NEET Exam > NEET Questions > A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a...
Start Learning for Free
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now?
Most Upvoted Answer
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after s...
**Solution:**
To solve this problem, we can use Graham's Law of Effusion, which states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Since the pressure and temperature remain constant, we can assume that the gas behaves ideally and that the molar mass is directly proportional to the mass of the gas.
Let's break down the problem into steps:
**Step 1: Calculate the initial molar mass of helium**
The molar mass of helium (He) is approximately 4 g/mol. Therefore, the initial number of moles of helium in the balloon can be calculated as follows:
Number of moles of helium = Mass of helium / Molar mass of helium
Number of moles of helium = 1 g / 4 g/mol
Number of moles of helium = 0.25 mol
**Step 2: Calculate the final number of moles of helium**
Since 0.27 g of helium effused out of the balloon, the mass of helium remaining in the balloon is:
Remaining mass of helium = Initial mass of helium - Mass of helium effused
Remaining mass of helium = 1 g - 0.27 g
Remaining mass of helium = 0.73 g
Using the molar mass of helium, we can calculate the final number of moles of helium:
Number of moles of helium = Remaining mass of helium / Molar mass of helium
Number of moles of helium = 0.73 g / 4 g/mol
Number of moles of helium = 0.1825 mol
**Step 3: Calculate the final radius of the balloon**
We know that the volume of a balloon is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas it contains. Therefore, we can use the ideal gas law to relate the initial and final volumes of the balloon:
V1 / V2 = n1 / n2
Where:
V1 = Initial volume of the balloon
V2 = Final volume of the balloon
n1 = Initial number of moles of helium
n2 = Final number of moles of helium
Since the radius of the balloon is directly proportional to the cube root of its volume, we can rewrite the equation as:
(r1)^3 / (r2)^3 = n1 / n2
Where:
r1 = Initial radius of the balloon
r2 = Final radius of the balloon
Plugging in the values, we get:
(10 cm)^3 / (r2)^3 = 0.25 mol / 0.1825 mol
Simplifying the equation:
(r2)^3 = (10 cm)^3 * (0.1825 mol / 0.25 mol)
(r2)^3 = (10 cm)^3 * (0.73)
Taking the cube root of both sides:
r2 = (10 cm) * (0.73)^(1/3)
Using a calculator, we find:
r2 ≈ 9.14 cm
Therefore, the radius of the balloon after 0.27 g of helium effused out is approximately 9.14 cm.
To solve this problem, we can use Graham's Law of Effusion, which states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Since the pressure and temperature remain constant, we can assume that the gas behaves ideally and that the molar mass is directly proportional to the mass of the gas.
Let's break down the problem into steps:
**Step 1: Calculate the initial molar mass of helium**
The molar mass of helium (He) is approximately 4 g/mol. Therefore, the initial number of moles of helium in the balloon can be calculated as follows:
Number of moles of helium = Mass of helium / Molar mass of helium
Number of moles of helium = 1 g / 4 g/mol
Number of moles of helium = 0.25 mol
**Step 2: Calculate the final number of moles of helium**
Since 0.27 g of helium effused out of the balloon, the mass of helium remaining in the balloon is:
Remaining mass of helium = Initial mass of helium - Mass of helium effused
Remaining mass of helium = 1 g - 0.27 g
Remaining mass of helium = 0.73 g
Using the molar mass of helium, we can calculate the final number of moles of helium:
Number of moles of helium = Remaining mass of helium / Molar mass of helium
Number of moles of helium = 0.73 g / 4 g/mol
Number of moles of helium = 0.1825 mol
**Step 3: Calculate the final radius of the balloon**
We know that the volume of a balloon is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas it contains. Therefore, we can use the ideal gas law to relate the initial and final volumes of the balloon:
V1 / V2 = n1 / n2
Where:
V1 = Initial volume of the balloon
V2 = Final volume of the balloon
n1 = Initial number of moles of helium
n2 = Final number of moles of helium
Since the radius of the balloon is directly proportional to the cube root of its volume, we can rewrite the equation as:
(r1)^3 / (r2)^3 = n1 / n2
Where:
r1 = Initial radius of the balloon
r2 = Final radius of the balloon
Plugging in the values, we get:
(10 cm)^3 / (r2)^3 = 0.25 mol / 0.1825 mol
Simplifying the equation:
(r2)^3 = (10 cm)^3 * (0.1825 mol / 0.25 mol)
(r2)^3 = (10 cm)^3 * (0.73)
Taking the cube root of both sides:
r2 = (10 cm) * (0.73)^(1/3)
Using a calculator, we find:
r2 ≈ 9.14 cm
Therefore, the radius of the balloon after 0.27 g of helium effused out is approximately 9.14 cm.
Community Answer
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after s...
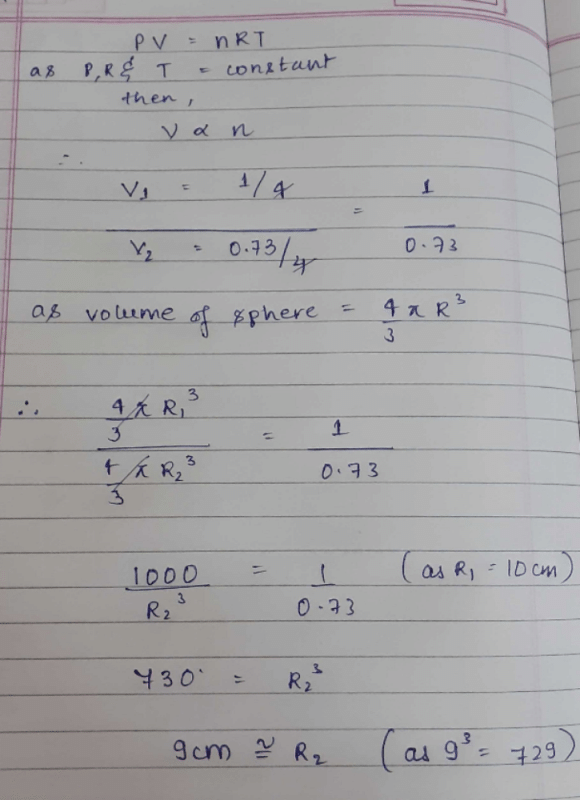

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now?
Question Description
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now?.
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now?.
Solutions for A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now?, a detailed solution for A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? has been provided alongside types of A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A balloon is filled with 1 gm of he and had a radius of 10 cm .after sometime 0.27 gm of he effused out of the balloon. If pressure and temp. Remains constant what would be the radius of balloon now? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























