NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Endocrine glands and its hormones?
Start Learning for Free
Endocrine glands and its hormones?
Most Upvoted Answer
Endocrine glands and its hormones?
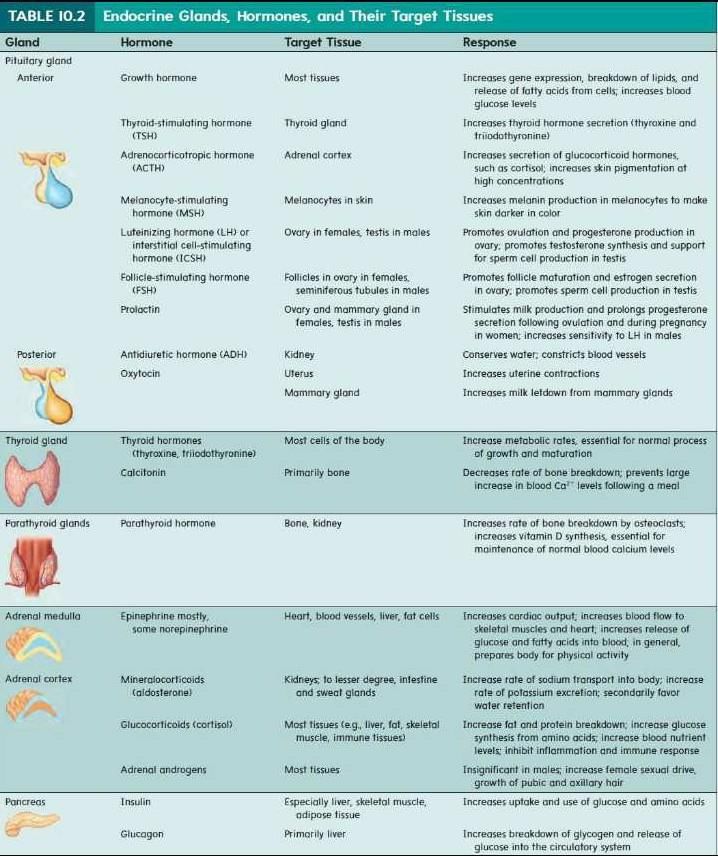
Endocrine glands are specialized organs in the human body that produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones act as chemical messengers and play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. Here is a detailed explanation of some important endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete:
1. Pituitary Gland:
- Often referred to as the "master gland" as it controls the function of other endocrine glands.
- Secretes several hormones including growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
2. Thyroid Gland:
- Located in the neck, it produces thyroid hormones.
- Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
3. Parathyroid Glands:
- Small glands located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
- Secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium and phosphate levels in the blood.
4. Adrenal Glands:
- Situated on top of each kidney.
- Adrenal cortex produces hormones such as cortisol (stress response), aldosterone (regulates salt balance), and sex hormones.
- Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are involved in the body's response to stress.
5. Pancreas:
- Functions as both an exocrine and endocrine gland.
- Endocrine cells in the pancreas called islets of Langerhans secrete hormones including insulin (lowers blood sugar) and glucagon (raises blood sugar).
6. Ovaries (in females):
- Produce estrogen (regulates menstrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics) and progesterone (prepares uterus for pregnancy).
7. Testes (in males):
- Synthesize testosterone (regulates sperm production, development of secondary sexual characteristics).
8. Pineal Gland:
- Located in the brain, it secretes melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles and influences reproductive function.
9. Thymus:
- Plays a role in the development of the immune system, particularly during childhood.
- Secretes thymosin, which stimulates the maturation of T-lymphocytes.
10. Hypothalamus:
- Although not a gland itself, it plays a vital role in endocrine regulation.
- Produces releasing and inhibiting hormones that control the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.
These endocrine glands and their hormones work together to maintain homeostasis, regulate growth and development, control metabolism, and influence various physiological functions in the body.
1. Pituitary Gland:
- Often referred to as the "master gland" as it controls the function of other endocrine glands.
- Secretes several hormones including growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), prolactin, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
2. Thyroid Gland:
- Located in the neck, it produces thyroid hormones.
- Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
3. Parathyroid Glands:
- Small glands located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
- Secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium and phosphate levels in the blood.
4. Adrenal Glands:
- Situated on top of each kidney.
- Adrenal cortex produces hormones such as cortisol (stress response), aldosterone (regulates salt balance), and sex hormones.
- Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are involved in the body's response to stress.
5. Pancreas:
- Functions as both an exocrine and endocrine gland.
- Endocrine cells in the pancreas called islets of Langerhans secrete hormones including insulin (lowers blood sugar) and glucagon (raises blood sugar).
6. Ovaries (in females):
- Produce estrogen (regulates menstrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics) and progesterone (prepares uterus for pregnancy).
7. Testes (in males):
- Synthesize testosterone (regulates sperm production, development of secondary sexual characteristics).
8. Pineal Gland:
- Located in the brain, it secretes melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles and influences reproductive function.
9. Thymus:
- Plays a role in the development of the immune system, particularly during childhood.
- Secretes thymosin, which stimulates the maturation of T-lymphocytes.
10. Hypothalamus:
- Although not a gland itself, it plays a vital role in endocrine regulation.
- Produces releasing and inhibiting hormones that control the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.
These endocrine glands and their hormones work together to maintain homeostasis, regulate growth and development, control metabolism, and influence various physiological functions in the body.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Endocrine glands and its hormones?
Question Description
Endocrine glands and its hormones? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Endocrine glands and its hormones? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Endocrine glands and its hormones?.
Endocrine glands and its hormones? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Endocrine glands and its hormones? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Endocrine glands and its hormones?.
Solutions for Endocrine glands and its hormones? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Endocrine glands and its hormones? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Endocrine glands and its hormones?, a detailed solution for Endocrine glands and its hormones? has been provided alongside types of Endocrine glands and its hormones? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Endocrine glands and its hormones? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.