GATE Exam > GATE Questions > Consider a small length of a beam subjected t...
Start Learning for Free
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,
- a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layer
- b)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layer
- c)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axis
- d)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has ...
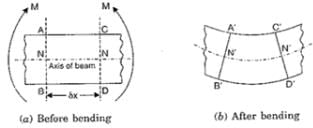
The axis of the beam is the neutral axis.
The amount by which a layer increases or decreases in length, depends upon the position of the layer w.r.t. N-N.
In the above fig. as we move from top layer to N-N, the length of the layer increases. While moving from bottom layer to N-N, the length of the layer decreases.
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has ...
Explanation:
When a beam is subjected to simple bending, different layers of the beam experience different amounts of elongation or compression. The layer that is farthest from the neutral axis experiences the greatest change in length.
Position of the Layer
The amount by which a layer increases or decreases in length depends on its position with respect to the neutral axis. The neutral axis is an imaginary line passing through the centroid of the beam's cross-section, where the stress and strain are zero.
Effect of Position on Elongation/Compression
The layers that are above the neutral axis (top layers) experience tension, leading to elongation, while the layers that are below the neutral axis (bottom layers) experience compression, leading to contraction.
Explanation of Options
a) The position of the top layer with respect to the bottom layer does not determine the amount of elongation or compression. The layers on both the top and bottom experience different amounts of elongation or compression.
b) Similarly, the position of the bottom layer with respect to the top layer does not determine the amount of elongation or compression. The layers on both the top and bottom experience different amounts of elongation or compression.
c) The correct option is C because the position of the layer with respect to the neutral axis determines the amount of elongation or compression it experiences. Layers farther from the neutral axis experience greater elongation or compression.
d) The position of the top layer with respect to the axis N-N does not directly determine the amount of elongation or compression. The position of the layer with respect to the neutral axis is the key factor.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, which states that the amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length depends on its position with respect to the neutral axis.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider a small length of a beam subjected to simple bending. It has two sections AB and CD normal to the axis of the beam N-N. The amount by which the layer increases or decreases in length,a)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. bottom layerb)depends on position of bottom layer w.r.t. top layerc)depends on position of that layer w.r.t. to neutral axisd)depends on position of top layer w.r.t. to axis N-NCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















