NEET Exam > NEET Questions > what is the main difference between electric ...
Start Learning for Free
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild???
Most Upvoted Answer
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electri...
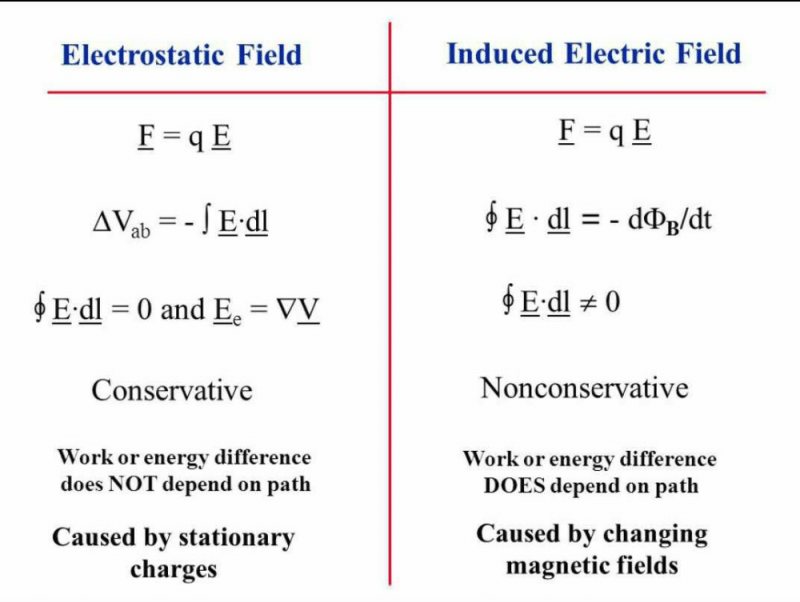
Community Answer
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electri...
The Main Difference between Electric Field and Induced Electric Field
Introduction:
Electric fields are a fundamental concept in physics that describe the force experienced by charged particles due to the presence of other charges. They play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of electrical phenomena. In certain situations, the presence of an electric field can induce another electric field, known as an induced electric field. Although both electric fields and induced electric fields are related to the presence of charges, there are key differences between them.
Main Differences:
1. Origin:
- The electric field is generated by stationary charges. It exists around any charged object and is created by the distribution of charges.
- The induced electric field, on the other hand, is generated by the presence of a changing magnetic field. It is not caused by stationary charges but rather by the variation of magnetic fields over time.
2. Source:
- The source of the electric field is the charged particles themselves. For example, a positive charge creates an electric field that repels other positive charges and attracts negative charges.
- The source of the induced electric field is a changing magnetic field. When a magnetic field changes with time, it induces an electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field's direction and the rate of change.
3. Direction:
- The electric field points away from positive charges and towards negative charges. It follows the direction in which a positive test charge would move if placed in the field.
- The induced electric field depends on the direction of the changing magnetic field. It follows a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux, as described by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
4. Strength:
- The strength of the electric field is determined by the magnitude of the charges and their distribution. It decreases with distance according to the inverse square law.
- The strength of the induced electric field is determined by the rate of change of the magnetic field and the distance from the source of the changing field. It follows a similar inverse square law as the electric field.
5. Time Variability:
- The electric field remains constant as long as the charges creating it remain stationary. It does not depend on time variations.
- The induced electric field only exists when the magnetic field is changing with time. Once the magnetic field stabilizes, the induced electric field disappears.
Conclusion:
In summary, the main difference between electric fields and induced electric fields lies in their origin, source, direction, strength, and time variability. Electric fields are created by stationary charges and their distribution, while induced electric fields are generated by changing magnetic fields. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending and analyzing various electrical phenomena.
Introduction:
Electric fields are a fundamental concept in physics that describe the force experienced by charged particles due to the presence of other charges. They play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of electrical phenomena. In certain situations, the presence of an electric field can induce another electric field, known as an induced electric field. Although both electric fields and induced electric fields are related to the presence of charges, there are key differences between them.
Main Differences:
1. Origin:
- The electric field is generated by stationary charges. It exists around any charged object and is created by the distribution of charges.
- The induced electric field, on the other hand, is generated by the presence of a changing magnetic field. It is not caused by stationary charges but rather by the variation of magnetic fields over time.
2. Source:
- The source of the electric field is the charged particles themselves. For example, a positive charge creates an electric field that repels other positive charges and attracts negative charges.
- The source of the induced electric field is a changing magnetic field. When a magnetic field changes with time, it induces an electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field's direction and the rate of change.
3. Direction:
- The electric field points away from positive charges and towards negative charges. It follows the direction in which a positive test charge would move if placed in the field.
- The induced electric field depends on the direction of the changing magnetic field. It follows a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux, as described by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
4. Strength:
- The strength of the electric field is determined by the magnitude of the charges and their distribution. It decreases with distance according to the inverse square law.
- The strength of the induced electric field is determined by the rate of change of the magnetic field and the distance from the source of the changing field. It follows a similar inverse square law as the electric field.
5. Time Variability:
- The electric field remains constant as long as the charges creating it remain stationary. It does not depend on time variations.
- The induced electric field only exists when the magnetic field is changing with time. Once the magnetic field stabilizes, the induced electric field disappears.
Conclusion:
In summary, the main difference between electric fields and induced electric fields lies in their origin, source, direction, strength, and time variability. Electric fields are created by stationary charges and their distribution, while induced electric fields are generated by changing magnetic fields. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending and analyzing various electrical phenomena.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild???
Question Description
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild???.
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild???.
Solutions for what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild???, a detailed solution for what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? has been provided alongside types of what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is the main difference between electric feild and induced electric feild??? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























