and p. In the molecule N2, these atomic orbitals combine to form five MOs: two bonding MOs, two antibonding MOs, and one nonbonding MO.
The two bonding MOs are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they help to hold the two nitrogen atoms together. The nonbonding MO is filled with two electrons, which are shared equally between the two nitrogen atoms and do not contribute to the bond strength.
The two antibonding MOs are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they weaken the bond between the two nitrogen atoms. When all five valence electrons are placed into the MOs, there are four electrons in the antibonding MOs and one electron in the nonbonding MO.
Therefore, according to molecular orbital theory, there are four electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) is a theoretical model that describes the behavior of electrons in molecules based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is used to explain and predict the properties of molecules, including their electronic and magnetic properties, bond lengths, bond angles, and so on.
In MOT, the electrons in a molecule are treated as waves that are described by molecular orbitals (MOs), which are mathematical functions that represent the probability of finding an electron at a given point in space. These MOs are formed by combining the atomic orbitals of the atoms in the molecule.
Antibonding orbitals are MOs that have a higher energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed. When electrons occupy these orbitals, they weaken the bond between the atoms in the molecule, making it more likely to break apart.
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, which are represented by the atomic orbitals s and p. In the molecule N2, these atomic orbitals combine to form five MOs: two bonding MOs, two antibonding MOs, and one nonbonding MO.
The two bonding MOs are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they help to hold the two nitrogen atoms together. The nonbonding MO is filled with two electrons, which are shared equally between the two nitrogen atoms and do not contribute to the bond strength.
The two antibonding MOs are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are formed, and they weaken the bond between the two nitrogen atoms. When all five valence electrons are placed into the MOs, there are four electrons in the antibonding MOs and one electron in the nonbonding MO.
Therefore, according to molecular orbital theory, there are four electrons present in the antibonding orbitals of nitrogen.
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?- a) Cu
- b)S
- c)C
- d)zn
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals. Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
a)
Cu
b)
S
c)
C
d)
zn
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
C element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products.
- a)
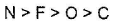
- b)
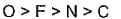
- c)
- d)
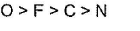
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The second ionization energy refers to the energy required to remove the electron from the corresponding monovalent cation of the respective atom.
It is expected to increase from left to right in the periodic table with the decrease in atomic size.
Since the Oxygen atom gets a stable electronic configuration, 2s22p3 after removing one electron, the O+ shows greater ionization energy than F+ as well as N+.
Thus, correct order will be: O > F > N > C
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is - a)Na
- b)CI
- c)Ar
- d)Si
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the third period of the periodic table the element having smallest size is
a)
Na
b)
CI
c)
Ar
d)
Si
|
|
Aarav Sharma answered |
The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon.
In a period from left to right atomic size decreases due to Increase in nuclear charge.
but the noble gases are bigger than the halogens as they have octet and sort of repulsion occurs in the shells.
so the smallest element in a period is the halogen.so chlorine Cl is the smallest.
Which is the strongest acid in the following : [NEET 2013]- a)HClO3
- b)HClO4
- c)H2SO3
- d)H2SO4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the strongest acid in the following : [NEET 2013]
a)
HClO3
b)
HClO4
c)
H2SO3
d)
H2SO4

|
Surbhi Das answered |
HClO4 is the strongest acid amongst all because the oxidation state or Cl is maximum (+7).
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of- a)[Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
- b) FeSO4.NO2
- c)[Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
- d)FeSO4.HNO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO3– ion. It is due to the formation of
a)
[Fe(H2O)5 (NO)]2+
b)
FeSO4.NO2
c)
[Fe(H2O)4(NO)2]2+
d)
FeSO4.HNO3

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
When freshly prepared solution of FeSO4 is added in a solution containing NO3– ion, it leads to formation of a brown coloured complex. This is known as brown ring test of nitrate.
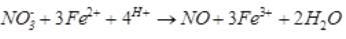
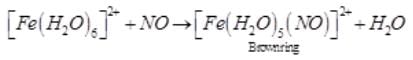
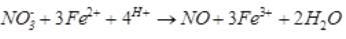
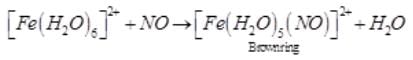

