NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?
Start Learning for Free
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton
?
?
Verified Answer
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?
Difference between Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
Location of Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
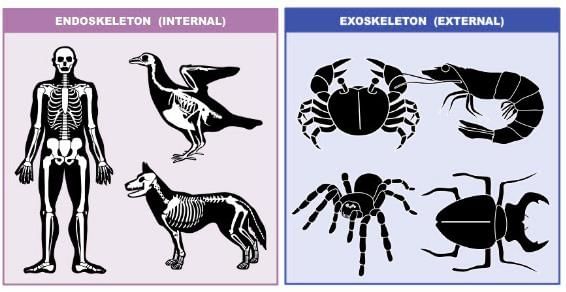
An endoskeleton is located on the inside of the body of an animal while an exoskeleton is located on the outside of the body of an animal.
Development of Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
In vertebrate animals with an endoskeleton, cartilage and bone is deposited. In invertebrates such as arthropods chitin and protein is deposited, while in some molluscs, a calcium carbonate shell is deposited.
Support and body size of Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
An endoskeleton can support a large body size but an exoskeleton cannot support a large body size.
Movement of Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
An endoskeleton enables movement by muscles pulling on bones, while an exoskeleton enables movement by having membranous joints between appendages.
Protection from predators
Animals with an endoskeleton are protected from predators by moving away using muscles that are joined to their bones, while animals with an exoskeleton are protected from predators by having exoskeleton modifications such as spines or camouflage colors.
Protection from physical forces
An endoskeleton is usually stronger and provides more protection from physical forces than an exoskeleton.
Repair and replacement
Vertebrate endoskeleton takes a long time to heal with cartilage and then bone being deposited. An exoskeleton can be replaced quite quickly with chitin and protein, or calcium carbonate being deposited.
Blood supply of Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
An endoskeleton contains a blood supply, but this is not the case with an exoskeleton.
Animal examples
An endoskeleton is found in chordates such as vertebrates while an exoskeleton is found in arthropods and some molluscs.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?
Endoskeleton - inside bones of body and it give support nd shape is known as endoskeleton ...
Exoskeleton - A hard outer covering that protect body is known sa exoskeleton..
Exoskeleton - A hard outer covering that protect body is known sa exoskeleton..
Community Answer
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?
Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton are two types of structural frameworks found in animals. They provide support, protection, and serve as attachment points for muscles and organs. While both types of skeletons serve similar functions, they have distinct differences in their composition and location within the body.
An endoskeleton is an internal skeleton present in many vertebrates, including humans. It is composed of bone and/or cartilage and is located within the body. The endoskeleton provides structural support and protection for various organs and tissues.
An exoskeleton is an external skeleton found in many invertebrates, such as insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is composed of a hard, protective outer covering and is located outside the body.
While both endoskeletons and exoskeletons provide support and protection, they have several key differences:
Introduction
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton are two types of structural frameworks found in animals. They provide support, protection, and serve as attachment points for muscles and organs. While both types of skeletons serve similar functions, they have distinct differences in their composition and location within the body.
Endoskeleton
An endoskeleton is an internal skeleton present in many vertebrates, including humans. It is composed of bone and/or cartilage and is located within the body. The endoskeleton provides structural support and protection for various organs and tissues.
- Composition: The endoskeleton is primarily made up of bones, which are rigid and provide strength and structure. These bones are connected by joints, allowing for movement.
- Function: The main function of the endoskeleton is to provide support for the body, protect delicate organs, and serve as attachment points for muscles, allowing for movement and locomotion.
- Advantages: Some advantages of an endoskeleton include flexibility, as it allows for a wider range of movements, and the ability to grow and repair itself, as bones can regenerate.
- Examples: Examples of animals with endoskeletons include humans, mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish.
Exoskeleton
An exoskeleton is an external skeleton found in many invertebrates, such as insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is composed of a hard, protective outer covering and is located outside the body.
- Composition: The exoskeleton is primarily made up of chitin, a tough and flexible material. It is rigid and provides protection against predators, injuries, and desiccation.
- Function: The main function of the exoskeleton is to provide support, protect the soft internal tissues, and prevent water loss. It also serves as a surface for muscle attachment.
- Advantages: Some advantages of an exoskeleton include providing a strong and durable barrier against physical damage, pathogens, and dehydration. It also offers protection during molting, a process where the old exoskeleton is shed and a new one is formed.
- Examples: Examples of animals with exoskeletons include insects (such as beetles, ants, and grasshoppers), crabs, lobsters, spiders, and scorpions.
Comparison
While both endoskeletons and exoskeletons provide support and protection, they have several key differences:
- Location: Endoskeletons are internal, located within the body, while exoskeletons are external, covering the body.
- Composition: Endoskeletons are primarily made up of bones, while exoskeletons are composed of chitin.
- Mobility: Endoskeletons offer greater flexibility and range of movement, while ex
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?
Question Description
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?.
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?.
Solutions for Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Endoskeleton and exoskeleton?, a detailed solution for Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? has been provided alongside types of Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Endoskeleton and exoskeleton? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























