Physics Exam > Physics Questions > Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the ...
Start Learning for Free
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay law
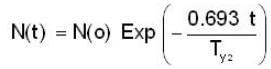
where N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.
An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would be
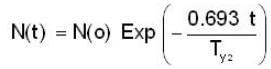
where N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.
An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would be
- a)983
- b)839
- c)539
- d)313
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere de...
We know the time
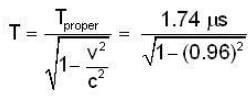
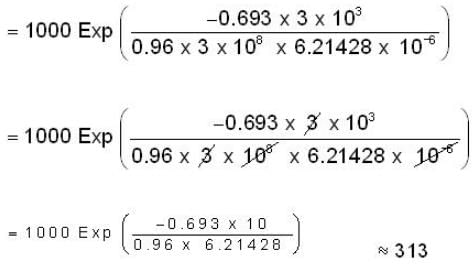
= 6.21428 sec
Then According to question
travelled distance = 3 x 103 m
velocity = 0.96 x 3 x 108 m/sec
Then time taken by the muons to reach the sea level is t = travelled distance /velocity
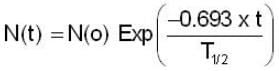
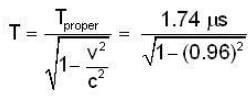
= 6.21428 sec
Then According to question
travelled distance = 3 x 103 m
velocity = 0.96 x 3 x 108 m/sec
Then time taken by the muons to reach the sea level is t = travelled distance /velocity
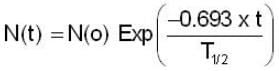

Most Upvoted Answer
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere de...
We know the time

= 6.21428 sec
Then According to question
travelled distance = 3 x 103 m
velocity = 0.96 x 3 x 108 m/sec
Then time taken by the muons to reach the sea level is t = travelled distance /velocity



= 6.21428 sec
Then According to question
travelled distance = 3 x 103 m
velocity = 0.96 x 3 x 108 m/sec
Then time taken by the muons to reach the sea level is t = travelled distance /velocity



|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Similar Physics Doubts
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2024 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Cosmic ray muons generated at the top of the earth's atmosphere decay according to the radioactive decay lawwhere N(t) is the number of muons at time t, and T1/2 = 1.74 μs is the proper half-life of the muon. Immediately after generation, most of these muons shoot down towards the Earth's surface. Some of these muons decay on the way, but their interactions with the atmosphere is negligible.An observer on the top of a mountain of height 3.0 km above mean sea level detects muons with the speed 0.96 cover a period of time and counts 1000 muons. The number of muons of the same speed detected by an observer at mean level in the same period of time would bea)983b)839c)539d)313Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