- a)
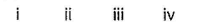

- b)
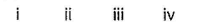

- c)
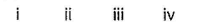
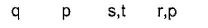
- d)
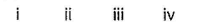
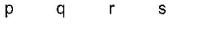
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
(i) Nitrogen is a non-metal.
(ii) Phosphorus is a non-metal.
(iii) Arsenic is a metalloid and shows Sublimation.
(iv) Bismuth is metal and shows the Inert pair effect.
(ii) Phosphorus is a non-metal.
(iii) Arsenic is a metalloid and shows Sublimation.
(iv) Bismuth is metal and shows the Inert pair effect.
Hence, option A is correct.
Which of the following is a polar molecule ? [NEET 2013]- a)SF4
- b)SiF4
- c)XeF4
- d)BF3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a polar molecule ? [NEET 2013]
a)
SF4
b)
SiF4
c)
XeF4
d)
BF3

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
SF4 has 4 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons, sp3d hybridisation leads to irregular shape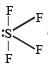 and resultant
and resultant
 and resultant
and resultantμ ≠ 0.
- a)
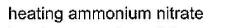
- b)

- c)

- d)
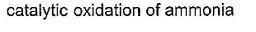
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Gauri Datta answered |
Oxidation of ammonia with CuO produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
The gaseous chemical produced in this reaction is nitrogen gas (N2), which is also obtained by reacting excess ammonia with chlorine. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Explanation:
- Ammonium nitrate: Heating ammonium nitrate results in the decomposition of ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas, water vapor, and oxygen gas. The reaction is represented as:
NH4NO3 → N2 + 2H2O + O2
- Potassium dichromate: Heating potassium dichromate results in the production of oxygen gas and potassium chromate. The reaction is represented as:
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2
- Catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia involves the use of a catalyst (such as platinum or palladium) to oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas and water vapor. The reaction is represented as:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO2 + O2 → 2N2O5
N2O5 → N2 + 2.5O2
- Reacting excess ammonia with chlorine: This reaction involves the reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine gas to produce nitrogen gas and hydrochloric acid. The reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Therefore, option B, reacting excess ammonia with chlorine, is the correct answer.
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
The gaseous chemical produced in this reaction is nitrogen gas (N2), which is also obtained by reacting excess ammonia with chlorine. This reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Explanation:
- Ammonium nitrate: Heating ammonium nitrate results in the decomposition of ammonium nitrate into nitrogen gas, water vapor, and oxygen gas. The reaction is represented as:
NH4NO3 → N2 + 2H2O + O2
- Potassium dichromate: Heating potassium dichromate results in the production of oxygen gas and potassium chromate. The reaction is represented as:
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2
- Catalytic oxidation of ammonia: Catalytic oxidation of ammonia involves the use of a catalyst (such as platinum or palladium) to oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas and water vapor. The reaction is represented as:
4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO2 + O2 → 2N2O5
N2O5 → N2 + 2.5O2
- Reacting excess ammonia with chlorine: This reaction involves the reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine gas to produce nitrogen gas and hydrochloric acid. The reaction is represented as:
2NH3 + Cl2 → N2 + 2HCl
Therefore, option B, reacting excess ammonia with chlorine, is the correct answer.
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?- a)N2
- b)O2
- c)NO+
- d)CN-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electron(s) ?
a)
N2
b)
O2
c)
NO+
d)
CN-
|
|
Priya Chavan answered |
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
- a)

