NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generat...
Start Learning for Free
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generates
- a)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acid
- b)Propanoic acid and ammonium salt
- c)Ethanoic acid and ammonium salt
- d)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and m...
(a) : Alkyl isocyanides are hydrolysed by dilute mineral acids to form primary amines.Read more on Sarthaks.com - https://www.sarthaks.com/44040/ethyl-isocyanide-on-hydrolysis-in-acidic-medium-generates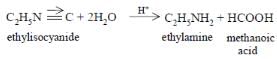
View all questions of this test

Most Upvoted Answer
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and m...
Acidic hydrolysis of ethyl isocyanide results in the formation of ethylamine salt and methanoic acid. Here's a detailed explanation of the process:
1. Definition of Ethyl Isocyanide:
- Ethyl isocyanide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C2H5NC. It consists of an ethyl group (C2H5) attached to a nitrogen atom (N) with a triple bond to a carbon atom (C).
2. Acidic Hydrolysis:
- Acidic hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a compound reacts with water under acidic conditions to produce two or more products.
- In the case of ethyl isocyanide, when it undergoes acidic hydrolysis, it reacts with water (H2O) in the presence of an acid catalyst.
3. Reaction Mechanism:
- The acidic hydrolysis of ethyl isocyanide proceeds through a nucleophilic attack by water on the isocyanide carbon atom.
- The nitrogen atom in ethyl isocyanide is relatively electron deficient due to the presence of the triple bond, making it susceptible to attack by nucleophiles.
- The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom, breaking the triple bond and forming a new bond with the carbon atom.
- Simultaneously, the nitrogen atom forms a bond with a hydrogen ion (H+) from the acid catalyst to maintain its positive charge.
- As a result, the ethyl group is released as an ethylamine cation (C2H5NH3+) and the carbon atom is now bonded to an oxygen atom from the water molecule.
4. Products of Acidic Hydrolysis:
- The products of acidic hydrolysis of ethyl isocyanide are ethylamine salt and methanoic acid.
- The ethylamine cation (C2H5NH3+) combines with an anion (negative ion) from the acid catalyst, such as chloride (Cl-) or acetate (CH3COO-), to form the ethylamine salt.
- The carbon atom, now bonded to an oxygen atom, forms a carboxylic acid functional group, specifically methanoic acid (HCOOH), also known as formic acid.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Ethylamine salt and methanoic acid.
1. Definition of Ethyl Isocyanide:
- Ethyl isocyanide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C2H5NC. It consists of an ethyl group (C2H5) attached to a nitrogen atom (N) with a triple bond to a carbon atom (C).
2. Acidic Hydrolysis:
- Acidic hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a compound reacts with water under acidic conditions to produce two or more products.
- In the case of ethyl isocyanide, when it undergoes acidic hydrolysis, it reacts with water (H2O) in the presence of an acid catalyst.
3. Reaction Mechanism:
- The acidic hydrolysis of ethyl isocyanide proceeds through a nucleophilic attack by water on the isocyanide carbon atom.
- The nitrogen atom in ethyl isocyanide is relatively electron deficient due to the presence of the triple bond, making it susceptible to attack by nucleophiles.
- The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom, breaking the triple bond and forming a new bond with the carbon atom.
- Simultaneously, the nitrogen atom forms a bond with a hydrogen ion (H+) from the acid catalyst to maintain its positive charge.
- As a result, the ethyl group is released as an ethylamine cation (C2H5NH3+) and the carbon atom is now bonded to an oxygen atom from the water molecule.
4. Products of Acidic Hydrolysis:
- The products of acidic hydrolysis of ethyl isocyanide are ethylamine salt and methanoic acid.
- The ethylamine cation (C2H5NH3+) combines with an anion (negative ion) from the acid catalyst, such as chloride (Cl-) or acetate (CH3COO-), to form the ethylamine salt.
- The carbon atom, now bonded to an oxygen atom, forms a carboxylic acid functional group, specifically methanoic acid (HCOOH), also known as formic acid.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Ethylamine salt and methanoic acid.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Ethyl isocyanide on acidic hydrolysis generatesa)Ethylamine salt and methanoic acidb)Propanoic acid and ammonium saltc)Ethanoic acid and ammonium saltd)Methyl amine salt and ethanoic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















