NEET Exam > NEET Questions > 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicar...
Start Learning for Free
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzyme
- a)Carbonic anhydrase
- b)Carbonic hydrase
- c)Carbaminase
- d)Carbonates
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Car...
**Answer:**
**Carbonic Anhydrase: The Key Enzyme**
Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the transportation of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the body. It catalyzes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into bicarbonate and a hydrogen ion. This reaction occurs rapidly and helps maintain the acid-base balance in various tissues and organs.
**Transport of Carbon Dioxide**
Carbon dioxide produced during cellular respiration needs to be transported from the tissues to the lungs for elimination. The majority of carbon dioxide is transported in the form of bicarbonate (HCO3-) ions. This transport occurs through three main processes:
1. **Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Bicarbonate:** Carbonic anhydrase facilitates the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and a hydrogen ion. This reaction occurs in red blood cells. The enzyme speeds up the reaction, allowing the formation of bicarbonate to take place rapidly.
2. **Transport of Bicarbonate:** Bicarbonate ions are transported out of the red blood cells and into the plasma, where they can be transported to the lungs. This occurs through the exchange of chloride ions (Cl-) via the chloride shift mechanism. Bicarbonate ions move out of the red blood cells in exchange for chloride ions, which move into the cell.
3. **Conversion of Bicarbonate back to Carbon Dioxide:** In the lungs, carbon dioxide needs to be regenerated from bicarbonate for elimination. Carbonic anhydrase also facilitates this reaction, converting bicarbonate back to carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide can then be exhaled from the lungs.
**Significance of Carbonic Anhydrase**
Carbonic anhydrase plays a crucial role in the transportation of carbon dioxide in the body. Without this enzyme, the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and vice versa would occur at a much slower rate, leading to an imbalance in the acid-base equilibrium. This enzyme ensures efficient transportation of carbon dioxide, maintaining the required levels of bicarbonate ions in the blood and tissues.
**Conclusion**
In summary, carbonic anhydrase is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions, which are then transported in the blood plasma. This enzyme plays a crucial role in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body and ensuring efficient elimination of carbon dioxide from the lungs.
**Carbonic Anhydrase: The Key Enzyme**
Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the transportation of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the body. It catalyzes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into bicarbonate and a hydrogen ion. This reaction occurs rapidly and helps maintain the acid-base balance in various tissues and organs.
**Transport of Carbon Dioxide**
Carbon dioxide produced during cellular respiration needs to be transported from the tissues to the lungs for elimination. The majority of carbon dioxide is transported in the form of bicarbonate (HCO3-) ions. This transport occurs through three main processes:
1. **Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Bicarbonate:** Carbonic anhydrase facilitates the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and a hydrogen ion. This reaction occurs in red blood cells. The enzyme speeds up the reaction, allowing the formation of bicarbonate to take place rapidly.
2. **Transport of Bicarbonate:** Bicarbonate ions are transported out of the red blood cells and into the plasma, where they can be transported to the lungs. This occurs through the exchange of chloride ions (Cl-) via the chloride shift mechanism. Bicarbonate ions move out of the red blood cells in exchange for chloride ions, which move into the cell.
3. **Conversion of Bicarbonate back to Carbon Dioxide:** In the lungs, carbon dioxide needs to be regenerated from bicarbonate for elimination. Carbonic anhydrase also facilitates this reaction, converting bicarbonate back to carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide can then be exhaled from the lungs.
**Significance of Carbonic Anhydrase**
Carbonic anhydrase plays a crucial role in the transportation of carbon dioxide in the body. Without this enzyme, the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and vice versa would occur at a much slower rate, leading to an imbalance in the acid-base equilibrium. This enzyme ensures efficient transportation of carbon dioxide, maintaining the required levels of bicarbonate ions in the blood and tissues.
**Conclusion**
In summary, carbonic anhydrase is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions, which are then transported in the blood plasma. This enzyme plays a crucial role in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body and ensuring efficient elimination of carbon dioxide from the lungs.
Community Answer
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Car...
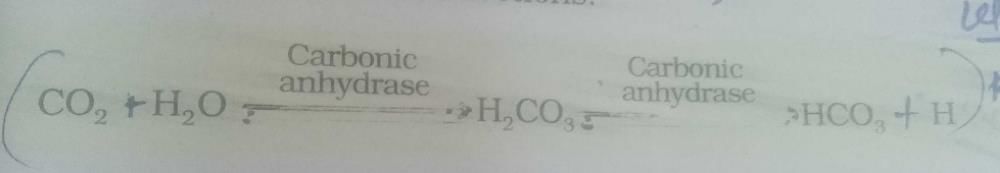
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice 70% of carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate by the enzymea)Carbonic anhydraseb)Carbonic hydrasec)Carbaminased)CarbonatesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