- b)
- c)
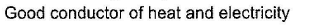
- d)
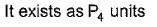
Correct answer is 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Rahul Desai answered |
(a.c) Being goad conductor of neat and elecnicky, black phosphorus is a most stabte allotrope of phosphorus
Which of the following is thermally the most stable?- a)H2Te
- b)H2S
- c)H2O
- d)H2Se
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is thermally the most stable?
a)
H2Te
b)
H2S
c)
H2O
d)
H2Se

|
Ujwal Patel answered |
Stability of hydrides decreases down the group so most stable is H2O
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?- a)P4O10
- b)POCI3
- c)Cone.H2SO4
- d)P4O6
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 8-12) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following can act as dehydrating agent ?
a)
P4O10
b)
POCI3
c)
Cone.H2SO4
d)
P4O6

|
Raksha Nambiar answered |
Dehydrating agents are substances that have the ability to remove water from other substances. They are commonly used in chemical reactions where the removal of water is necessary. In the given options, the substances that can act as dehydrating agents are:
a) P4O10 (Phosphorus pentoxide):
- Phosphorus pentoxide is a powerful dehydrating agent.
- It reacts vigorously with water to form phosphoric acid, removing water from the system.
- The chemical reaction is as follows: P4O10 + 6H2O → 4H3PO4
b) POCI3 (Phosphorus trichloride):
- Phosphorus trichloride is also a dehydrating agent.
- It reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, removing water from the system.
- The chemical reaction is as follows: POCI3 + 3H2O → H3PO3 + 3HCl
c) Cone.H2SO4 (Concentrated sulfuric acid):
- Concentrated sulfuric acid is a highly effective dehydrating agent.
- It has a strong affinity for water and can remove water molecules from other substances.
- Sulfuric acid reacts with water to release a large amount of heat, which is an indication of its dehydrating properties.
d) P4O6 (Phosphorus trioxide):
- Phosphorus trioxide is not a dehydrating agent.
- It is a reducing agent and reacts with water to form phosphorous acid (H3PO3), not removing water from the system.
Therefore, the correct options are a) P4O10, b) POCI3, and c) Cone.H2SO4, as they can act as dehydrating agents by removing water from other substances.
a) P4O10 (Phosphorus pentoxide):
- Phosphorus pentoxide is a powerful dehydrating agent.
- It reacts vigorously with water to form phosphoric acid, removing water from the system.
- The chemical reaction is as follows: P4O10 + 6H2O → 4H3PO4
b) POCI3 (Phosphorus trichloride):
- Phosphorus trichloride is also a dehydrating agent.
- It reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, removing water from the system.
- The chemical reaction is as follows: POCI3 + 3H2O → H3PO3 + 3HCl
c) Cone.H2SO4 (Concentrated sulfuric acid):
- Concentrated sulfuric acid is a highly effective dehydrating agent.
- It has a strong affinity for water and can remove water molecules from other substances.
- Sulfuric acid reacts with water to release a large amount of heat, which is an indication of its dehydrating properties.
d) P4O6 (Phosphorus trioxide):
- Phosphorus trioxide is not a dehydrating agent.
- It is a reducing agent and reacts with water to form phosphorous acid (H3PO3), not removing water from the system.
Therefore, the correct options are a) P4O10, b) POCI3, and c) Cone.H2SO4, as they can act as dehydrating agents by removing water from other substances.
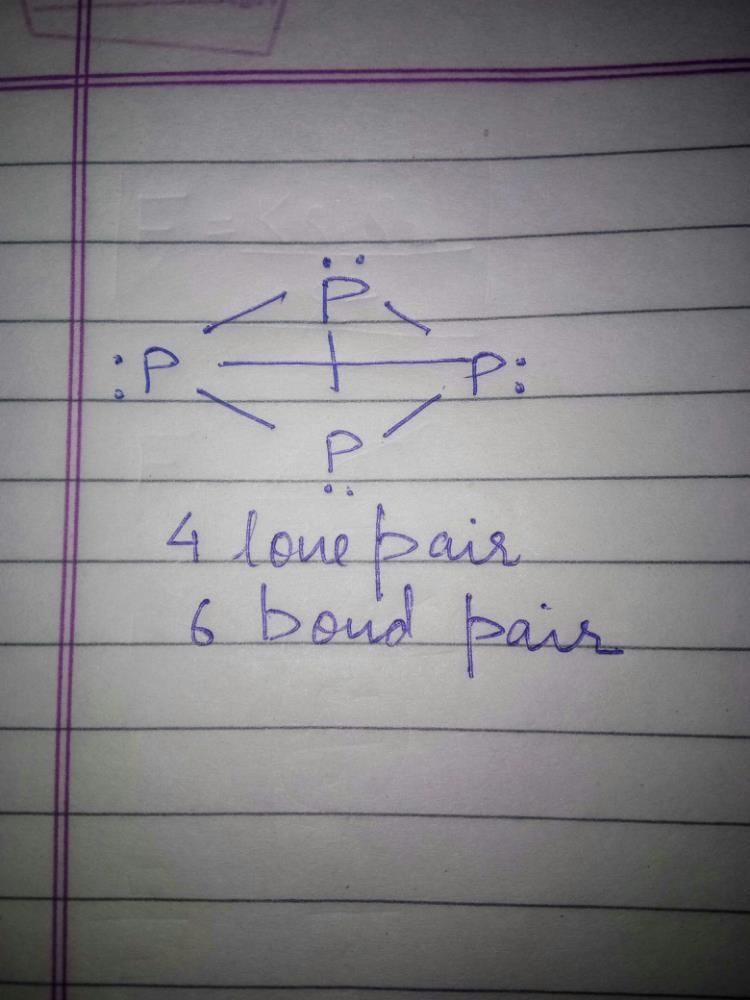
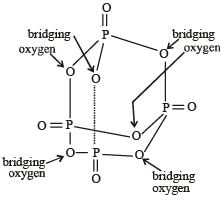
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively - a)12 and 4
- b)8 and 8
- c)12 and 16
- d)12 and 12
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of P – O bonds and lone pairs of electron present in P4O6 molecule respectively
a)
12 and 4
b)
8 and 8
c)
12 and 16
d)
12 and 12

