Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > Synchronous generator can _________ reactive ...
Start Learning for Free
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:
- a)Neither generates nor absorbs
- b)Absorb
- c)Generate and absorb
- d)Generate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates...
The reactive power of a synchronous generator is given by,
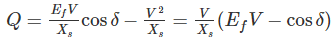
1) When EfV = cosδ then generator works under unity power factor condition
2) When EfV > cosδ then reactive power will be positive, i.e. generator supplies reactive power
3) When EfV < cosδ then reactive power will be negative, i.e. generator absorbs reactive power
Most Upvoted Answer
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates...
Synchronous Generator and Reactive Power
Synchronous generators are widely used in electrical power systems to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. One of the important characteristics of a synchronous generator is its ability to generate and absorb reactive power. Reactive power is a component of electrical power that is responsible for creating and sustaining magnetic fields in inductive loads such as motors and transformers.
1. Definition of Reactive Power:
Reactive power is the power that oscillates between the generator and the load due to the presence of inductive or capacitive elements in the circuit. It is measured in volt-amperes reactive (VAR) and is denoted by the symbol Q. Reactive power does not perform any useful work but is essential for maintaining voltage levels and ensuring the stability of the power system.
2. Generation of Reactive Power:
Synchronous generators can generate reactive power when they are connected to an electrical grid. The generator, when operated with a leading power factor (lagging reactive power), supplies reactive power to the grid. This is achieved by adjusting the excitation current or field voltage of the generator. By increasing the excitation, the generator produces a leading current that leads the voltage waveform. This leading current supplies reactive power to the grid.
3. Absorption of Reactive Power:
Synchronous generators can also absorb reactive power from the grid when they are operated with a lagging power factor (leading reactive power). In this mode, the generator acts as a load and consumes reactive power from the grid. By decreasing the excitation, the generator produces a lagging current that lags behind the voltage waveform. This lagging current absorbs reactive power from the grid.
4. Importance of Reactive Power Control:
The ability of synchronous generators to generate and absorb reactive power is crucial for maintaining voltage stability and regulating the power flow in electrical power systems. By controlling the excitation levels, the generator can adjust the amount of reactive power it supplies or absorbs. This control helps to maintain system voltages within acceptable limits and prevents voltage collapse or instability.
In conclusion, synchronous generators have the capability to both generate and absorb reactive power. This ability is essential for maintaining voltage stability and regulating power flow in electrical power systems. By adjusting the excitation levels, the generator can control the amount of reactive power it supplies or absorbs, ensuring the proper functioning of the power system.
Synchronous generators are widely used in electrical power systems to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. One of the important characteristics of a synchronous generator is its ability to generate and absorb reactive power. Reactive power is a component of electrical power that is responsible for creating and sustaining magnetic fields in inductive loads such as motors and transformers.
1. Definition of Reactive Power:
Reactive power is the power that oscillates between the generator and the load due to the presence of inductive or capacitive elements in the circuit. It is measured in volt-amperes reactive (VAR) and is denoted by the symbol Q. Reactive power does not perform any useful work but is essential for maintaining voltage levels and ensuring the stability of the power system.
2. Generation of Reactive Power:
Synchronous generators can generate reactive power when they are connected to an electrical grid. The generator, when operated with a leading power factor (lagging reactive power), supplies reactive power to the grid. This is achieved by adjusting the excitation current or field voltage of the generator. By increasing the excitation, the generator produces a leading current that leads the voltage waveform. This leading current supplies reactive power to the grid.
3. Absorption of Reactive Power:
Synchronous generators can also absorb reactive power from the grid when they are operated with a lagging power factor (leading reactive power). In this mode, the generator acts as a load and consumes reactive power from the grid. By decreasing the excitation, the generator produces a lagging current that lags behind the voltage waveform. This lagging current absorbs reactive power from the grid.
4. Importance of Reactive Power Control:
The ability of synchronous generators to generate and absorb reactive power is crucial for maintaining voltage stability and regulating the power flow in electrical power systems. By controlling the excitation levels, the generator can adjust the amount of reactive power it supplies or absorbs. This control helps to maintain system voltages within acceptable limits and prevents voltage collapse or instability.
In conclusion, synchronous generators have the capability to both generate and absorb reactive power. This ability is essential for maintaining voltage stability and regulating power flow in electrical power systems. By adjusting the excitation levels, the generator can control the amount of reactive power it supplies or absorbs, ensuring the proper functioning of the power system.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Synchronous generator can _________ reactive power:a)Neither generates nor absorbsb)Absorbc)Generate and absorbd)GenerateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























