Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > And last one is what is difference between El...
Start Learning for Free
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet?
Most Upvoted Answer
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent...
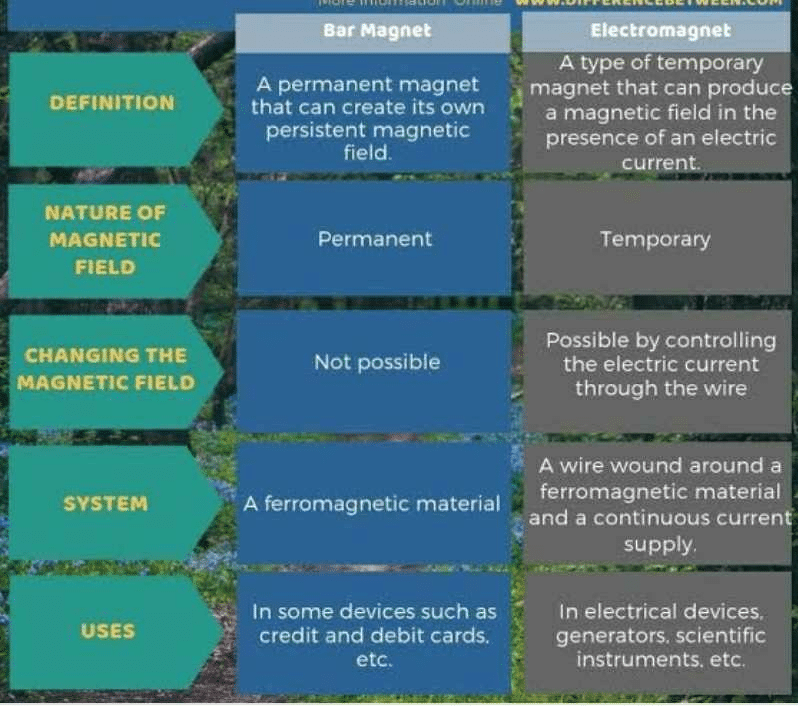
Community Answer
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent...
Electromagnet vs Permanent Magnet
Introduction
Electromagnets and permanent magnets are two types of magnets with different characteristics and applications. While both generate a magnetic field, they differ in their ability to produce a magnetic effect, the presence of a power source, and the ability to control the strength of the magnetic field.
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is generated by an electric current. It consists of a coil of wire wound around a magnetic core, typically made of iron. When an electric current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. The strength of the magnetic field can be altered by changing the amount of current flowing through the coil. Once the electric current is removed, the magnetic field disappears.
Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet, as the name suggests, is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties without the need for an external power source. It is typically made of certain materials such as iron, nickel, cobalt, or alloys like neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) or samarium-cobalt (SmCo). These materials have naturally occurring magnetic properties that allow them to generate a magnetic field.
Differences
1. Power Source: The most significant difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet is the need for a power source. Electromagnets require an electric current to produce a magnetic field, while permanent magnets do not need any external power source.
2. Magnetic Effect: Electromagnets can produce a magnetic effect as long as the electric current flows through the coil. On the other hand, permanent magnets always have a magnetic field and can exert a magnetic force without the need for an electric current.
3. Control of Magnetic Field: The strength of the magnetic field in an electromagnet can be easily controlled by adjusting the amount of current flowing through the coil. In contrast, the strength of a permanent magnet's magnetic field is fixed based on its material composition and cannot be altered.
4. Applications: Electromagnets are widely used in various applications that require the ability to control the strength of the magnetic field, such as electric motors, MRI machines, and magnetic separators. Permanent magnets find applications in devices like speakers, refrigerator magnets, and generators.
In summary, electromagnets rely on an electric current to generate a magnetic field and offer the advantage of controllable magnetic strength. Permanent magnets, on the other hand, do not require an external power source and have a fixed magnetic field strength.
Introduction
Electromagnets and permanent magnets are two types of magnets with different characteristics and applications. While both generate a magnetic field, they differ in their ability to produce a magnetic effect, the presence of a power source, and the ability to control the strength of the magnetic field.
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is generated by an electric current. It consists of a coil of wire wound around a magnetic core, typically made of iron. When an electric current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. The strength of the magnetic field can be altered by changing the amount of current flowing through the coil. Once the electric current is removed, the magnetic field disappears.
Permanent Magnet
A permanent magnet, as the name suggests, is a magnet that retains its magnetic properties without the need for an external power source. It is typically made of certain materials such as iron, nickel, cobalt, or alloys like neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) or samarium-cobalt (SmCo). These materials have naturally occurring magnetic properties that allow them to generate a magnetic field.
Differences
1. Power Source: The most significant difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet is the need for a power source. Electromagnets require an electric current to produce a magnetic field, while permanent magnets do not need any external power source.
2. Magnetic Effect: Electromagnets can produce a magnetic effect as long as the electric current flows through the coil. On the other hand, permanent magnets always have a magnetic field and can exert a magnetic force without the need for an electric current.
3. Control of Magnetic Field: The strength of the magnetic field in an electromagnet can be easily controlled by adjusting the amount of current flowing through the coil. In contrast, the strength of a permanent magnet's magnetic field is fixed based on its material composition and cannot be altered.
4. Applications: Electromagnets are widely used in various applications that require the ability to control the strength of the magnetic field, such as electric motors, MRI machines, and magnetic separators. Permanent magnets find applications in devices like speakers, refrigerator magnets, and generators.
In summary, electromagnets rely on an electric current to generate a magnetic field and offer the advantage of controllable magnetic strength. Permanent magnets, on the other hand, do not require an external power source and have a fixed magnetic field strength.
Attention Class 10 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 10 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 10.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet?
Question Description
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet?.
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? for Class 10 2024 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet?.
Solutions for And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet?, a detailed solution for And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? has been provided alongside types of And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice And last one is what is difference between Electromagnet and permanent magnet? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