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Number of P – O bonds = 12
Number of pair of electron = 16
Number of pair of electron = 16
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below

- a)

- b)

- c)
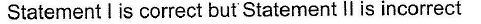
- d)
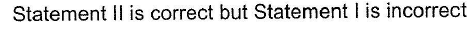
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below

This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Pranjal Pillai answered |
P — P single bond in P4 molecule is much weaker
(213 kJ mol-1) than N ≡ N triple bond (941.4 kJ mol-1) in N2.
Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent? [2009]- a)Br2
- b)I2
- c)Cl2
- d)F2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent? [2009]
a)
Br2
b)
I2
c)
Cl2
d)
F2

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Standard reduction potential of halogens are positive and decreases from fluorine to iodine. Therefore halogens act as strong oxidising agent and their oxidising power decreases from fluorine to iodine.
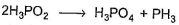 in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
in this equivalent weight of the acid in the reactant side is obtained by dividing molecular weight with
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Abc Bcd answered |
Because there are two molecules of acid in balanced equation.
Which of the following is the strongest Lewis base?
- a)NBr3
- b)NF3
- c)NCl3
- d)NI3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the strongest Lewis base?
a)
NBr3
b)
NF3
c)
NCl3
d)
NI3
|
|
Shanaya Choudhary answered |
Correct Answer :- D
- Lewis bases need to be able to donate electrons. Fluorine is the most electronegative element in the halogens followed by chlorine, bromine and iodine.
- Due to fluorine being strongly electronegative, it draws the electron density towards itself which makes it difficult for nitrogen atom to donate its lone pair of electrons. So, NF is the least basic. This trend follows the strength of electronegativity of the halides.
- Since iodine is least electronegative, it is the most basic trihalide of nitrogen.
So, we have the trend, in decreasing order of basic strength:
NF3 < NCl3 < NBr3 < NI3
Number of chemical species having negative oxidation state for nitrogen among NF3, NCI3, NH2OH, NH3,CH3NH2, NH-2, L13N, N20, HCN, HNC, NO-2
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of chemical species having negative oxidation state for nitrogen among
NF3, NCI3, NH2OH, NH3,CH3NH2, NH-2, L13N, N20, HCN, HNC, NO-2

