NEET Exam > NEET Questions > What is the difference between endothermic an...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?
Verified Answer
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?
Endothermic Reactions
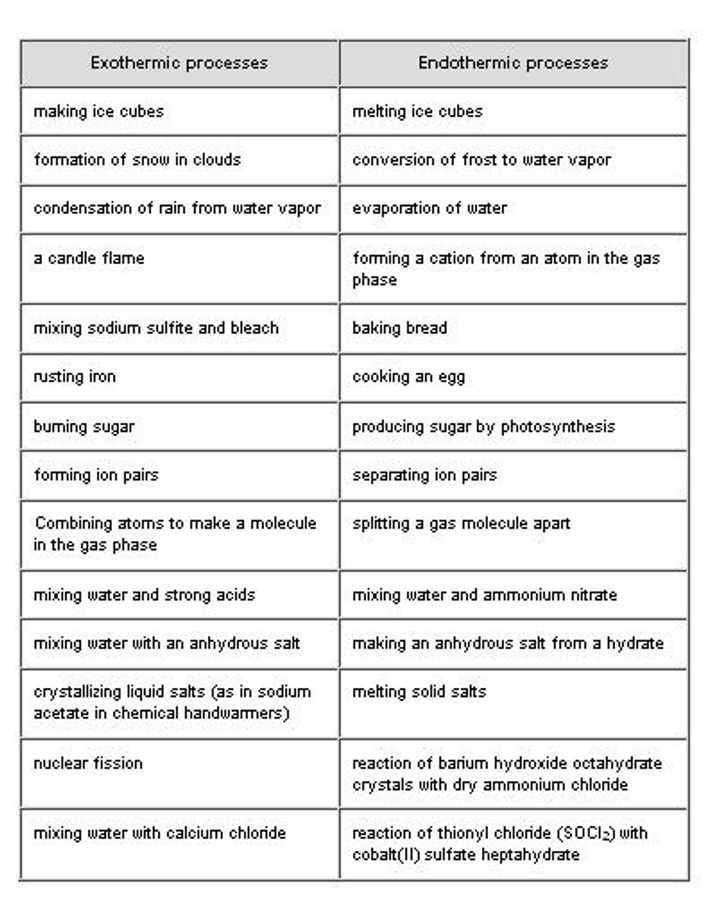
The endothermic process is a term that describes a reaction where the system absorbs the energy from its surrounding in the form of heat. Few examples of endothermic process is photosynthesis, evaporating liquids, melting ice, dry ice, alkanes cracking, thermal decomposition, ammonium chloride in water and much more.
Exothermic Reactions
The exothermic reaction is the opposite of an endothermic reaction. It releases energy by light or heat to its surrounding. Few examples are neutralization, burning a substance, reactions of fuels, deposition of dry ice, respiration, solution of sulfuric acid into water and much more.
Difference Between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Endothermic Reaction
Endothermic Reaction
- A reaction that the system absorbs energy from its surrounding in the form of heat.
- The energy is absorbed from the surround into the reaction
- The energy in the form of heat
- Melting ice, evaporation, cooking, gas molecules, photosynthesis are few examples
Exothermic Reaction
- A reaction that releases energy from the system in the form of heat.
- The energy is released from the system to its environment.
- Energy is released as heat, electricity, light or sound.
- Rusting iron, settling, chemical bonds, explosions, nuclear fission are few examples.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?
Community Answer
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?
Endothermic means the process in which energy is used to carry out the reaction and exothermic means that energy is released as a result of the reaction which takes place ...
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?
Question Description
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?.
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?.
Solutions for What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























