NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Mendel’s law of independent assortment ...
Start Learning for Free
Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :
- a)Non-homologous chromosomes
- b)Homologous chromosomes
- c)Extra nuclear genetic element
- d)Same chromosome
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for gen...
Non-homologous Chromosome The law of independent assortment holds true as long as two different genes are on separate chromosomes. When the genes are on separate chromosome, the two alleles of one gene (A and a) will segregate into gametes independently of the two alleles of the other gene (B and b). Equal numbers of four different gametes will form AB, aB, Ab, ab. But if the two genes are on the same chromosome, then they will be linked and will segregate together during meiosis, producing only two kinds of gametes.
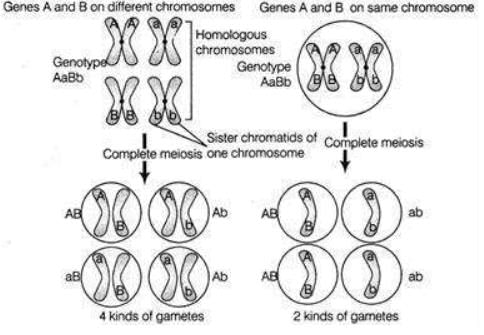
Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same gene insame order but the alleles for each trait may not be the same. Extra nuclear genetic elements are also called as plasmids and shows the pattern of maternal inheritance.

Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same gene insame order but the alleles for each trait may not be the same. Extra nuclear genetic elements are also called as plasmids and shows the pattern of maternal inheritance.
Most Upvoted Answer
Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for gen...
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment states that the alleles of different genes segregate independently of one another during gamete formation. This principle is crucial for understanding genetic variation.
Independent Assortment and Chromosome Type
- Non-Homologous Chromosomes:
- Genes located on non-homologous chromosomes assort independently.
- This means that the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene located on a different chromosome.
- Homologous Chromosomes:
- Genes on homologous chromosomes are often linked and do not assort independently due to physical proximity.
- Extra Nuclear Genetic Elements:
- While these can show some independence, they do not follow Mendel's laws as strictly as nuclear genes do.
- Same Chromosome:
- Genes located on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together due to linked inheritance, violating independent assortment.
Conclusion
In summary, Mendel's law of independent assortment is applicable to genes on non-homologous chromosomes. This law is fundamental in genetics and explains the random combination of traits seen in offspring, helping to understand the diversity of genetic outcomes. Understanding this concept is essential for NEET preparation and genetics as a whole.
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment states that the alleles of different genes segregate independently of one another during gamete formation. This principle is crucial for understanding genetic variation.
Independent Assortment and Chromosome Type
- Non-Homologous Chromosomes:
- Genes located on non-homologous chromosomes assort independently.
- This means that the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene located on a different chromosome.
- Homologous Chromosomes:
- Genes on homologous chromosomes are often linked and do not assort independently due to physical proximity.
- Extra Nuclear Genetic Elements:
- While these can show some independence, they do not follow Mendel's laws as strictly as nuclear genes do.
- Same Chromosome:
- Genes located on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together due to linked inheritance, violating independent assortment.
Conclusion
In summary, Mendel's law of independent assortment is applicable to genes on non-homologous chromosomes. This law is fundamental in genetics and explains the random combination of traits seen in offspring, helping to understand the diversity of genetic outcomes. Understanding this concept is essential for NEET preparation and genetics as a whole.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Mendel’s law of independent assortment always holds good for genes situated on the :a)Non-homologous chromosomesb)Homologous chromosomesc)Extra nuclear genetic elementd)Same chromosomeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