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
(8) Except in 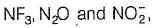 in all others N has negative oxidation states
in all others N has negative oxidation states
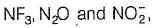 in all others N has negative oxidation states
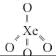
in all others N has negative oxidation statesWhich of the following statements is not correct about XeF2?
- a)It can be obtained by direct reaction between F2 and Xe at high pressure
- b)XeF2 undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give O2 and Xe
- c)XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent
- d)XeF2 contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct about XeF2?
a)
It can be obtained by direct reaction between F2 and Xe at high pressure
b)
XeF2 undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give O2 and Xe
c)
XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent
d)
XeF2 contains two bond pairs and three lone pairs
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
XeF2 is obtained by direct reaction of Xe and F2 at high pressure. It undergoes alkali hydrolysis to produce Xe and O2. XeF2 is a powerful reducing agent where Xe+2 can change to +6 state.
Ozone can be detected by using- a)Silver
- b)Sodium
- c)Mercury
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ozone can be detected by using
a)
Silver
b)
Sodium
c)
Mercury
d)
None of these

|
Aarya Dasgupta answered |
Ozone is detected by using Hg.
At what temperature white phosphorous changes to red phosphorous?- a)300° C
- b)450° C
- c)50° C
- d)400° C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what temperature white phosphorous changes to red phosphorous?
a)
300° C
b)
450° C
c)
50° C
d)
400° C
|
|
Ananya Singh answered |
According to NCERT, red phosphorus is obtained by heating white phosphorus at 573 K in an inert atmosphere for several days. In degree celius, temperature = 300⁰ C (573K - 273).
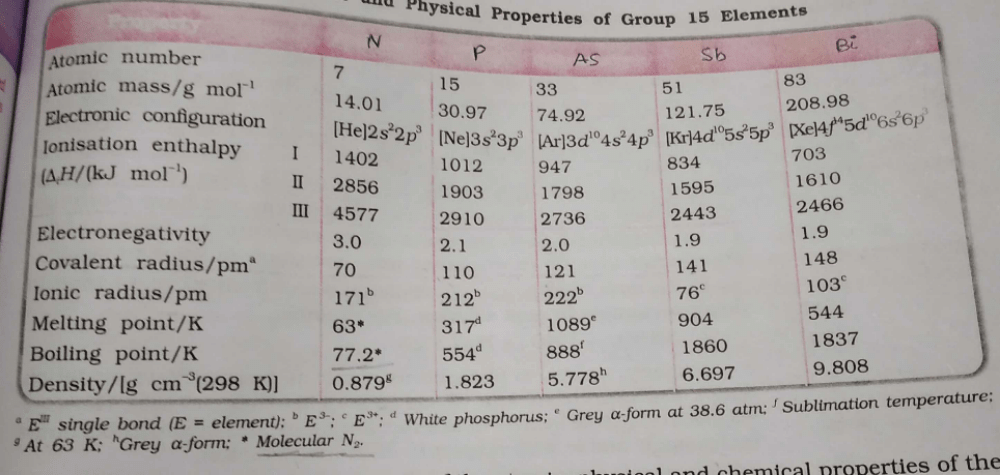
Which are correct statements ?
- a)The melting point of antimony is higher than bismuth
- b)Ionisation energy of C < O < N
- c)In 15th group, all show allotropy except bismuth and nitrogen
- d)Maximum covalency of nitrogen and Phosphorus are 4 and 5 respectively
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which are correct statements ?
a)
The melting point of antimony is higher than bismuth
b)
Ionisation energy of C < O < N
c)
In 15th group, all show allotropy except bismuth and nitrogen
d)
Maximum covalency of nitrogen and Phosphorus are 4 and 5 respectively
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Option A: Bismuth has 6 electron shells, whereas Antimony has 5 electron shells. Because of this, the attractive force between two Bismuth atoms is less due to electron shielding, resulting in bismuth possessing a lower boiling point than antimony.
