GATE Exam > GATE Questions > The steady state error of a control system ca...
Start Learning for Free
The steady state error of a control system can be reduced by
- a)increasing time constant of the system only.
- b)increasing gain constant of the system only.
- c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.
- d)none of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasi...
Time constant of the system,
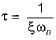
When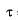 is increased means damping is reduced, thus steady state error reduces.
is increased means damping is reduced, thus steady state error reduces.
Also, when gain of the system increases, then damping reduces and therefore, steady state error reduces.

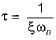
When
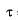 is increased means damping is reduced, thus steady state error reduces.
is increased means damping is reduced, thus steady state error reduces.Also, when gain of the system increases, then damping reduces and therefore, steady state error reduces.

Most Upvoted Answer
The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasi...
Introduction:
The steady-state error is an important parameter to evaluate the performance of a control system. It quantifies the difference between the desired output and the actual output of the system when it reaches a stable condition. The steady-state error can be reduced by modifying certain parameters of the control system.
Explanation:
To understand why increasing both the time constant and gain of the system can reduce the steady-state error, let's first understand what these parameters mean and how they affect the system's response.
- Time constant: The time constant of a control system is a measure of how quickly the system responds to changes in the input. A higher time constant means the system takes longer to reach a steady-state. It is typically associated with the dynamics of the system.
- Gain constant: The gain constant determines the amplification of the input signal by the control system. A higher gain amplifies the input signal more, resulting in a larger output signal. It is typically associated with the control action of the system.
Now, let's see how increasing both the time constant and gain of the system can reduce the steady-state error:
1. Increasing the time constant:
When the time constant is increased, the system responds more slowly to changes in the input. This means that the system takes more time to reach its steady-state. As a result, the steady-state error decreases because the system has more time to adjust and match the desired output.
2. Increasing the gain constant:
When the gain constant is increased, the system amplifies the input signal more. This means that even small deviations between the desired and actual output are amplified, leading to a larger corrective action. As a result, the steady-state error decreases because the system can quickly and accurately reduce the difference between the desired and actual output.
3. Combined effect:
When both the time constant and gain of the system are increased, the system becomes more responsive and sensitive to changes in the input. The increased time constant allows the system to adjust slowly and accurately to reach its steady-state, while the increased gain amplifies the corrective action. This combination helps in reducing the steady-state error to a greater extent.
Conclusion:
Increasing both the time constant and gain of a control system can effectively reduce the steady-state error. The increased time constant allows the system to adjust slowly and accurately, while the increased gain amplifies the corrective action. By modifying these parameters, the control system can better match the desired output and improve its performance.
The steady-state error is an important parameter to evaluate the performance of a control system. It quantifies the difference between the desired output and the actual output of the system when it reaches a stable condition. The steady-state error can be reduced by modifying certain parameters of the control system.
Explanation:
To understand why increasing both the time constant and gain of the system can reduce the steady-state error, let's first understand what these parameters mean and how they affect the system's response.
- Time constant: The time constant of a control system is a measure of how quickly the system responds to changes in the input. A higher time constant means the system takes longer to reach a steady-state. It is typically associated with the dynamics of the system.
- Gain constant: The gain constant determines the amplification of the input signal by the control system. A higher gain amplifies the input signal more, resulting in a larger output signal. It is typically associated with the control action of the system.
Now, let's see how increasing both the time constant and gain of the system can reduce the steady-state error:
1. Increasing the time constant:
When the time constant is increased, the system responds more slowly to changes in the input. This means that the system takes more time to reach its steady-state. As a result, the steady-state error decreases because the system has more time to adjust and match the desired output.
2. Increasing the gain constant:
When the gain constant is increased, the system amplifies the input signal more. This means that even small deviations between the desired and actual output are amplified, leading to a larger corrective action. As a result, the steady-state error decreases because the system can quickly and accurately reduce the difference between the desired and actual output.
3. Combined effect:
When both the time constant and gain of the system are increased, the system becomes more responsive and sensitive to changes in the input. The increased time constant allows the system to adjust slowly and accurately to reach its steady-state, while the increased gain amplifies the corrective action. This combination helps in reducing the steady-state error to a greater extent.
Conclusion:
Increasing both the time constant and gain of a control system can effectively reduce the steady-state error. The increased time constant allows the system to adjust slowly and accurately, while the increased gain amplifies the corrective action. By modifying these parameters, the control system can better match the desired output and improve its performance.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Question Description
The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The steady state error of a control system can be reduced bya)increasing time constant of the system only.b)increasing gain constant of the system only.c)increasing both the time constant and gain of the system.d)none of the above.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