Option B: In a period of moving from left to right, the ionization energy increases. Since N has a table half-filled 2p subshell which requires large energy.
Thus, the correct order of ionization energy is C < O < N.
Option C: Except N and Bi, all the group 15 elements exhibits allotropy. The allotropes of phosphorous are rather complex but essentially, there are three allotropic forms known as white, red, and black phosphorous.
Option D: Maximum covalency of N & P are 4 and 5.
Option B: In a period of moving from left to right, the ionization energy increases. Since N has a table half-filled 2p subshell which requires large energy.
Thus, the correct order of ionization energy is C < O < N.
Option C: Except N and Bi, all the group 15 elements exhibits allotropy. The allotropes of phosphorous are rather complex but essentially, there are three allotropic forms known as white, red, and black phosphorous.
Option D: Maximum covalency of N & P are 4 and 5.
Hence, option A,B,C,D is correct.
Which is the correct order w.r.t the given property? - a)N > P > As > Sb > Bi (Atomic mass)
- b)N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Electronegativity)
- c)N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Covalent radii)
- d)N = P > As > Sb > Bi (Density)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the correct order w.r.t the given property?
a)
N > P > As > Sb > Bi (Atomic mass)
b)
N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Electronegativity)
c)
N > P > As > Sb = Bi (Covalent radii)
d)
N = P > As > Sb > Bi (Density)
|
|
Roshni Desai answered |
I'm sorry, but the question is incomplete. Please provide more information about the property being referred to.
In the all oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3-hybridised state. All these acids contain P—OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ‘ous’ acids (oxidation state of P is + 1 or + 3) also have P—H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable.
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below: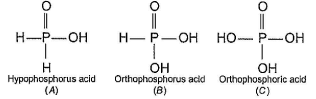
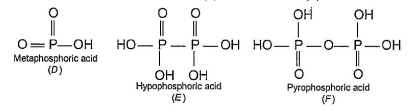 Q. Which of the acids show reducing properties?
Q. Which of the acids show reducing properties?- a)A and C
- b)A and B
- c)A , B and D
- d)C, D, E and F
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the all oxyacids of phosphorus, each phosphorus atom is in sp3-hybridised state. All these acids contain P—OH bonds, the hydrogen atom of which are ionisable imparting acidic nature to the compound. The ‘ous’ acids (oxidation state of P is + 1 or + 3) also have P—H bonds in which hydrogens are not ionisable.
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below:
The presence of P—H bonds in these acids imparts reducing properties. The structure of some oxyacids are drawn below:
Q.
Which of the acids show reducing properties?
a)
A and C
b)
A and B
c)
A , B and D
d)
C, D, E and F

|
Kirti Choudhary answered |
Reducing property is due to P...H bond
Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?- a)Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs
- b)Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments
- c)Radon is used in radiotherapy of cancer
- d)Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a use of noble gases?
a)
Argon is widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs
b)
Neon is used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments
c)
Radon is used in radiotherapy of cancer
d)
Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
|
|
Arindam Chaudhary answered |
Helium is filled in tubes of cycles and scooters tyres
Helium is not used for filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres. It is primarily used in other applications such as:
Argon:
- Widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs to prevent the filament from oxidizing.
- Used in welding and metal fabrication to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases.
Neon:
- Used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments due to its ability to produce a bright light when an electric current passes through it.
- Also commonly used in neon signs for advertising.
Radon:
- Used in radiotherapy of cancer as a radiation source to destroy cancer cells.
- It can also be used in some geological research applications to trace the movement of underground gases.
In contrast, helium is typically used in applications such as:
- Cryogenics to achieve low temperatures
- In filling balloons for various purposes
- In cooling nuclear reactors and MRI machines
Therefore, while noble gases have a variety of important uses, filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres with helium is not one of them.
Helium is not used for filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres. It is primarily used in other applications such as:
Argon:
- Widely used for filling incandescent electric bulbs to prevent the filament from oxidizing.
- Used in welding and metal fabrication to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases.
Neon:
- Used in safety devices for protecting electrical instruments due to its ability to produce a bright light when an electric current passes through it.
- Also commonly used in neon signs for advertising.
Radon:
- Used in radiotherapy of cancer as a radiation source to destroy cancer cells.
- It can also be used in some geological research applications to trace the movement of underground gases.
In contrast, helium is typically used in applications such as:
- Cryogenics to achieve low temperatures
- In filling balloons for various purposes
- In cooling nuclear reactors and MRI machines
Therefore, while noble gases have a variety of important uses, filling tubes of cycles and scooters tyres with helium is not one of them.
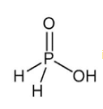 is the structure of
is the structure of- a)Phosphorous acid
- b)Hypophosphorus Acid
- c)Phosphoric acid
- d)Pyrophosphoric acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Phosphorous acid
b)
Hypophosphorus Acid
c)
Phosphoric acid
d)
Pyrophosphoric acid
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Of course..this is a structure of hypo phosphorus acid. It is a mineral acid with formula H4P2O6.In hypophosphorus acid,the phosphorus bonds are identical and joined with p-p bond .there is also joined oxygen and hydrogen bonds as the structure follows.
Most metal oxides are
- a)Covalent in nature
- b)Acidic in nature
- c)Basic in nature
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most metal oxides are
a)
Covalent in nature
b)
Acidic in nature
c)
Basic in nature
d)
None of these

|
Rashi Bose answered |
Most metal oxides are ionic crystals with high melting and boiling points. They are compounds that contain at least one metal and one oxygen atom, and are generally basic in nature. Metal oxides are basic because they react with acids to form salt and water, neutralizing the acids.
In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order: [2009]- a)MF > MCl > MBr > MI
- b)MF > MCl > MI > MBr
- c)MI > MBr > MCl > MF
- d)MCl > MI > MBr > MF
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order: [2009]
a)
MF > MCl > MBr > MI
b)
MF > MCl > MI > MBr
c)
MI > MBr > MCl > MF
d)
MCl > MI > MBr > MF

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
MI > MBr > MCl > MF. As the size of the anion decreases covalency decreases.
Which one of the following arrangements does not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it ? [2008]- a)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidizing power
- b)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electron gain enthalpy
- c)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
- d)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity.
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements does not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it ? [2008]
a)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidizing power
b)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electron gain enthalpy
c)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
d)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity.
|
|
Nisha Pillai answered |
From the given options we find option (a) is correct. The oxidising power of halogens follow the order F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 . Option (b) is incorrect because it in not the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of halogens. The correct order is Cl2 > F2 > Br2 > I2 . The low value of F2 than Cl2 is due to its small size. Option (c) is incorrect. The correct order of bond dissociation energies of halogens is Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2 . Option (d) is correct. It is the correct order of electronegativity values of halogens. Thus option (b) and (c) are incorrect.
Direction (Q. No. 20) This section is bassed on Statment I and Statment II. II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3Statement II : NF3 ionises to give F- ions in aqueous solutio- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statemen I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct. explanation of Statment I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 20) This section is bassed on Statment I and Statment II. II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3
Statement II : NF3 ionises to give F- ions in aqueous solutio
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statemen I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct. explanation of Statment I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Rashi Bose answered |
Due to e- withdrawing capacity of fluorideion, it withdraws. from nitrogen in NF3 make it weakerlig and while presence of e- donating methyl group makes the nitrogen in N(CH3)3 a strong ligand. In aqueous medium, NF3 furnishes fluorideion.
Number of moles of NaOH needed to neutralise one mole each of H3PO2, H3PO3 and H3PO4 respectively are- a)3, 3 and 3
- b)1, 2 and 3
- c)2, 2 and 3
- d)2, 1 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of moles of NaOH needed to neutralise one mole each of H3PO2, H3PO3 and H3PO4 respectively are
a)
3, 3 and 3
b)
1, 2 and 3
c)
2, 2 and 3
d)
2, 1 and 3

|
Gauri Sharma answered |
H3PO2, H3PO3 and H3PO4 are mono, di and tribasic acids respectively.
Which is the correct order of basic strength ?- a) NH2OH < N2H4 < NH3
- b) N2H4 < NH2OH < NH3
- c) NH3 < N2H4 < NH2OH
- d) NH2OH < NH3 < N2H4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the correct order of basic strength ?
a)
NH2OH < N2H4 < NH3
b)
N2H4 < NH2OH < NH3
c)
NH3 < N2H4 < NH2OH
d)
NH2OH < NH3 < N2H4

|
Ashish Nambiar answered |
NH2OH and NH2—NH2 may be considered as NH3 derivatives in which H is replaced but — OH and NH2 respectively. Due to their electron withdrawing nature, these groups decreases electron density over nitrogen making them less basic. The effect of — OH group is stronger than —NH2
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
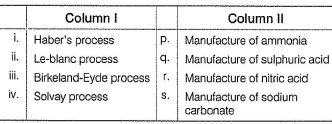
- a)i ii iii iv
p s r s
- b)

- c)

- d)
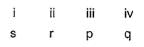
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
a)
i ii iii iv
p s r s
p s r s
b)

c)

d)
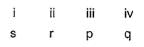

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a)Helium has the lowest boiling point among the noble gases
- b)Argon is used in electric bulbs
- c)Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration
- d)Xe forms XeF6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
Helium has the lowest boiling point among the noble gases
b)
Argon is used in electric bulbs
c)
Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration
d)
Xe forms XeF6
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Air is also the most important source for the other noble gases.T races of krypton are found in various minerals, the most important source of Krypton is Earth's atmosphere. Helium obtained from natural gas and radon is obtained as a byproduct during radioactive disintegration.
So Rn is obtained during radioactive disintegration not Kr.
So Krypton is obtained during radioactive disintegration is the wrong statement.
Which is incorrect among the following options?
- a)Acidic Character of H3PO4 > H3PO3 > H3PO2
- b)Oxidation state of nitrogen N2O < NO < N2O3 < N2O5
- c) Basicity NH3 > PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3
- d)Boiling point of SbH3 > AsH3 > NH3 > PH3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is incorrect among the following options?
a)
Acidic Character of H3PO4 > H3PO3 > H3PO2
b)
Oxidation state of nitrogen N2O < NO < N2O3 < N2O5
c)
Basicity NH3 > PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3
d)
Boiling point of SbH3 > AsH3 > NH3 > PH3

|
Saptarshi Ghoshal answered |
Acidic Character of P oxyacids is due to P—H bonds in the acid. Correct reducing property order is
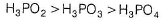
Which among the following does not exhibit positive oxidation state?- a)Fluorine
- b)Chlorine
- c)Oxygen
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following does not exhibit positive oxidation state?
a)
Fluorine
b)
Chlorine
c)
Oxygen
d)
Nitrogen

|
Prashanth Banerjee answered |
Fluorine is most electronegative element therefore can only gain electrons. Thus it only shows negative oxidation state.
Which compound is used as the cooling liquid in refrigerators?- a)Ammonia
- b)Phosphine
- c)Nitrous oxide
- d)Ozone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which compound is used as the cooling liquid in refrigerators?
a)
Ammonia
b)
Phosphine
c)
Nitrous oxide
d)
Ozone

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
NH3 is used as cooling liquid in refrigerators.
Chapter doubts & questions for P-block elements - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of P-block elements - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily